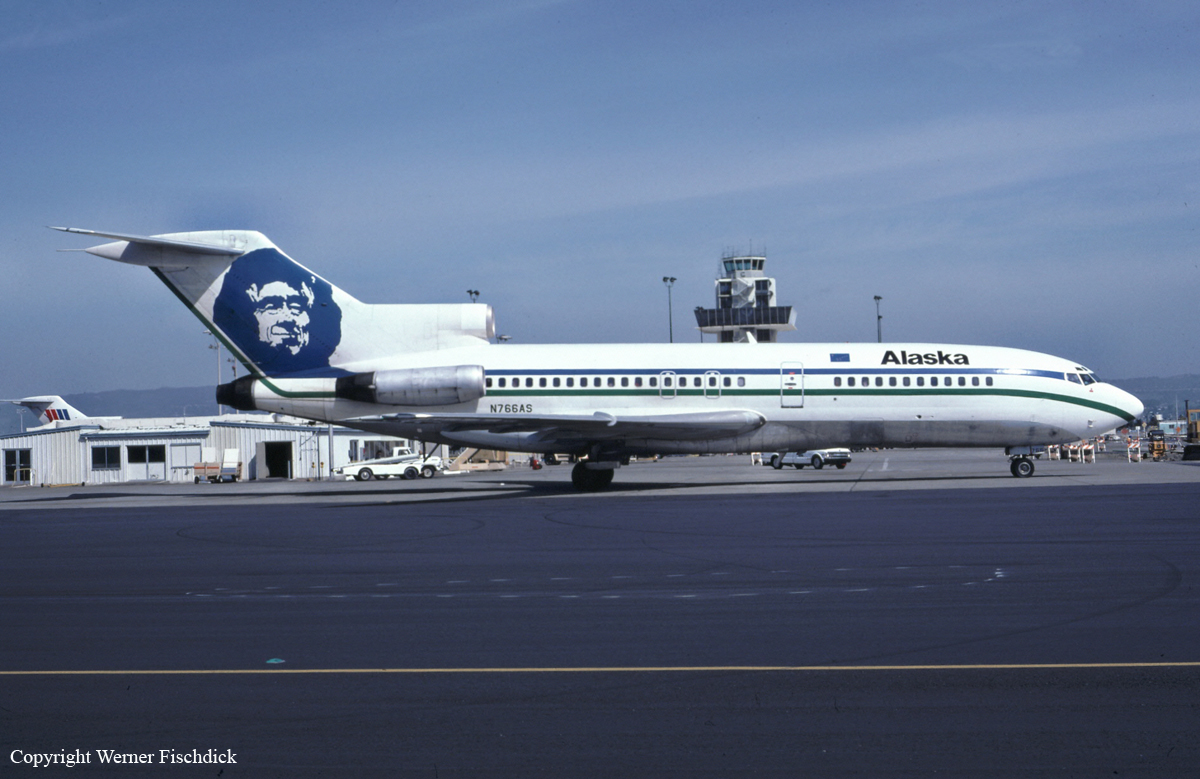
Crash of a Boeing 727-22QC in Windsor Locks
Date & Time:
May 3, 1991 at 0553 LT
Registration:
N425EX
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Windsor Locks - Boston
MSN:
19095
YOM:
1966
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
3600.00
Aircraft flight hours:
46981
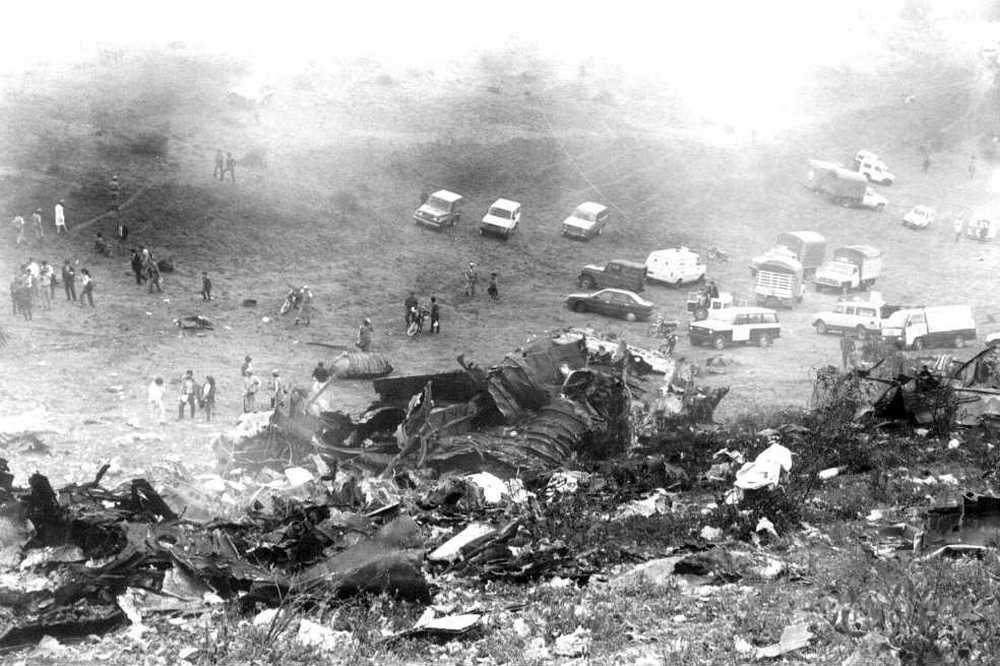
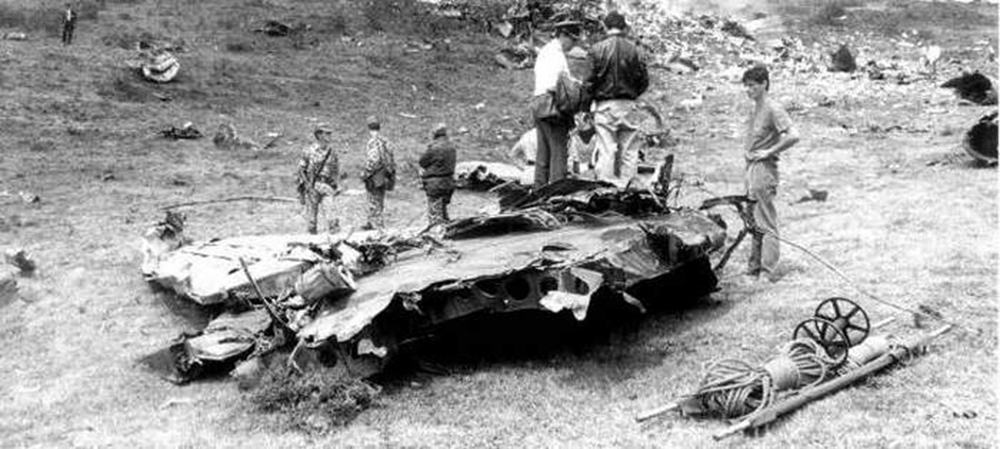
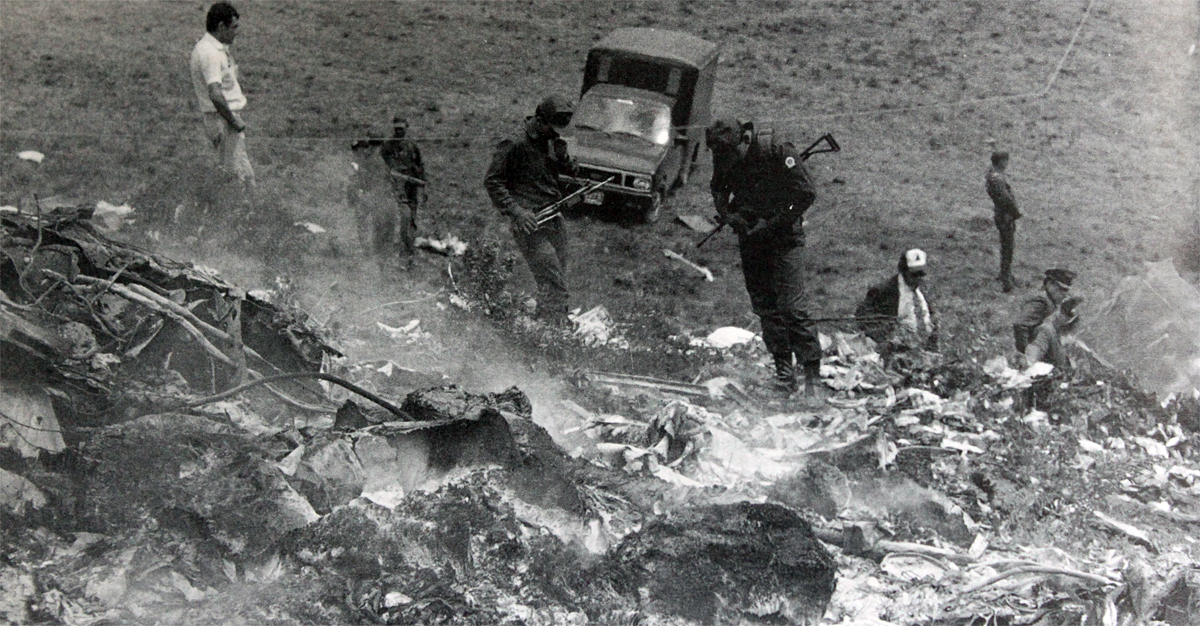
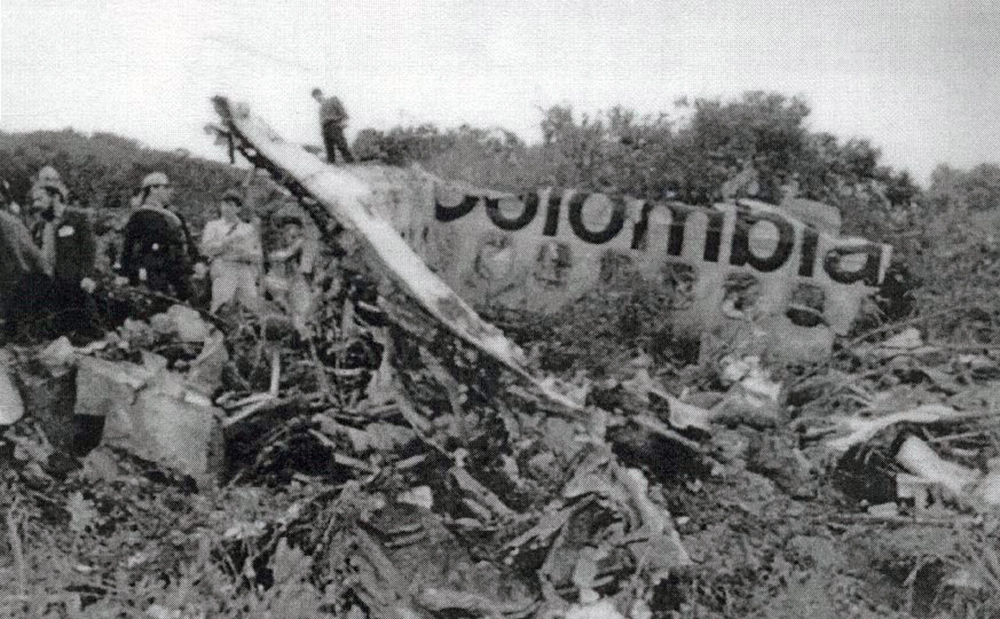
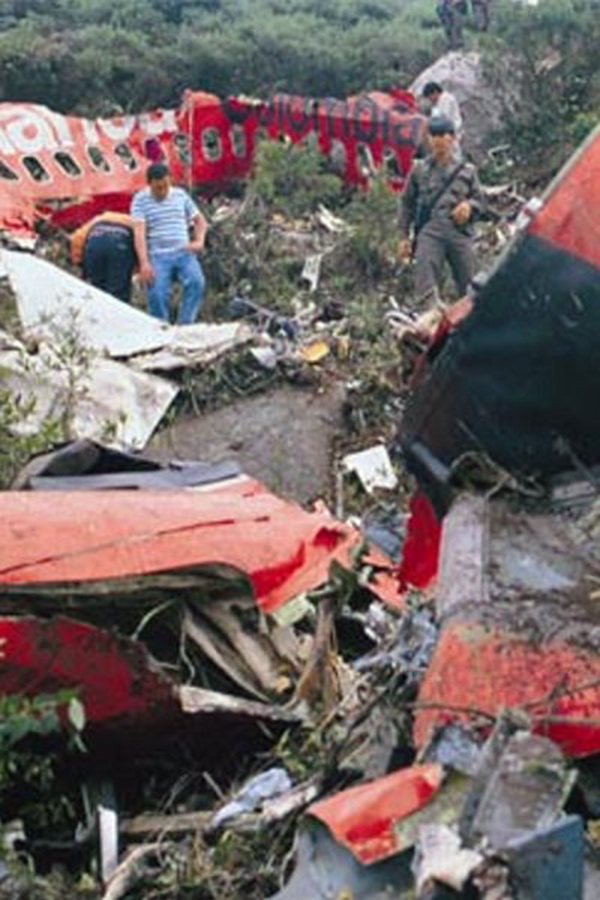
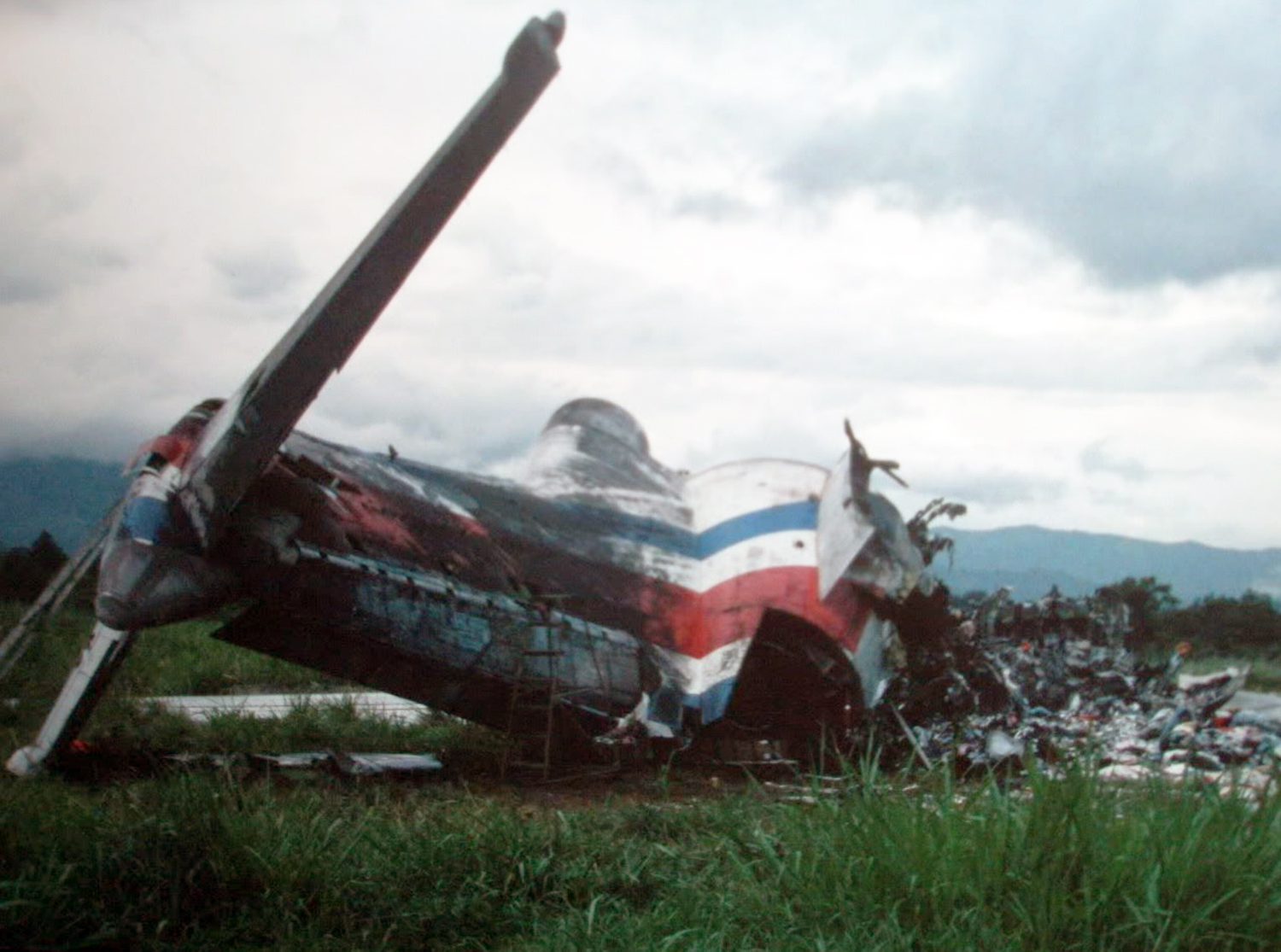
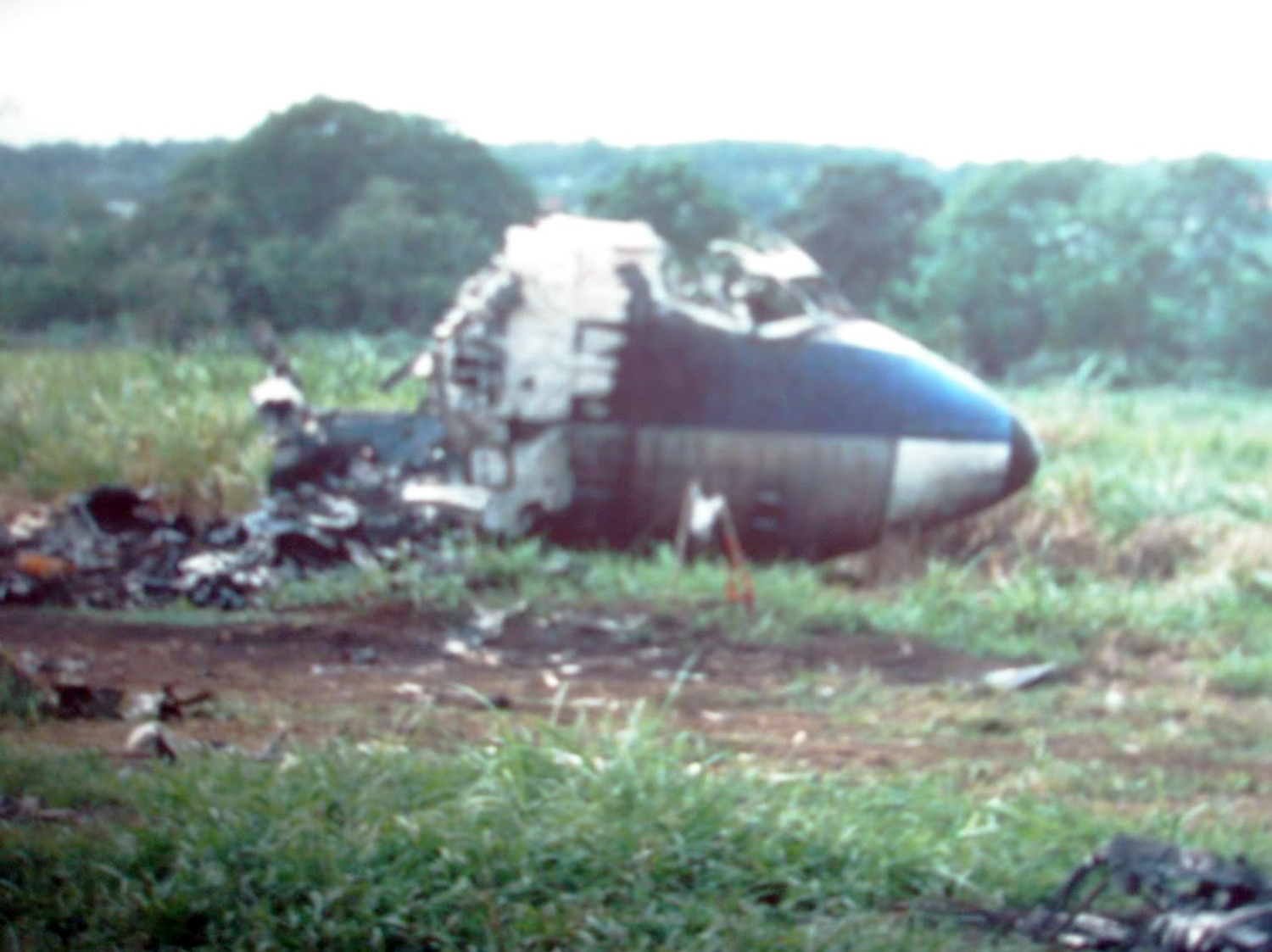
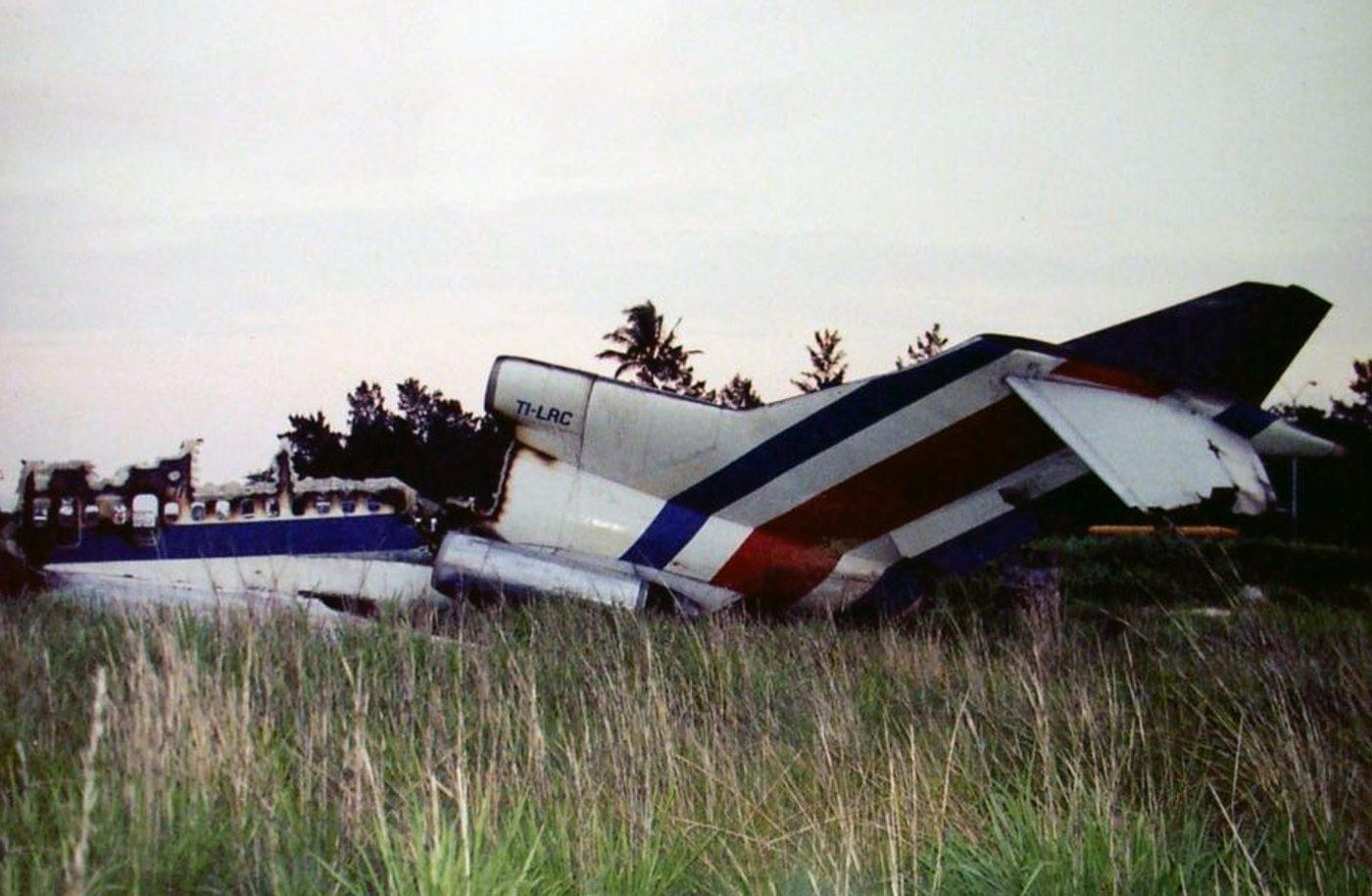
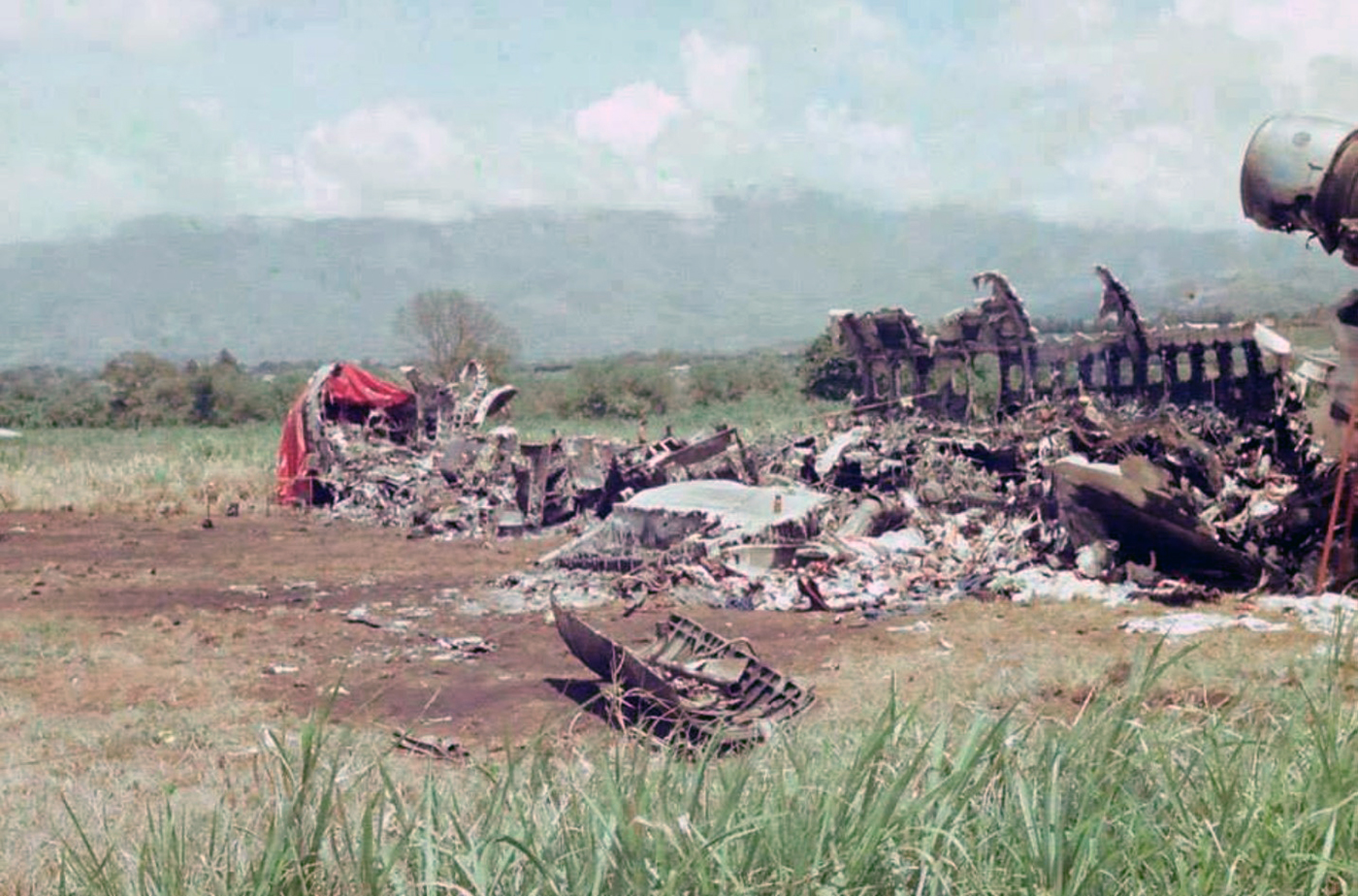
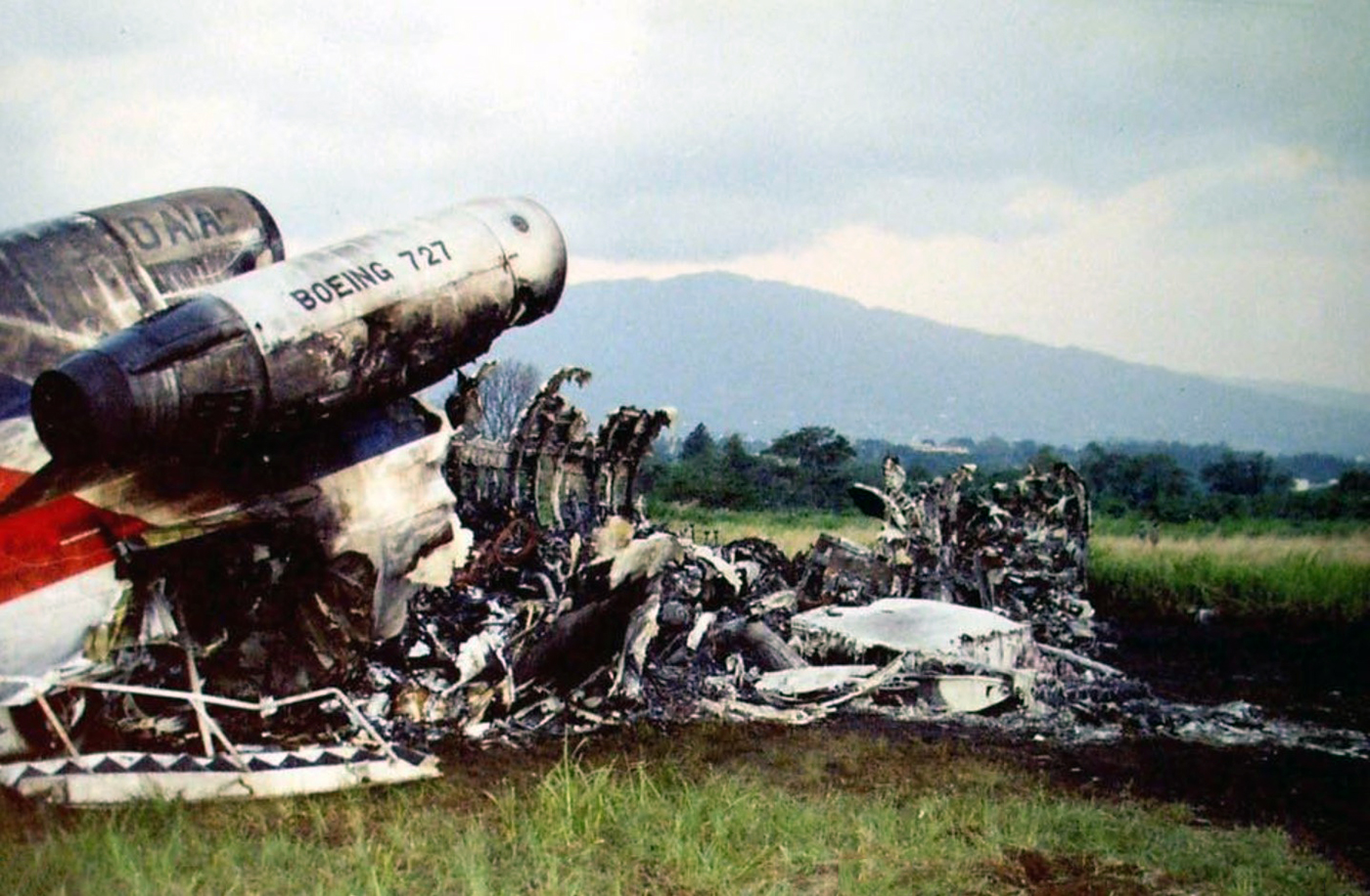
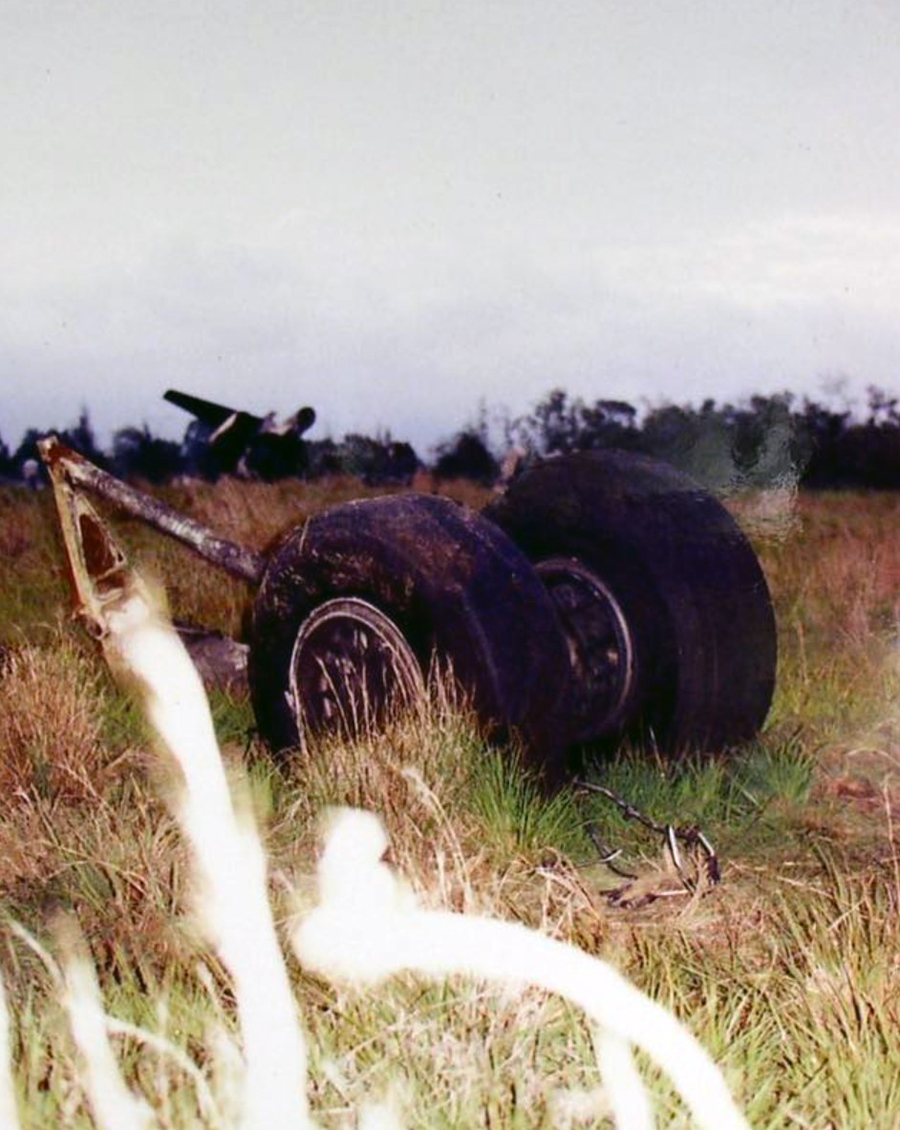
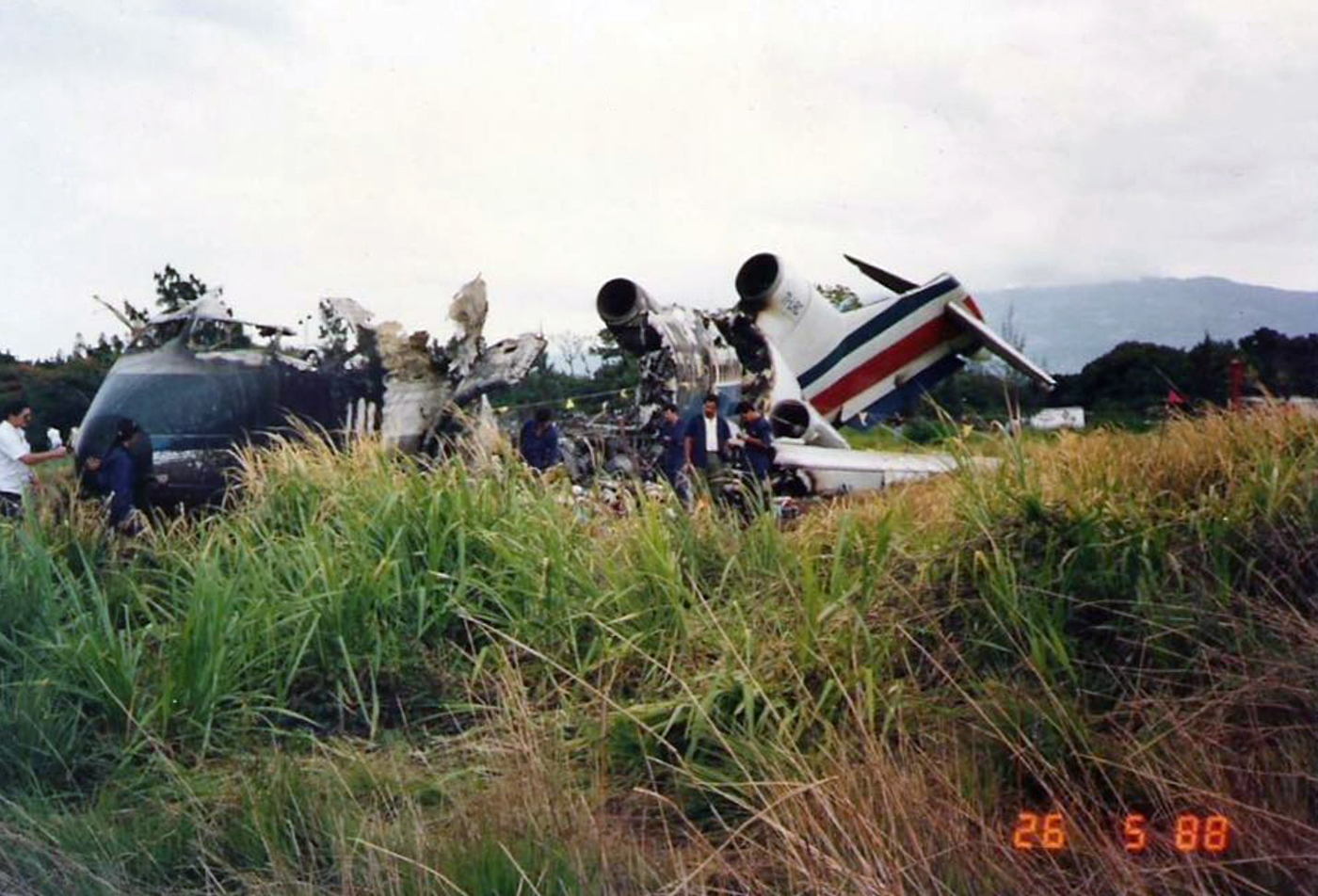
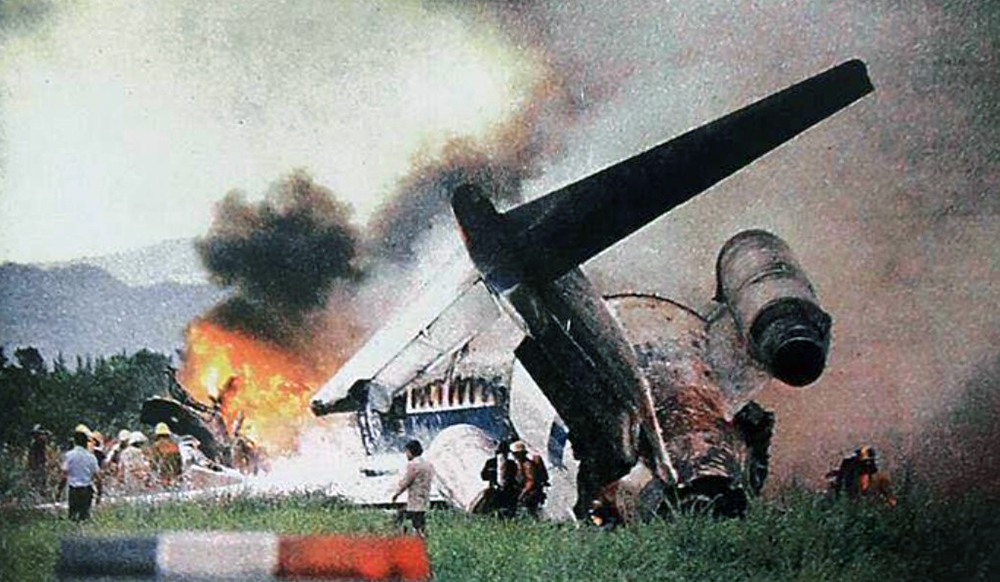
Circumstances:
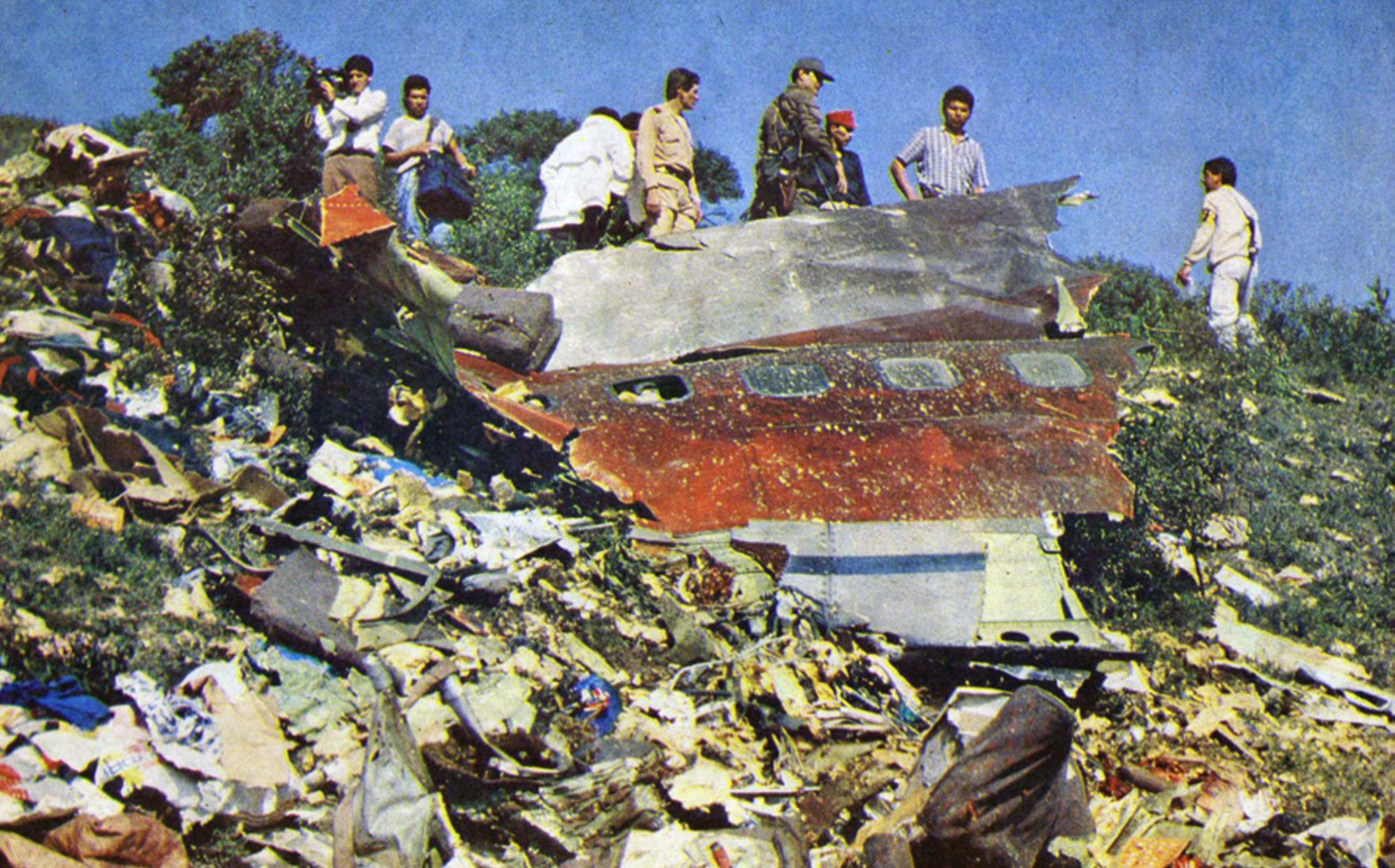
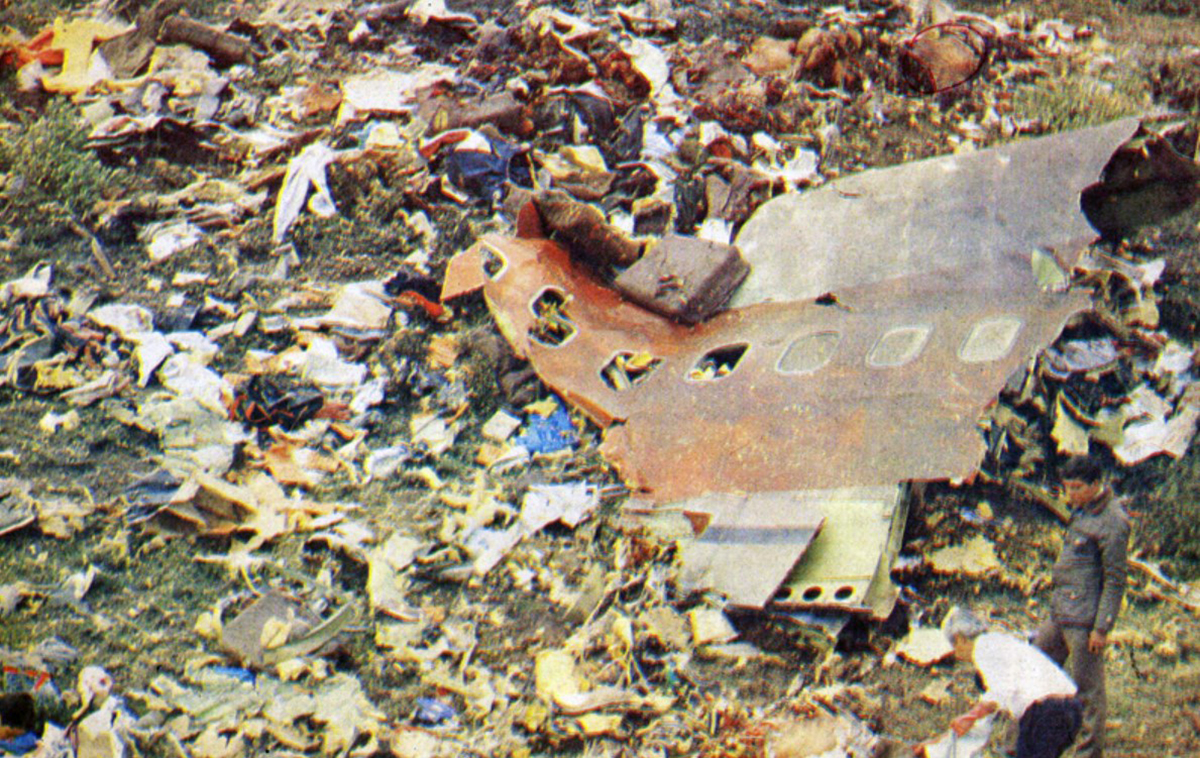
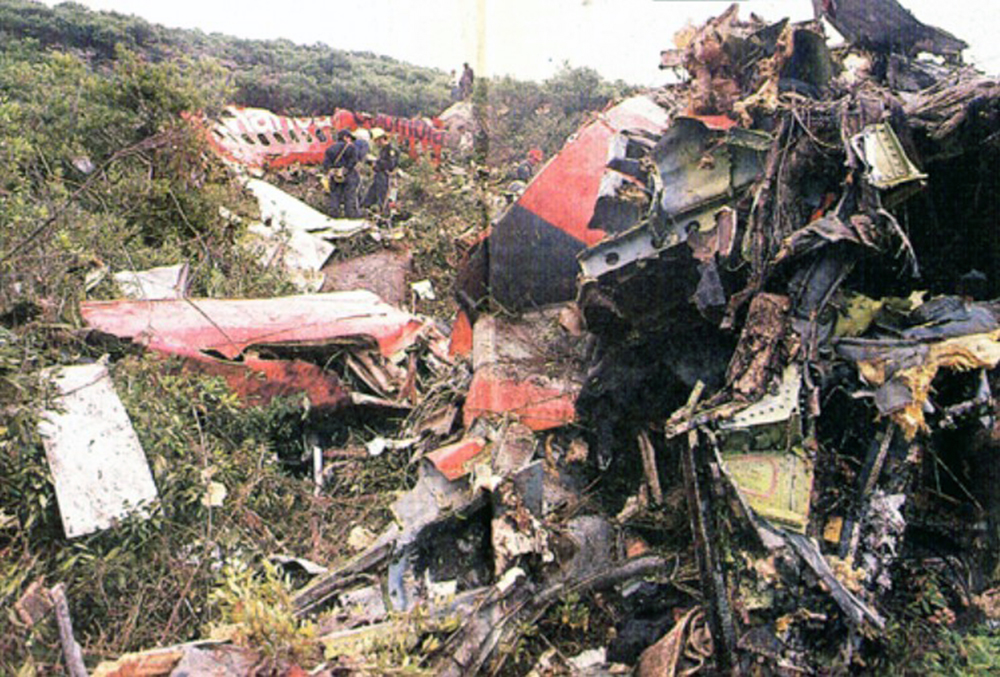
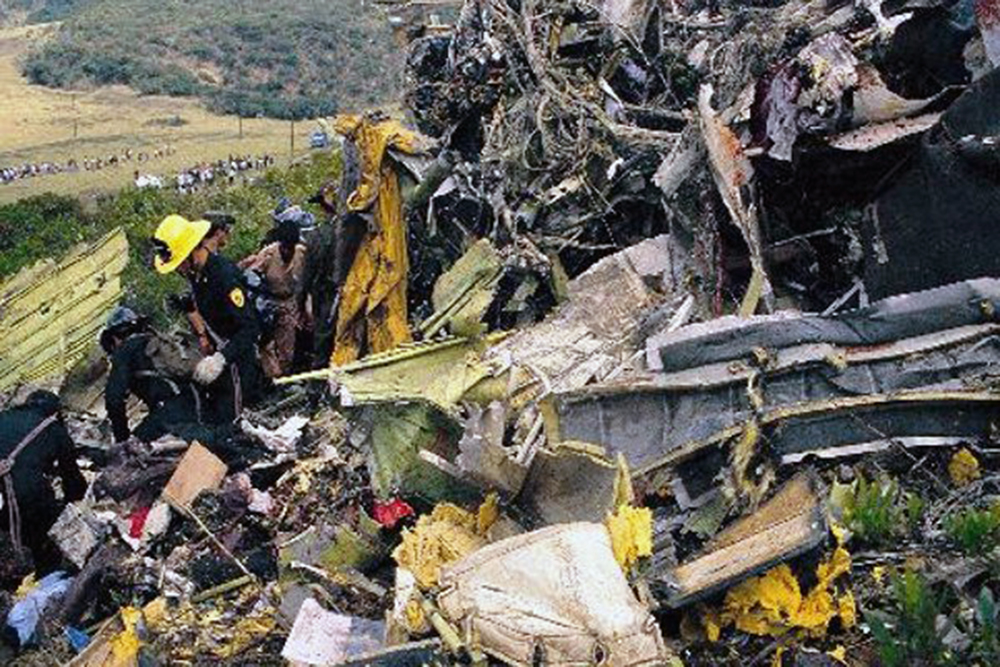
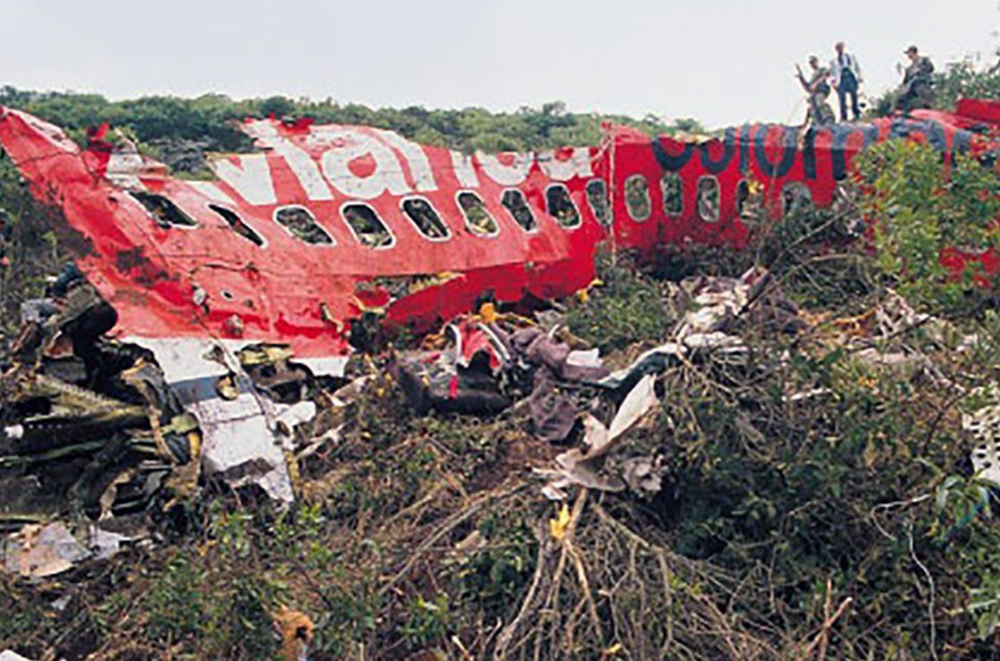
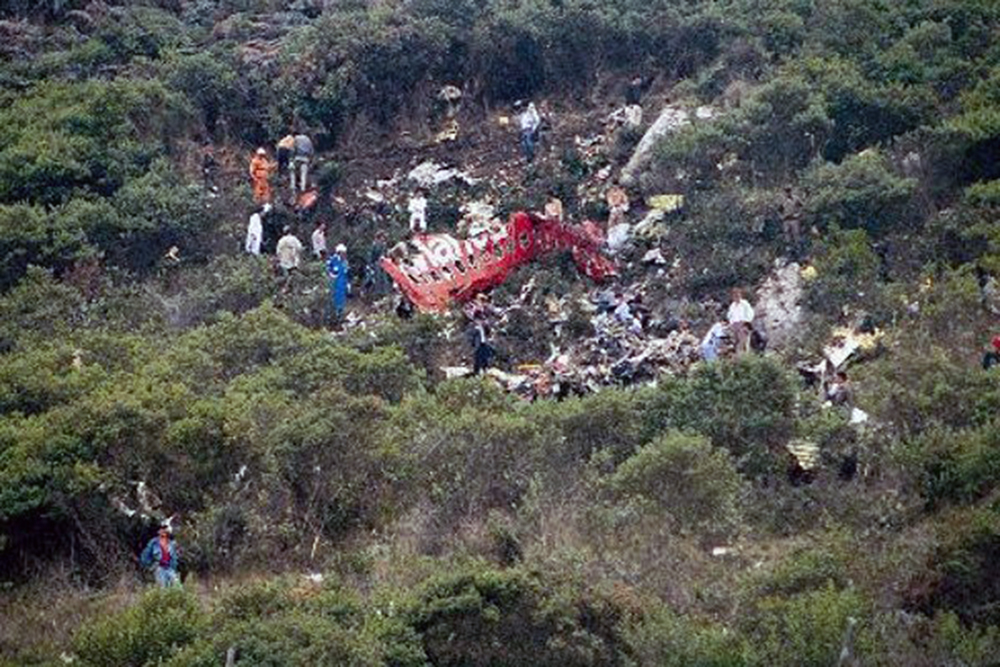
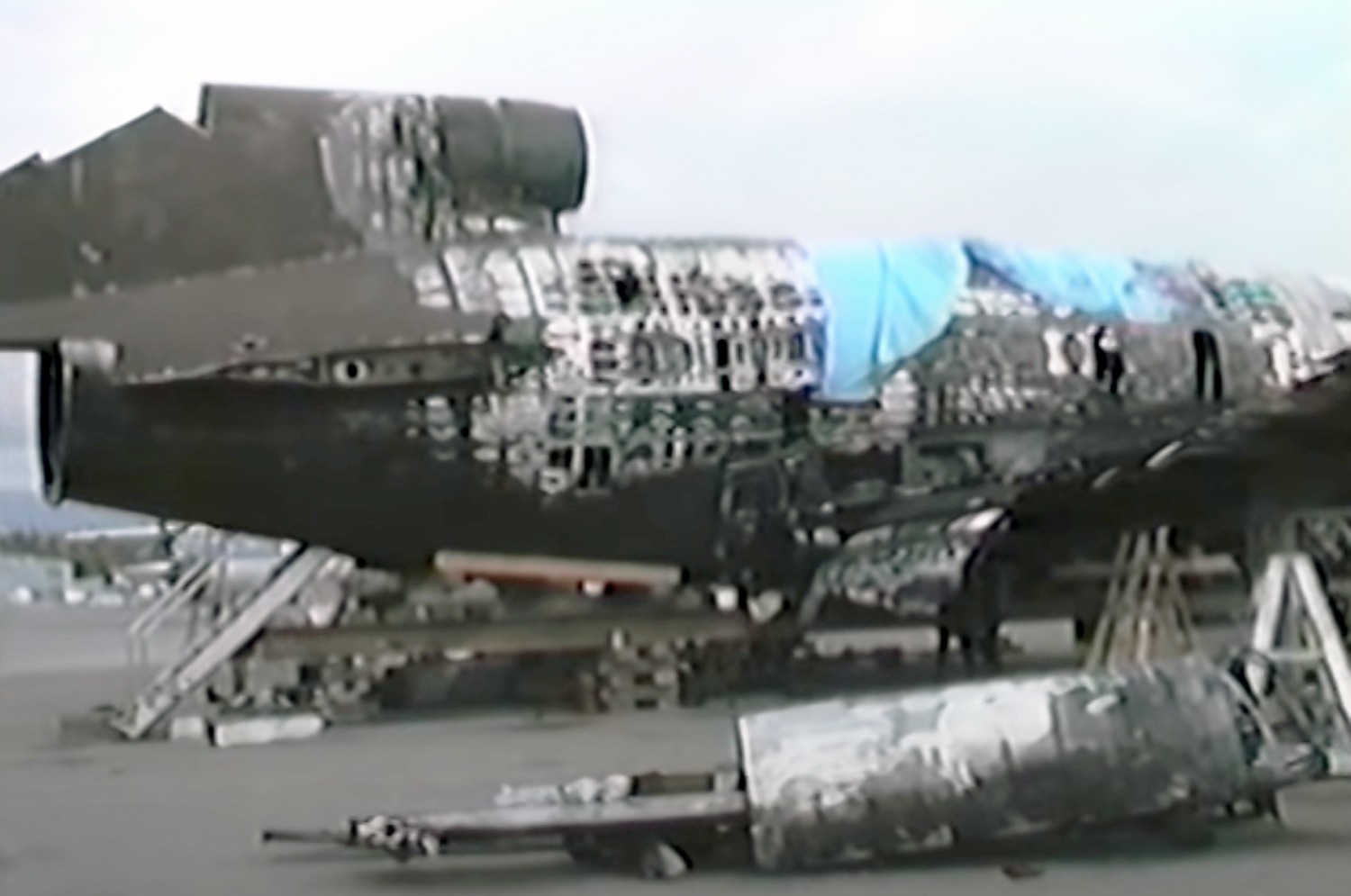
N425EX was on the takeoff roll when the flightcrew experienced a 'thump' that resounded through the airplane. They also observed erratic engine indications from the n°3 engine. The captain aborted the takeoff and stopped the airplane on the runway. The fire warning system activated on the n°3 engine after the airplane came to rest. The crew attempted to extinguish the fire with the airplane's fire extinguishing system; however, they were unsuccessful. The post accident examination of the n°3 engine revealed the high pressure compressor disk had failed due to a fatigue crack that originated from a corrosion pit. The shrapnel from the disk penetrated the engine nacelle and severed the main fuel line for the engine. The fuel ignited and burned into the fuselage, igniting the 12,600 lbs of cargo (US Mail).
Probable cause:
A catastrophic and uncontained failure of the n°3 engine which resulted in a fuel fed fire.
Final Report: