Country
Crash of a Boeing 727-30 near Kindu: 41 killed
Date & Time:
Oct 10, 1998 at 1105 LT
Registration:
9Q-CSG
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Kindu - Kinshasa
MSN:
18369
YOM:
1965
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
38
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
41
Circumstances:
Three minutes after takeoff from Kindu Airport, while climbing, the captain contacted ATC and reported an explosion in the rear of the aircraft. He was able to maintain contact with ATC for few minutes when the aircraft crashed in a jungle some 39 km east of the Airport, 11 minutes later. The aircraft was totally destroyed upon impact and all 41 occupants were killed, among them 20 woman and children.
Probable cause:
It was determined that the aircraft had been shot down by a SAM-7 surface-to-air missile.

Ground accident of a Boeing 727-51C in Denver
Date & Time:
Oct 1, 1997 at 0436 LT
Registration:
N414EX
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Denver – San Francisco
MSN:
18899/256
YOM:
1966
Flight number:
RYN607
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
7305.00
Aircraft flight hours:
47098
Aircraft flight cycles:
45215
Circumstances:
As the cargo jet was taxiing for takeoff in a non movement area, it was struck by an airport employee shuttle bus. The airplane captain was seriously injured. Visual meteorological conditions prevailed, and the collision occurred during predawn hours. The bus driver said he stopped at the stop sign, turned on the 4-way flasher lights, and looked both ways. He saw one inbound aircraft to the right that had stopped. He did not see the airplane approaching from the left as he started across the cargo ramp. The airplane crew stated they did not see the bus until seconds before impact. Airplane skid marks, measuring 22 and 24 feet in length, were noted on the taxiway. No bus skid marks were noted on the roadway.
Probable cause:
Failure of the bus driver to yield the right of way to oncoming traffic due to his inadequate visual lookout. Factors were visibility restrictions, inadequate driver training by management, and the flight crew's inadequate visual lookout due to their attention being diverted by performing the pre takeoff checklist.
Final Report:
Crash of a Boeing 727-23F in Lucapa
Date & Time:
Aug 19, 1997
Registration:
D2-TJC
Survivors:
Yes
MSN:
19180
YOM:
1966
Crew on board:
4
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
Damaged beyond repair following a hard landing at Lucapa Airport. All four crew members escaped uninjured.
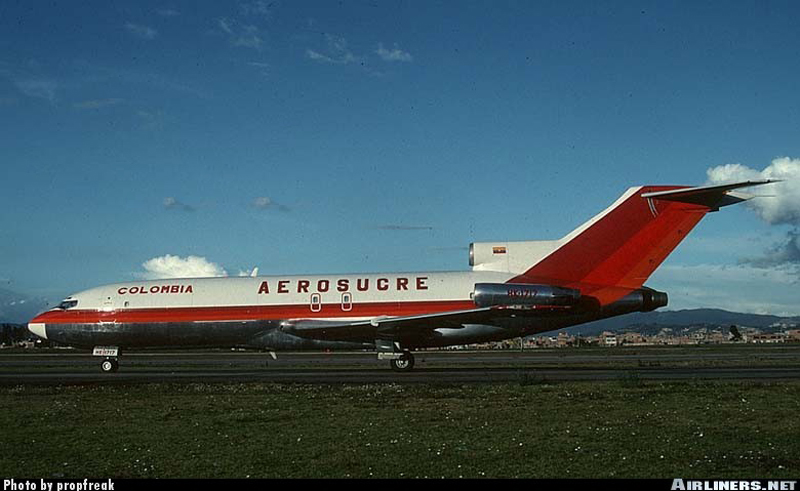
Crash of a Boeing 727-21F in Bogotá
Date & Time:
Jun 25, 1997 at 0122 LT
Registration:
HK-1717
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Bogotá – Barranquilla
MSN:
18993/215
YOM:
1965
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
3
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
8664.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
292
Aircraft flight hours:
51014
Circumstances:
During the takeoff roll un runway 31 at Bogotá-El Dorado Airport, at a speed of 130 knots, the crew heard two explosions. As the aircraft started to vibrate, the captain decided to abandon the takeoff procedure and initiated an emergency braking manoeuvre. Unable to stop within the remaining distance, the aircraft overran, rolled for 497 metres then lost its nose gear and came to rest. All six occupants escaped uninjured while the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.
Probable cause:
It was determined that the tread on the left front tyre (nose gear) deflated and broke off during takeoff, causing severe vibrations. This caused the antiskid system to be unserviceable and the aircraft could not be stopped on the remaining distance as the runway surface was humid. It was also reported that no information were available from both CVR and FDR systems. At the time of the accident, the total weight of the aircraft was 1,461 kilos above MTOW, making the decision speed (V1) to be higher by reducing the stopping distance, which was insufficient when discontinuing the pilot controls takeoff in wet runway conditions.
Final Report:

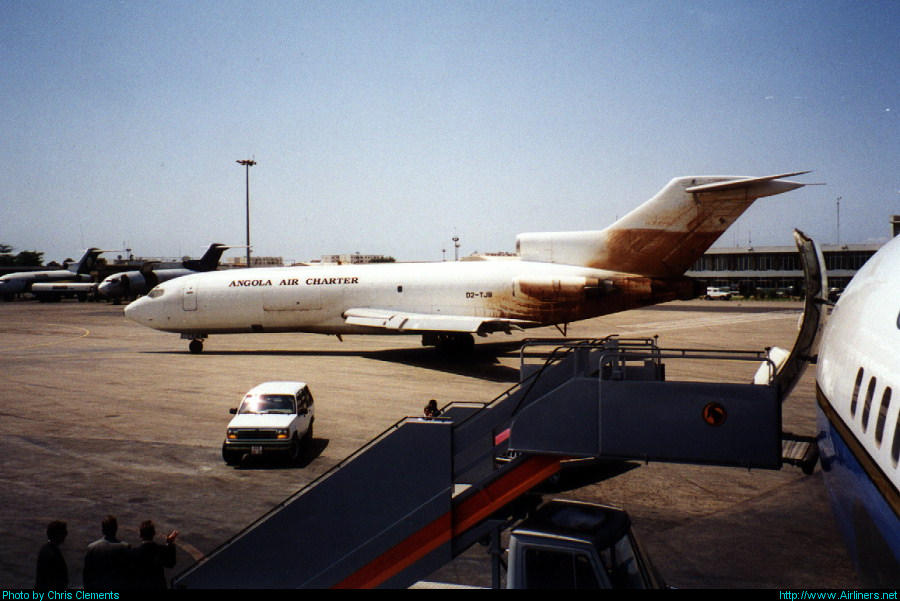
Crash of a Boeing 727-21F in Huambo
Date & Time:
Jan 31, 1995
Registration:
D2-TJB
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Luanda - Huambo
MSN:
19005
YOM:
1966
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
While descending to Huambo-Albano Machado Airport, the crew was informed by ATC that works were in progress and the first 500 metres portion of the runway 01/19 was closed to traffic. Following a wrong approach configuration, the aircraft landed too far down the runway (about half way down) and was unable to stop within the remaining distance. It overran, lost its undercarriage and came to rest 250 metres further. All three crew members escaped uninjured while the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.
Probable cause:
Wrong approach configuration on part of the crew who landed the aircraft too far down the runway, causing the landing distance available to be insufficient. As the landing was obviously missed, the crew failed to initiate a go-around procedure. Also, it was reported that the braking action was poor due to the presence of puddles and potholes in the runway surface.

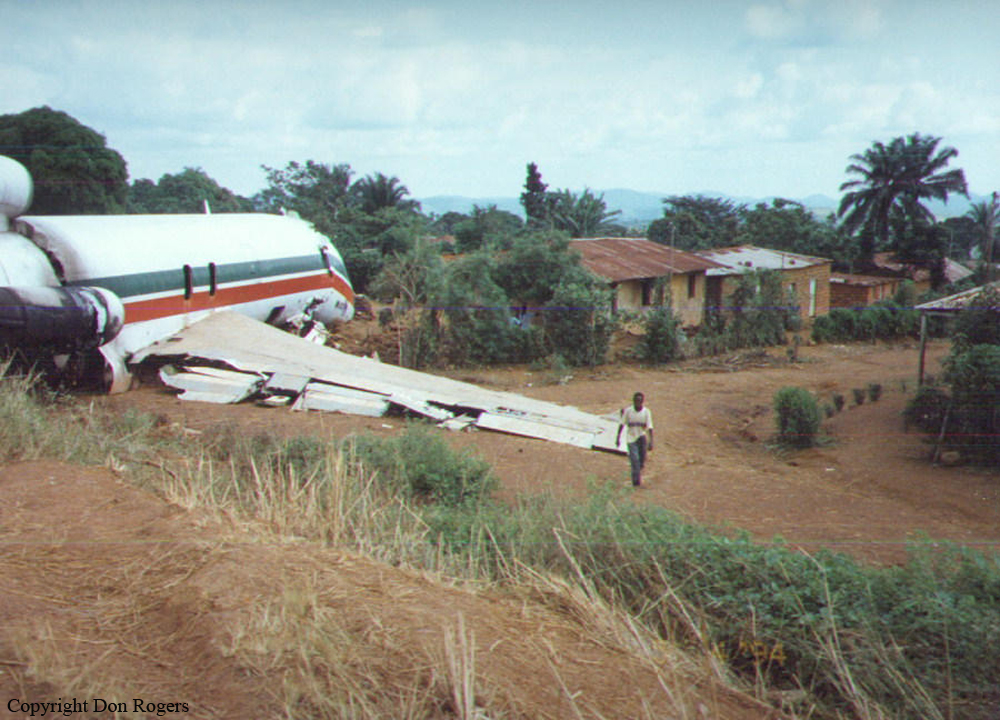
Crash of a Boeing 727-44F in M'Banza Kongo: 7 killed
Date & Time:
Apr 27, 1994 at 1610 LT
Registration:
S9-TAN
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Luanda - M'Banza Kongo
MSN:
18893
YOM:
1965
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
7
Circumstances:
On final approach to M'Banza Kongo Airport, the aircraft was too low and struck the ground 3,200 metres short of runway. It reached a little altitude then descended again and struck the ground a second time two metres short of runway. On impact, the left main gear struck a drainage ditch and was torn off. The aircraft slid on the ground, veered to the right when the right wing struck a bus. All three crew members escaped with minor injuries while seven people in the bus were killed.
Probable cause:
The M'Banza Kongo runway is relatively short and the crew must complete a low approach to be able to land as early as possible. Here, the crew completed a too low approach, causing the aircraft to struck the ground twice before runway threshold.

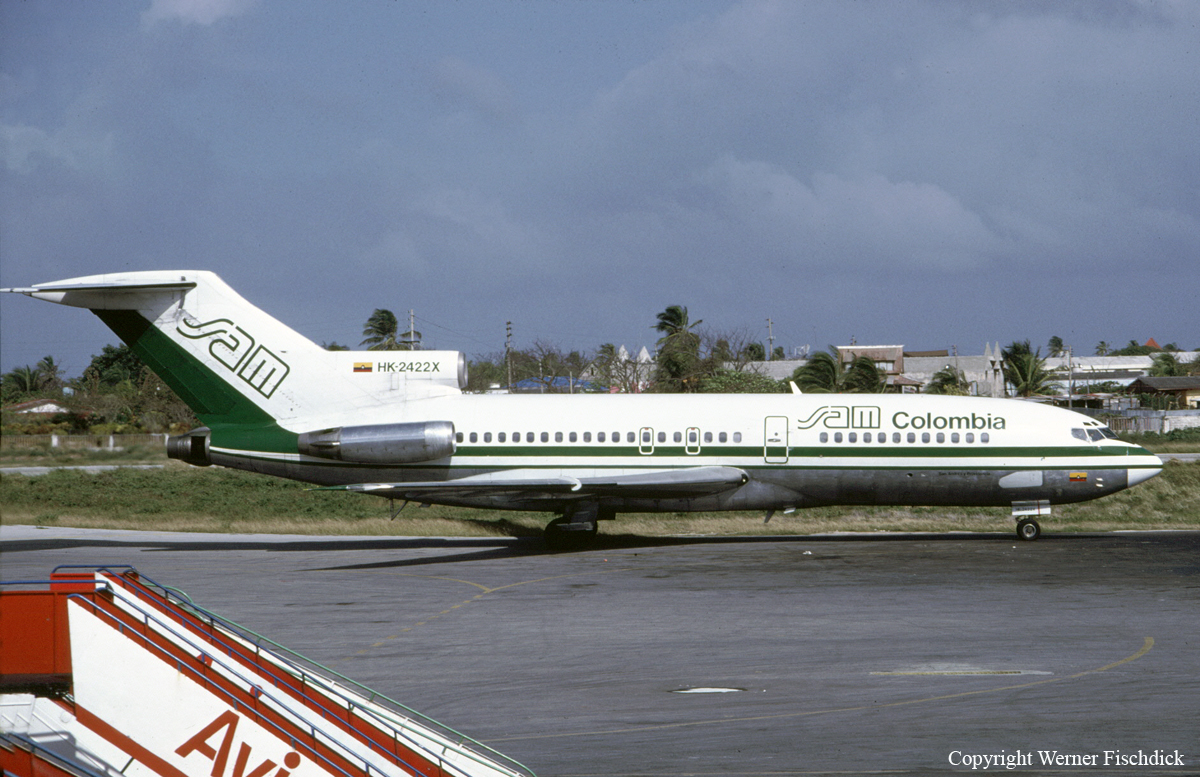
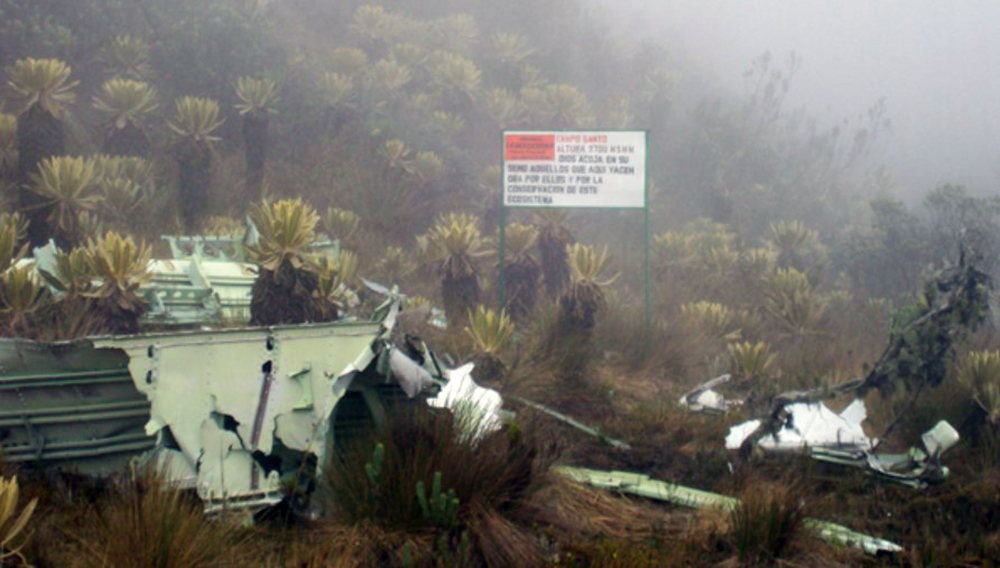
Crash of a Boeing 727-46 on Mt Páramo Frontino: 132 killed
Date & Time:
May 19, 1993 at 1506 LT
Registration:
HK-2422X
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Panama City – Medellín – Bogotá
MSN:
18876
YOM:
1965
Flight number:
MM501
Crew on board:
7
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
125
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
132
Circumstances:
On the leg from Panama City to Medellín, the crew was approaching the Abejorral NDB at an altitude of 16,000 feet and was cleared to descend to FL120. Few minutes later, while descending to the altitude of 12,300 feet in poor weather conditions, the three engine aircraft struck the slope of Mt Páramo Frontino located about 85 km northwest of Medellín-José María Córdova Airport. The aircraft disintegrated on impact and all 132 occupants were killed. At the time of the accident, the visibility was poor due to clouds, mist and rain.
Probable cause:
It was determined that the accident was the consequence of a controlled flight into terrain after the crew mistakenly initiated the descent prematurely, causing the aircraft to descend below the minimum prescribed altitude. It was established that the crew reported to be over the Abejorral NDB while in fact, the aircraft did not reach already this beacon. Thunderstorm activity probably influenced some instruments and the RNG VOR was out of service since few month following a terrorist attack.