Crash of a Boeing 737-210C in Yellowknife
Date & Time:
May 22, 2001 at 1325 LT
Registration:
C-GNWI
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Edmonton – Yellowknife
MSN:
21066
YOM:
1975
Flight number:
7F953
Crew on board:
6
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
98
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
7000.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
840
Circumstances:
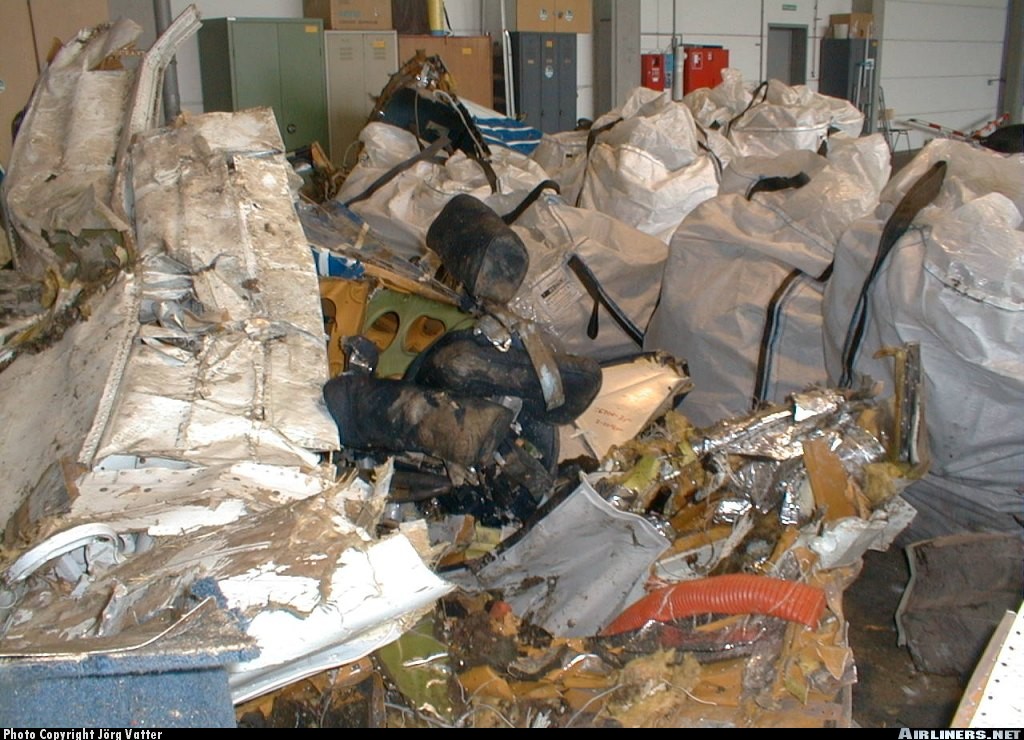
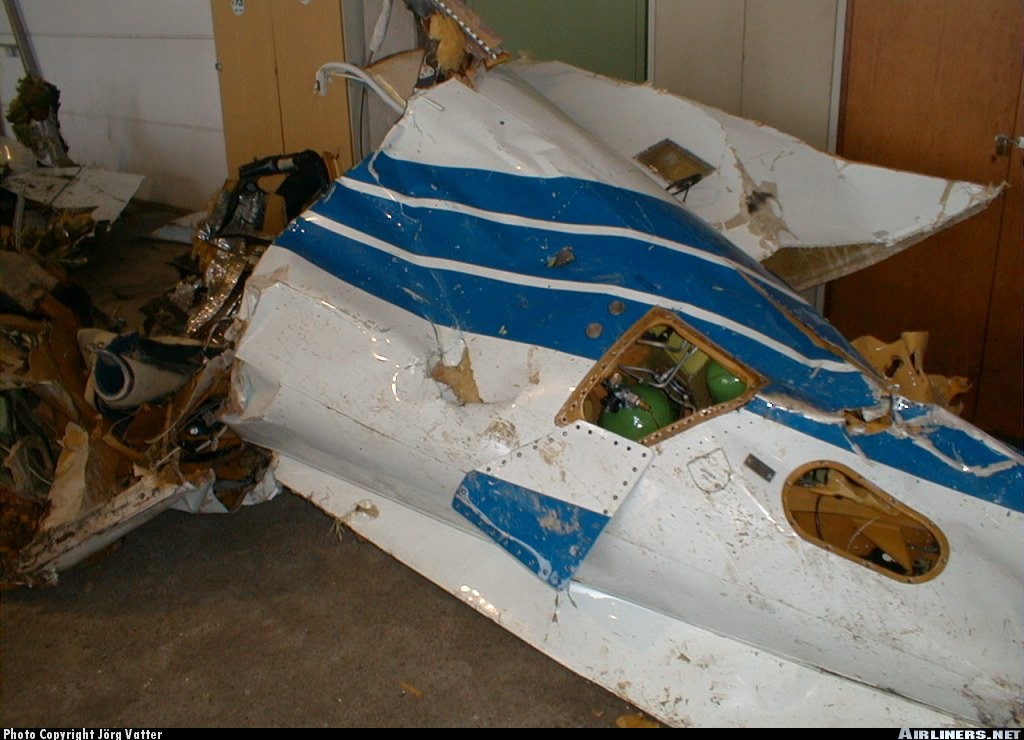
First Air Flight 953, a Boeing 737-210C, serial number 21066, was on a scheduled flight from Edmonton, Alberta, to Yellowknife, Northwest Territories. On board were 2 flight crew, 4 cabin crew, and 98 passengers. The flight departed Edmonton at 1130 mountain daylight time, with an estimated time en route of 1 hour 35 minutes. As the aircraft approached Yellowknife, the spoilers were armed, and the aircraft was configured for a visual approach and landing on Runway 33. The computed Vref was 128 knots, and target speed was 133 knots. While in the landing flare, the aircraft entered a higher-than-normal sink rate, and the pilot flying (the first officer) corrected with engine power and nose-up pitch. The aircraft touched down on the main landing gear and bounced twice. While the aircraft was in the air, the captain took control and lowered the nose to minimize the bounce. The aircraft landed on its nose landing-gear, then on the main gear. The aircraft initially touched down about 1300 feet from the approach end of Runway 33. Numerous aircraft rubber scrub marks were present in this area and did not allow for an accurate measurement. During the third touchdown on the nose landing-gear, the left nose-tire burst, leaving a shimmy-like mark on the runway. The aircraft was taxied to the ramp and shut down. The aircraft was substantially damaged. There were no reported injuries to the crew or the passengers. The accident occurred at 1325, during the hours of daylight.
Probable cause:
Findings as to Causes and Contributing Factors:
1. Incorrect bounced landing recovery procedures were carried out when the captain pushed forward on the control column to prevent a further bounce, and the aircraft landed nosewheel first.
2. The high sink rate on the initial flare was not recognized and corrected in time to prevent a bounced landing and a subsequent bounced landing.
Other Findings:
1. The power increase during the flair resulted in the speedbrake/spoilers retracting.
2. The captain had not received a line check of at least three sectors before returning to flight duties, although this check was required to regain competency after pilot proficiency check expiry.
1. Incorrect bounced landing recovery procedures were carried out when the captain pushed forward on the control column to prevent a further bounce, and the aircraft landed nosewheel first.
2. The high sink rate on the initial flare was not recognized and corrected in time to prevent a bounced landing and a subsequent bounced landing.
Other Findings:
1. The power increase during the flair resulted in the speedbrake/spoilers retracting.
2. The captain had not received a line check of at least three sectors before returning to flight duties, although this check was required to regain competency after pilot proficiency check expiry.
Final Report: