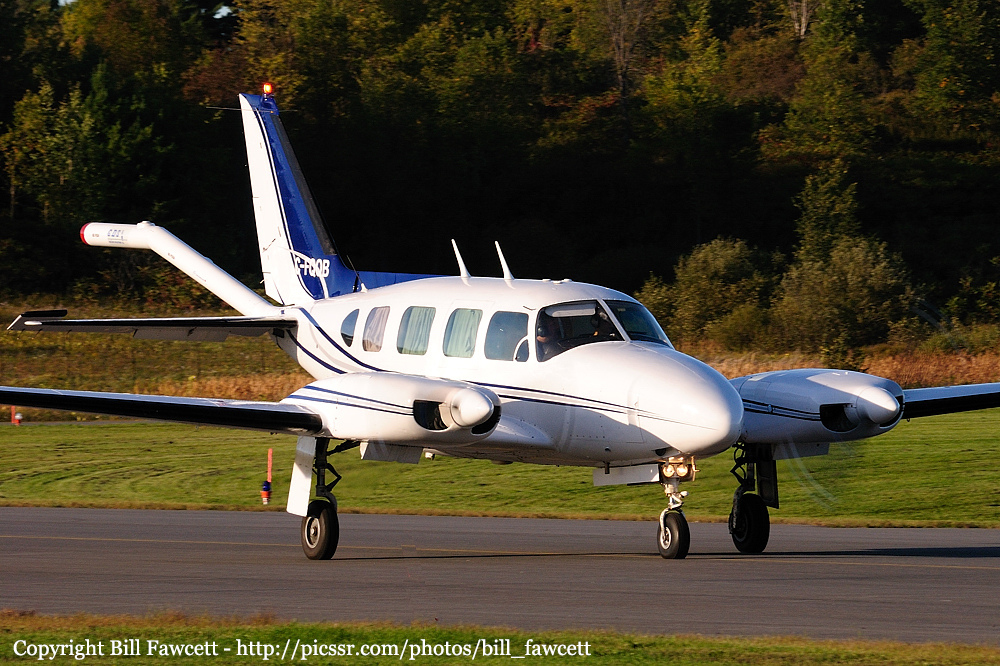
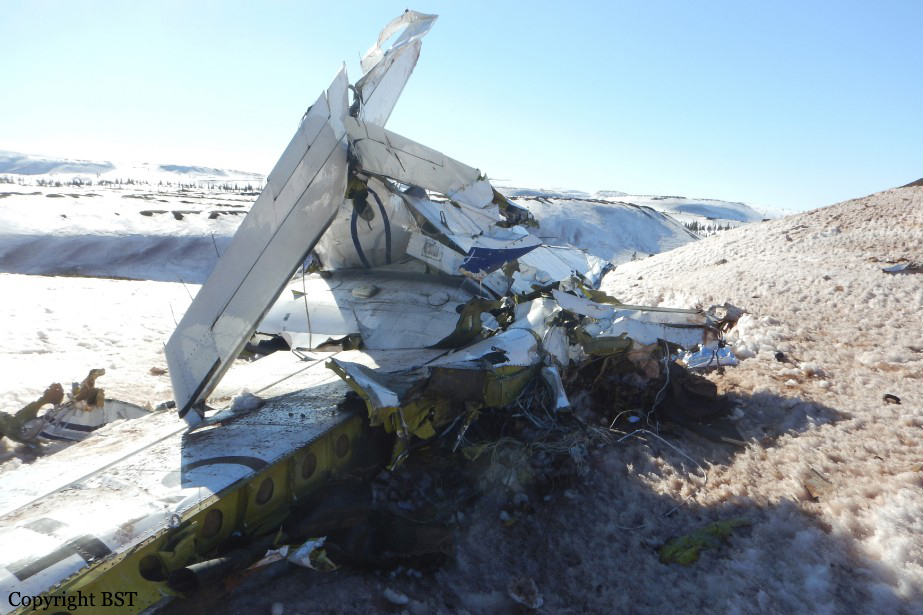
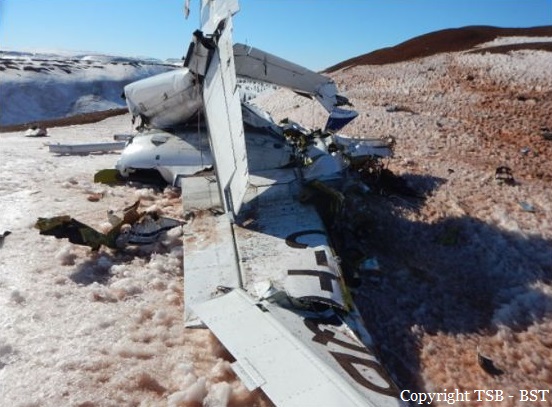
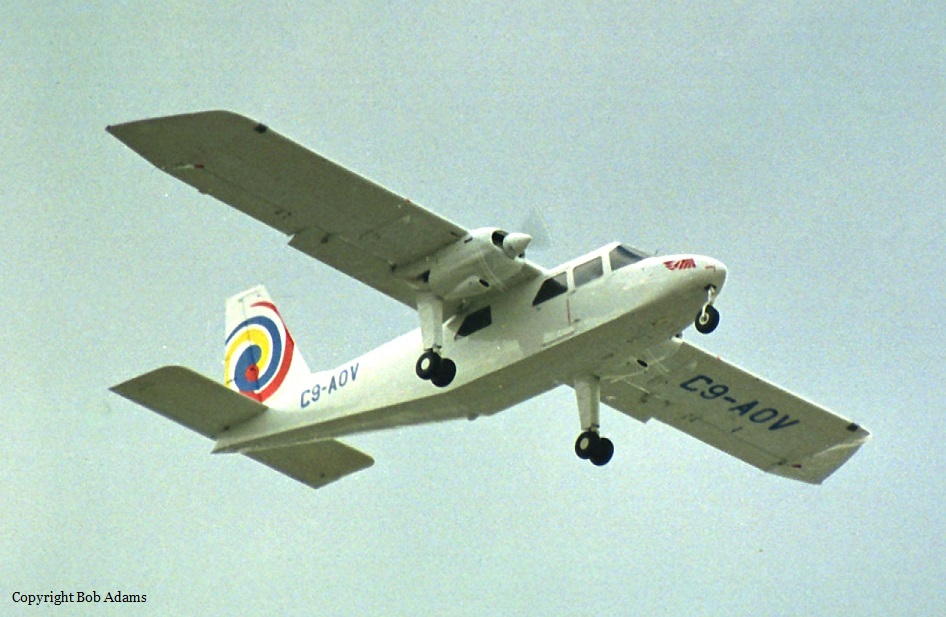
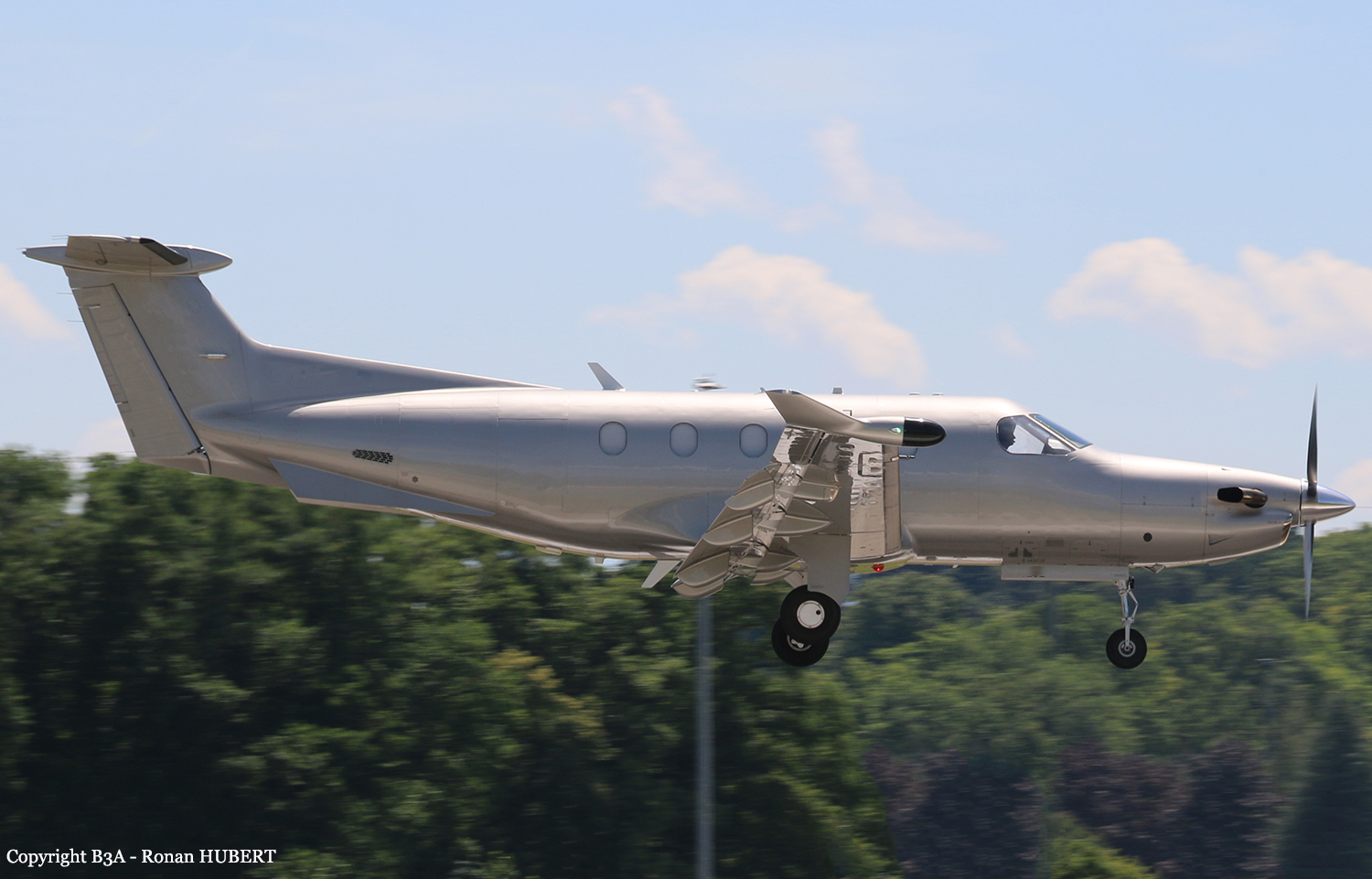
Crash of a Piper PA-31-310 Navajo in Schefferville: 2 killed
Date & Time:
Apr 30, 2017 at 1756 LT
Registration:
C-FQQB
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Schefferville - Schefferville
MSN:
31-310
YOM:
1968
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
2
Captain / Total hours on type:
110.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
650
Aircraft flight hours:
20180
Circumstances:
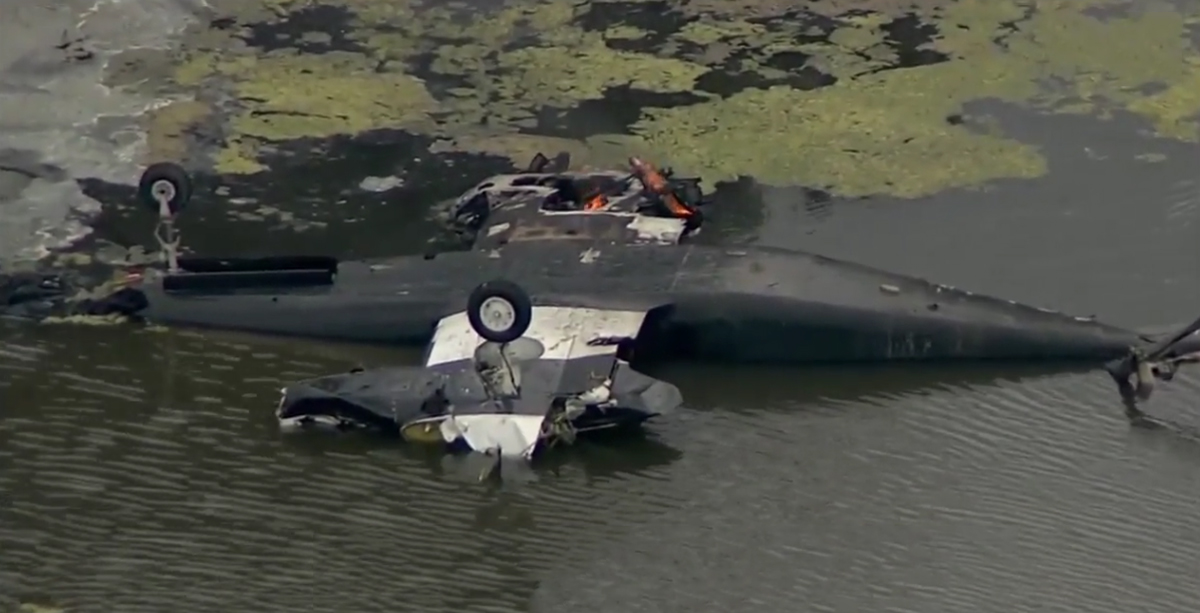
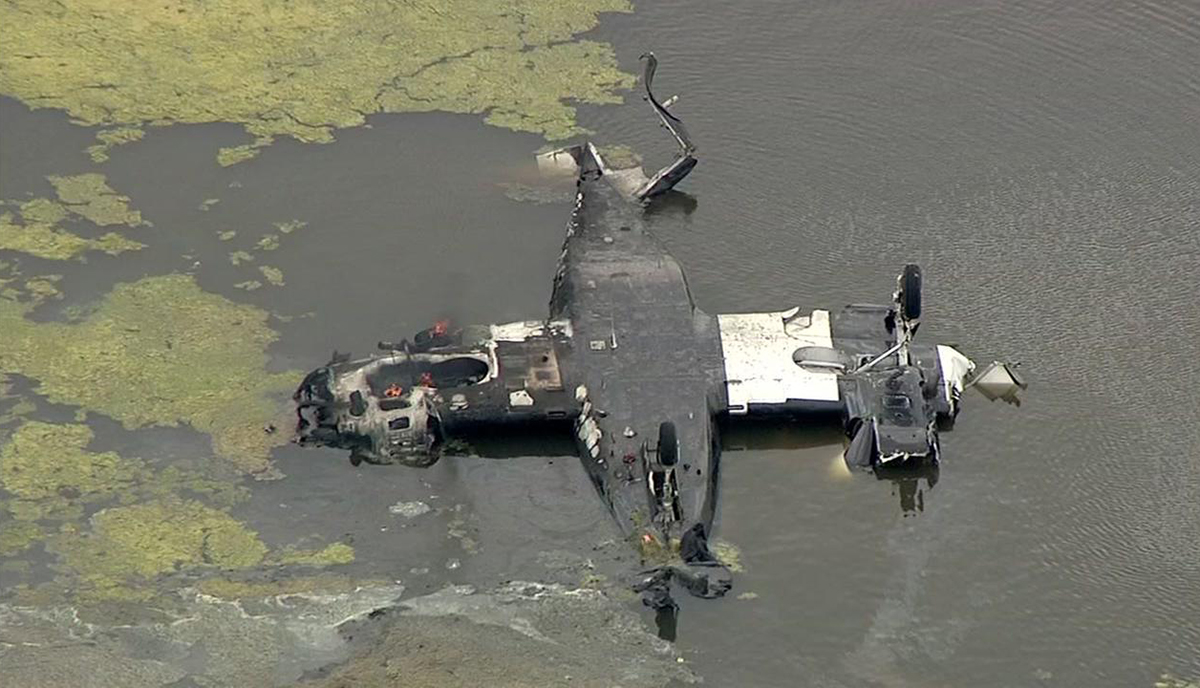
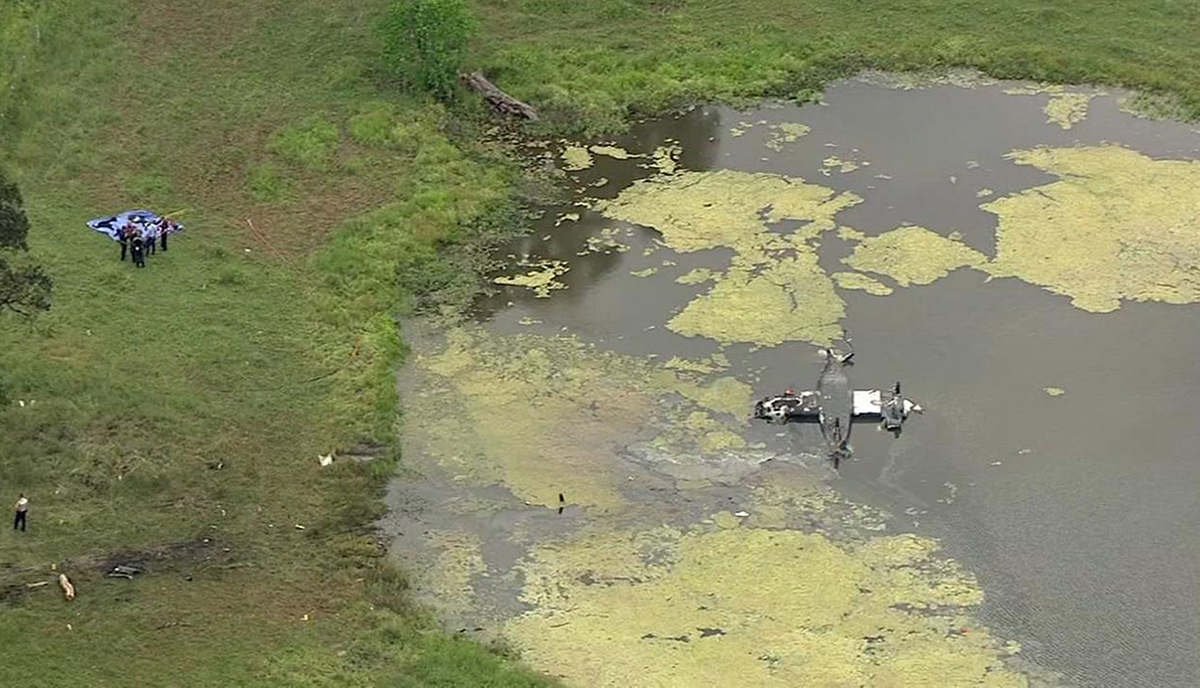
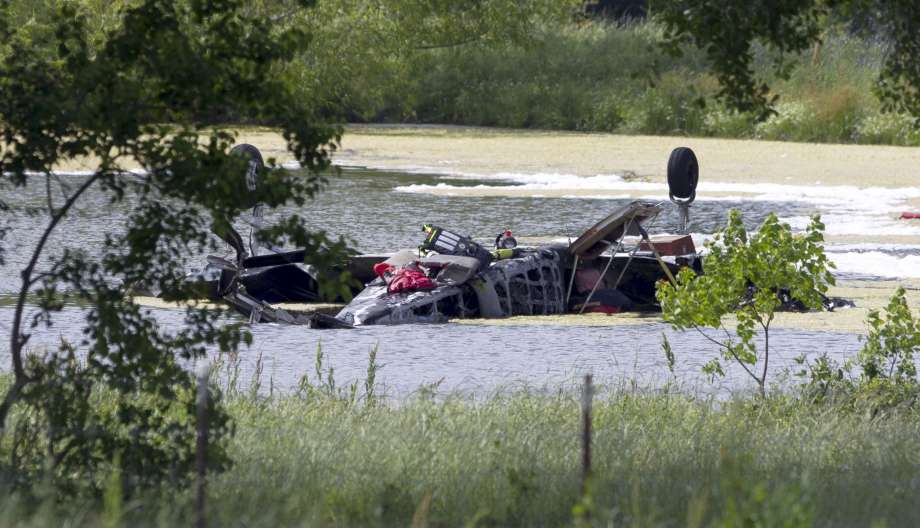
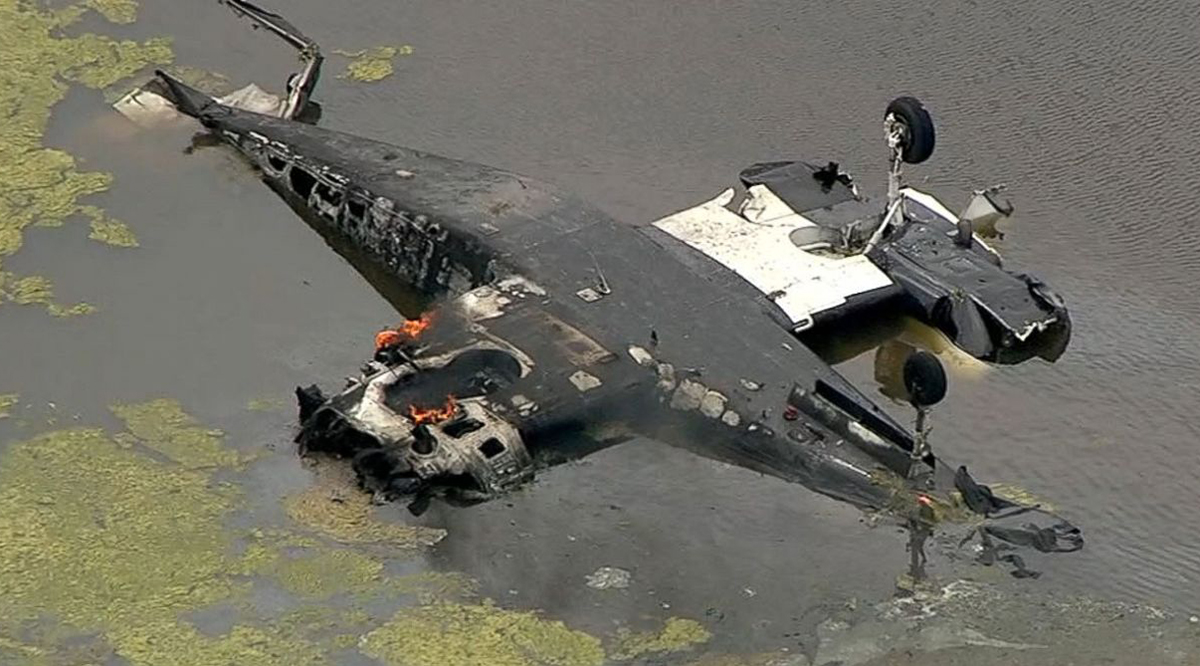
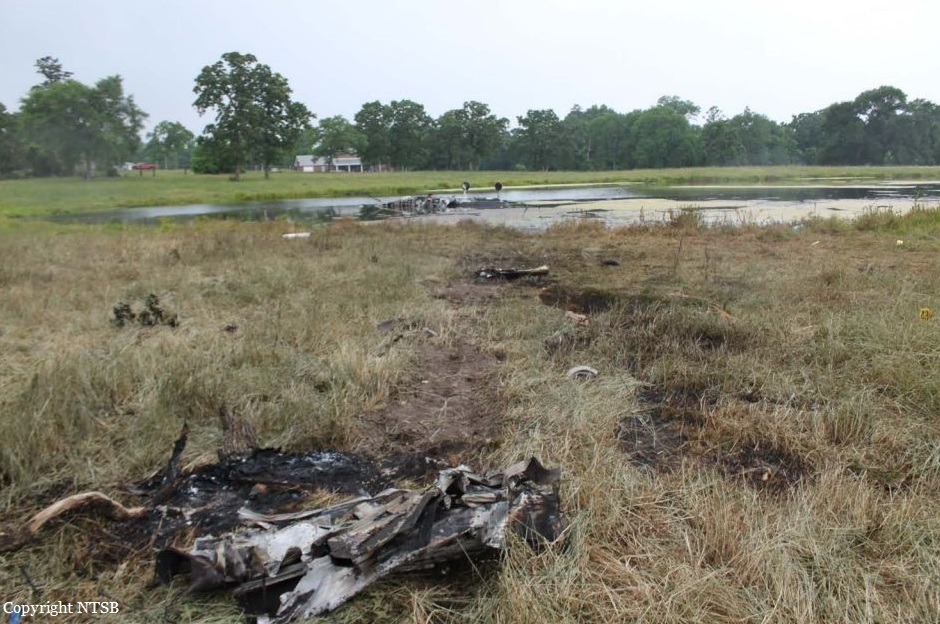
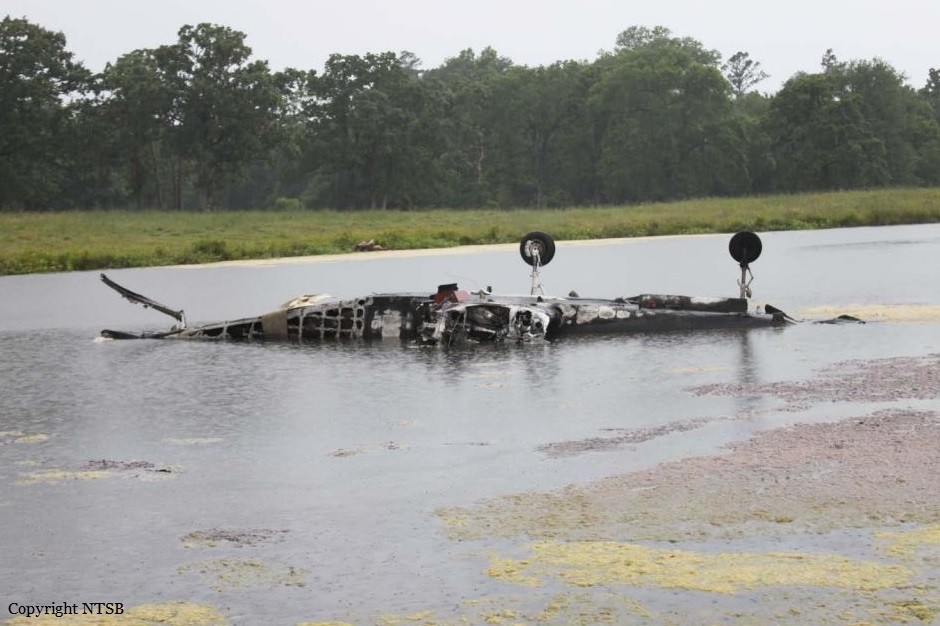
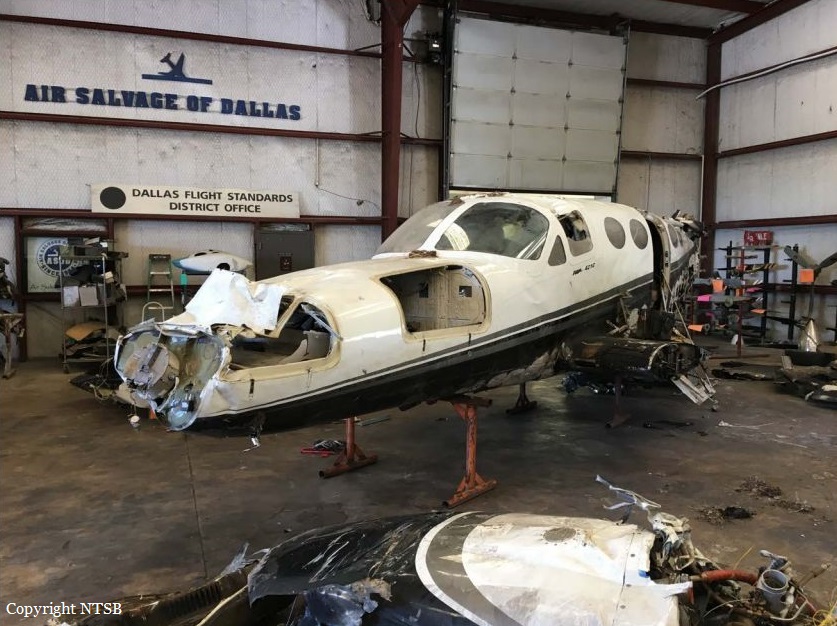
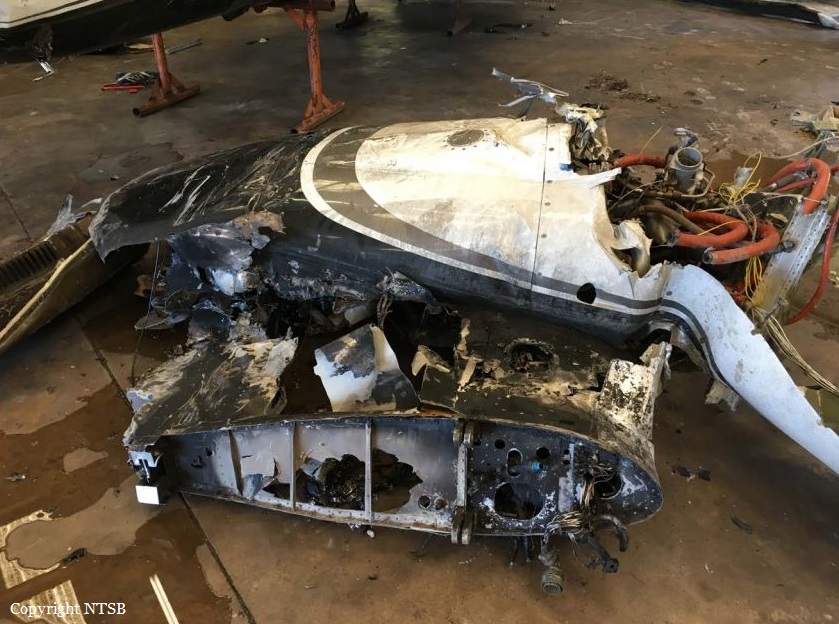
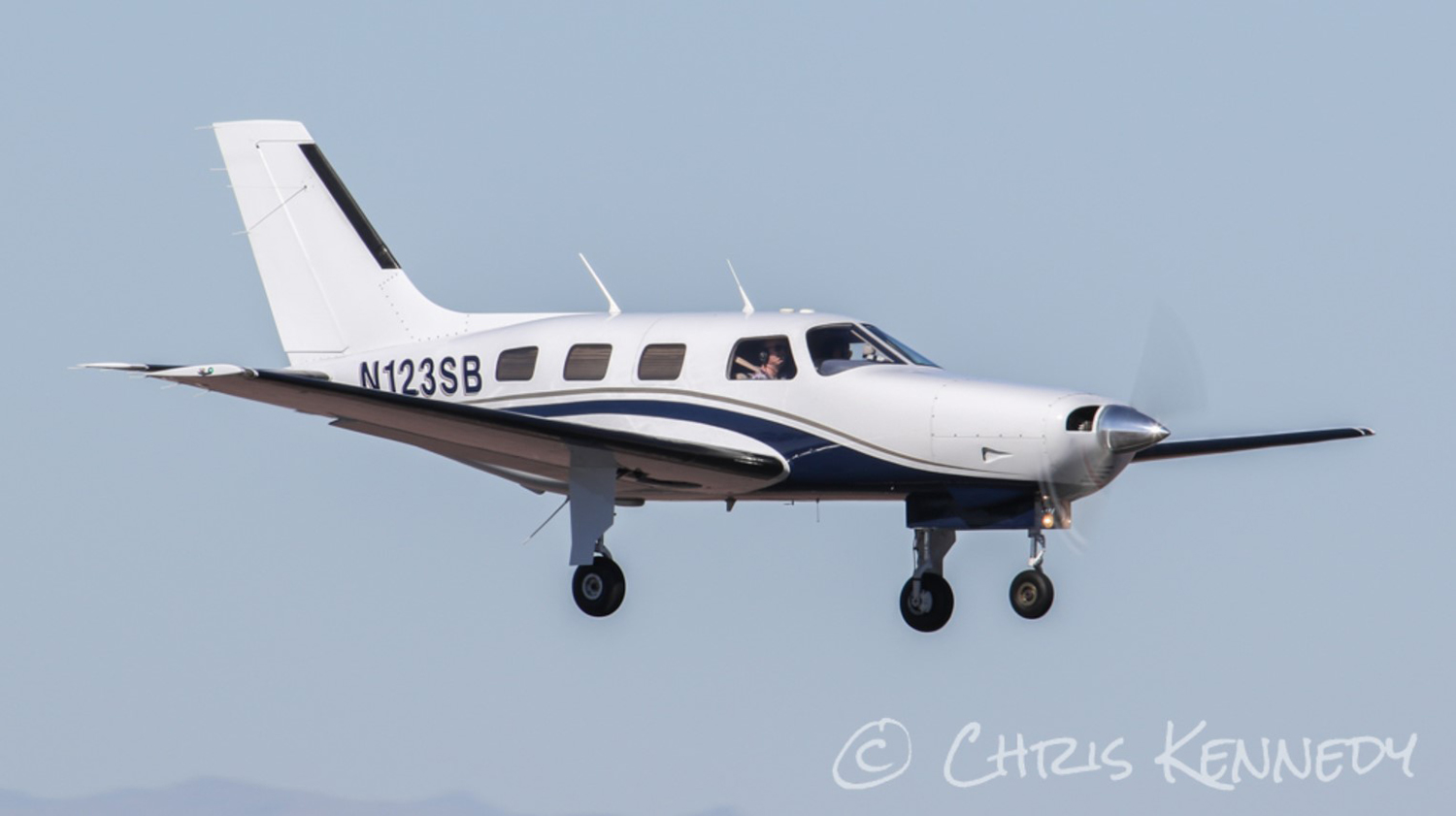
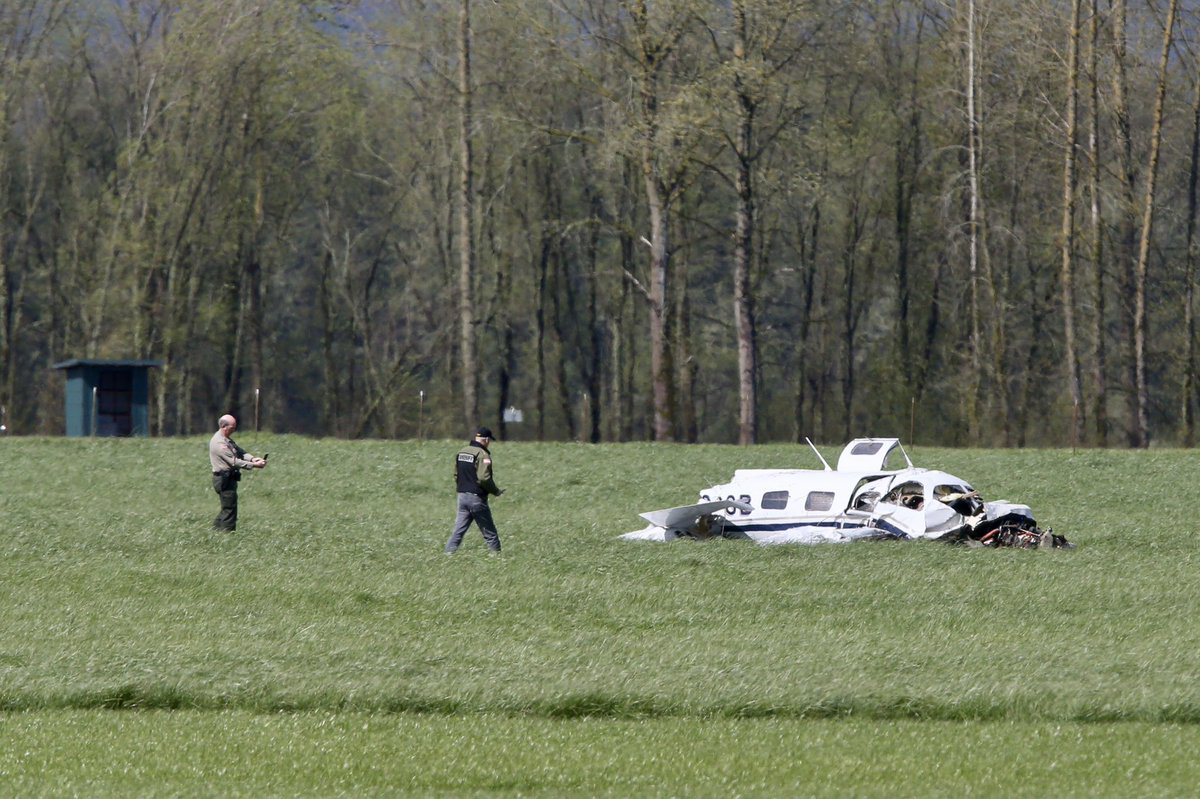
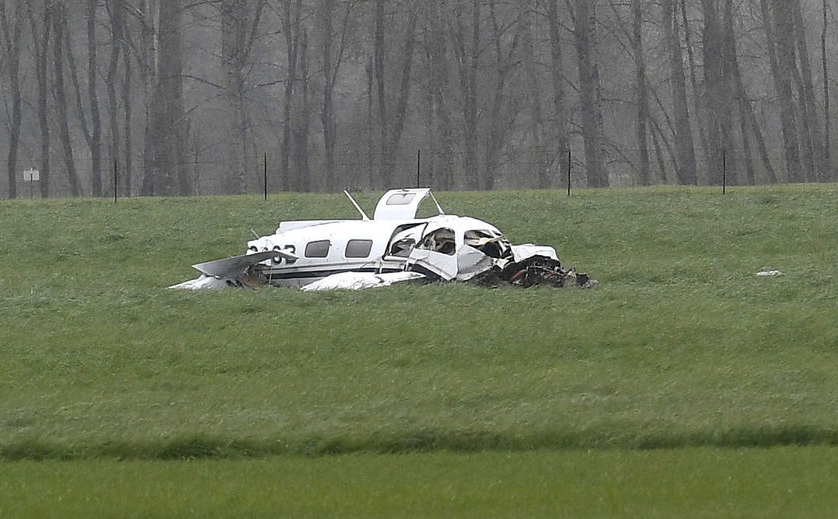
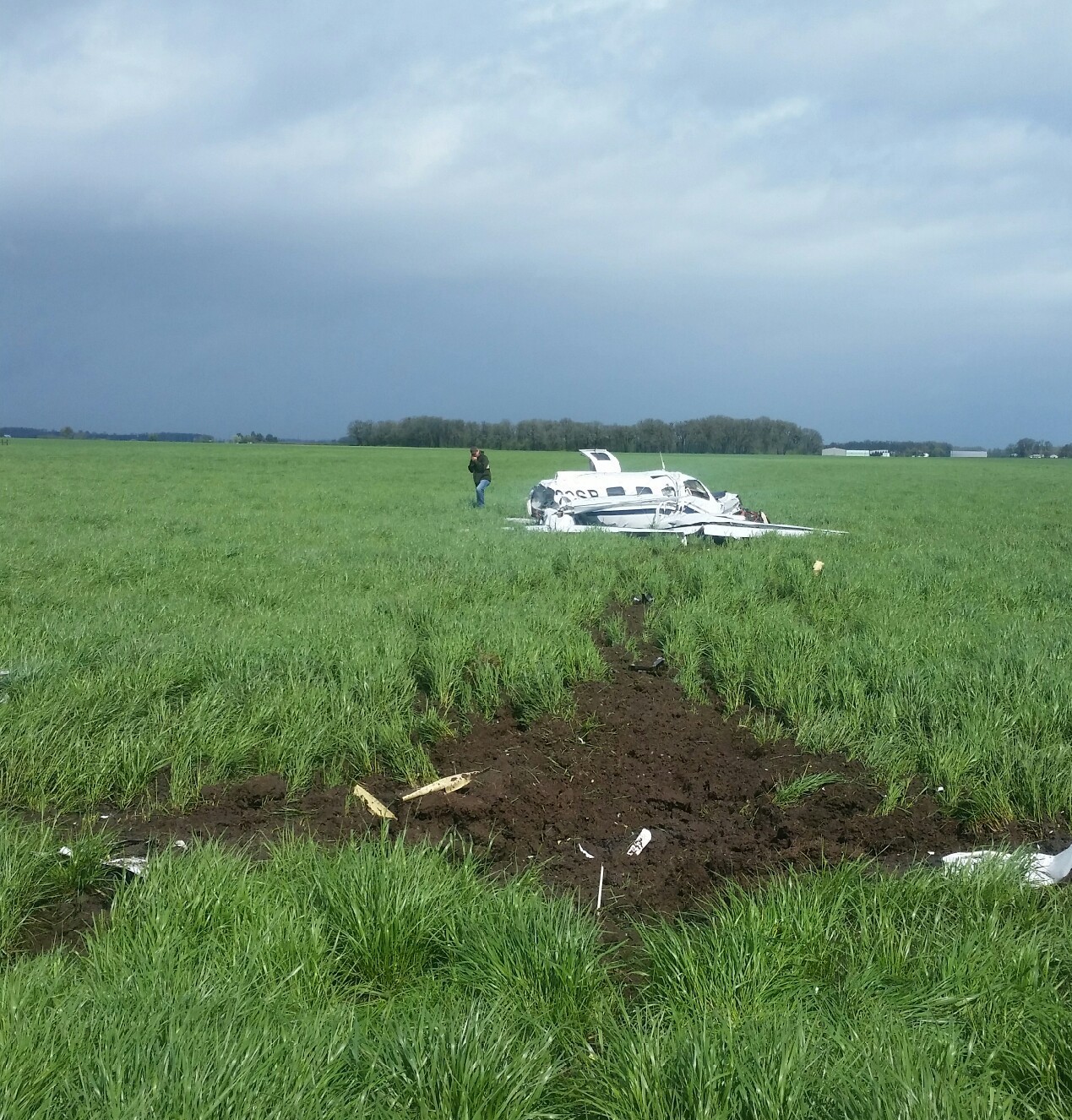
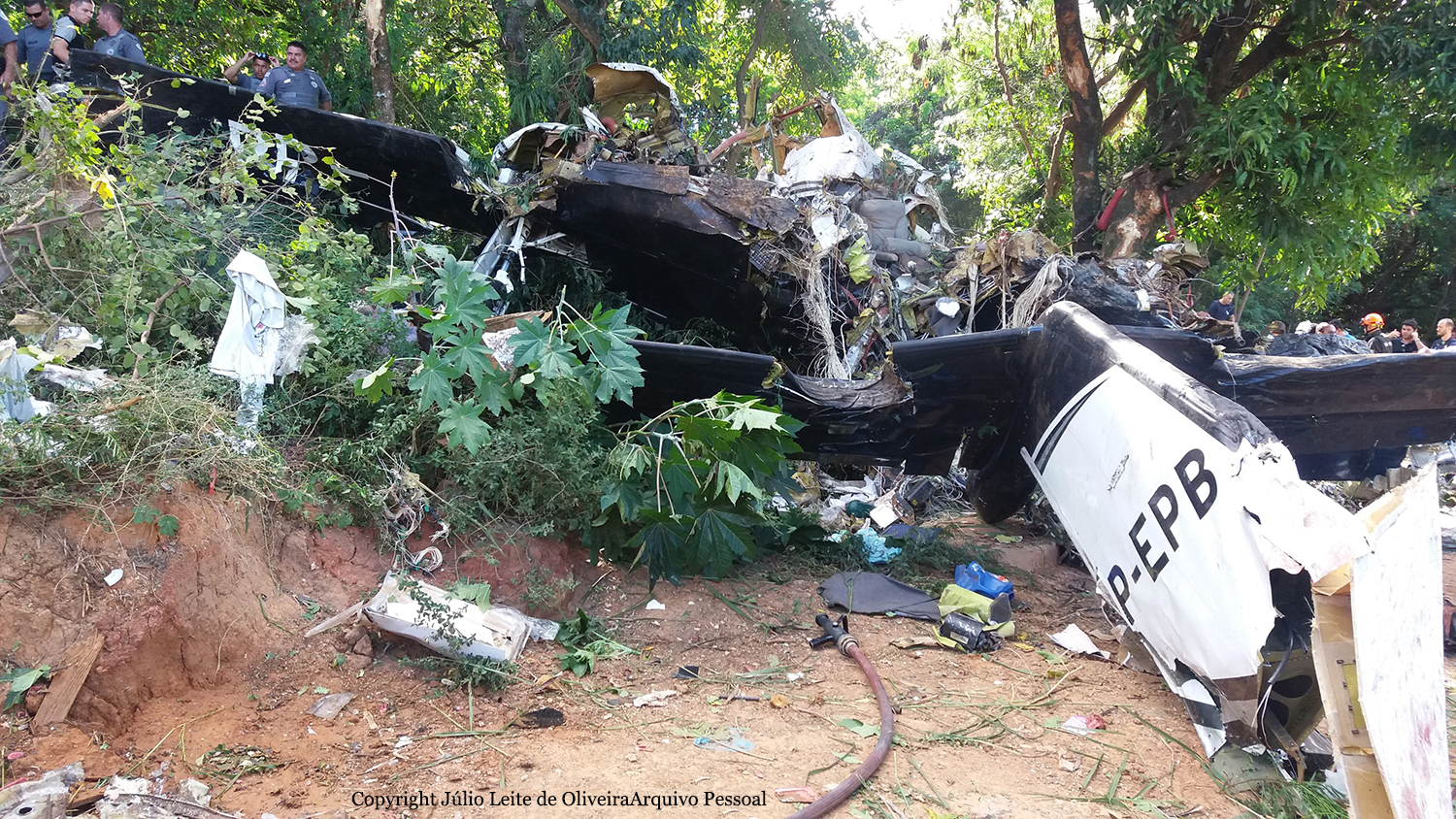
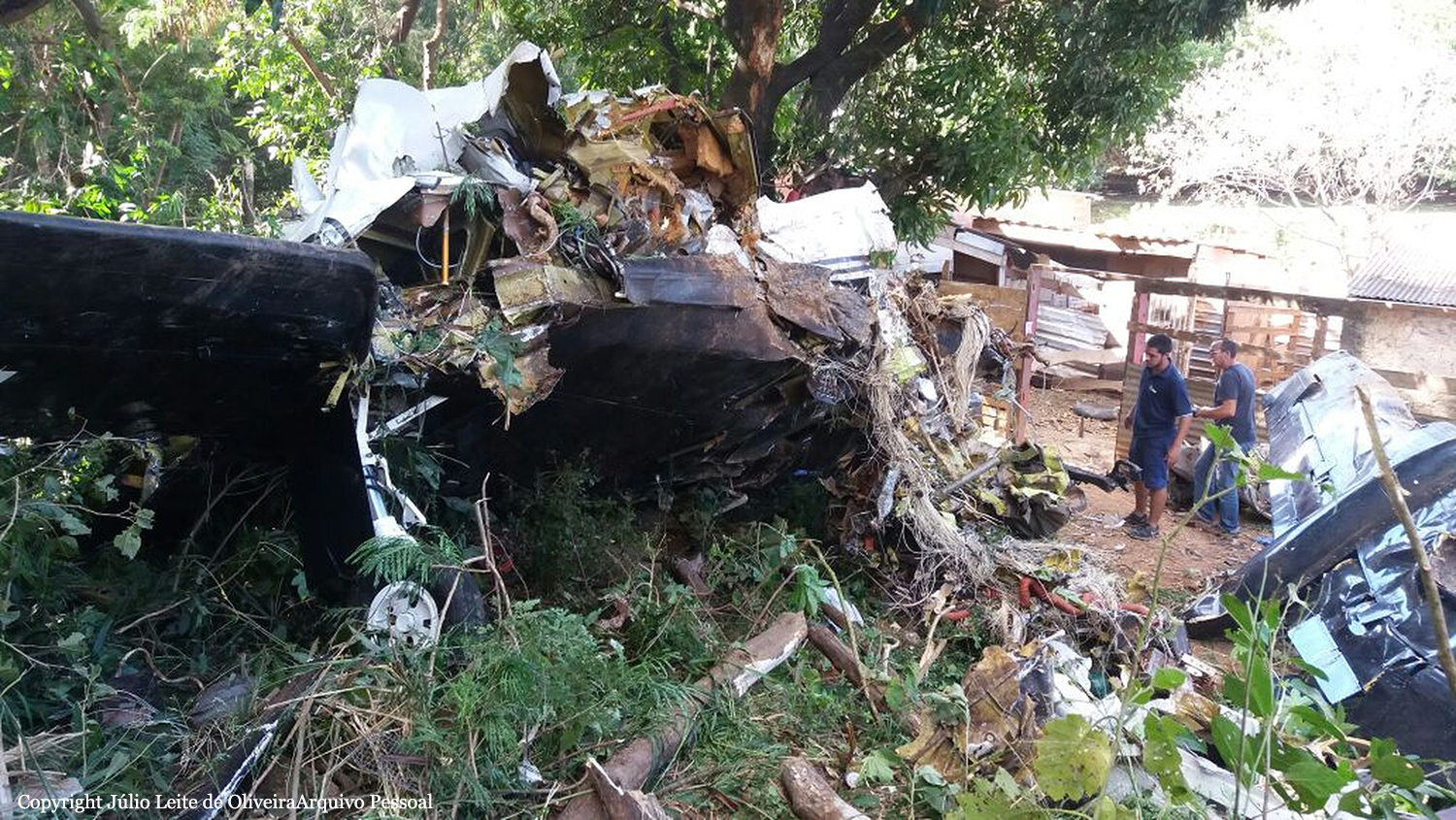
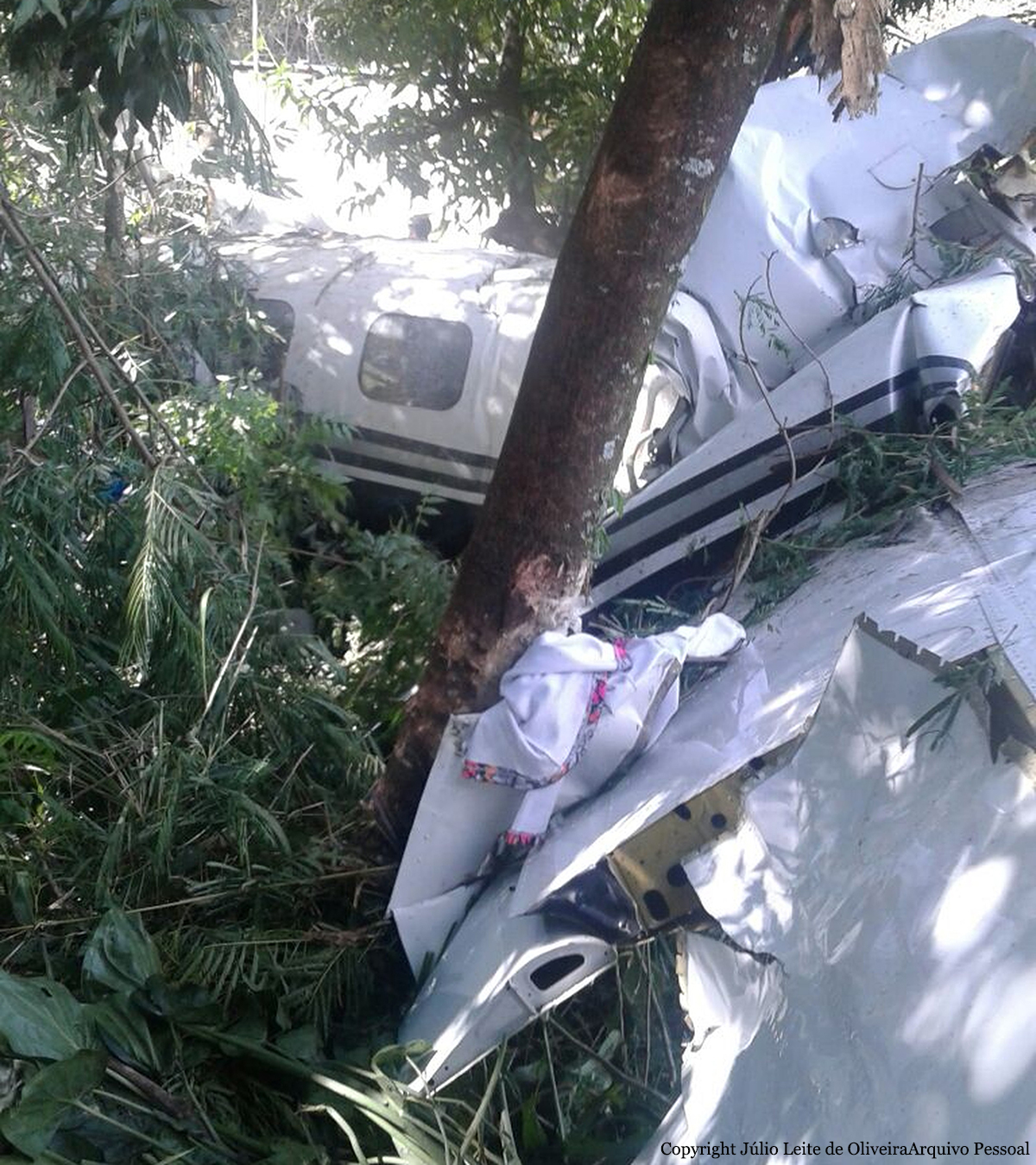
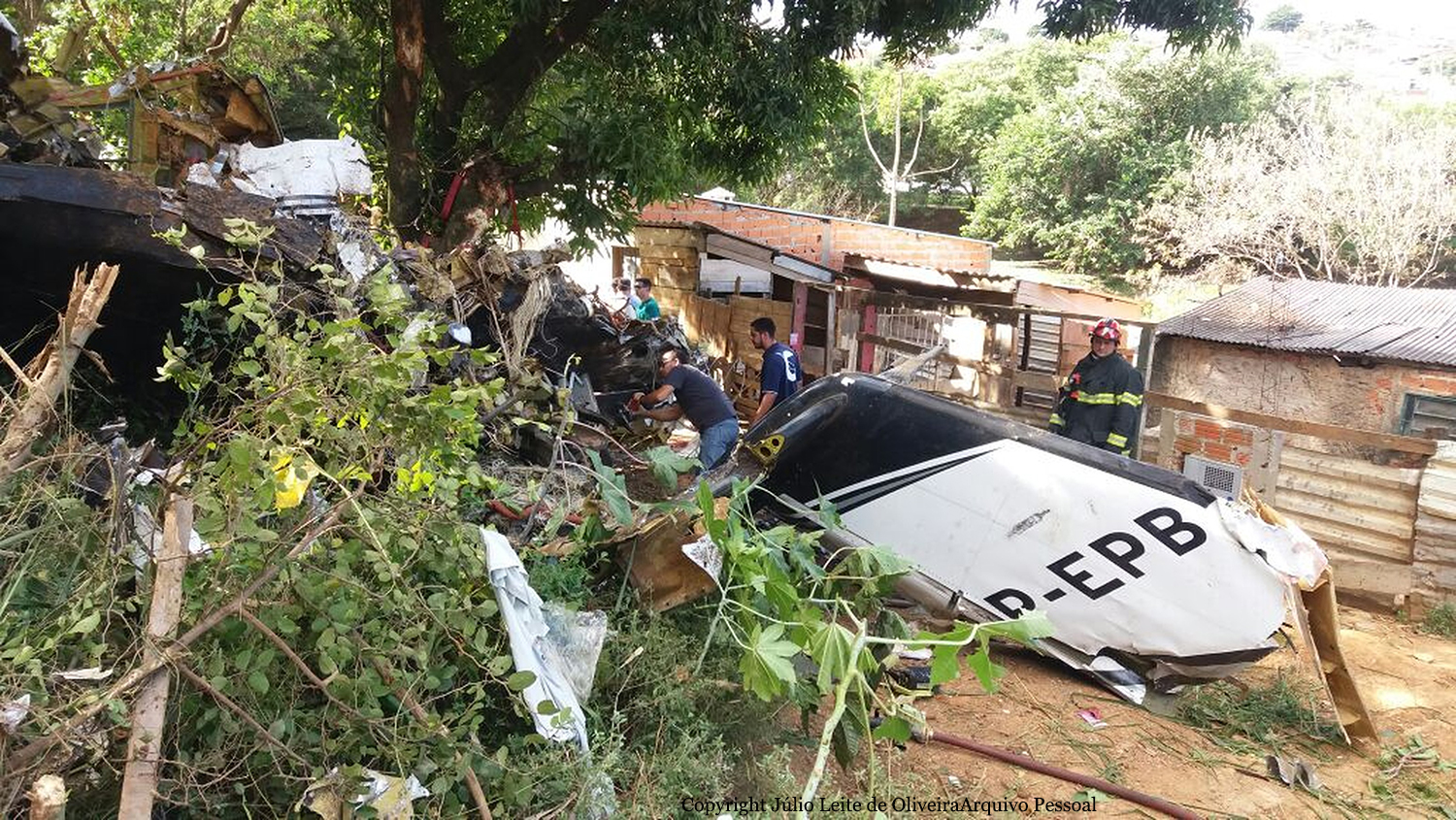
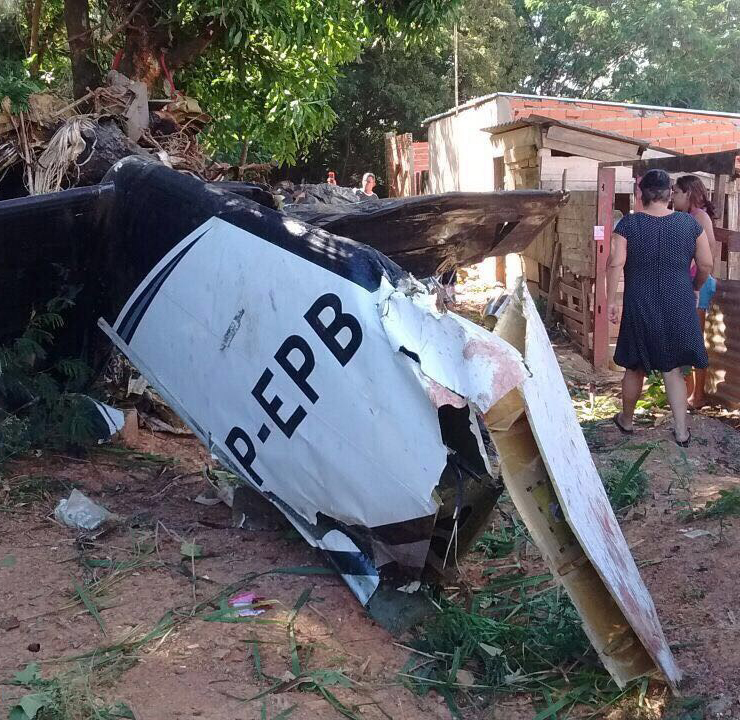
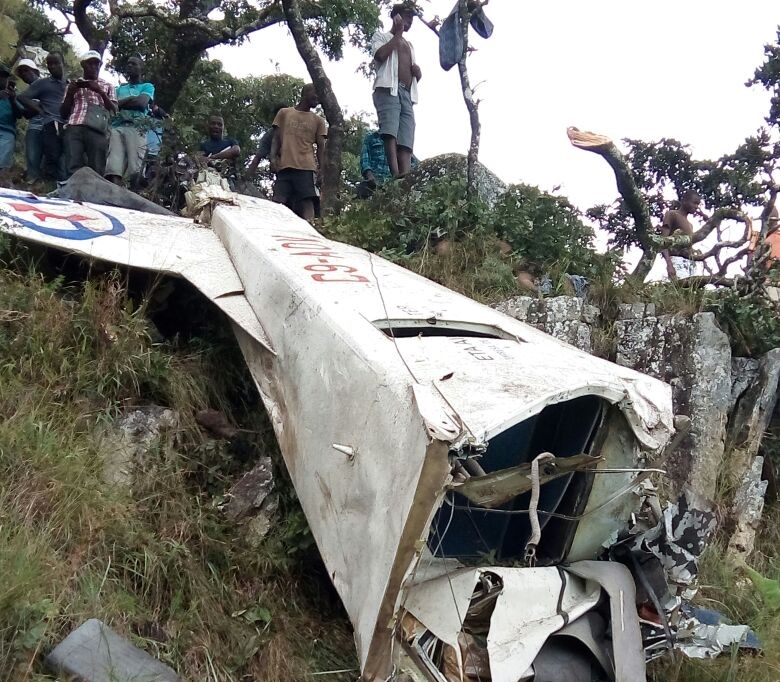
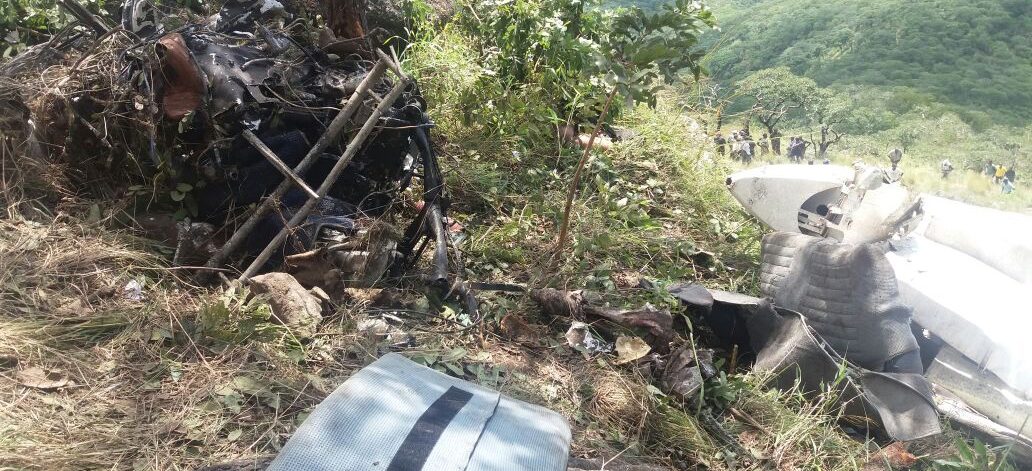
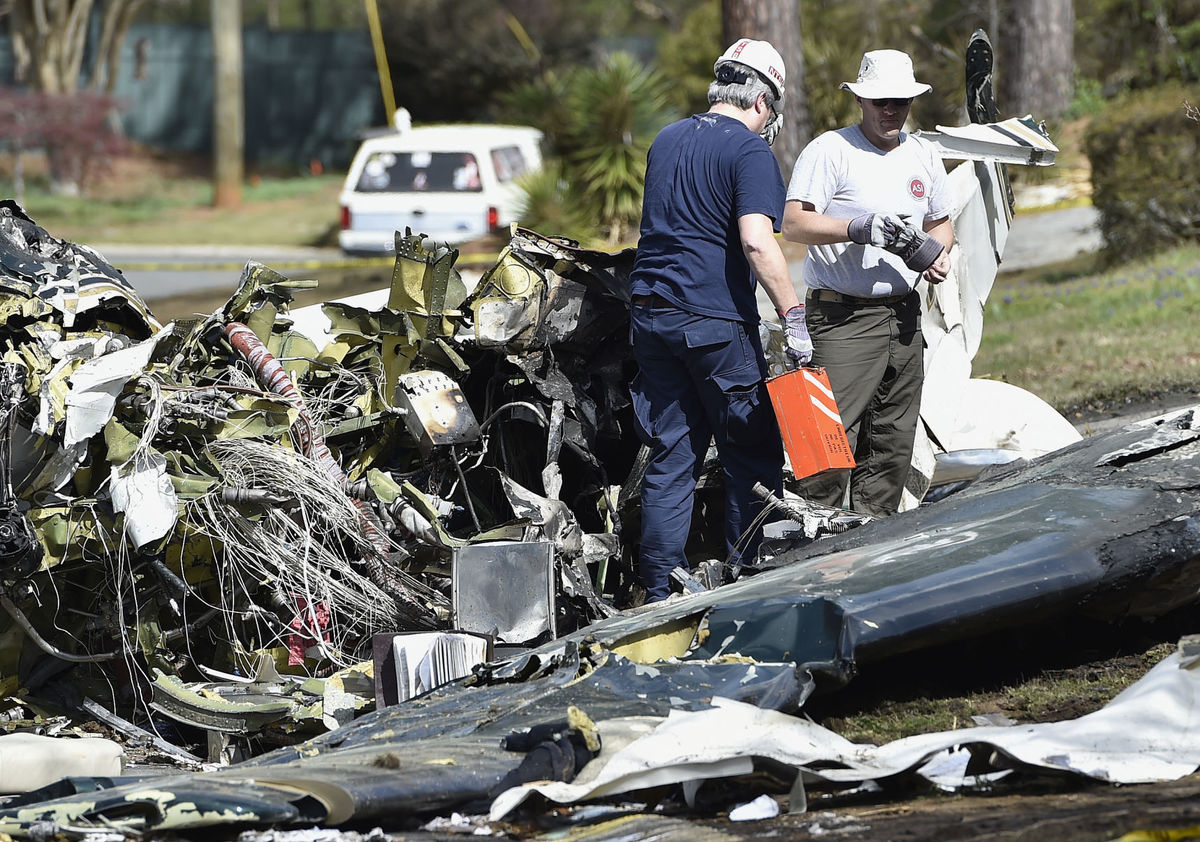
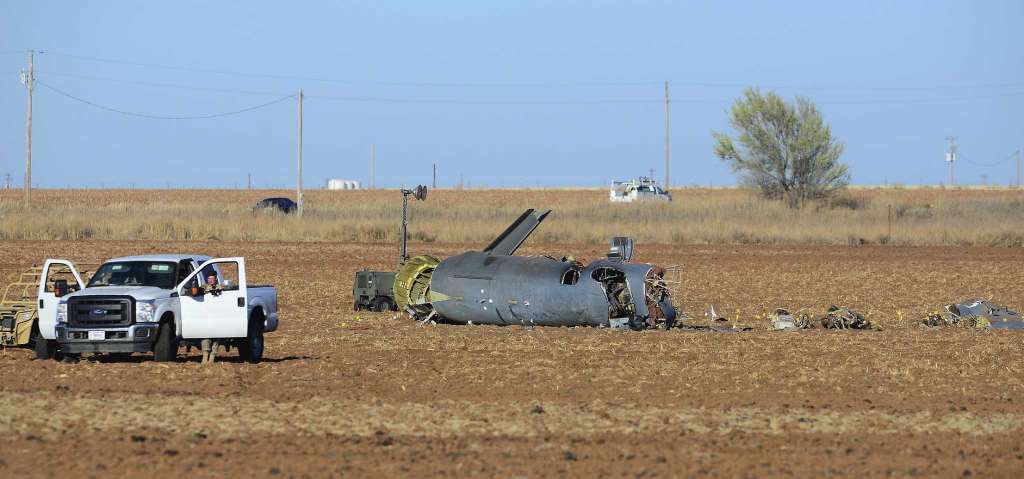
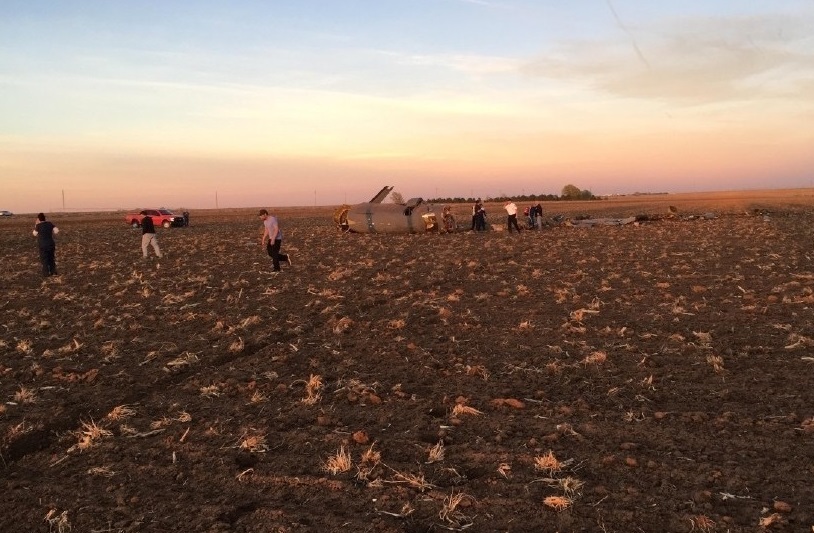
The Piper PA-31 (registration C-FQQB, serial number 31-310) operated by Exact Air Inc., with 2 pilots on board, was conducting its 2nd magnetometric survey flight of the day, from Schefferville Airport, Quebec, under visual flight rules. At 1336 Eastern Daylight Time, the aircraft took off and began flying toward the survey area located 90 nautical miles northwest of the airport. After completing the magnetometric survey work at 300 feet above ground level, the aircraft began the return flight segment to Schefferville Airport. At that time, the aircraft descended and flew over the terrain at an altitude varying between 100 and 40 feet above ground level. At 1756, while the aircraft was flying over railway tracks, it struck power transmission line conductor cables and crashed on top of a mine tailings deposit about 3.5 nautical miles northwest of Schefferville Airport. Both occupants were fatally injured. The accident occurred during daylight hours. Following the impact, there was no fire, and no emergency locator transmitter signal was captured.
Probable cause:
Findings:
Findings as to causes and contributing factors:
- Sensation seeking, mental fatigue, and an altered risk perception very likely contributed to the fact that, immediately after completing the magnetometric survey work, the pilot flying descended to an altitude varying between 100 and 40 feet above ground level and maintained this altitude until the aircraft collided with the wires.
- It is highly likely that the pilots were unaware that there was a power transmission line in their path.
- The pilot flying did not detect the power transmission line in time to avoid it, and the aircraft collided with the wires, which were 70 feet above the ground.
- Despite the warning regarding low-altitude flying in the Transport Canada Aeronautical Information Manua, and in the absence of minimum-altitude restrictions imposed by the company, the pilot chose to descend to a very low altitude on the return flight; as a result, this flight segment carried an unacceptable level of risk.
Findings as to risk:
- If pilots fly at low altitude, there is a risk that they will collide with wires, given that these are extremely difficult to see in flight.
- If lightweight flight data recording systems are not used to closely monitor flight operations, there is a risk that pilots will deviate from established procedures and limits, thereby reducing safety margins.
- If Transport Canada does not take concrete measures to facilitate the use of lightweight flight data recording systems and flight data monitoring, there is a risk that operators will be unable to proactively identify safety deficiencies before they cause an accident.
- If safety management systems are not required, assessed, and monitored by Transport Canada in order to ensure continual improvement, there is an increased risk that companies will be unable to effectively identify and mitigate the hazards involved in their operations.
- Not wearing a safety belt increases the risk of injury or death in an accident.
- The current emergency locator transmitter system design standards do not include a requirement for a crashworthy antenna system. As a result, there is a risk that potentially life-saving search‑and‑rescue services will be delayed if an emergency locator transmitter antenna is damaged during an occurrence.
Findings as to causes and contributing factors:
- Sensation seeking, mental fatigue, and an altered risk perception very likely contributed to the fact that, immediately after completing the magnetometric survey work, the pilot flying descended to an altitude varying between 100 and 40 feet above ground level and maintained this altitude until the aircraft collided with the wires.
- It is highly likely that the pilots were unaware that there was a power transmission line in their path.
- The pilot flying did not detect the power transmission line in time to avoid it, and the aircraft collided with the wires, which were 70 feet above the ground.
- Despite the warning regarding low-altitude flying in the Transport Canada Aeronautical Information Manua, and in the absence of minimum-altitude restrictions imposed by the company, the pilot chose to descend to a very low altitude on the return flight; as a result, this flight segment carried an unacceptable level of risk.
Findings as to risk:
- If pilots fly at low altitude, there is a risk that they will collide with wires, given that these are extremely difficult to see in flight.
- If lightweight flight data recording systems are not used to closely monitor flight operations, there is a risk that pilots will deviate from established procedures and limits, thereby reducing safety margins.
- If Transport Canada does not take concrete measures to facilitate the use of lightweight flight data recording systems and flight data monitoring, there is a risk that operators will be unable to proactively identify safety deficiencies before they cause an accident.
- If safety management systems are not required, assessed, and monitored by Transport Canada in order to ensure continual improvement, there is an increased risk that companies will be unable to effectively identify and mitigate the hazards involved in their operations.
- Not wearing a safety belt increases the risk of injury or death in an accident.
- The current emergency locator transmitter system design standards do not include a requirement for a crashworthy antenna system. As a result, there is a risk that potentially life-saving search‑and‑rescue services will be delayed if an emergency locator transmitter antenna is damaged during an occurrence.
Final Report: