Date & Time:
Aug 31, 1988 at 0901 LT
Operator:

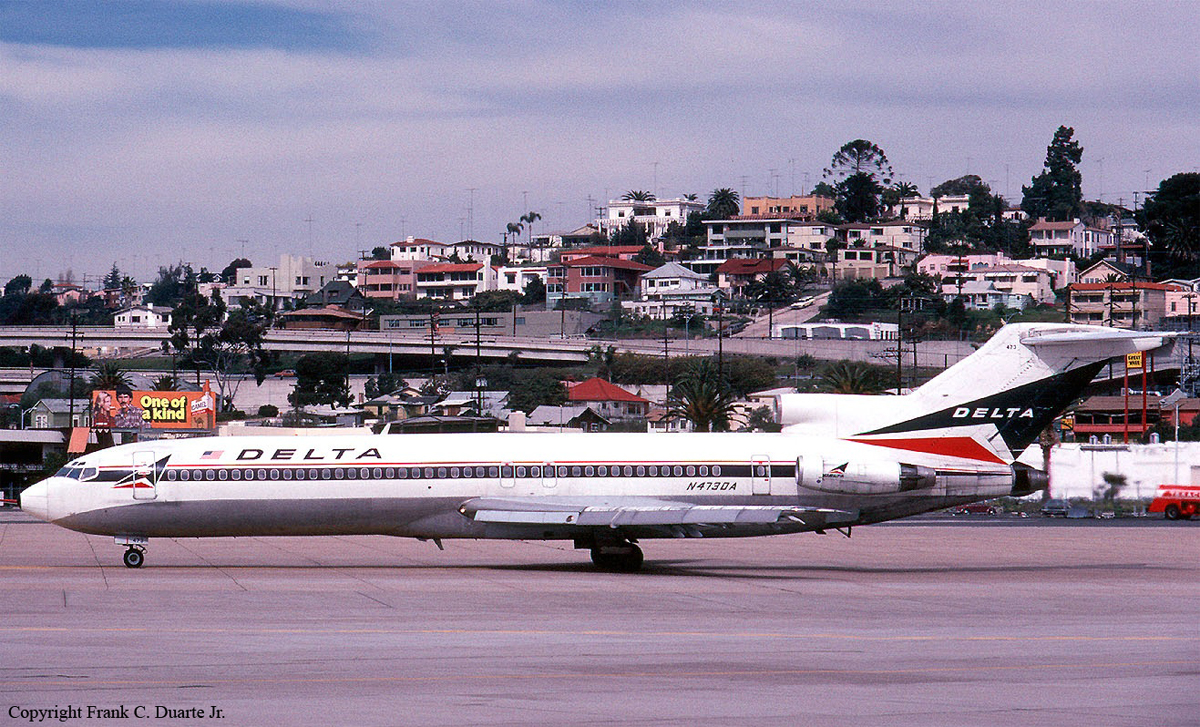
Schedule:
Jackson - Dallas - Salt Lake City
Crew fatalities:
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Captain / Total flying hours:
17000
Captain / Total hours on type:
7000.00
Copilot / Total flying hours:
6500
Copilot / Total hours on type:
4000
Aircraft flight hours:
43023
Circumstances:
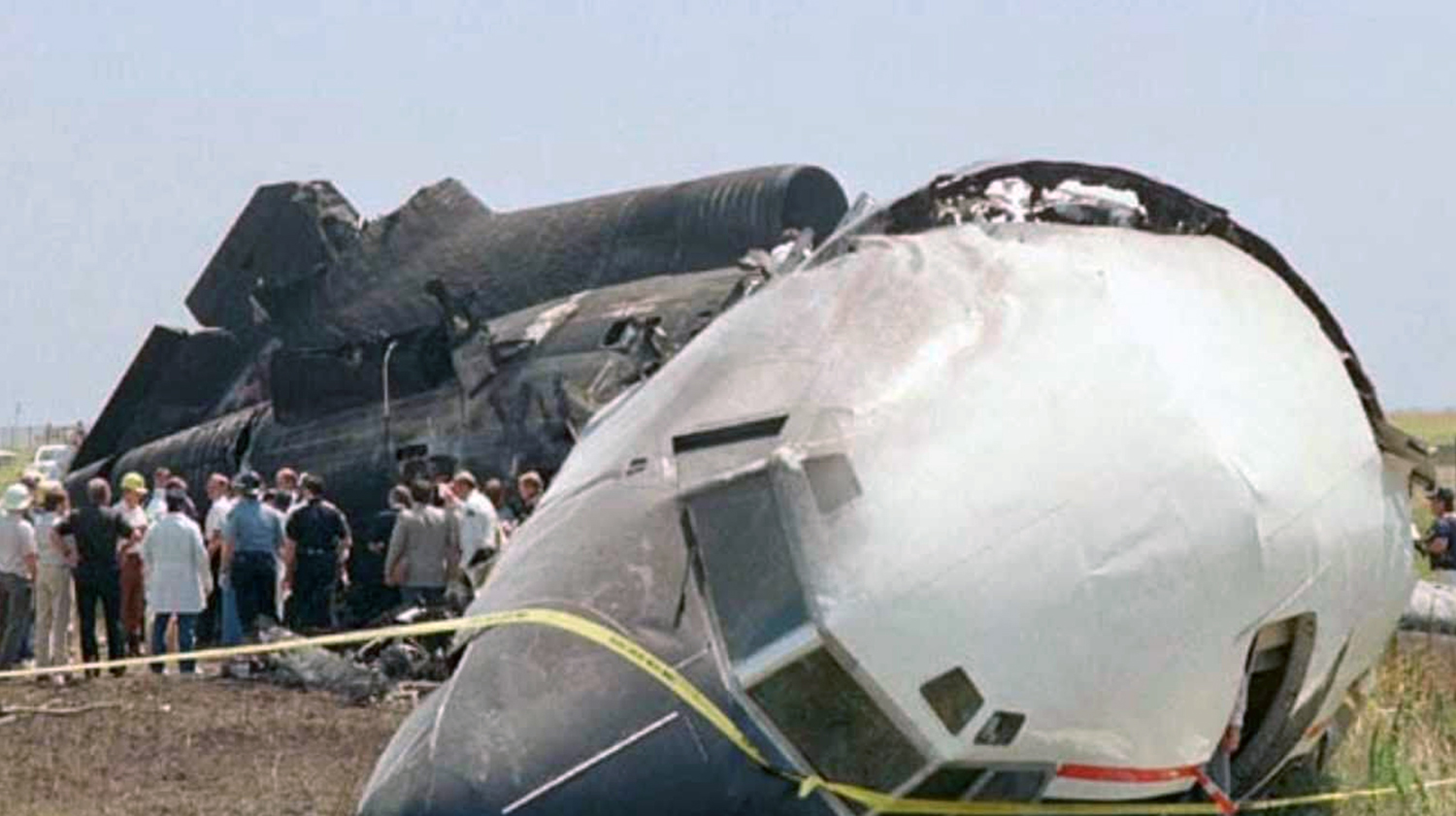
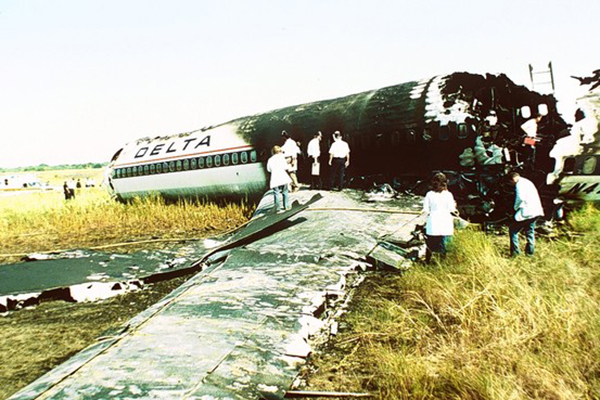
Flight DL1141 (Jackson - Dallas - Salt Lake City) left Gate 15 at 08:30 and was instructed to taxi to runway 18L. When first in line for takeoff (at 08:59) the flight was cleared for takeoff. The takeoff was uneventful until the airplane reached the rotation phase (at 154 knots, 6017 feet down the runway). As the main gear wheels left the ground, the airplane began to roll violently, causing the right wingtip to contact the runway (1033 feet after lift-off), followed by compressor surges. The plane continued and struck the ILS localizer antenna array 1000 feet past the end of runway 18L. After impacting the antenna installation, the airplane remained airborne for an additional 400 feet, then struck the ground, traversed a ground depression and slid sideways until it came to rest near the airport perimeter fence, 3200 feet from the runway end. Parts of the aircraft had separated in the slide and a fire had erupted in the right wing area, quickly engulfing the rear, right side of the airplane after it came to rest. Twelve passengers and two crew members were killed. The aircraft was destroyed.
Probable cause:
The board determines that the accident was caused mainly by the captain and first officer's inadequate cockpit discipline which resulted in the flight crew's attempt to takeoff without the wing flaps and slats properly configured; and the failure of the takeoff configuration warning system to alert the crew that the airplane was not properly configured for the takeoff. Contributing to the accident was Delta's slow implementation of necessary modifications to its operating procedures, manuals, checklists, training and crew checking programs which were necessitated by significant changes in the airline following rapid growth and merger. Also contributing to the accident was the lack of sufficiently aggressive action by the FAA to have known deficiencies corrected by Delta and the lack of sufficient accountability within the FAA's air carrier inspection process.
Findings:
Occurrence #1: loss of control - in flight
Phase of operation: takeoff - initial climb
Findings
1. (c) preflight planning/preparation - improper - pilot in command
2. (c) overconfidence in personal ability - pilot in command
3. (c) procedures/directives - not followed - copilot/second pilot
4. (c) procedures/directives - not followed - pilot in command
5. (f) procedure inadequate - company/operator management
6. (f) insufficient standards/requirements, operation/operator - FAA (organization)
7. (f) inadequate method of compliance determination record keeping - FAA (organization)
8. (c) lowering of flaps - not performed
9. (c) lowering of slats - not performed
10. (c) safety system (other) - inoperative
----------
Occurrence #2: in flight collision with terrain/water
Phase of operation: descent - uncontrolled
Final Report: