Ground accident of a Boeing KC-135R Stratotanker in Bishkek
Date & Time:
Sep 26, 2006 at 2010 LT
Registration:
63-8886
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Bishkek - Bishkek
MSN:
18734
YOM:
1964
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
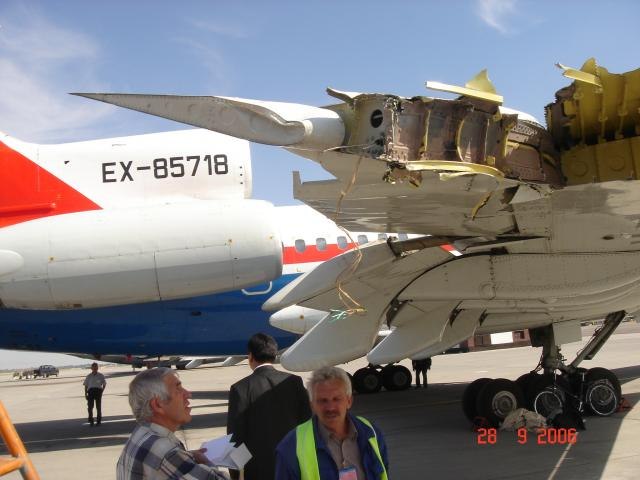
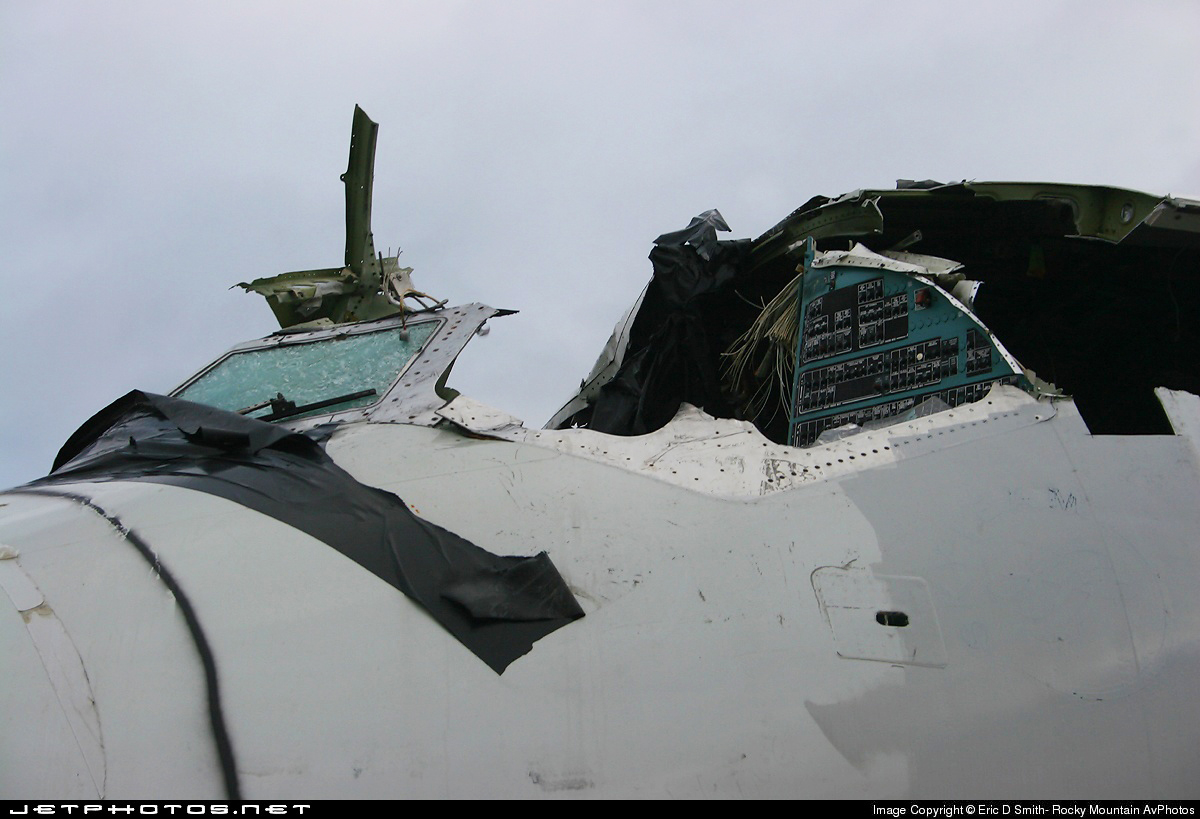
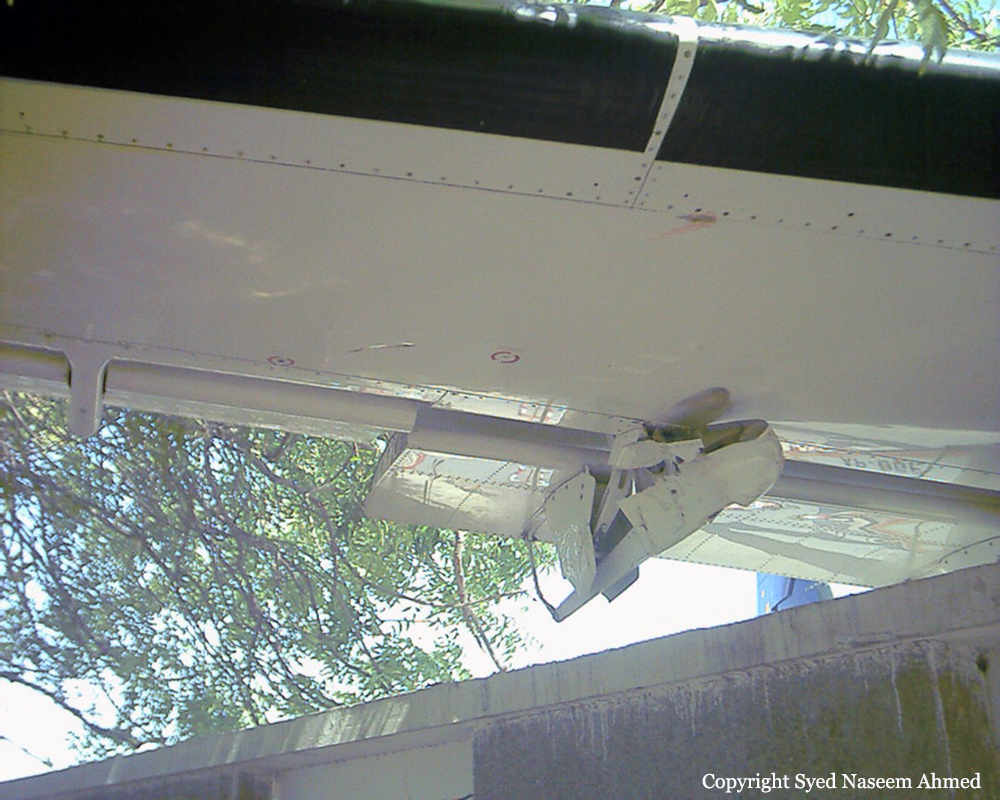
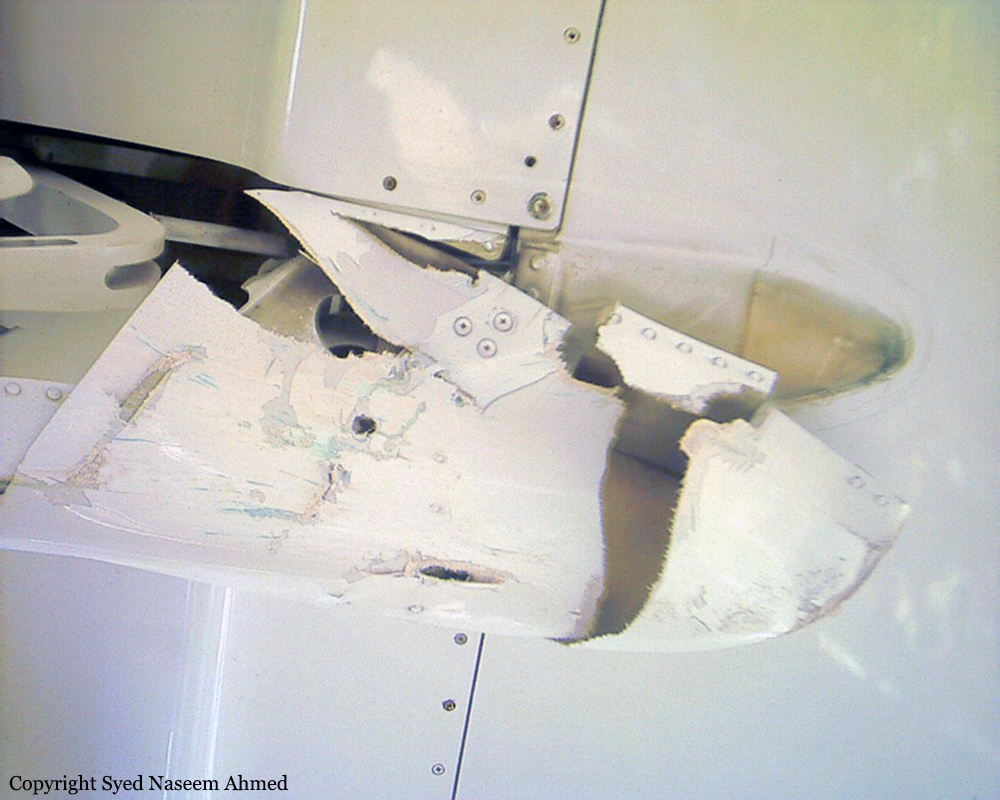
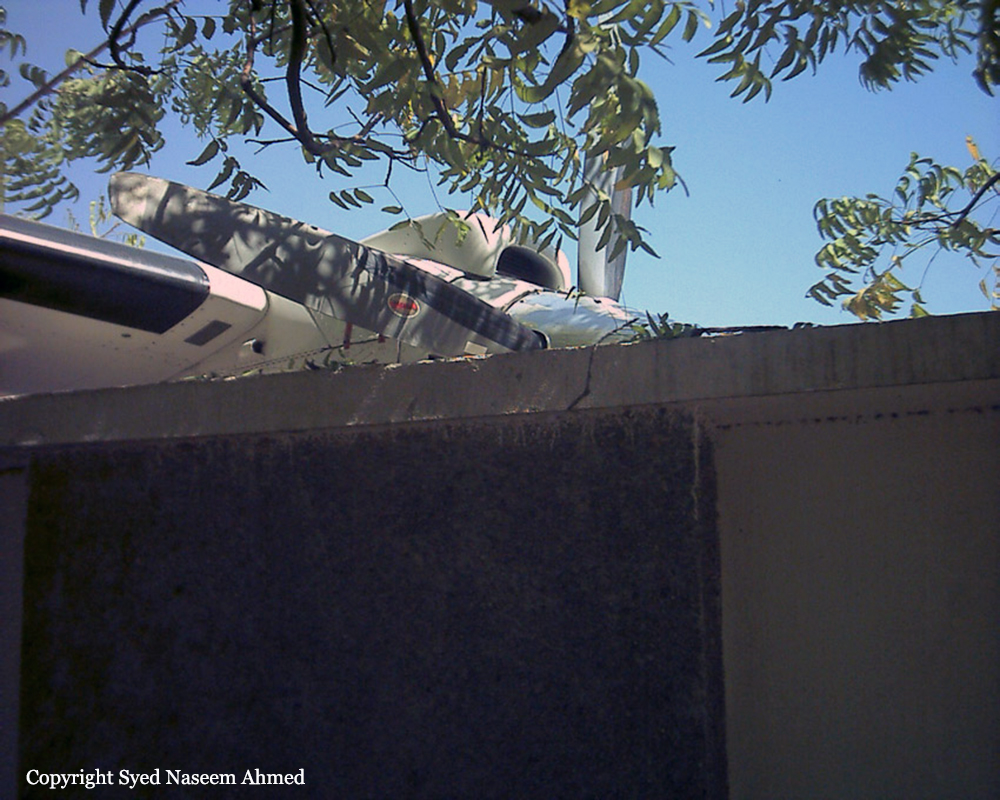
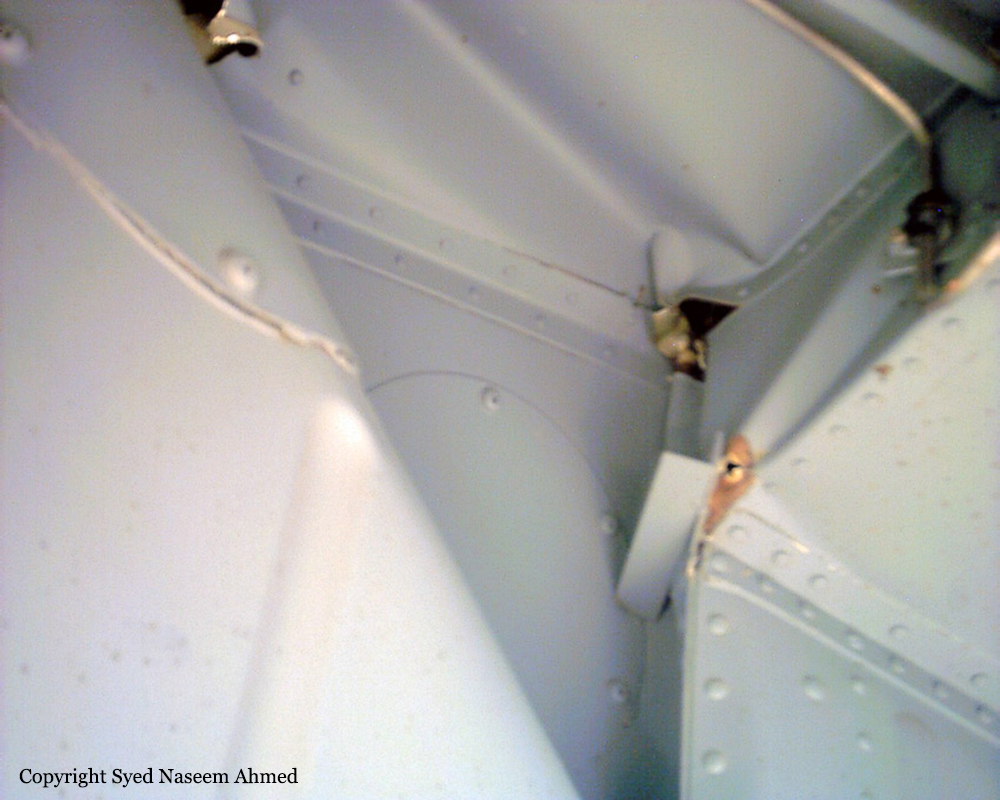
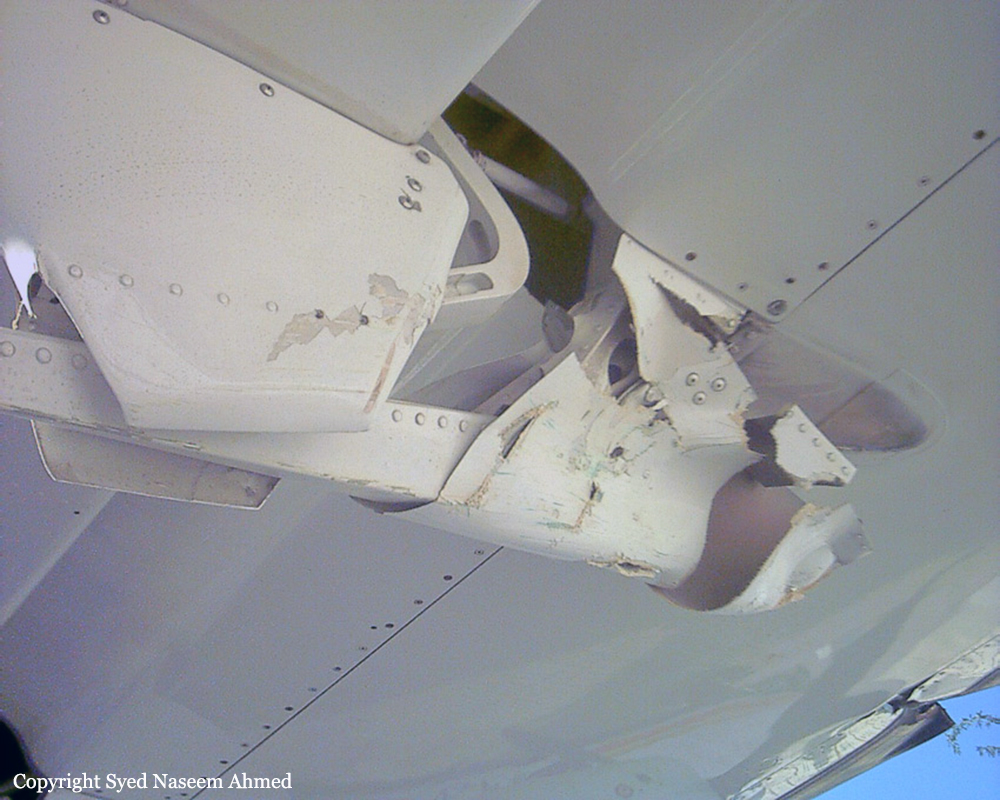
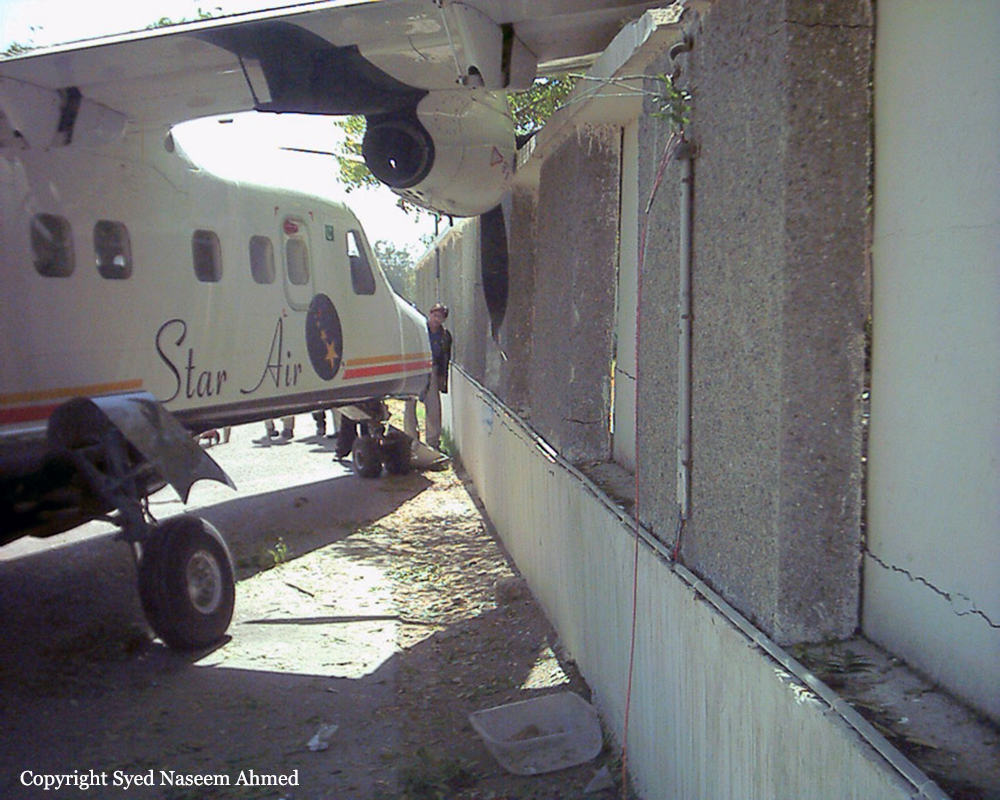
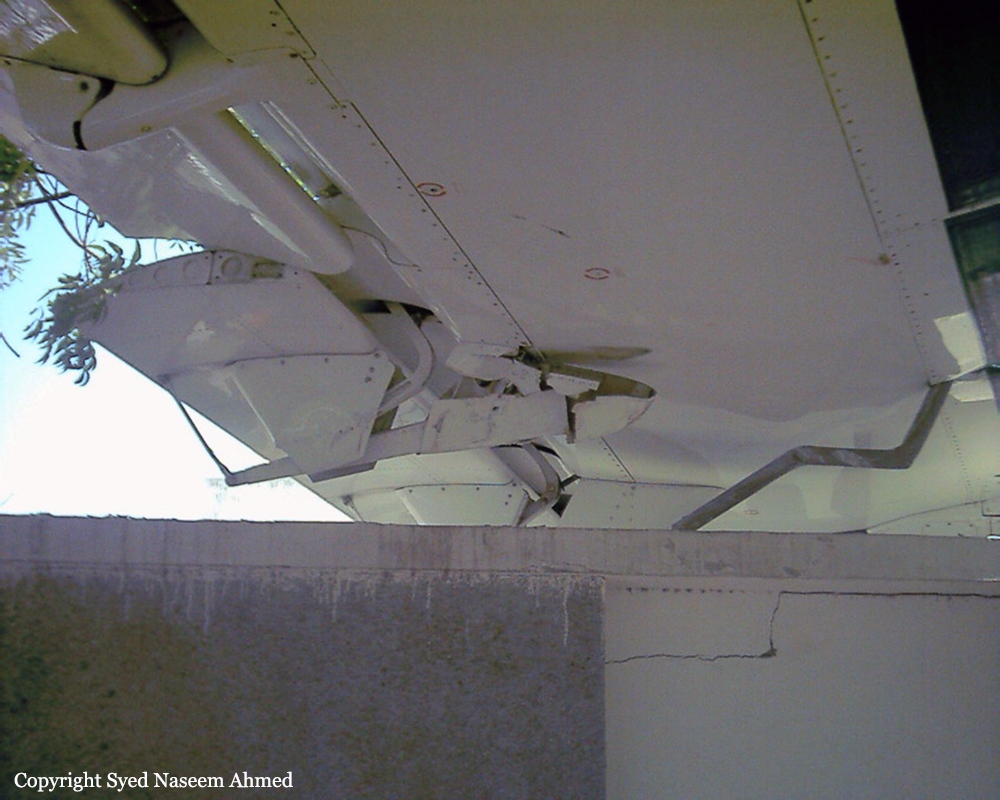
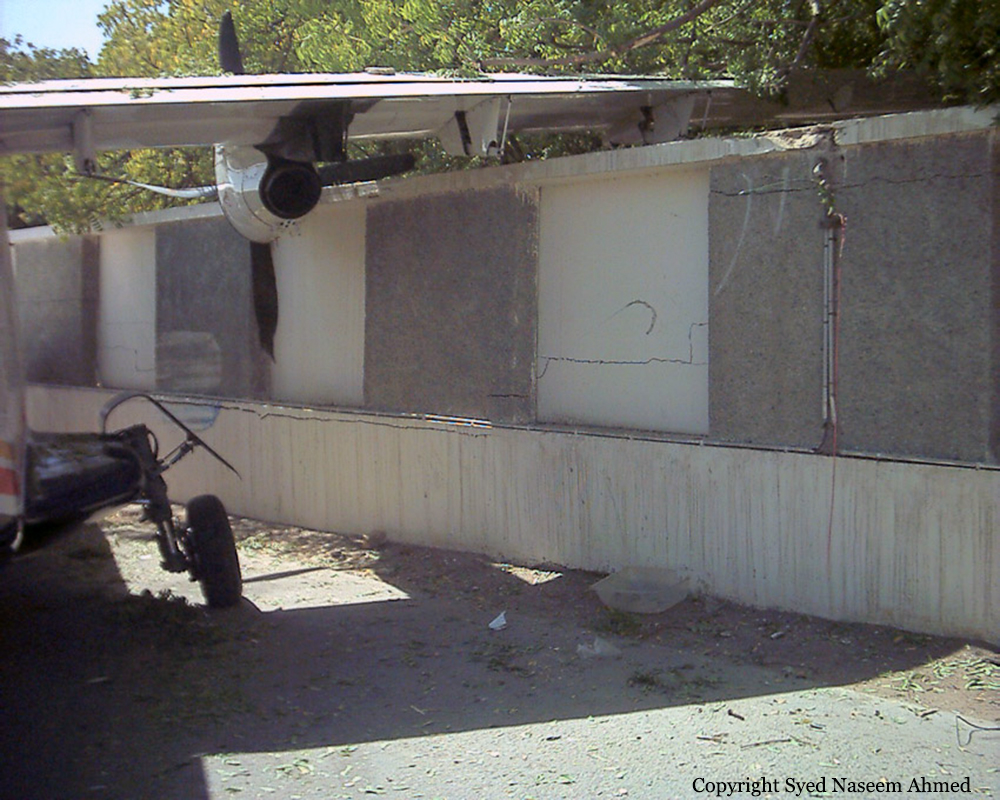
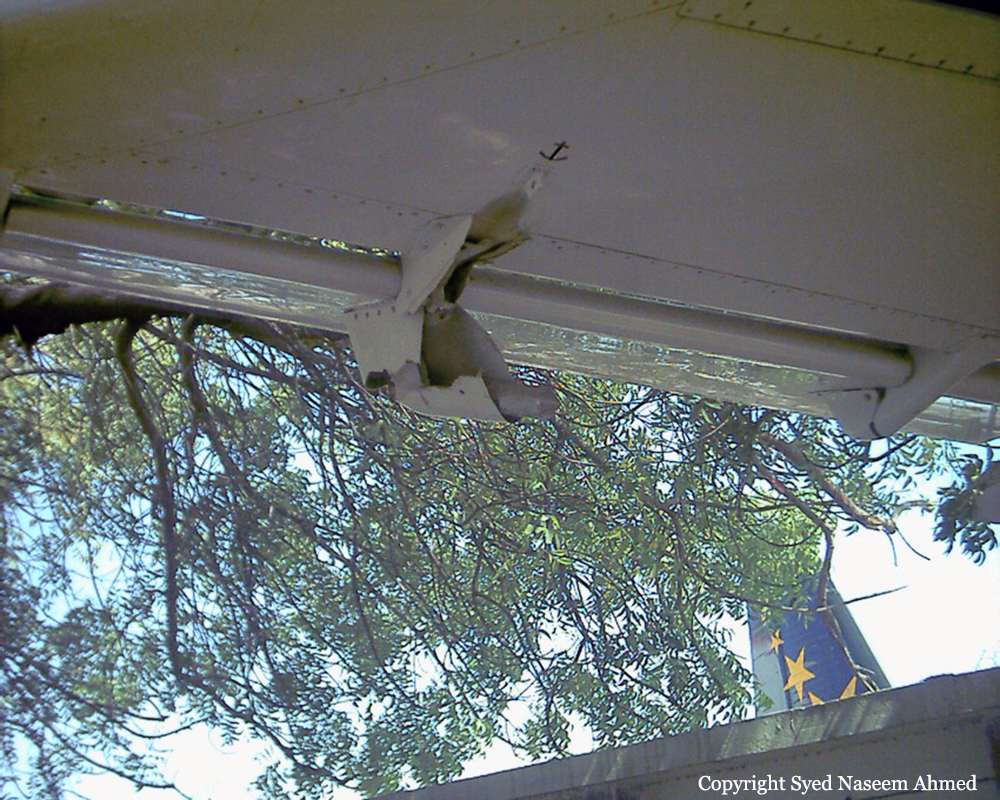
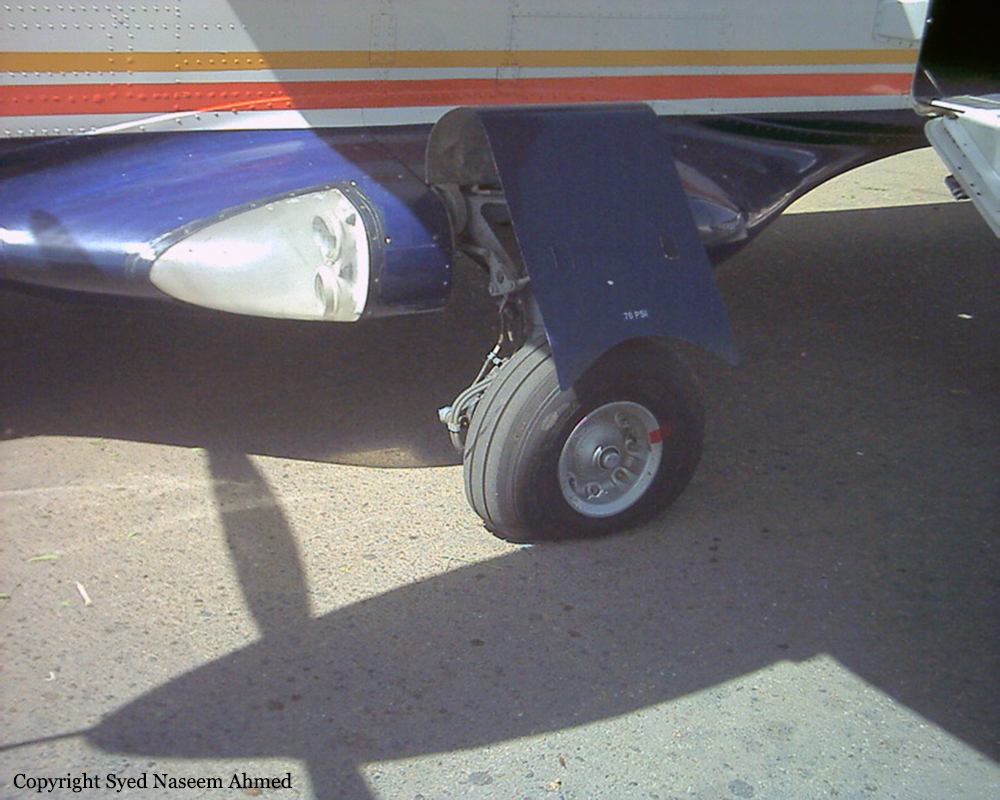
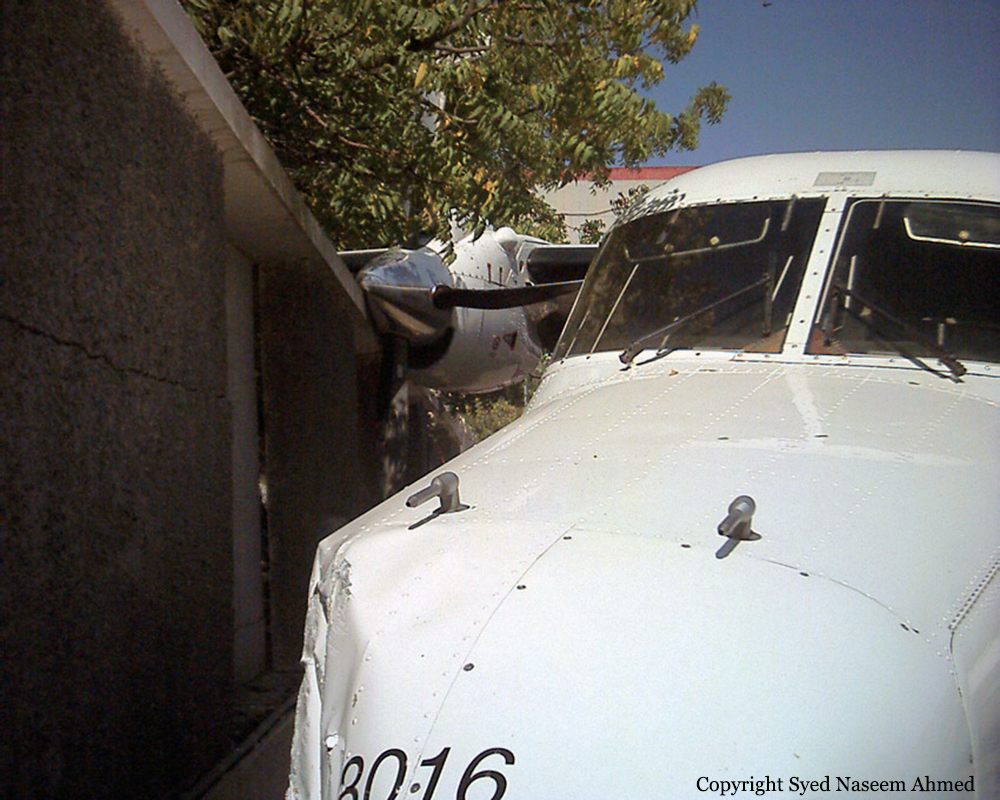
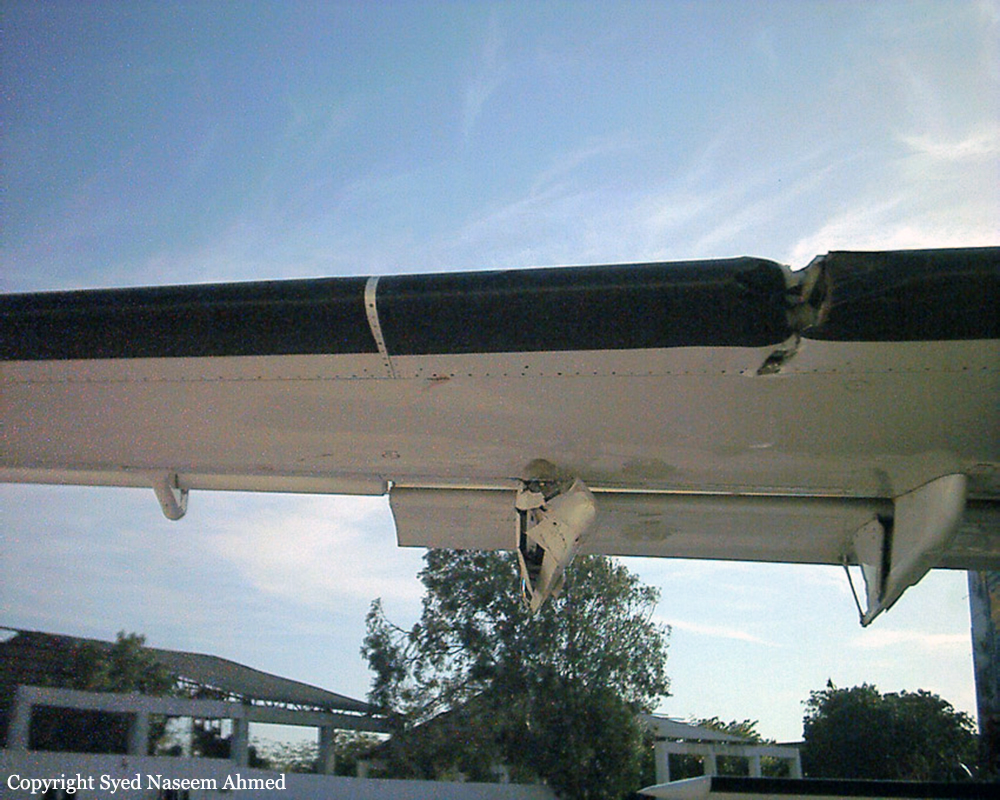
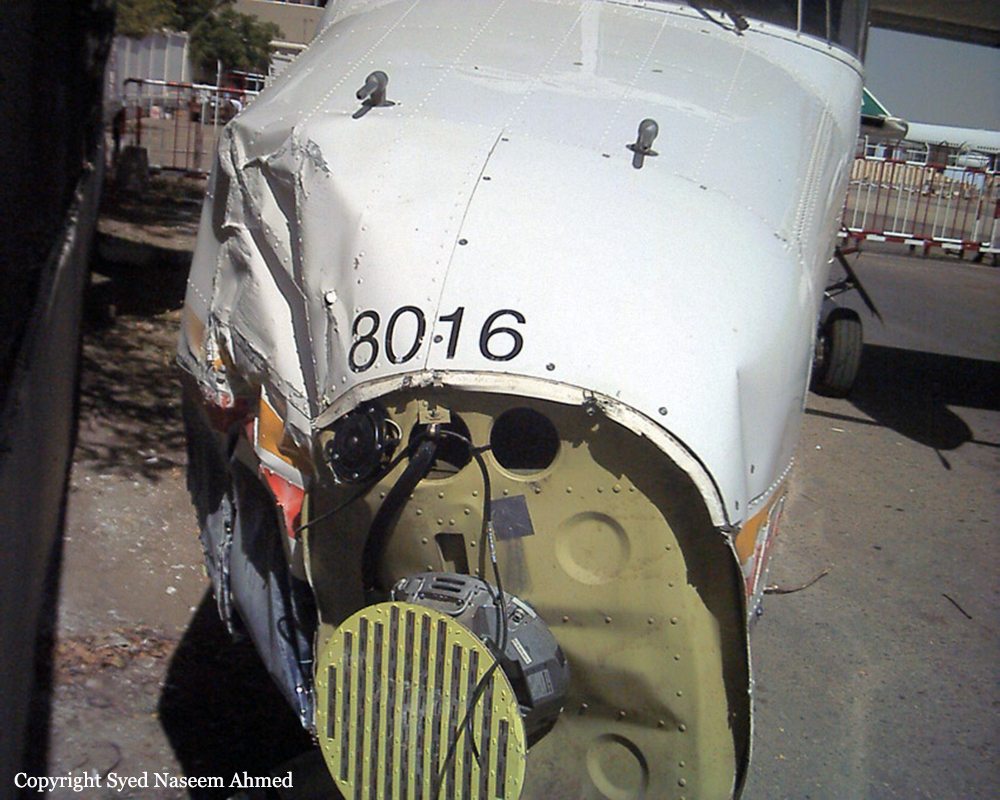
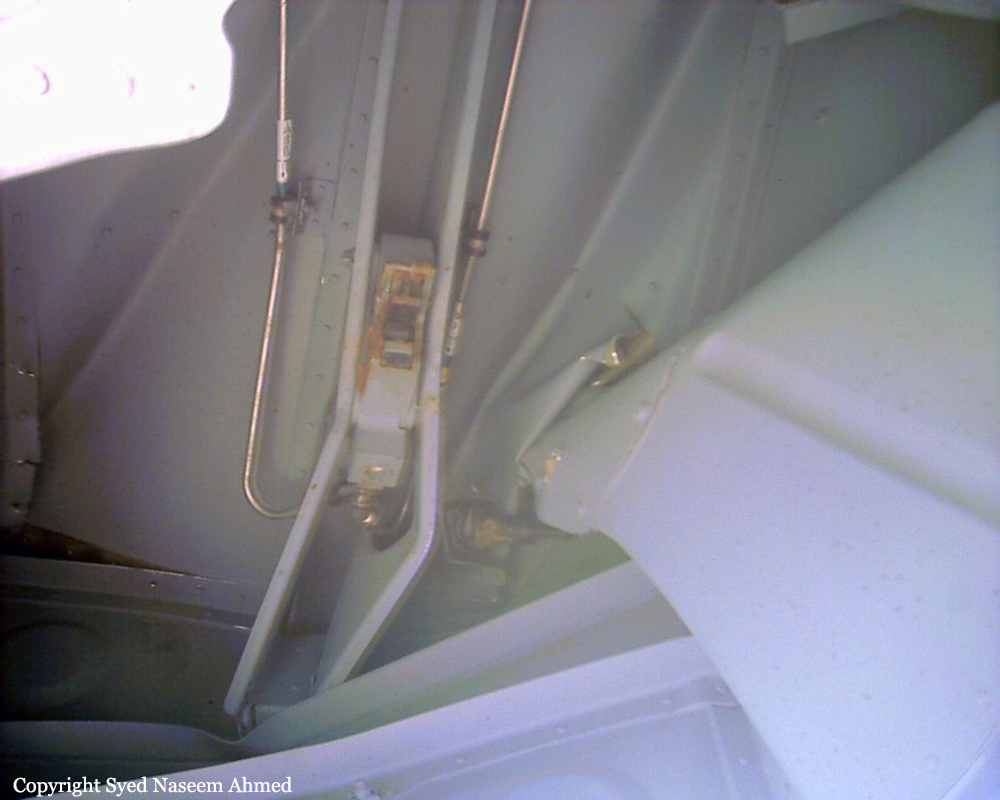
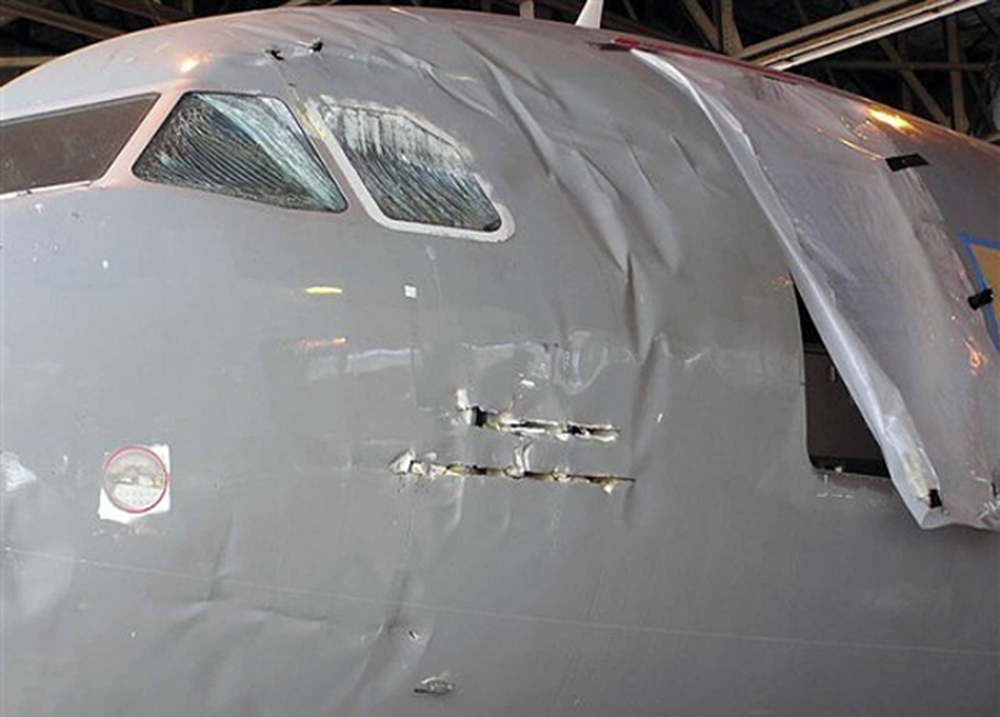
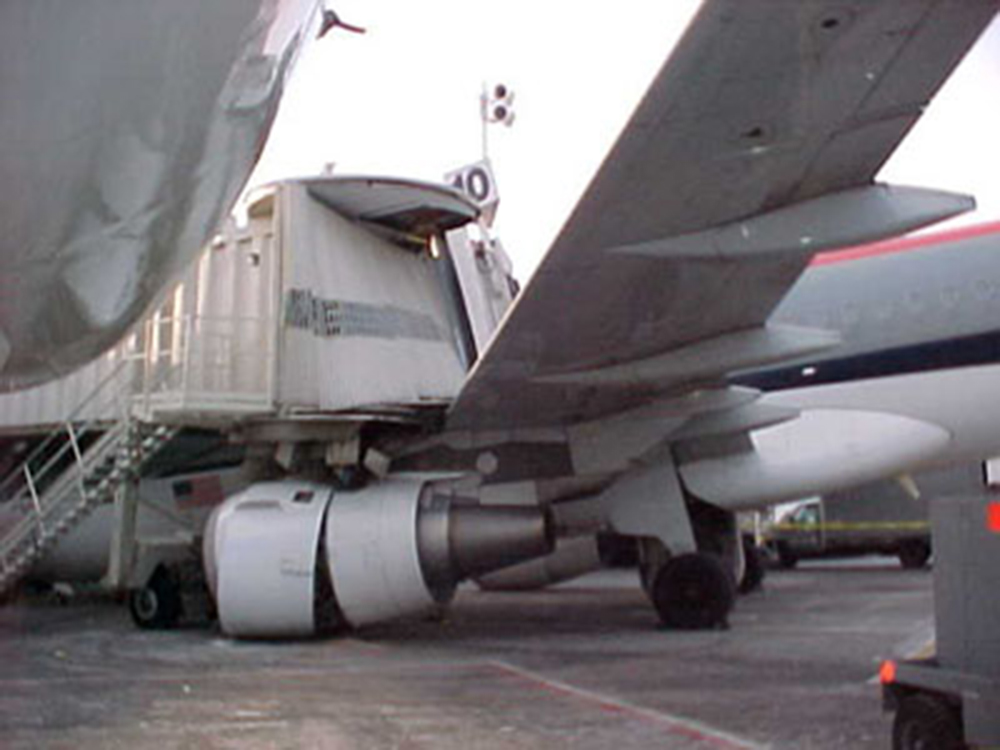
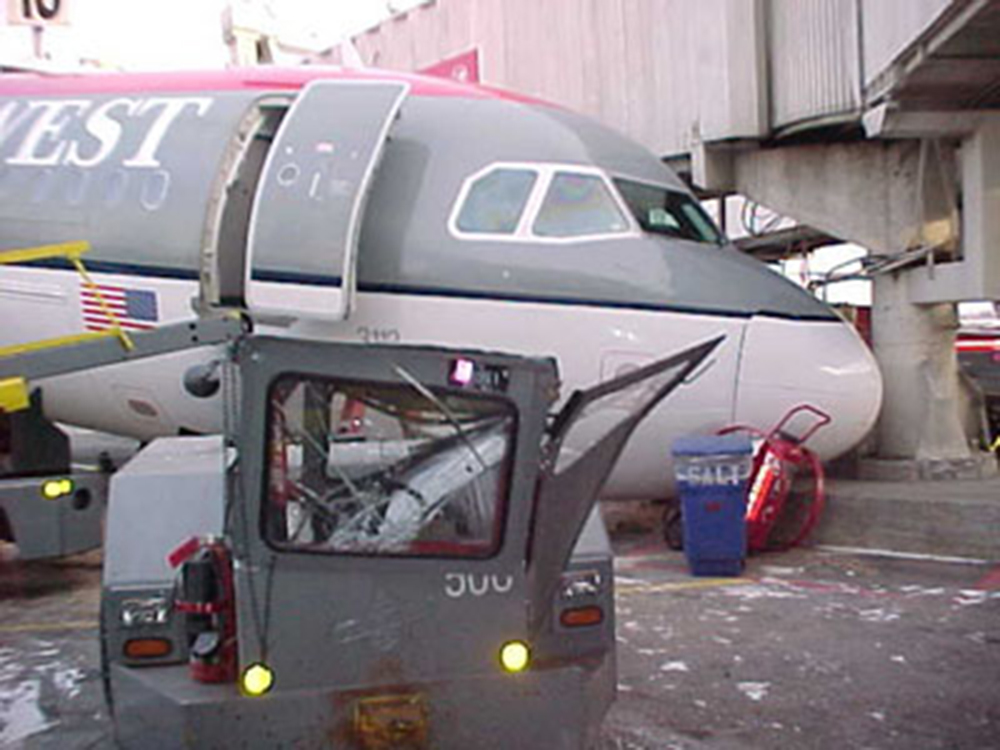
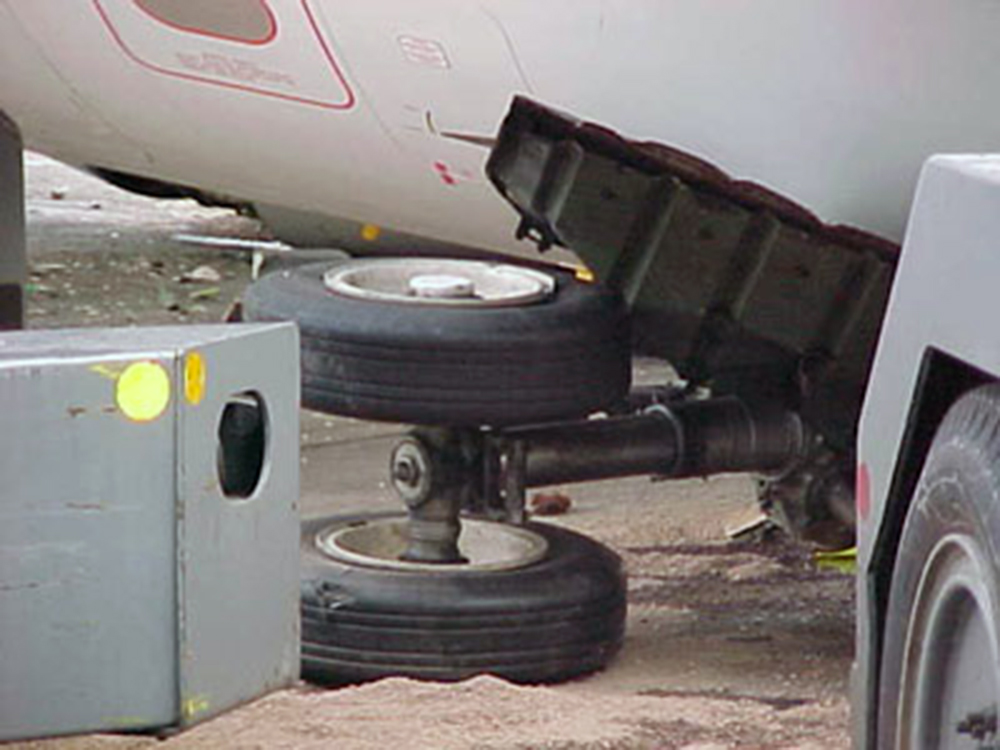
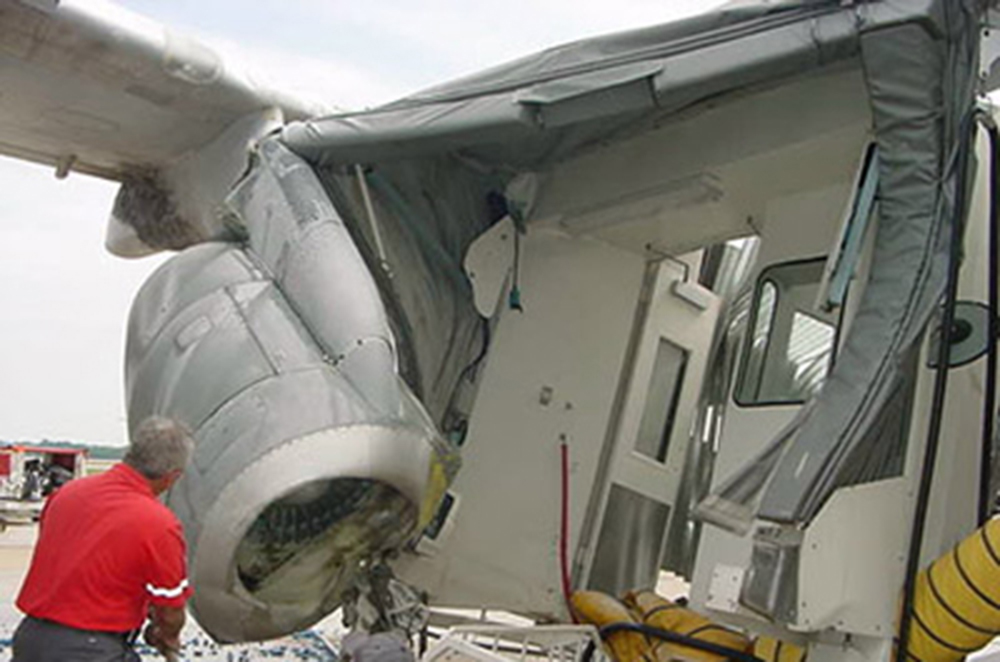
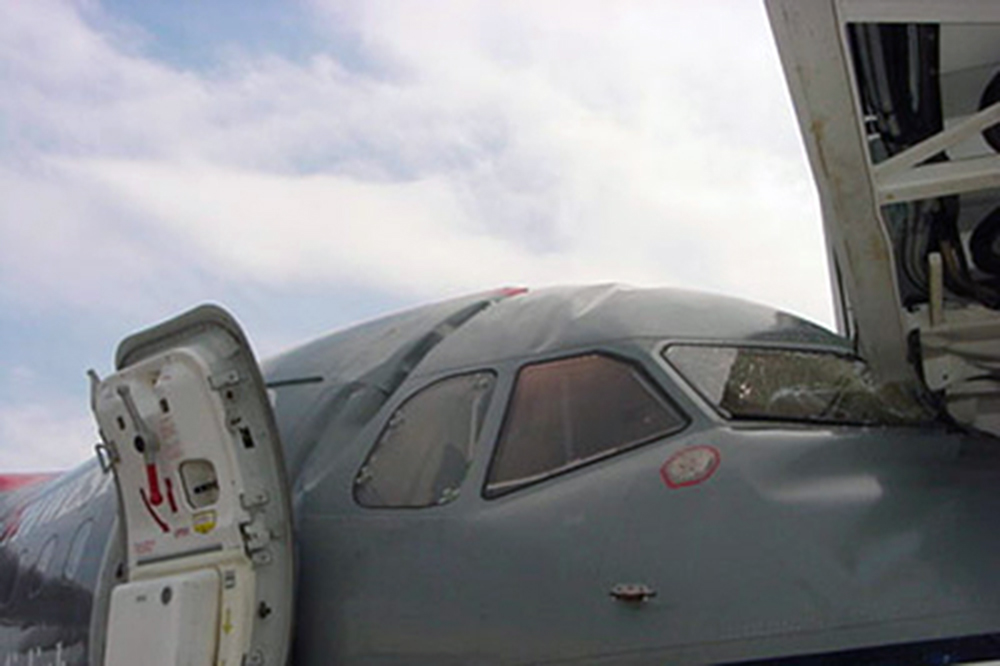
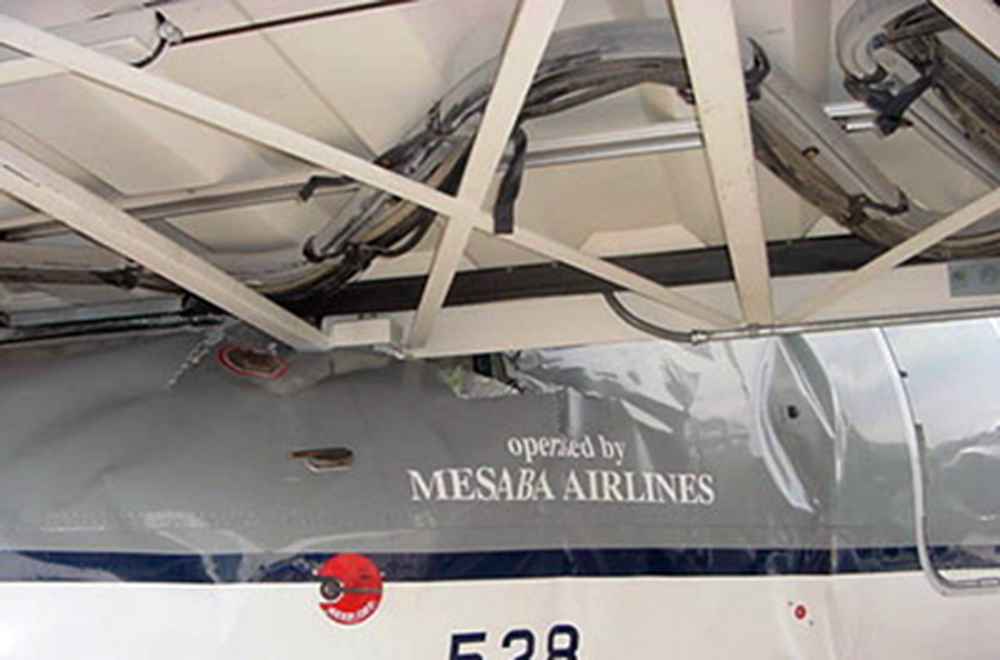
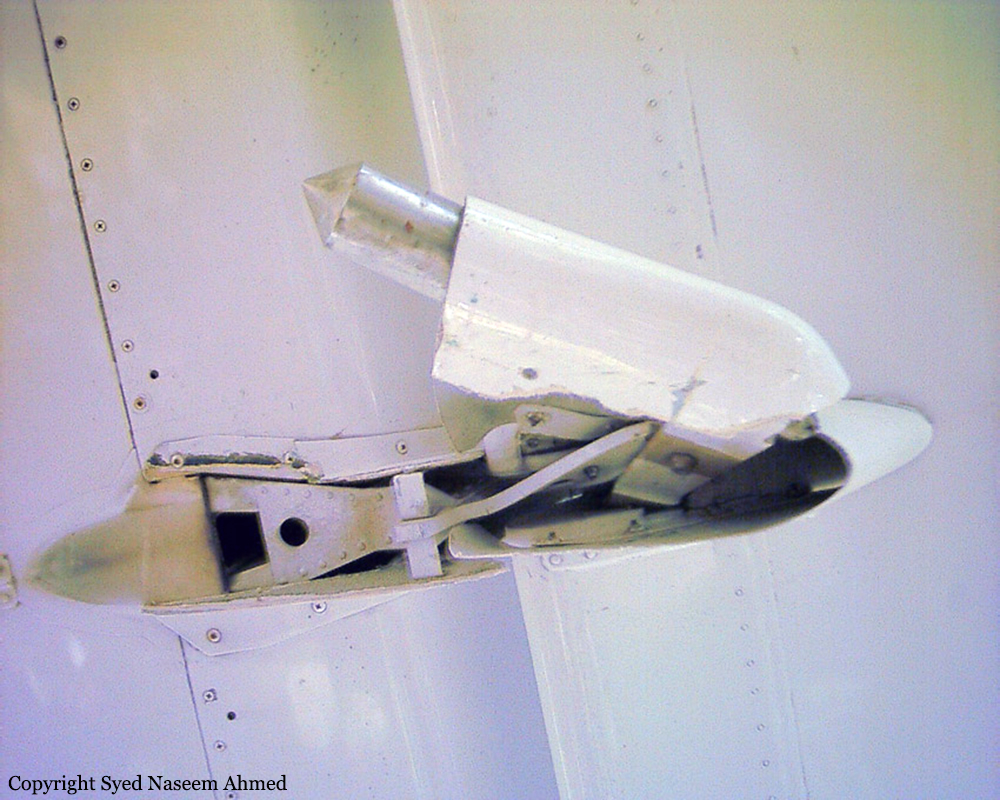
On Sept. 26, at approximately 8:03 p.m. local time, a KC-135R landed at Manas International Airport following a combat mission over Afghanistan. After landing, the KC-135R was parked at the intersection of the active runway and a taxiway while the crew awaited clarification on instructions from the air traffic control tower. The KC-135R was struck by a host nation TU-154 that was taking off. The TU-154's right wing struck the fairing of the KC-135R's No. 1 engine. The force of the impact nearly severed the No. 1 engine from KC-135R and destroyed a portion of the aircraft's left wing. The TU-154 lost approximately six feet of its right wingtip, but was able to get airborne and return to the airport for an emergency landing with no additional damage to the aircraft. The three aircrew members on board the KC-135R, as well as the nine aircrew members and 52 passengers aboard the TU-154, survived the accident. None of the aircrew or passengers on board the TU-154 sustained any injuries. One KC-135 crew member sustained minor abrasions while evacuating the aircraft.
Probable cause:
The collision between the TU-154 and KC-135R aircraft was clearly an accident and not the result of any intentional conduct. The Accident Investigation Board, convened by AMC, determined that the accident was caused by the Kyrgyzaeronavigation air traffic controller who cleared a civilian airliner for takeoff without verifying that the KC-135R was clear of the runway. In addition to the air traffic controller, the AIB found evidence of several contributing factors involving the KC-135R aircrew, conflicting published airport notices, and a tower liaison employed by the U.S. Government to facilitate communication between the tower and U.S. aircrews. Although the AIB found the air traffic controller primarily at fault, the U.S. KC-135R crew and tower liaison shared responsibility for ensuring the KC-135R cleared the runway to a safe location following landing. The accident might have been avoided had any of them exercised better awareness of their situation.
In conclusion, the AIB determined the principal cause of the mishap was the Kyrgyzaeronavigation controller clearing the TU-154 for takeoff without verifying that KC-135R was clear of the runway, there was evidence the following factors also contributed to the mishap:
- The Kyrgyz air traffic controller's instruction to vacate at taxiway Golf after dark conflicted with a published Notice to Airmen (NOTAM) that limited that taxiway's use to daylight hours. The contractor safety liaison (LNO) employed by the U.S. Air Force to facilitate communication between its aircrews and Kyrgyz controllers did not clarify the apparent discrepancy.
- After questioning the Kyrgyz controller's instruction to vacate the runway at taxiway Golf, the LNO instructed the KC-135R crew to hold short of Alpha. The mishap KC-135R crew misperceived the LNO's instructions and responded "holding short of Golf." The LNO failed to catch the read-back error.
- The Kyrgyz controller failed to maintain awareness of the KC-135R's location.
- The LNO failed to maintain situational awareness and intervene when the controller's actions endangered the KC-135R and aircrew.
The KC-135R is assigned to the 92nd Air Refueling Wing, Fairchild Air Force Base, Wash. While deployed at Manas AB, the KC-135R and its aircrew were assigned to U.S. Central Command's 376th Air Expeditionary Wing, flying missions supporting coalition aircraft over Afghanistan.
In conclusion, the AIB determined the principal cause of the mishap was the Kyrgyzaeronavigation controller clearing the TU-154 for takeoff without verifying that KC-135R was clear of the runway, there was evidence the following factors also contributed to the mishap:
- The Kyrgyz air traffic controller's instruction to vacate at taxiway Golf after dark conflicted with a published Notice to Airmen (NOTAM) that limited that taxiway's use to daylight hours. The contractor safety liaison (LNO) employed by the U.S. Air Force to facilitate communication between its aircrews and Kyrgyz controllers did not clarify the apparent discrepancy.
- After questioning the Kyrgyz controller's instruction to vacate the runway at taxiway Golf, the LNO instructed the KC-135R crew to hold short of Alpha. The mishap KC-135R crew misperceived the LNO's instructions and responded "holding short of Golf." The LNO failed to catch the read-back error.
- The Kyrgyz controller failed to maintain awareness of the KC-135R's location.
- The LNO failed to maintain situational awareness and intervene when the controller's actions endangered the KC-135R and aircrew.
The KC-135R is assigned to the 92nd Air Refueling Wing, Fairchild Air Force Base, Wash. While deployed at Manas AB, the KC-135R and its aircrew were assigned to U.S. Central Command's 376th Air Expeditionary Wing, flying missions supporting coalition aircraft over Afghanistan.
Final Report: