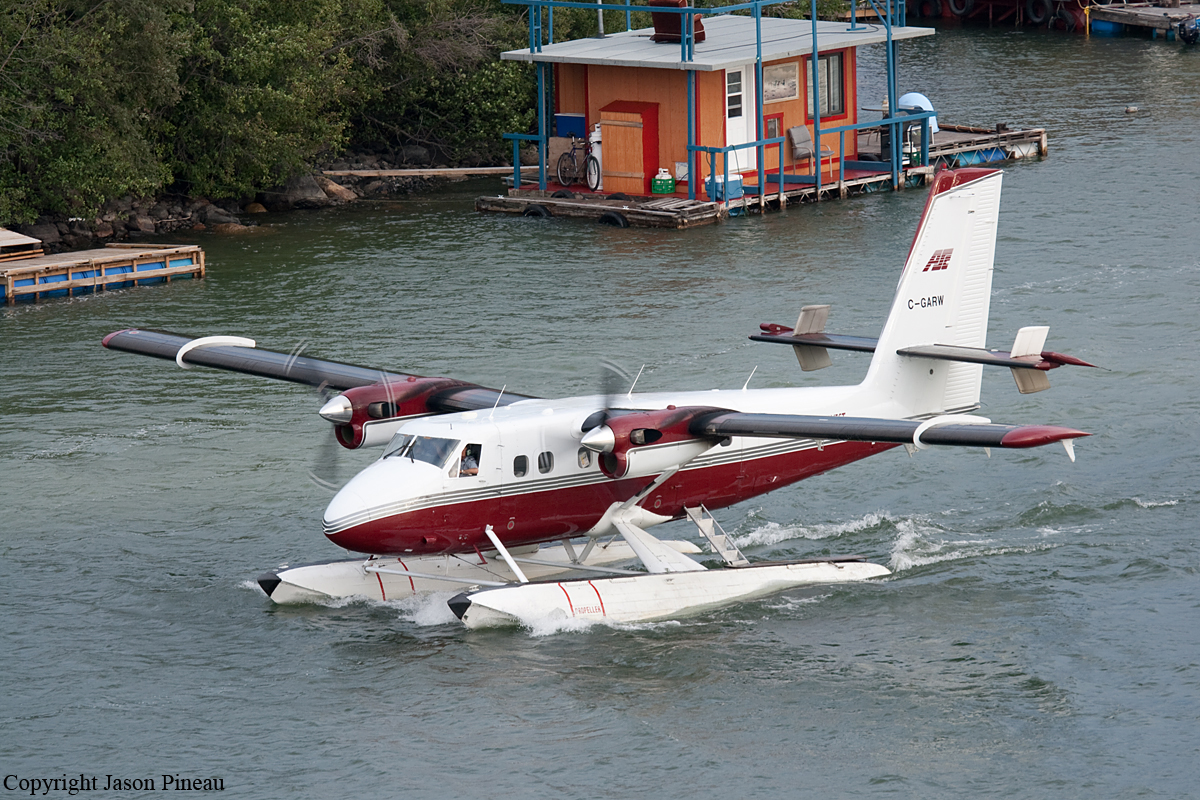
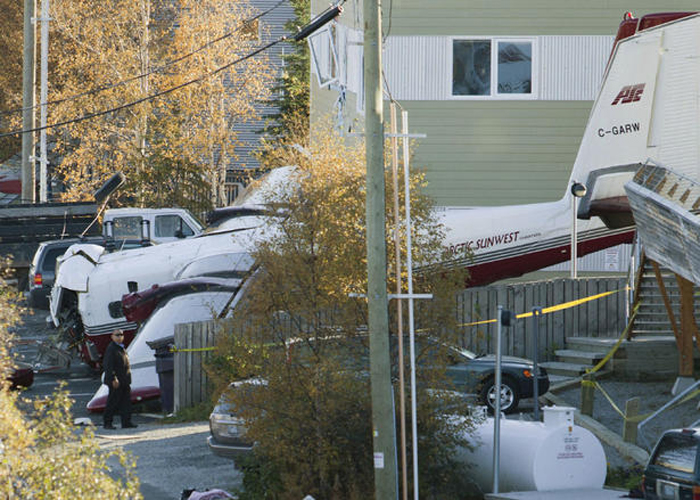
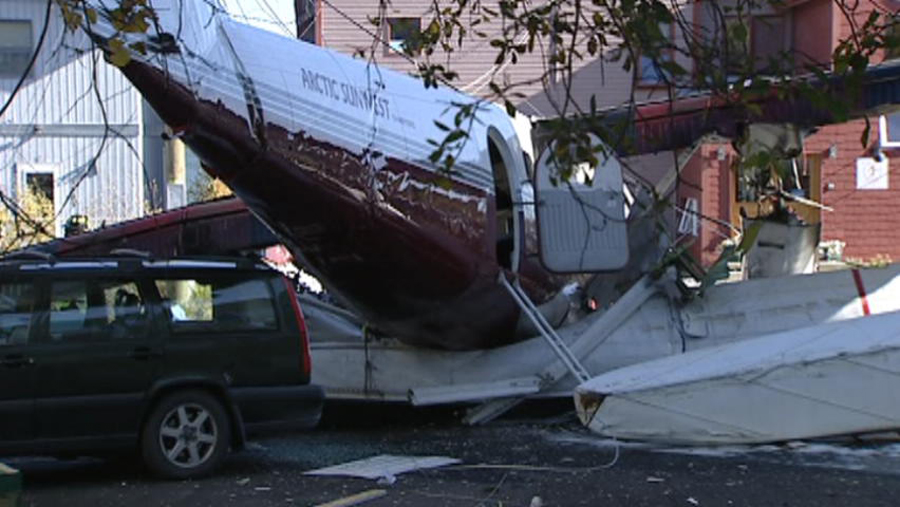
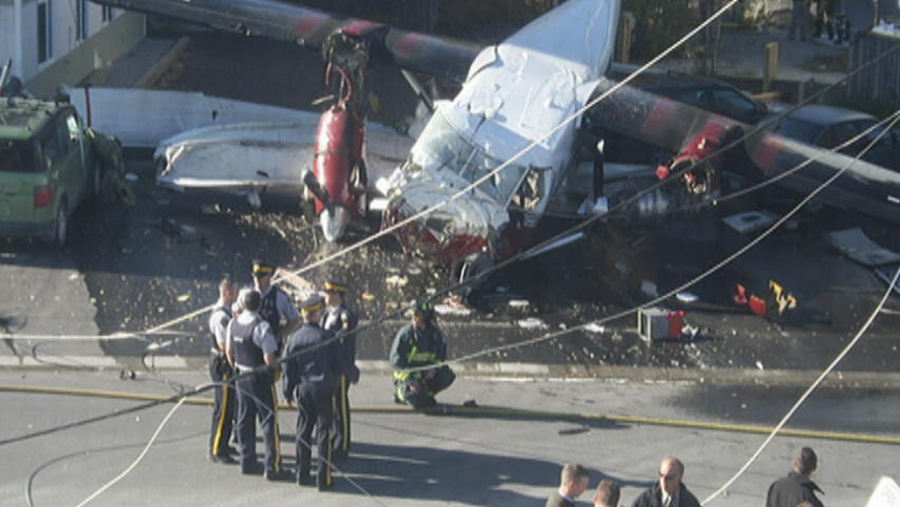
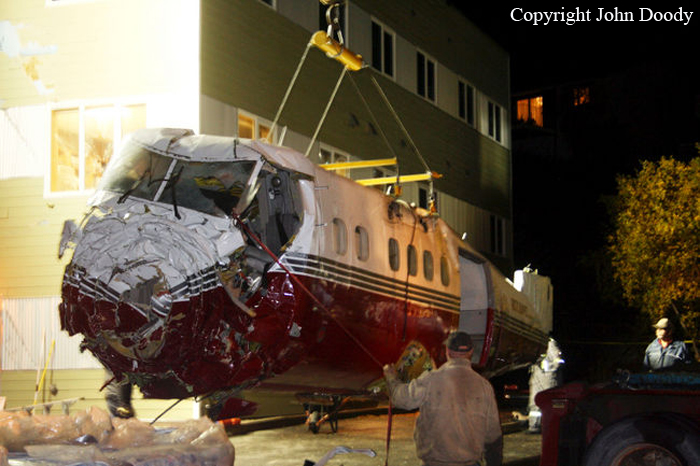
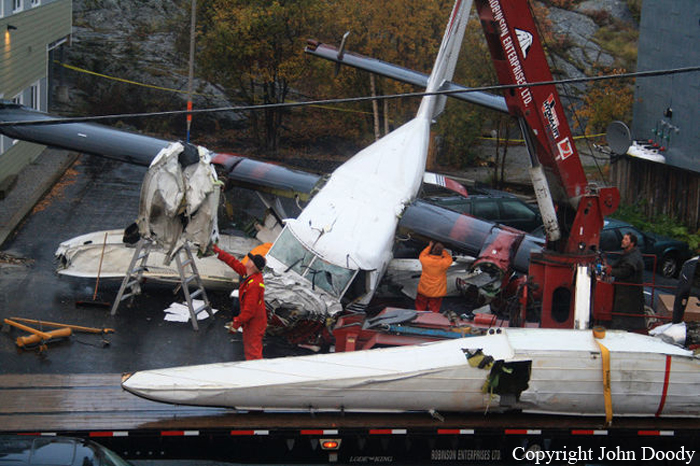
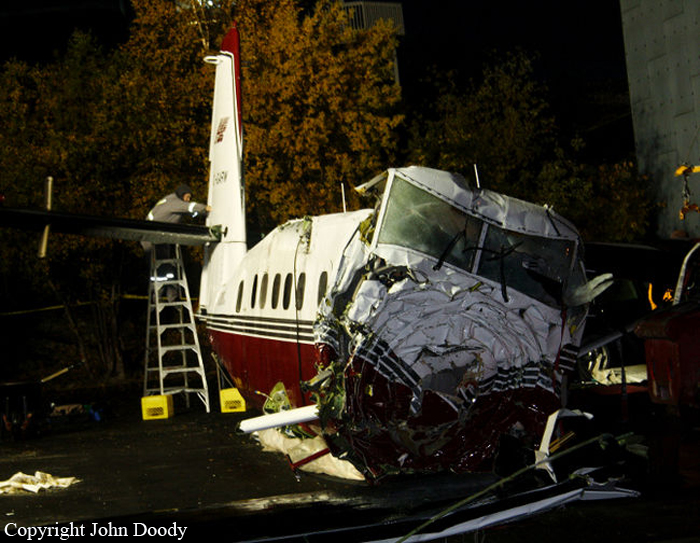
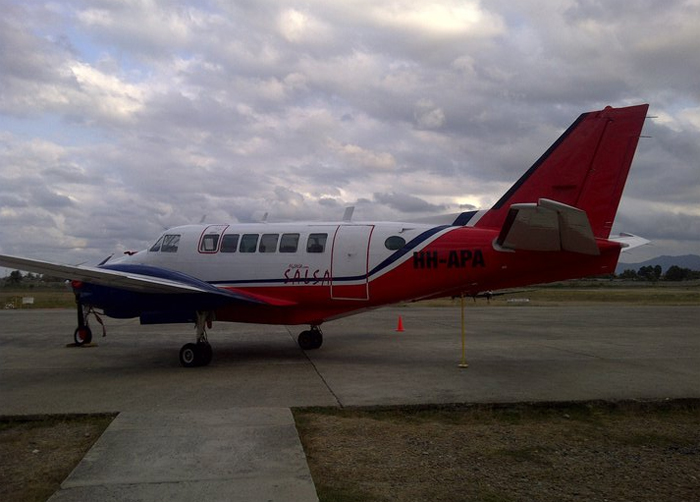
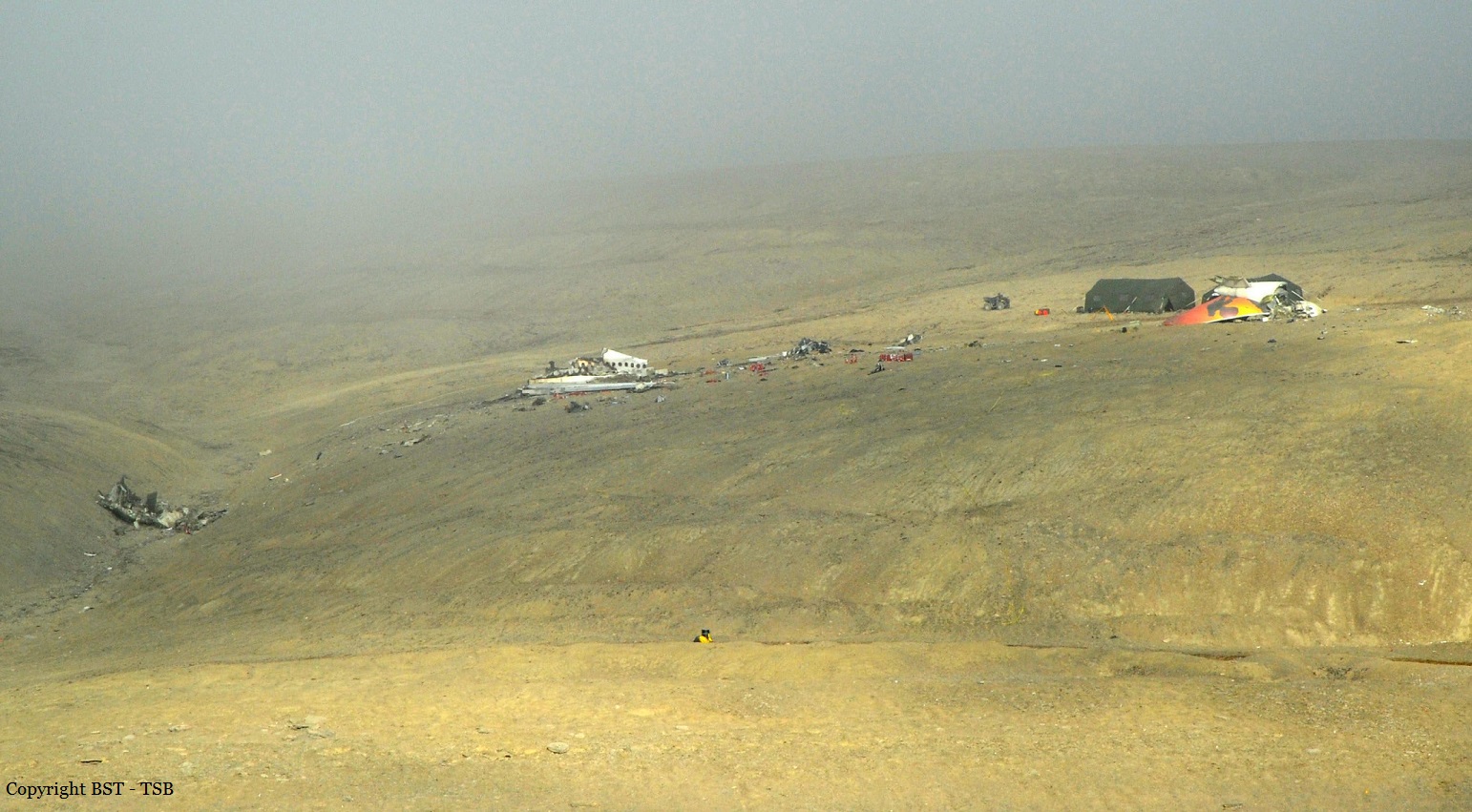
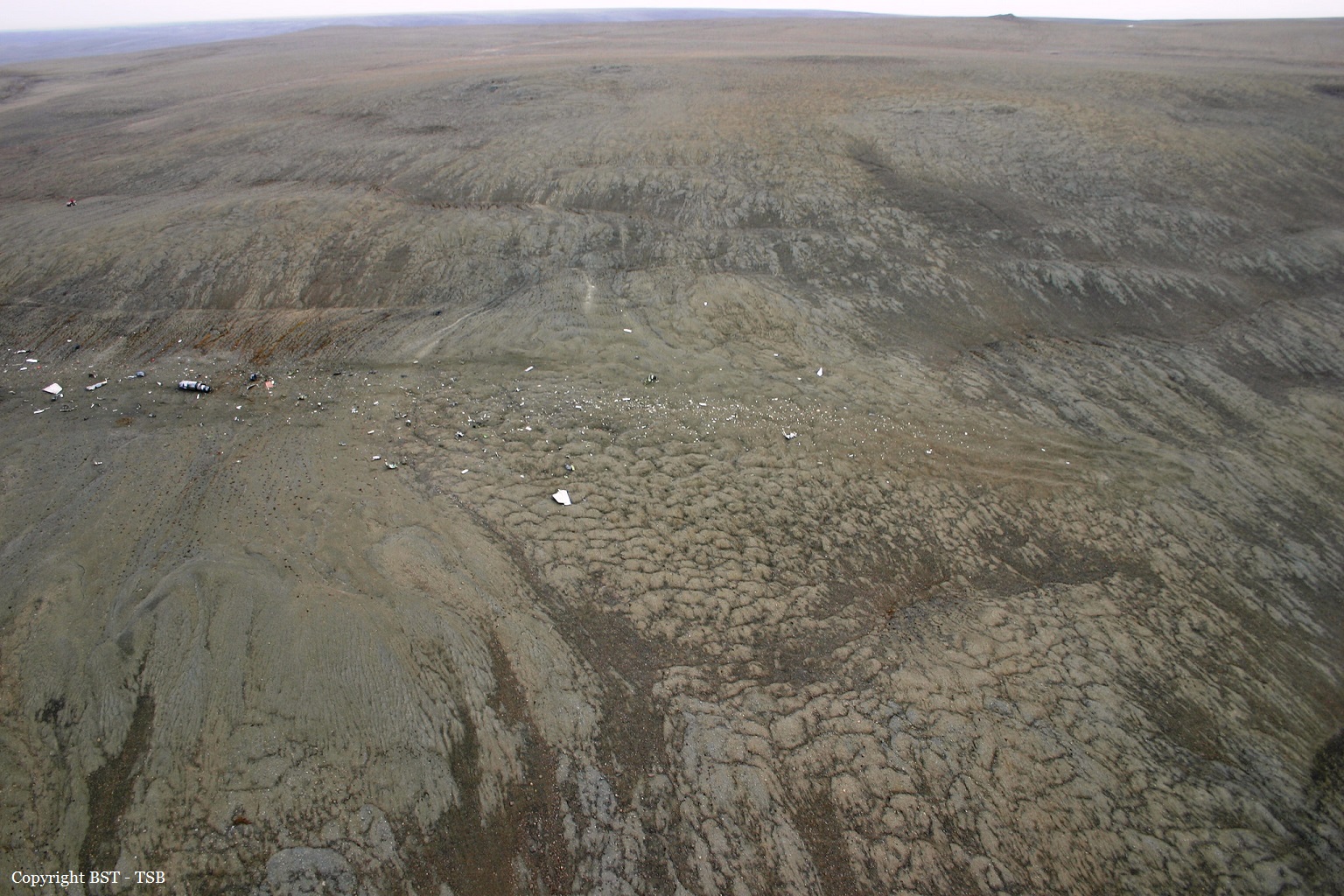
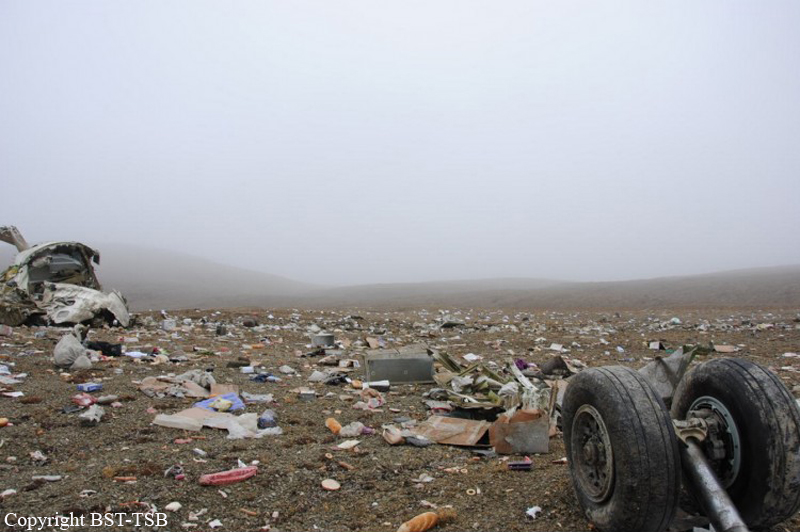
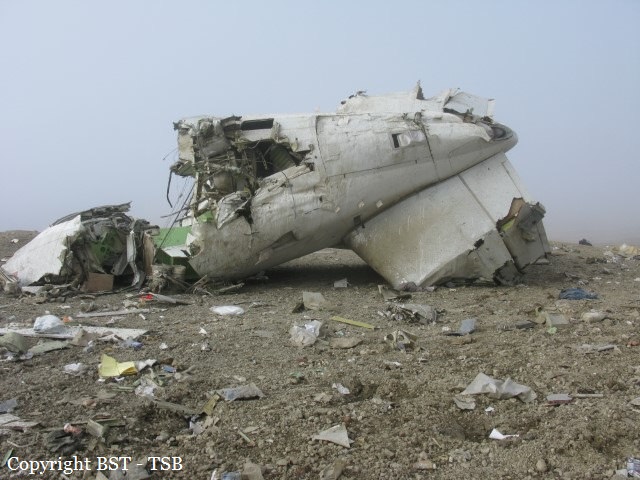
Circumstances:
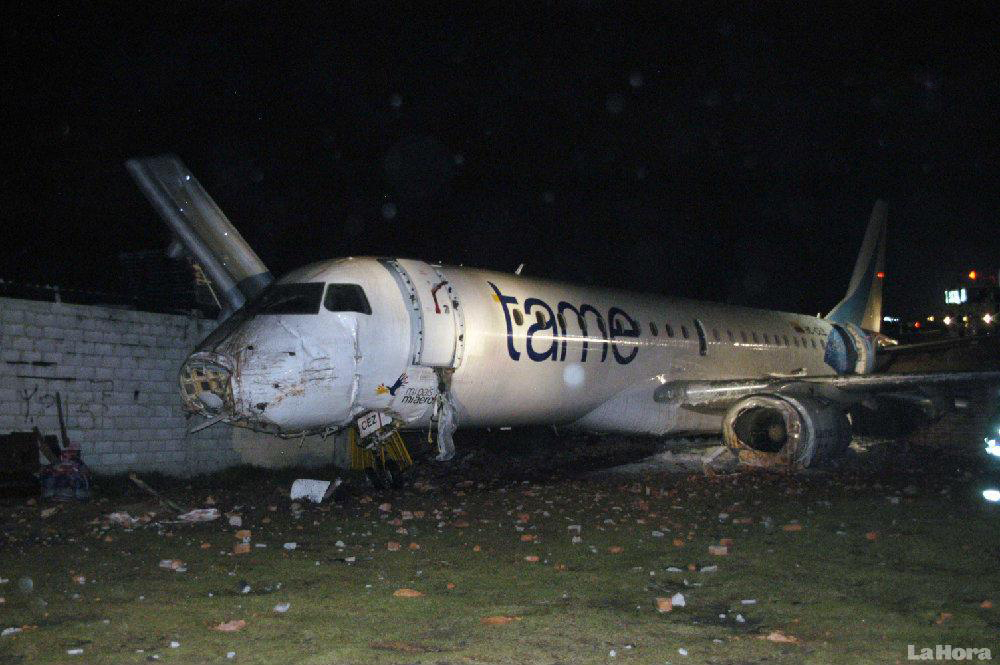
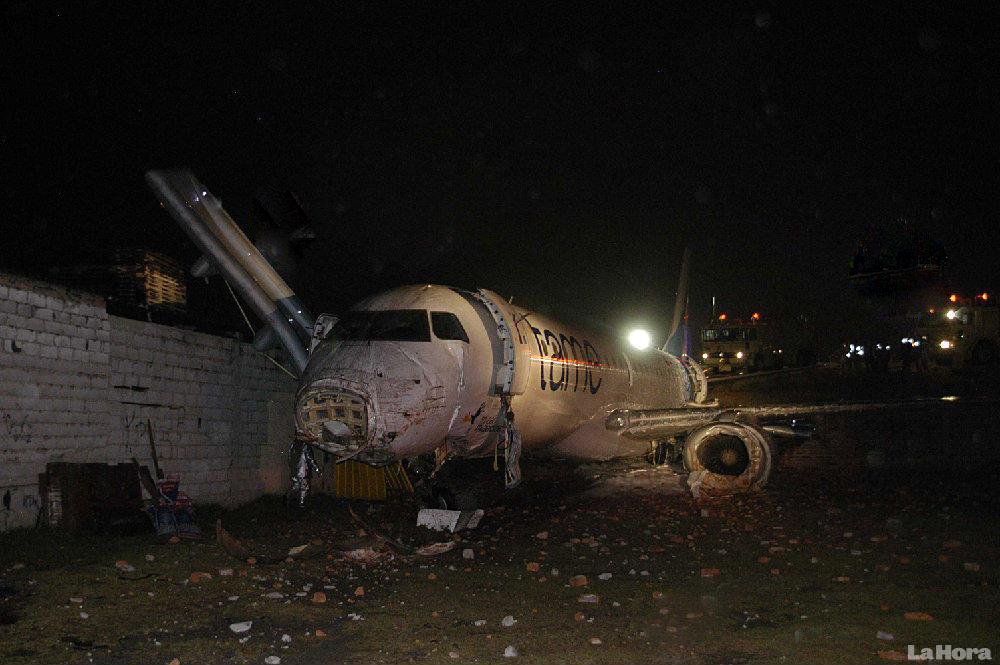
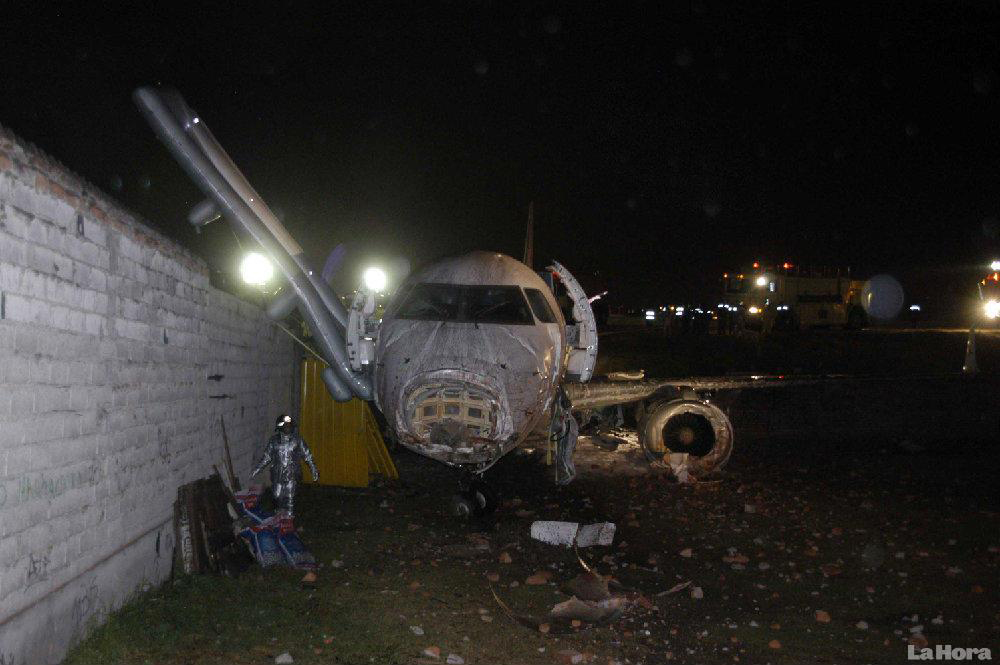
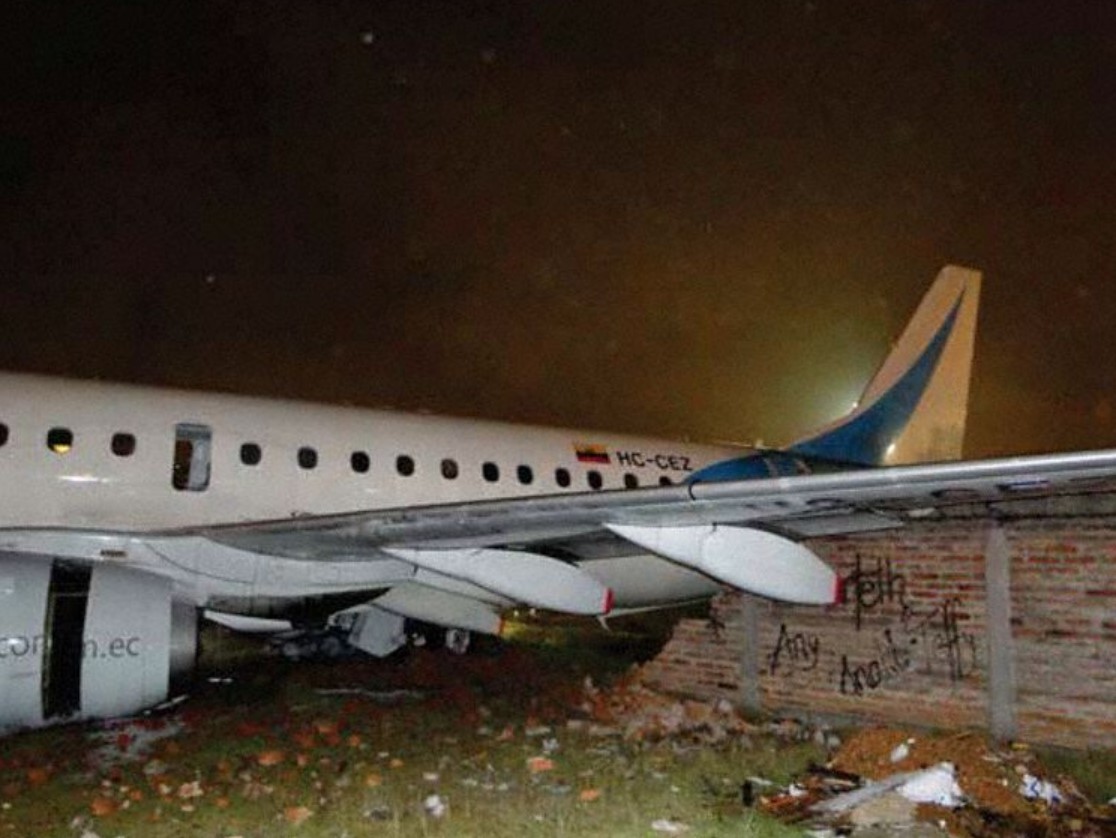
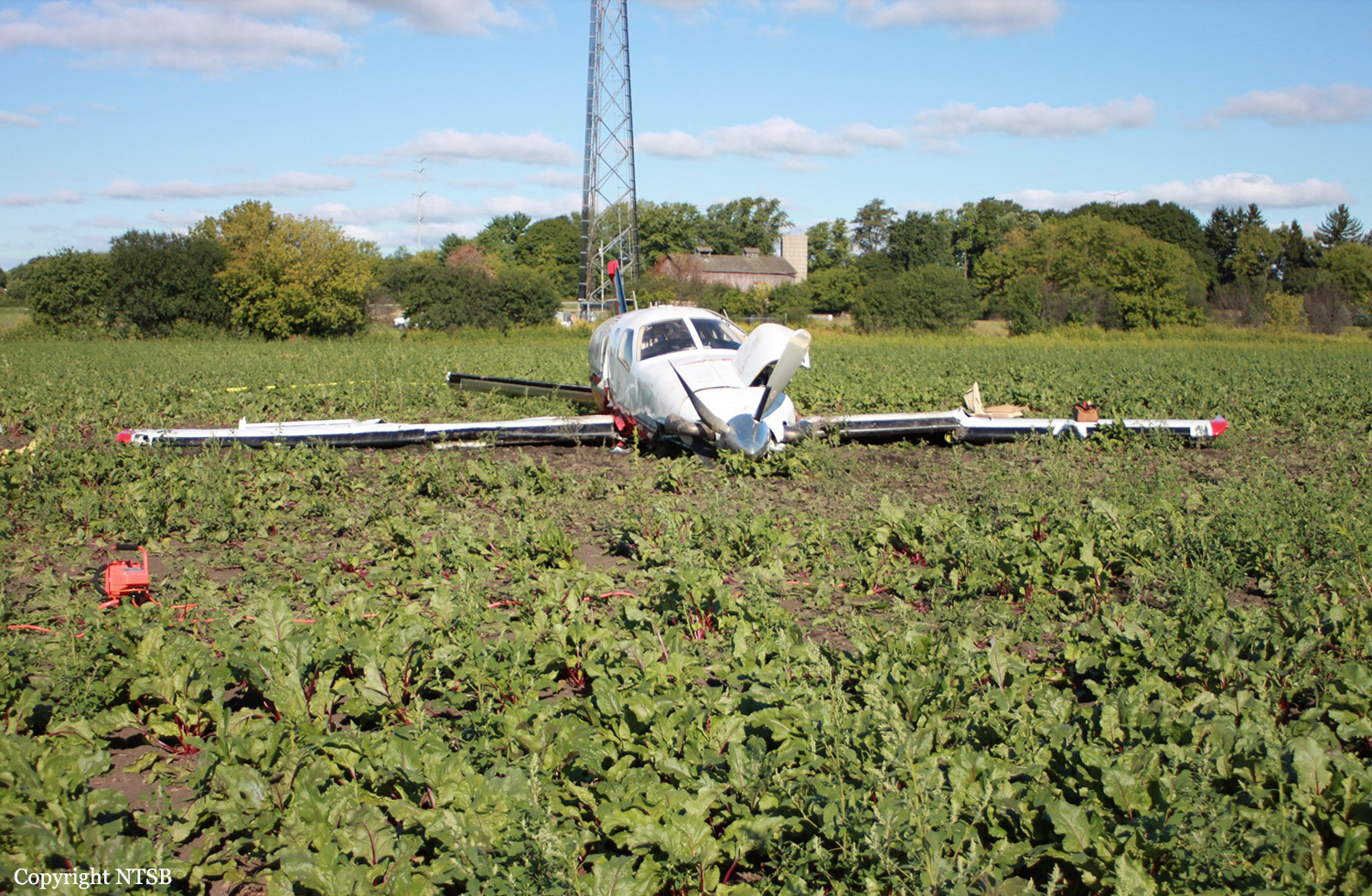
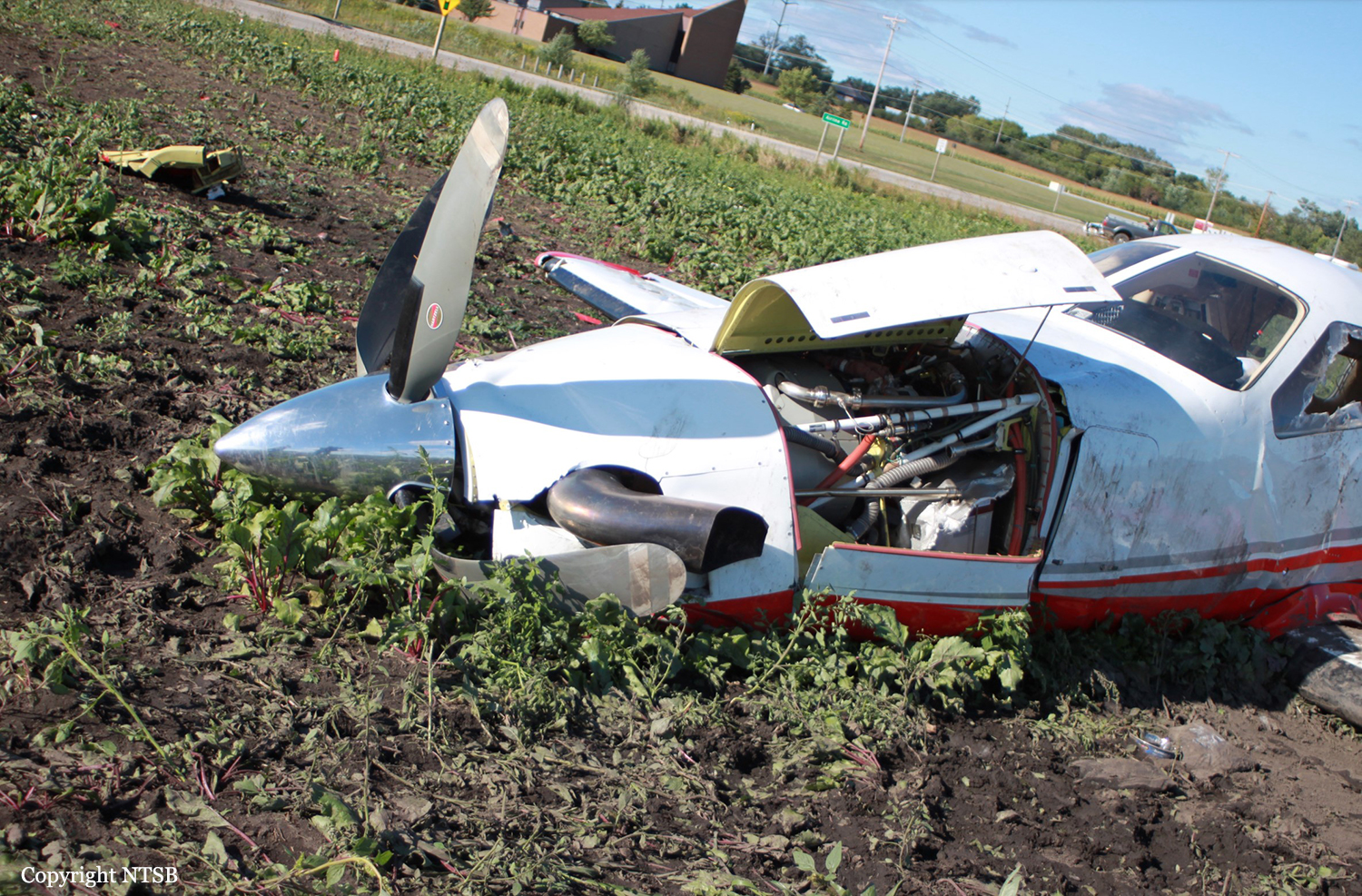
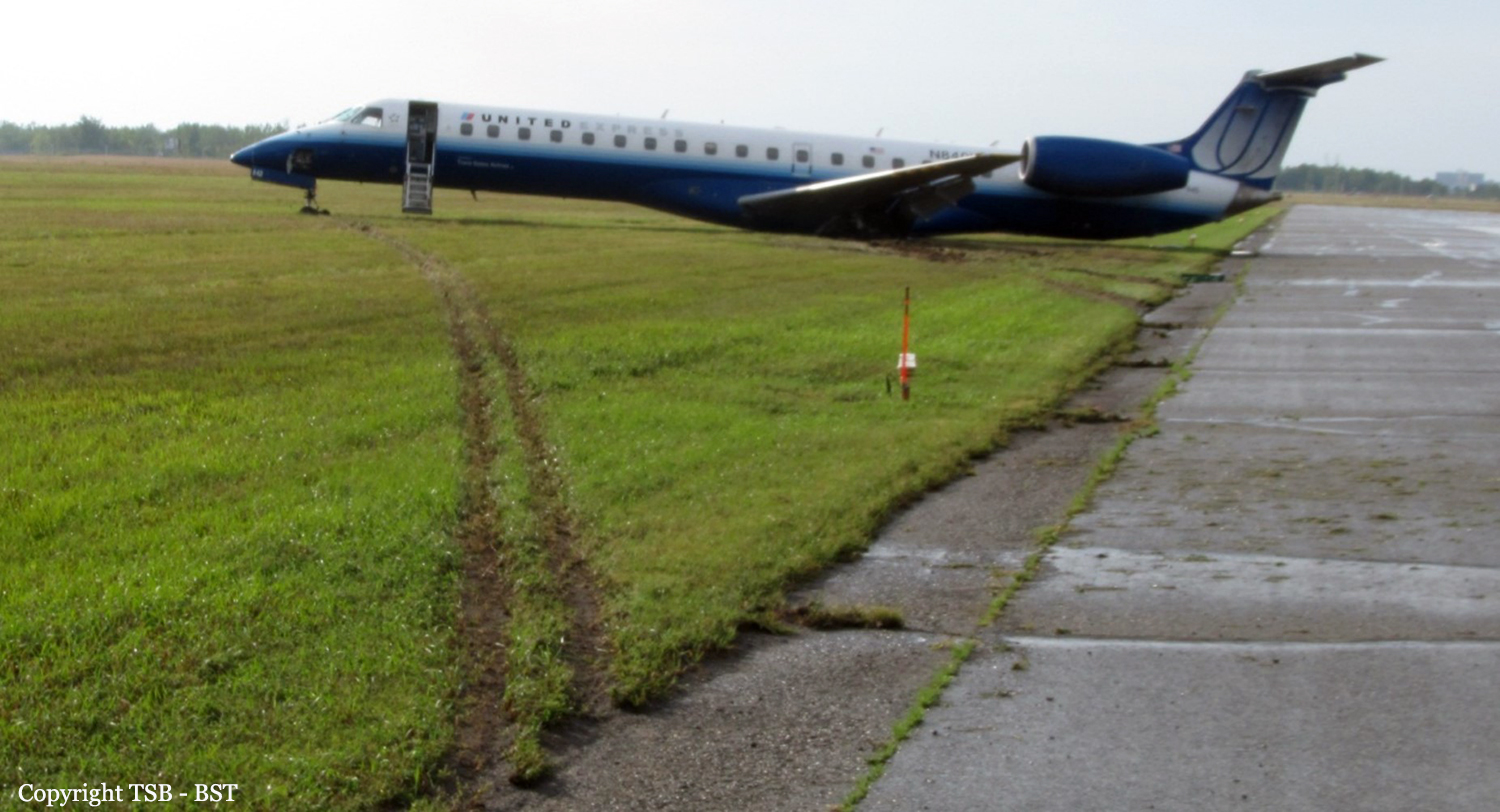
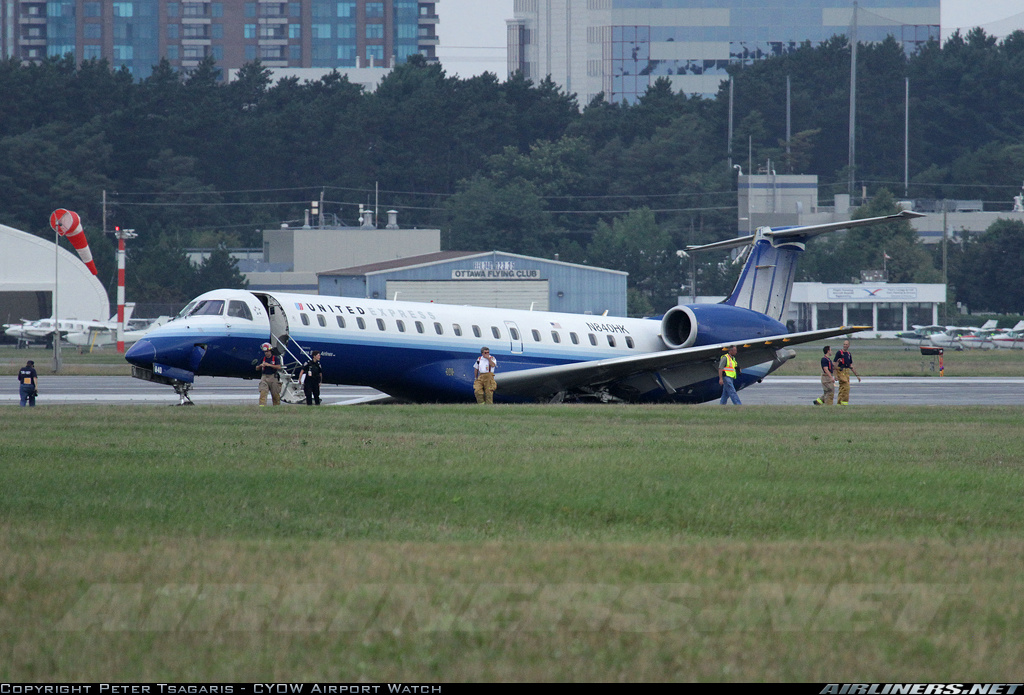
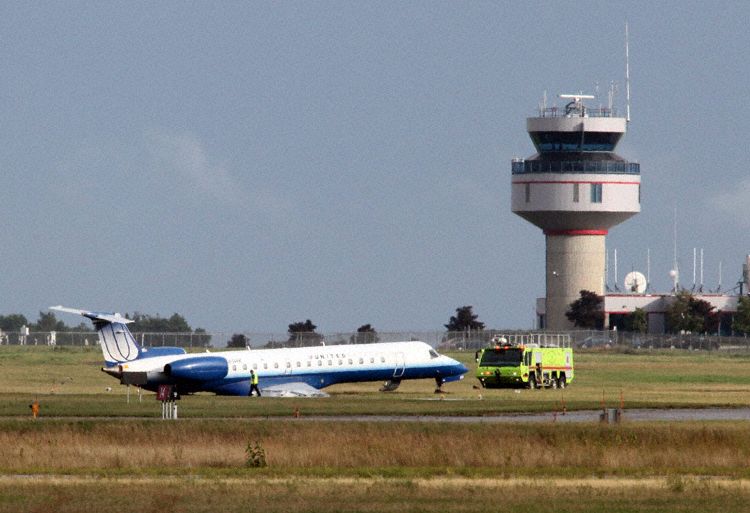
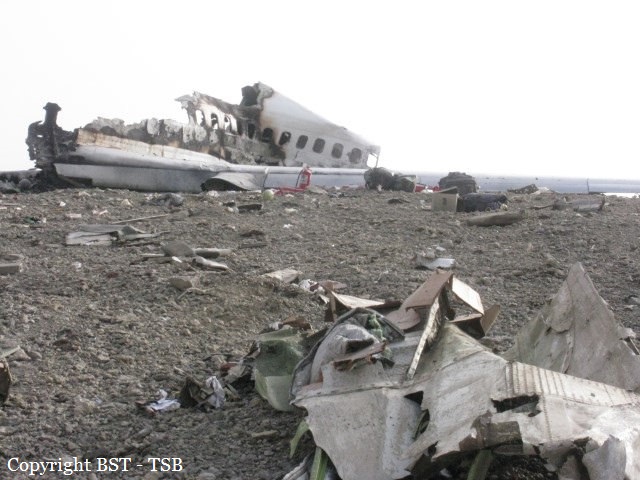
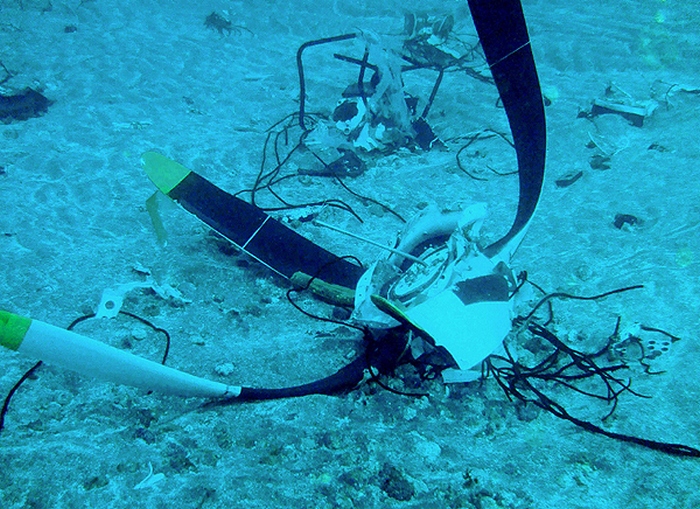
At 1406, United Express Flight 3363 (LOF3363), operated by Trans States Airlines LLC (TSA), departed Chicago O’Hare International Airport, Chicago, United States. Before commencing the descent into Ottawa/Macdonald-Cartier International Airport (CYOW), Ontario, the flight crew obtained the automatic terminal information service (ATIS) information Yankee for CYOW issued at 1411. Based on the reported wind speed and direction, the flight crew calculated the approach speed (VAPP) to be 133 knots indicated airspeed (KIAS). Runway 25 was identified in ATIS information Yankee as the active runway. However, as a result of a previous overrun on Runway 07/25 in August 2010, TSA prohibited its flight crews from landing or taking off on Runway 07/25 when the surface is reported as damp or wet. Because rain showers were forecast for CYOW and Runway 32 was the longest runway, the flight crew decided at 1506 to carry out an instrument landing system (ILS) approach to Runway 32. At 1524, the CYOW terminal air traffic controller (ATC) advised the flight crew that it was starting to rain heavily at CYOW. About 2 minutes later, the aircraft intercepted the glideslope for the ILS to Runway 32. Final descent was initiated, the landing gear was extended, and the flaps were selected to 22°. Upon contacting the CYOW tower controller, the flight crew was advised that moderate rain had just started at the airport and the wind was reported as 310° magnetic (M) at 10 knots. The aircraft crossed the GREELY (YYR) final approach fix at 4.3 nautical miles (nm), slightly above the glideslope at 174 KIAS. About 1528, the aircraft passed through 1000 feet above ground level (agl) at 155 knots. Moments later, the flaps were selected to 45°. The airspeed at the time was approximately 145 KIAS. The tower controller advised the flight crew that the wind had changed to 320°M at 13 knots gusting to 20 knots. To compensate for the increased wind speed, the flight crew increased the VAPP to 140 KIAS. About 1 minute later, at 1529, the aircraft crossed the threshold of Runway 32 at about 45 feet agl, at an airspeed of 139 KIAS. As the aircraft crossed the runway threshold, the intensity of the rain increased, so the flight crew selected the windshield wipers to high. When the aircraft was about 20 feet agl, engine power was reduced and a flare was commenced. Just before touchdown, the aircraft encountered a downpour sufficient to obscure the crew’s view of the runway. Perceiving a sudden increase in descent rate, at approximately 5 feet agl, the captain applied maximum thrust on both engines. The master caution light illuminated, and a voice warning stated that the flaps were not in a take-off configuration. Maximum thrust was maintained for 7 seconds. The aircraft touched down smoothly 2700 feet beyond the threshold at 119 KIAS; the airspeed was increasing, and the aircraft became airborne again. The aircraft touched down a second time at 3037 feet beyond the threshold, with the airspeed increasing through 125 KIAS. Airspeed on touchdown peaked at 128 KIAS as the nosewheel was lowered to the ground, and then the thrust levers were retarded to flight idle. The outboard spoilers almost immediately deployed, and about 8 seconds later, the inboard spoilers deployed. The aircraft was about 20 feet right of the runway centreline when it touched down for the second time. Once the nosewheel was on the ground, the captain applied maximum brakes. The flight crew almost immediately noted that the aircraft began skidding. The captain then requested the first officer to apply maximum brakes as well. The aircraft continued to skid, and no significant brake pressure was recorded until about 14 seconds after the outboard spoilers deployed, when brake pressure suddenly increased to its maximum. During this time, the captain attempted to steer the aircraft back to the runway centreline. As the aircraft skidded down the runway, it began to yaw to the left. Full right rudder was applied, but was ineffective in correcting the left yaw. Sufficient water was present on the runway surface to cause the aircraft tires to send a spray of water, commonly known as a rooster tail, to a height of over 22 feet, trailing over 300 feet behind the aircraft. At some point during the landing roll, the captain partially applied the emergency/parking brake (EPB), and when no braking action was felt, the EPB was engaged further. With no perceivable deceleration being felt, the EPB was stowed. The aircraft continued to skid down the runway until about 7500 feet from the threshold, at which point it started skidding sideways along the runway. At 1530, the nosewheel exited the paved surface, 8120 feet from the threshold, at approximately 53 knots, on a heading of 271°M. The aircraft came to rest on a heading of 211°M, just off the left side of the paved surface. After coming to a stop, the flight crew carried out the emergency shutdown procedure as per the company Quick Reference Handbook (QRH), and consulted with the flight attendant on the status of everyone in the passenger cabin. The flight crew determined that there was no immediate threat and decided to hold the passengers on board. When the aircraft exited the runway surface, the tower activated the crash alarm. The CYOW airport rescue and firefighting (ARFF) services responded, and were on scene approximately 3 minutes after the activation of the crash alarm. Once ARFF personnel had conducted a thorough exterior check of the aircraft, they informed the flight crew that there was a fuel leak. The captain then called for an immediate evacuation of the aircraft. The passengers evacuated through the main cabin door, and moved to the runway as directed by the flight crew and ARFF personnel. The evacuation was initiated approximately 12 minutes after the aircraft came to a final stop. After the evacuation was complete, the firefighters sprayed foam around the aircraft where the fuel had leaked.
Probable cause:
Findings as to causes and contributing factors:
1. Heavy rainfall before and during the landing resulted in a 4–6 mm layer of water contaminating the runway.
2. The occurrence aircraft’s airspeed during final approach exceeded the company prescribed limits for stabilized approach criteria. As a result, the aircraft crossed the runway threshold at a higher than recommended VREF airspeed.
3. A go-around was not performed, as per standard operating procedures, when the aircraft’s speed was greater than 5 knots above the appropriate approach speed during the stabilized portion of the approach.
4. The application of engine thrust just before touchdown caused the aircraft to touch down 3037 feet from the threshold at a higher than recommended airspeed.
5. The combination of a less than firm landing and underinflated tires contributed to the aircraft hydroplaning.
6. The emergency/parking brake was applied during the landing roll, which disabled the anti-skid braking system and prolonged the skid.
7. The aircraft lost directional control as a result of hydroplaning and veered off the runway.
Findings as to risk:
1. The typical and frequently used technique for differential braking that pilots are trained to use may not be effective when anti-skid systems require different techniques.
2. If aircraft electrical power is applied with an active fuel leak, there is a risk that an electrical spark could ignite the fuel and start a fire.
3. The use of non-grooved runways increases the risk of hydroplaning, which may result in runway excursions.
4. If there is an absence of information and training about non-grooved runways, there is a risk that crews will not carry out the appropriate landing techniques when these runways are wet.
5. The use of thrust reversers reduces the risk of runway excursions when landing on wet runways.
6. If pilots do not comply with standard operating procedures, and companies do not assure compliance, then there is a risk that occurrences resulting from such deviations will persist.
Other findings:
1. The central maintenance computer was downloaded successfully; however, there were no data present in the memory unit.
2. Although the Transportation Safety Board was able to download high-quality data from the flight data recorder, the parameters that were not recorded due to the model type and input to the flight data recorder made it more difficult to determine the sequence of events.