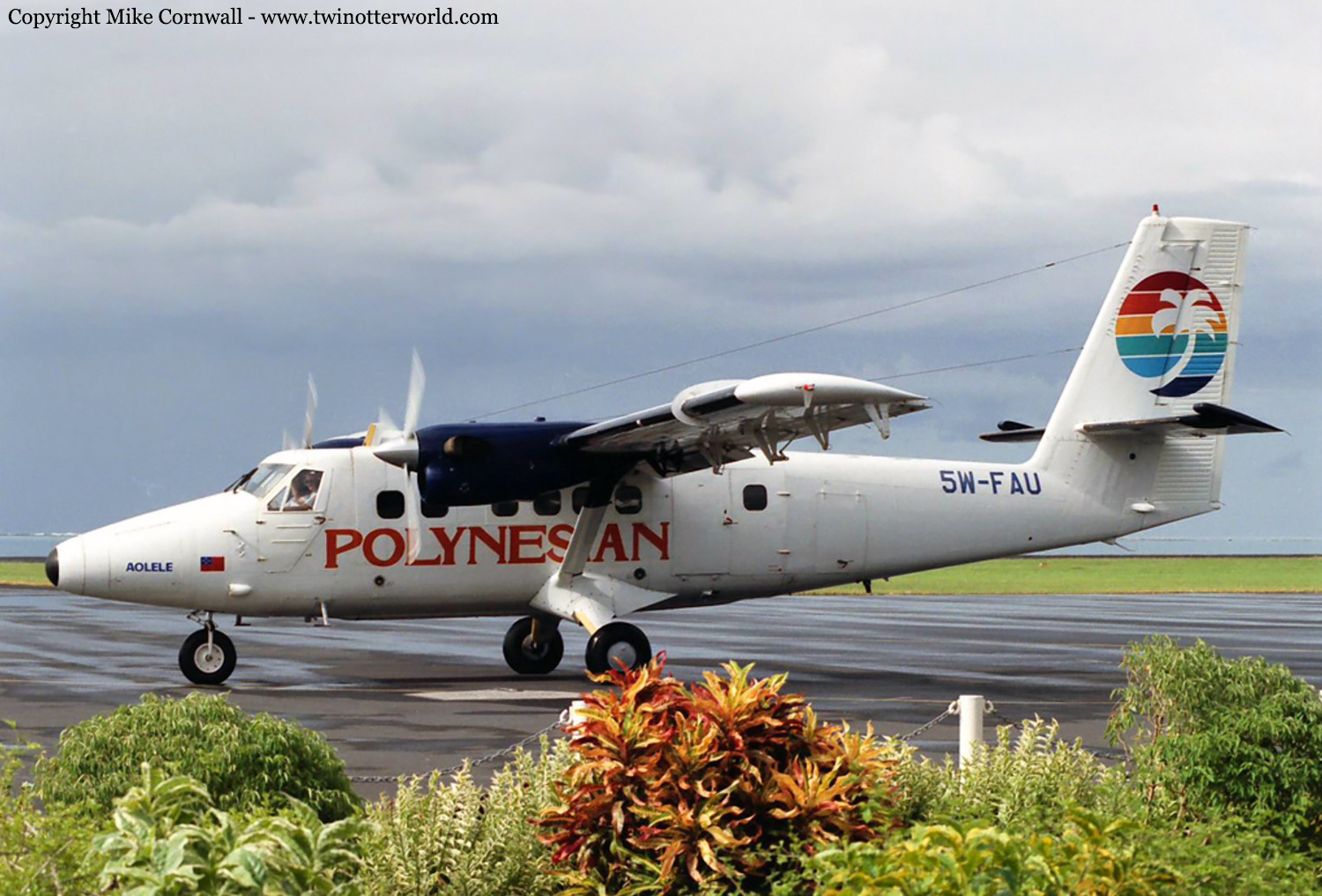
Crash of a De Havilland DHC-6 Twin Otter 300 in Apia: 3 killed
Date & Time:
Jan 7, 1997 at 1038 LT
Registration:
5W-FAU
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Pago Pago - Apia
MSN:
678
YOM:
1980
Flight number:
PH211
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
3
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
3
Circumstances:
At about 1038 hours on Tuesday 7 January 1997, Polynesian Airlines’ DHC-6 (Twin Otter) 5W FAU collided with the western slopes of Mt Vaea, Apia, in conditions of low cloud and heavy rain. The aeroplane was on a scheduled flight from Pago Pago to Fagali’i, and was being flown to Fagali’i by visual reference after having made an instrument approach to Faleolo. The captain and two passengers lost their lives in the accident. The first officer and one passenger survived.
Probable cause:
The following causal factors were identified:
• The decision by the captain to continue the flight toward Fagali’i in reduced visibility and subsequently in cloud.
• Mis-identification of ground features, or an inappropriate heading and altitude flown, as a result of inadequate visual reference.
• Insufficient forward visibility to ensure effective and timely action to avoid a collision with terrain.
• The decision by the captain to continue the flight toward Fagali’i in reduced visibility and subsequently in cloud.
• Mis-identification of ground features, or an inappropriate heading and altitude flown, as a result of inadequate visual reference.
• Insufficient forward visibility to ensure effective and timely action to avoid a collision with terrain.