Date & Time:
Sep 3, 1989 at 2045 LT
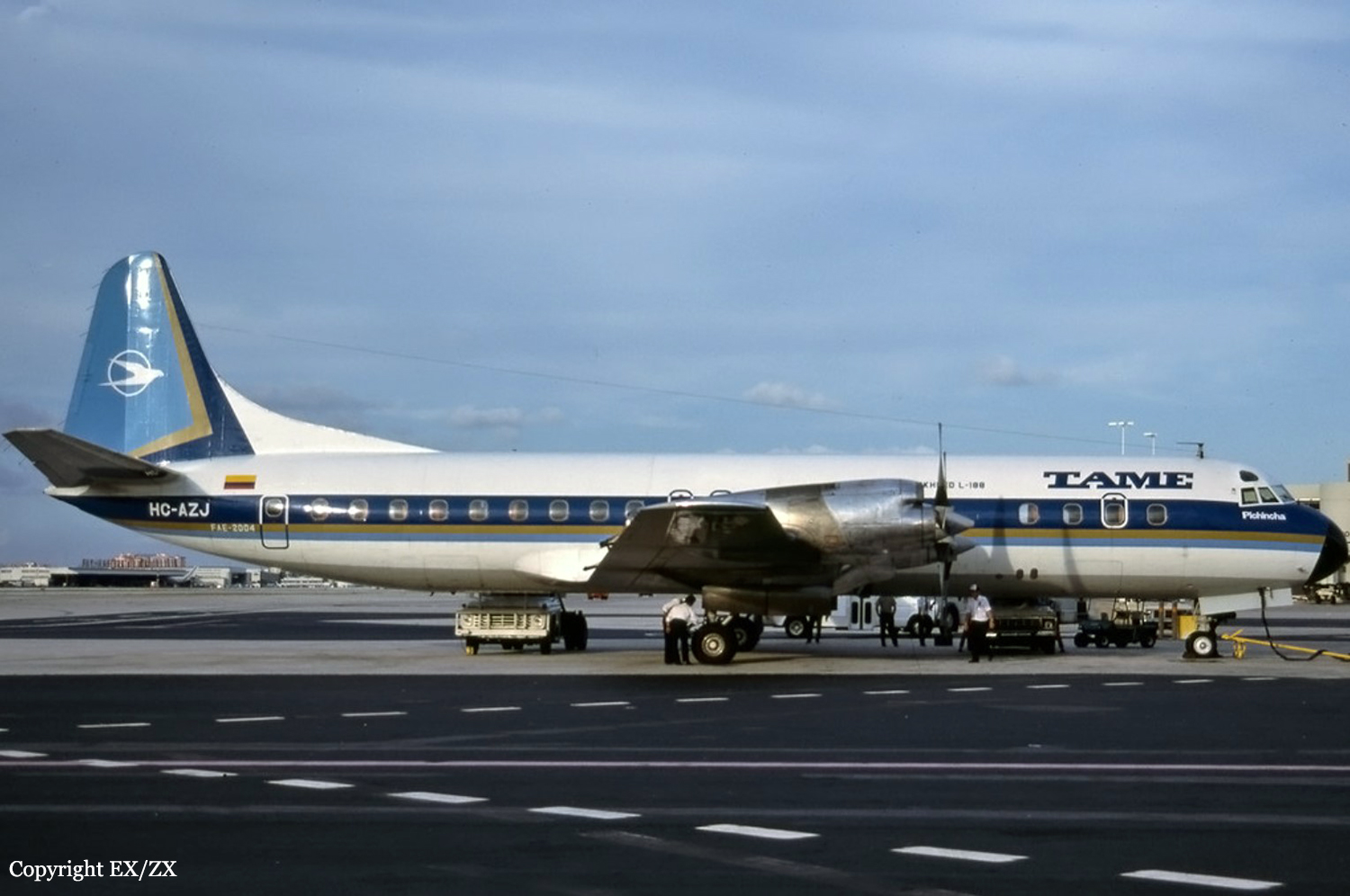
Operator:

Schedule:
São Paulo – Marabá – Belém
Crew fatalities:
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Captain / Total flying hours:
6928
Captain / Total hours on type:
980.00
Copilot / Total flying hours:
884
Copilot / Total hours on type:
442
Aircraft flight hours:
33373
Circumstances:
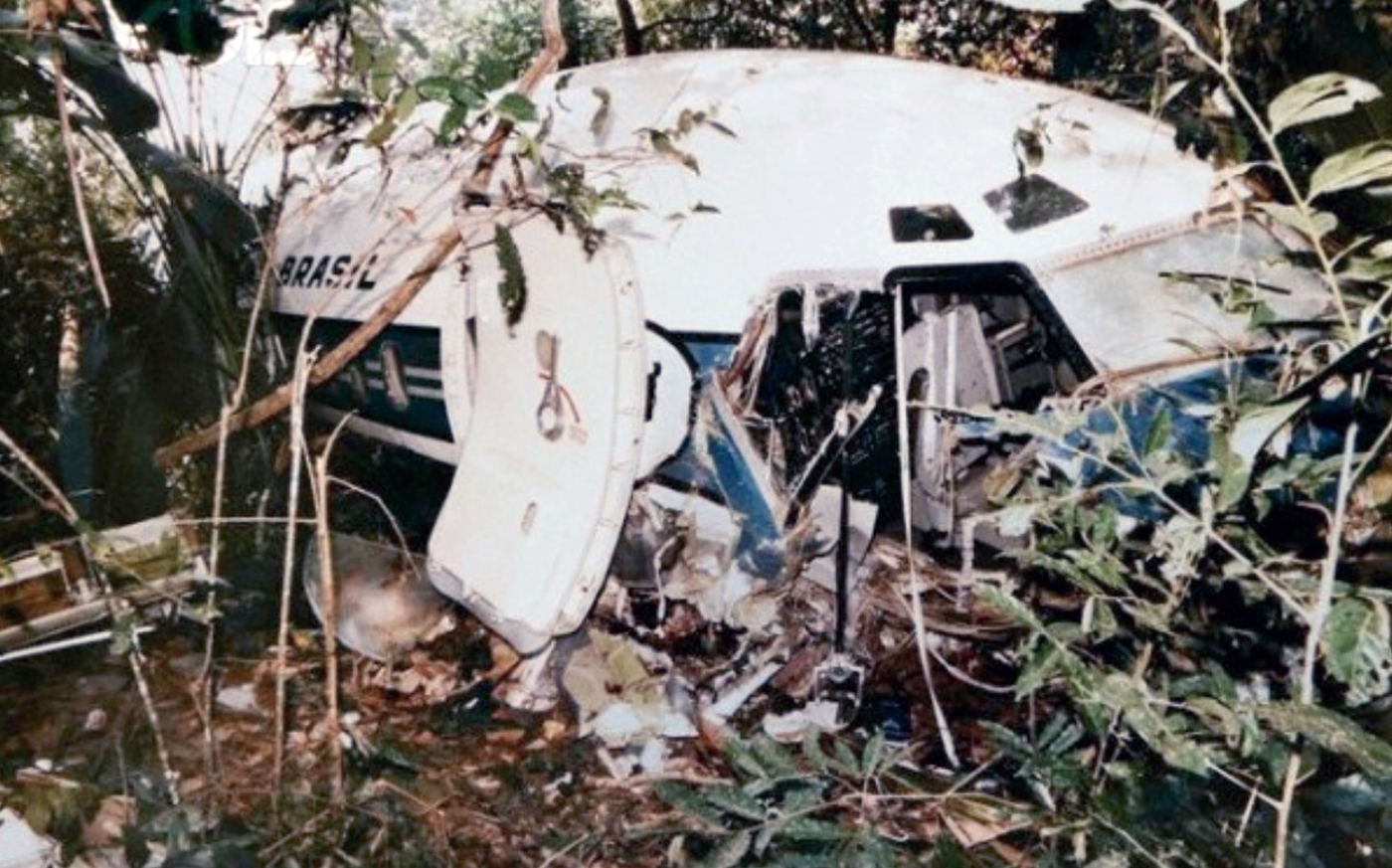
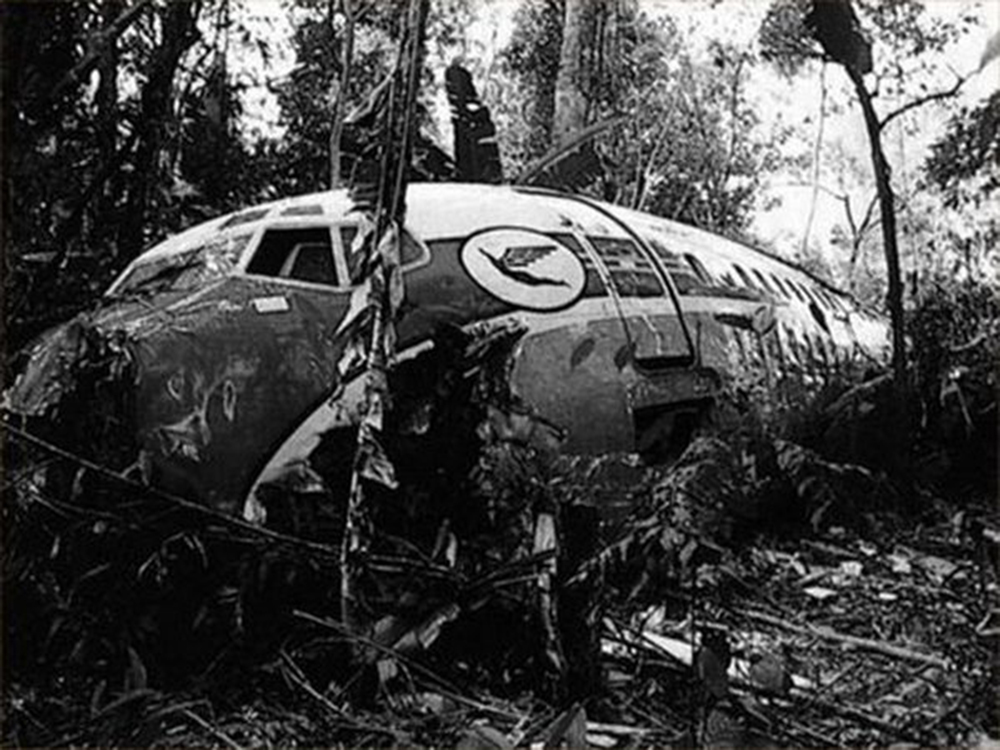
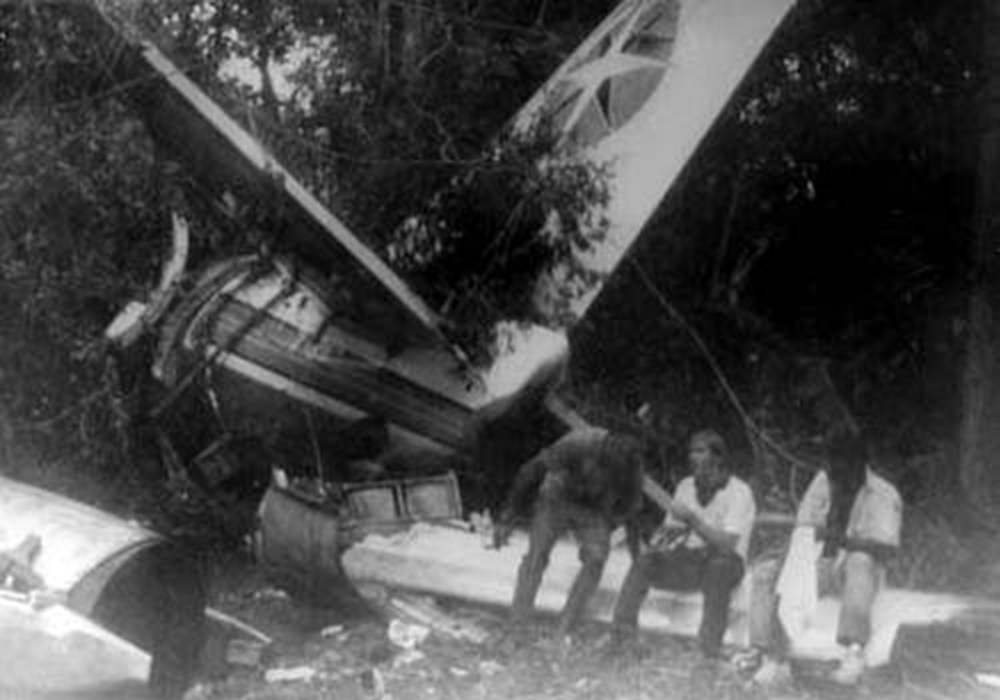
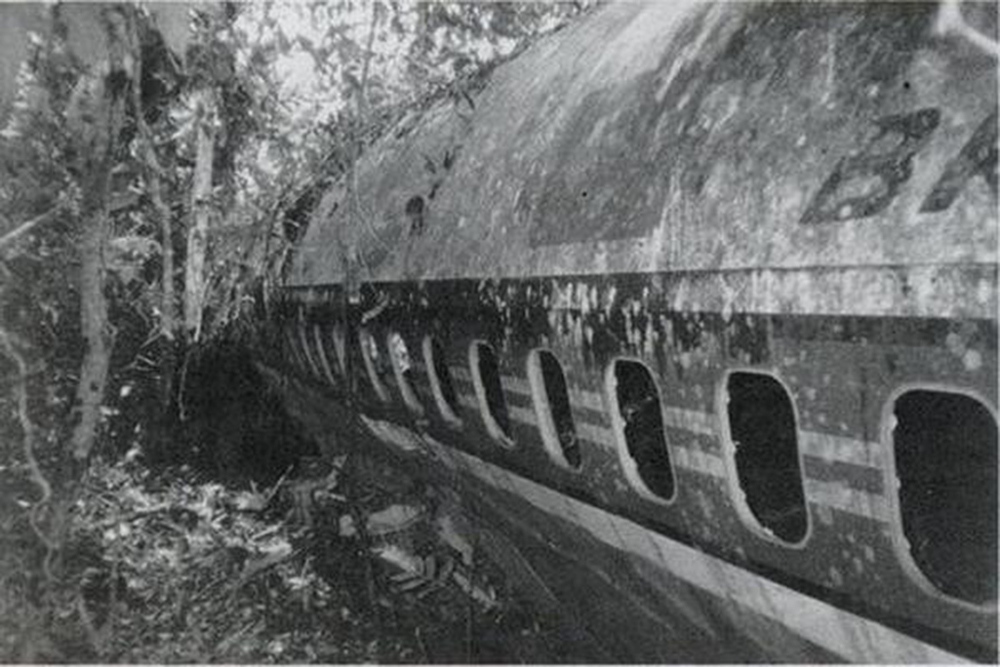
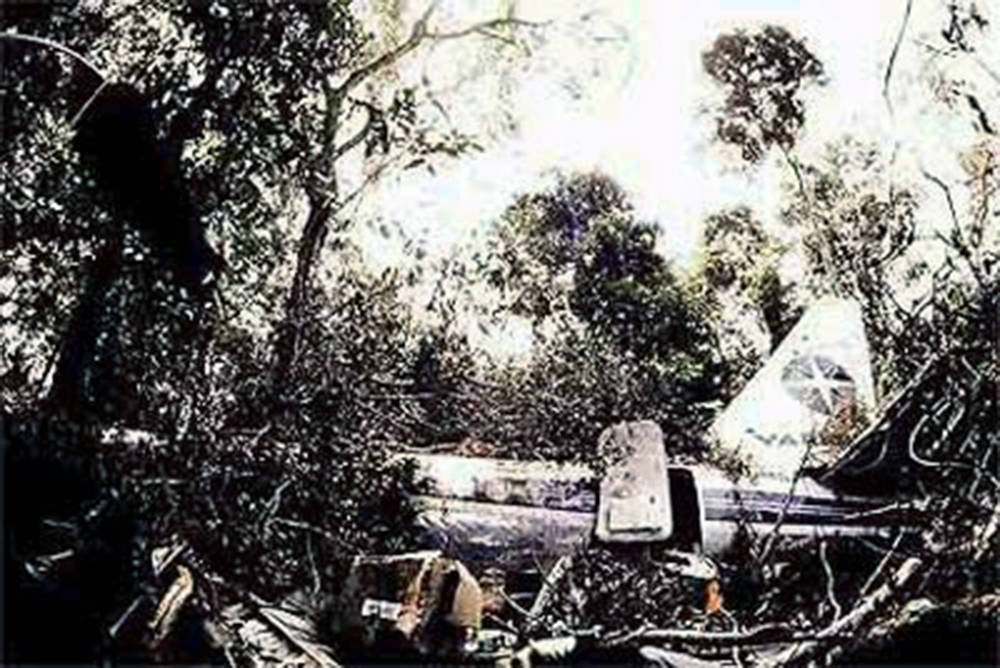
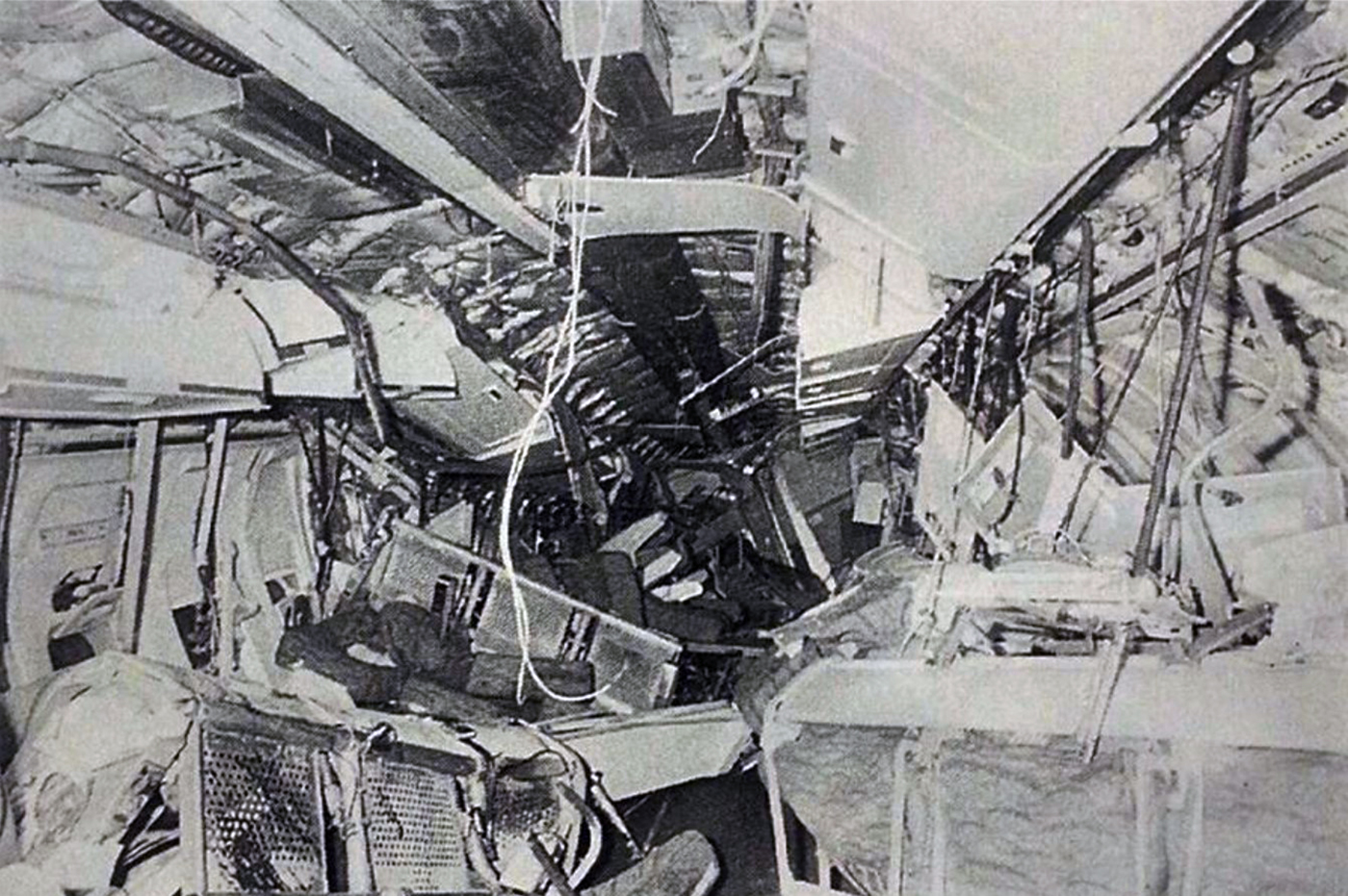
Following a wrong flight preparation and erroneous computer setting regarding the route, the crew computerized 027° instead of 270°. After takeoff from Marabá Airport at 1725LT, the crew was cleared to climb to FL290 and maintained heading of 270° for 40 minutes. The flight was then cleared to descend to FL200 by Belém ACC. However, the crew failed to find navigational aids and lost radio contact. Course was changed to 090 degrees as the aircraft further descended down to FL40. The crew then followed a river, heading 165 degrees. Because of the sunset and haze the pilot's had difficulty navigating. Also, they failed to establish radio contact on several frequencies and failed to find navaids in the area. After the crew found the NDB, both engines stopped due to fuel exhaustion. The captain elected to make an emergency landing when the aircraft crashed in the jungle about 60 km from São José do Xingu. Rescue teams arrived on site 44 hours later. 42 occupants were injured while 12 passengers were killed. The aircraft was destroyed. It appeared that the computerized flight plan used a four digit representation of the magnetic bearing with the last digit being a tenth of a degree without any decimal separator. A course of '027.0' was presented as '0270'.
Probable cause:
A. Human Factor
1) Physiological aspect - Did not contribute to the accident.
2) Psychological aspect - The following psychological variables contributed to the accident:
a) Misleading perception - In the reading of the plan and incorrect heading insertion by the commander.
b) Reinforcement - In the reading and incorrect heading insertion by the co-pilot and heading conference placed by the commander.
c) Marginal attention and level of attention - The non-recognition of conditions that would mean being far from the objective: request for "VHF bridge" when other aircraft were talking normally with the Control; "reception" of commercial stations, and non-receipt of destination NDB, etc.
d) Predisposition - Maintaining the urge to go to the established objective (Belém).
e) Predisposition duration - Maintenance of FL040 for a long time.
f) Reinforcement of predisposition - Reception of boundaries when selecting Belem's radio frequencies.
g) Attention Fixing - Permanent search for headings, radio contacts or river contours, as an alternative, to reach the fixed goal.
h) Blocks - Delays in identifying the initial headings error and plotting itself in navigation.
i) Geographical position error.
B. Material Factor - Did not contribute to the accident.
C. Operational Factor
1) Poor supervision - Inadequate graphical representation of the Computer Flight Plan.
2) Poor cockpit coordination - No supervision of cockpit activities. Actions were not supervised, but imitated.
3) Poor support staff - Lack of radio contact by the operator's Flight Coordination with the aircraft in flight, after the significant landing delay in Belém, thus breaking the chain of events of the accident.
4) Pilot aspect characterized by environmental influence - Difficulties of visualization due to sunset and dry fog: Radio aid markings received from great distances, originating from the ionospheric propagation of electromagnetic waves.
5) Pilot aspect characterized by poor planning - Lack of route letters to cross the flight plan information.
6) Pilot aspect characterized by poor judgment - Inadequate evaluation and use of radio-navigation equipment, resulting in the pursuit of markings without causing tuning and identification.
7) Pilot aspect characterized by other operational factors - Operational doctrine firming.
Final Report: