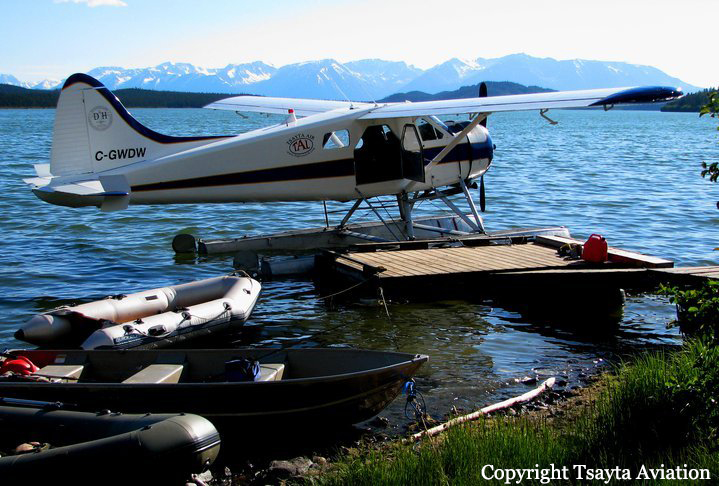
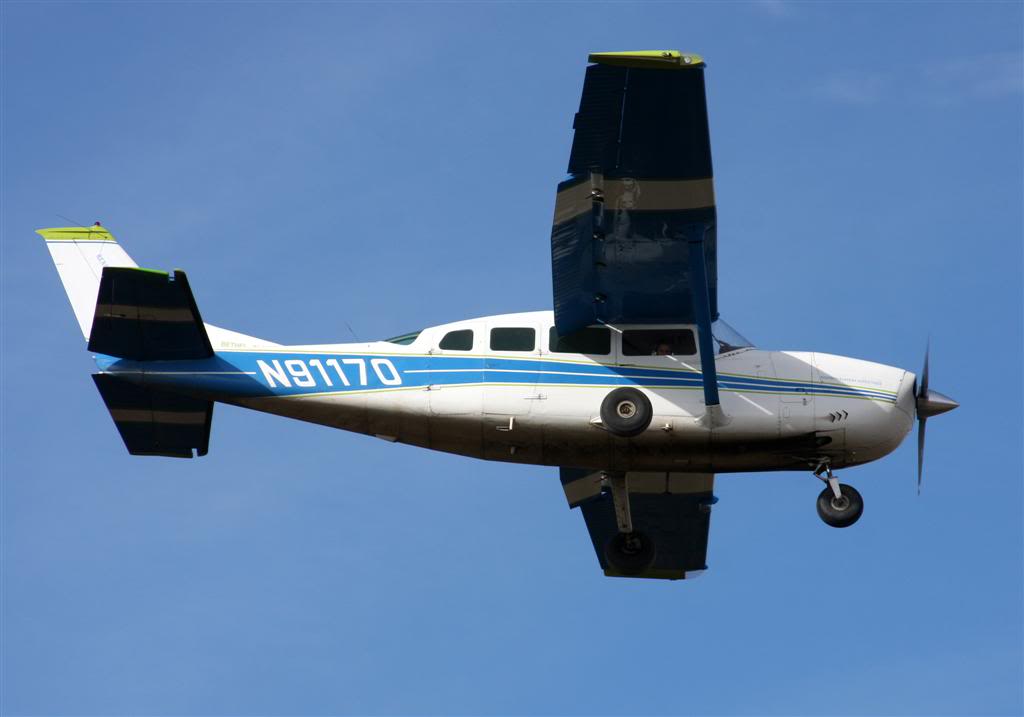
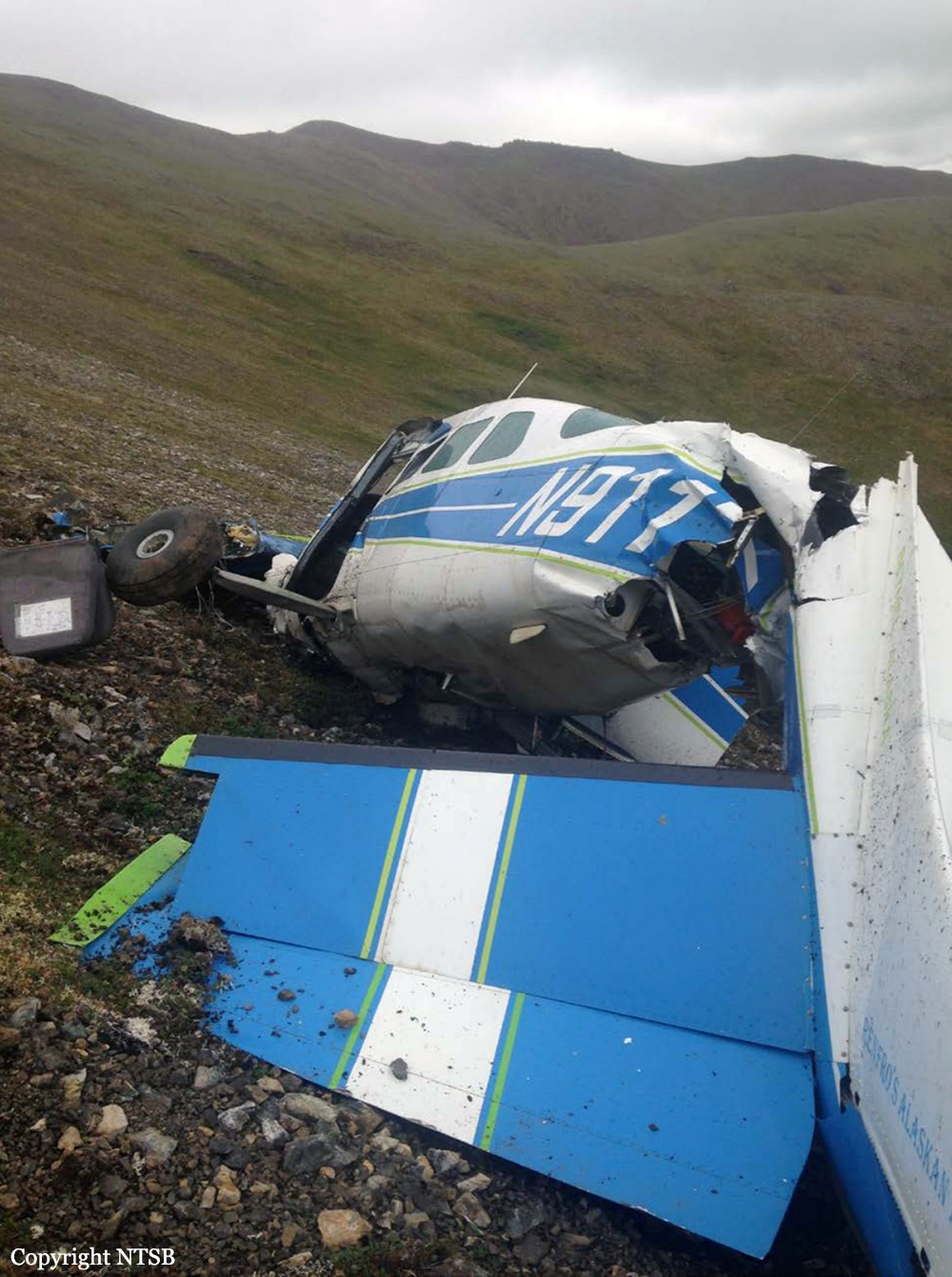
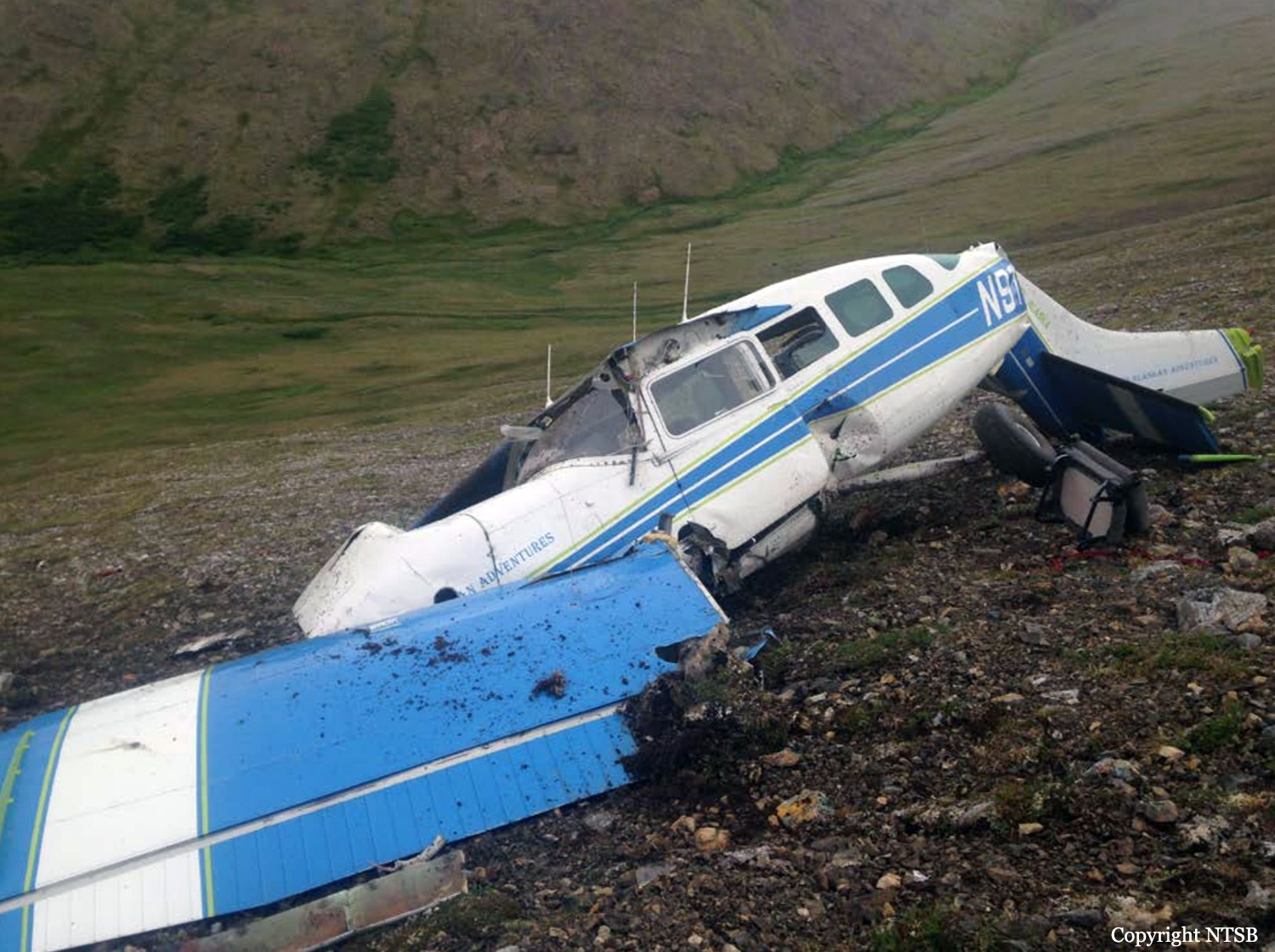
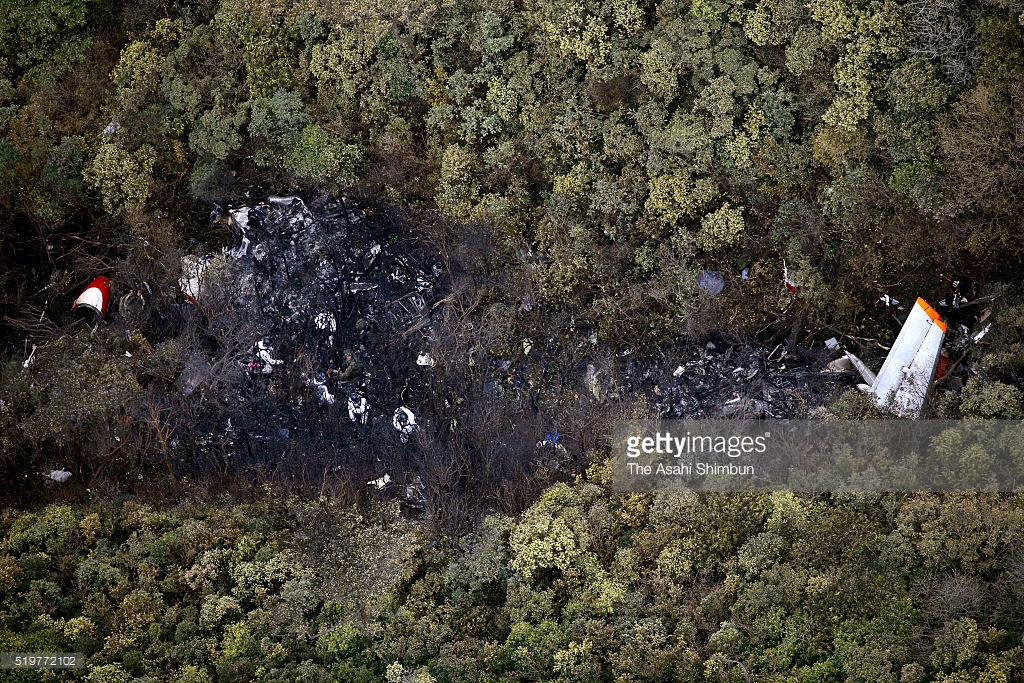
Crash of a Cessna 208B Grand Caravan near Togiak: 3 killed
Date & Time:
Oct 2, 2016 at 1157 LT
Registration:
N208SD
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Quinhagak – Togiak
MSN:
208B-0491
YOM:
1995
Flight number:
HAG3153
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
1
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
3
Captain / Total hours on type:
781.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
84
Aircraft flight hours:
20562
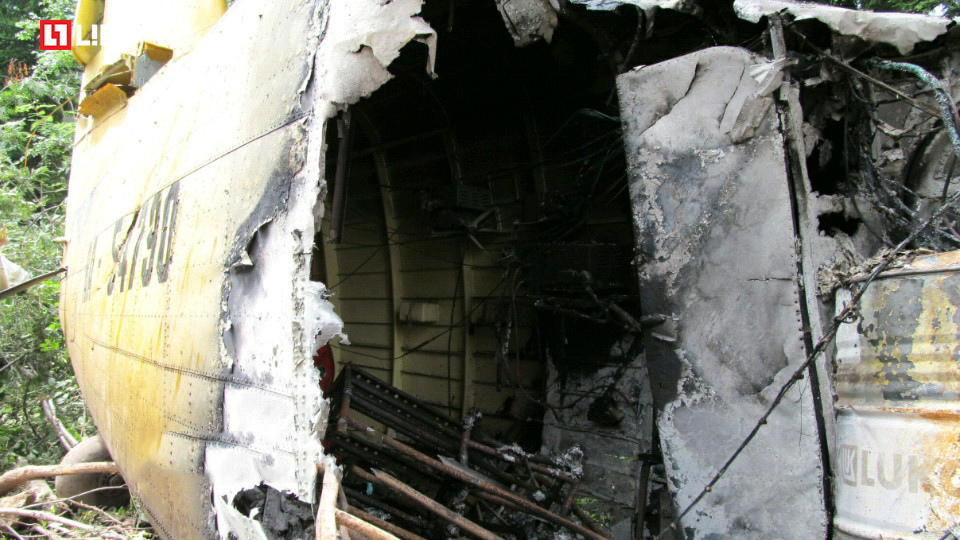
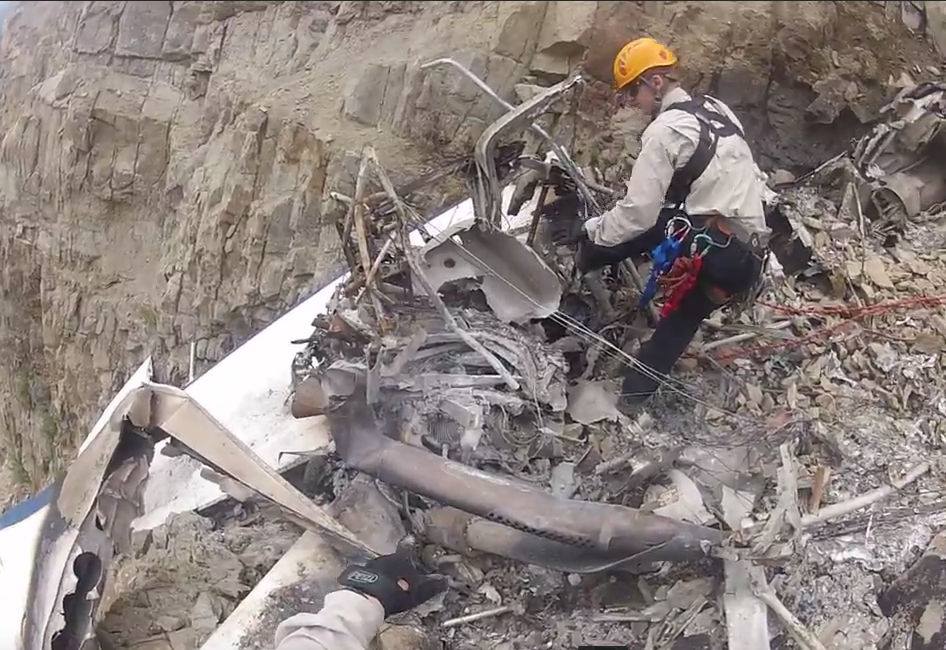
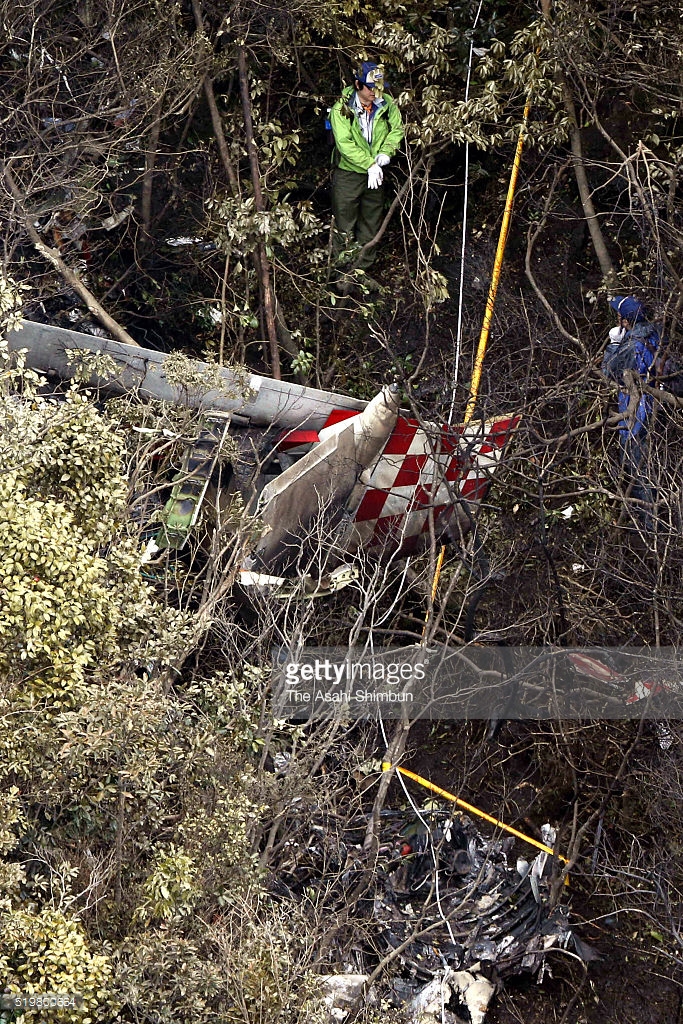
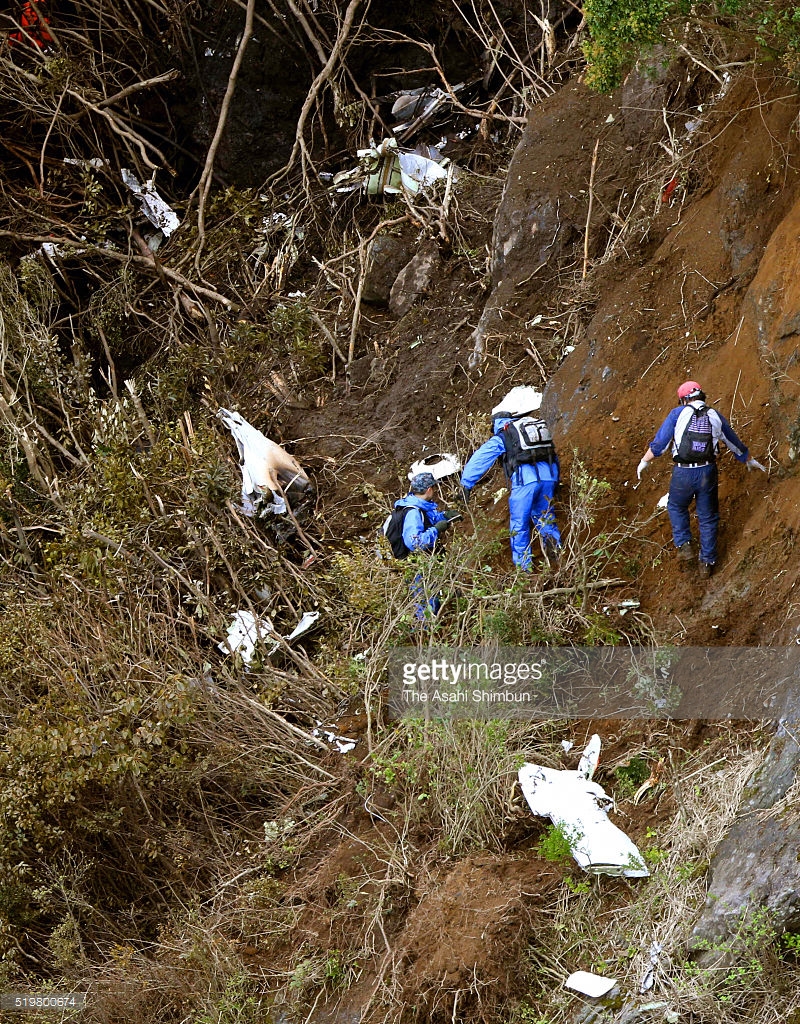
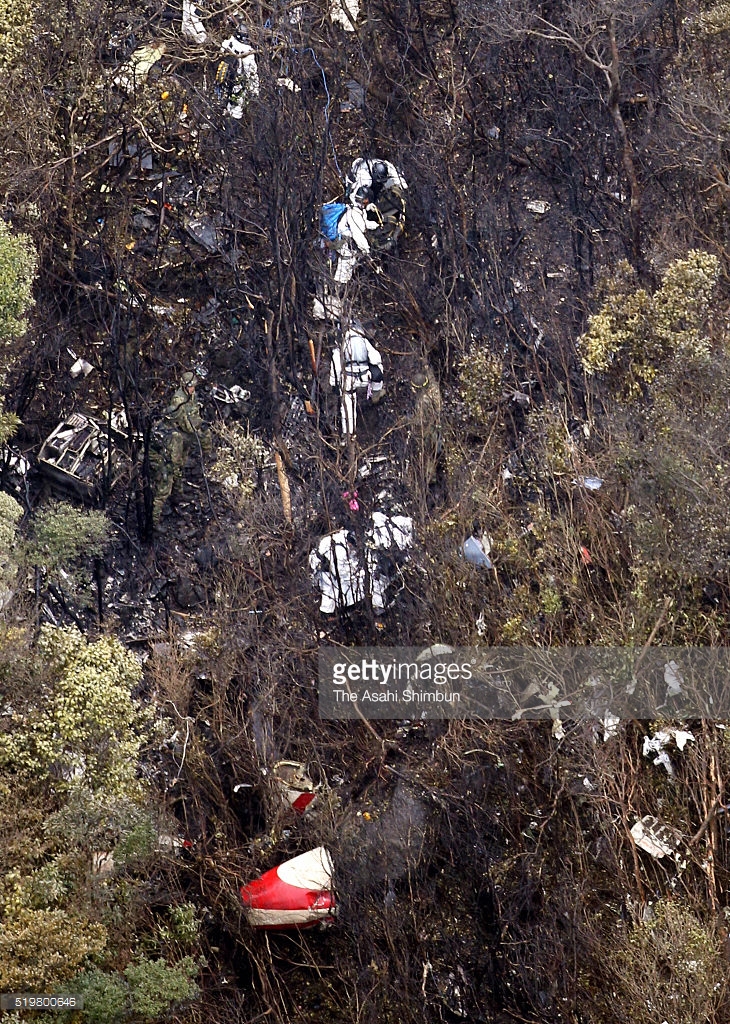
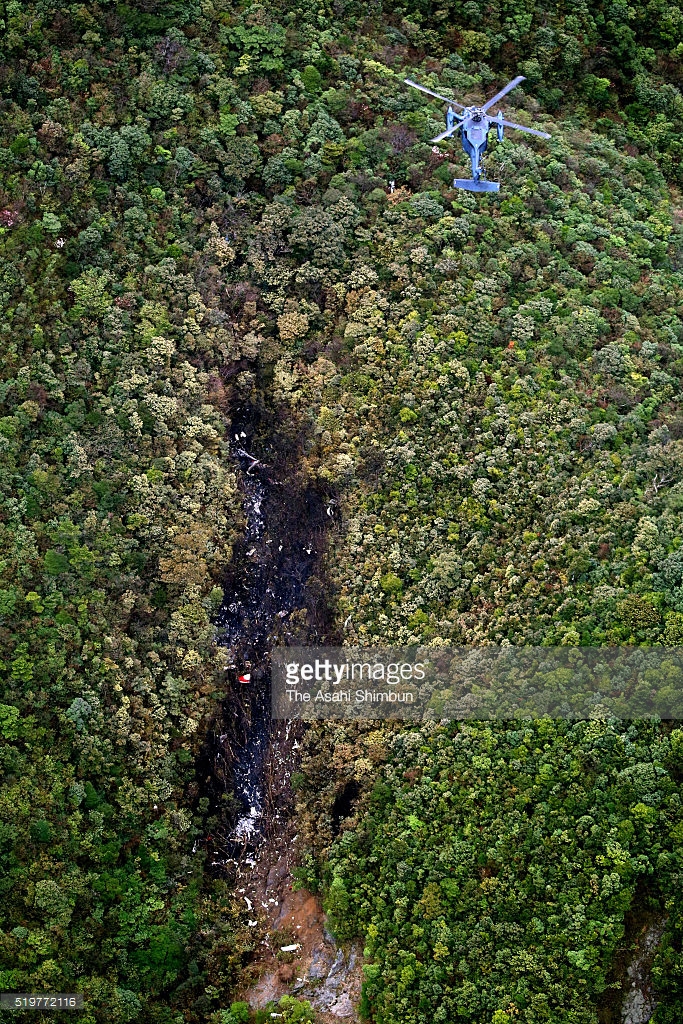
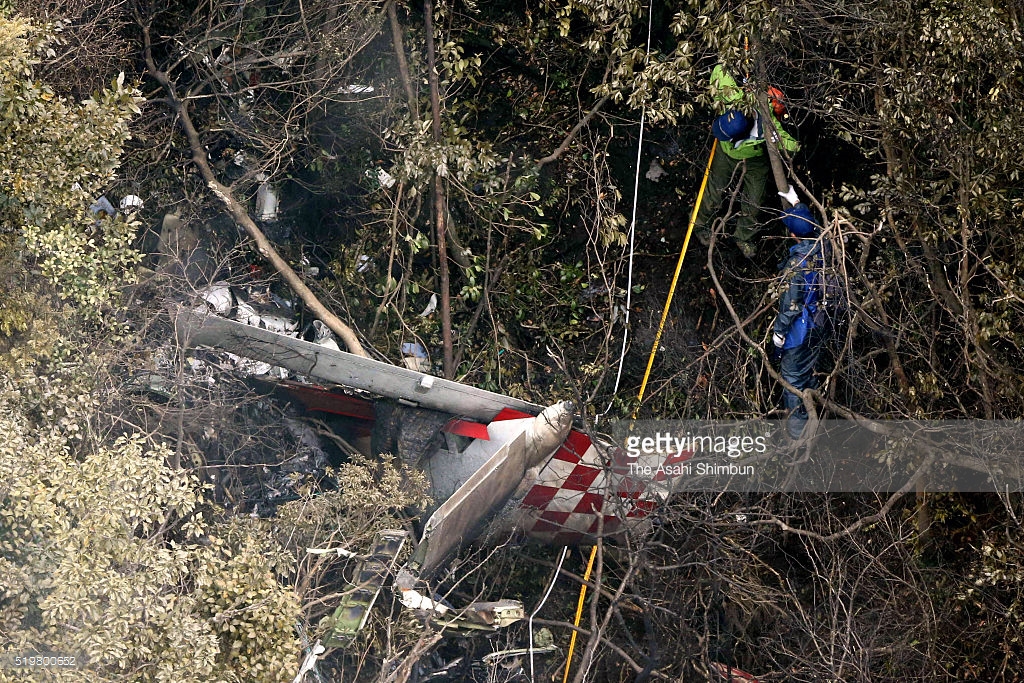
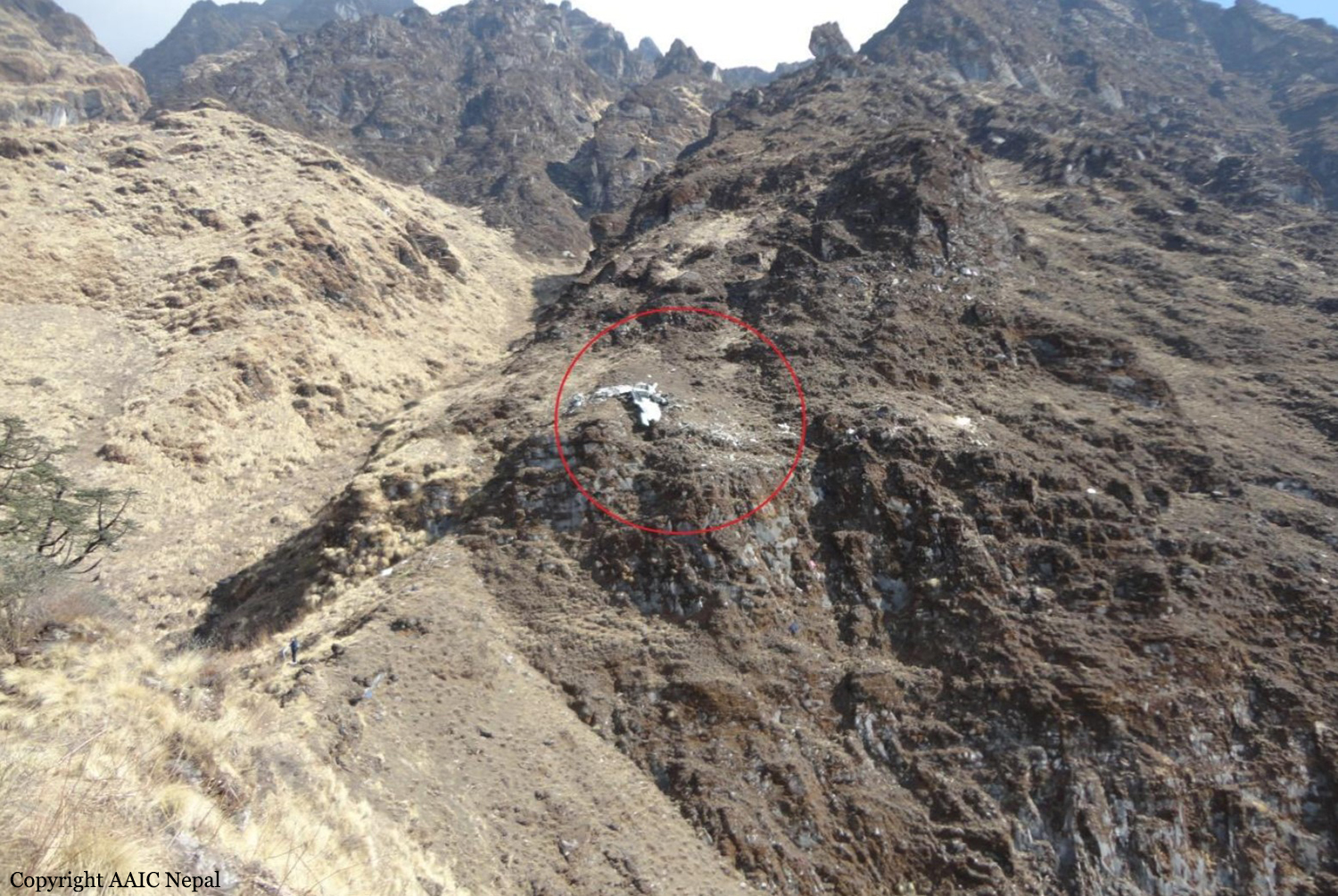
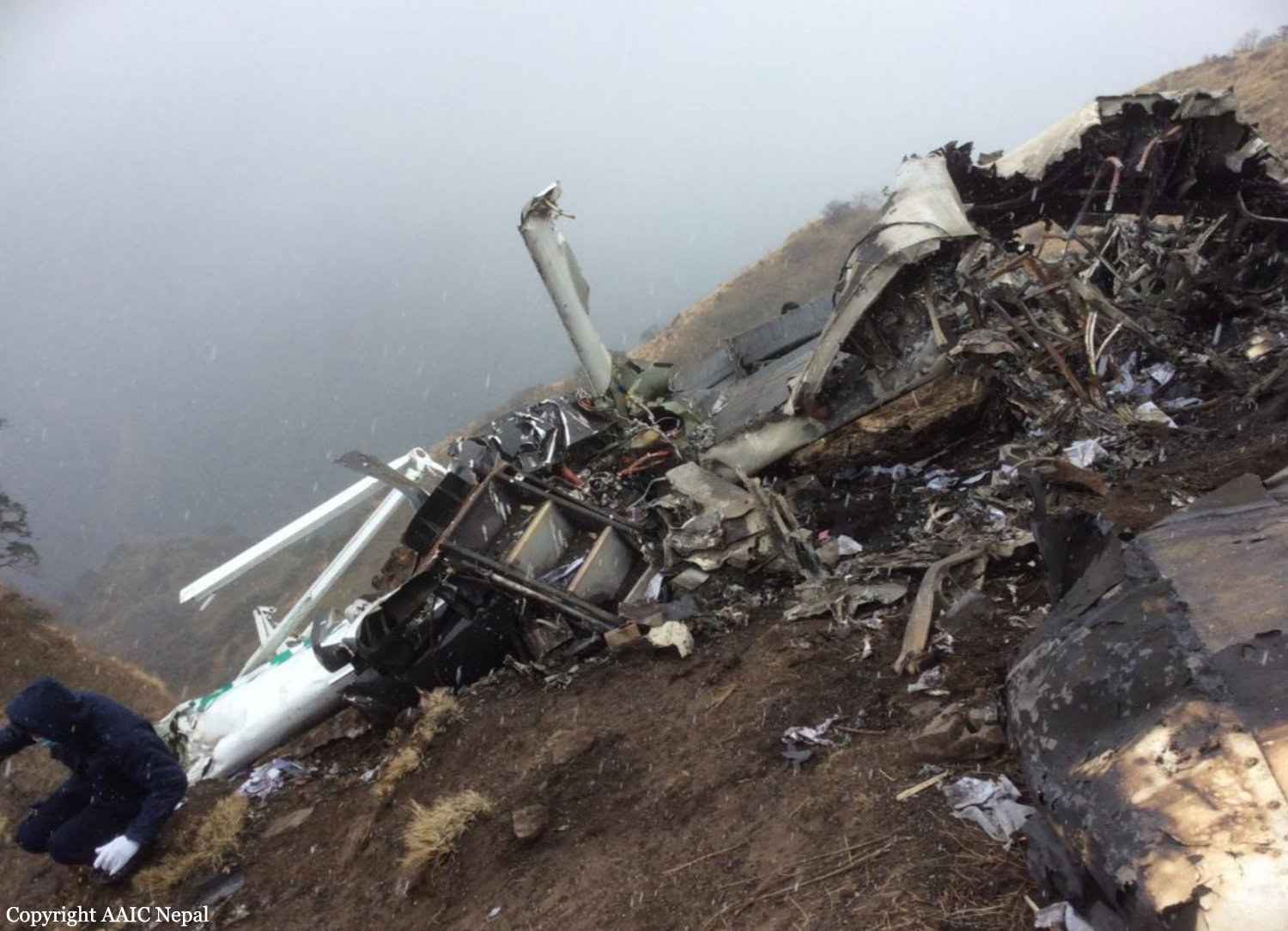
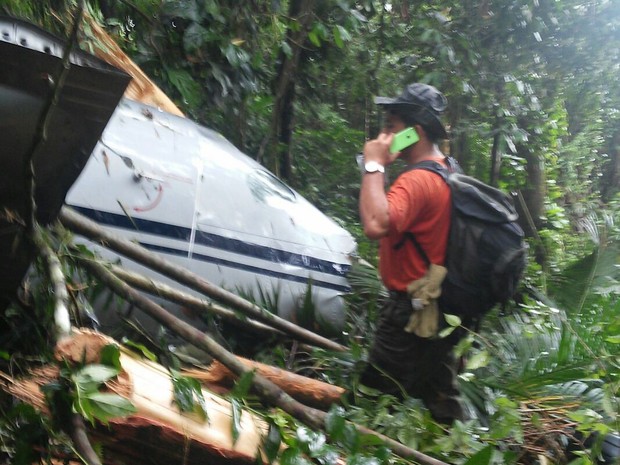
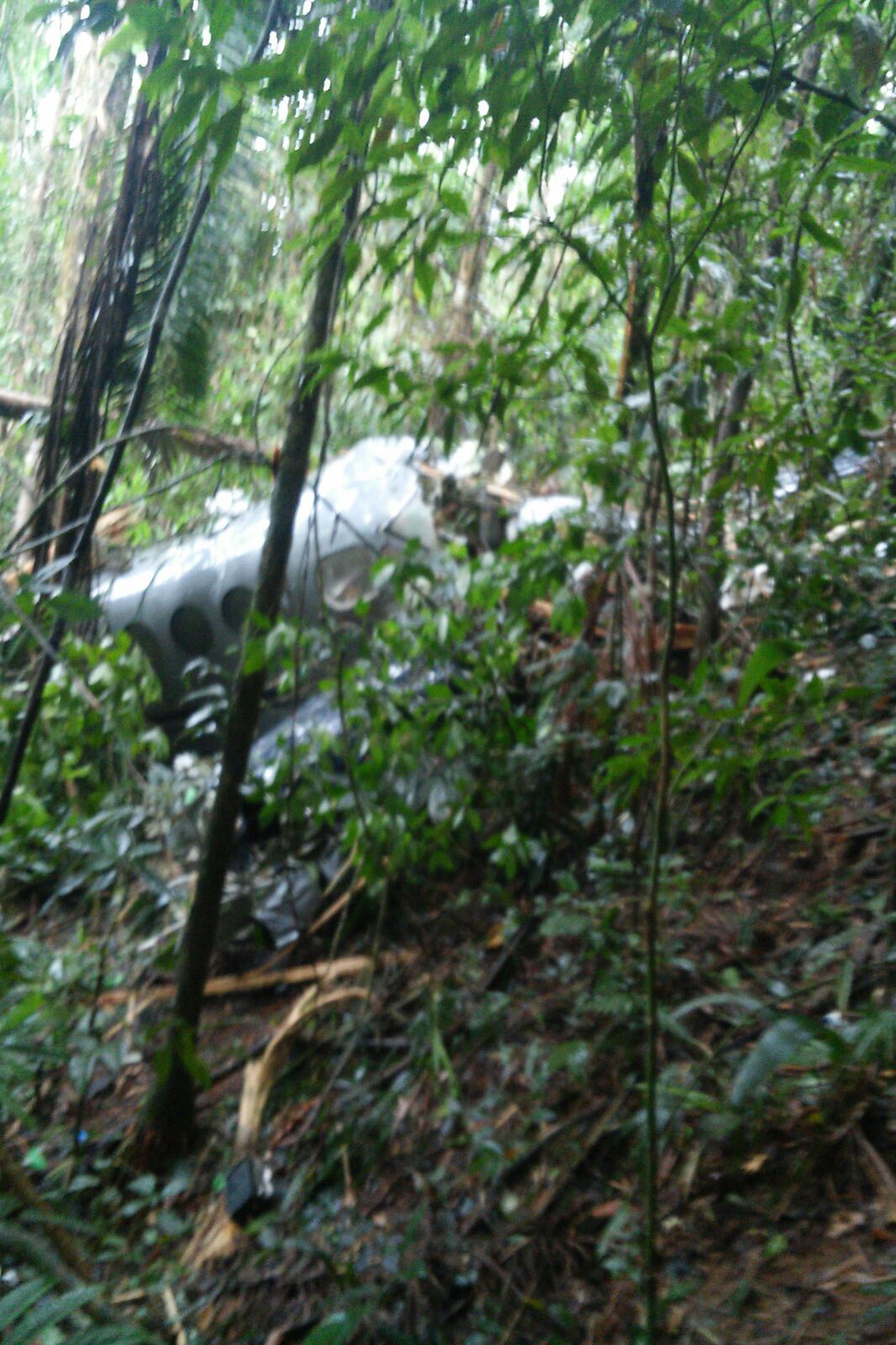
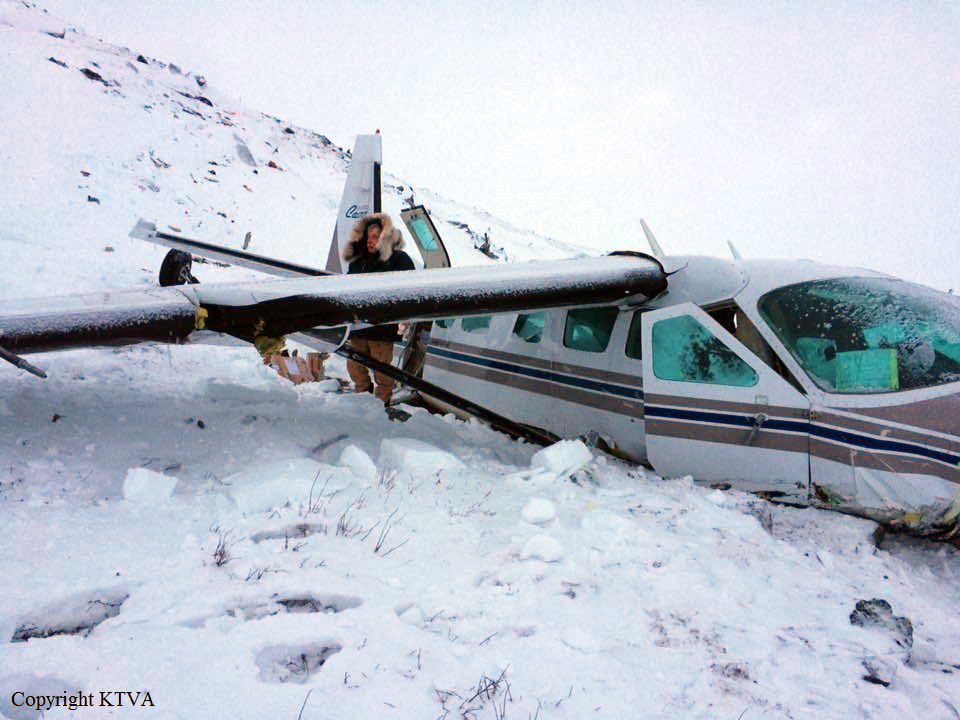
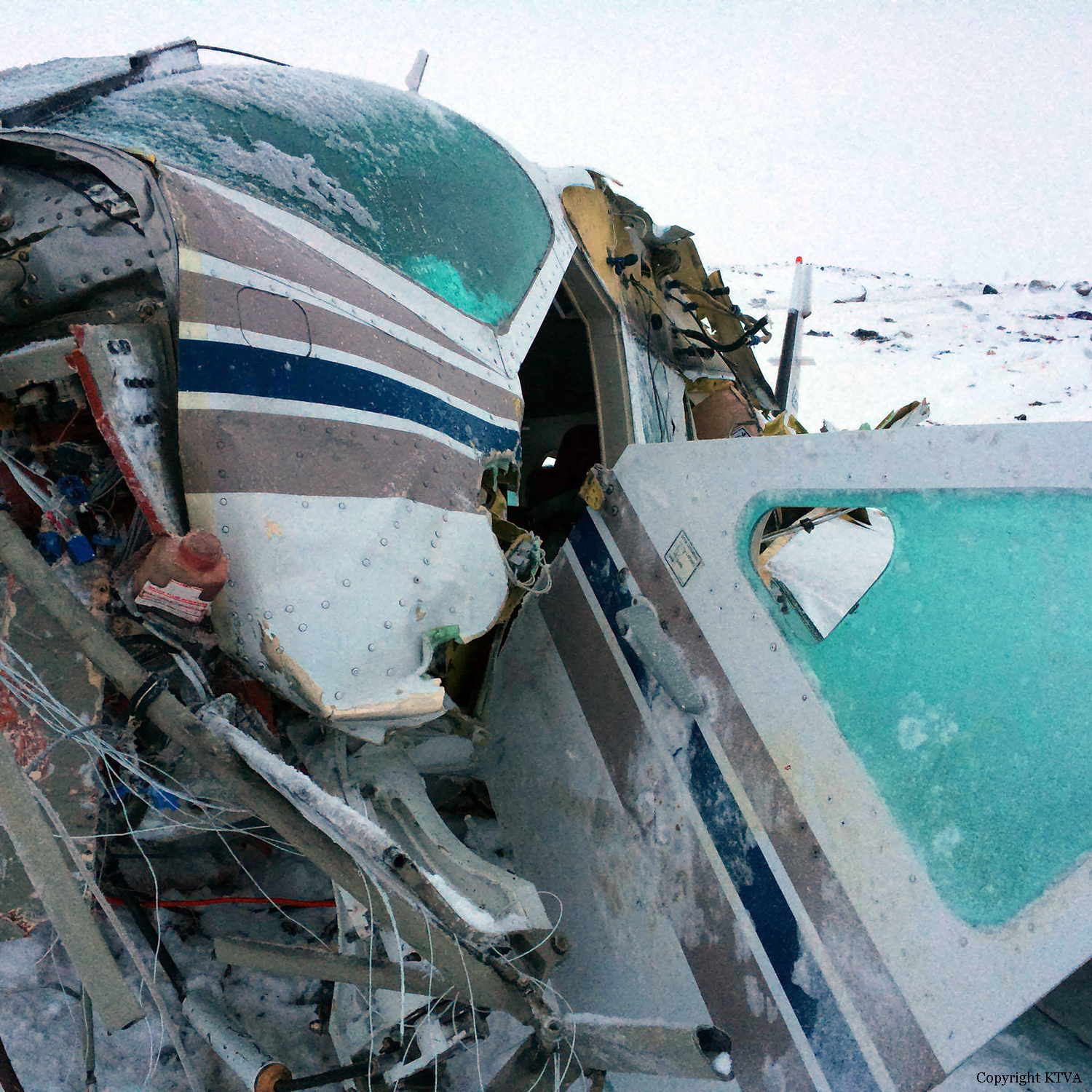
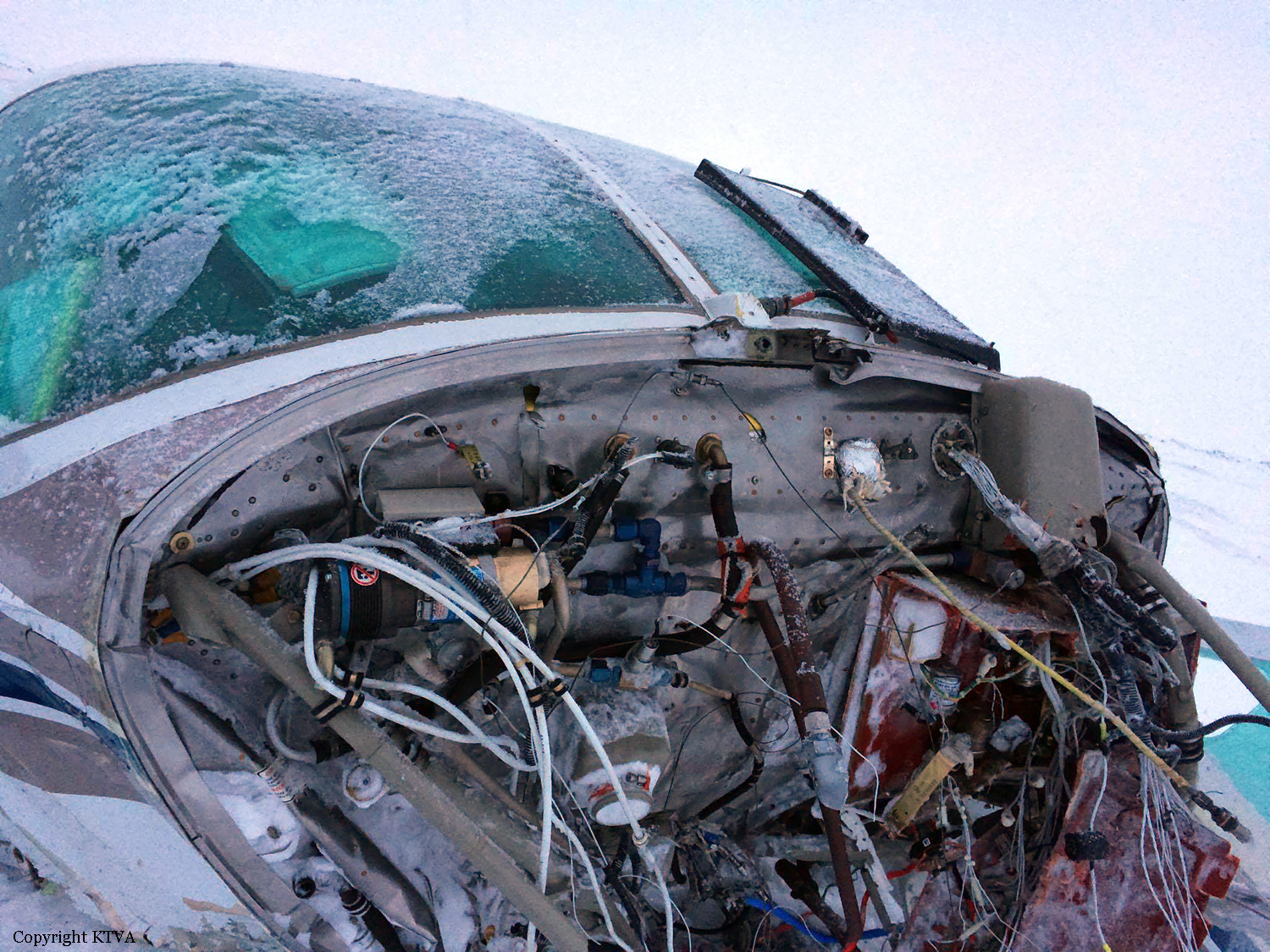
Circumstances:
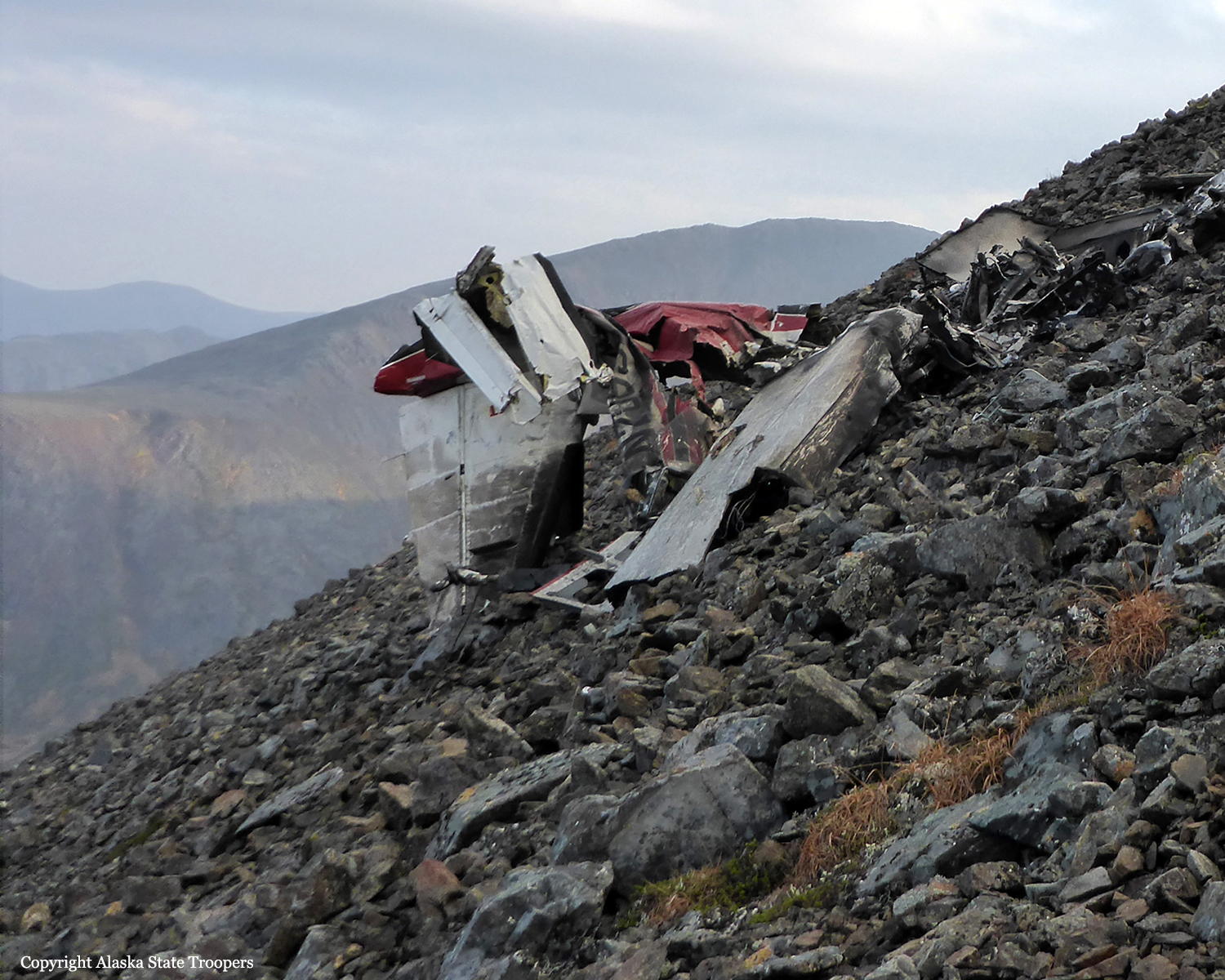
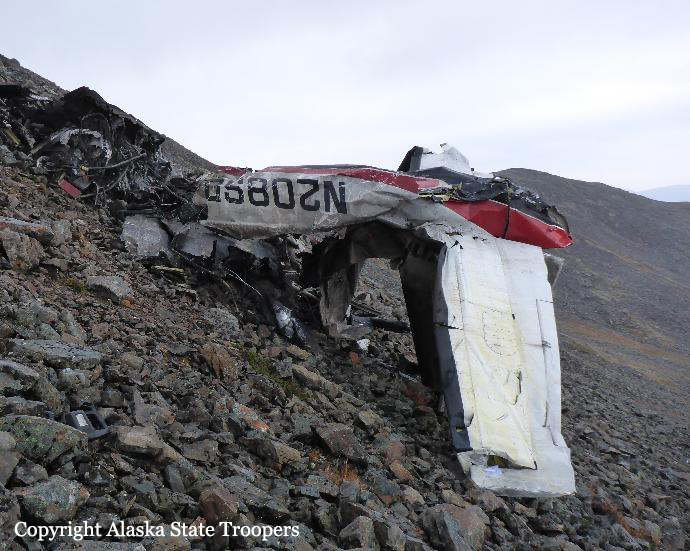
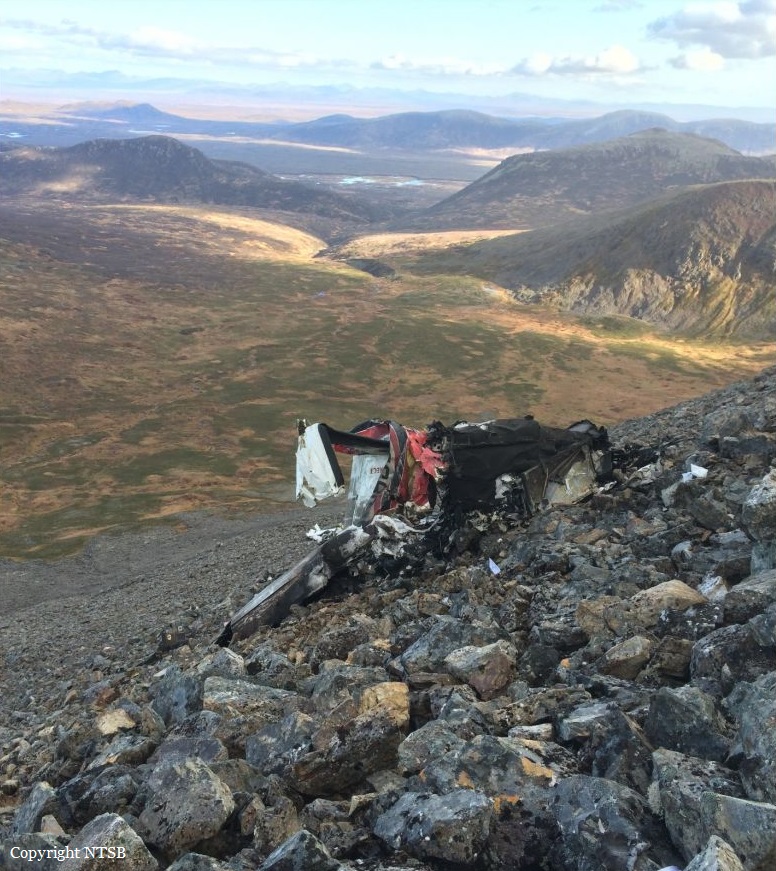
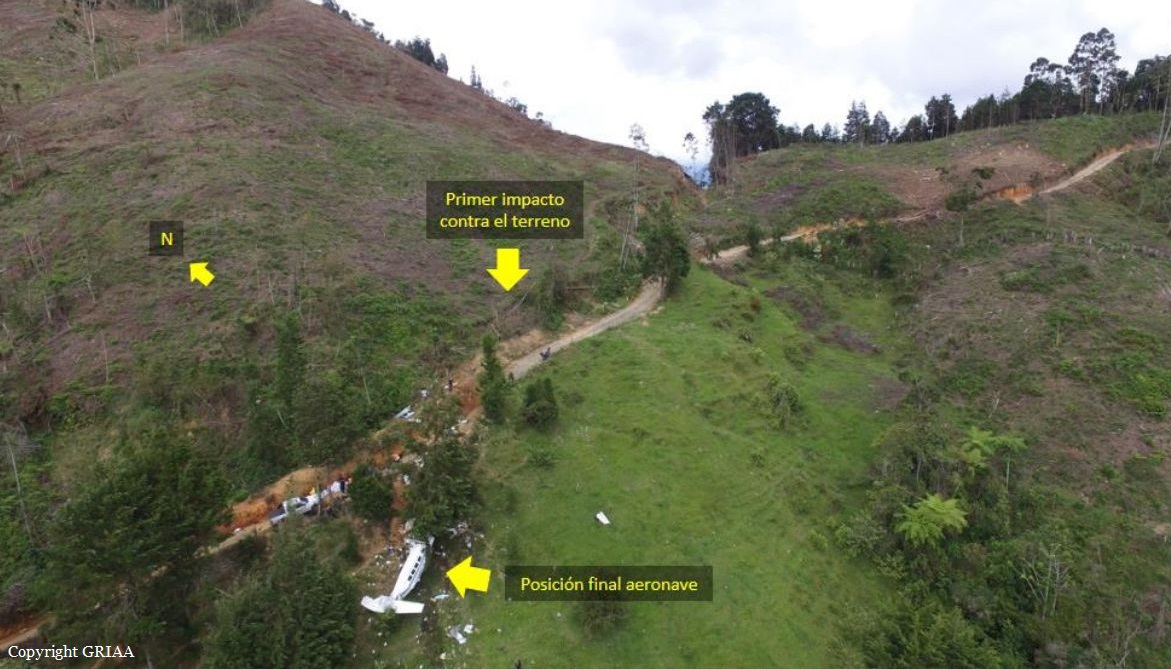
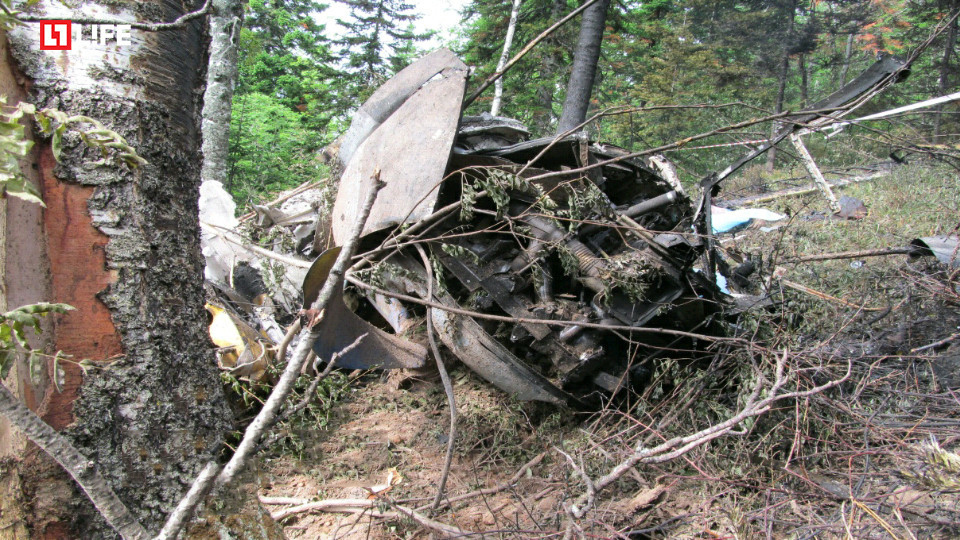
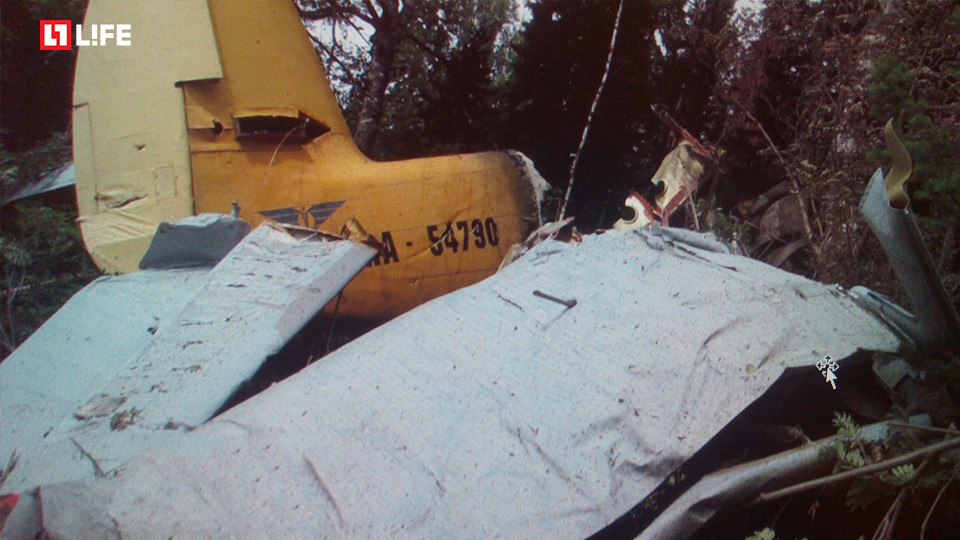
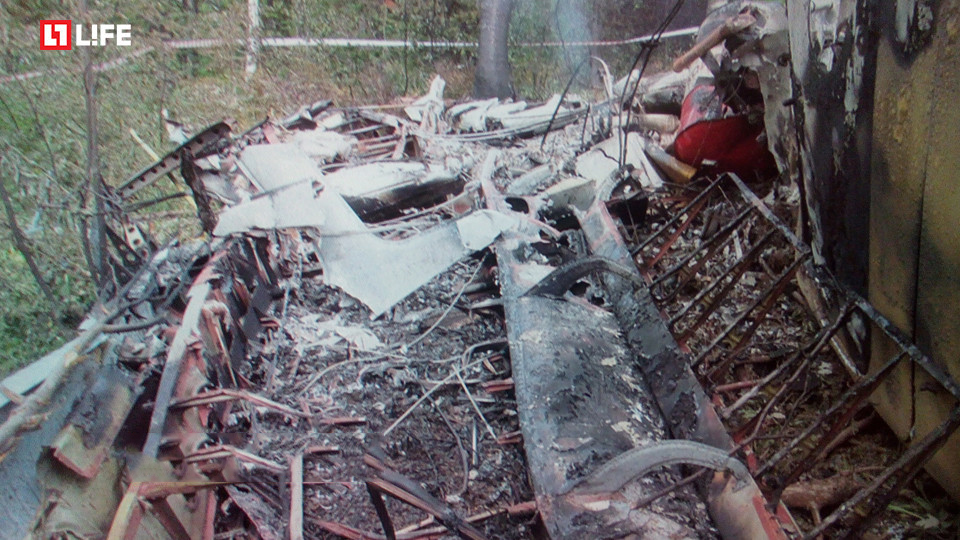
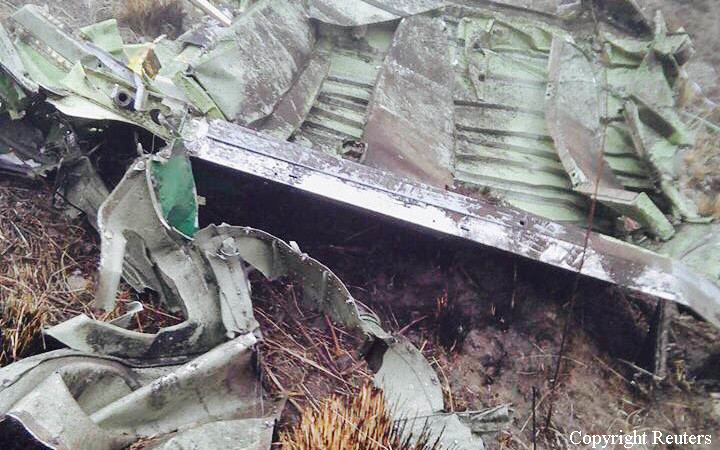
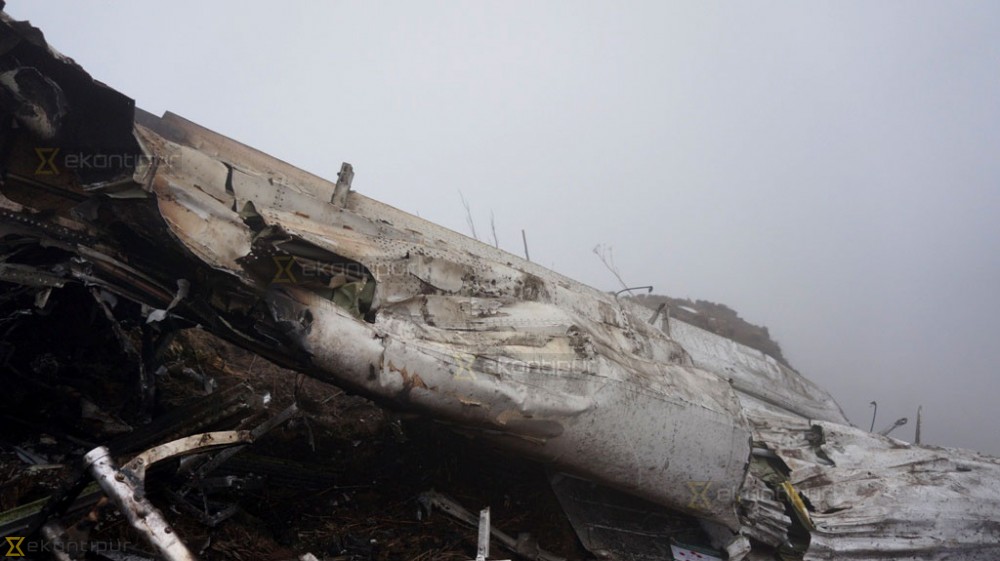
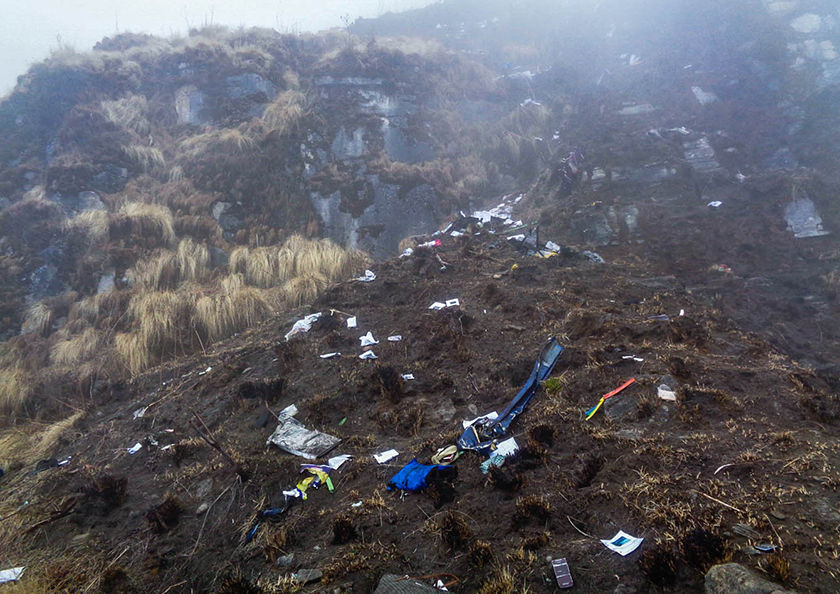
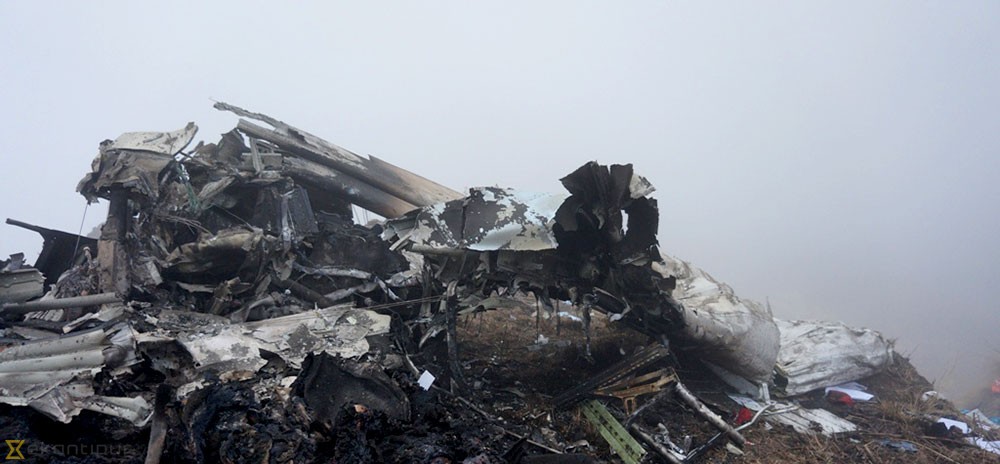
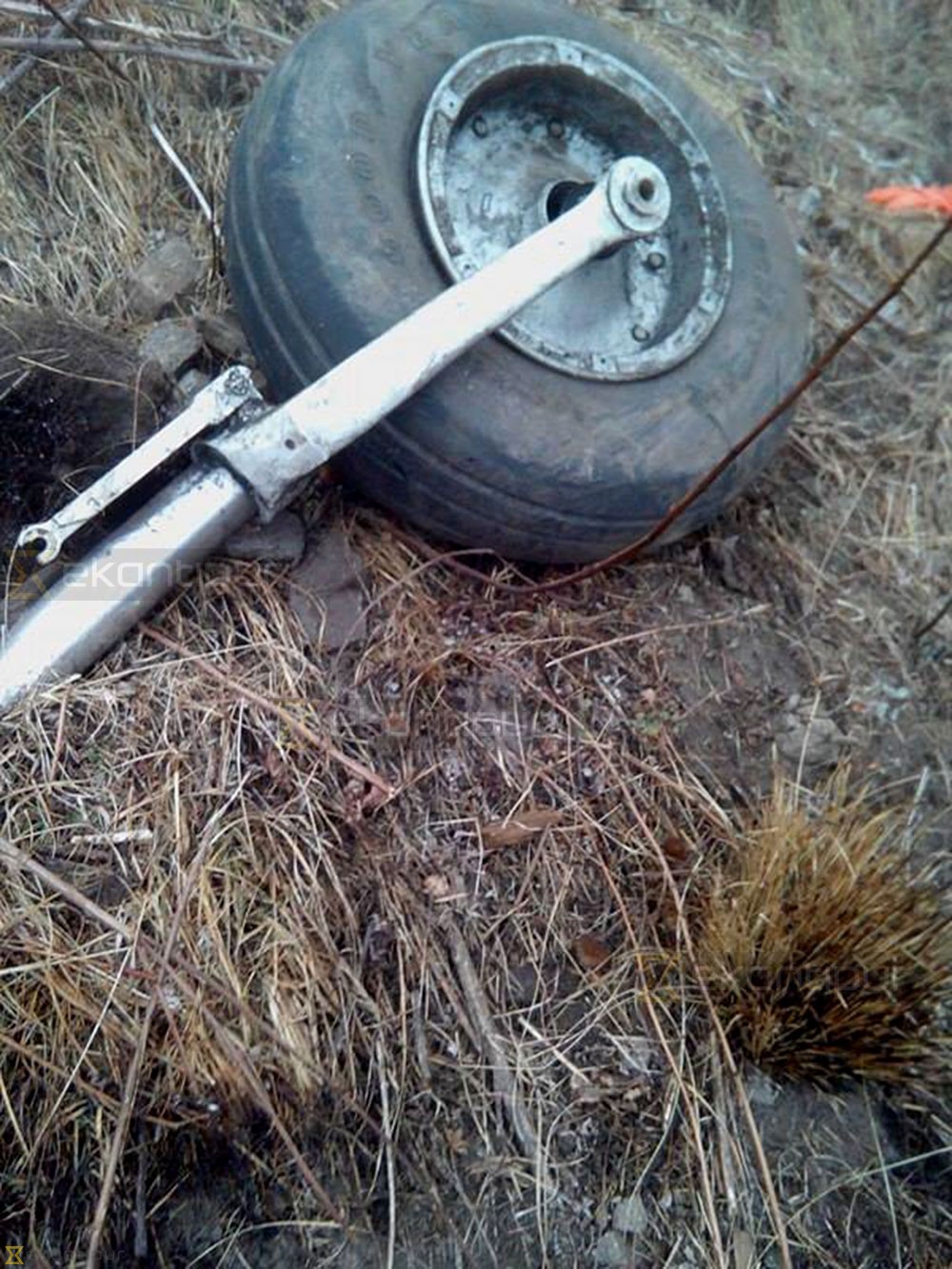
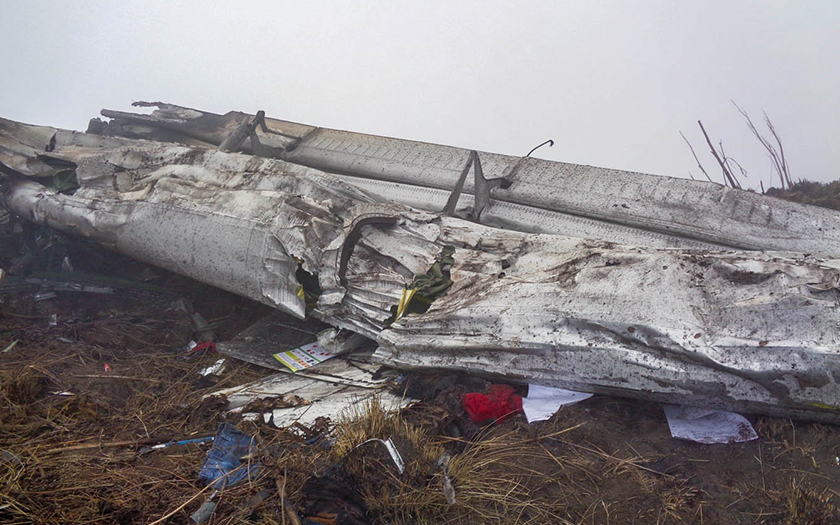
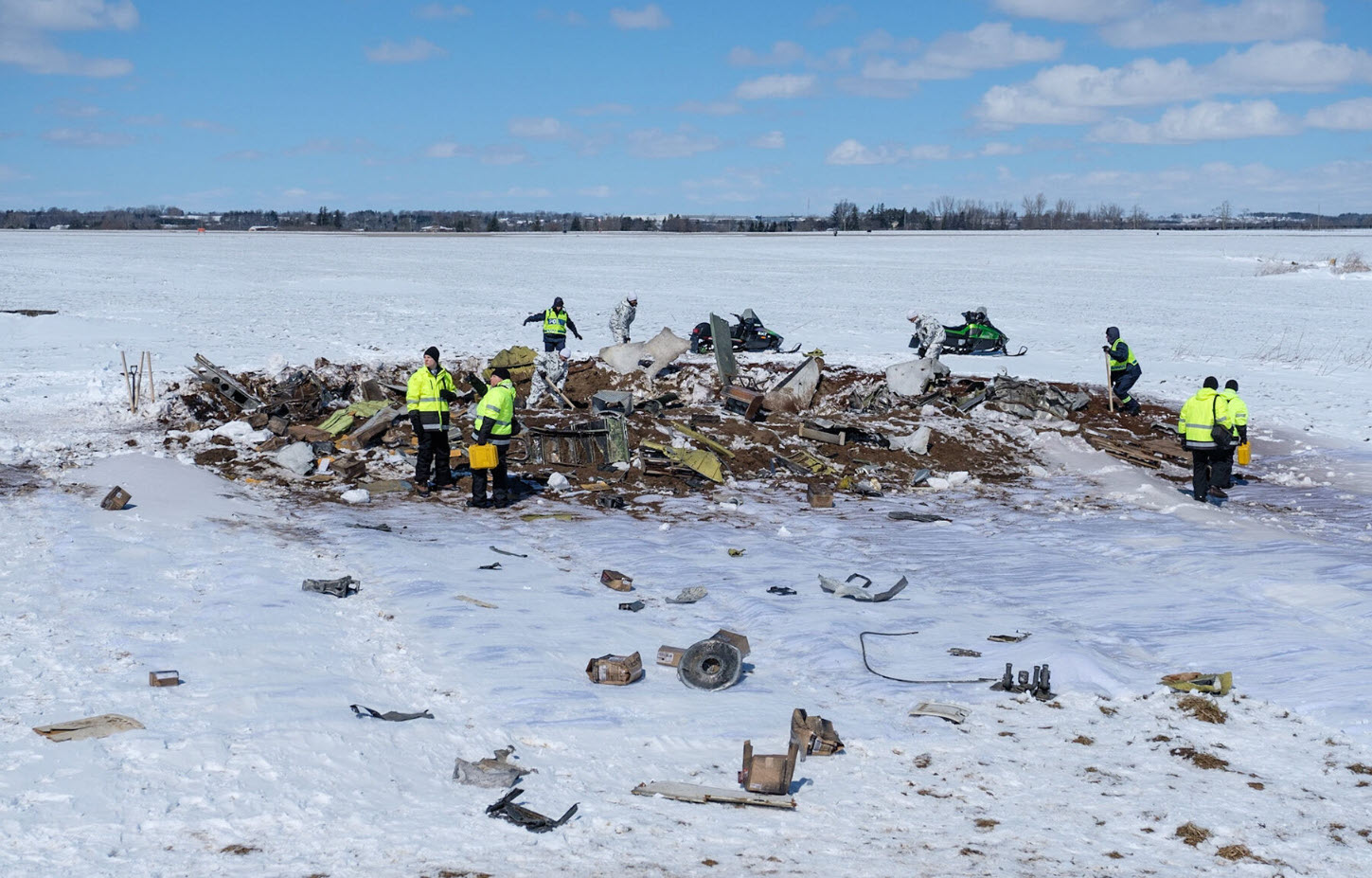
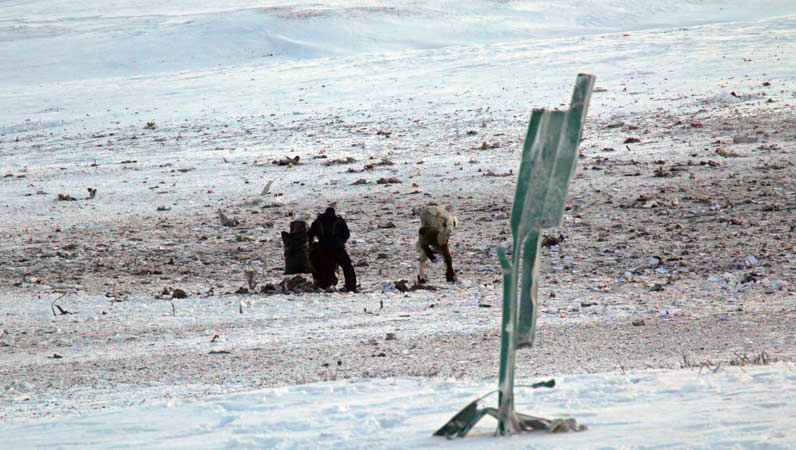
On October 2, 2016, about 1157 Alaska daylight time, Ravn Connect flight 3153, a turbine powered Cessna 208B Grand Caravan airplane, N208SD, collided with steep, mountainous terrain about 10 nautical miles northwest of Togiak Airport (PATG), Togiak, Alaska. The two commercial pilots and the passenger were killed, and the airplane was destroyed. The scheduled commuter flight was operated under visual flight rules by Hageland Aviation Services, Inc., Anchorage, Alaska, under the provisions of Title 14 Code of Federal Regulations Part 135. Visual meteorological conditions prevailed at PATG (which had the closest weather observing station to the accident site), but a second company flight crew (whose flight departed about 2 minutes after the accident airplane and initially followed a similar route) reported that they observed unexpected fog, changing clouds, and the potential for rain along the accident route. Company flight-following procedures were in effect. The flight departed Quinhagak Airport, Quinhagak, Alaska, about 1133 and was en route to PATG.
Probable cause:
The flight crew's decision to continue the visual flight rules flight into deteriorating visibility and their failure to perform an immediate escape maneuver after entry into instrument meteorological conditions, which resulted in controlled flight into terrain (CFIT). Contributing to the accident were:
- Hageland's allowance of routine use of the terrain inhibit switch for inhibiting the terrain awareness and warning system alerts and inadequate guidance for uninhibiting the alerts, which reduced the margin of safety, particularly in deteriorating visibility;
- Hageland's inadequate crew resource management (CRM) training;
- The Federal Aviation Administration's failure to ensure that Hageland's approved CRM training contained all the required elements of Title 14 Code of Federal Regulations 135.330;
- Hageland's CFIT avoidance ground training, which was not tailored to the company's operations and did not address current CFIT-avoidance technologies.
- Hageland's allowance of routine use of the terrain inhibit switch for inhibiting the terrain awareness and warning system alerts and inadequate guidance for uninhibiting the alerts, which reduced the margin of safety, particularly in deteriorating visibility;
- Hageland's inadequate crew resource management (CRM) training;
- The Federal Aviation Administration's failure to ensure that Hageland's approved CRM training contained all the required elements of Title 14 Code of Federal Regulations 135.330;
- Hageland's CFIT avoidance ground training, which was not tailored to the company's operations and did not address current CFIT-avoidance technologies.
Final Report: