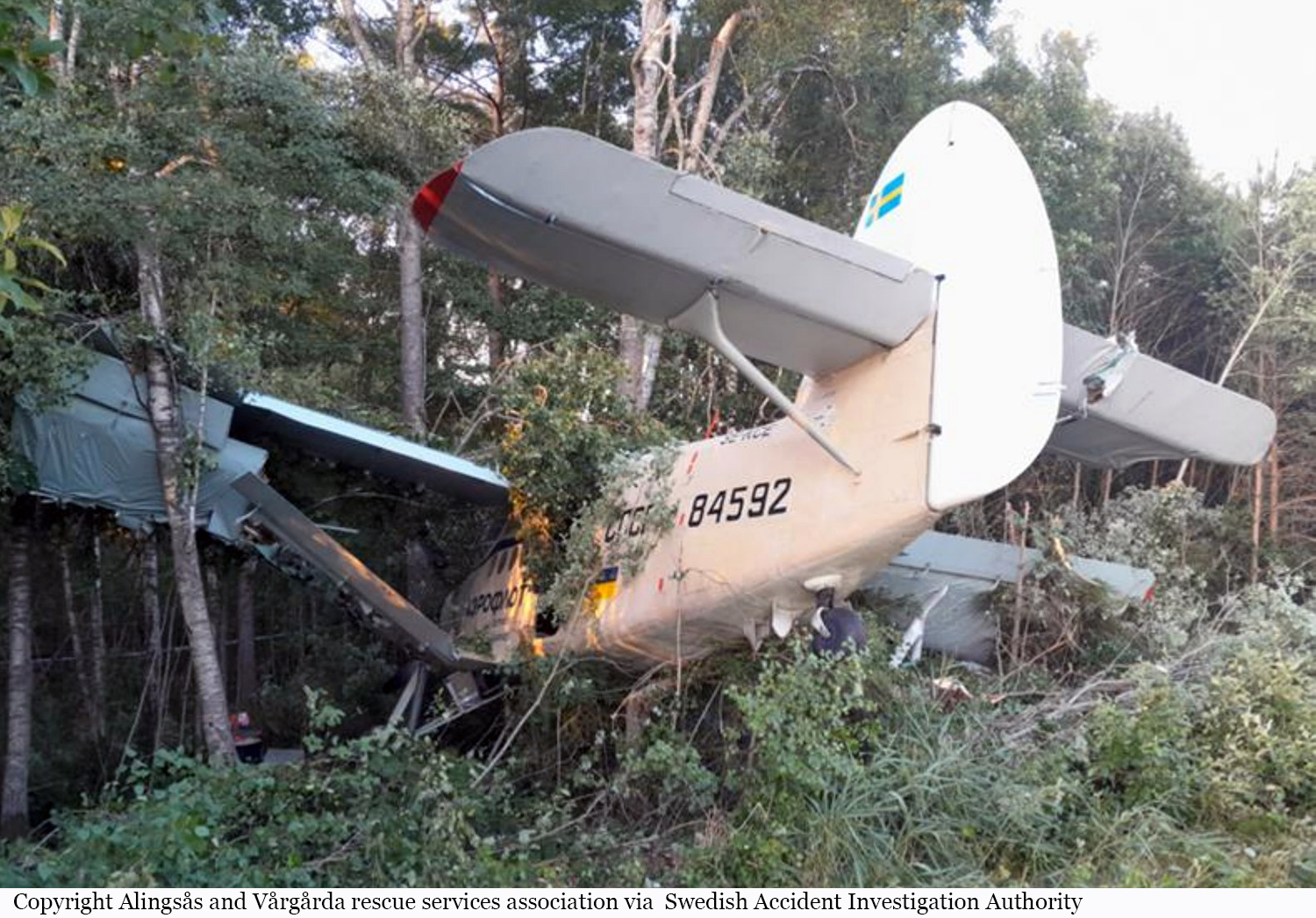
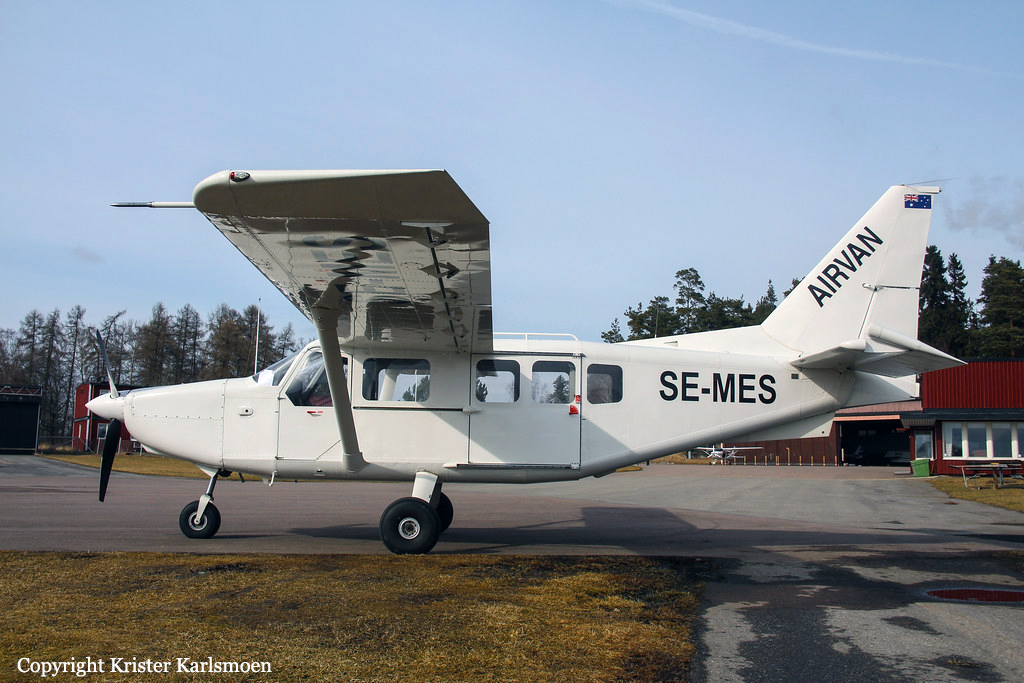
Crash of a PZL-Mielec AN-2R in Vårgårda
Date & Time:
Jul 8, 2023 at 1533 LT
Registration:
SE-KCE
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Kattleberg - Vårgårda - Tumberg
MSN:
1G189-59
YOM:
1981
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
4
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
1600.00
Aircraft flight hours:
5150
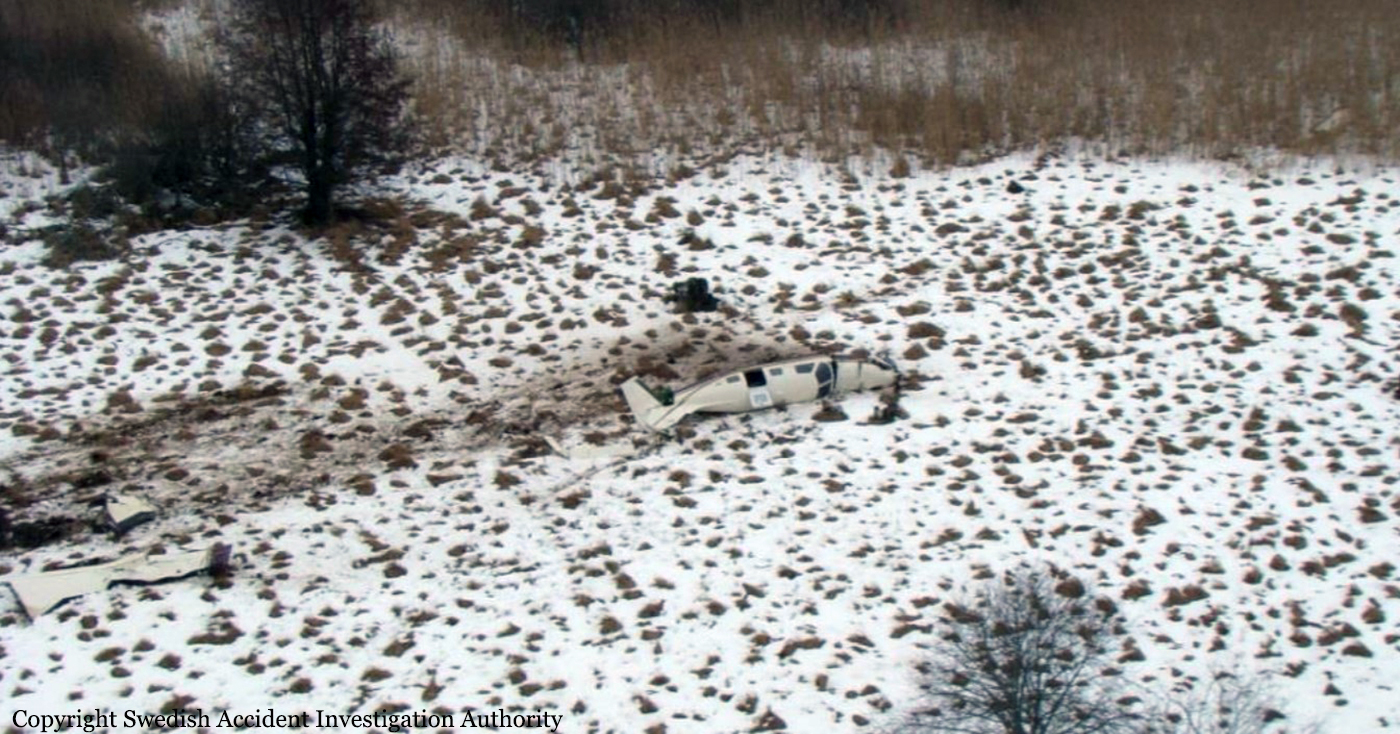
Circumstances:
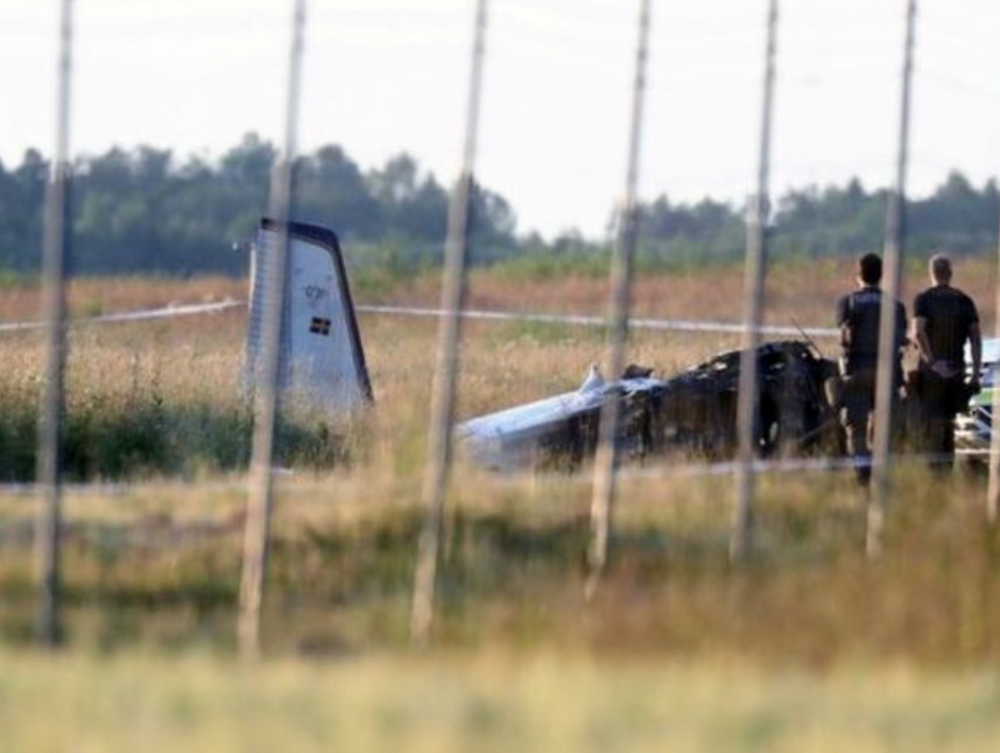
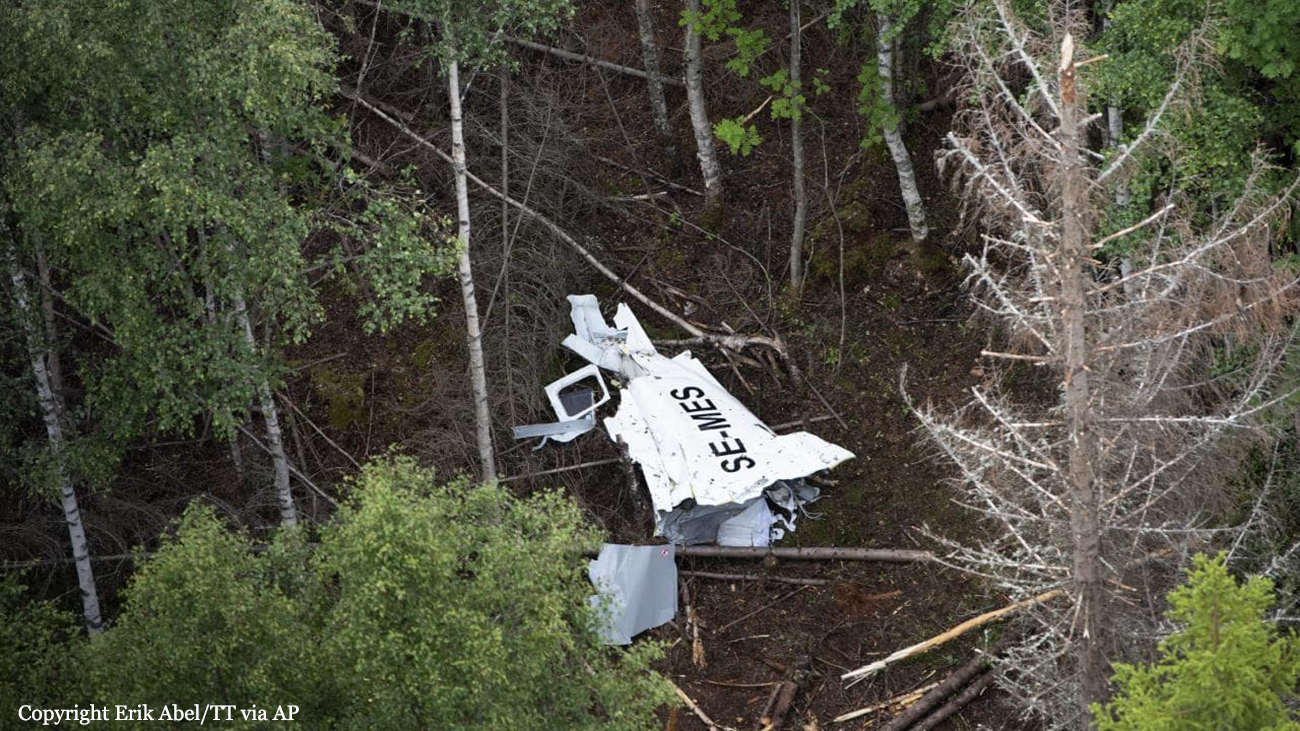
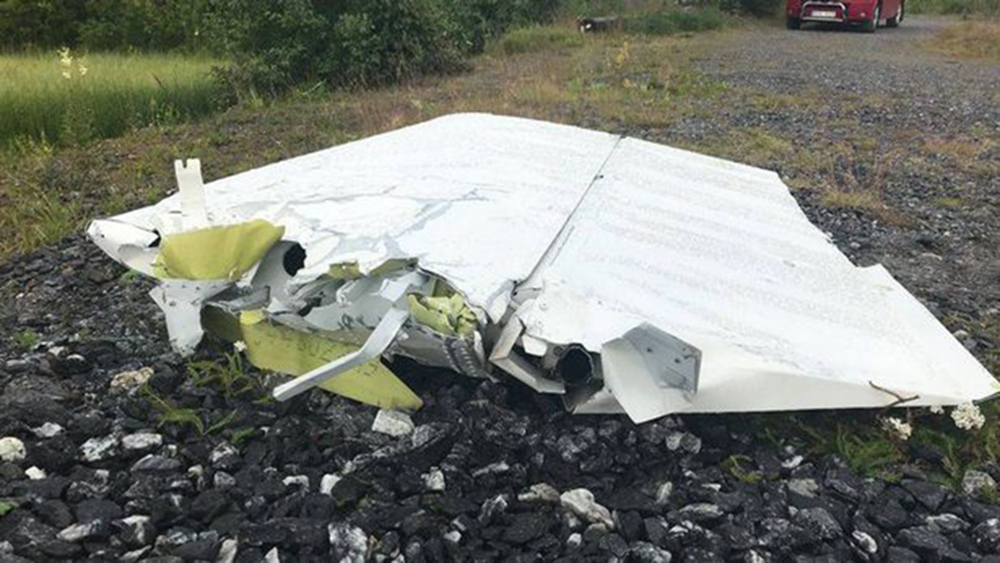
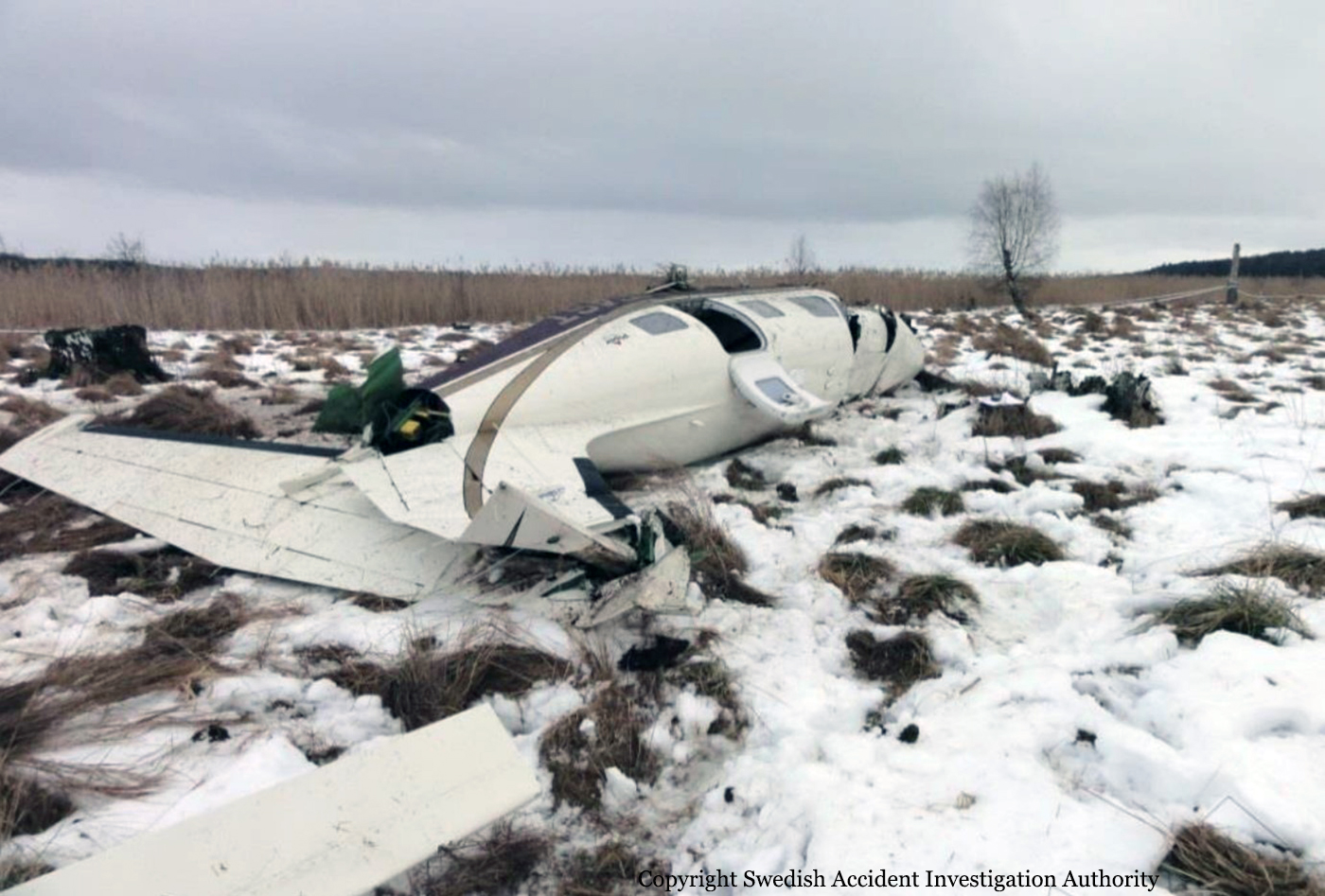
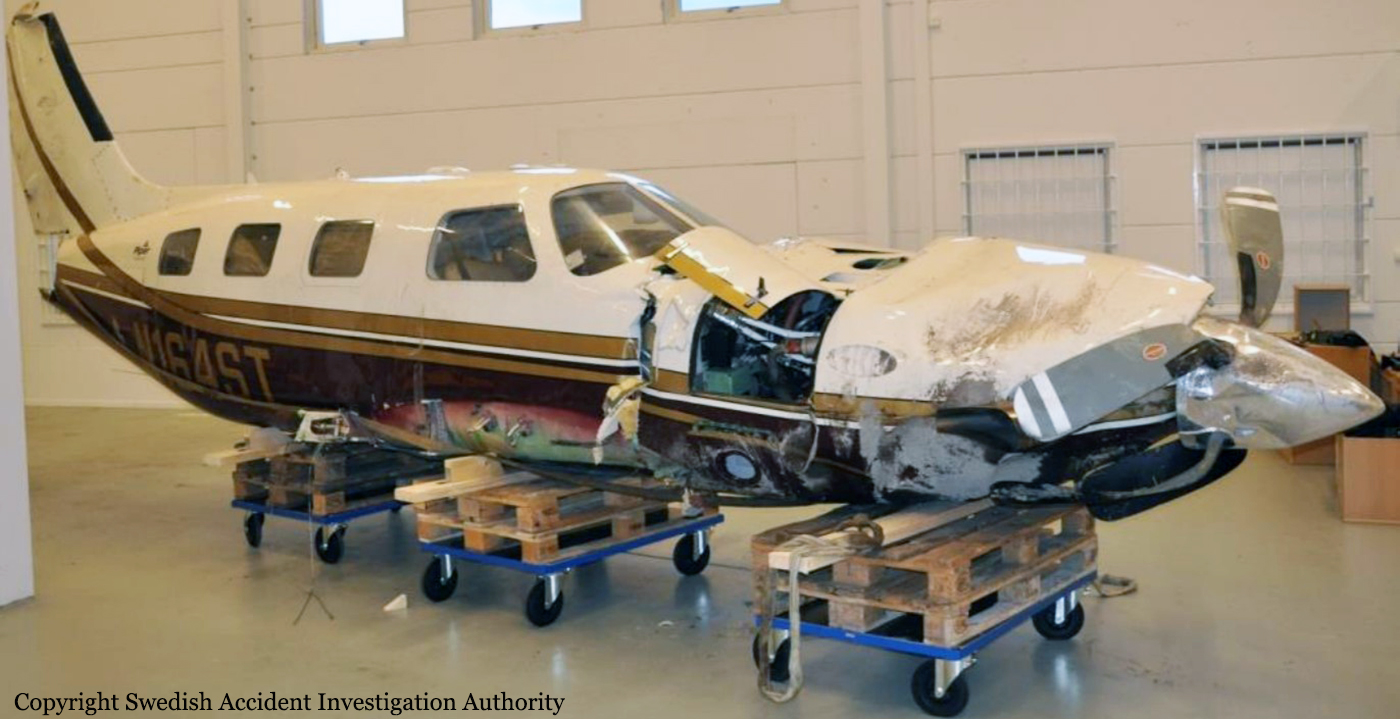
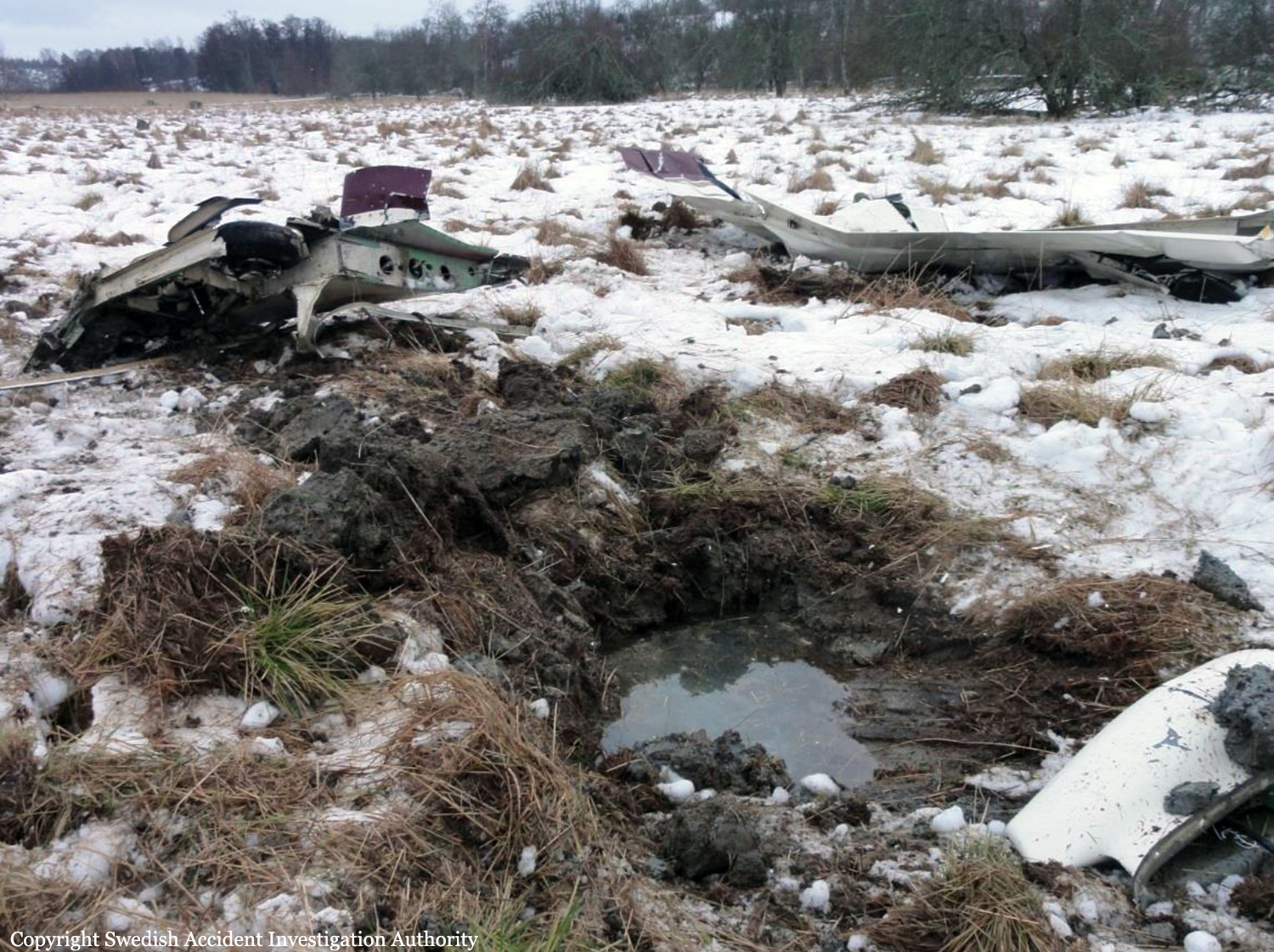
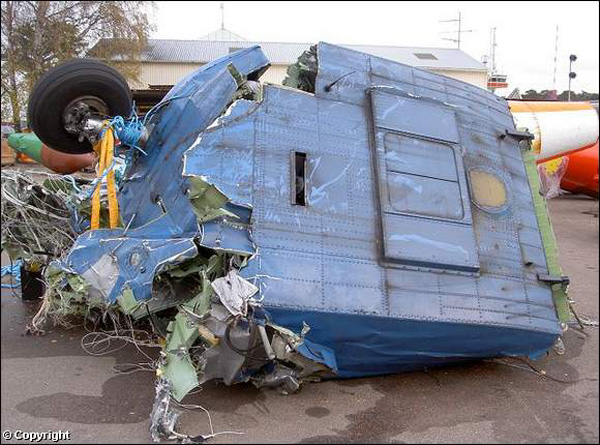
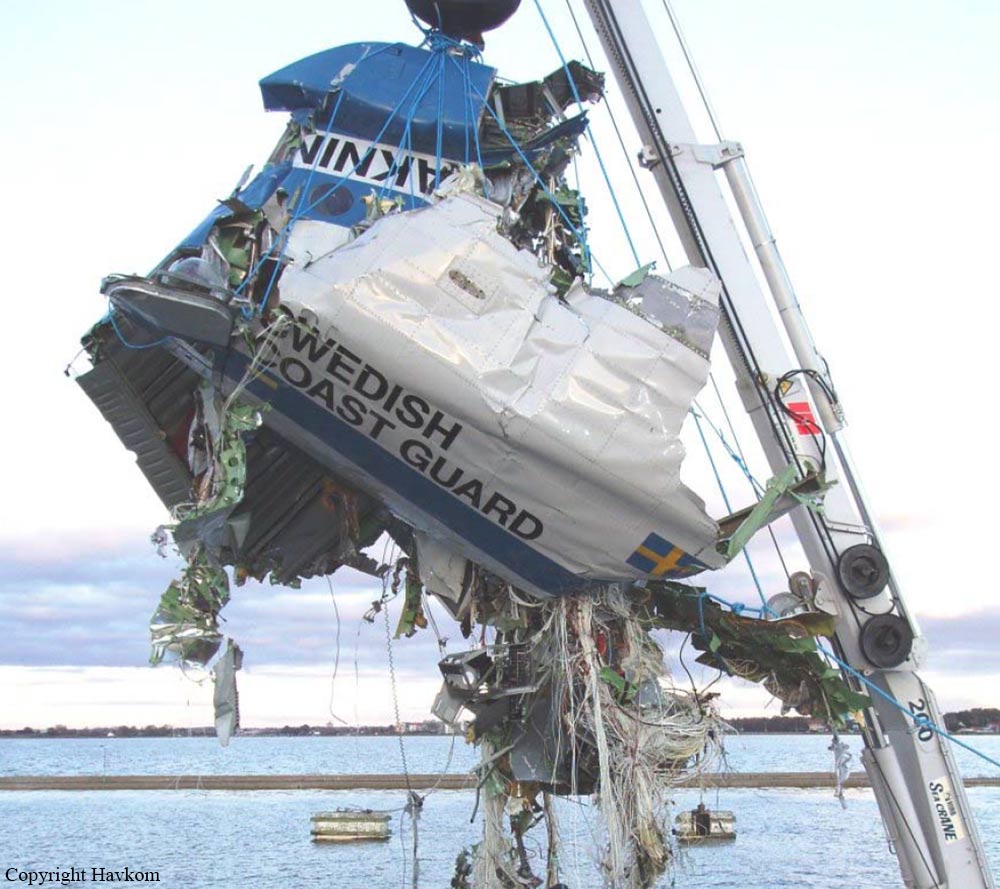
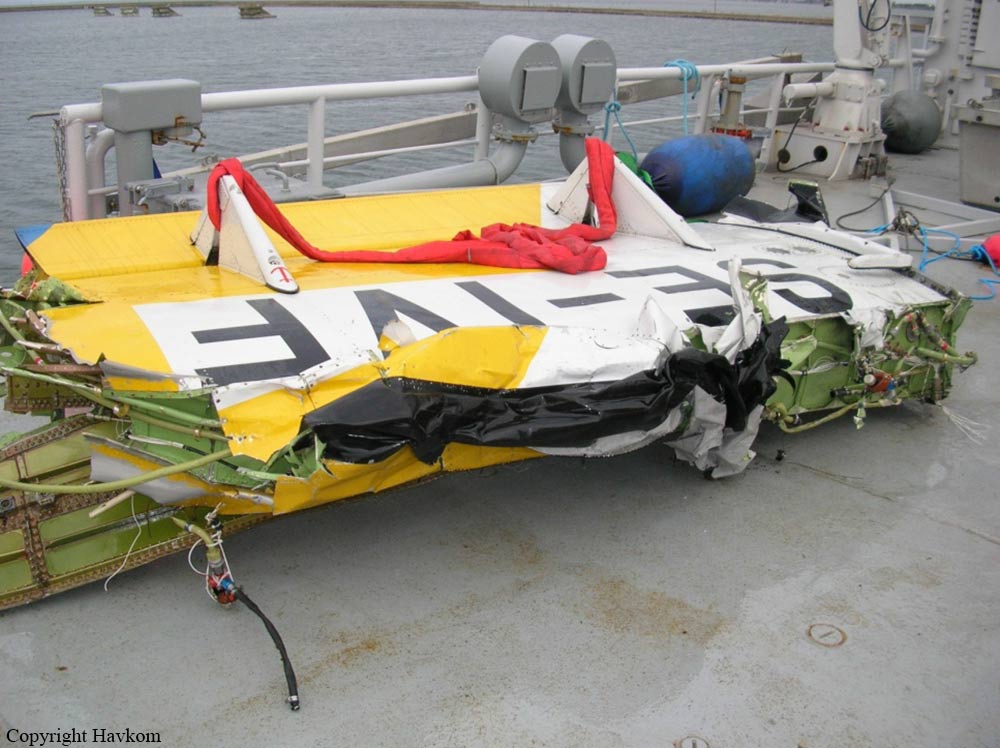
The flight, which was a private flight, was the third of the day. The pilot had landed on a field at Tumberg just north of Vårgårda and after a ground stop they planned to take off from the field. On board were one pilot and four passengers. The pilot decided to take off from the field in an easterly direction because there were obstacles in the form of buildings and lamp posts in the westerly direction. There were trees at the end of the field to the east, but the pilot assessed that these did not pose a problem and that the field was long enough for a take-off in an easterly direction. No precise calculations were made to determine the required take-off distance. The pilot initiated the take-off and set the engine controls to full take-off power. According to the pilot and the passenger in the right front seat, the indicated values for engine rpm and manifold pressure were normal. The acceleration of the aircraft was also perceived as normal. At lift-off, the aircraft rolled to the right and the pilot felt that the aircraft did not climb as expected. The pilot pulled hard on the control yoke and tried to climb over the trees at the end of the field. However, he failed to manoeuvre the aircraft away from the trees and as a result the aircraft collided with the trees. No one was injured in the collision but the aircraft sustained significant damage.
Probable cause:
The accident was caused due to the fact that a robust method for performance calculation of the required take-off distance was not applied. This in term led to the commencement of the flight in spite of the lack of conditions for a safe start in the chosen direction. The investigation has shown that under the prevailing conditions, the required distance for a take-off exceeded the available distance. A safe take-off was therefore not possible in the chosen take-off direction.
Final Report: