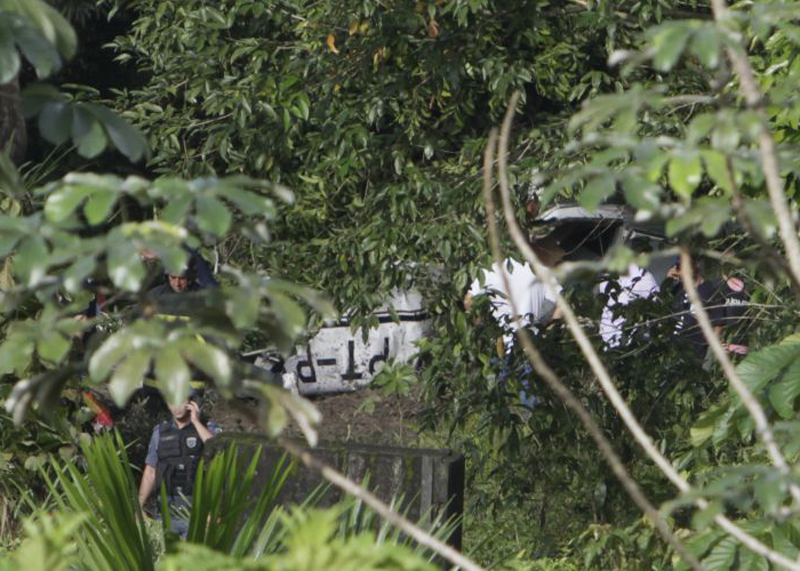Circumstances:
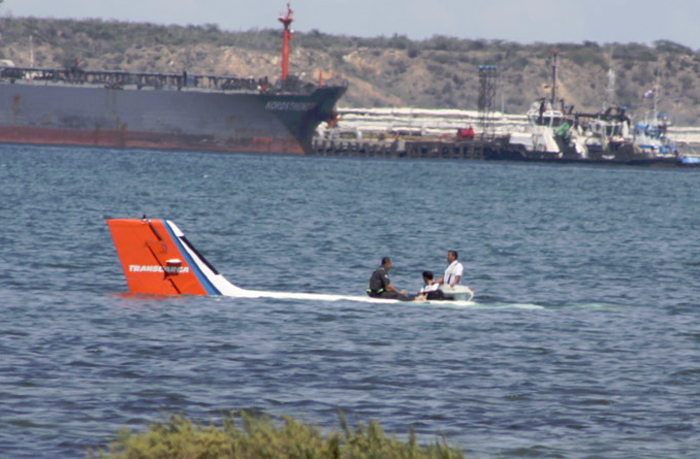
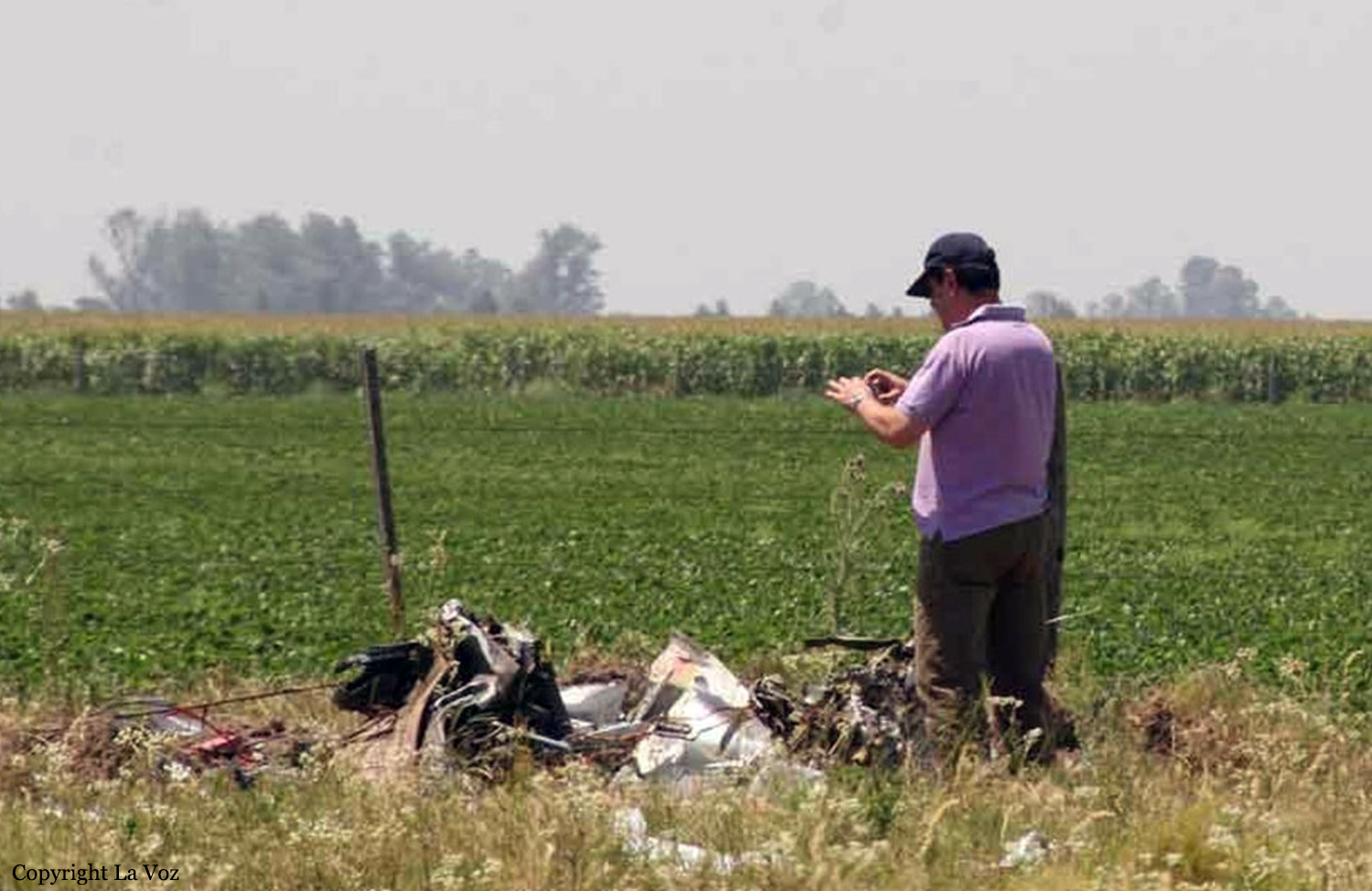
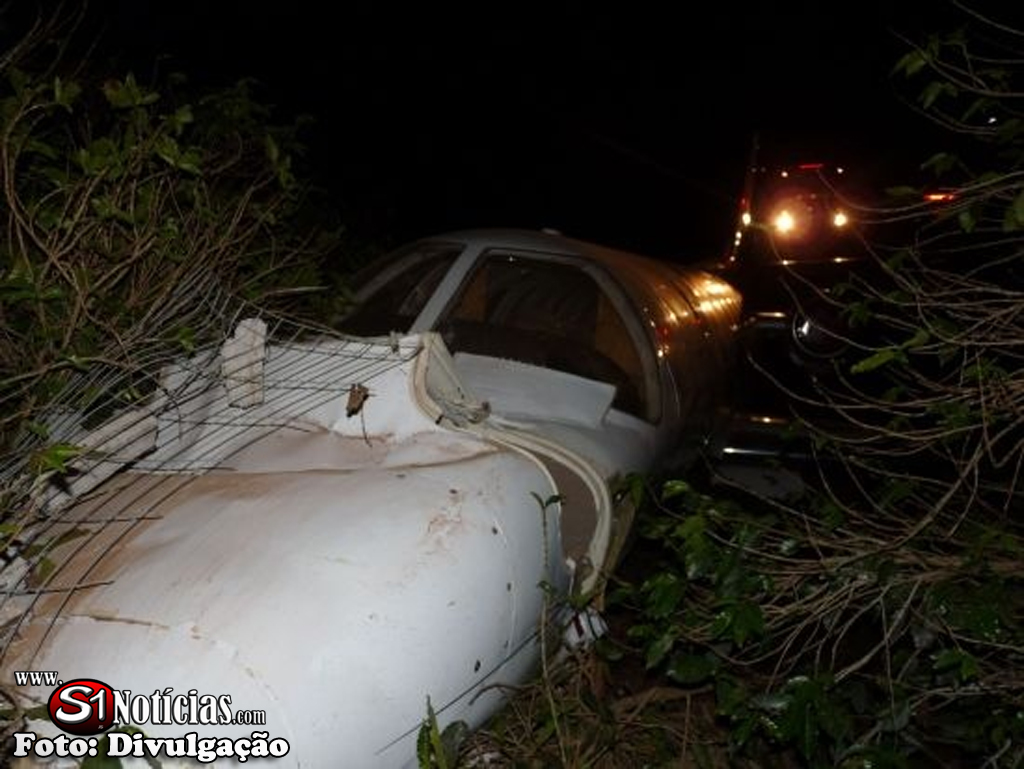
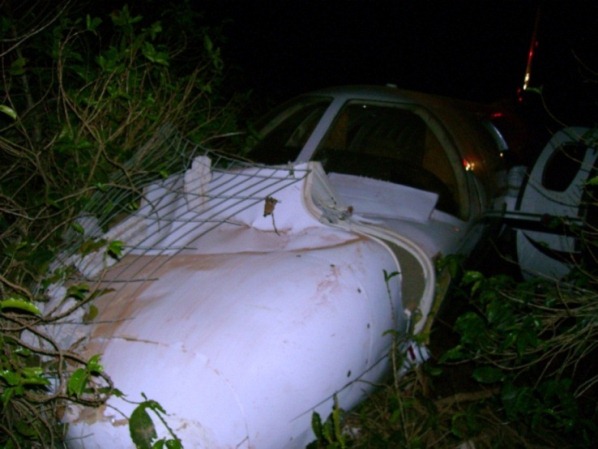
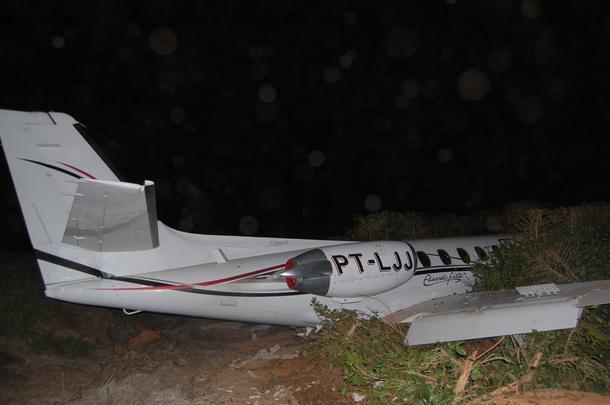
The aircraft departed São Paulo-Congonhas Airport at 1630LT on a flight to Belém, carrying two passengers and two pilots. During the approach to Belém-Val de Cans-Júlio Cezar Ribeiro Airport runway 06 by night, one of the engine flamed out. Few seconds later, the second engine failed as well. The crew ditched the aircraft in the Bay of Guajará, about 1,2 km short of runway 06 threshold. All four occupants were rescued by servicemen of the Naval Base who were on duty at the time of the accident. A pilot was slightly injured while three other occupants escaped uninjured. The aircraft sank and the wreckage was recovered 12 days later.
Probable cause:
The following findings were identified:
a) The pilots had valid aeronautical medical certificates;
b) The pilots had valid technical qualification certificates;
c) The aircraft captain had qualification and enough experience for the flight in question;
d) The copilot was under training;
e) The aircraft had a valid airworthiness certificate;
f) The planning of the flight from SBSP to SBBE was done by the pilot in command, who took in consideration an aircraft with a full load of fuel;
g) The flight plan read that the fuel endurance was 7 hours and 30 minutes of flight, for an estimated elapse time of 5 hours and 40 minutes at FL230;
h) When the aircraft was passing over the city of Palmas, State of Tocantins, the pilots decided, in conjunction, to proceed non-stop to the destination, discarding the need to make an intermediate landing for refueling;
i) The aircraft was registered in the passenger transport category (TPP) and was engaged in the transport of a sick person;
j) The fuel quantity indicators and the fuel flow indicators of the aircraft were not showing dependable information;
k) The flight plan for the leg betwren SBSP and SBBE contained information of sick person transportation, but there was no sick person on board;
l) The aircraft made a ditching near the banks of Guajará Bay, at a distance of approximately 1,200 meters from the threshold of runway 06 of SBBE;
m) The passengers and crew were rescued by Brazilian Navy servicemen on duty on the Naval Base of Val de Cans;
n) One of the pilots and both passengers got out uninjured, while the other pilot suffered minor injuries; and
o) The aircraft sustained substantial damage.
Contributing factors:
Concerning the operation of the aircraft
a) Attitude – a contributor
The captain failed to comply with norms and procedures by accepting to fly an aircraft on his day of rest, even knowing that he was to start his on-call duty hours as soon as he landed in SBBE.
He also showed to be overconfident when he decided to fly directly from SBSP to SBBE, trusting the 7-hour fuel endurance of his aircraft and the fuel consumption information displayed by the instruments, even after identifying their malfunction. The pilot under training, in turn, was complacent by accepting and agreeing with the pilot-in-command’s decision, without questioning his calculations or motivations for flying direct to the destination.
b) Motivation – a contributor
The captain was eager to return to SBBE on that same day, because he was supposed to start his on-call duty hours in the air taxi company for which he worked.
c) Decision-making process – a contributor
The captain failed to comply with important aspects concerning the route conditions and aircraft instruments by making a decision to fly directly from SBSP to SBBE.
Psychosocial information
a) Communication – a contributor
There was lack of assertiveness on the part of the copilot since he did not question the captain’s calculations and/or motivations to fly non-stop, when he (the copilot) considered that making a stop for refueling would be safer.
b) External influence – a contributor
The involvement of the captain with activities of another company on that same day, in addition to events belonging to his private life, had influence on his decisions in the initial planning of the flight and during the flight en route.
Organizational information
a) Work organization – a contributor
The company delegated responsibility for the entire planning of the flight to the pilots. Therefore, there was not any interference on the part of the company in the crew’s work day and in the legs defined for the flight.
b) Organizational culture – a contributor
The fact that the company performed an operation for which it was not certified reflected the fragility of an organizational culture which allowed it to perform activities unfavorable to operational safety.
Operational Factor
Concerning the operation of the aircraft
a) Flight indiscipline – a contributor
On several occasions during the flight, the pilots failed to comply with the norms and regulations in force, such as the sections 91.167 and 91.205 of the RBHA 91, the Pilot Operating Handbook and FAA Approved Airplane Flight Manual, and the Lei do Aeronauta (Law of the Aeronaut, Law nº 7.183 of 5 April 1984).
b) Training – undetermined
Before the ditching, the pilot unlocked the rear door of the aircraft and, then, failed to instruct the passengers as to the opening of the emergency exit. This fact shows a probable deviation in the process of training previously received by the captain, since the procedure prescribed for the situation was to abandon the aircraft through the emergency exit, which had to be unlocked after the ditching.
c) Piloting judgment – a contributor
At the moment of their decision to proceed non-stop to the destination, there was an inappropriate evaluation on the part of the crew, because they did not consider the hourly consumption until that point, and the malfunction of the fuel capacity indicator did not allow them to know the exact amount of fuel remaining in the tanks.
d) Flight planning – a contributor
There was a mistake on the part of the captain relative to the planning of the flight, since, in addition to a total flight time of 5 hours and 40 minutes, he did not consider the fuel necessary to fly to an alternate airport plus 45 minutes of flight. The captain and the pilot under training made an inappropriate evaluation of the effects brought by the operational conditions along the flight route.