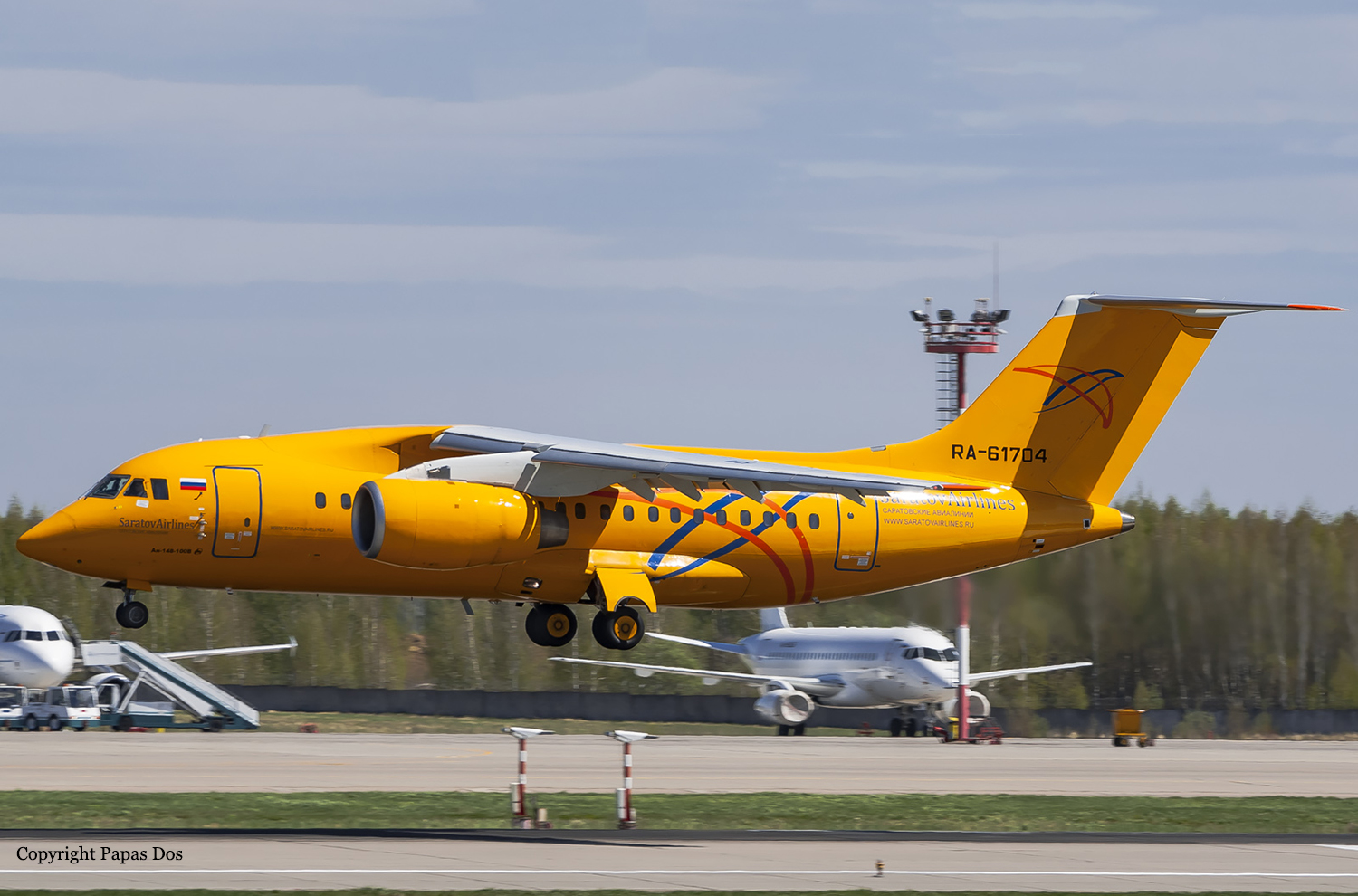
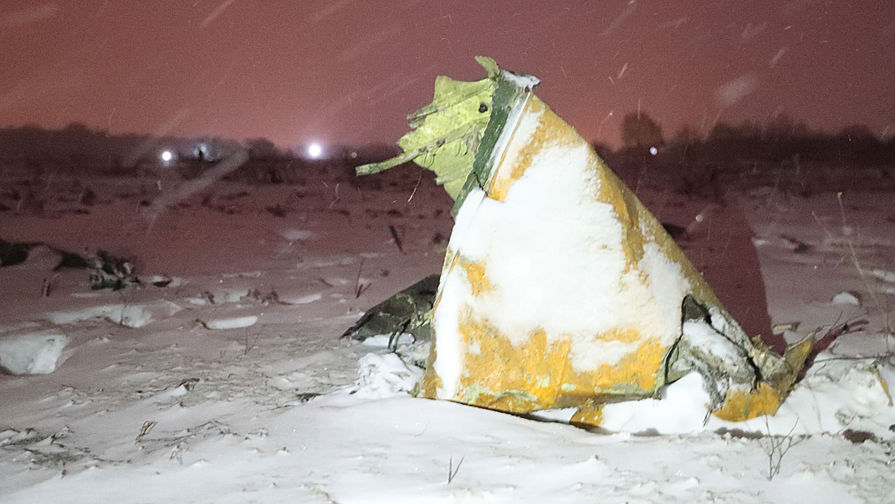
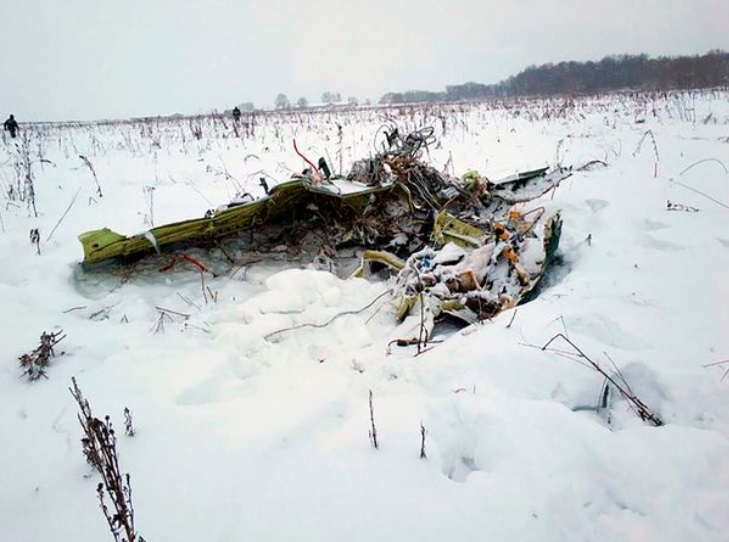
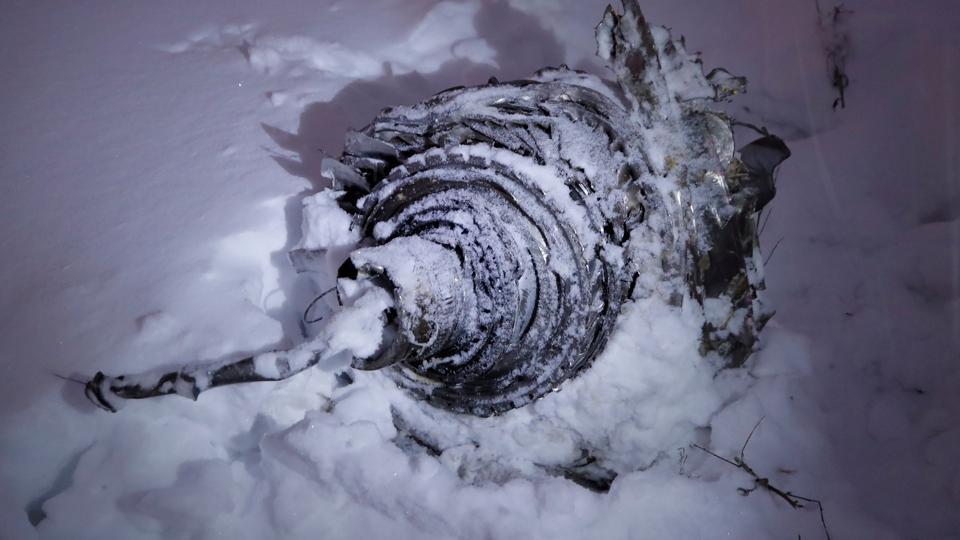
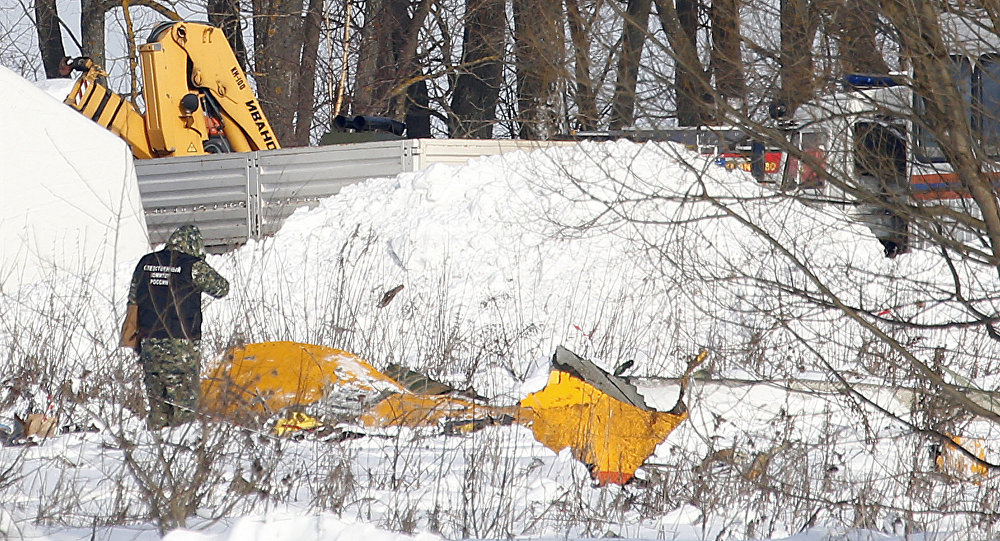
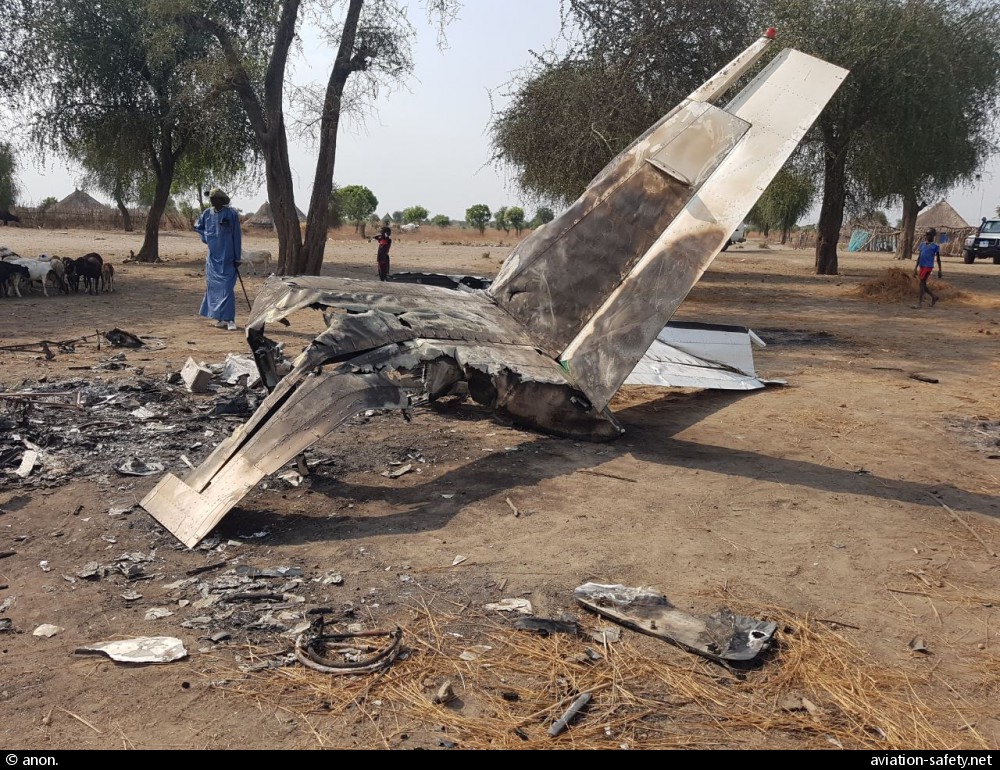
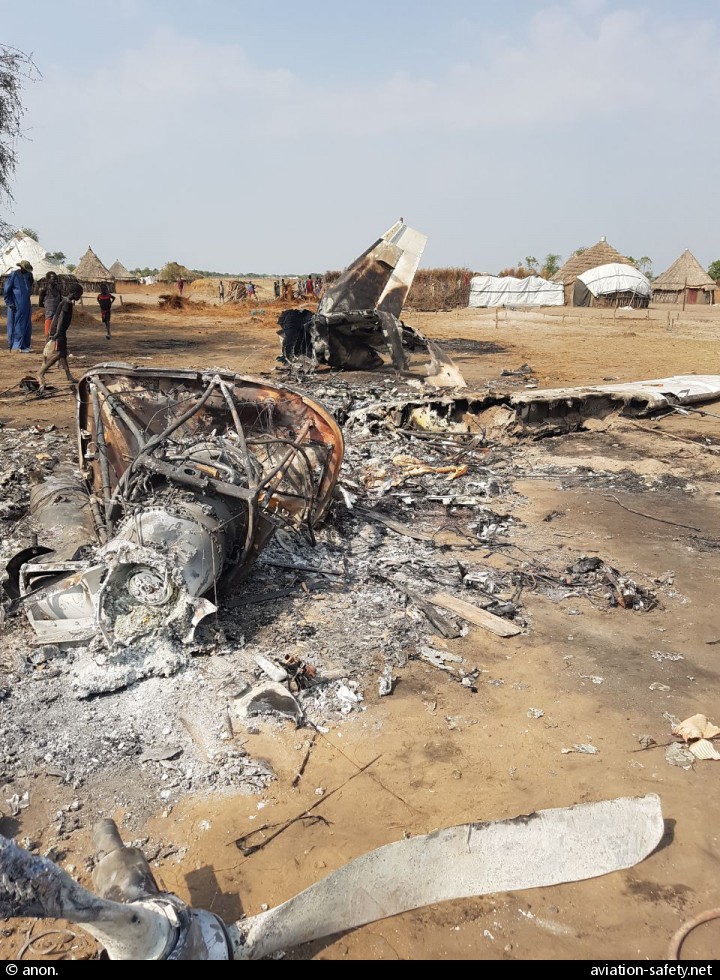
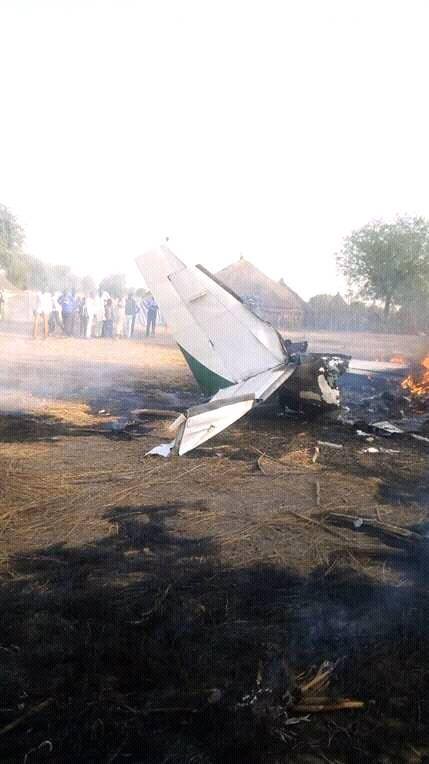
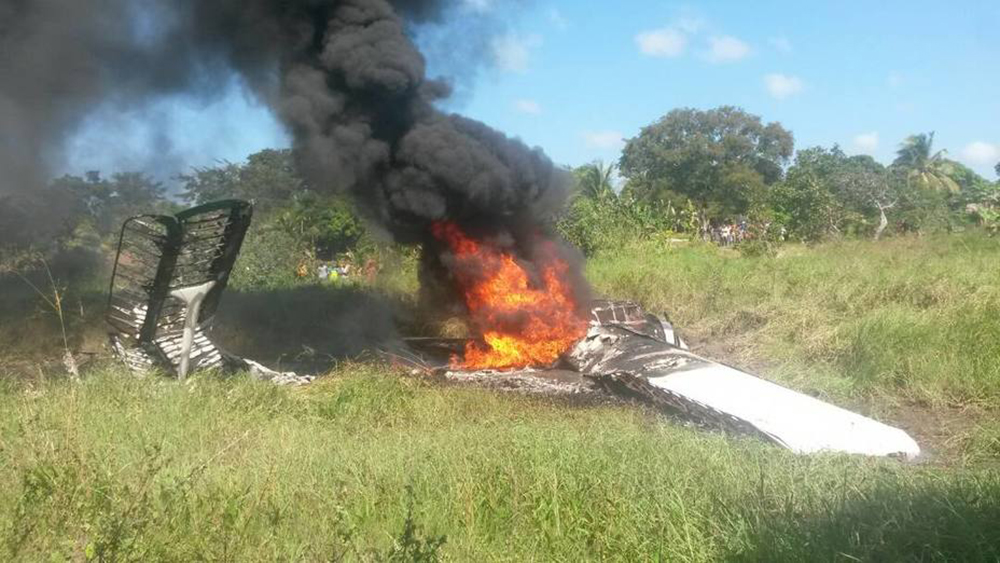
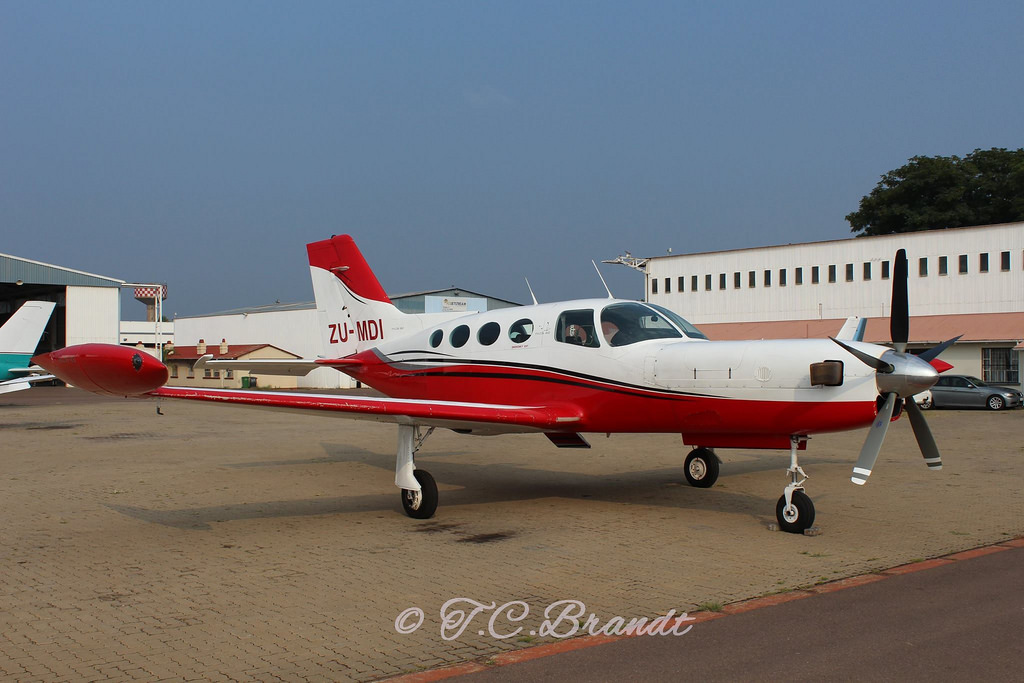
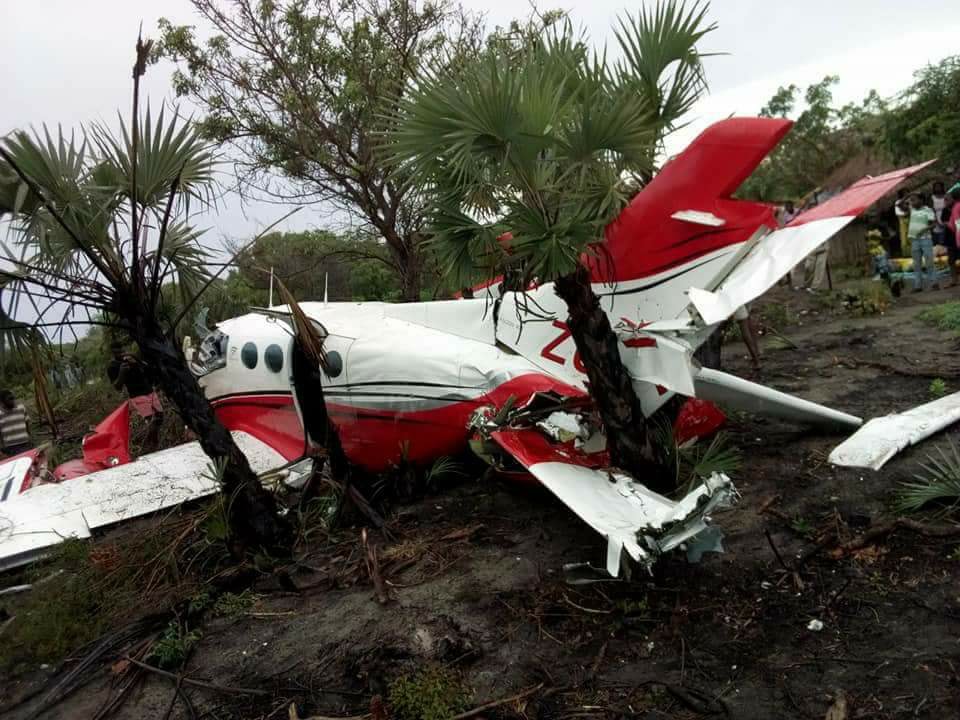
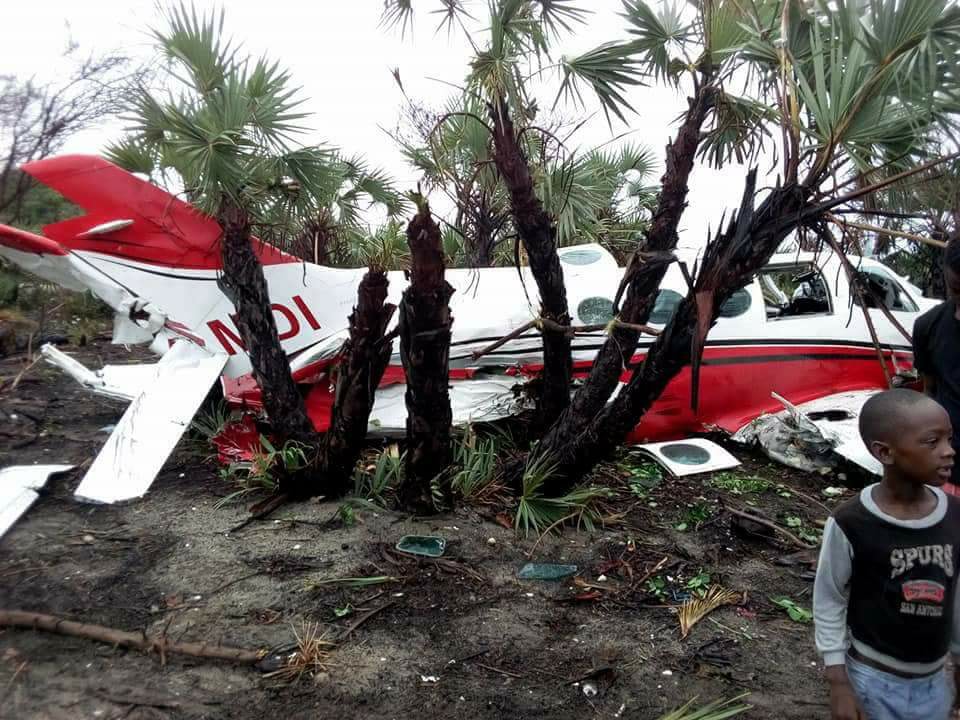
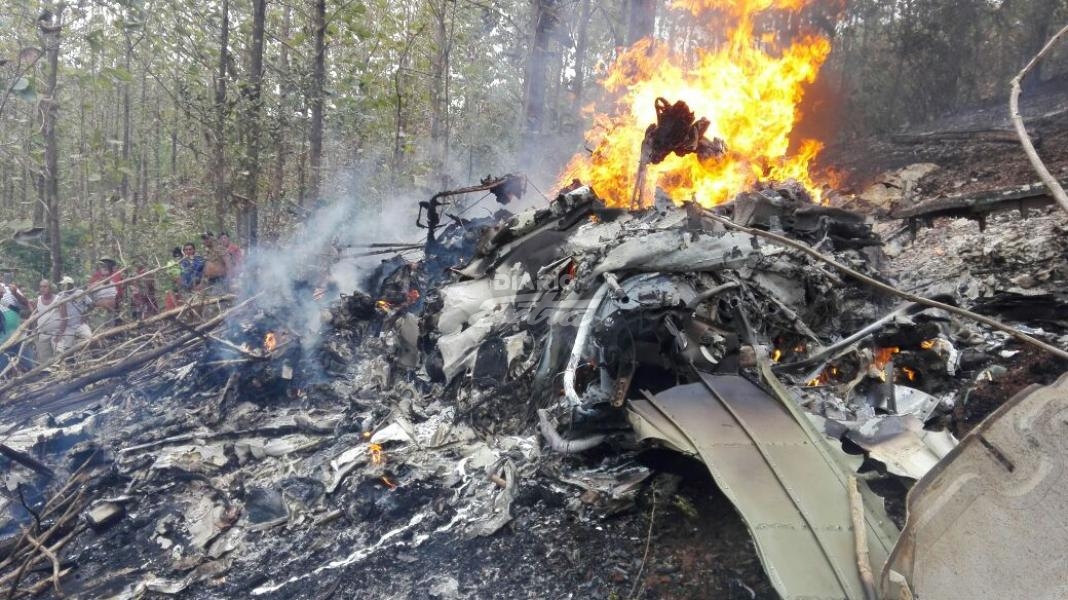
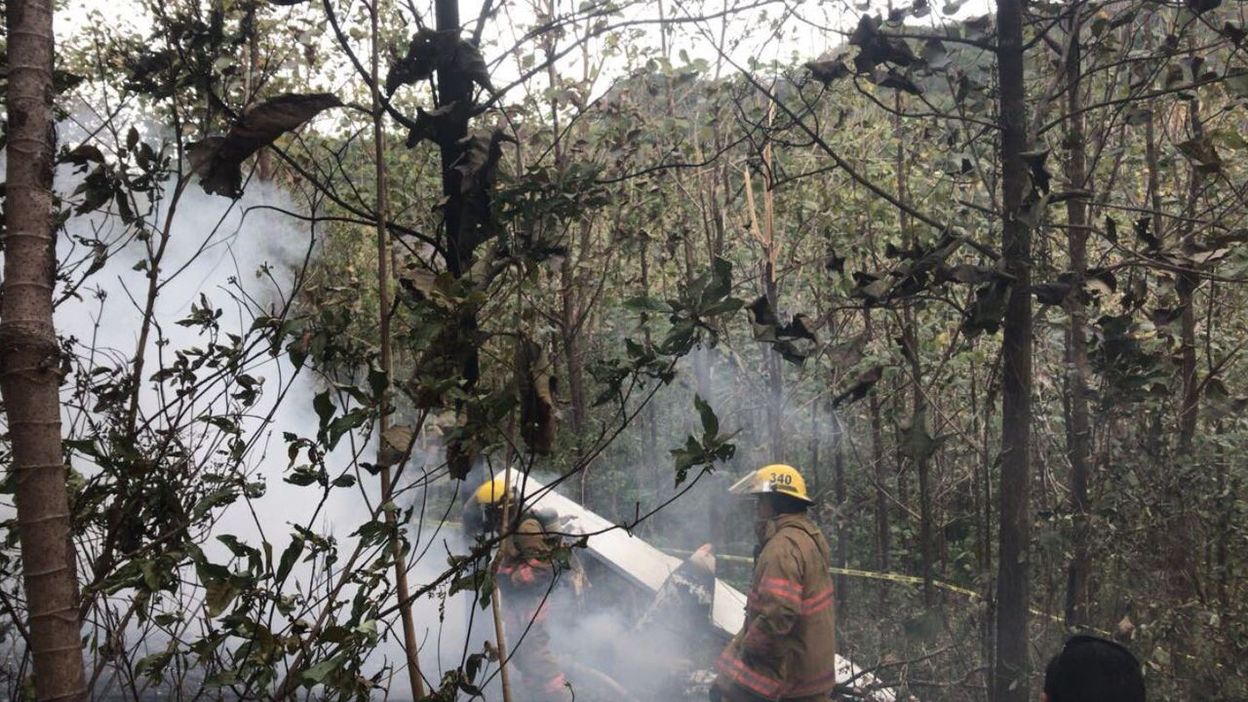
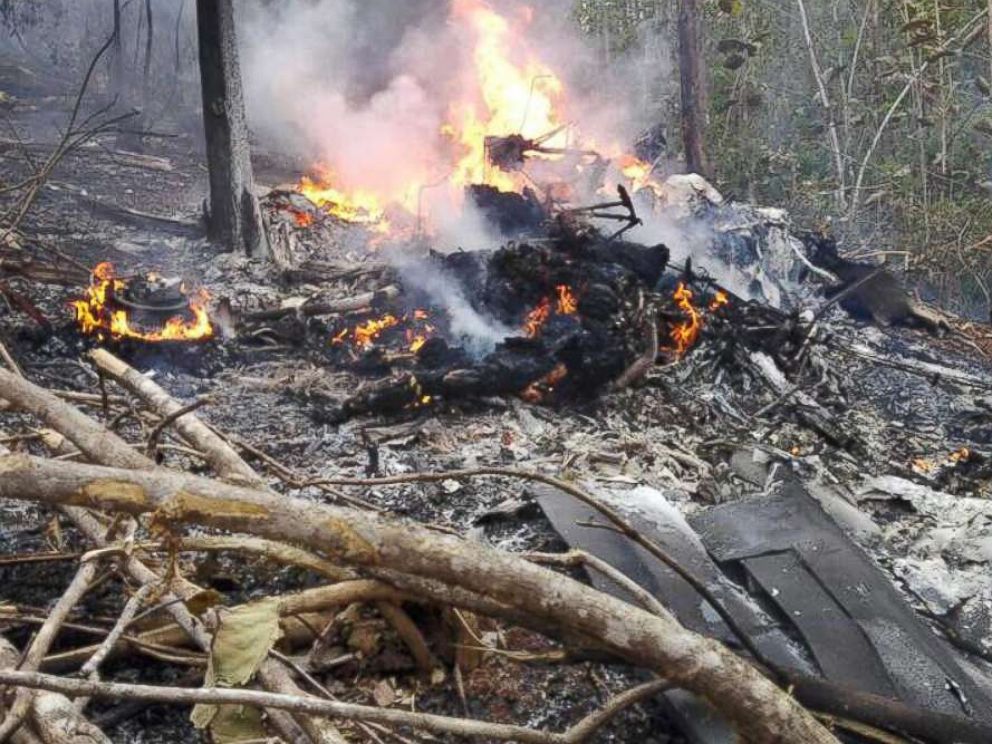
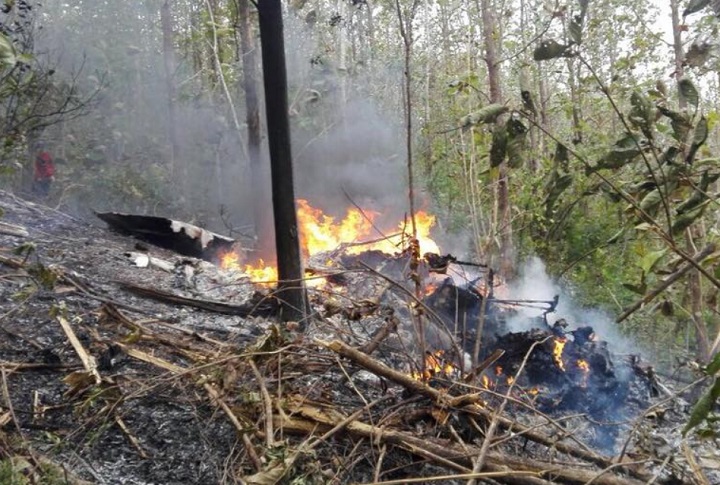
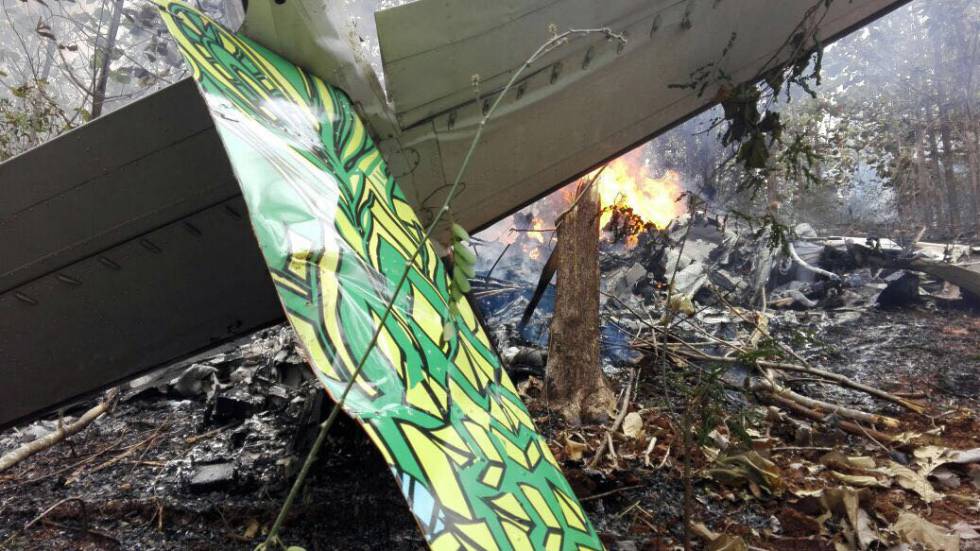
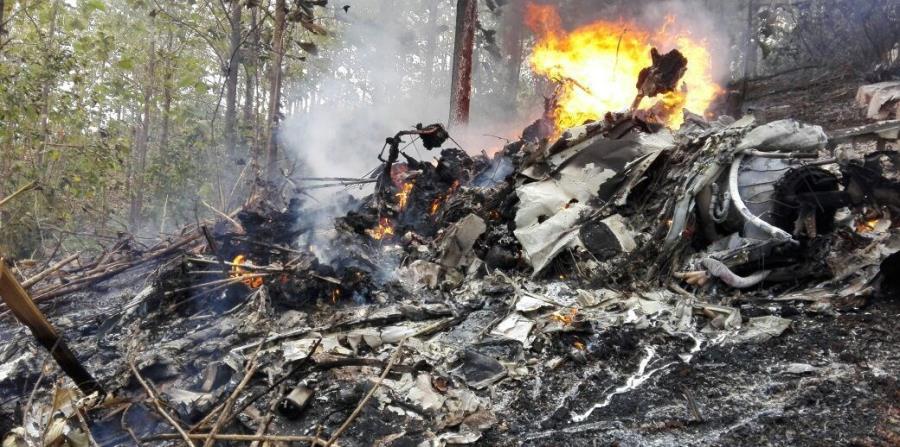
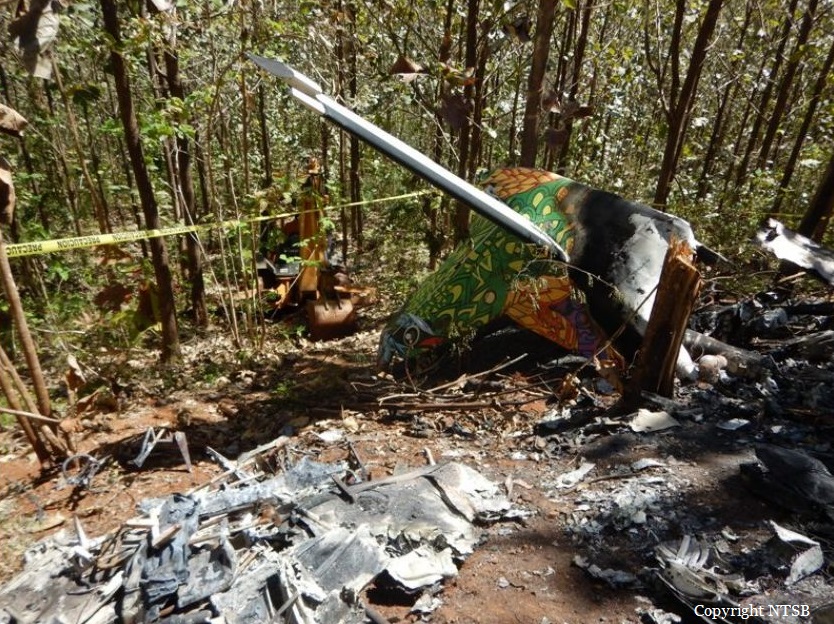
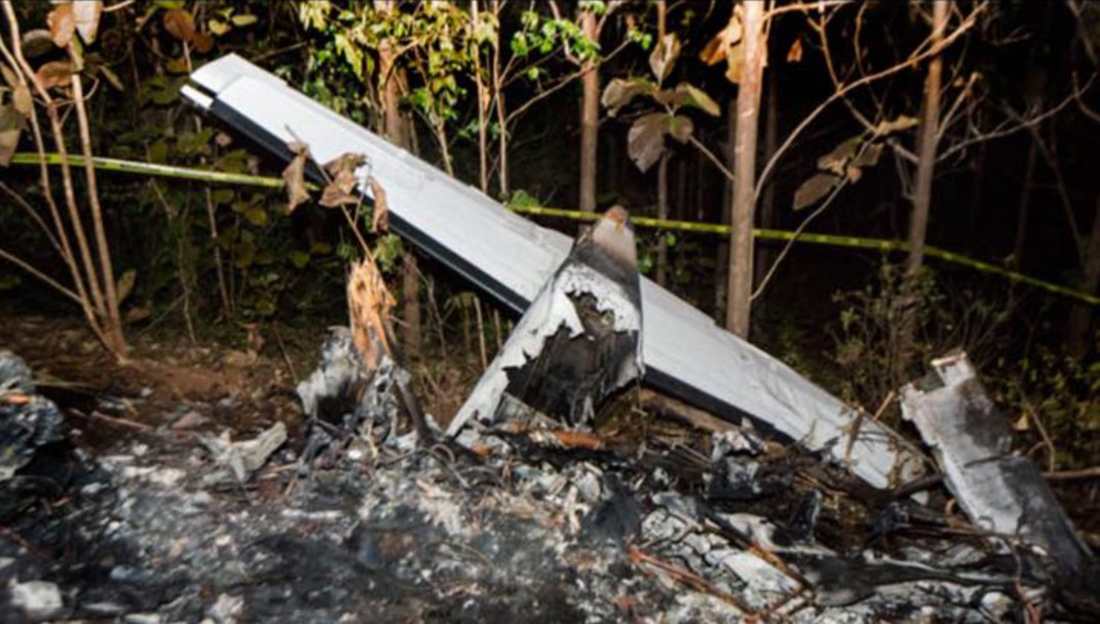
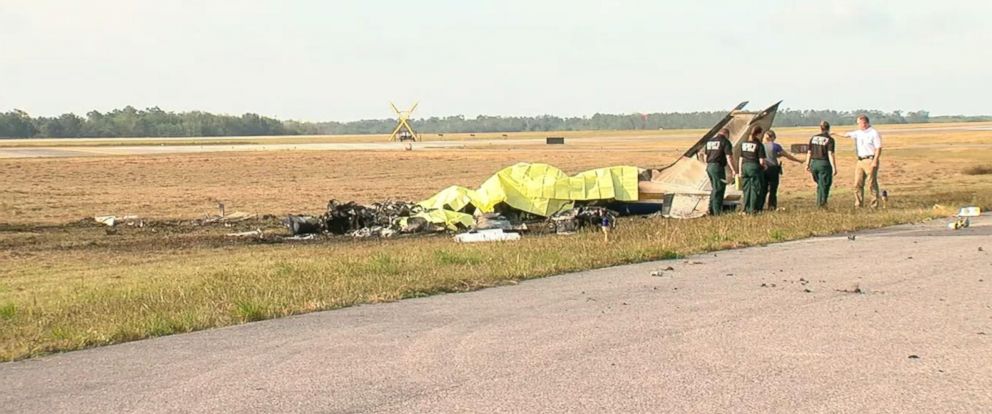
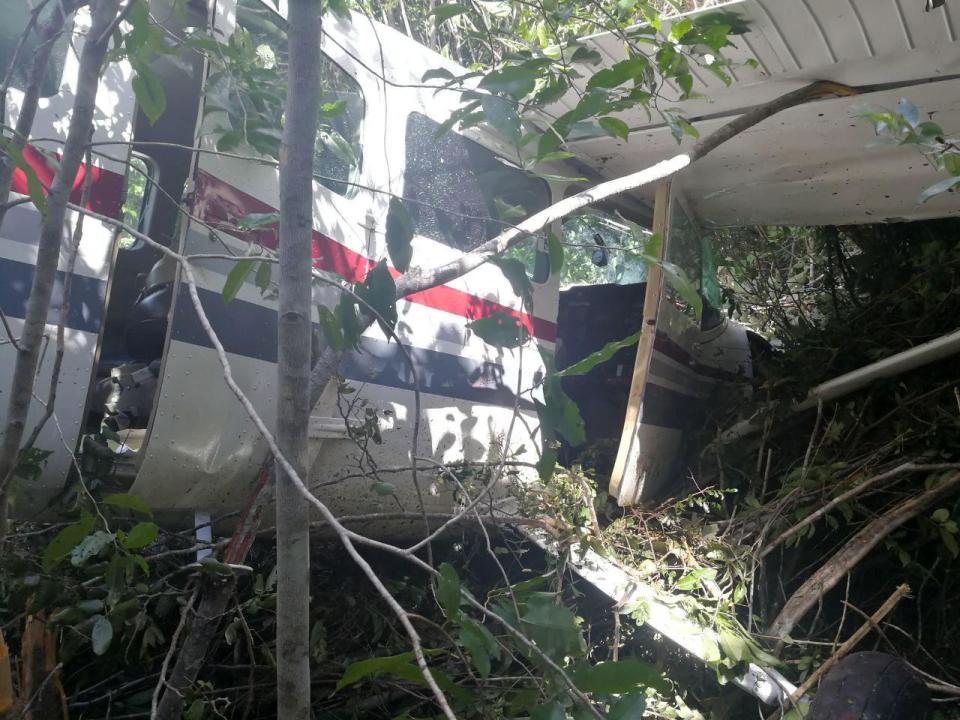
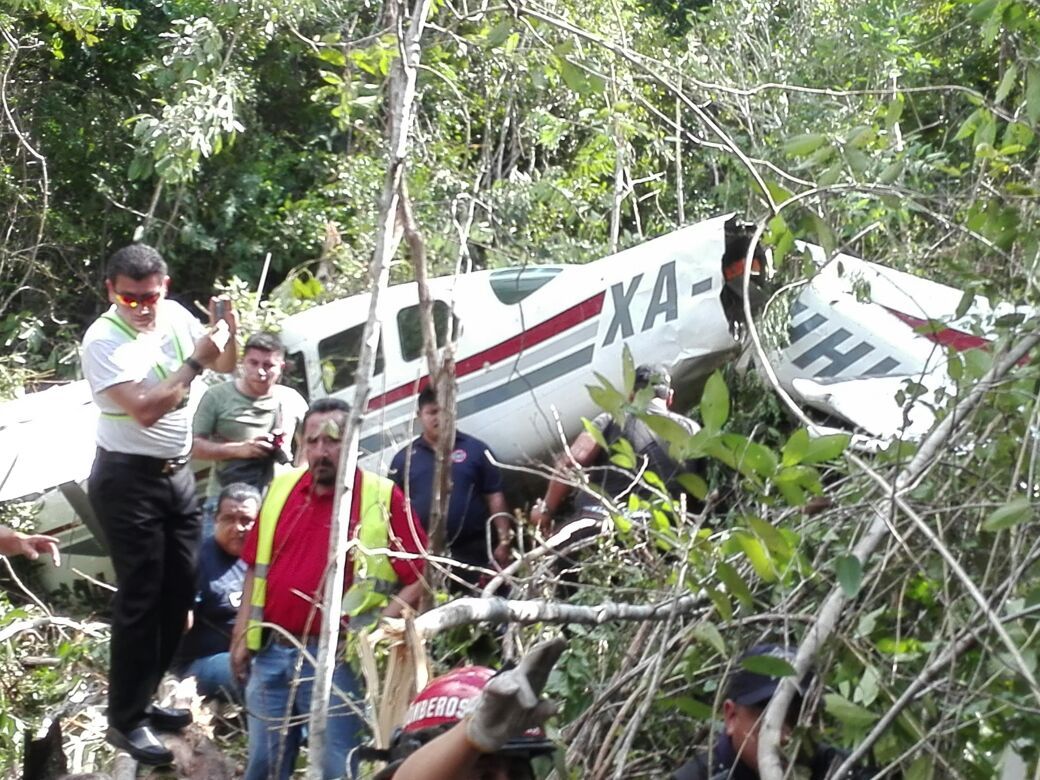
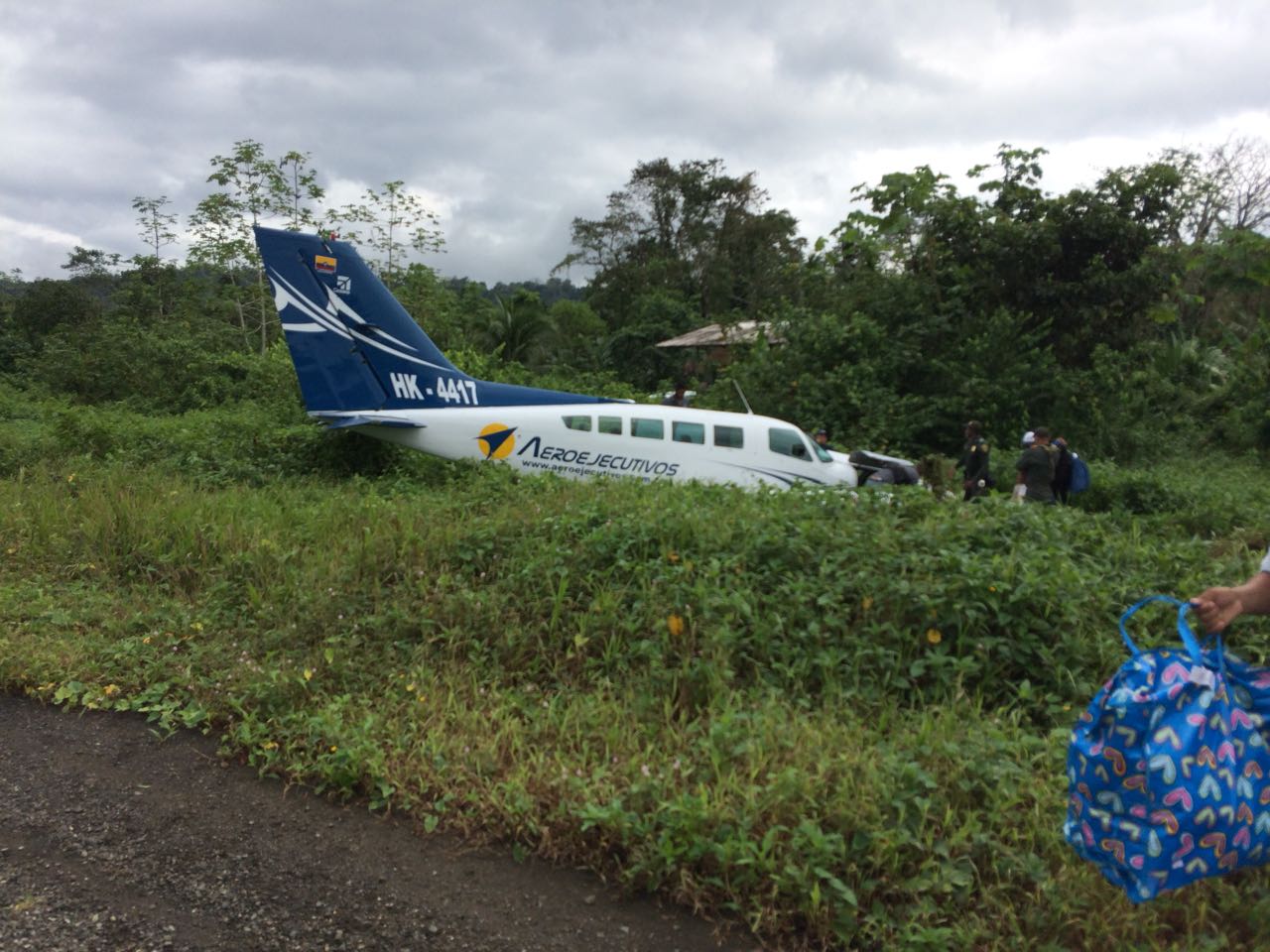
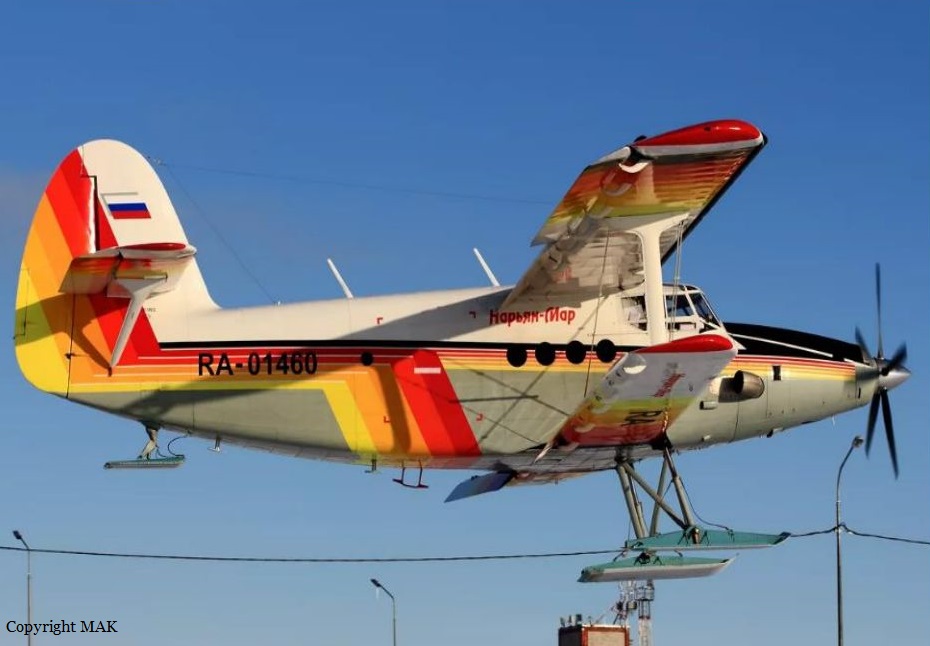
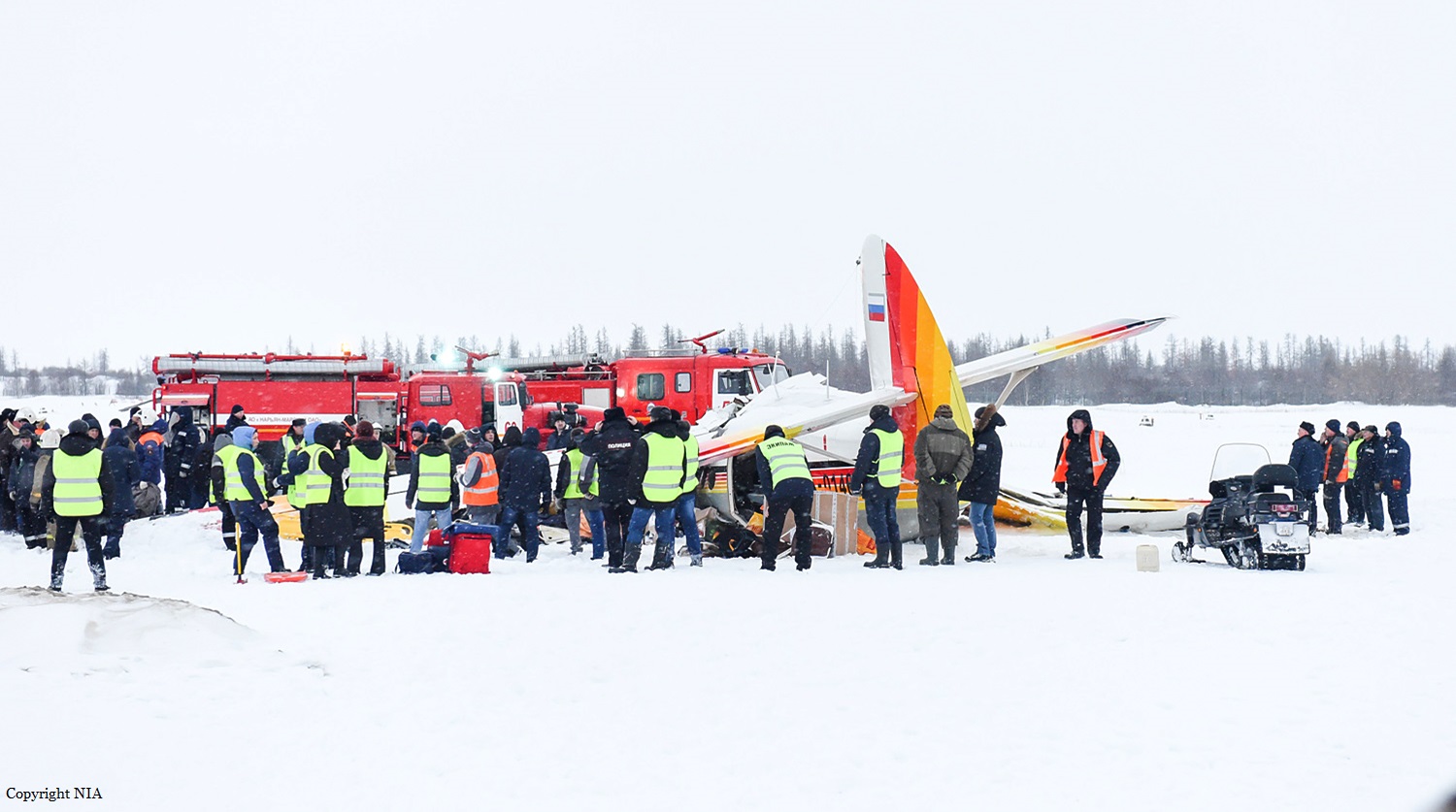
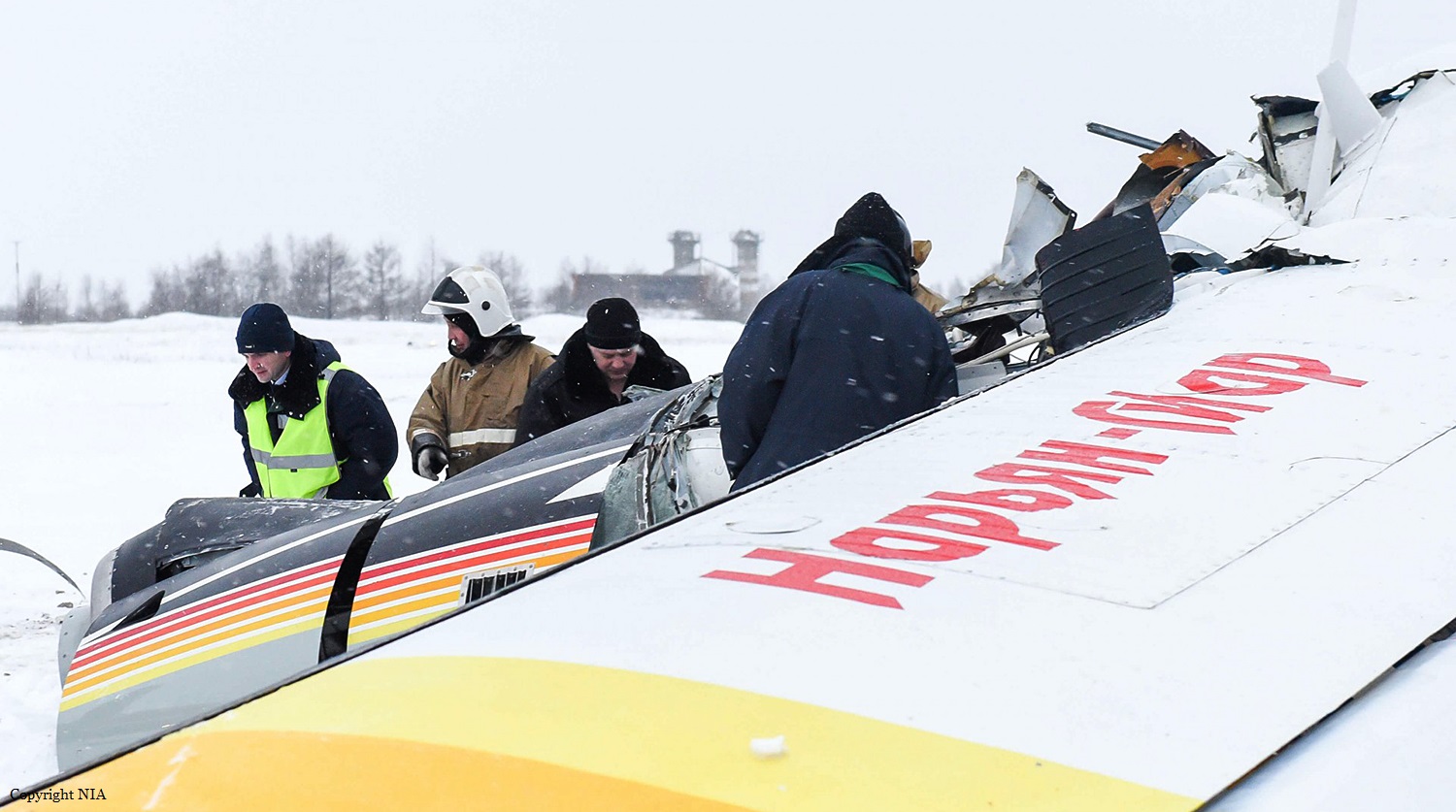
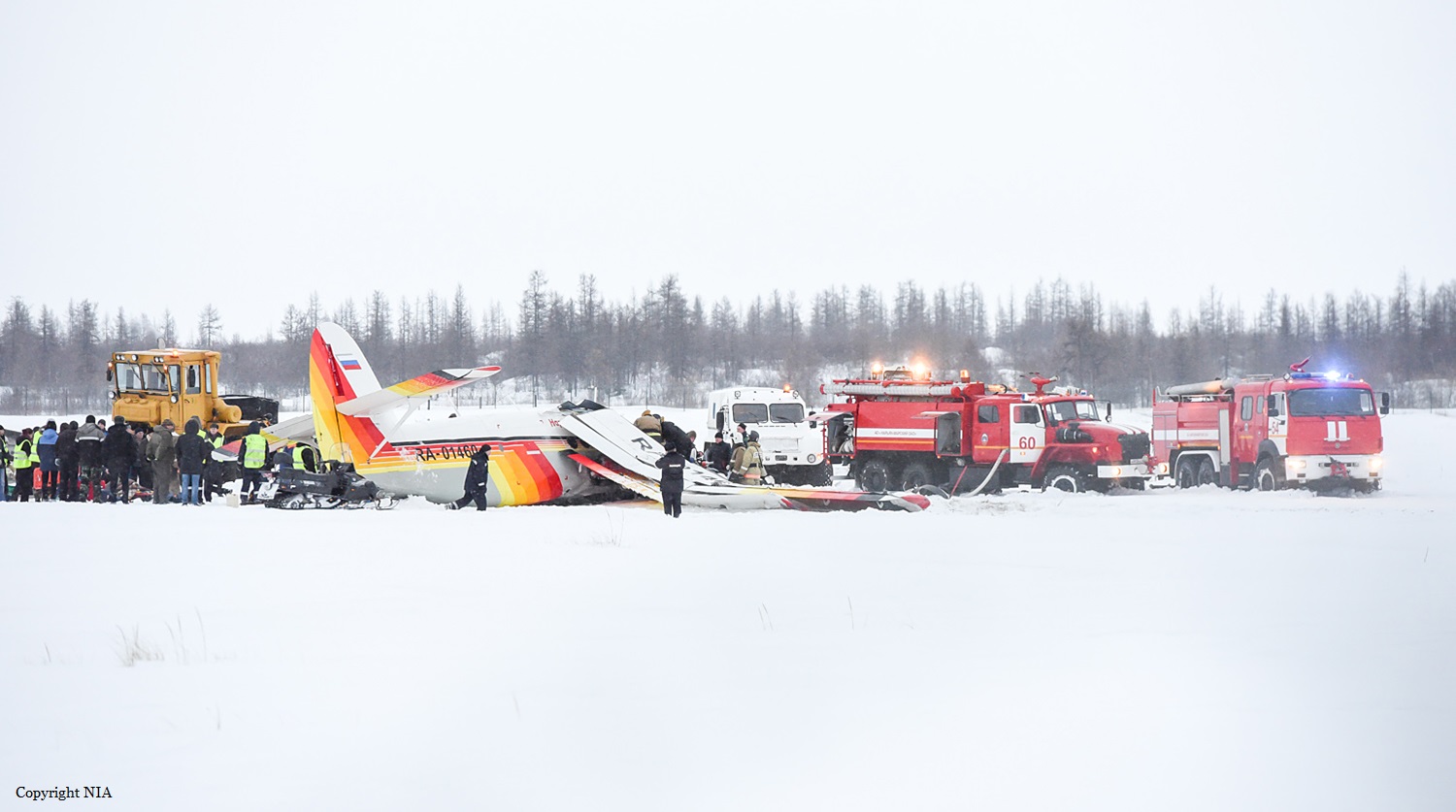
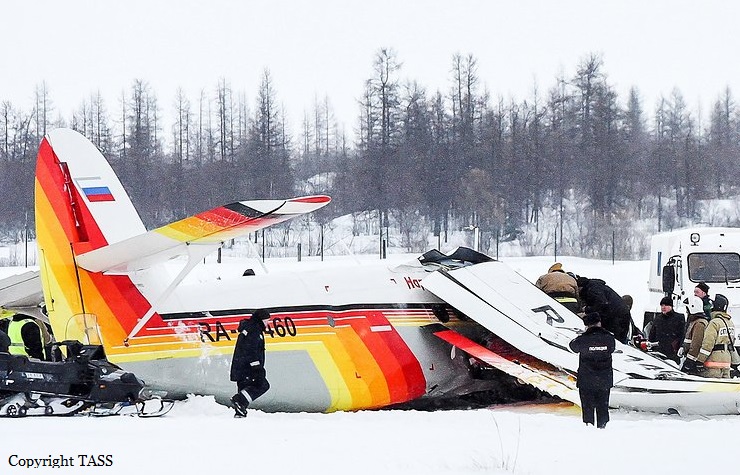
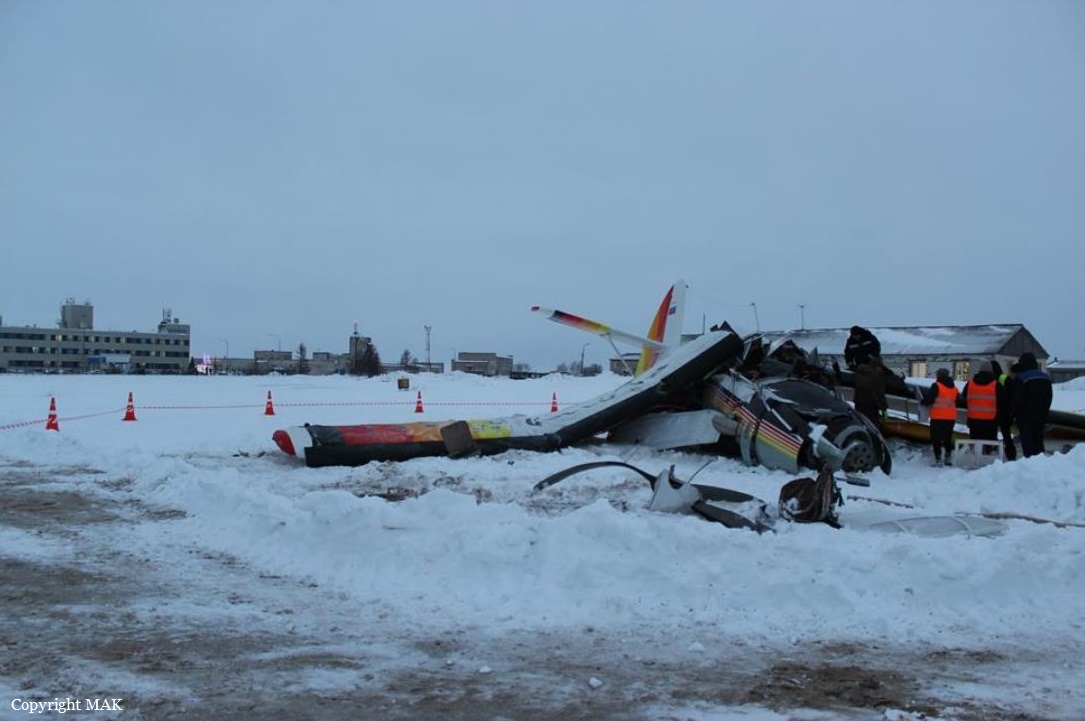
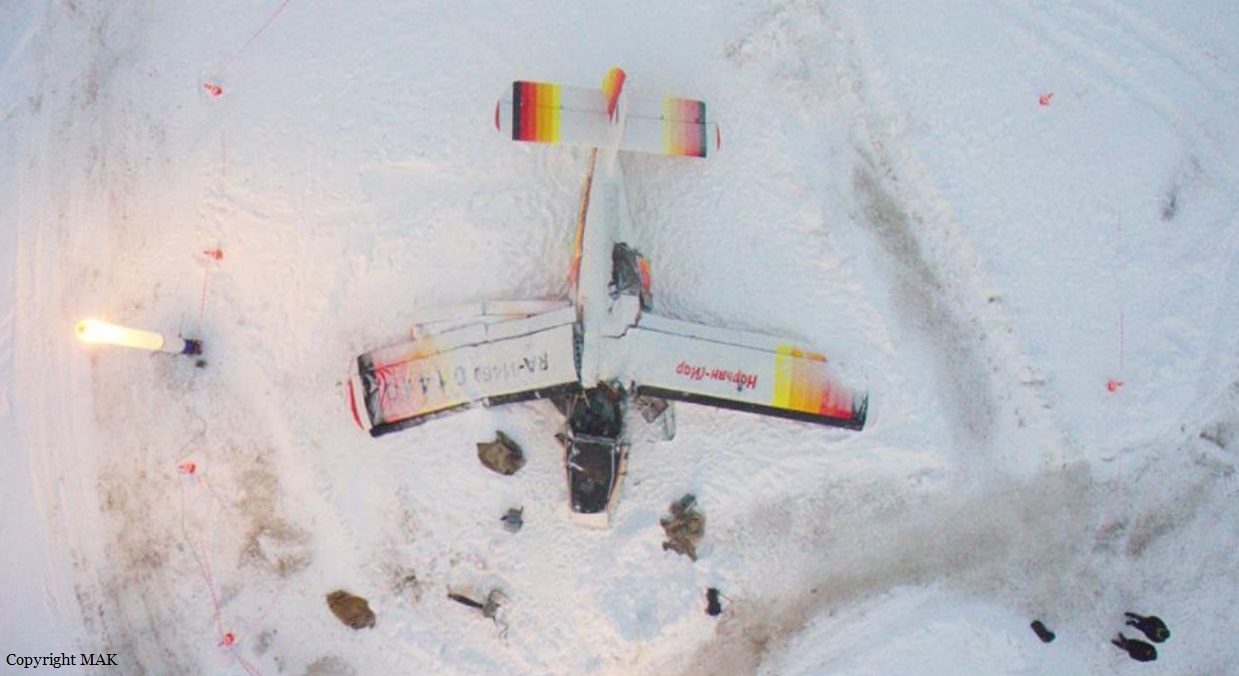
Crash of an Antonov AN-148-100B in Stepanovskoye: 71 killed
Date & Time:
Feb 11, 2018 at 1427 LT
Registration:
RA-61704
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Moscow – Orsk
MSN:
27015040004
YOM:
2010
Flight number:
6W703
Crew on board:
6
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
65
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
71
Captain / Total hours on type:
1323.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
720
Aircraft flight hours:
16249
Aircraft flight cycles:
8397
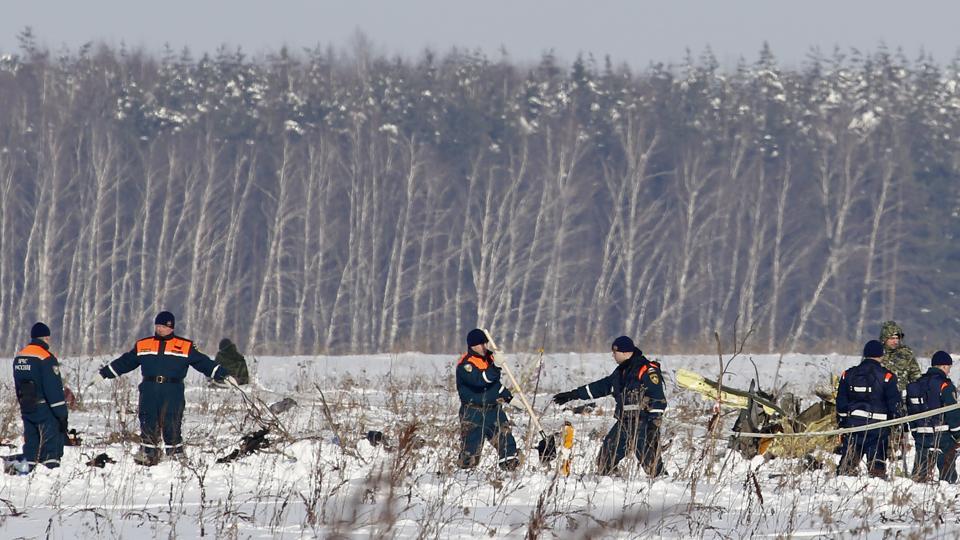
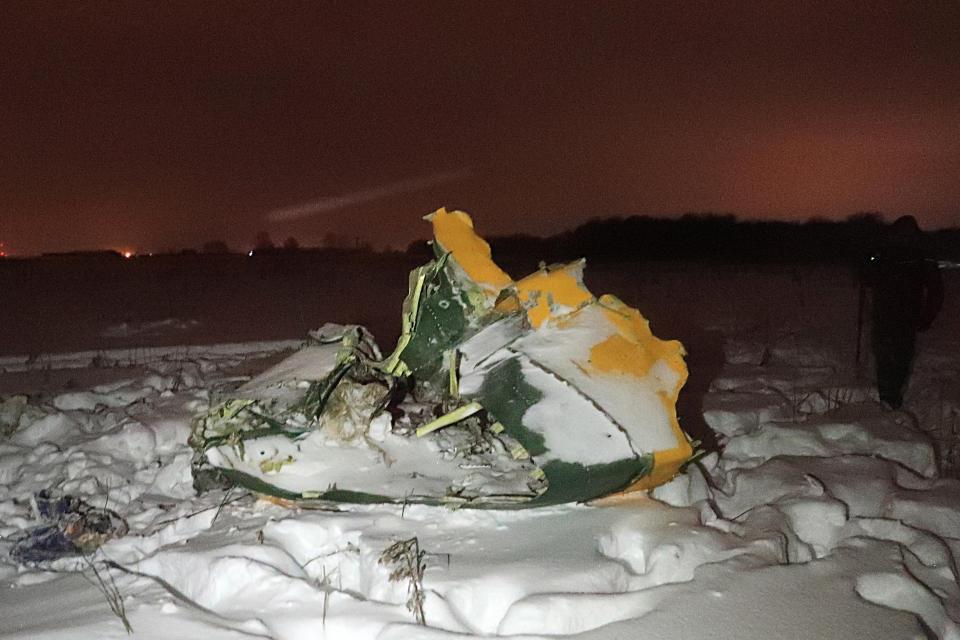
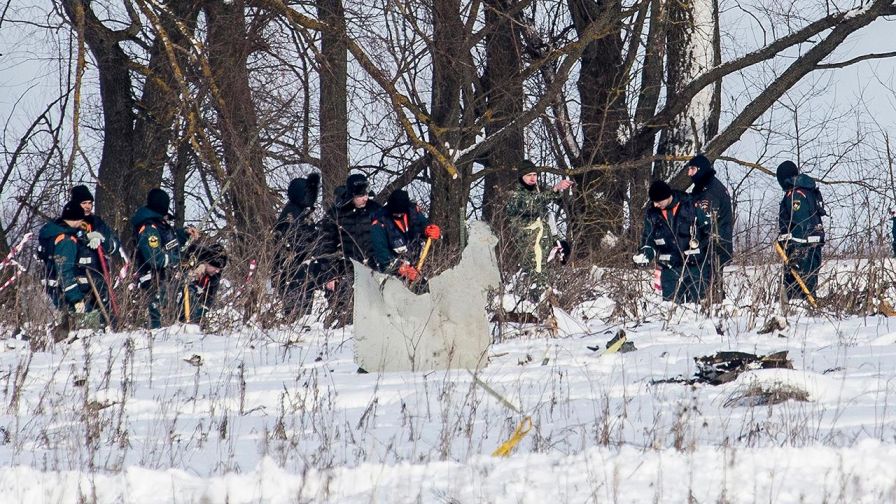
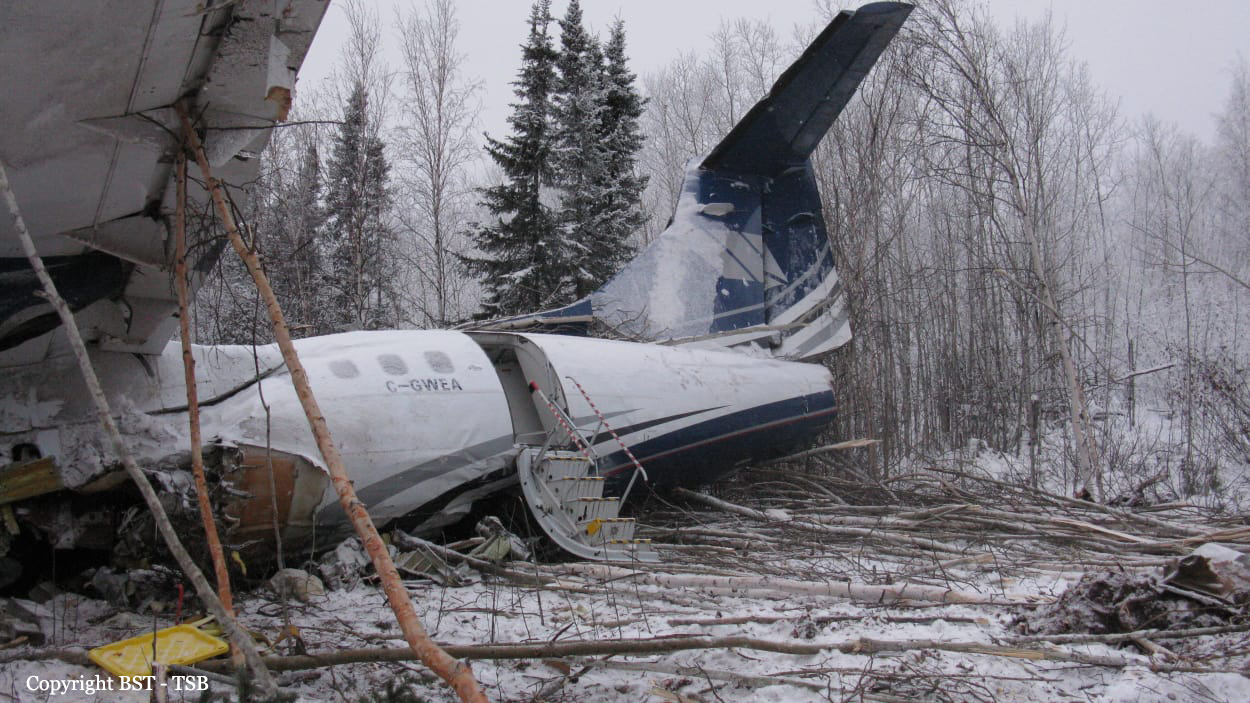
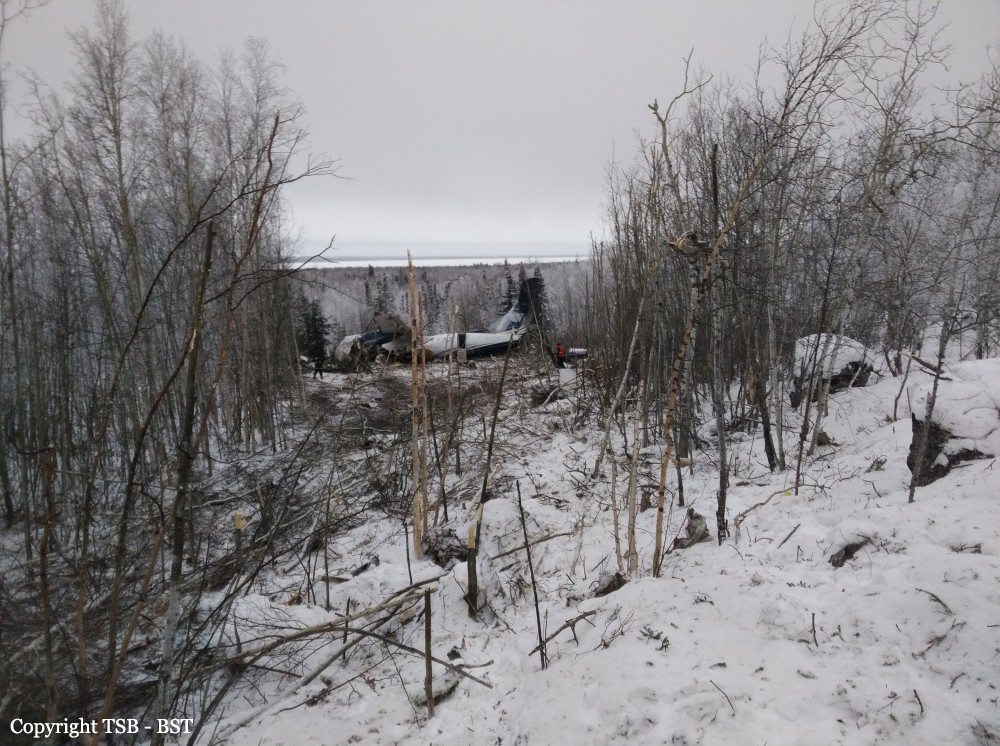
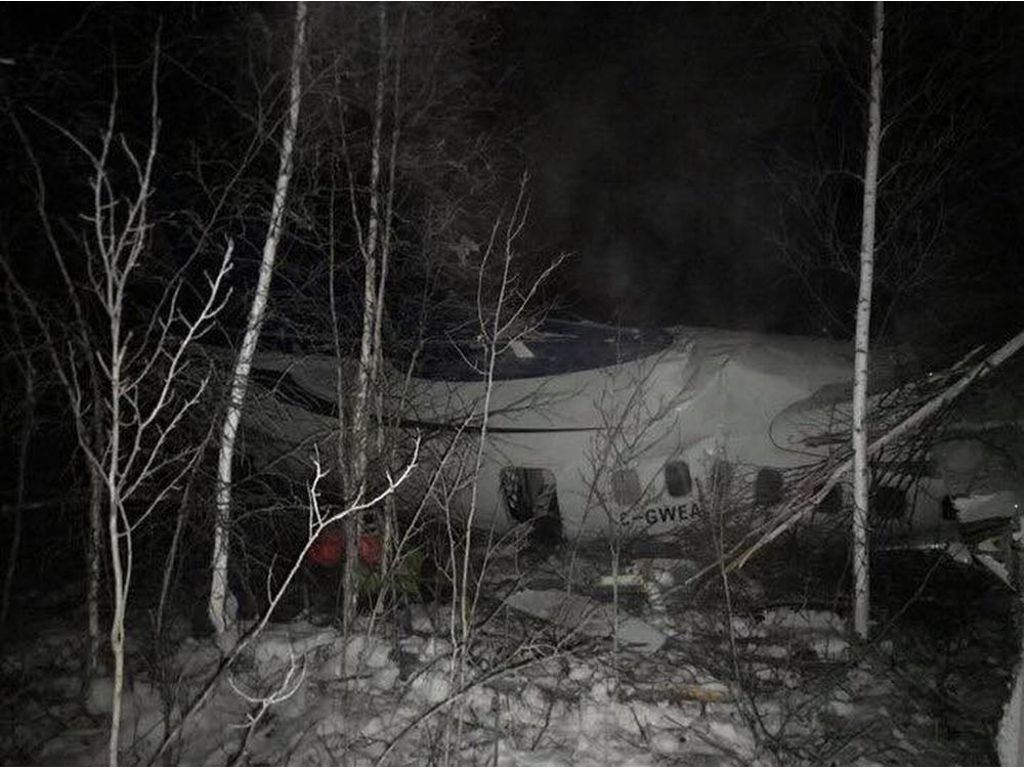
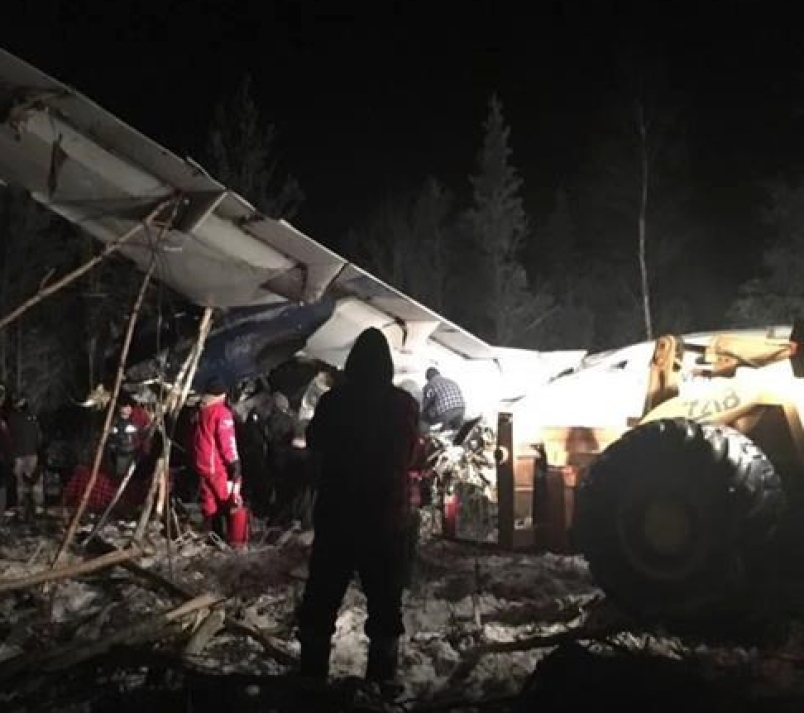
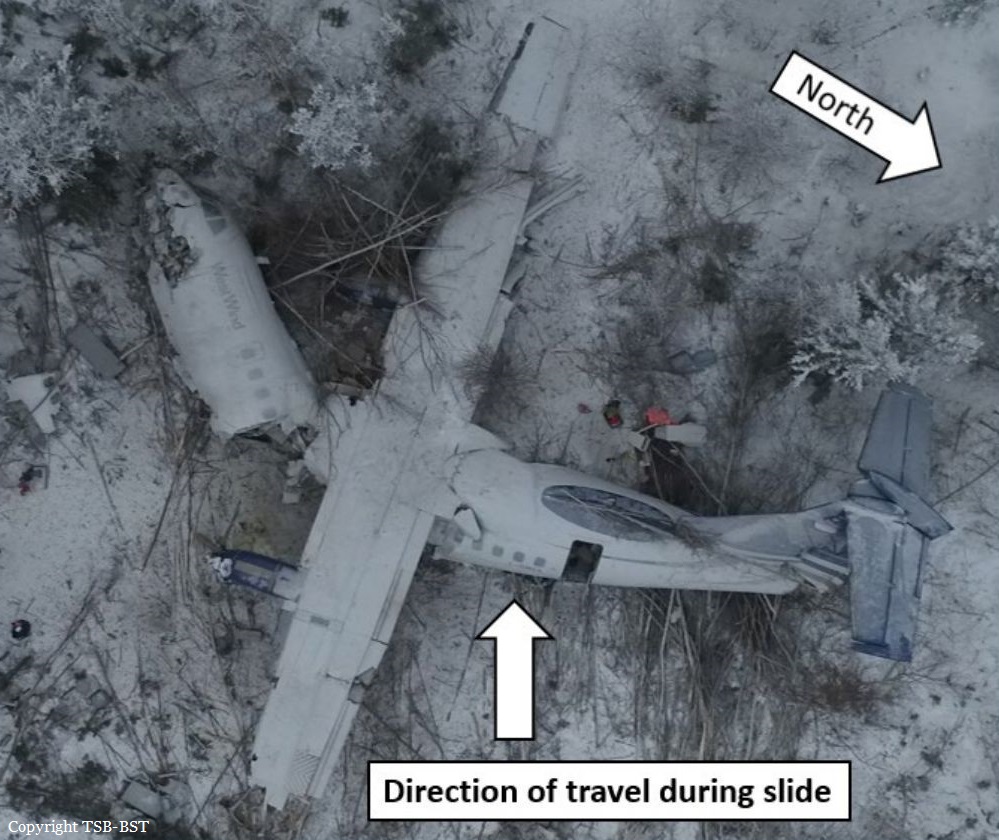
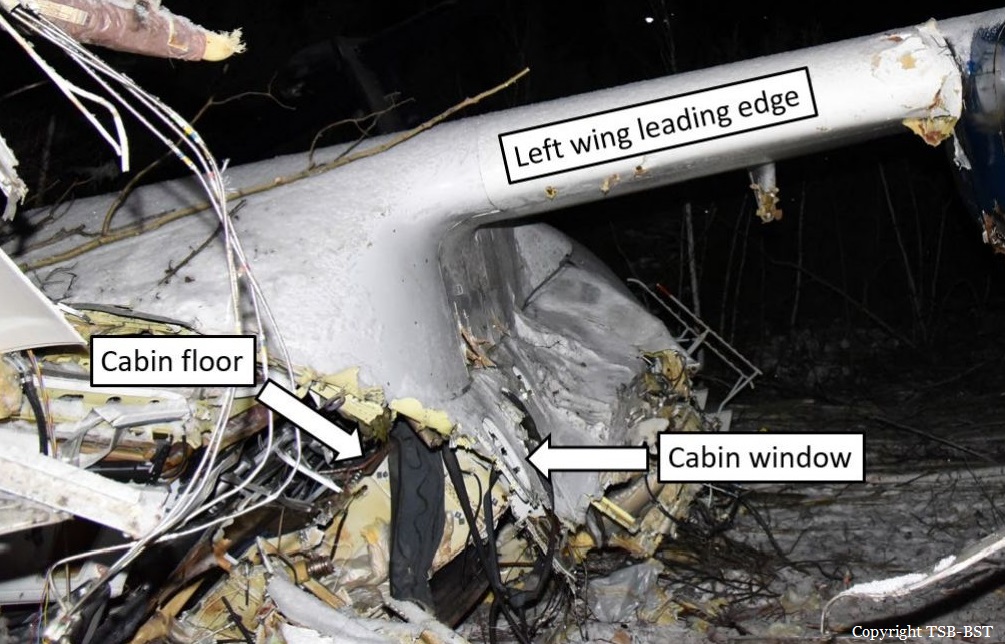
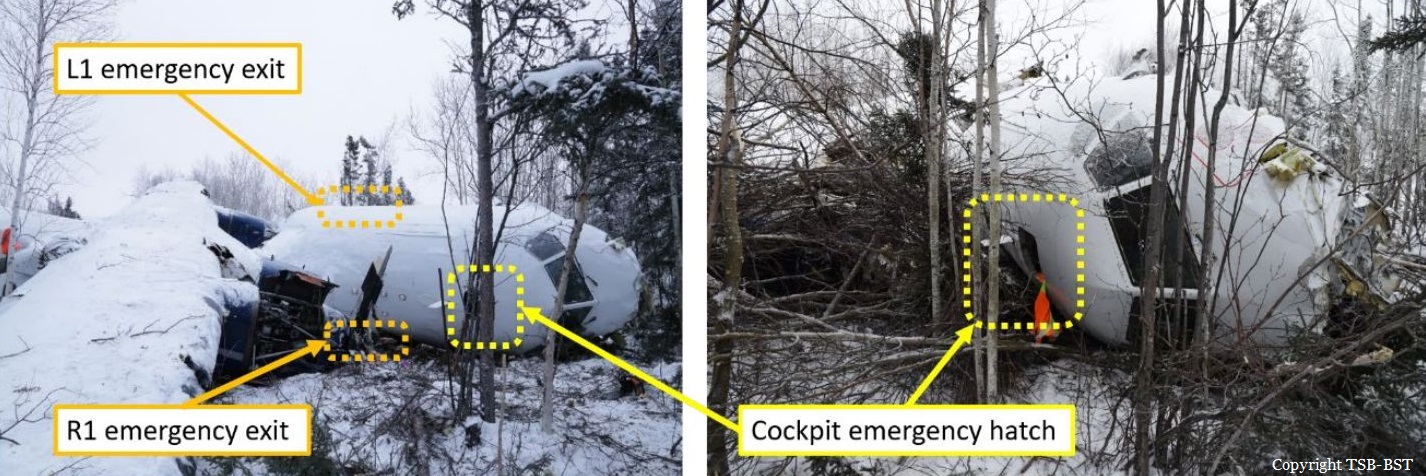
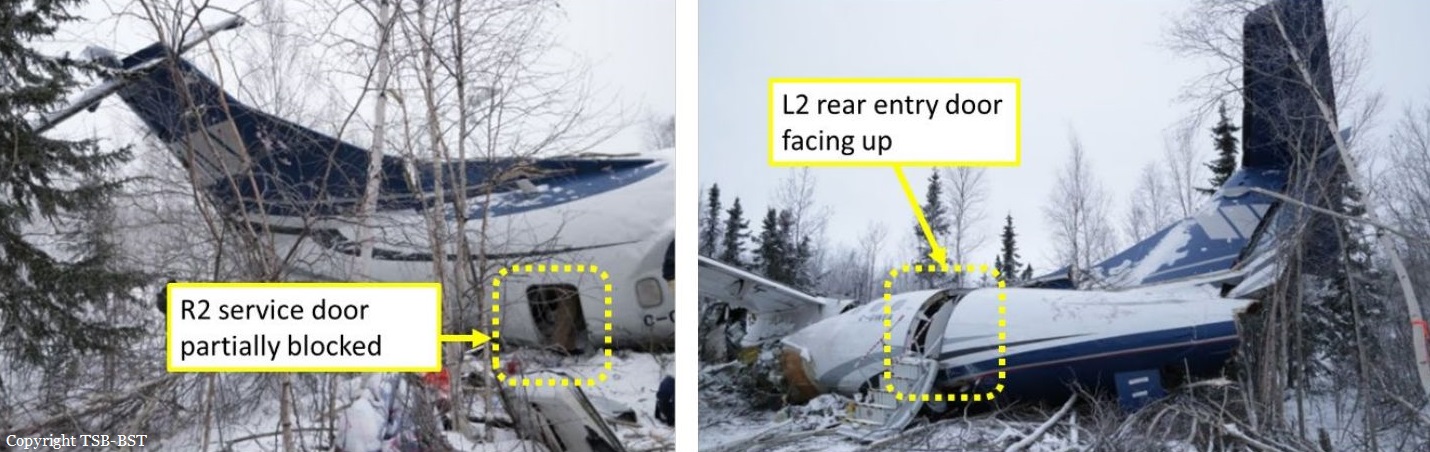
Circumstances:
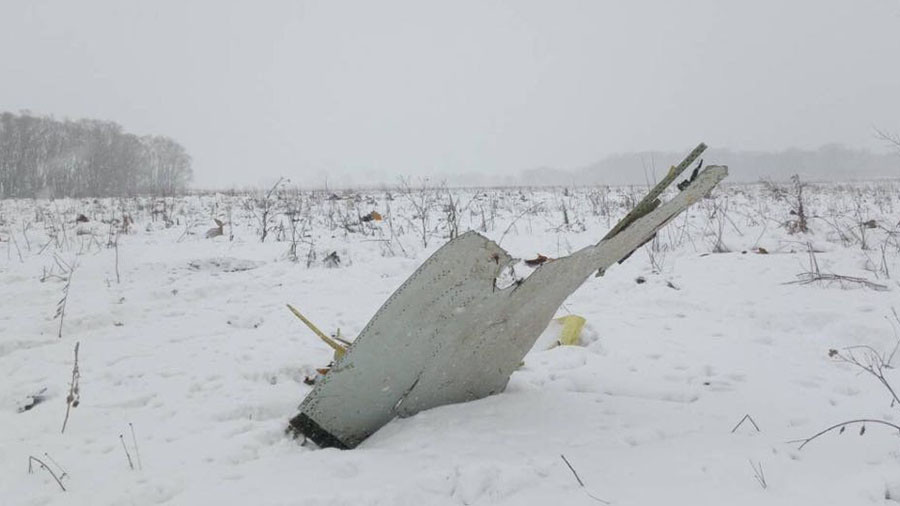
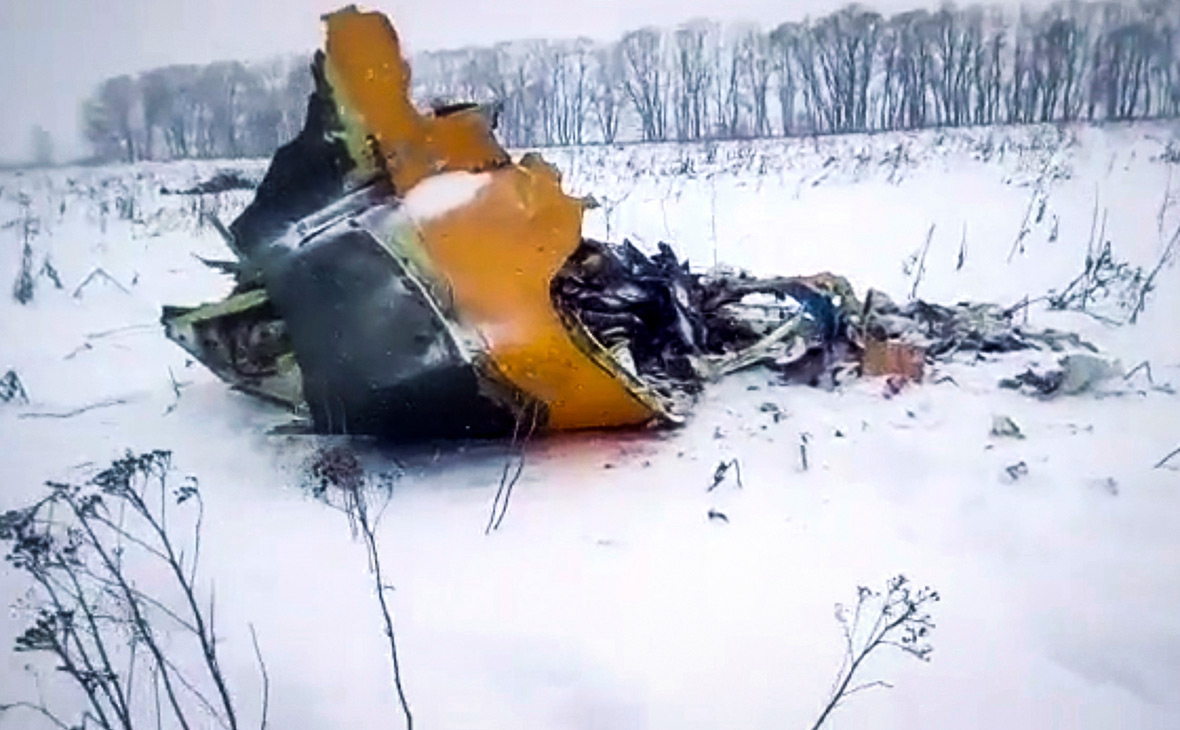
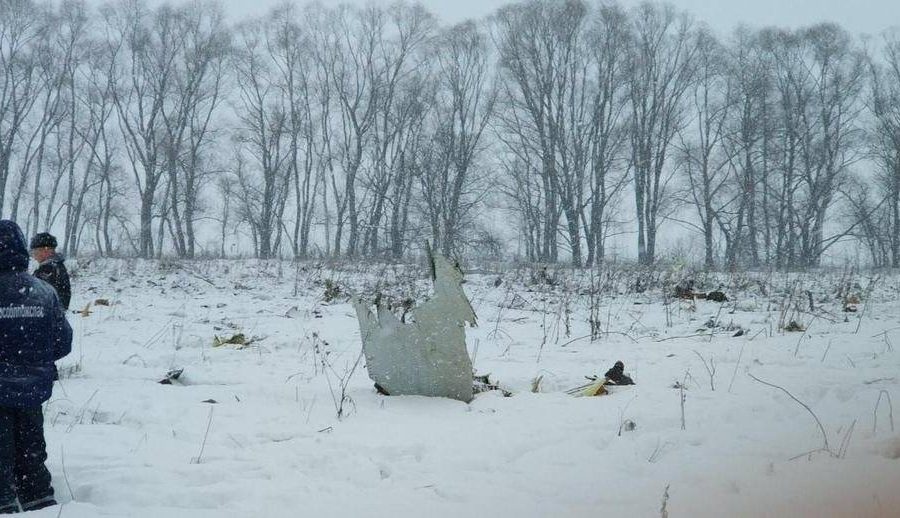
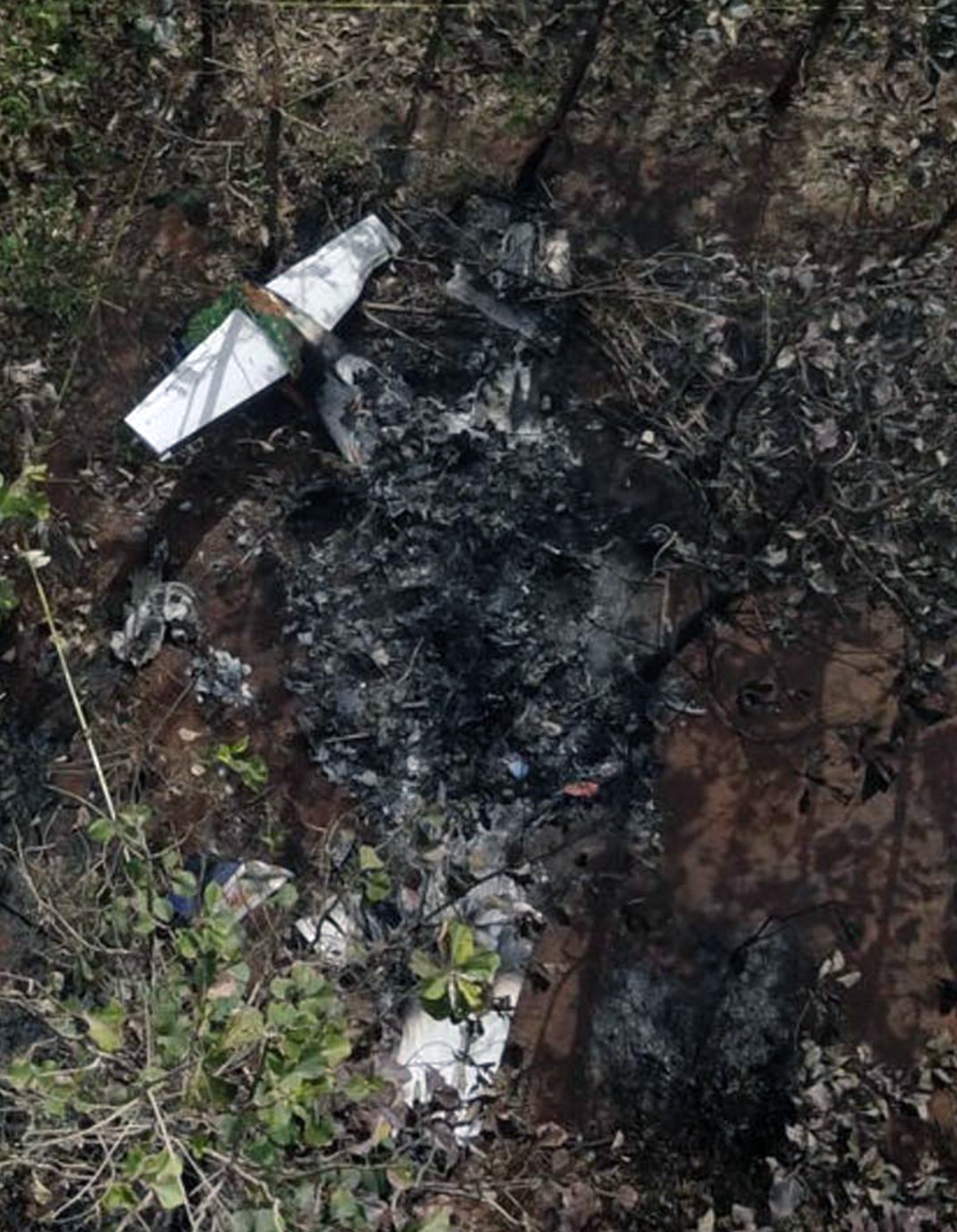
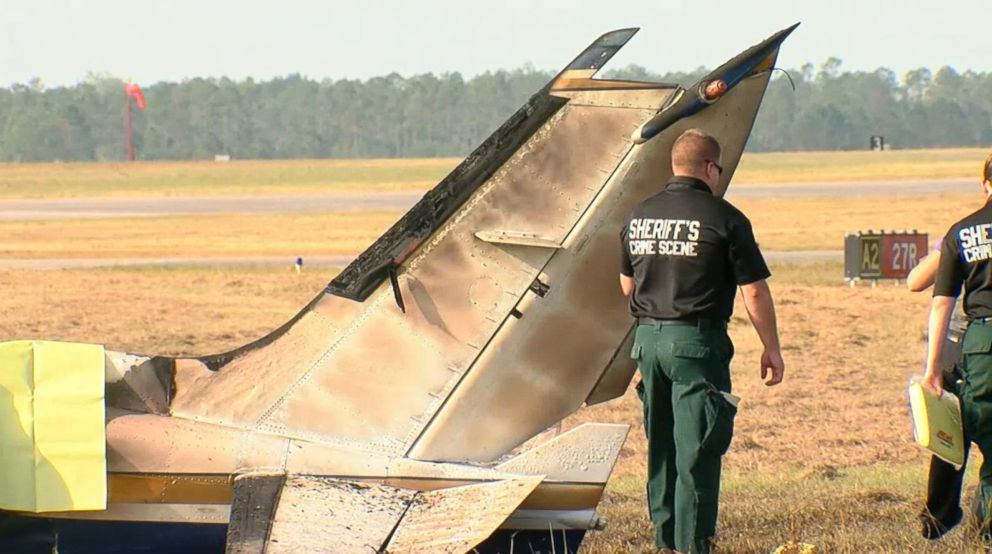
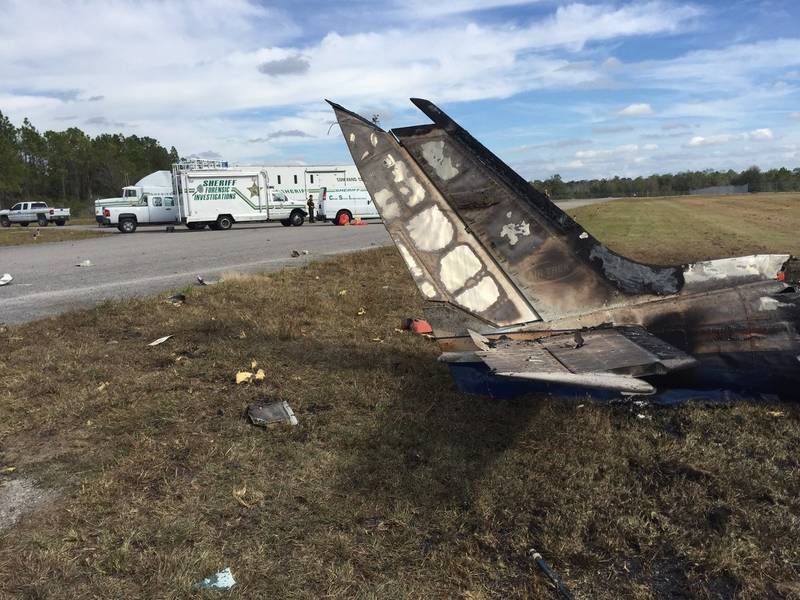
The twin engine aircraft departed runway 14R at Moscow-Domodedovo Airport at 1421LT. Six minutes later, while climbing to an altitude of 6,000 feet in light snow showers, the airplane descended then disintegrated in a snow covered field located in Argunovo, about 37 km southeast of the Airport, one minute later. The aircraft was totally destroyed and debris were scattered on more than one km. All 71 occupants were killed. Both recording systems have been recovered. A day after the crash, Russian Authorities confirmed that the aircraft was intact until the final impact with the ground. Preliminary reports indicates speed variations on all three ASI's three minutes after rotation. 50 seconds after the automatic pilot was disconnected, the airplane experienced vertical loads between 0,5 and 1,5 G. then pitched down to an angle of 35°. Five seconds prior to impact, the airplane banked right to 25°. Preliminary investigations shows that the incorrect data on ASI's was caused by icing of the Pitot tubes as the heating systems was off, apparently because the crew failed to activate it.
Probable cause:
The accident was the consequence of erroneous actions on part of the crew while climbing in instrument meteorological conditions at unreliable readings of instrument speed caused by icing (blockage with ice) of all three Pitot tubes. This caused the aircraft to become uncontrollable, enter a dive and eventually collide with the ground. The accident was then considered as a loss of control in flight (LOC-I). The investigation revealed systemic weaknesses in the identification of hazards and risk control, the inoperability of the airline's flight safety management system and the lack of control over the level of training of crew members by aviation authorities at all levels, which led to the issuance of certificates of aviation personnel and the admission to the flights of the crew, which did not fully meet the qualification requirements. The following contributing factors were reported:
- Hurry of the crew in preparation for the flight due to the late arrival of the aircraft from the previous flight and attempts to "catch up" with the time,
- Skipping by the crew of the operation to switch on the Pitot tube heating before takeoff and failing to comply with the section of the check list "BEFORE TAKE-OFF", which provides for the control of this action,
- Design features of the An-148 aircraft in terms of the restrictions on the duration of Pitot tube heating operation on the ground, which led to the need to carry out operations to control the inclusion of Pitot tube heating and compliance with the principle of "dark cockpit" in a separate section of the "BEFORE THE FLIGHT" check list, which is performed immediately before the start of the takeoff run, which creates additional risks of missing these operations. These actions are provided in the section "ON THE RUNWAY START",
- Systematic failure of the airline's crews to comply with the "dark cockpit" principle and the requirements of the radar, which contributed to "getting used" to the takeoff with the presence of emergency and warning messages on the Integrated system and alarm indicator (KISS) and did not allow to identify the fact that the Pitot tube heating was not included. In the accident flight before takeoff, six warning messages were displayed on the KISS, including three messages about the absence of Pitot tube heating,
- Design features of the An-148 aircraft, connected with the impossibility to disable the display of a number of warning messages on the KISS even when performing the whole range of works provided for by the MMEL while ensuring the flight with delayed defects,
- Low safety culture in the airline, which was manifested in: systematic failure to record in the flight log the failures detected during the flight, as well as in the performance of flights with the failures not eliminated and/or not included in the list of delayed failures, accompanied by the corresponding messages on the KISS,
- Failure to take necessary measures in case of detection of previous facts of untimely activation of Pitot tube heating by crews based on the results of express analysis of flight information,
- Unreadiness of the crew to take actions in case of triggering the alarm "Speed of Emergency" due to the lack of appropriate theoretical training in the airline and the impossibility to work out this special situation on the flight simulation device and / or during airfield training and, as a consequence, failure to comply with the procedures provided for after triggering of this alarm,
- Absence of federal aviation regulations for certification of flight simulators, the development of which is provided for by the Air Code of the Russian Federation,
- Approval for the existing AN-148 flight simulators of the IFC Training LLC and the CTC of the Saint-Petersburg State University of Civil Aviation without taking into account their actual capabilities to reproduce special flight cases, as well as the provisions of FAR-128,
- Absence of specific values of flight parameters (engine operation mode, pitch and roll angles, etc.) in the aircraft's flight manual, which must be maintained by the crew of the airspeed alarm system, as well as absence of the situation with unreliable instrument speed readings (Unreliable Airspeed Procedure) in the list of special flight cases,
- Increased psycho-emotional tension of crew members at the final stage of the flight due to inability to understand the causes of speed fluctuations and, as a consequence, the captain falling under the influence of the "tunnel effect" with the formation of the dominating factor of speed control according to the "own" (left) airspeed indicator without a comprehensive assessment of flight parameters,
- Insufficient training of pilots in the field of human factor, methods of threat and error control and management of crew resources,
- Individual psychological peculiarities of pilots (for the captain - reduction of intellectual and behavioral flexibility, fixation on their own position with the inability (impossibility) to "hear" prompts from the second pilot; for the second pilot - violation of the organization and sequence of actions), which in a stressful situation in the absence of proper level of management of the crew resources came to the fore; loss of the captain's psychological performance (psychological stupor, psychological incapacitation), which resulted in complete loss of spatial orientation and did not allow reacting to correct prompts and actions of the co-pilot, including when triggering the PULL UP warning of the EGPWS system,
- Absence of psychological incapacitation criteria in the airline's AFM, which prevented the second pilot from taking more drastic measures,
- High annual leave arrears for special conditions, which could lead to fatigue and negatively affect the performance of the captain,
- Operation of the aircraft control system in the longitudinal channel in the reconfiguration mode with unreliable signals of instrument speed, not described in the operational documentation, related to a double increase in the transfer coefficient from the hand wheel to the steering wheel in the flight configuration and constant deviation of the steering wheel for diving (without deviation of the steering wheel) for about 60 seconds, which reduced the time required for the crew to recognize the situation.
- Hurry of the crew in preparation for the flight due to the late arrival of the aircraft from the previous flight and attempts to "catch up" with the time,
- Skipping by the crew of the operation to switch on the Pitot tube heating before takeoff and failing to comply with the section of the check list "BEFORE TAKE-OFF", which provides for the control of this action,
- Design features of the An-148 aircraft in terms of the restrictions on the duration of Pitot tube heating operation on the ground, which led to the need to carry out operations to control the inclusion of Pitot tube heating and compliance with the principle of "dark cockpit" in a separate section of the "BEFORE THE FLIGHT" check list, which is performed immediately before the start of the takeoff run, which creates additional risks of missing these operations. These actions are provided in the section "ON THE RUNWAY START",
- Systematic failure of the airline's crews to comply with the "dark cockpit" principle and the requirements of the radar, which contributed to "getting used" to the takeoff with the presence of emergency and warning messages on the Integrated system and alarm indicator (KISS) and did not allow to identify the fact that the Pitot tube heating was not included. In the accident flight before takeoff, six warning messages were displayed on the KISS, including three messages about the absence of Pitot tube heating,
- Design features of the An-148 aircraft, connected with the impossibility to disable the display of a number of warning messages on the KISS even when performing the whole range of works provided for by the MMEL while ensuring the flight with delayed defects,
- Low safety culture in the airline, which was manifested in: systematic failure to record in the flight log the failures detected during the flight, as well as in the performance of flights with the failures not eliminated and/or not included in the list of delayed failures, accompanied by the corresponding messages on the KISS,
- Failure to take necessary measures in case of detection of previous facts of untimely activation of Pitot tube heating by crews based on the results of express analysis of flight information,
- Unreadiness of the crew to take actions in case of triggering the alarm "Speed of Emergency" due to the lack of appropriate theoretical training in the airline and the impossibility to work out this special situation on the flight simulation device and / or during airfield training and, as a consequence, failure to comply with the procedures provided for after triggering of this alarm,
- Absence of federal aviation regulations for certification of flight simulators, the development of which is provided for by the Air Code of the Russian Federation,
- Approval for the existing AN-148 flight simulators of the IFC Training LLC and the CTC of the Saint-Petersburg State University of Civil Aviation without taking into account their actual capabilities to reproduce special flight cases, as well as the provisions of FAR-128,
- Absence of specific values of flight parameters (engine operation mode, pitch and roll angles, etc.) in the aircraft's flight manual, which must be maintained by the crew of the airspeed alarm system, as well as absence of the situation with unreliable instrument speed readings (Unreliable Airspeed Procedure) in the list of special flight cases,
- Increased psycho-emotional tension of crew members at the final stage of the flight due to inability to understand the causes of speed fluctuations and, as a consequence, the captain falling under the influence of the "tunnel effect" with the formation of the dominating factor of speed control according to the "own" (left) airspeed indicator without a comprehensive assessment of flight parameters,
- Insufficient training of pilots in the field of human factor, methods of threat and error control and management of crew resources,
- Individual psychological peculiarities of pilots (for the captain - reduction of intellectual and behavioral flexibility, fixation on their own position with the inability (impossibility) to "hear" prompts from the second pilot; for the second pilot - violation of the organization and sequence of actions), which in a stressful situation in the absence of proper level of management of the crew resources came to the fore; loss of the captain's psychological performance (psychological stupor, psychological incapacitation), which resulted in complete loss of spatial orientation and did not allow reacting to correct prompts and actions of the co-pilot, including when triggering the PULL UP warning of the EGPWS system,
- Absence of psychological incapacitation criteria in the airline's AFM, which prevented the second pilot from taking more drastic measures,
- High annual leave arrears for special conditions, which could lead to fatigue and negatively affect the performance of the captain,
- Operation of the aircraft control system in the longitudinal channel in the reconfiguration mode with unreliable signals of instrument speed, not described in the operational documentation, related to a double increase in the transfer coefficient from the hand wheel to the steering wheel in the flight configuration and constant deviation of the steering wheel for diving (without deviation of the steering wheel) for about 60 seconds, which reduced the time required for the crew to recognize the situation.
Final Report: