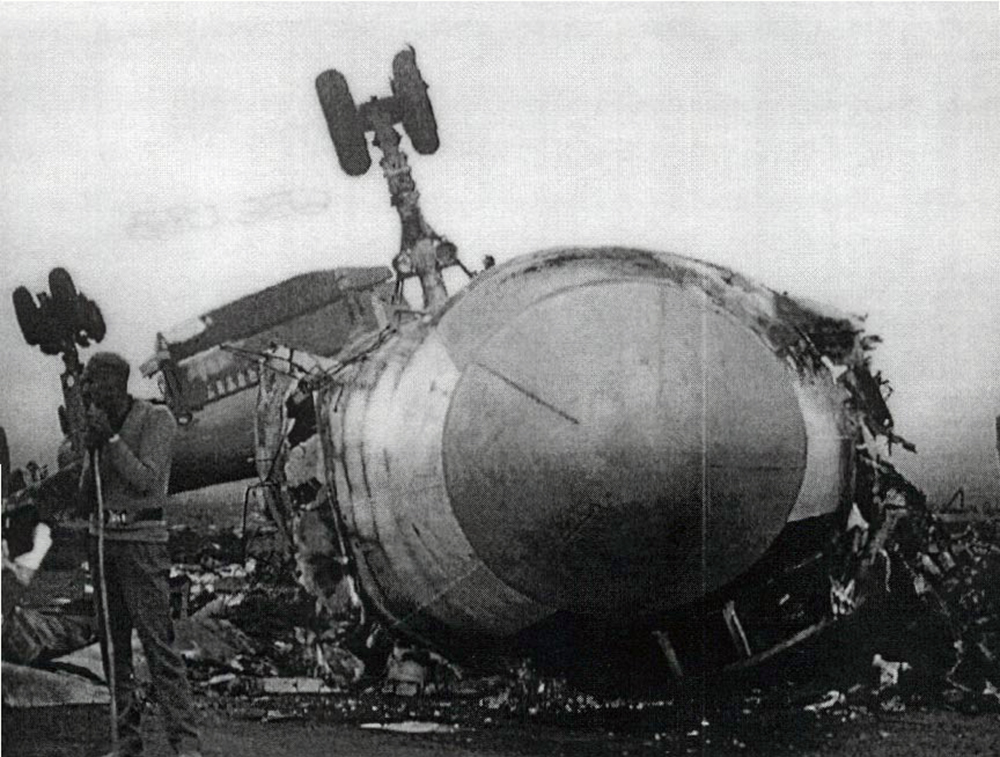
Crash of a Beechcraft A90 King Air in Marfa
Date & Time:
Jan 29, 1993 at 1940 LT
Registration:
N363N
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Houston - Marfa
MSN:
LJ-263
YOM:
1967
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
6
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
675.00
Aircraft flight hours:
6226
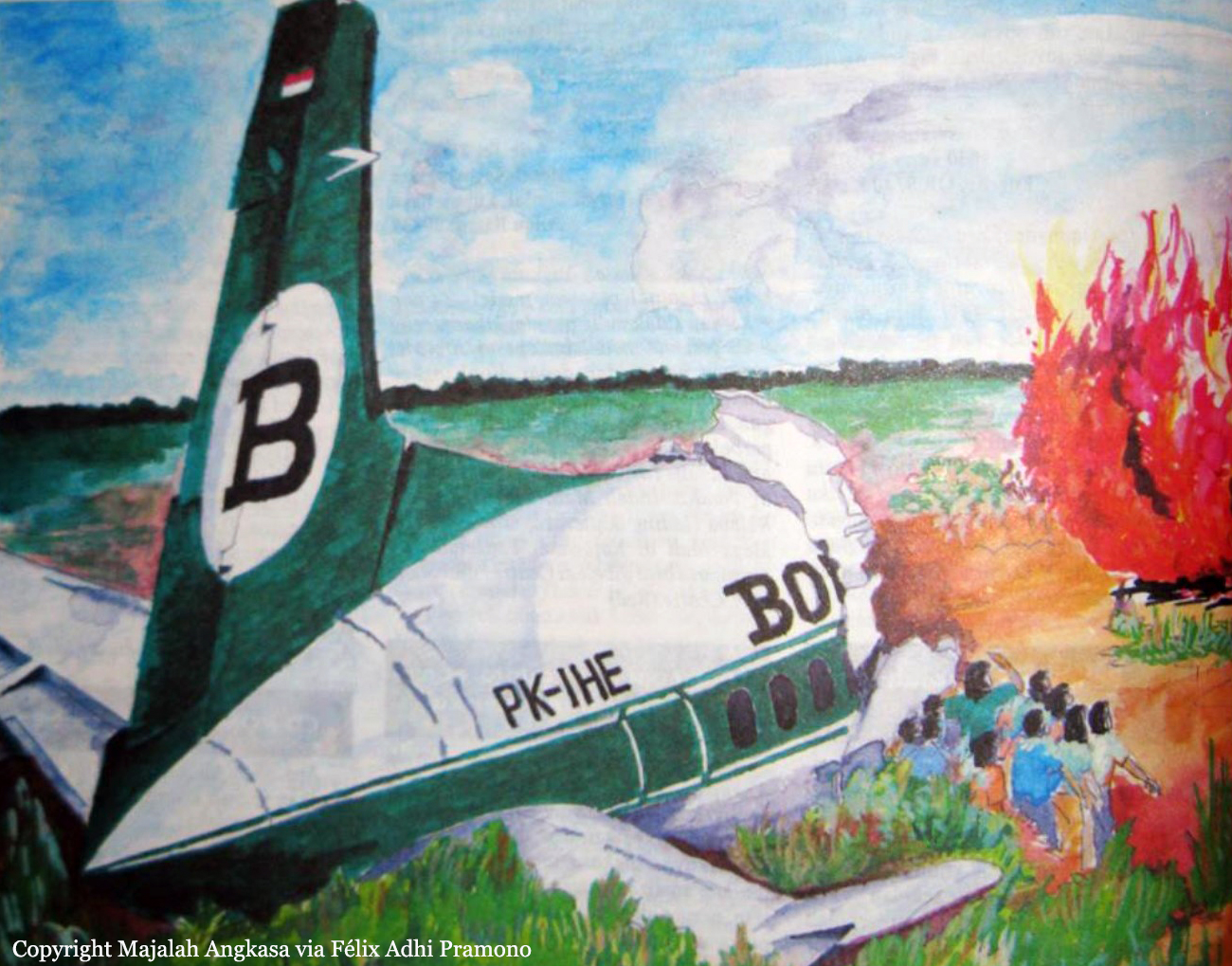
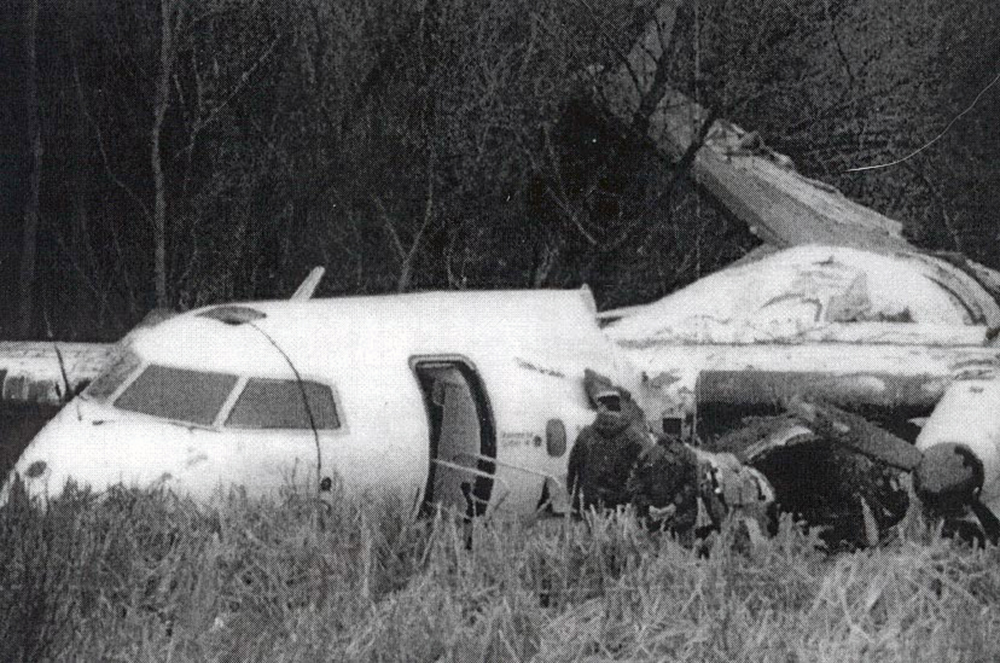
Circumstances:
During a dark night cross country in instrument meteorological conditions, the airplane was cleared for a VOR approach to runway 30. Due to unfavorable winds, the pilot elected to circle to land on runway 12. While on a right downwind, visual contact with the runway was lost and not reestablished. The pilot continued the descent on the base leg and impacted the terrain in a slight right turn.
Probable cause:
The pilot's continued descent below the proper altitude. Factors were the dark night, fog, and the crew's poor coordination.
Final Report: