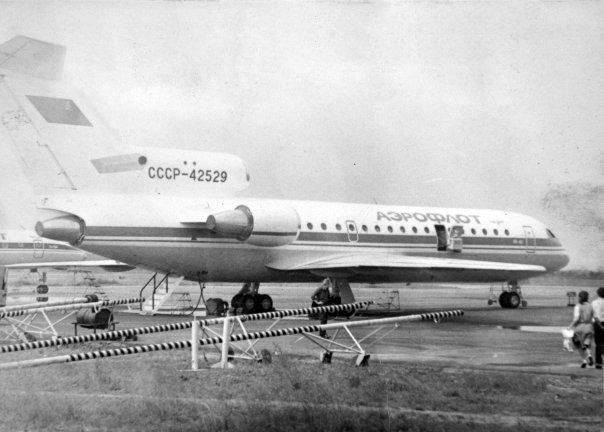
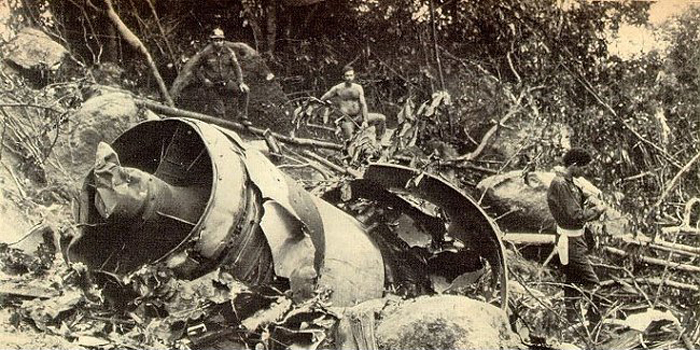
Crash of a Yakovlev Yak-42 in Verbovichi: 132 killed
Date & Time:
Jun 28, 1982 at 1051 LT
Registration:
CCCP-42529
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Leningrad - Kiev
MSN:
11 04 01 04
YOM:
1981
Flight number:
SU8641
Crew on board:
8
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
124
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
132
Aircraft flight hours:
795
Aircraft flight cycles:
496
Circumstances:
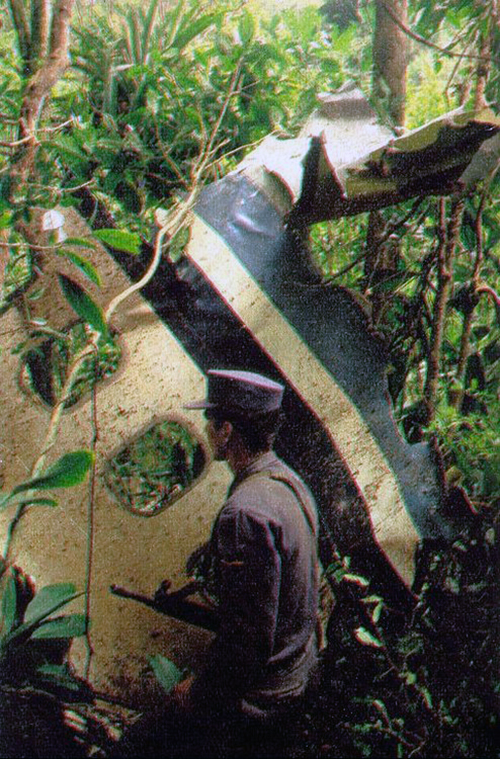
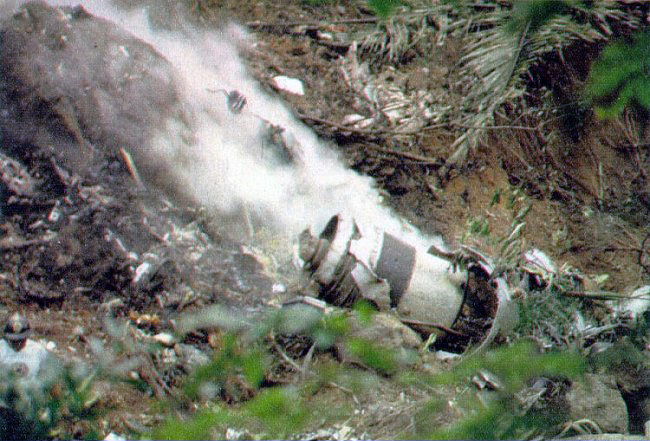
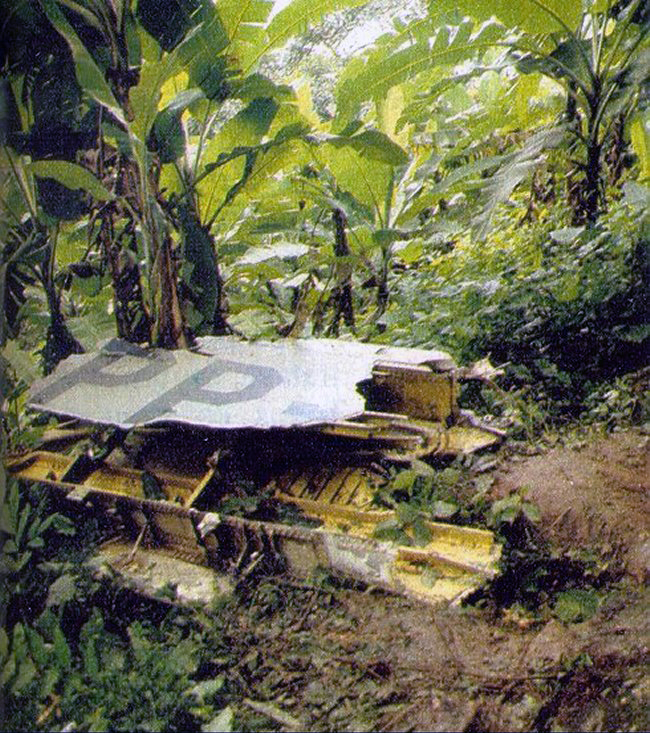
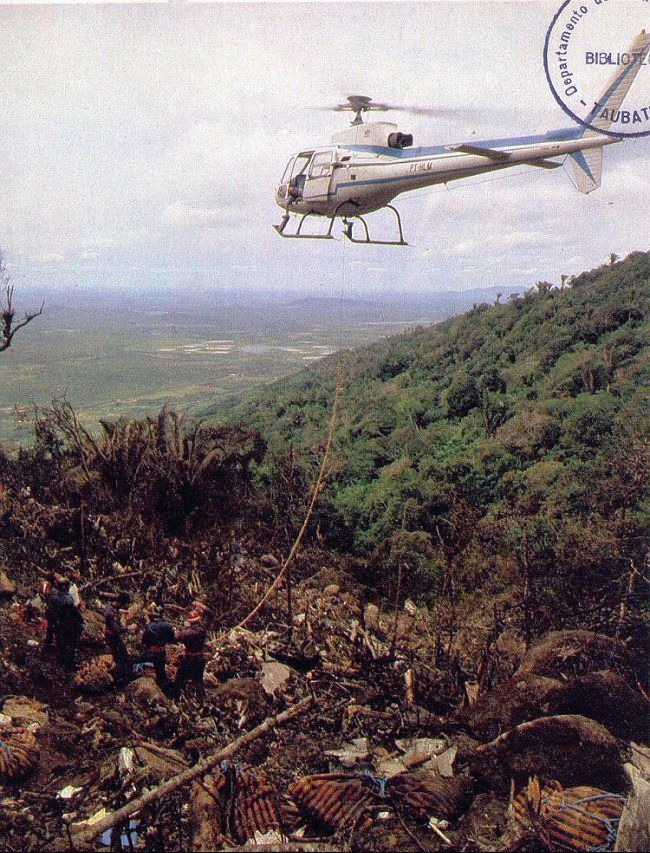
Enroute from Leningrad to Kiev, the crew was cleared to descend from 9,000 to 7,800 meters in order to avoid a thunderstorm area. Few minutes later, the three engine aircraft entered a dive. During an uncontrolled descent, the aircraft lost several elements then partially disintegrated and eventually crashed at a speed of 810 km/h in fields and wooded areas. A huge crater was found at the point of impact, near the village of Verbovichi, and debris scattered all around on an area of 22,7 km2 (6,5 km long and 3,5 km wide). The accident was not survivable.
Probable cause:
It was determined that the crew lost control of the airplane after the jackscrew connected to the stabilizers mechanism failed due to an abnormal wear and also a structural imperfection of its mechanism. This caused the stabilizers to move down and to remain blocked in the down position. Despite several attempts, the crew was unable to regain control of the aircraft. Aerodynamic forces caused few elements of the airplane to brake off as they exceeded their certification. Investigations revealed that it was not possible for those in charge of the Yak-42 maintenance to detect the jackscrew abnormal wear because of an incomplete maintenance program. Similar problems were found on other Yak-42 and its certificate of airworthiness was suspended during investigations. Following modifications and updates, the Yak-42 came back into service at the end of the year 1984.