Circumstances:
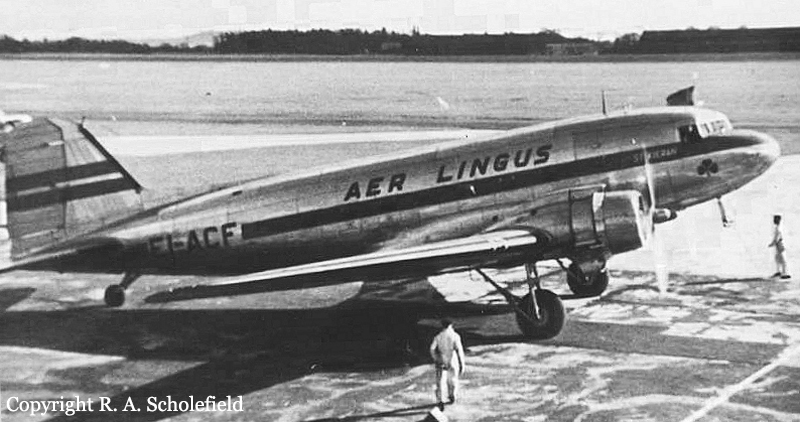
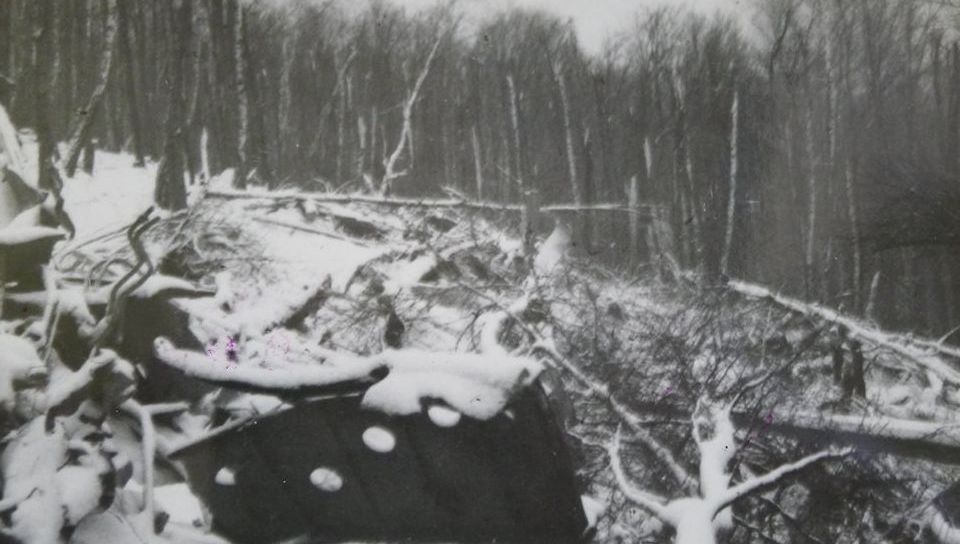
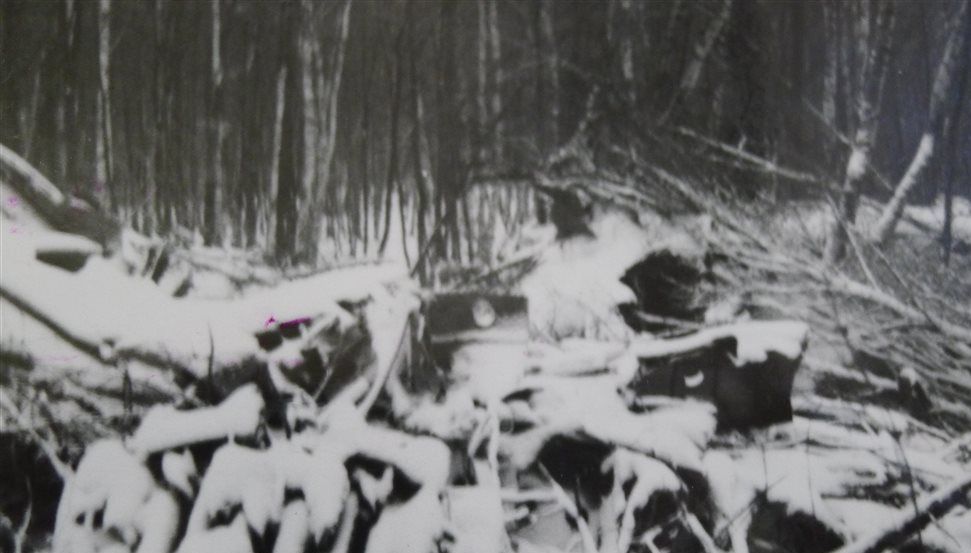
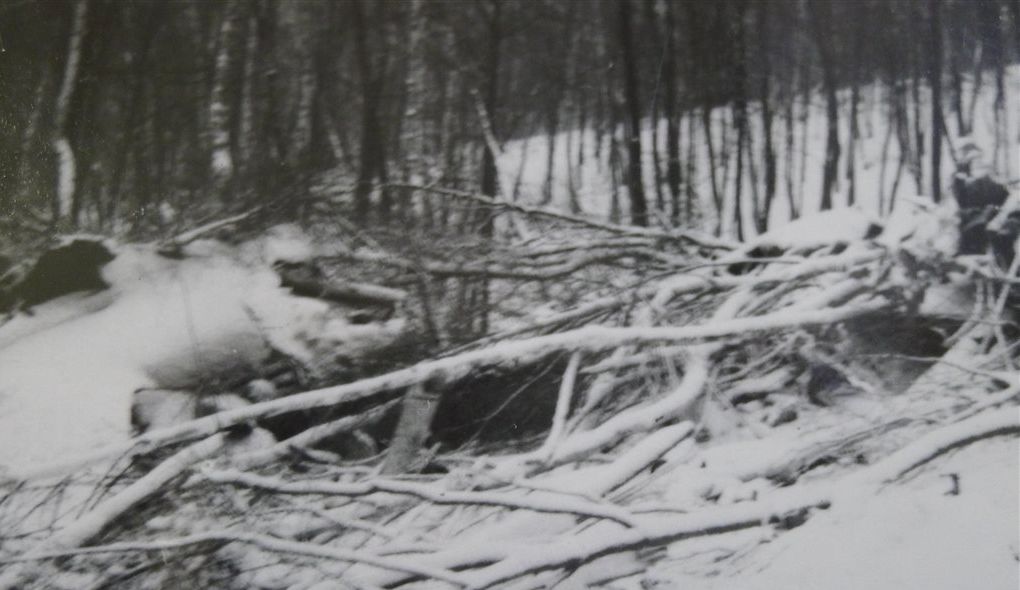
The flight departed Washington National Airport, Washington, D. C., at 0007 EST, April 13, with 12 passengers and crew consisting of Captain L. T. Brannan, Copilot O. T. Thorson, and Stewardess A. Long. At Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, 10 additional passengers plus relief crew Captain A. J. Lerette and Copilot W. E. Harshman boarded the aircraft. These pilots were deadheading to Fargo, North Dakota, where they were to relieve the other pilots. The destination for all passengers was Seattle, Washington. The flight stopped at Cleveland, Ohio, for fuel and oil and arrived at Chicago at 0735 CST. Shortly after takeoff at Chicago, the flight returned owing to rough operation of the left engine. The left magneto of this engine was replaced by a spare carried on the aircraft and the flight again departed at 1215 CST for Minneapolis, made a fuel stop there, and arrived at Fargo, North Dakota, at 16140 CST. Captain Brannan and Copilot Thorson left the flight at this point. One of the relief pilots inquired about the availability of an engine mechanic, stating that one of the engines was spitting and coughing. When he was told it would take about 15 minutes to get a mechanic, he said to disregard it. The left engine started with some difficulty. The flight departed Fargo at 1748 CST and made fuel stops at Billings, Montana, and Felts Field, Spokane, Washington. The pilots did not report any mechanical difficulties over this segment. The flight departed Spokane at 0035, April 14, on an IFR flight plan via Green Airway 2,5,000 feet to Ephrata, Washington, 7,000 feet to Ellensburg, Washington, and 8,000 feet to Seattle. Routine position reports were made, the last being over Ellensburg at 0143 and climbing to 8,000 feet from 7,000. At approximately 0200 the Seattle ARTC Center heard a call on 120.3 mega-cycles from an unidentified aircraft which was believed to be N 657143, advising that estimated time of arrival at Seattle was 0227 and that the aircraft was standing by on Boeing Field Tower frequency (118.3 megacycles). At 0207 the pilot of N 65743 reported an engine failure and requested further clearance. Seattle Center advised the aircraft to contact Seattle Approach Control or Boeing Tower as soon as practicable and cleared at to cross Seattle at or above 4,000, no delay expected. Later transmissions from the aircraft were on Boeing Field Tower frequency, rather than the Approach Control frequency of 119.5 megacycles. Signals from the aircraft were weak and difficult to read by both Approach Control (located in the Seattle-Tacoma Tower) and by the Boeing Field Tower. However, Approach Control had less difficulty than Boeing Field Tower in hearing the aircraft on 118.3 megacycles, so the controller cooperated with Boeing Tower in furnishing them with the content of messages through interphone. The pilot could apparently hear Boeing Tower, but not Approach Control. At 0214, Approach Control heard the pilot of N 65743 report that he was icing up and losing altitude. The flight was cleared for an approach to Boeing Field by the Boeing Field controller upon instructions from Approach Control, and was given current Seattle weather conditions. The last transmission from the aircraft was received at 0222, reporting that the flight was at 4,800 feet. Search and rescue activities were instituted shortly thereafter. Two crew members and five passengers were killed while 18 others were rescued. The aircraft was destroyed.
Probable cause:
The Board determines that the probable cause of this accident was the progressive failure of both engines, due to the lack of compliance with proper maintenance standards. The following findings were pointed out:
- The flight returned to Chicago a few minutes after departure owing to malfunction of the left engine, and the left magneto was changed; this magneto was later found to be in a satisfactory condition,
- Although engine malfunctions were again experienced while en route west of Chicago, the pilots failed to have the difficulties corrected,
- First one engine, then the other, progressively failed while the flight was on its last route segment, resulting in a crash in the Cascade Mountains,
- There was evidence that detonation and preignition took place in both engines and that they ultimately failed as a result of master rod bearing failures,
- Spark plugs in both engines had been operated beyond their normal maintenance inspection period and exhibited evidence of a condition conducive to detonation and preignition.