Circumstances:
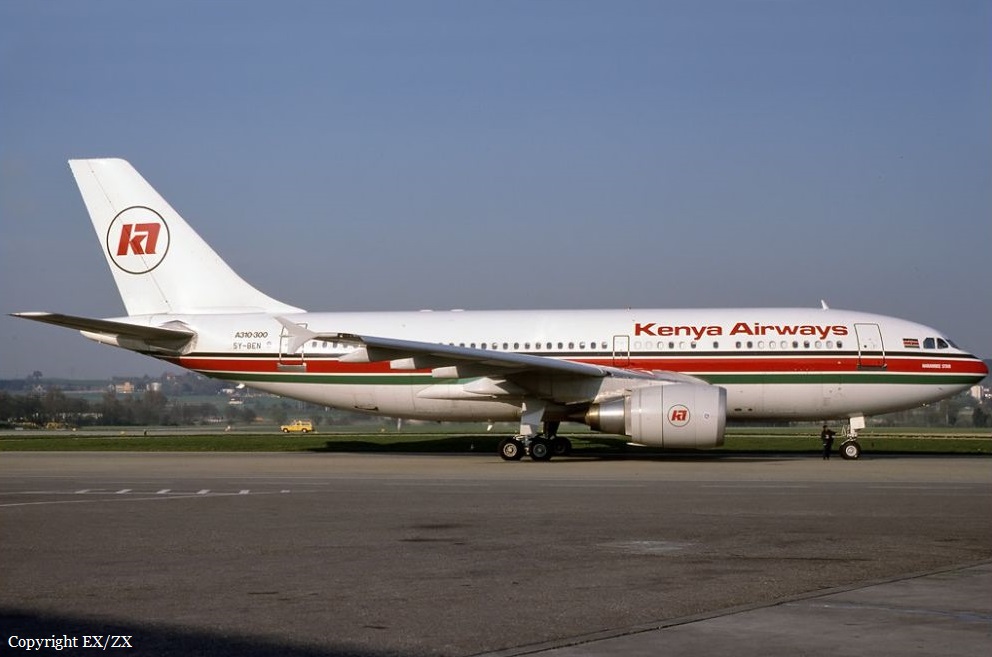
On Sunday 30 January 2000, the Kenya Airways Airbus 310-304, registered 5Y−BEN, was undertaking the scheduled international flight KQ 431 transporting passengers from Abidjan to Nairobi, via Lagos. On board there were 10 crewmembers and 169 passengers. On the same day, in the afternoon, 5Y-BEN had flown in from Nairobi and landed at Félix Houphouët-Boigny International Airport in Abidjan at 15 h 15. The unfavorable meteorological at Lagos had obliged the pilot, after a thirty minutes hold at Lagos, to divert to Abidjan. The relief crew, which had arrived two days previously on flight KQ 430 on Friday 28 January 2000, at 15 h 44, took over on board 5Y-BEN, to undertake flight KQ 431 from Abidjan to Nairobi, via Lagos. Departure was scheduled for 21 h 00, in accordance with the initial program. The copilot was pilot flying, the Captain was pilot not flying. At 20 h 55 min 22 s, the crew established contact with Abidjan Airport control tower and asked for start-up clearance. This was granted. At 20 h 56 min 09 s, the Captain ordered the checklist to be performed and announced the type of take-off by saying "Flex sixty" at 20 h 56 min 19 s. At 21 h 00 min 18 s, three minutes and nineteen seconds after the start-up of the first engine (engine n° 2), the Captain announced over the interphone that linked him with the ground mechanic “we have two normal start-ups”. At 21 h 01 min 07 s, the crew of 5Y-BEN asked for clearance to taxi. The tower controller put them on standby. A few seconds later, he cleared them to taxi. At 21 h 02 min 33 s, the Captain ordered the Copilot to set the flaps at 15°. Later, at 21 h 04 min 50 s , the copilot announced "trim: 0.9 nose up, Slats/flaps 15/15". The airplane began to taxi at 21 h 07 min 35 s, the tower controller informed the crew of the latest wind, cleared them to take off and asked the crew the call back when they reached flight level 40. At 21 h 07 min 45 s, the copilot read back the clearance. This was the last communication between the crew and the control tower. At 21 h 08 min 08 s, the copilot announced "Take-off checklist completed … cleared for take-off". At 21 h 08 min 18 s, the Captain applied take-off power and announced "thrust, SRS, and runway" then, nine seconds later “100 knots”. At 21 h 08 min 50 s, the Captain announced "V1 and Rotate(4)", then two seconds later "Positive". The airplane took off. At 21 h 08 min 57 s, the copilot announced "Positive rate of climb, gear up". Less than two seconds later the stall warning sounded. At 21 h 09 min 07 s, the automatic call out (AC) announced 300 feet. At 21 h 09 min 14 s, the copilot asked "what’s the problem?". From 21 h 09 min 16 s, the AC announced successively 200, 100, 50, 30, 20 and 10 feet. Meanwhile, at 21 h 09 min 18 s, the copilot ordered the aural warning to be cut. Two seconds later, the GPWS sounded the “Whoop...” alarm followed, a half a second later, by the AC announcement of 50 feet. At 21 h 09 min 22 s, an aural master warning started, immediately followed by an order from the Captain to climb: "Go up!", though this was preceded six tenths of a second by the AC announcement of 10 feet. At 21 h 09 min 23.9 s, end of the master warning, followed immediately within a tenth of a second by the noise of the impact. The time of the accident is presumed to be 21 h 09 min 24 s.
Probable cause:
The Commission of Inquiry concluded that the cause of the accident to flight KQ 431 on 30 January 2000 was a collision with the sea that resulted from the pilot flying applying one part of the procedure, by pushing forward on the control column to stop the stick shaker, following the initiation of a stall warning on rotation, while the airplane was not in a true stall situation. In fact, the FCOM used by the airline states that whenever a stall warning is encountered at low altitude (stick shaker activation), it should be considered as an immediate threat to the maintenance of a safe flight path. It specifies that at the first sign of an imminent stall or at the time of a stick shaker activation, the following actions must be undertaken simultaneously: thrust levers ion TOGA position, reduction of pitch attitude, wings level, check that speed brakes are retracted. The investigation showed that the pilot flying reduced the pitch attitude but did not apply TOGA thrust on the engines. The investigation was unable to determine if the crew performed the other two actions: leveling the wings and checking that the speed brakes were retracted.
The following elements contributed to the accident:
• the pilot flying’s action on the control column put the airplane into a descent without the crew realizing it, despite the radio altimeter callouts;
• the GPWS warnings that could have alerted the crew to an imminent contact with the sea were masked by the priority stall and overspeed warnings, in accordance
with the rules on the prioritization of warnings;
• the conditions for a takeoff performed towards the sea and at night provided no external visual references that would have allowed the crew to be aware of the
direct proximity of the sea.