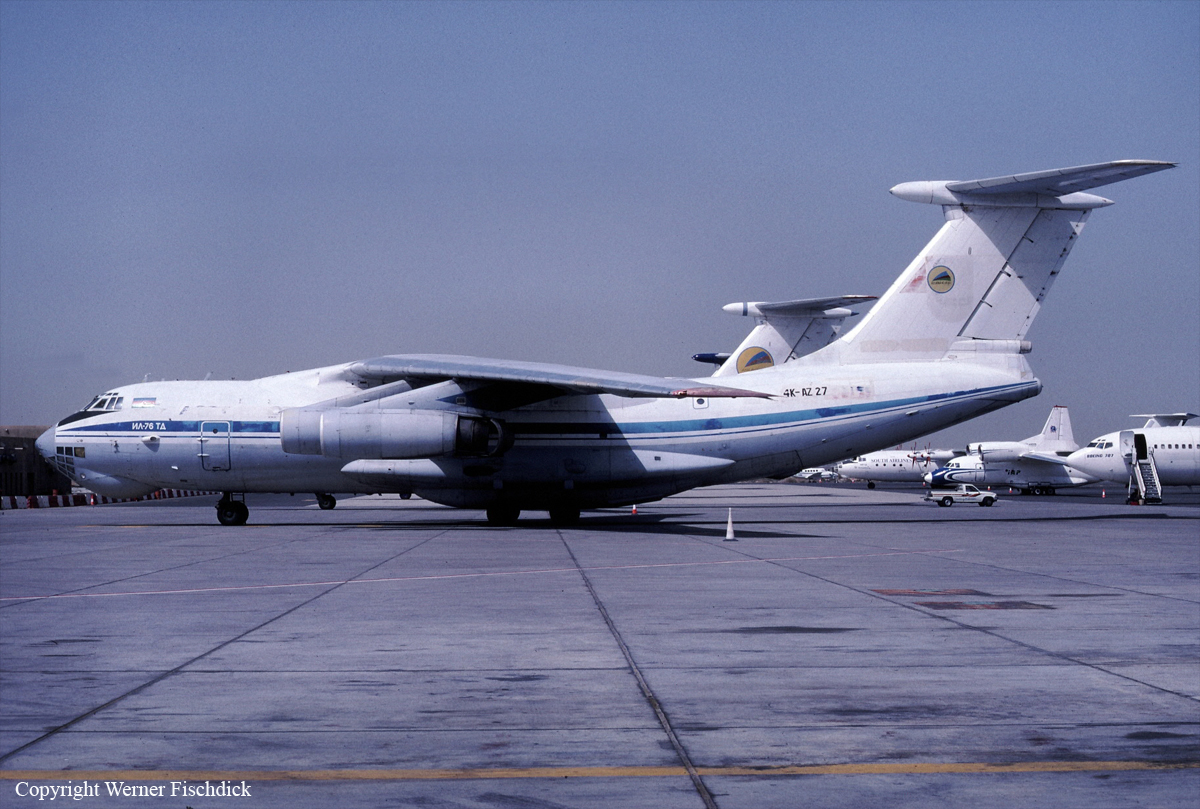
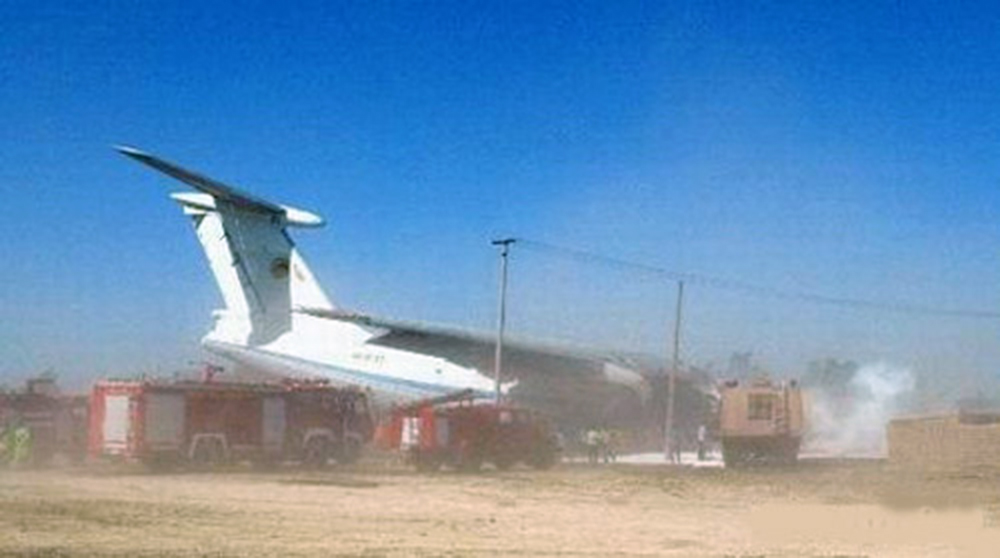
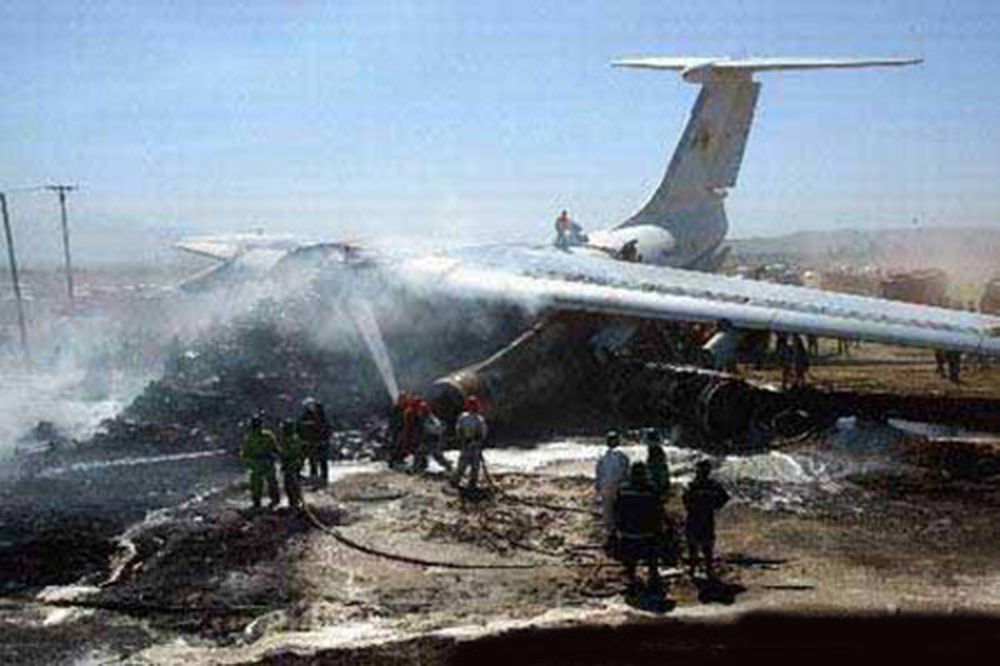
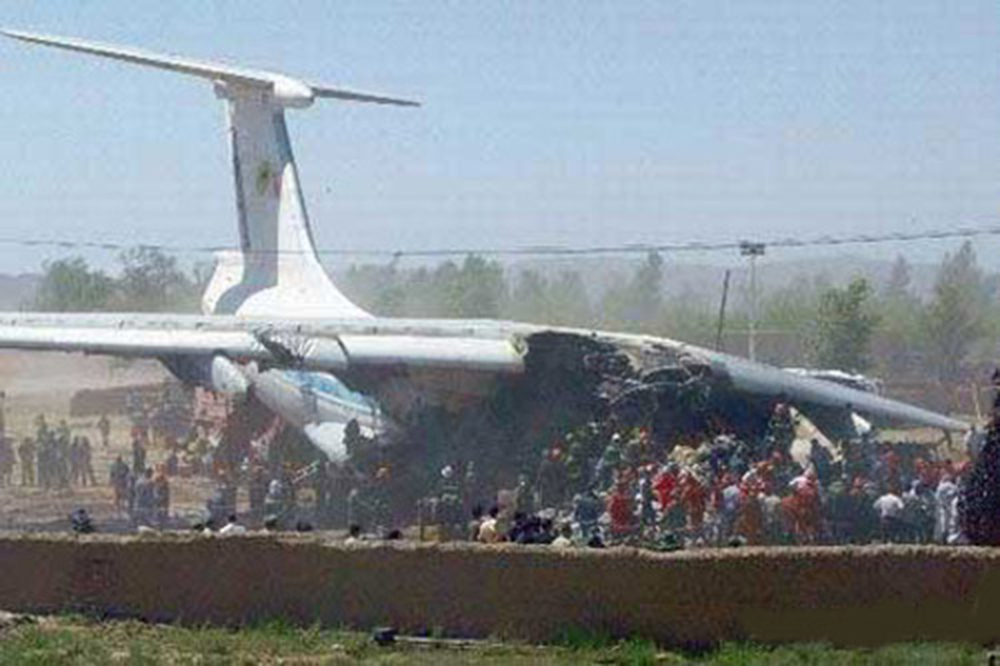
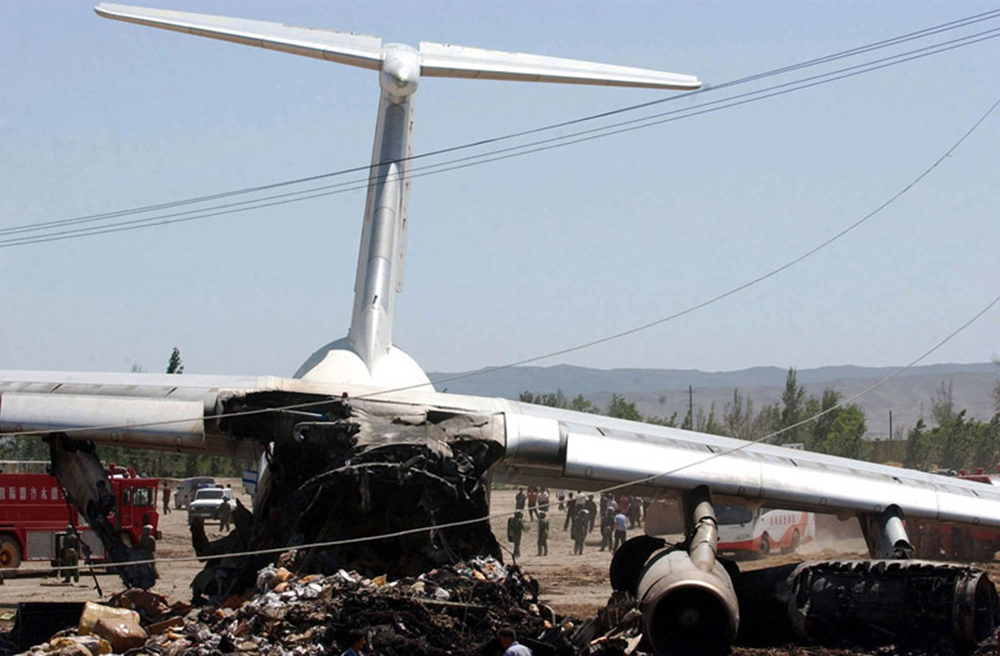
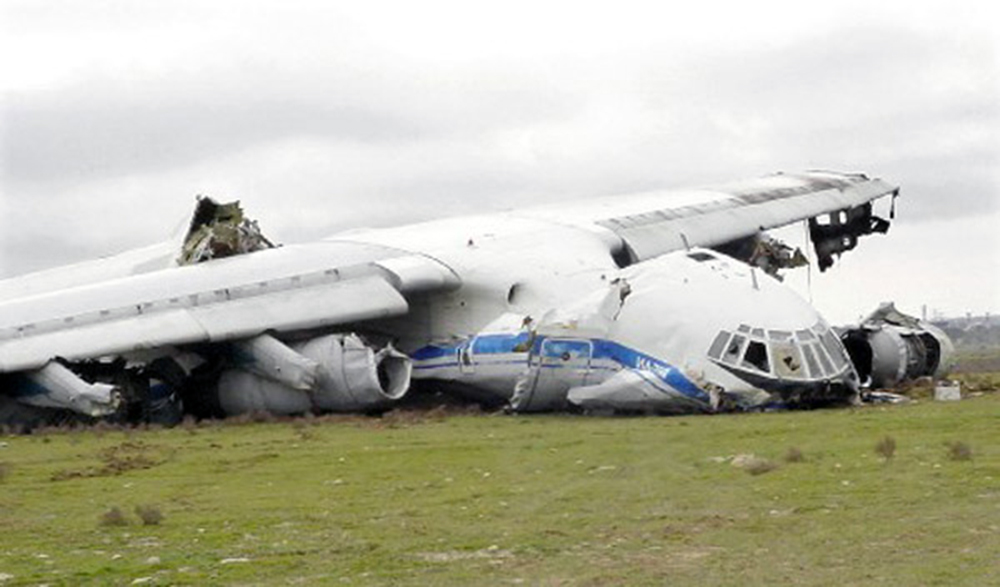
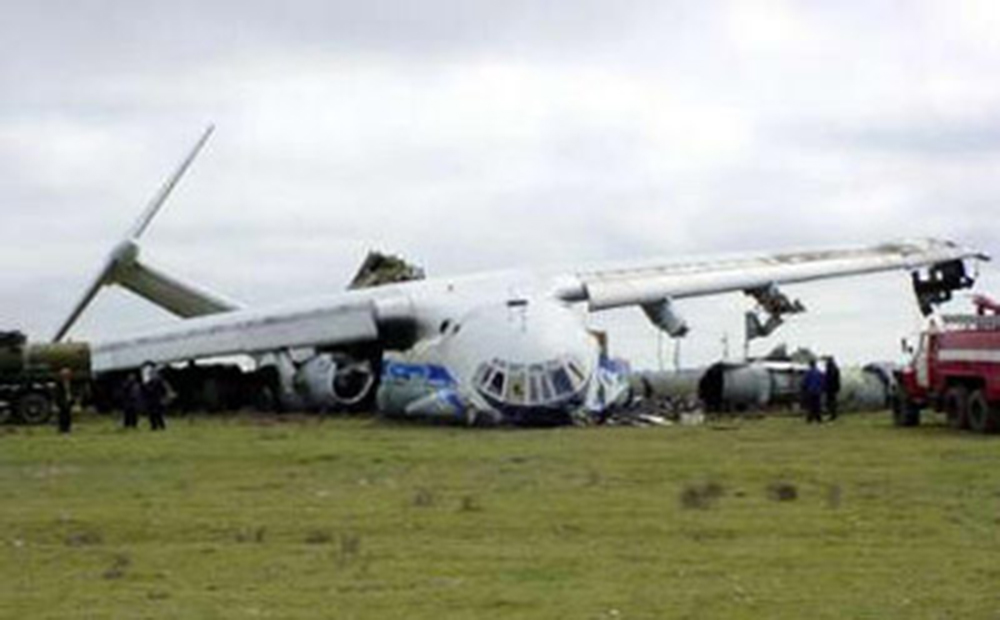
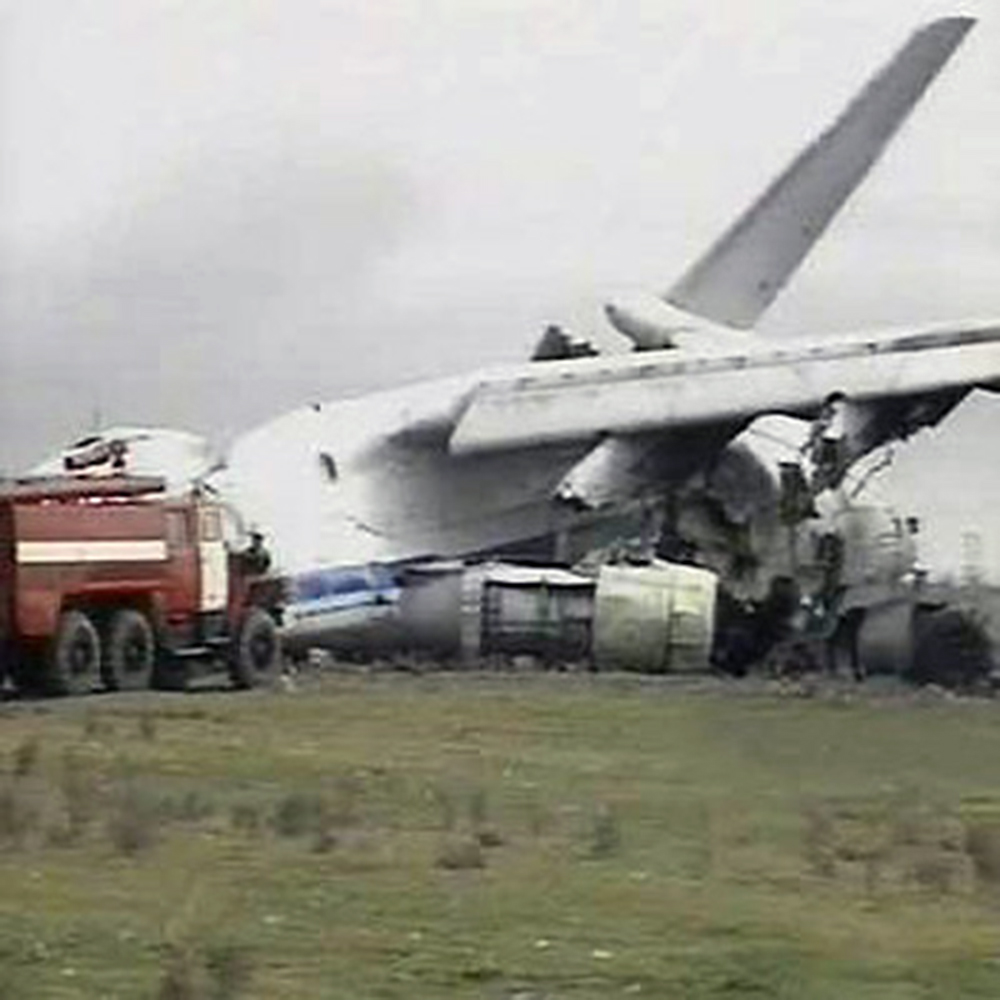
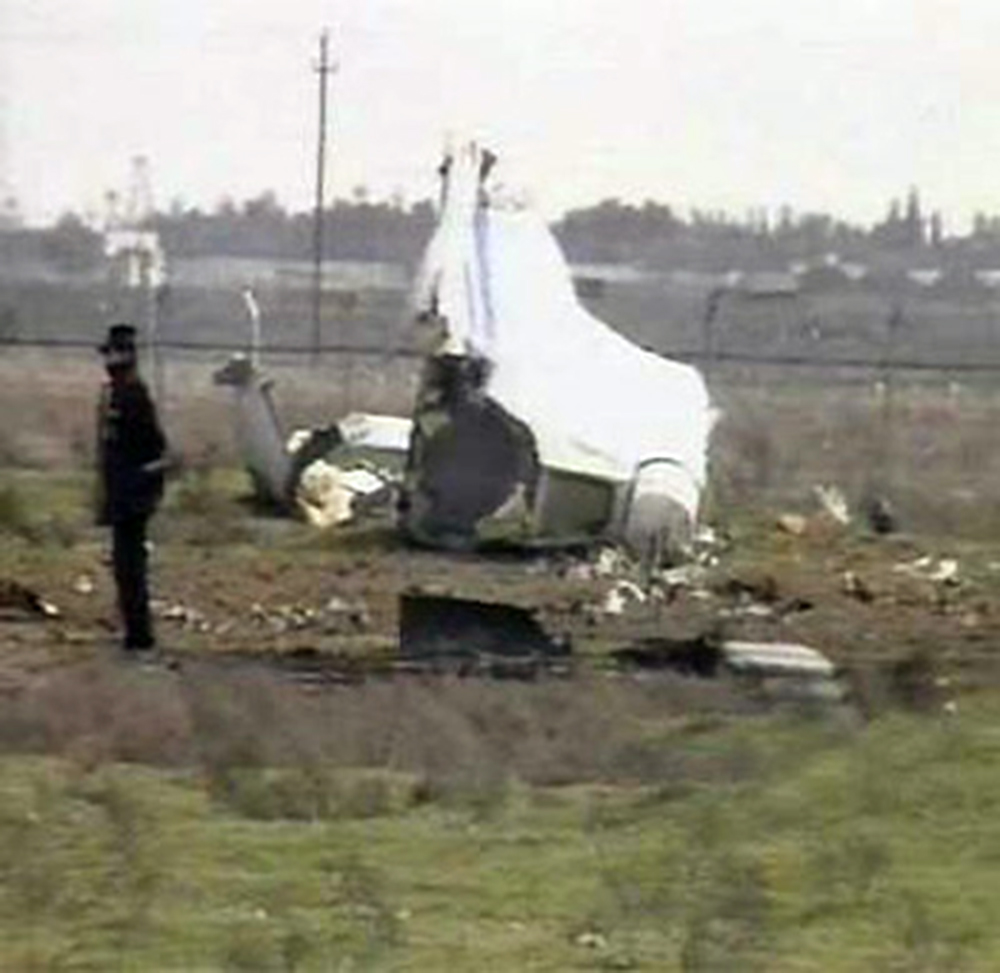
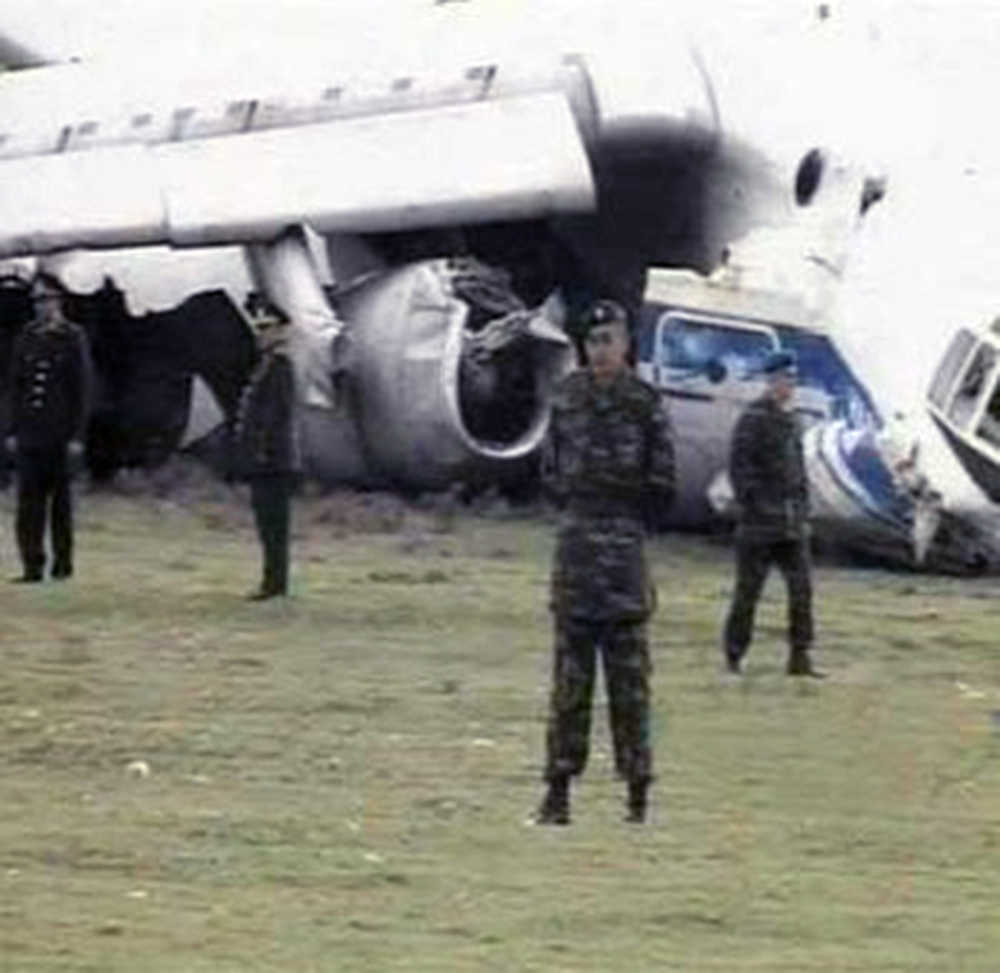
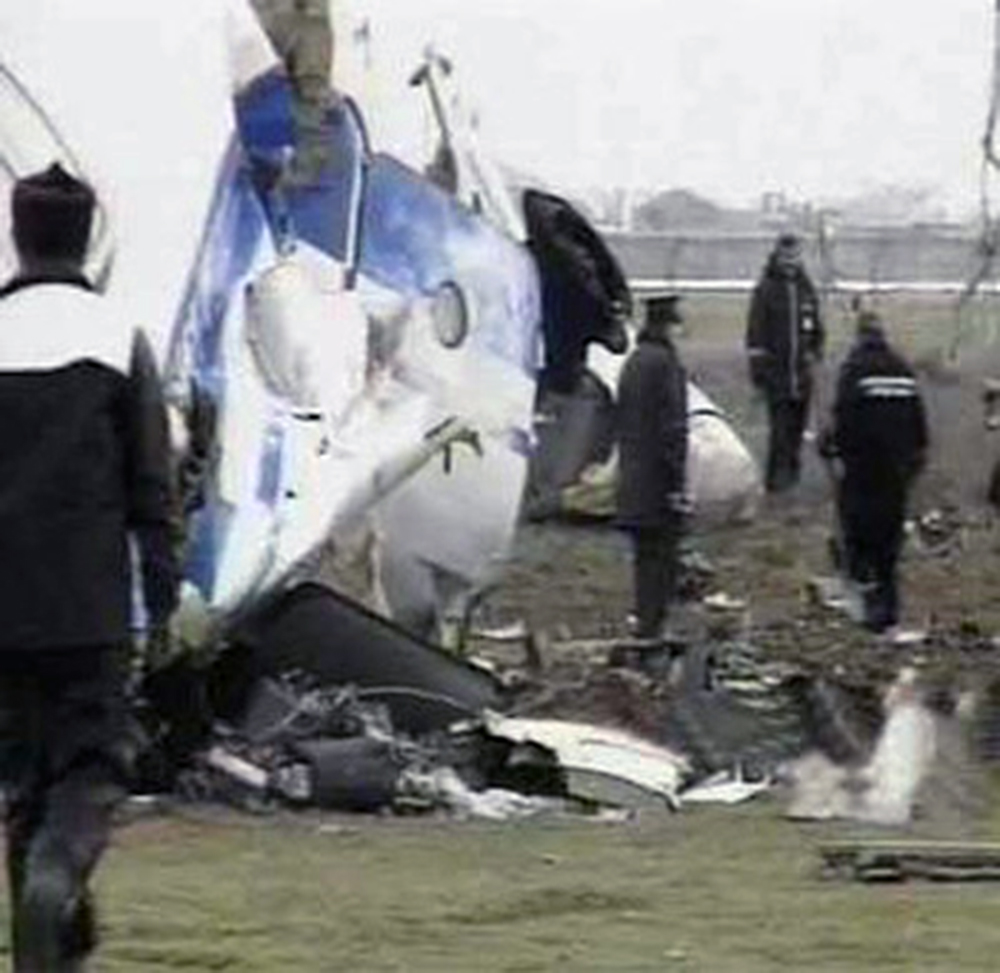
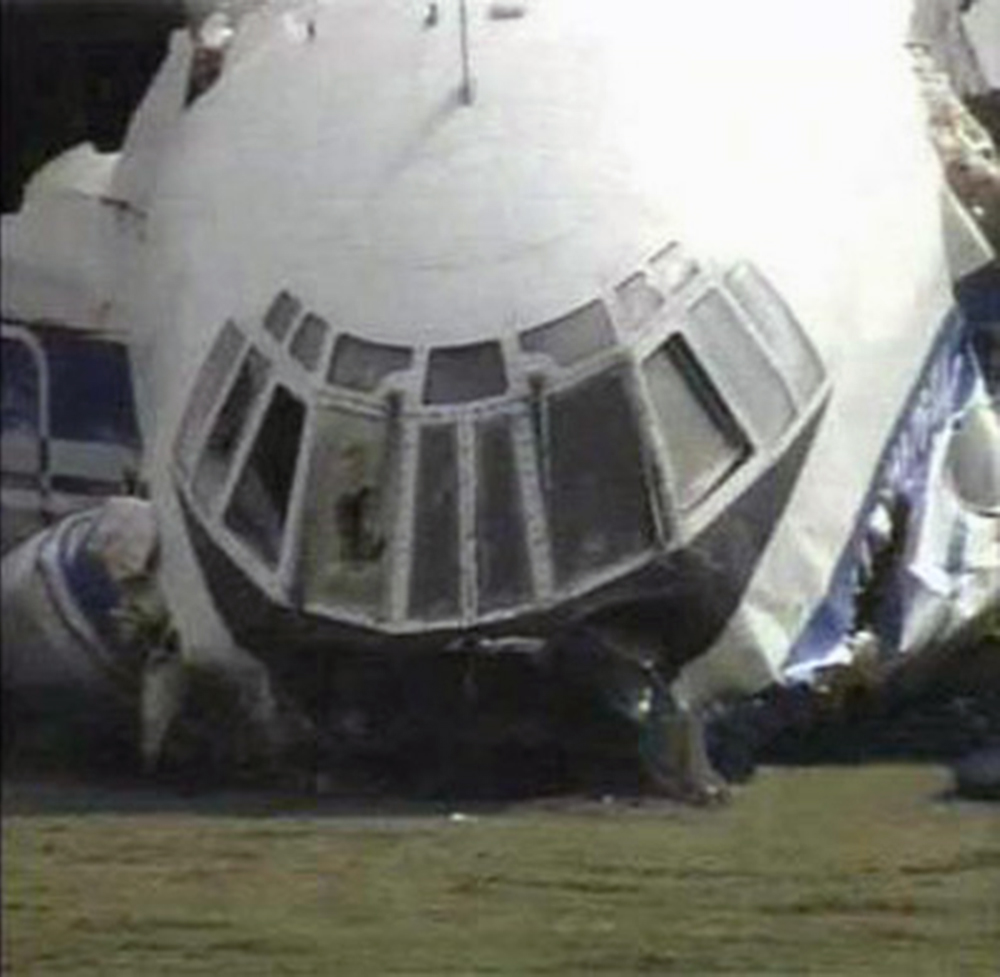
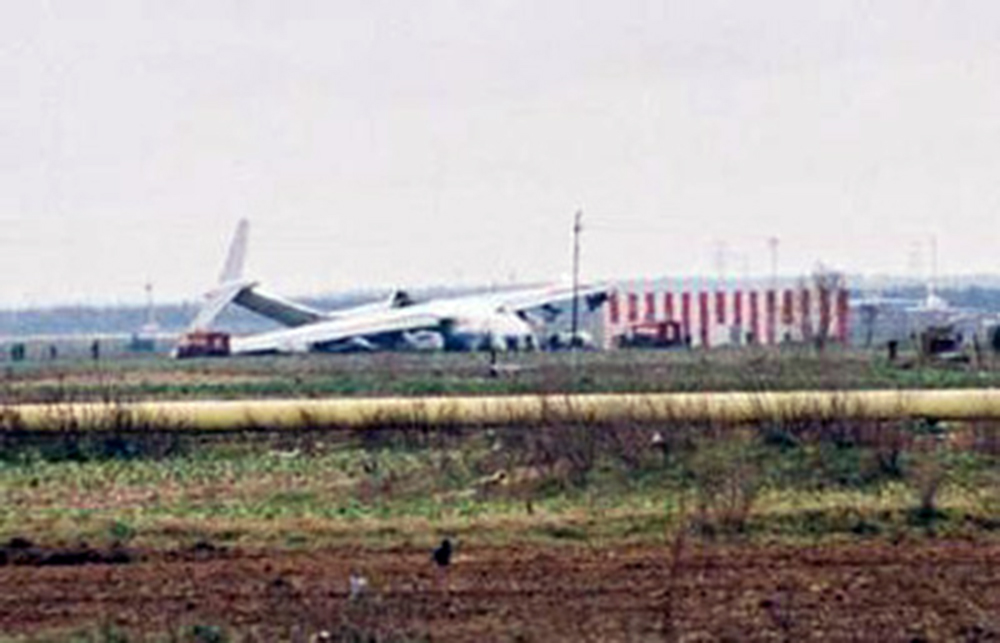
Crash of an Ilyushin II-76TD in Ürümqi: 7 killed
Date & Time:
May 18, 2004 at 1050 LT
Registration:
4K-AZ27
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Taiyuan – Ürümqi – Baku – Riga
MSN:
00534 60827
YOM:
1985
Crew on board:
7
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
7
Circumstances:
The aircraft was completing a cargo flight from Taiyuan to Riga with intermediate stops in Ürümqi and Baku, carrying seven crew members and a load of clothes. Two minutes after takeoff, while climbing, the aircraft stalled and crashed near a farm located 10 km from the airport. The aircraft was partially destroyed by impact forces and a post crash fire and all seven occupants were killed. Weather conditions were good at the time of the accident with a wind from 170 at 36 km/h.