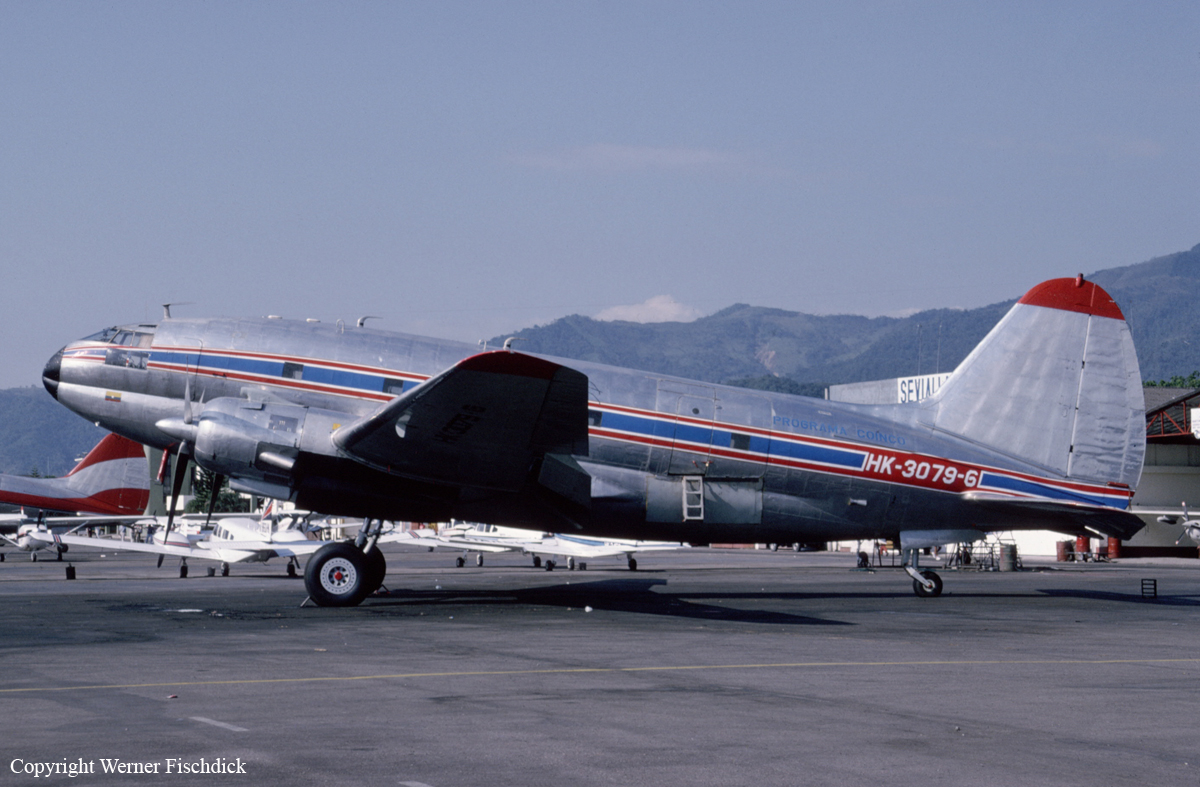
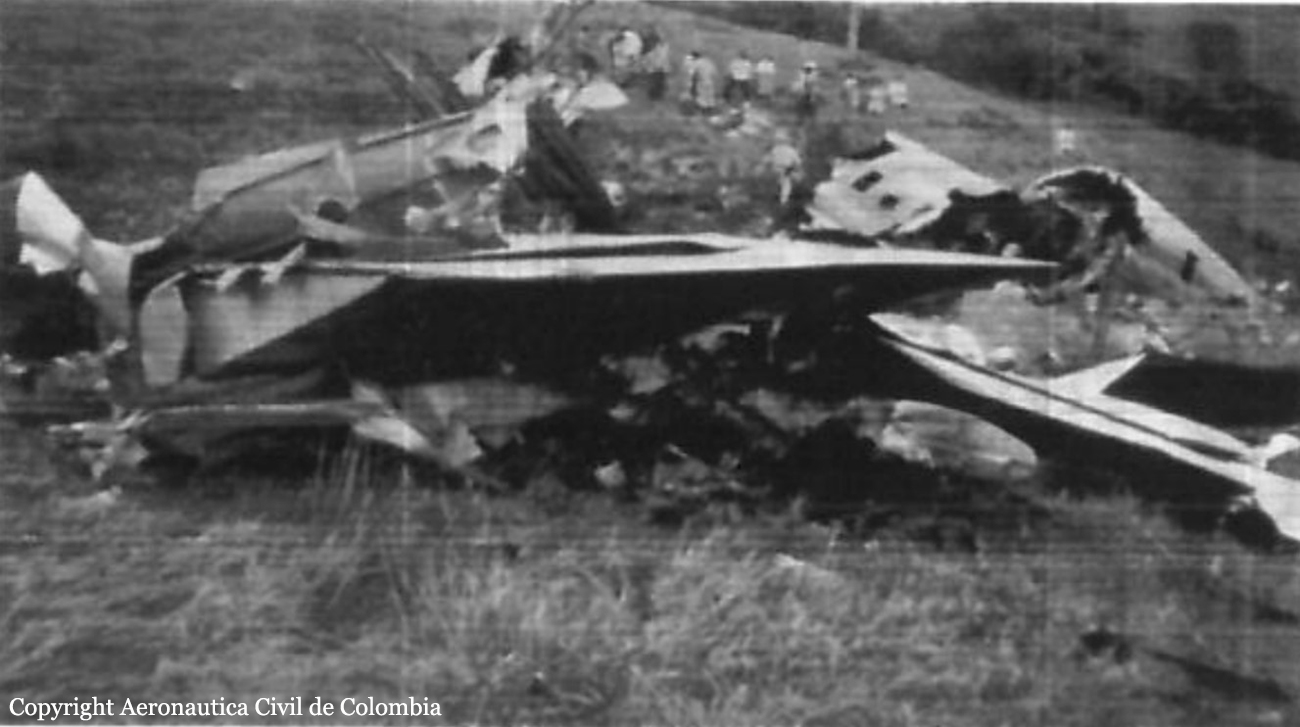
Crash of a De Havilland DHC-8-102 in Palmerston North: 4 killed
Date & Time:
Jun 9, 1995 at 0925 LT
Registration:
ZK-NEY
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Auckland - Palmerston North
MSN:
055
YOM:
1986
Flight number:
AN703
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
18
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
4
Captain / Total hours on type:
273.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
341
Aircraft flight hours:
22154
Aircraft flight cycles:
24976
Circumstances:
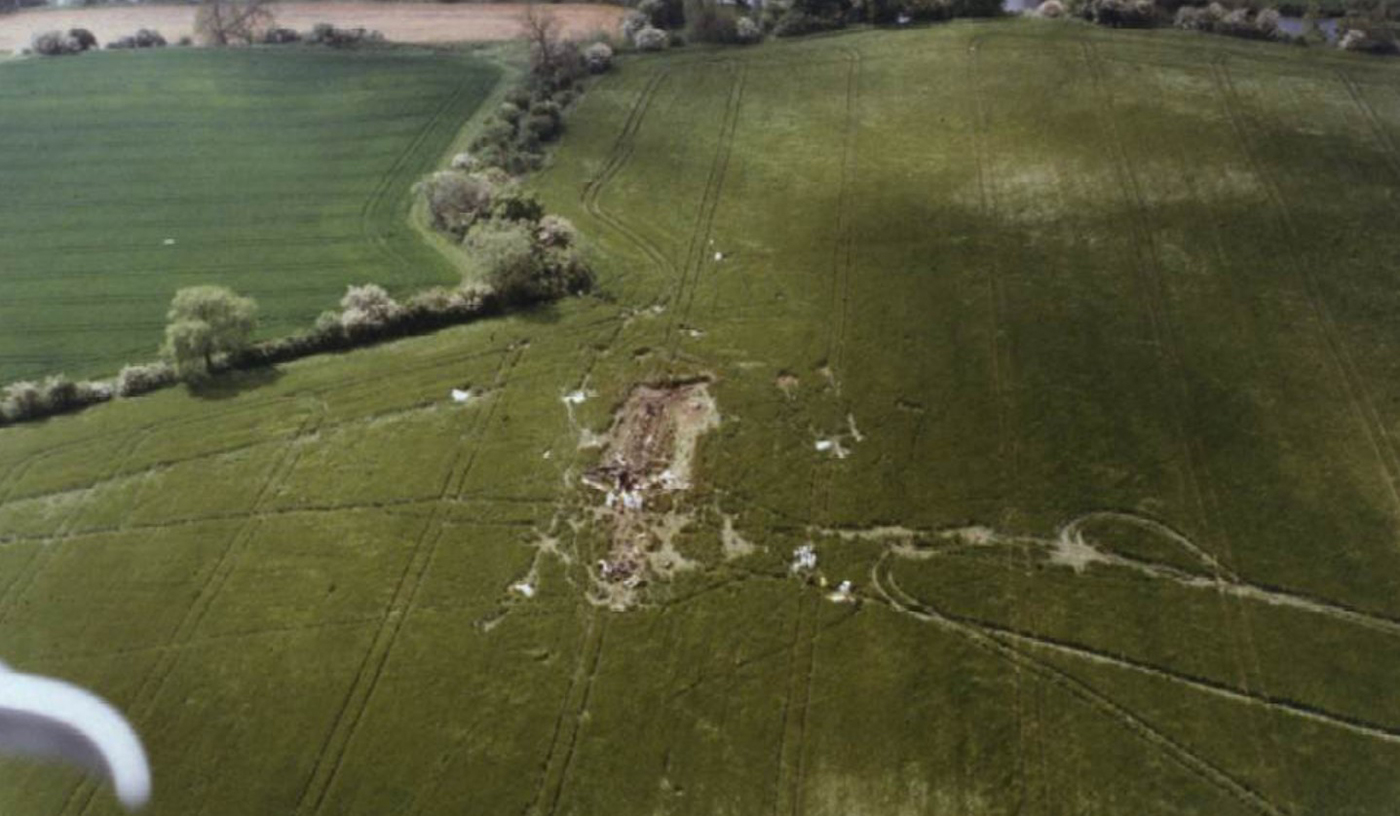
At 08:17 Ansett New Zealand Flight 703 departed Auckland (AKL) as scheduled bound for Palmerston North (PMR). To the north of Palmerston North the pilots briefed themselves for a VOR/DME approach to runway 07 which was the approach they preferred. Subsequently Air Traffic Control specified the VOR/DME approach for runway 25, due to departing traffic, and the pilots re-briefed for that instrument approach. The IMC involved flying in and out of stratiform cloud, but continuous cloud prevailed during most of the approach. The aircraft was flown accurately to join the 14 nm DME arc and thence turned right and intercepted the final approach track of 250° M to the Palmerston North VOR. During the right turn, to intercept the inbound approach track, the aircraft’s power levers were retarded to 'flight idle' and shortly afterwards the first officer advised the captain ".... 12 DME looking for 4000 (feet)". The final approach track was intercepted at approximately 13 DME and 4700 feet, and the first officer advised Ohakea Control "Ansett 703" was "established inbound". Just prior to 12 miles DME the captain called "Gear down". The first officer asked him to repeat what he had said and then responded "OK selected and on profile, ten - sorry hang on 10 DME we’re looking for four thousand aren’t we so - a fraction low". The captain responded, "Check, and Flap 15". This was not acknowledged but the first officer said, "Actually no, we’re not, ten DME we’re..... (The captain whistled at this point) look at that". The captain had noticed that the right hand main gear had not locked down: "I don’t want that." and the first officer responded, "No, that’s not good is it, so she’s not locked, so Alternate Landing Gear...?" The captain acknowledged, "Alternate extension, you want to grab the QRH?" After the First Officer’s "Yes", the captain continued, "You want to whip through that one, see if we can get it out of the way before it’s too late." The captain then stated, "I’ll keep an eye on the airplane while you’re doing that." The first officer located the appropriate "Landing Gear Malfunction Alternate Gear Extension" checklist in Ansett New Zealand’s Quick Reference Handbook (QRH) and began reading it. He started with the first check on the list but the captain told him to skip through some checks. The first officer responded to this instruction and resumed reading and carrying out the necessary actions. It was the operator’s policy that all items on the QRH checklists be actioned, or proceeded through, as directed by the captain. The first officer started carrying out the checklist. The captain in between advised him to pull the Main Gear Release Handle. Then the GPWS’s audio alarm sounded. Almost five seconds later the aircraft collided with terrain. The Dash 8 collided with the upper slope of a low range of hills.
Probable cause:
The captain not ensuring the aircraft intercepted and maintained the approach profile during the conduct of the non-precision instrument approach, the captain's perseverance with his decision to get the undercarriage lowered without discontinuing the instrument approach, the captain's distraction from the primary task of flying the aircraft safely during the first officer's endeavours to correct an undercarriage malfunction, the first officer not executing a Quick Reference Handbook procedure in the correct sequence, and the shortness of the ground proximity warning system warning.
Final Report: