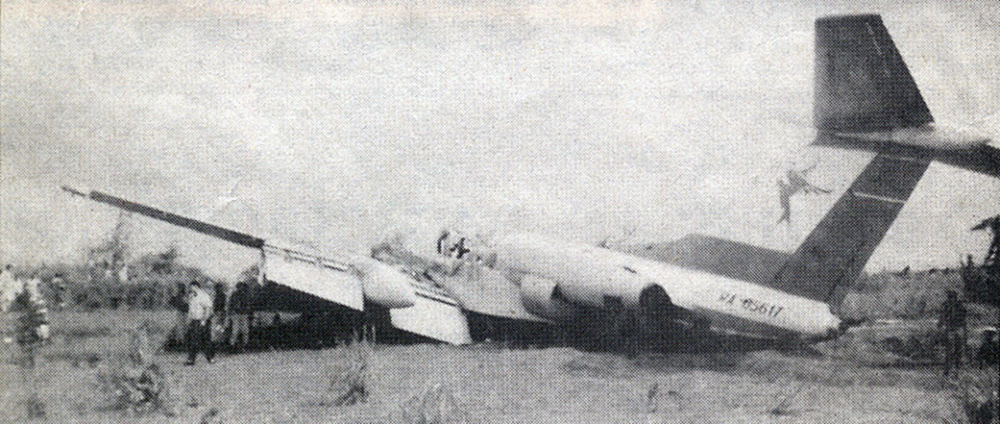
Crash of a Rockwell Turbo Commander 681 in Nassau
Date & Time:
Jun 30, 1995 at 1400 LT
Registration:
N70RF
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Miami - Puerto Plata
MSN:
681-6013
YOM:
1970
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
3
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
En route from Miami to Puerto Plata, while cruising at an altitude of 13,000 feet, the pilot informed ATC about the failure of the left engine and was cleared to divert to Nassau. On final approach to Nassau Airport, the aircraft struck a fence and crashed about 300 metres short of runway threshold. All four occupants were rescued and the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.
Probable cause:
Failure of the left engine in flight for unknown reasons.