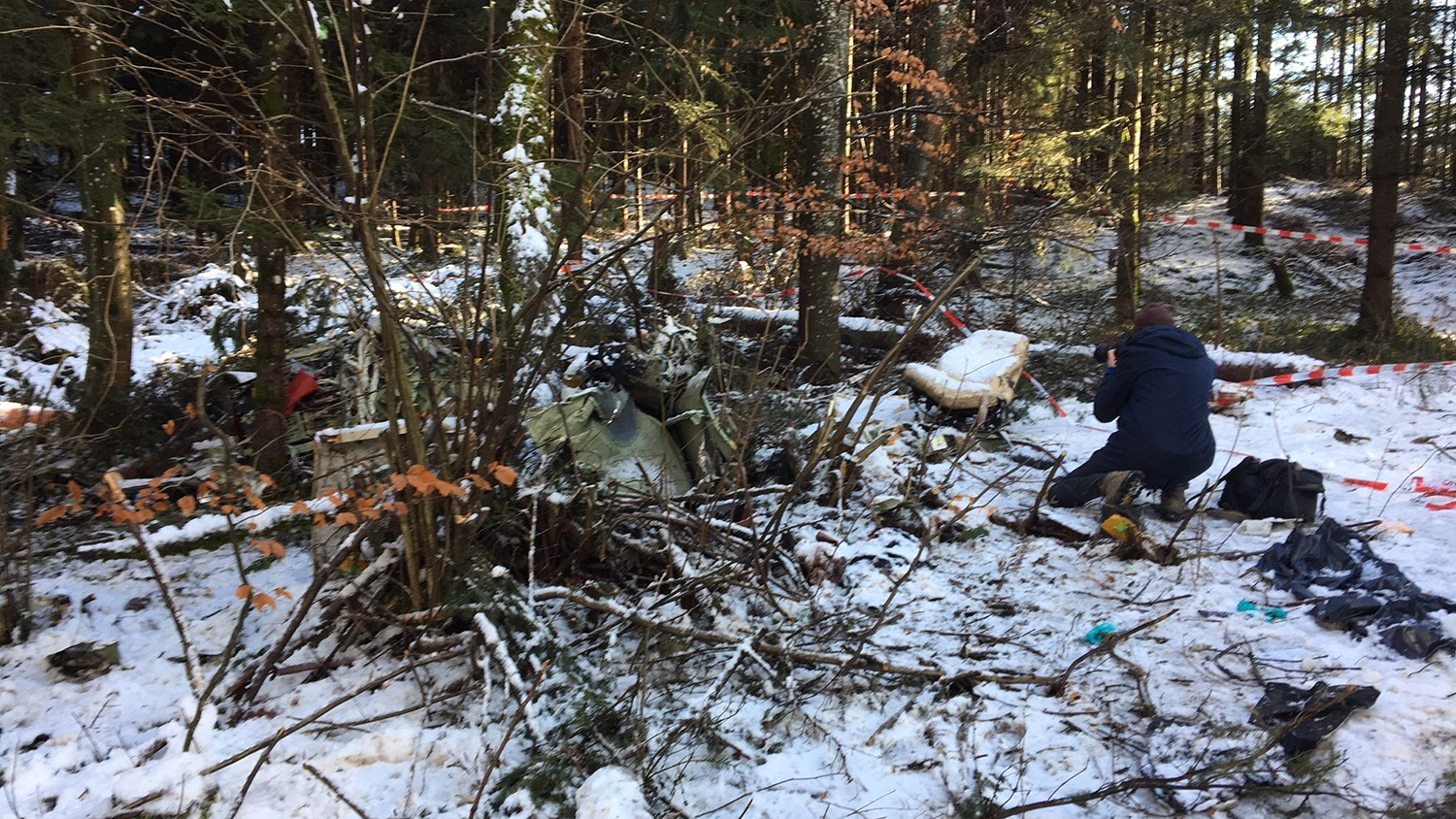
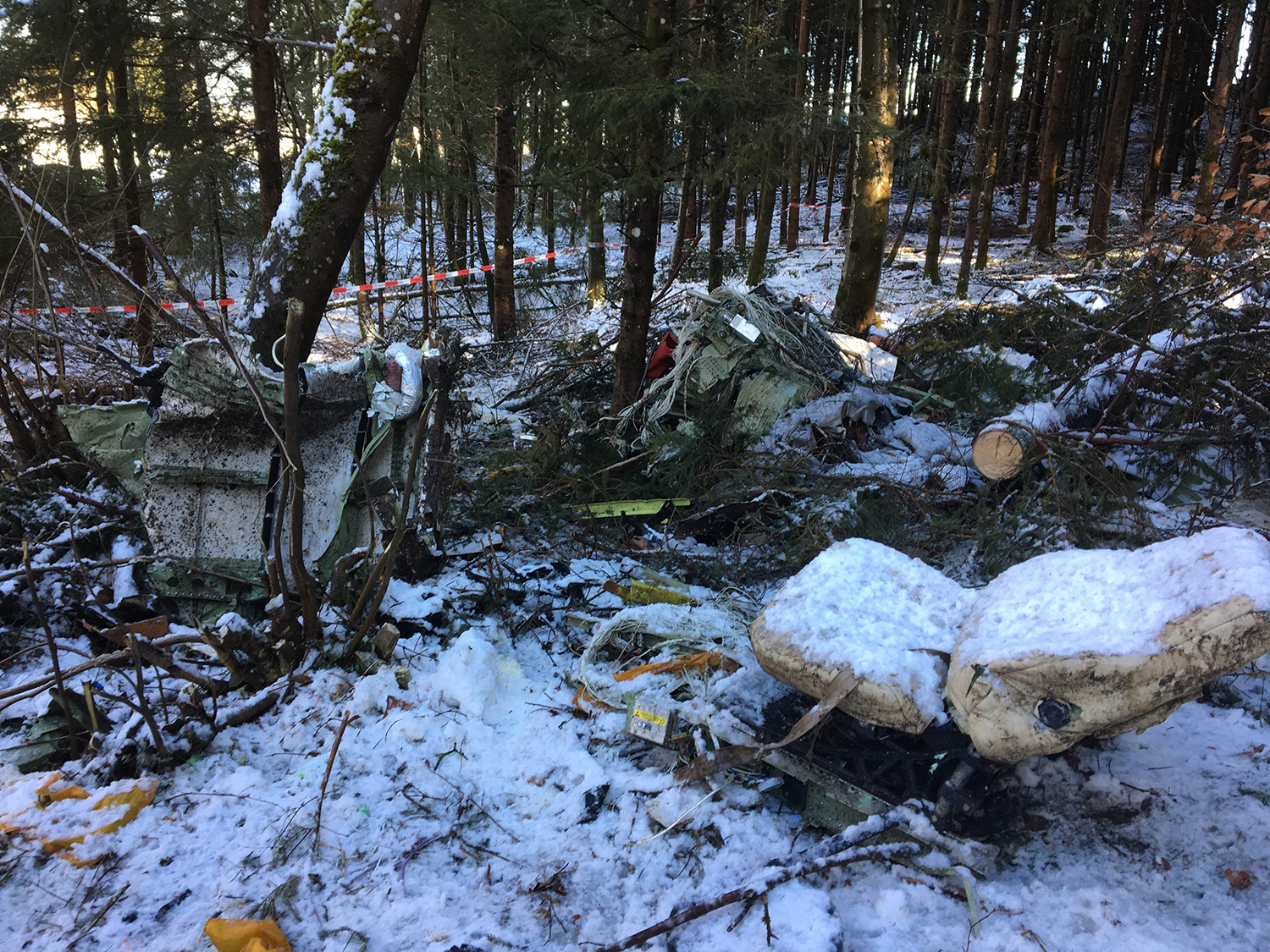
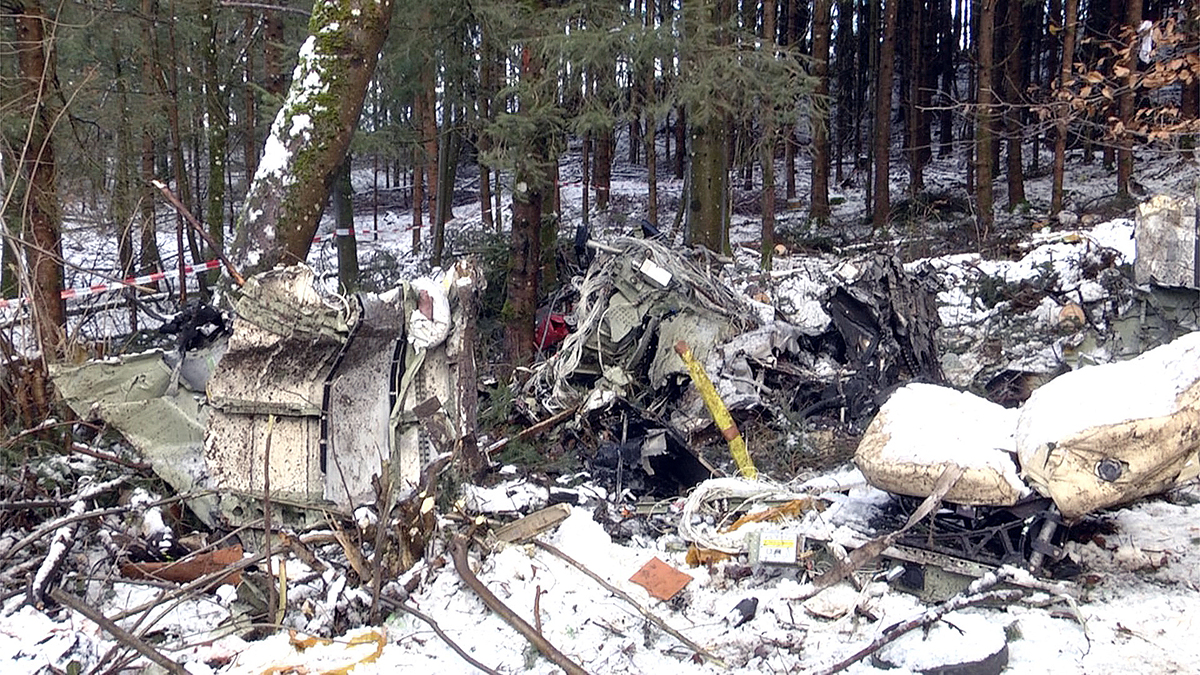
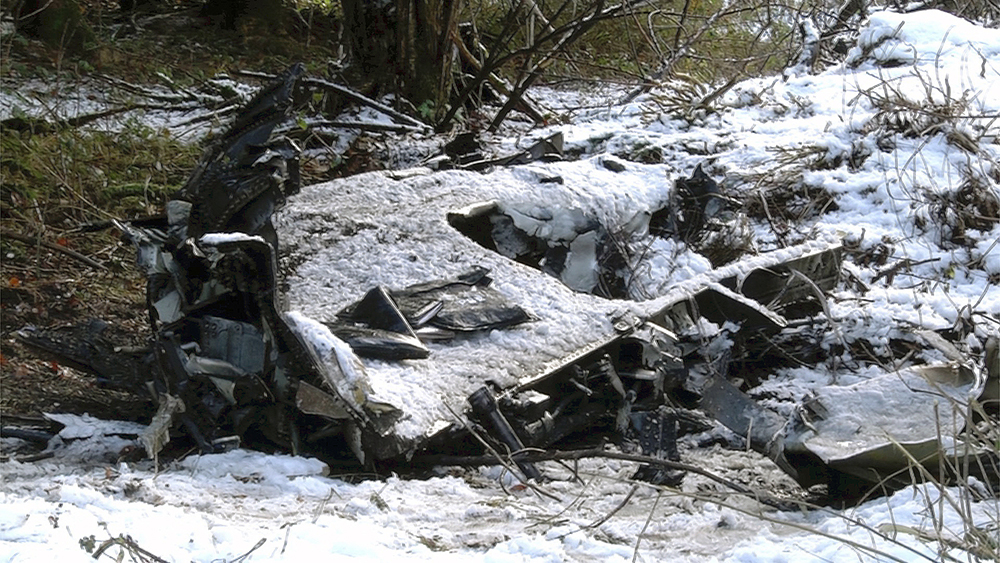
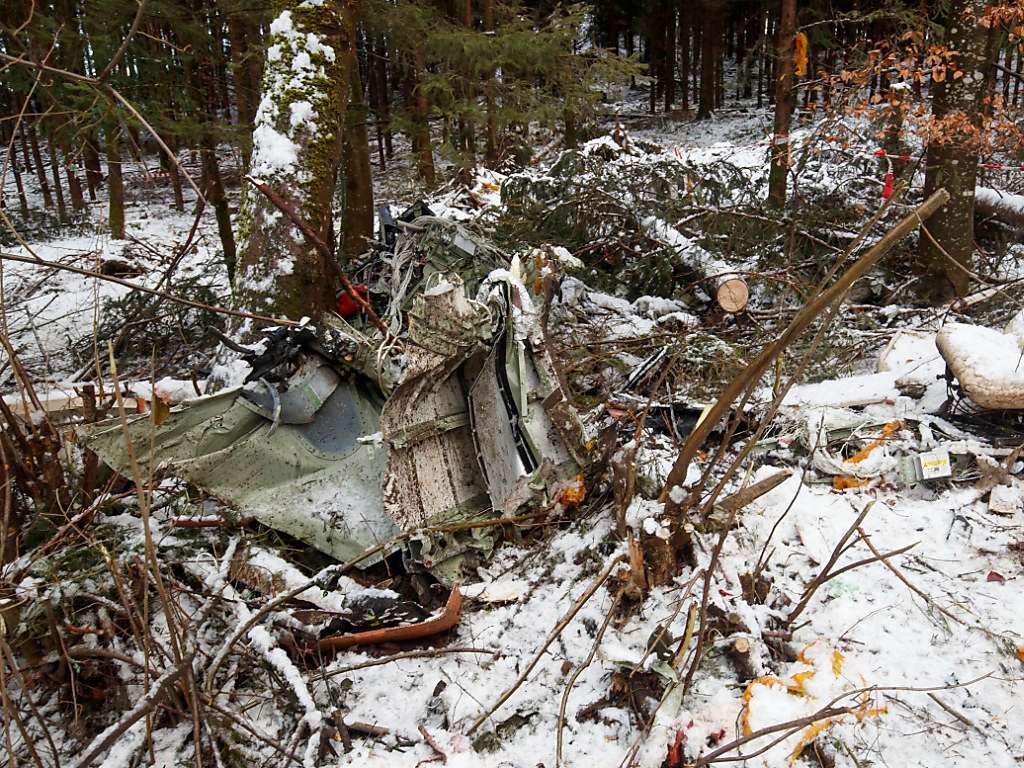
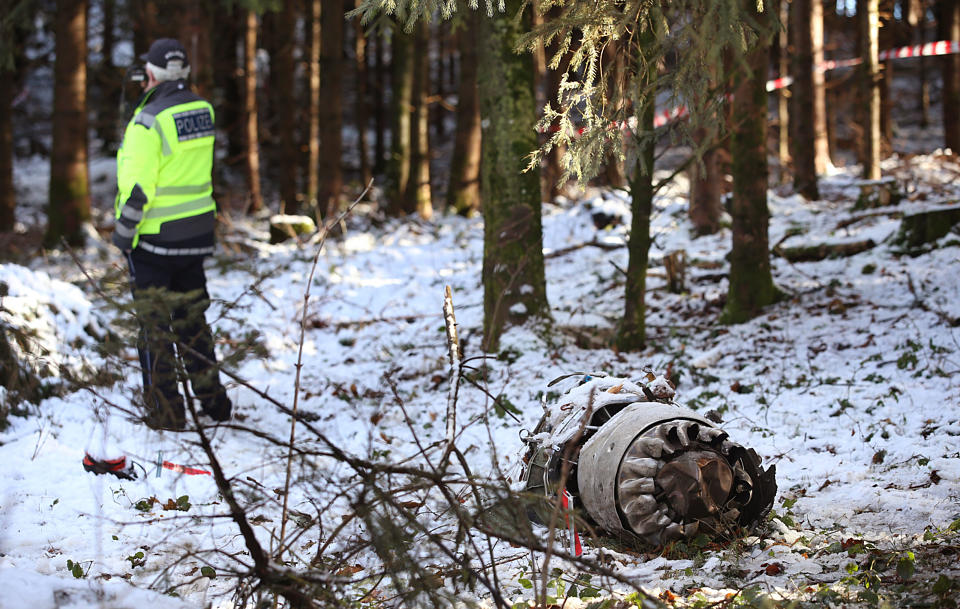
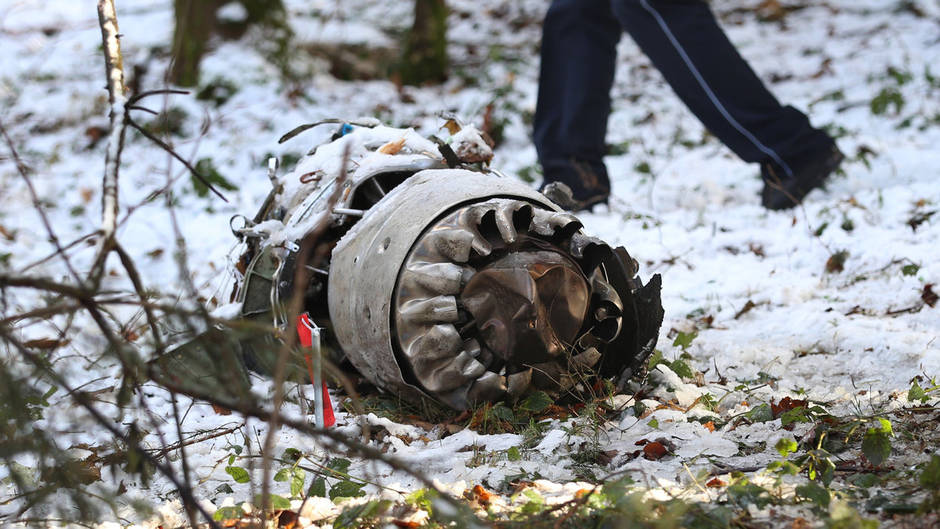
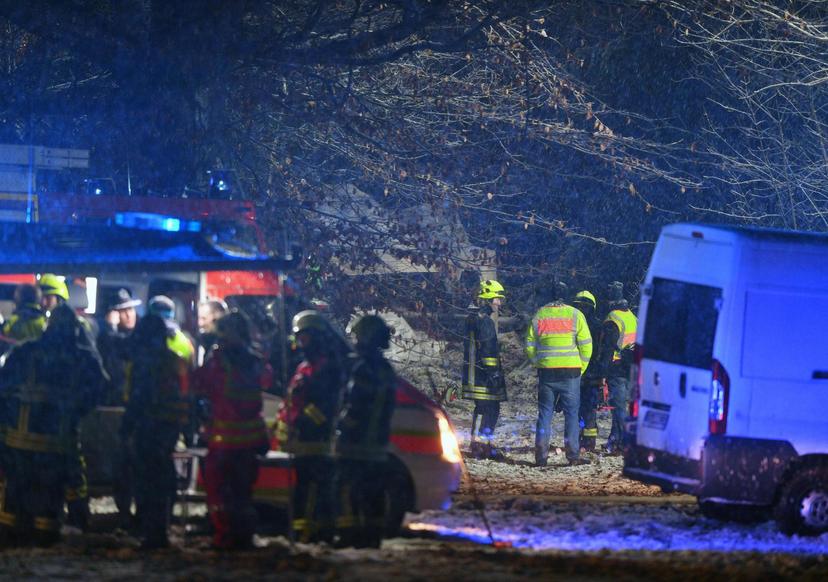
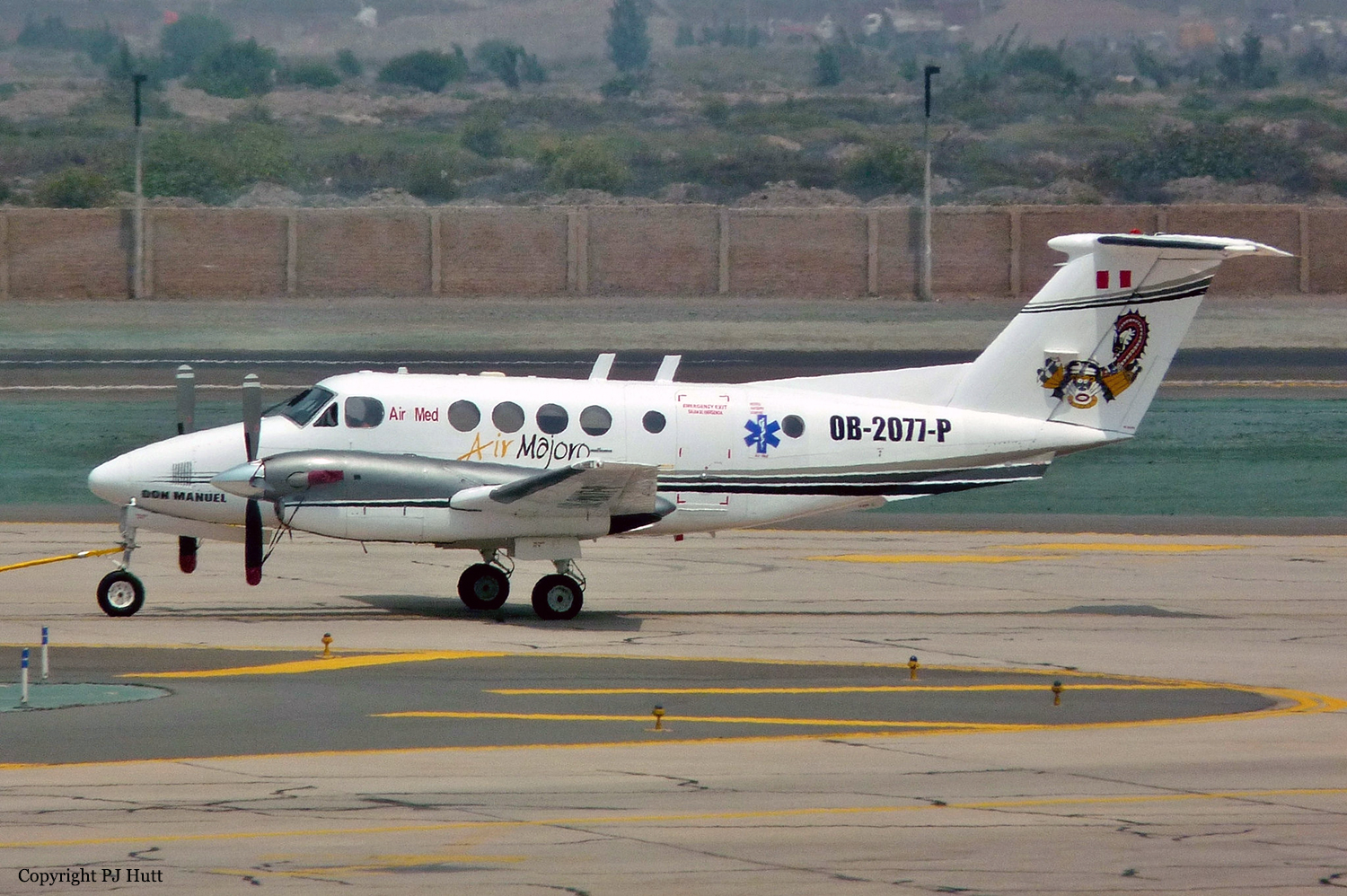
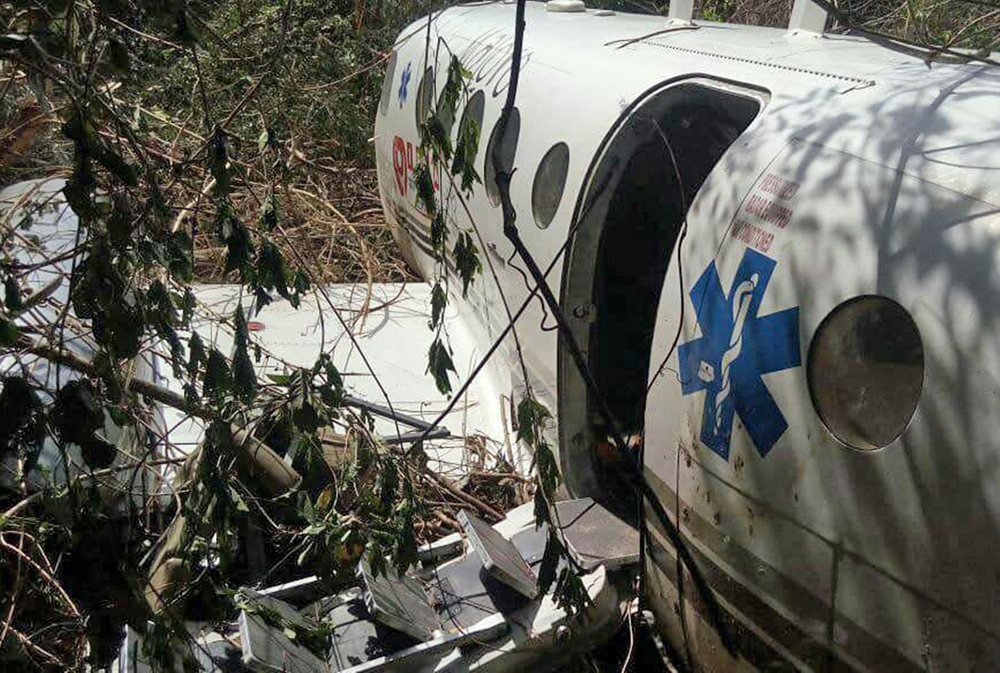
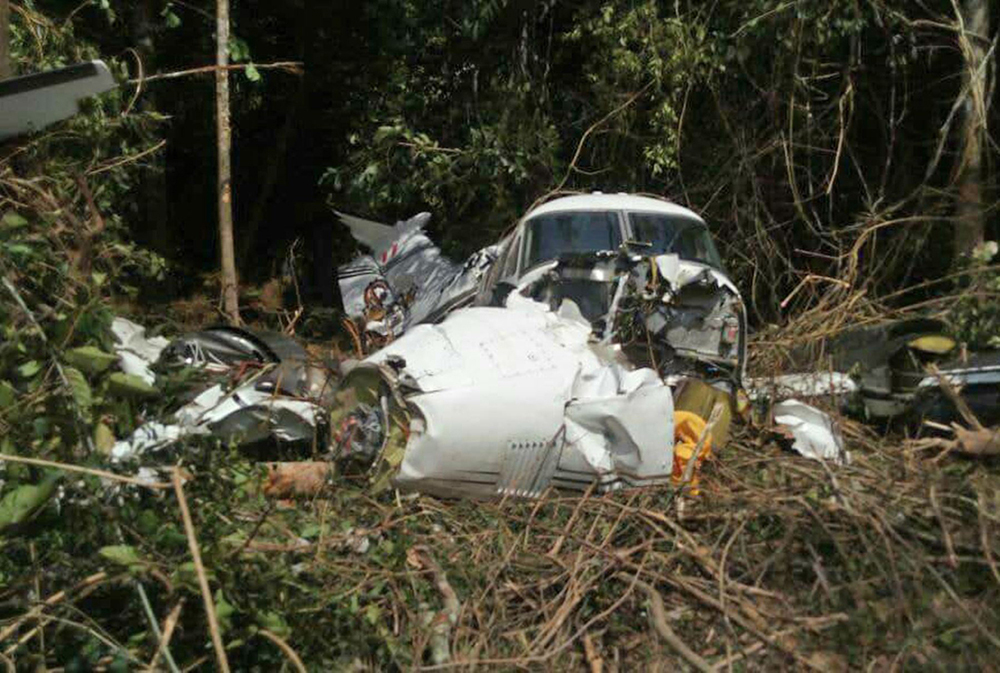
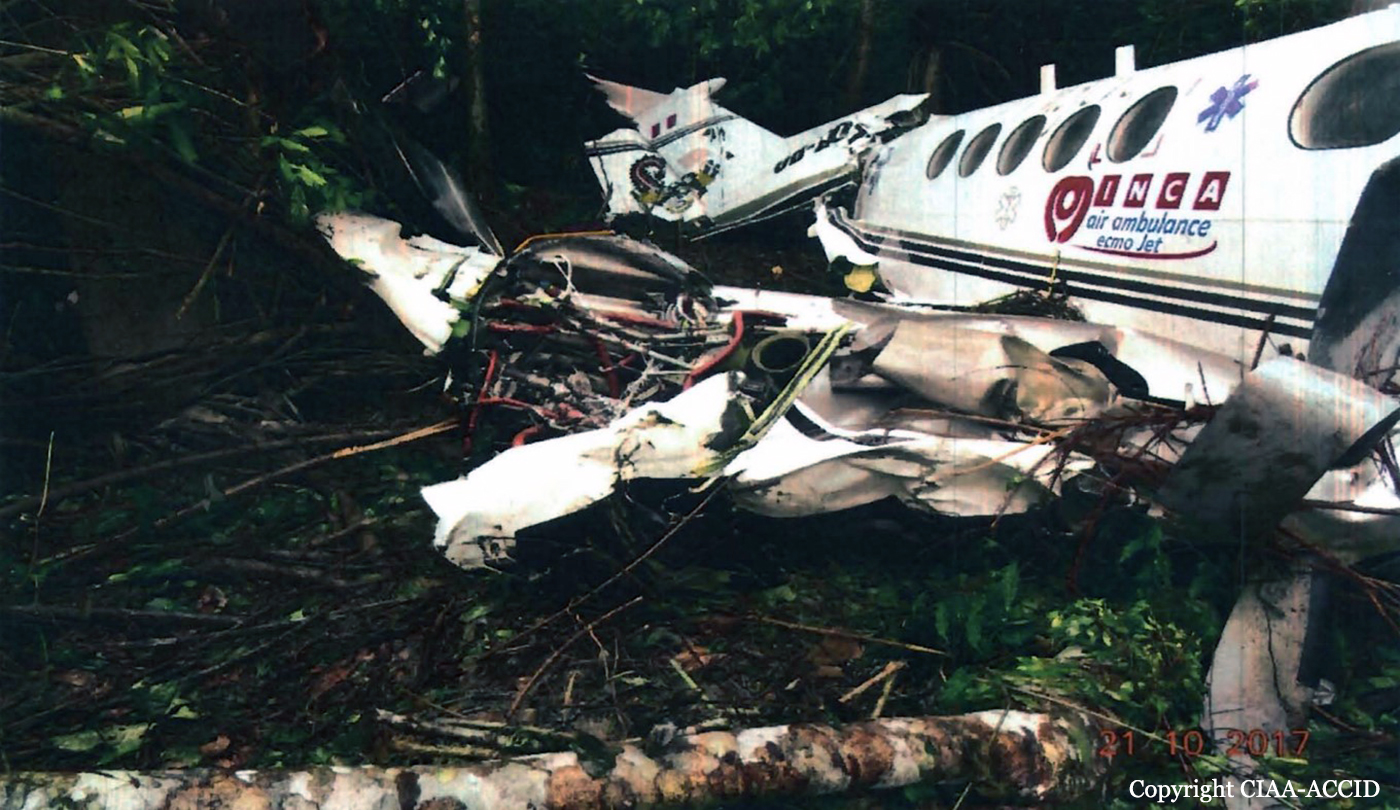
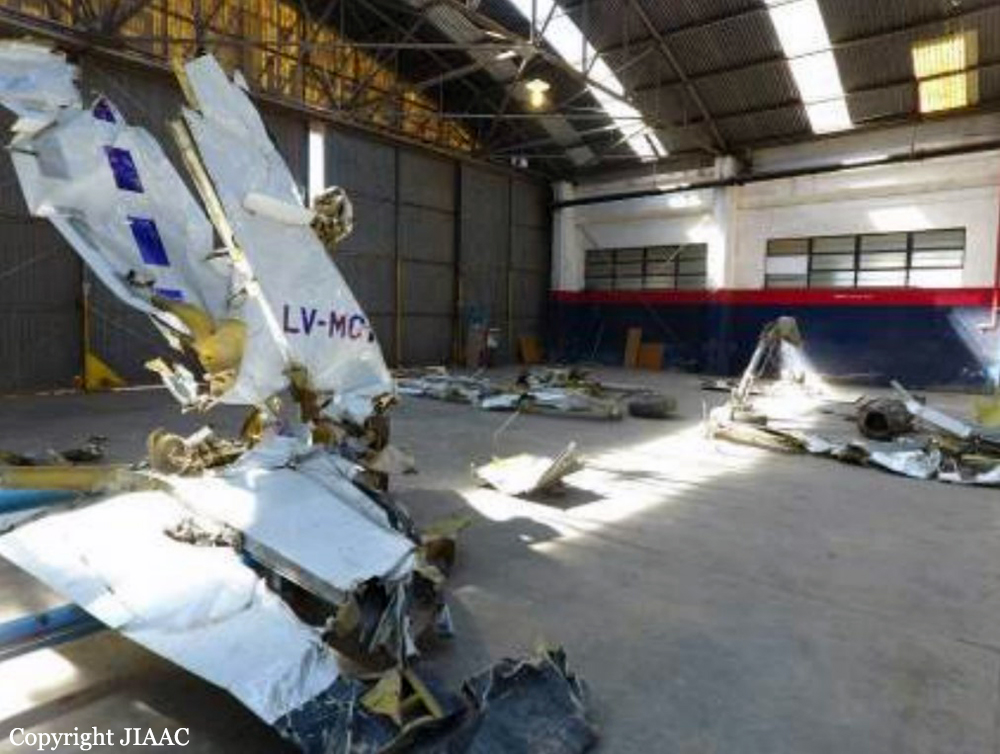
Crash of a Cessna 510 Citation Mustang in Sieberatsreute: 3 killed
Date & Time:
Dec 14, 2017 at 1814 LT
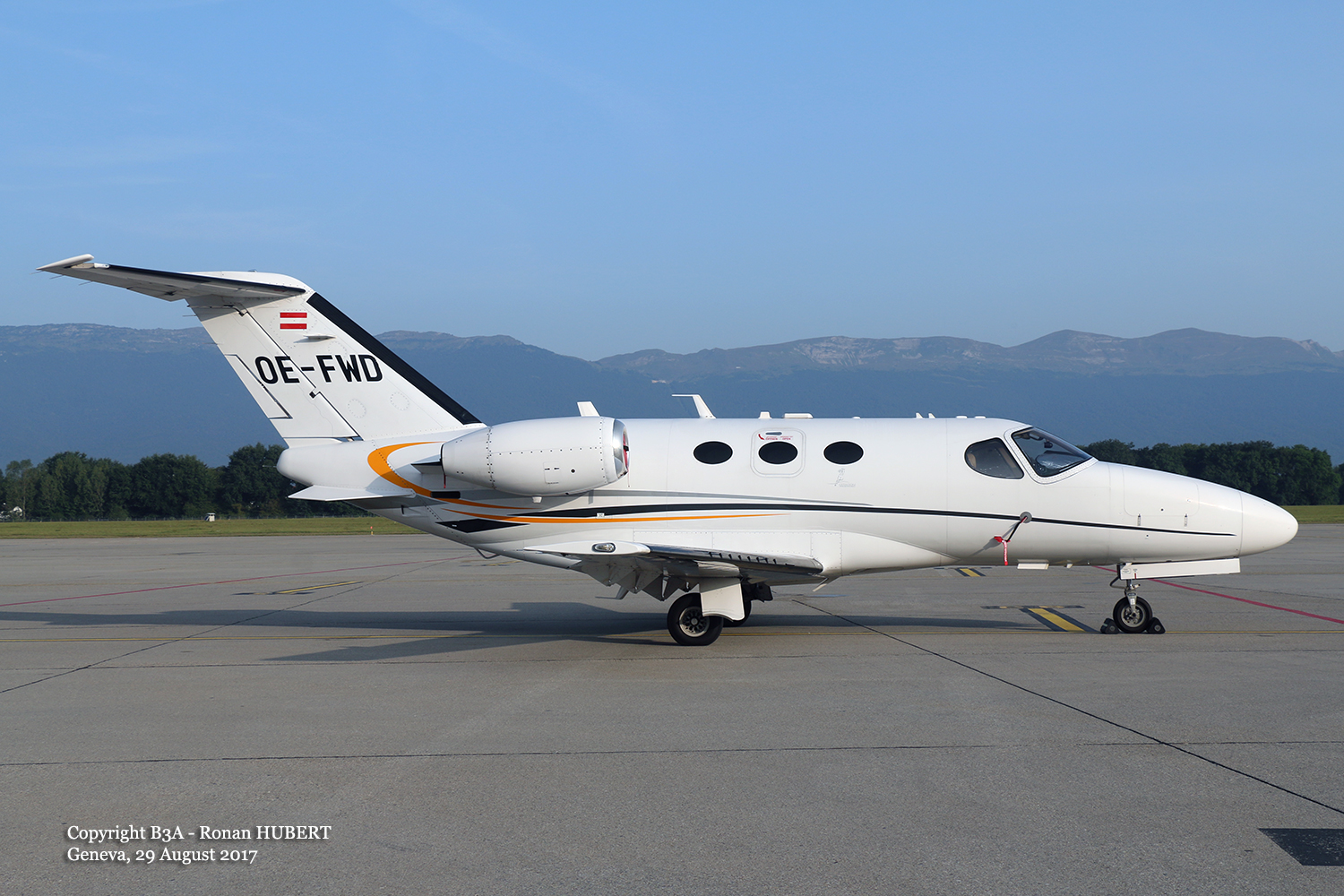
Registration:
OE-FWD
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Egelsbach – Friedrichshafen
MSN:
510-0049
YOM:
2007
Flight number:
STC228B
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
1
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
3
Captain / Total hours on type:
2000.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
140
Aircraft flight hours:
3606
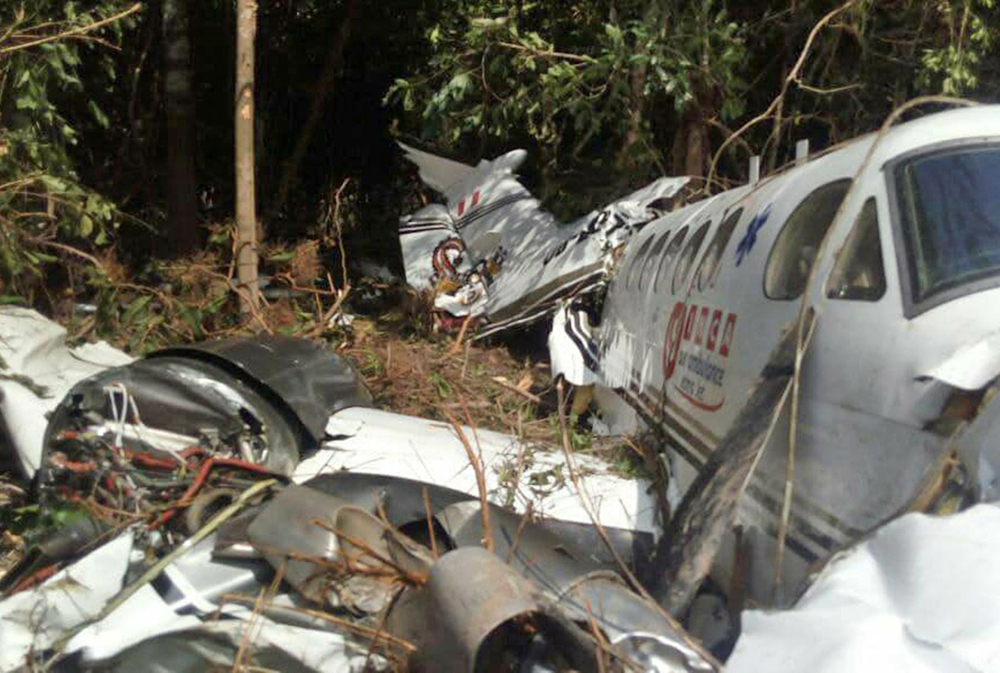
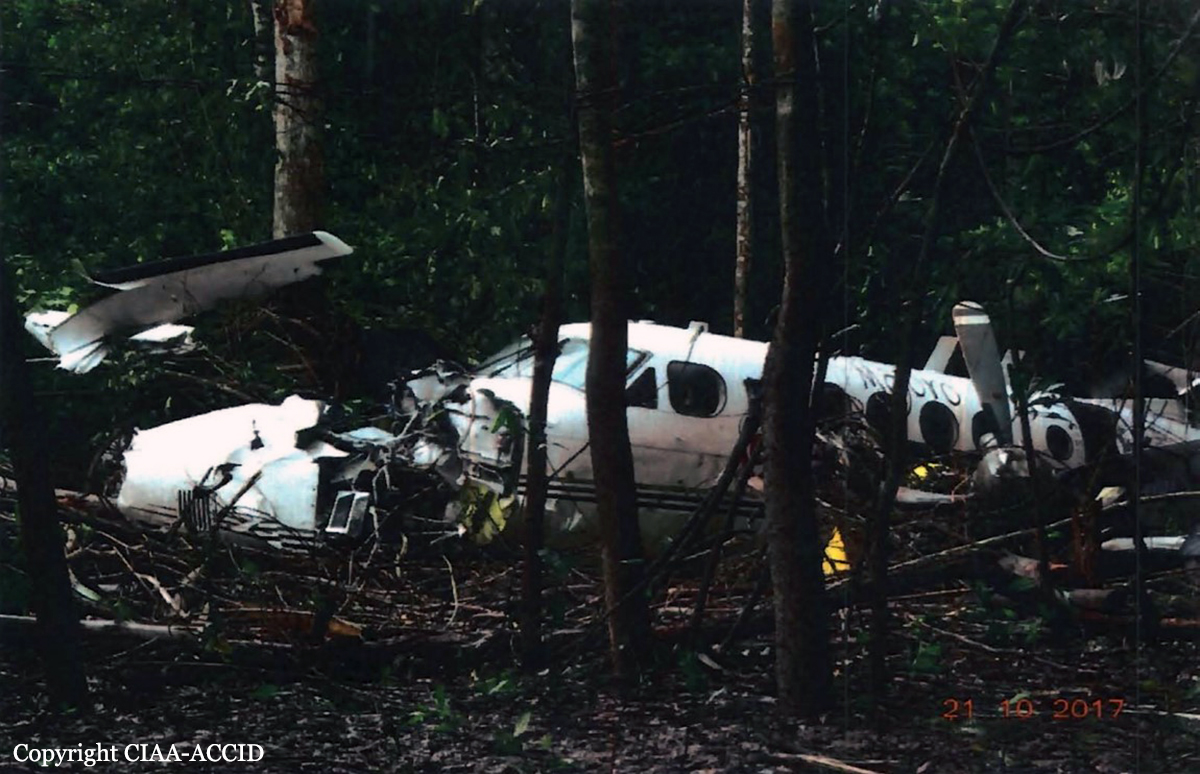
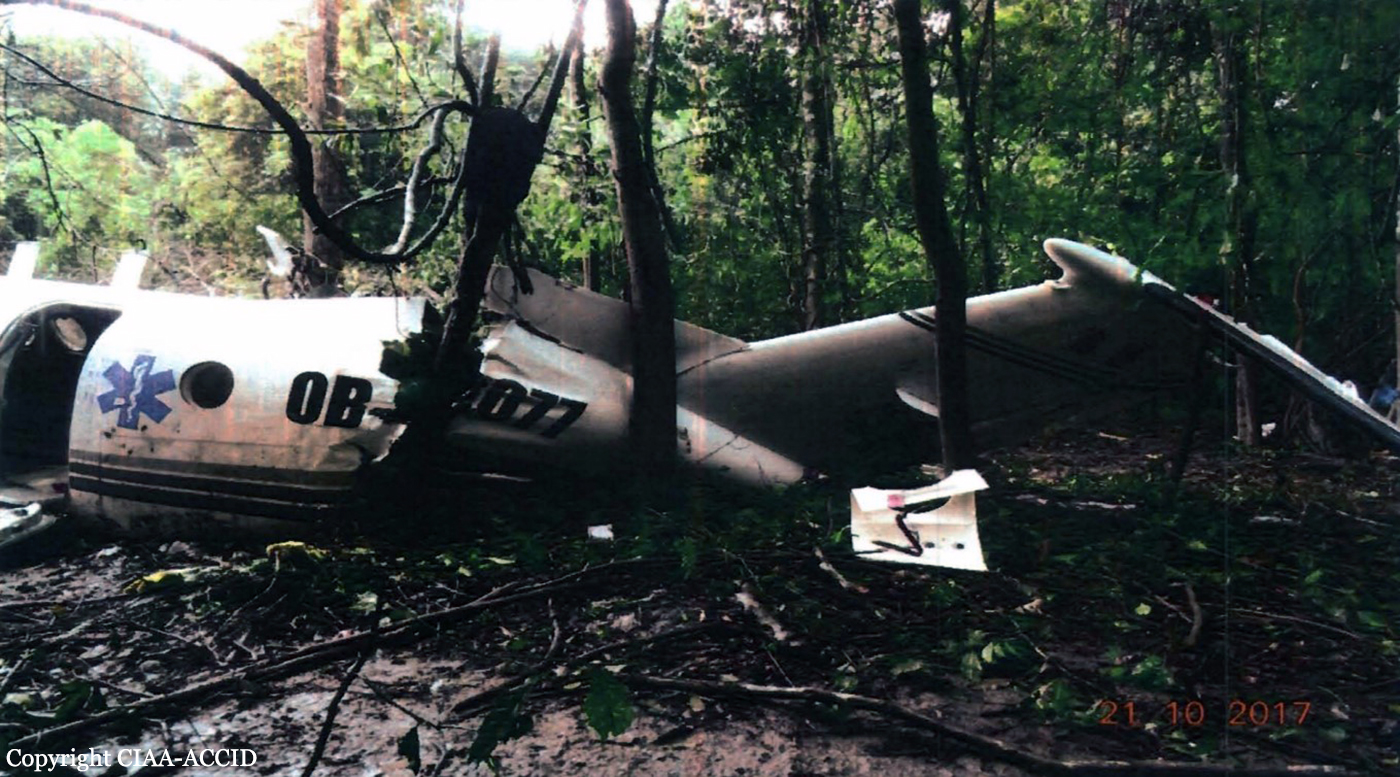
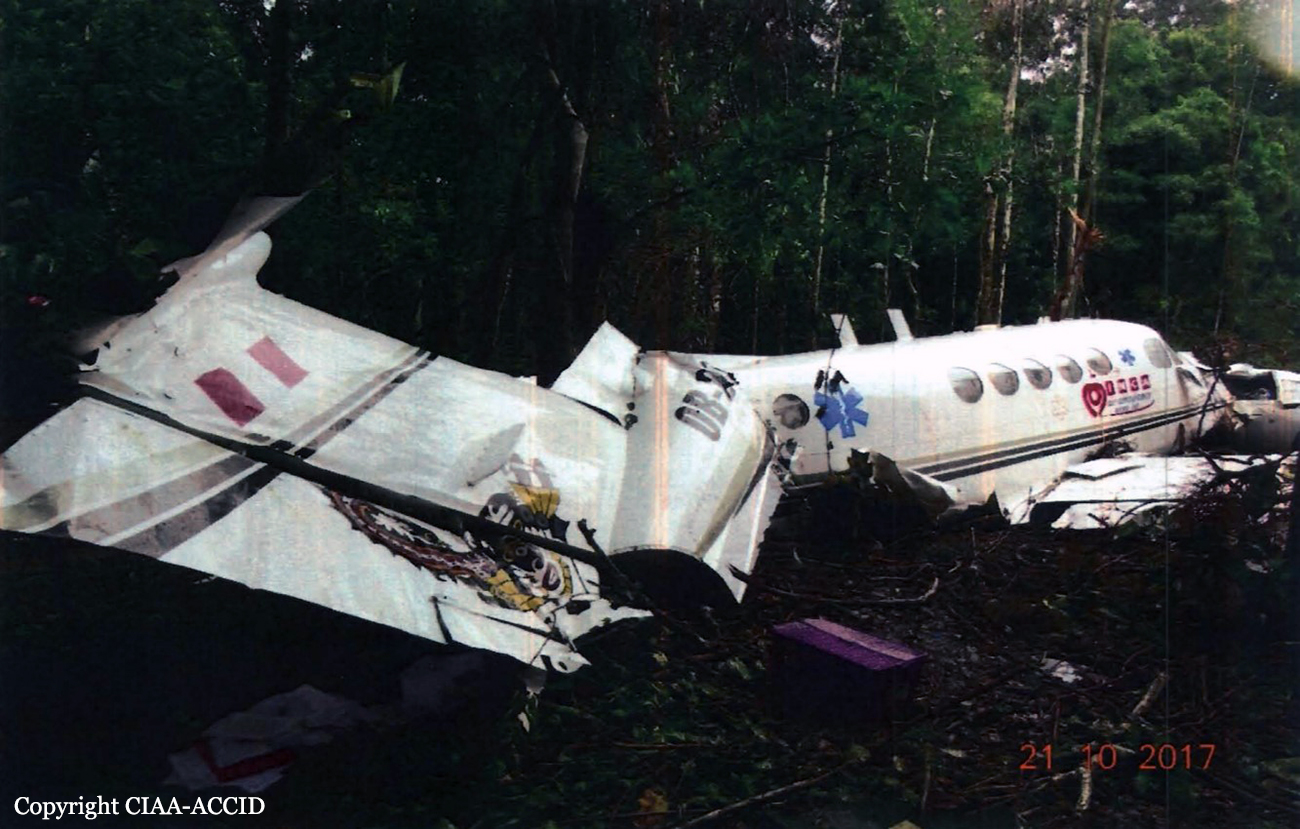
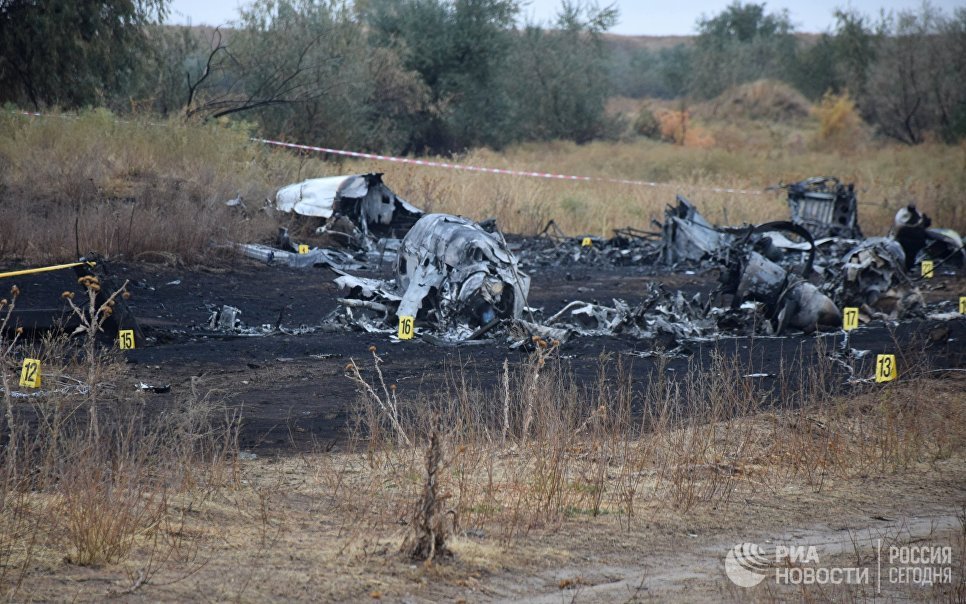
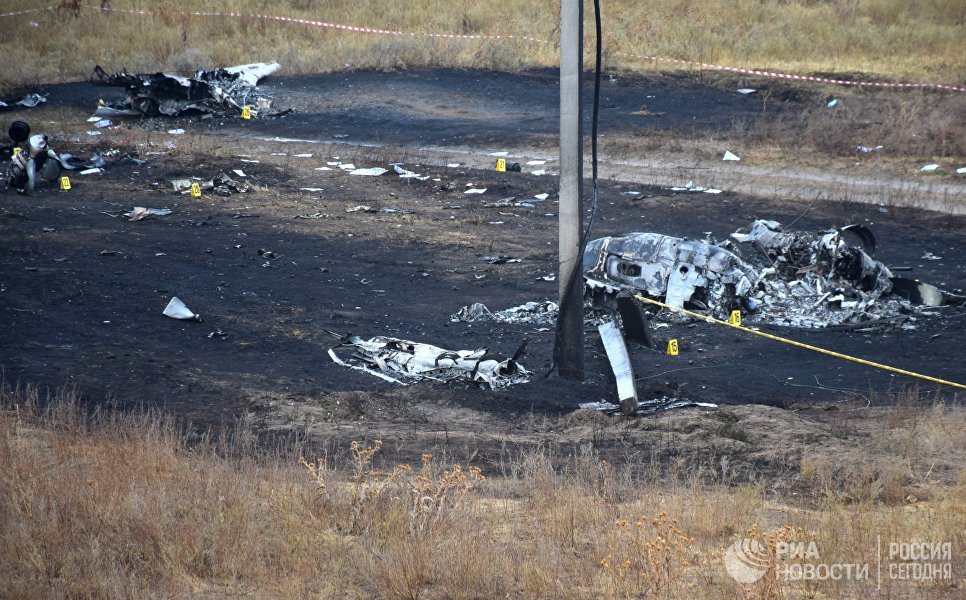
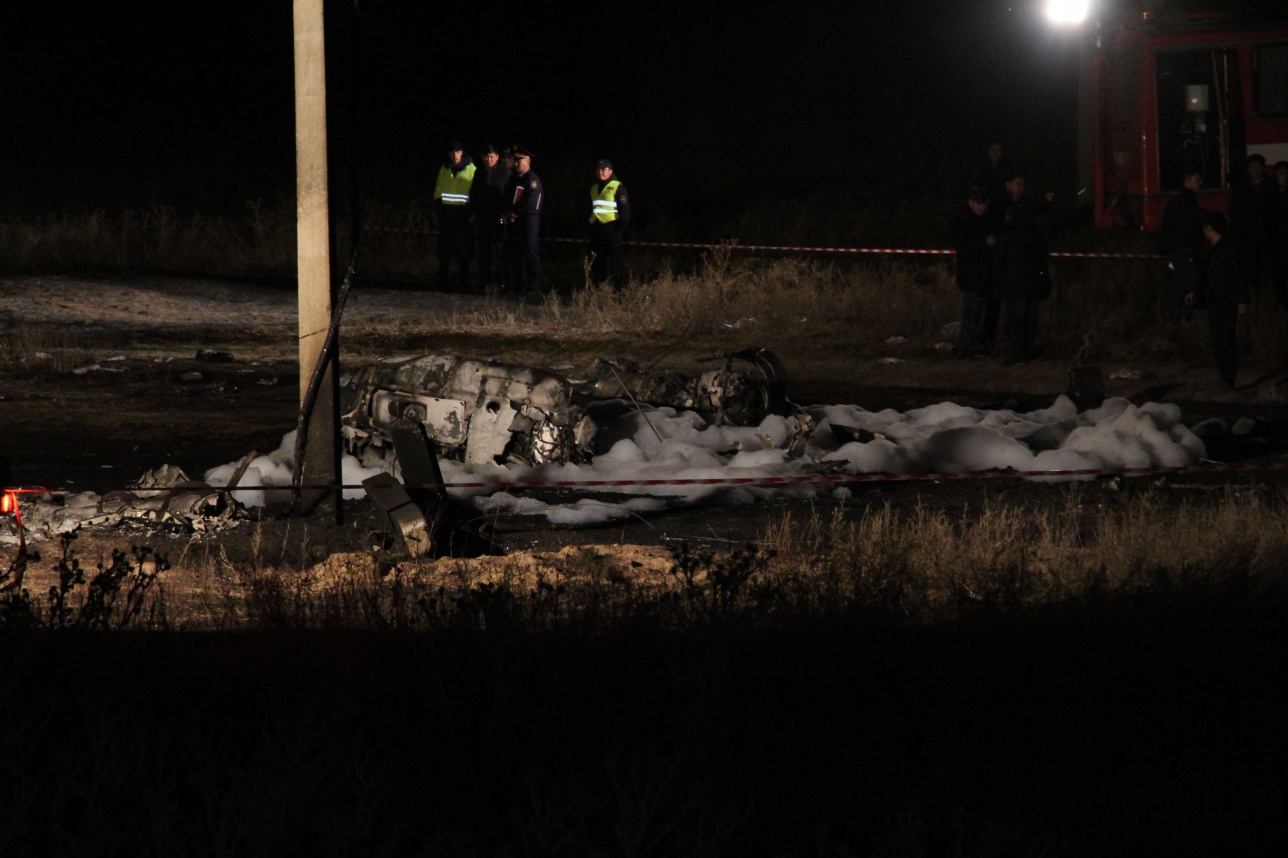
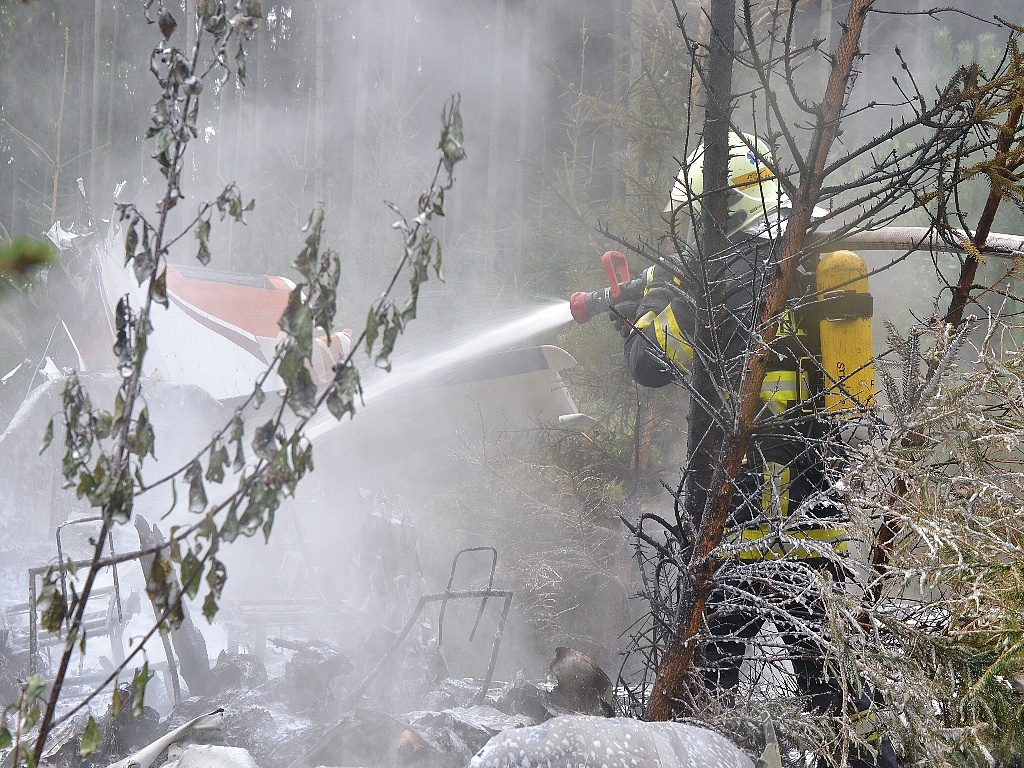
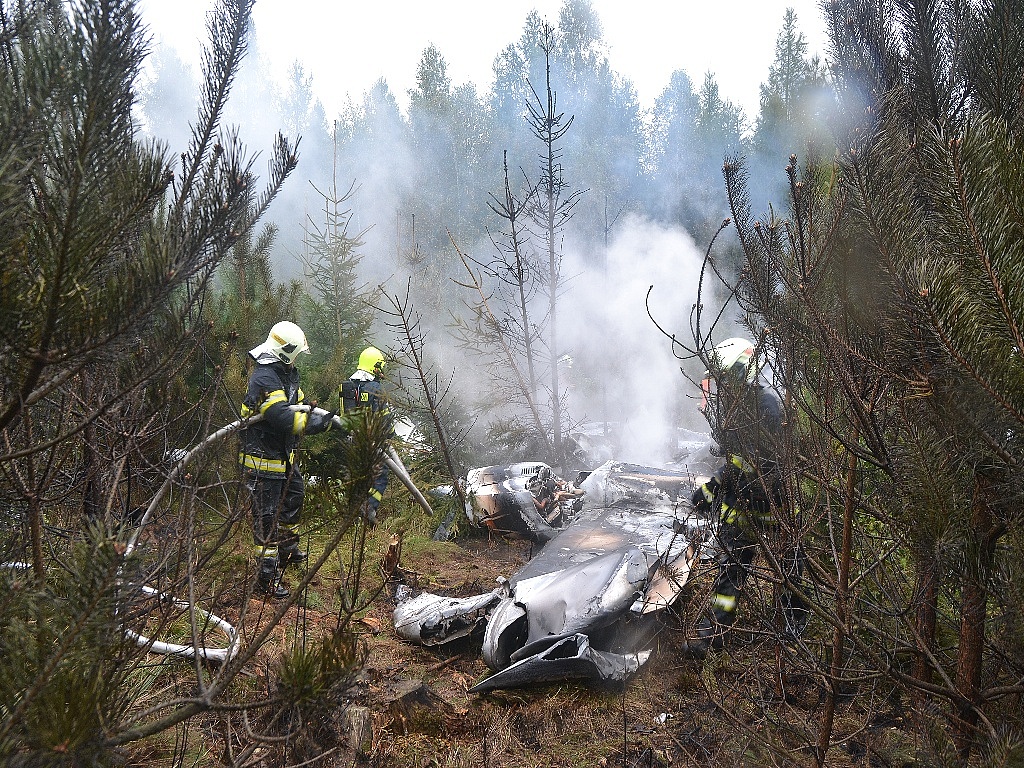
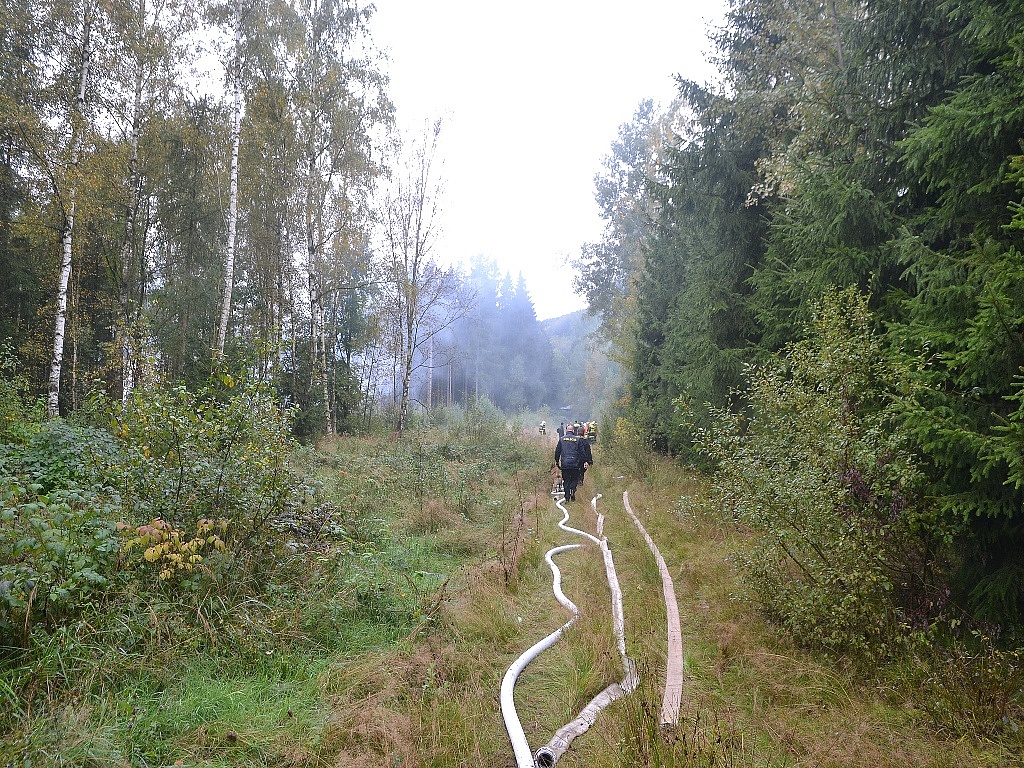
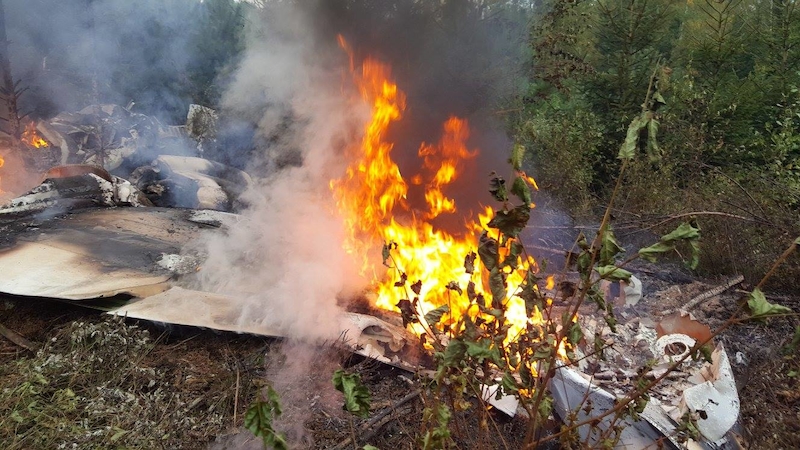
Circumstances:
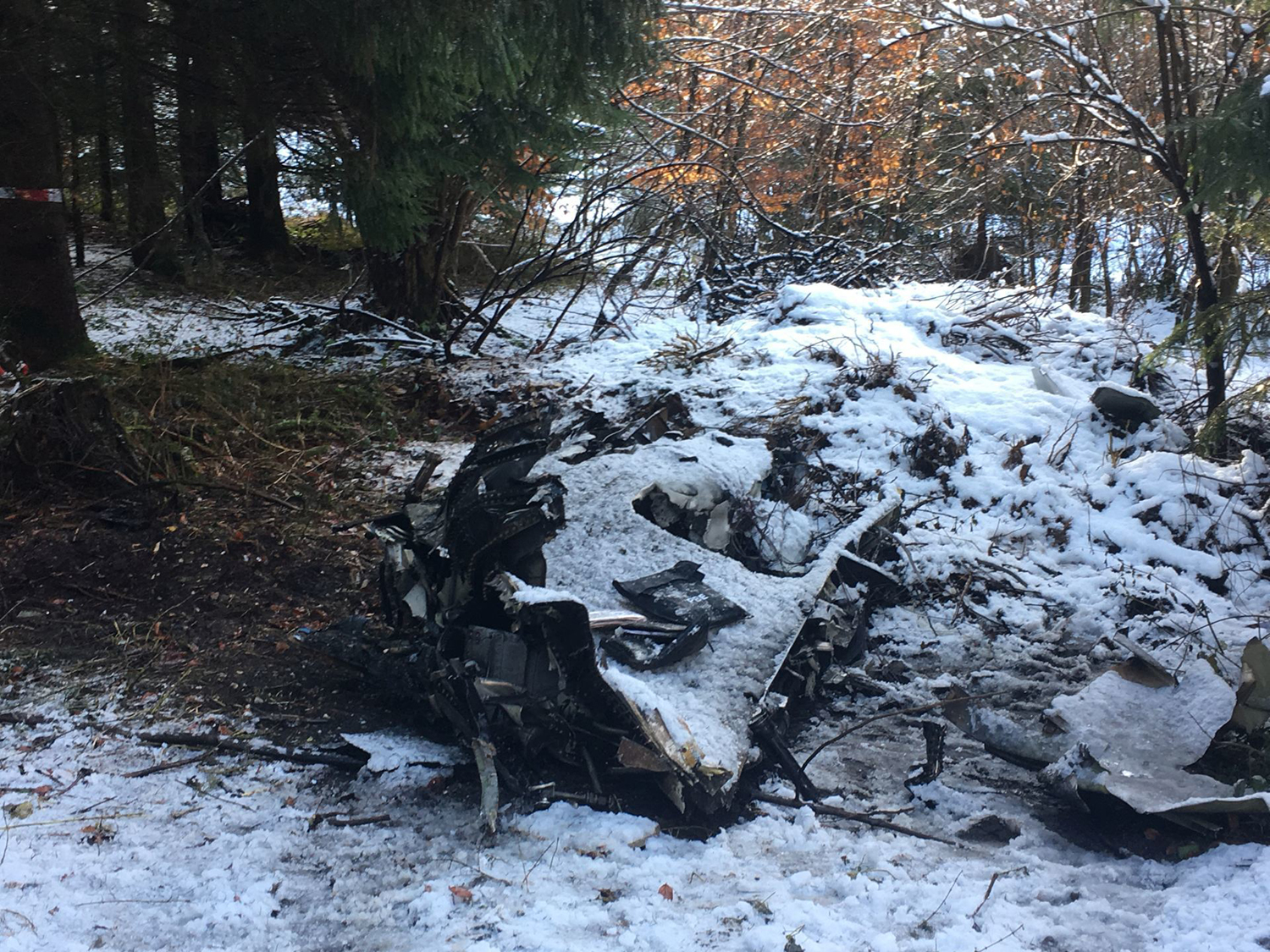
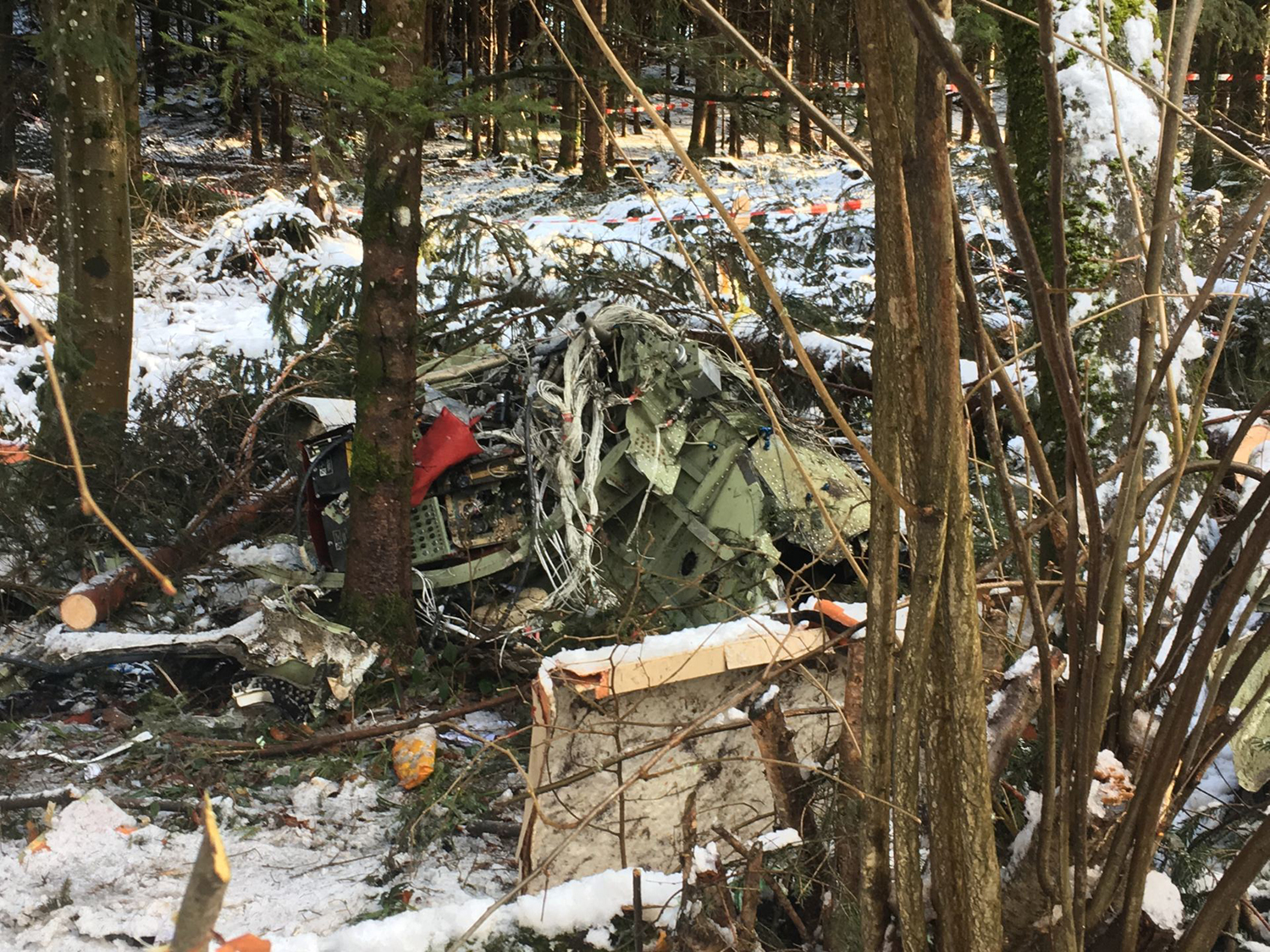
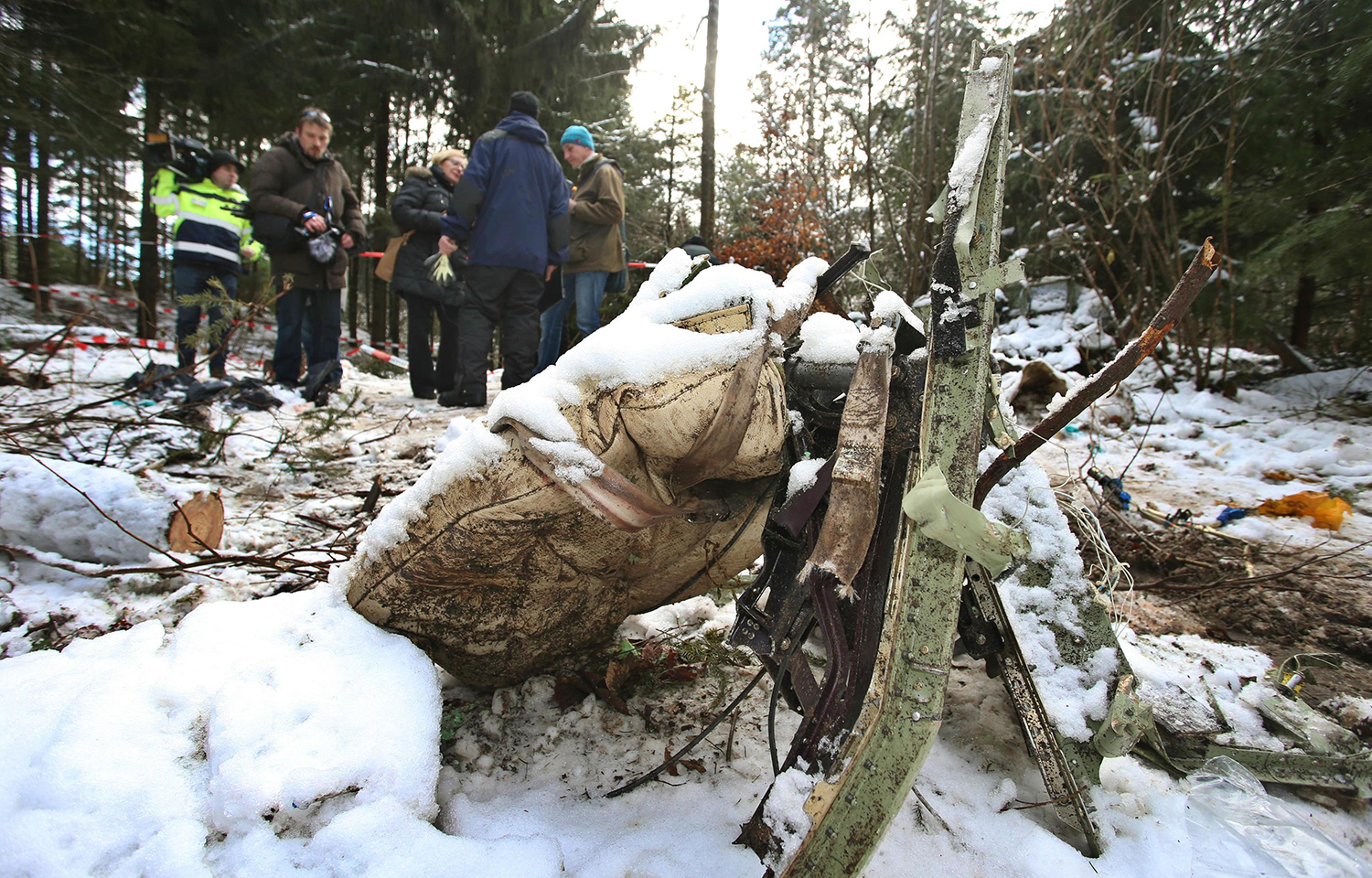
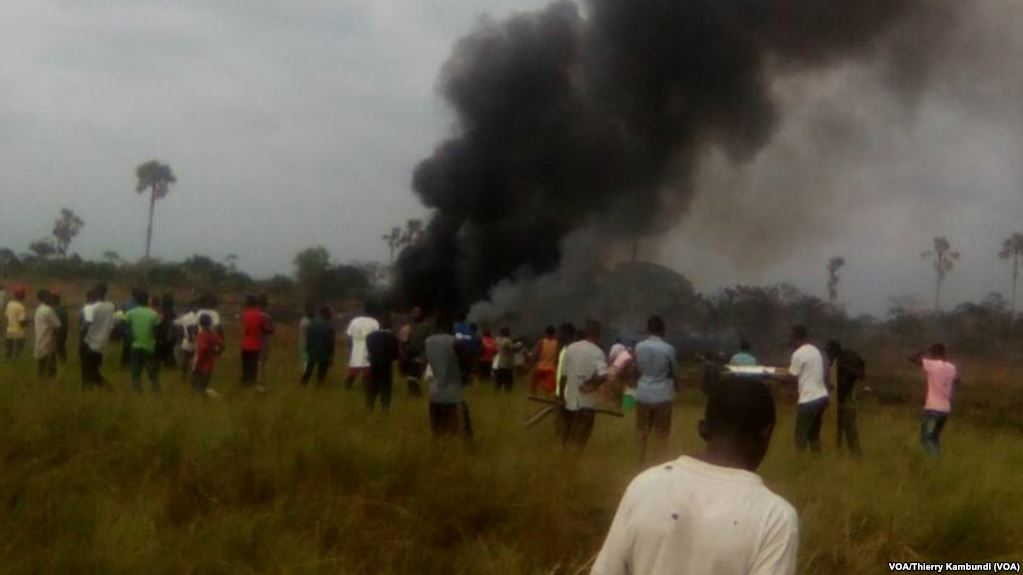
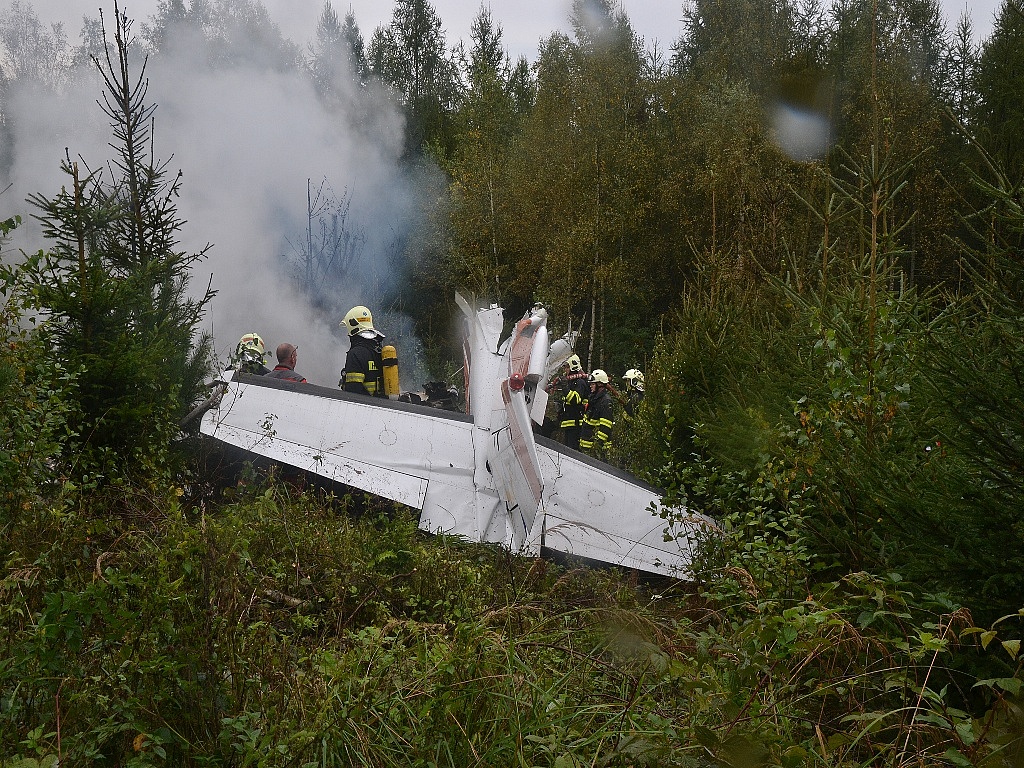
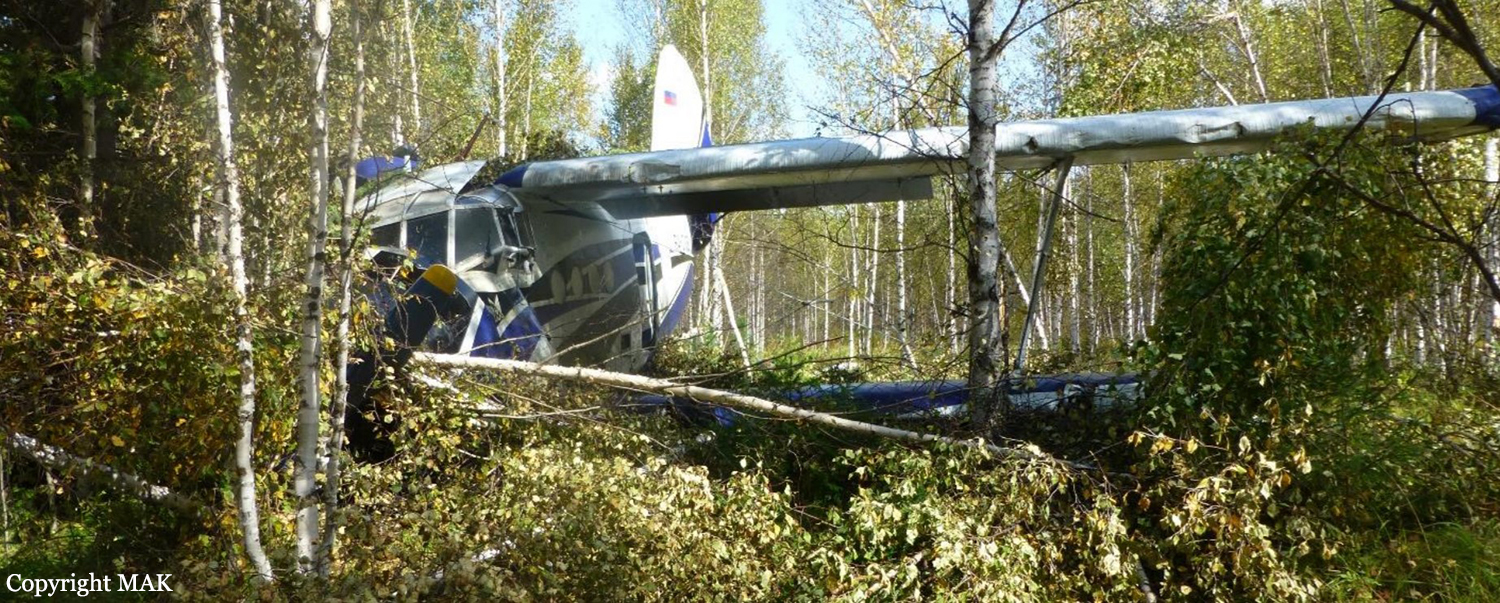
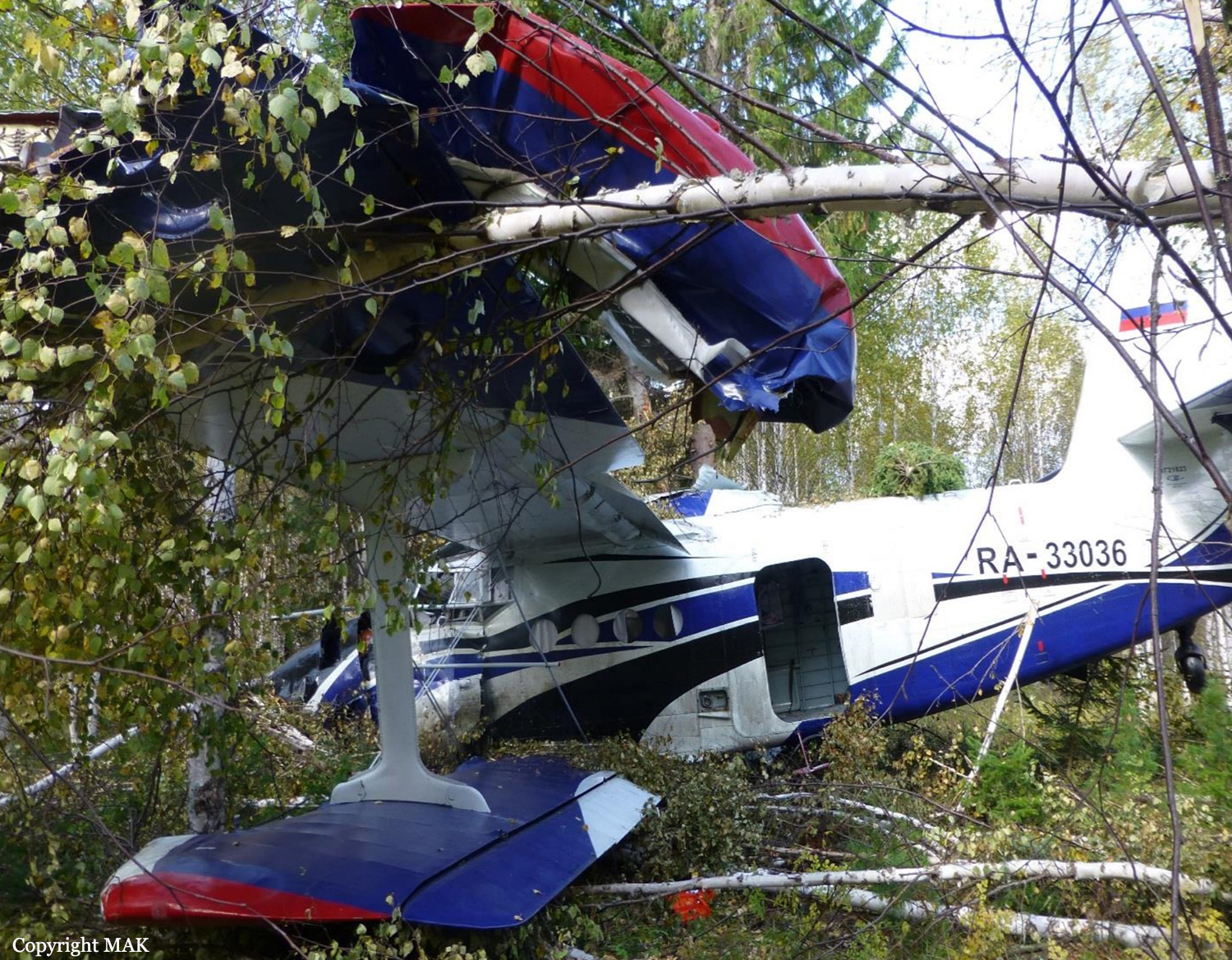
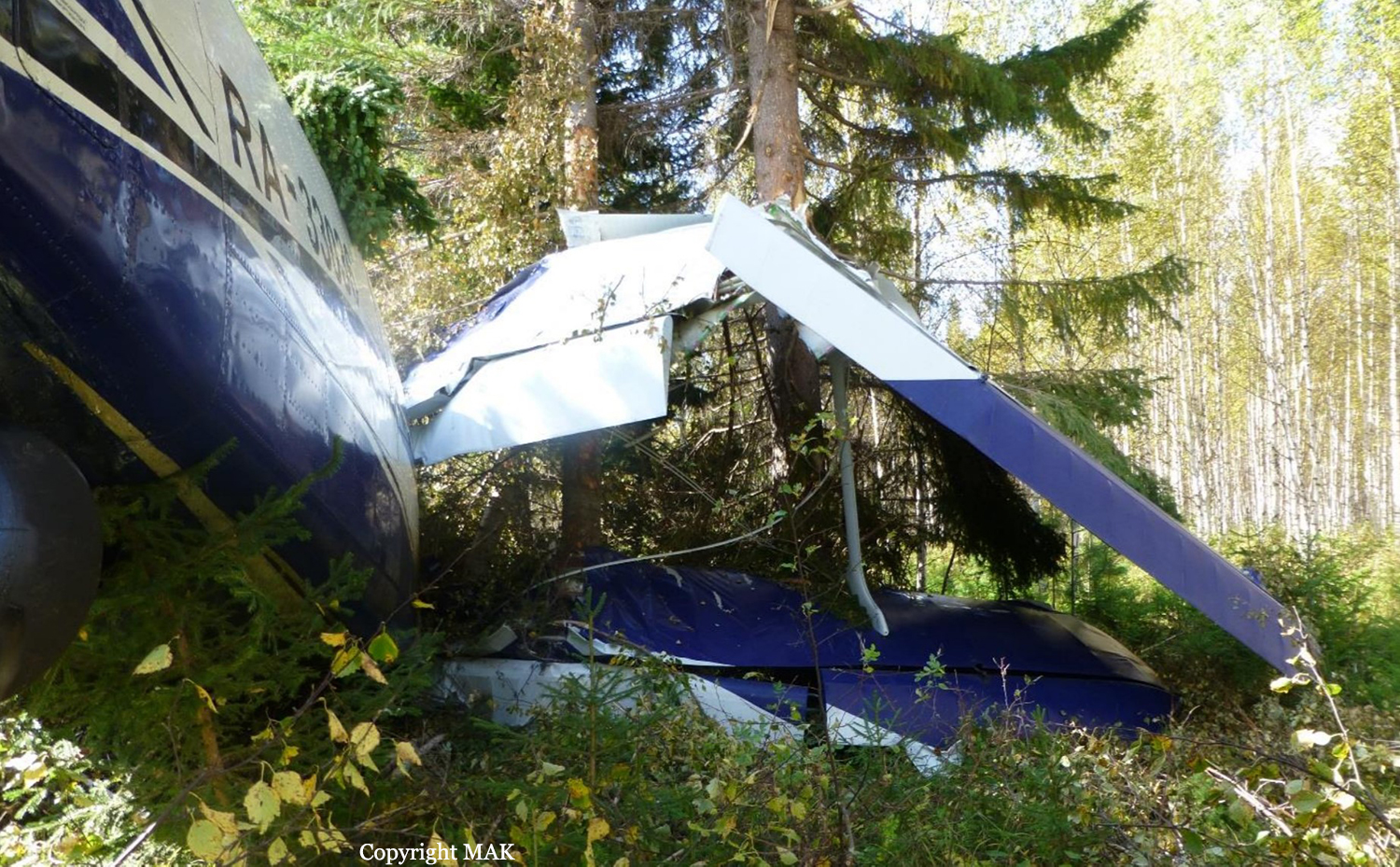
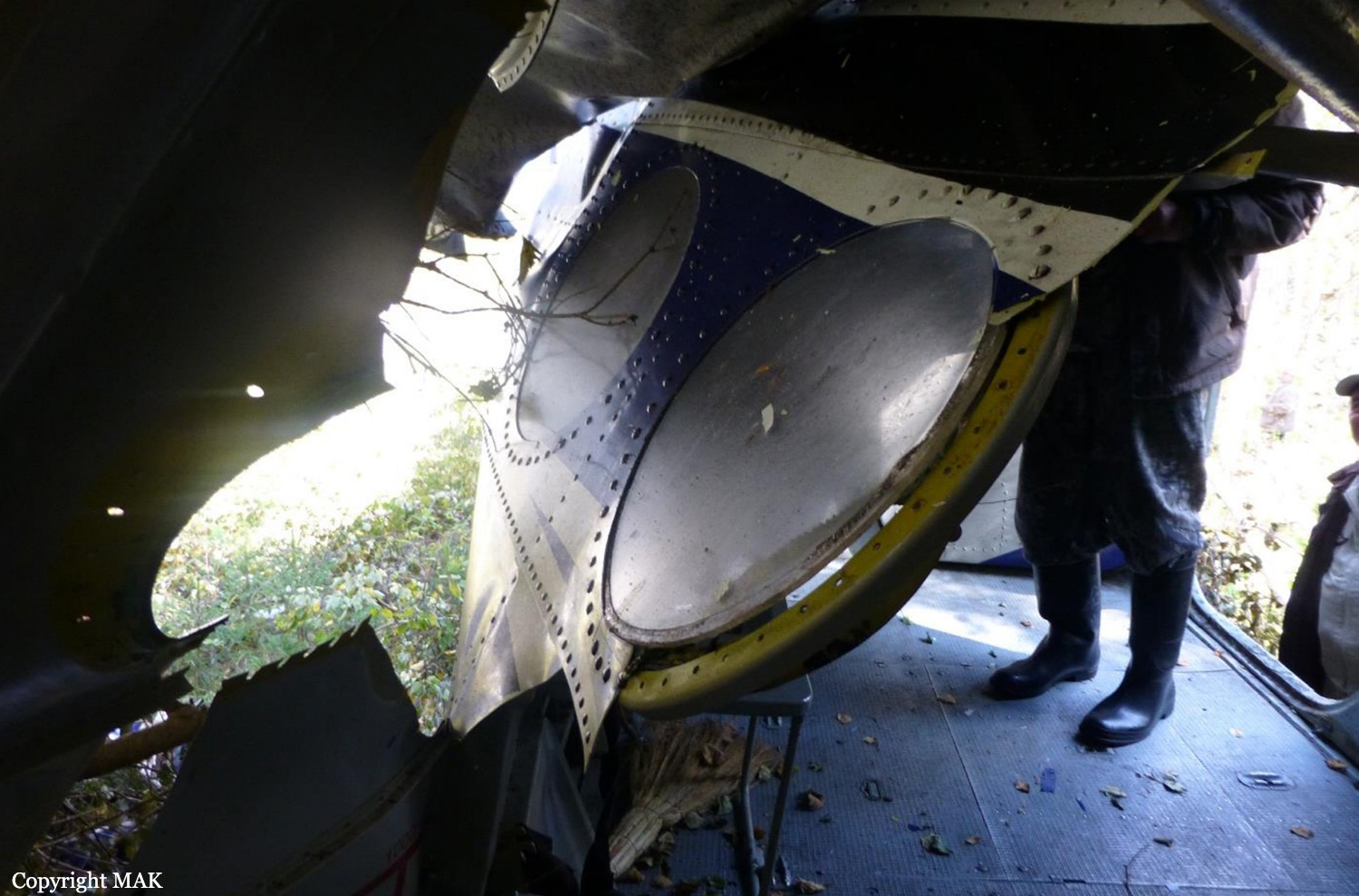
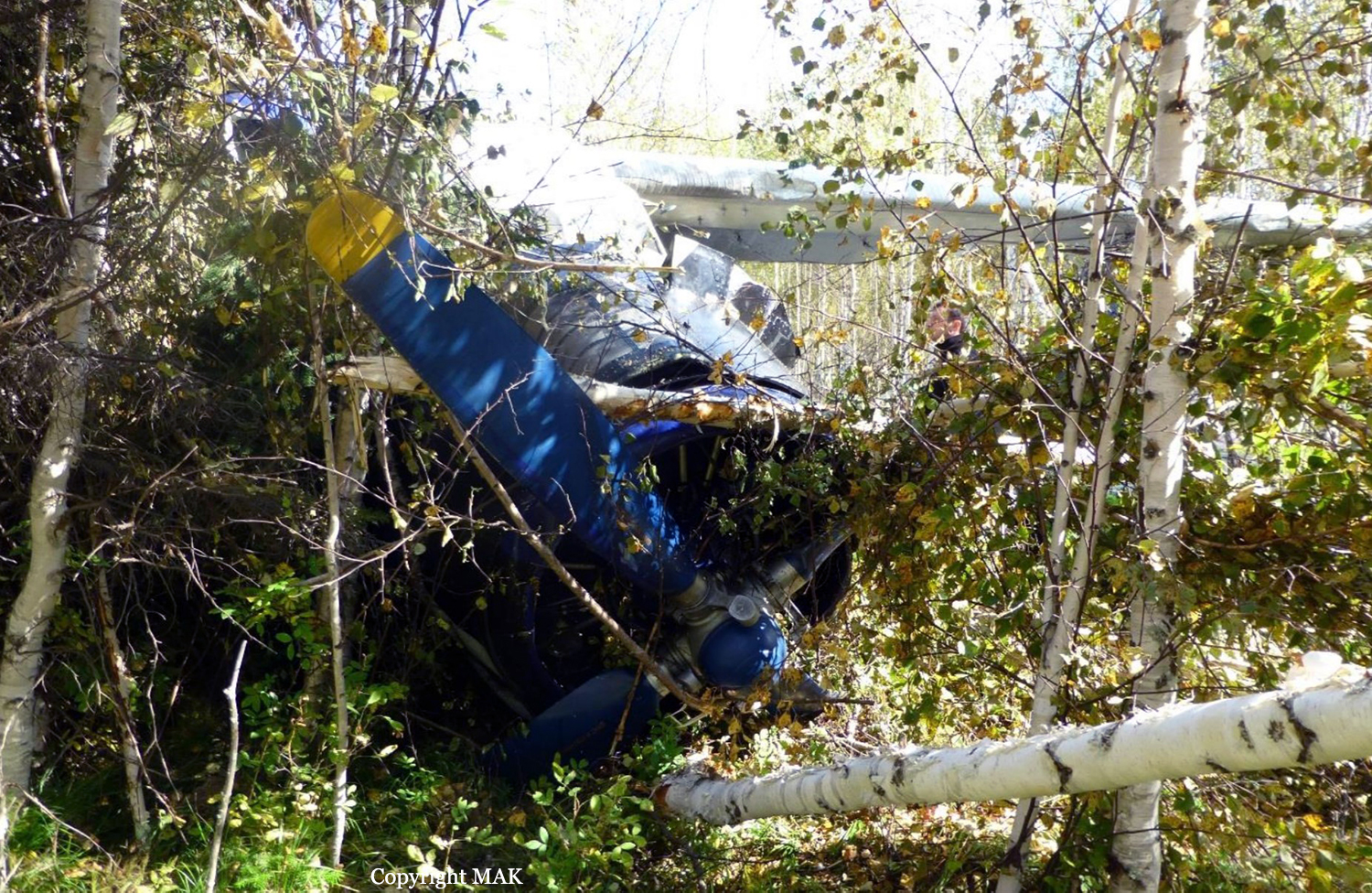
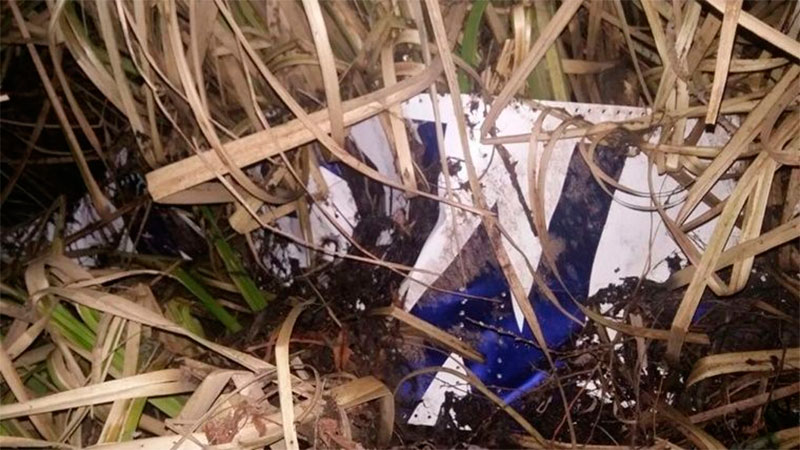
The airplane departed Egelsbach Airport at 1743LT on a charter flight to Friedrichshafen, carrying one passenger and two pilots. Following an uneventful flight at FL210, the crew contacted Zurich ARTCC and was cleared to start the descent and later told to expect a runway 24 ILS approach to Friedrichshafen-Bodensee Airport. After passing 4,000 feet on descent, at a speed of 240 knots, the crew was completing a last turn in clouds when the airplane entered a rapid and uncontrolled descent until it crashed in a wooded area located in Sieberatsreute, some 15 km short of runway 24. The airplane disintegrated on impact and all three occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
The aircraft accident was caused by a sudden loss of control of the aircraft in clouds while turning in for the approach to Friedrichshafen at night. Probably the frontal weather with light to moderate turbulence, snowfall and icing contributed to this. The absence of information about the events on board the aircraft meant that it was not possible to determine the causes of the loss of control.
Final Report: