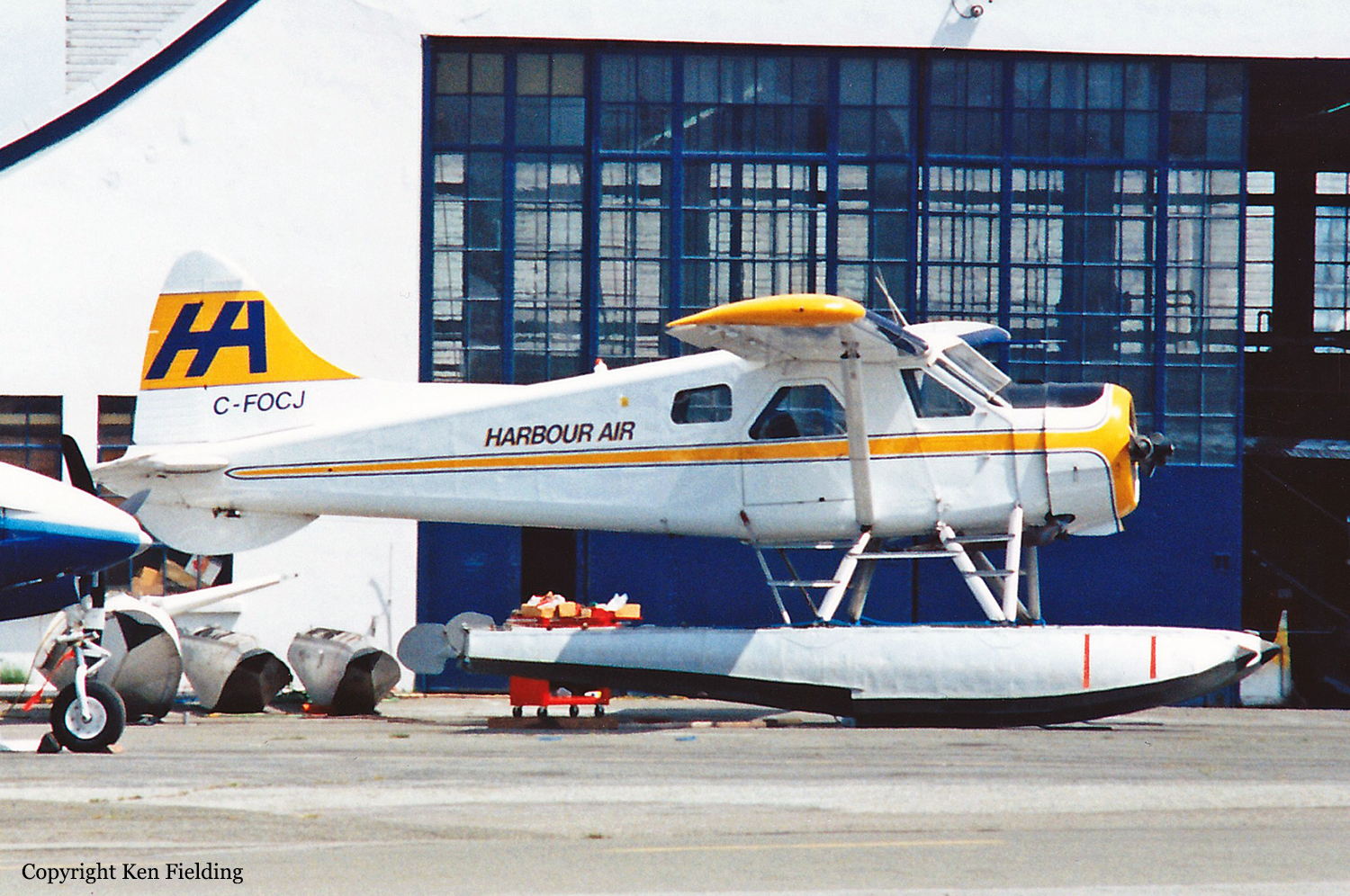
Crash of a De Havilland DHC-2 Beaver near Kincolith: 5 killed
Date & Time:
Aug 4, 1998 at 1758 LT
Registration:
C-FOCJ
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Prince Rupert - Kincolith
MSN:
39
YOM:
1949
Flight number:
H3709
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
4
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
5
Captain / Total hours on type:
1250.00
Aircraft flight hours:
22369
Circumstances:
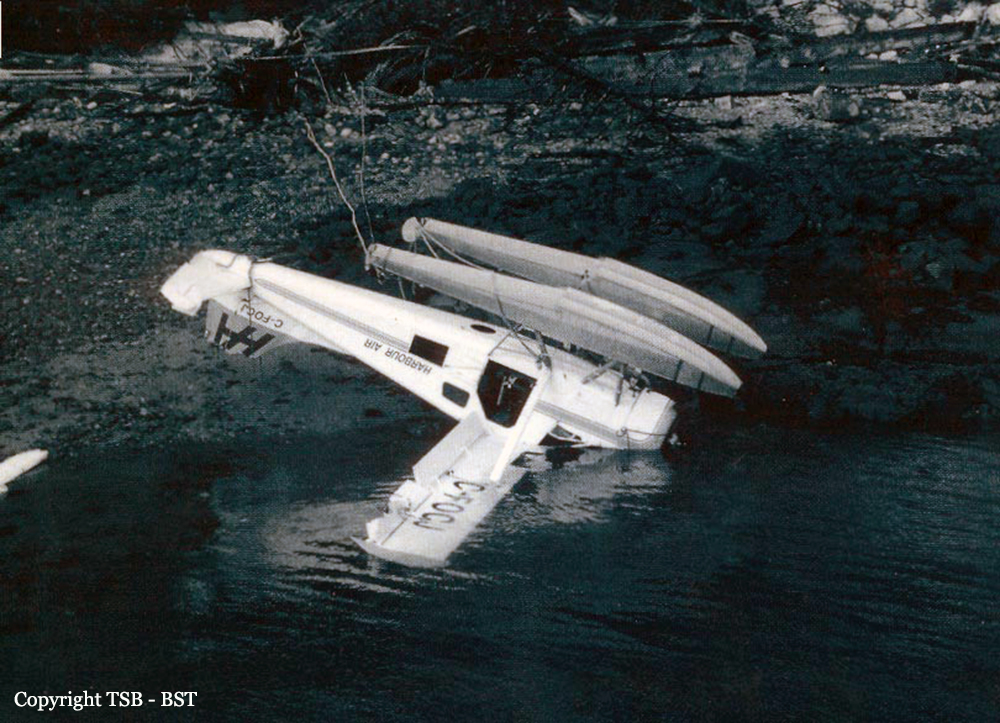
The float-equipped de Havilland DHC-2 Beaver, serial number 0039, departed Prince Rupert, British Columbia, at 1719 Pacific daylight time on a visual flight rules flight to Kincolith, British Columbia, with the pilot and four passengers on board. When the aircraft arrived at Kincolith at about 1750, witnesses watched it carry out three low approaches to the water landing area, each time descending to a few feet above the water before climbing away. On the fourth approach, at about 1758, the aircraft touched down, apparently in a controlled manner, and skipped on the water surface. The floats then dug into the water followed by the right wing, which was severed from the fuselage on water impact. The aircraft quickly overturned and came to rest inverted with only the bottom of the floats visible. Several members of the village community, who had been waiting for the aircraft on the Government Dock, rushed to the sunken aircraft in small boats but were unable to rescue the pilot or passengers inside the submerged cabin. The five occupants drowned in the accident, and the aircraft was substantially damaged.
Probable cause:
On touchdown, the float(s) struck the water and caused a flying attitude that the pilot could not control before the right wing dug in and the aircraft overturned. Contributing to the accident were conflicting wind and water conditions at the time of the occurrence.
Final Report: