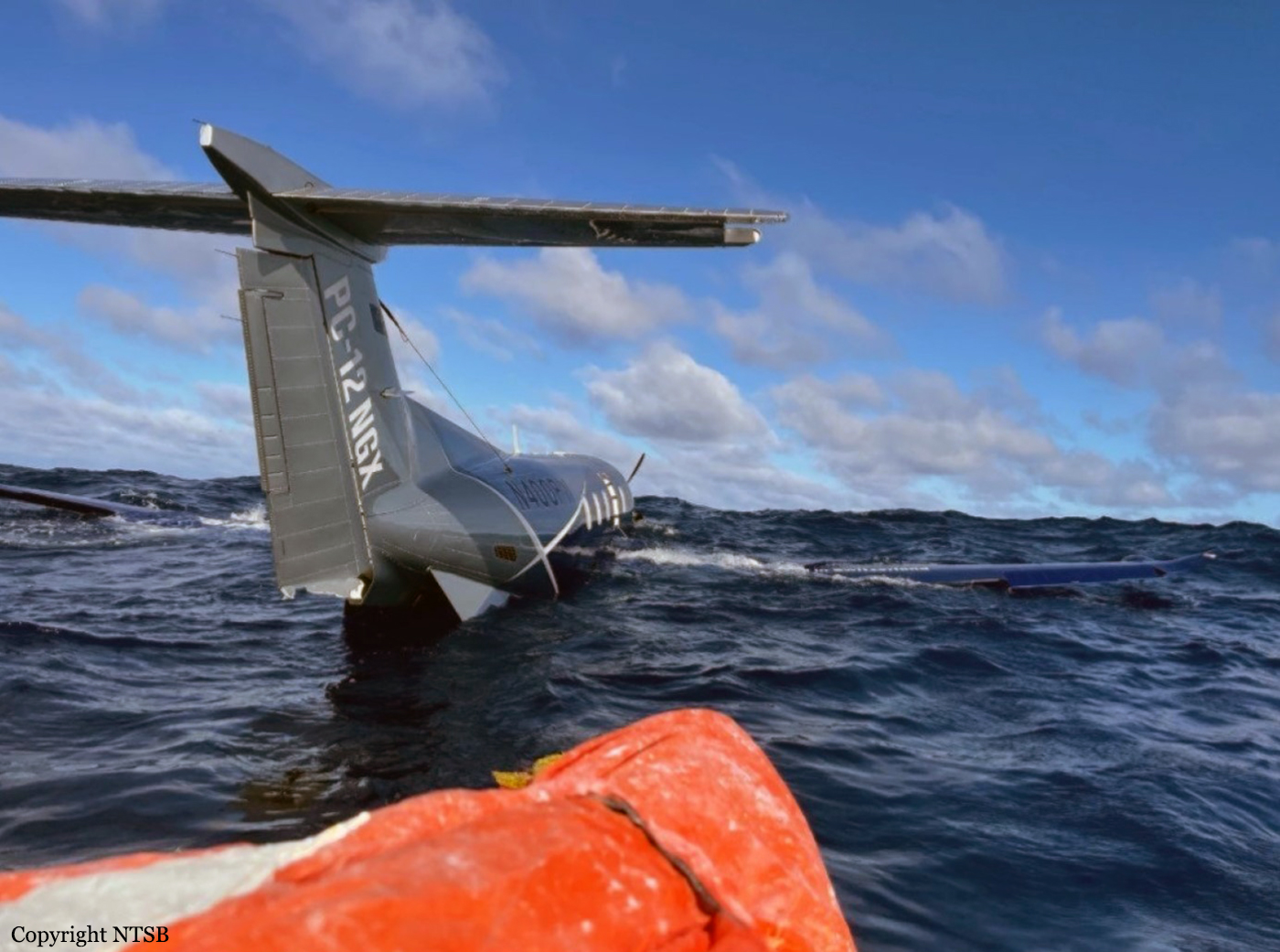
Crash of a Pilatus PC-12 NGX in the Pacific Ocean
Date & Time:
Nov 6, 2020 at 1520 LT
Registration:
N400PW
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Santa Maria - Hilo
MSN:
2003
YOM:
2020
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
22.00
Circumstances:
On November 6, 2020, about 1600 Pacific standard time, a Pilatus PC-12, N400PW, was substantially damaged when it was ditched in the Pacific Ocean about 1000 miles east of Hilo, Hawaii. The two pilots sustained no injuries. The airplane was operated as a Title 14 Code of Federal Regulations Part 91 ferry flight. According to the pilot-in-command (PIC), who was also the ferry company owner, he and another pilot were ferrying a new airplane from California to Australia. The first transoceanic leg was planned for 10 hours from Santa Maria Airport (KSMX), Santa Maria, California to Hilo Airport (PHTO), Hilo, Hawaii. The manufacturer had an auxiliary ferry fuel line and check valve installed in the left wing before delivery. About 1 month before the trip, the pilot hired a ferry company to install an internal temporary ferry fuel system for the trip. The crew attempted the first transoceanic flight on November 2, but the ferry fuel system did not transfer properly, so the crew diverted to Merced Airport (KMCE), Merced, California. The system was modified with the addition of two 30 psi fuel transfer pumps that could overcome the ferry system check valve. The final system consisted of 2 aluminum tanks, 2 transfer pumps, transfer and tank valves, and associated fuel lines and fittings. The ferry fuel supply line was connected to the factory installed ferry fuel line fitting at the left wing bulkhead, which then fed directly to the main fuel line through a check valve and directly to the turbine engine. The installed system was ground and flight checked before the trip. According to Federal Aviation Administration automatic dependent surveillance broadcast (ADS-B) data, the airplane departed KSMX about 1000. The pilots each stated that the ferry fuel system worked as designed during the flight and they utilized the operating procedures that were supplied by the installer. About 5 hours after takeoff, approaching ETNIC intersection, the PIC climbed the airplane to flight level 280. At that time, the rear ferry fuel tank was almost empty, and the forward tank was about 1/2 full. The crew was concerned about introducing air into the engine as they emptied the rear ferry tank, so the PIC placed the ignition switch to ON. According to the copilot (CP), she went to the cabin to monitor the transparent fuel line from the transfer pumps to ensure positive fuel flow while she transferred the last of the available rear tank fuel to the main fuel line. When she determined that all of the usable fuel was transferred, and fuel still remained in the pressurized fuel line, she turned the transfer pumps to off and before she could access the transfer and tank valves, the engine surged and flamed out. The PIC stated that the crew alerting system (CAS) fuel low pressure light illuminated about 5 to 15 seconds after the transfer pumps were turned off, and then the engine lost power and the propeller auto feathered. The PIC immediately placed the fuel boost pumps from AUTO to ON. The CP went back to her crew seat and they commenced the pilot operating handbook’s emergency checklist procedures for emergency descent and then loss of engine power in flight. According to both crew members, they attempted an engine air start. The propeller unfeathered and the engine started; however, it did not reach flight idle and movement of the power control lever did not affect the engine. The crew secured the engine and attempted another air start. The engine did not restart and grinding sounds and a loud bang were heard. The propeller never unfeathered and multiple CAS warning lights illuminated, including the EPECS FAIL light (Engine and Propeller Electronic Control System). The crew performed the procedures for a restart with EPECS FAIL light and multiple other starts that were unsuccessful. There were no flames nor smoke from either exhaust pipe during the air start attempts. About 8,000 ft mean sea level, the crew committed to ditching in the ocean. About 1600, after preparing the survival gear, donning life vests, and making mayday calls on VHF 121.5, the PIC performed a full flaps gear up landing at an angle to the sea swells and into the wind. He estimated that the swells were 5 to 10 ft high with crests 20 feet apart. During the landing, the pilot held back elevator pressure for as long as possible and the airplane landed upright. The crew evacuated through the right over wing exit and boarded the 6 man covered life raft. A photograph of the airplane revealed that the bottom of the rudder was substantially damaged. The airplane remained afloat after landing. The crew utilized a satellite phone to communicate with Oakland Center. The USCG coordinated a rescue mission. About 4 hours later, a C-130 arrived on scene and coordinated with a nearby oil tanker, the M/V Ariel, for rescue of the crew. According to the pilots, during the night, many rescue attempts were made by the M/V Ariel; however, the ship was too fast for them to grab lines and the seas were too rough. After a night of high seas, the M/V Ariel attempted rescue again; however, they were unsuccessful. That afternoon, a container ship in the area, the M/V Horizon Reliance, successfully maneuvered slowly to the raft, then the ship’s crew shot rope cannons that propelled lines to the raft, and they were able to assist the survivors onboard. The pilots had been in the raft for about 22 hours. The airplane was a new 2020 production PC-12 47E with a newly designed Pratt and Whitney PT6E-67XP engine which featured an Engine and Propeller Electronic Control System. The airplane is presumed to be lost at sea.
Probable cause:
A total loss of engine power due to fuel starvation for reasons that could not be determined based on the available evidence.
Final Report: