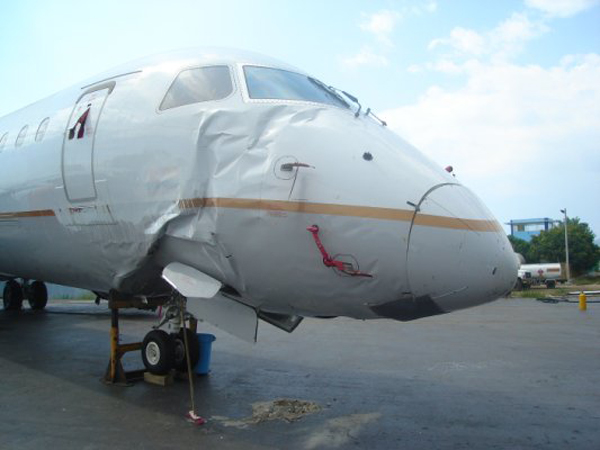
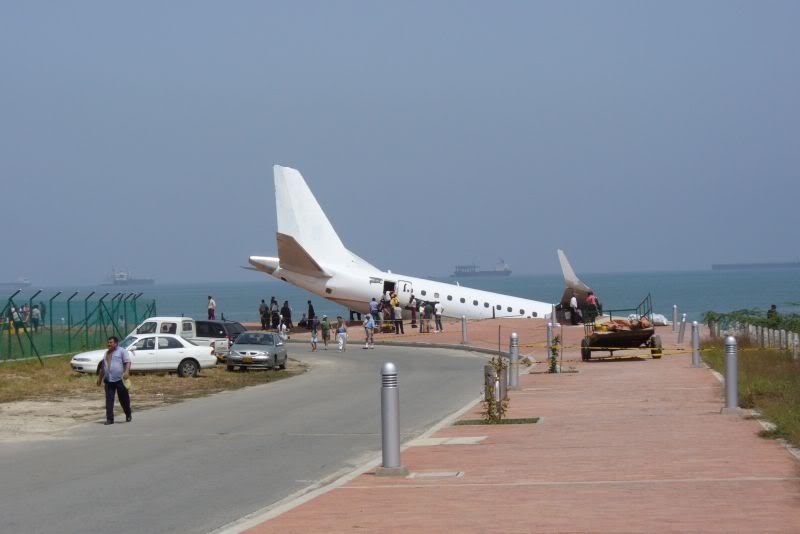
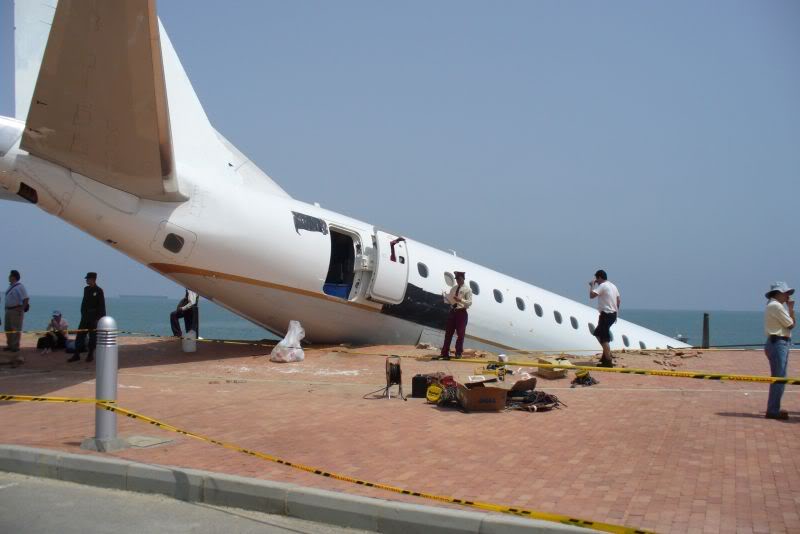
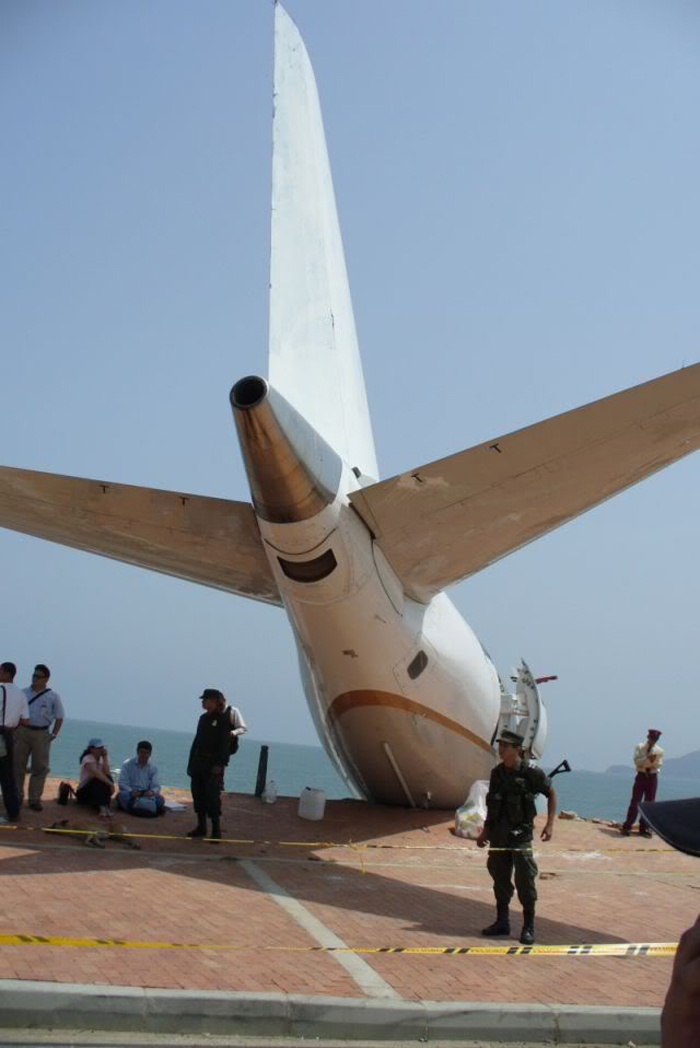
Circumstances:
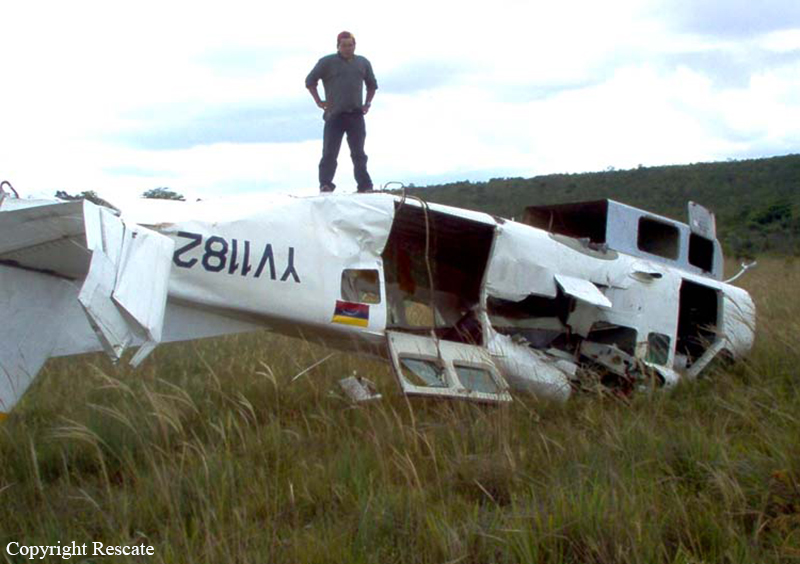
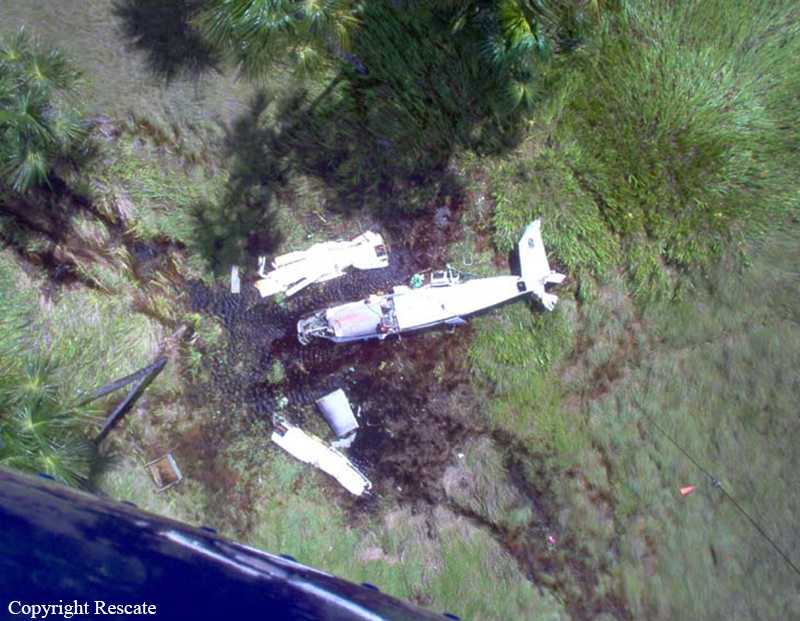
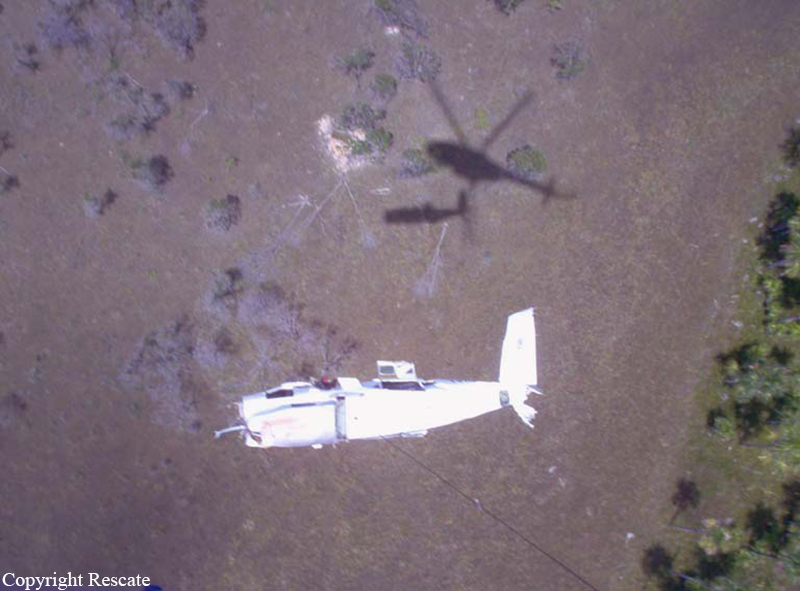
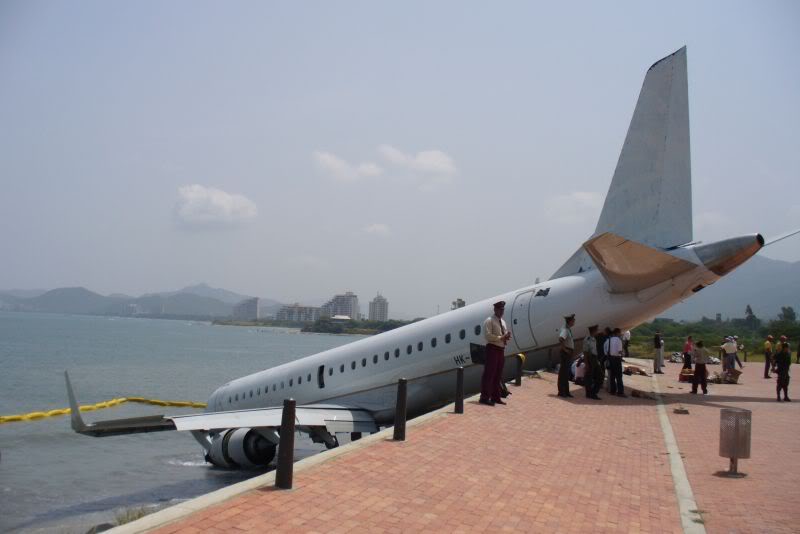
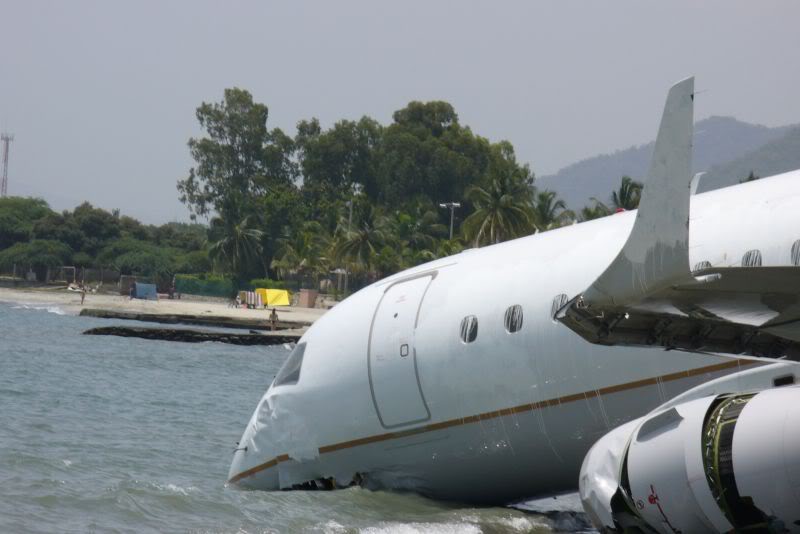
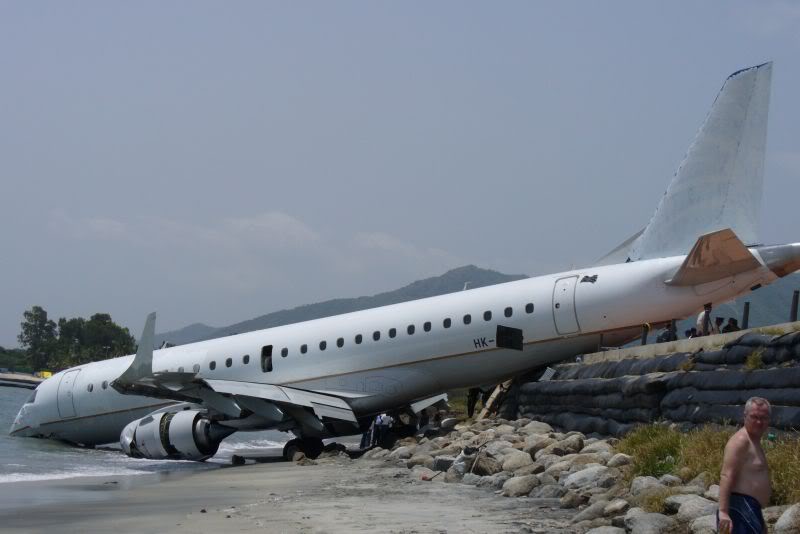
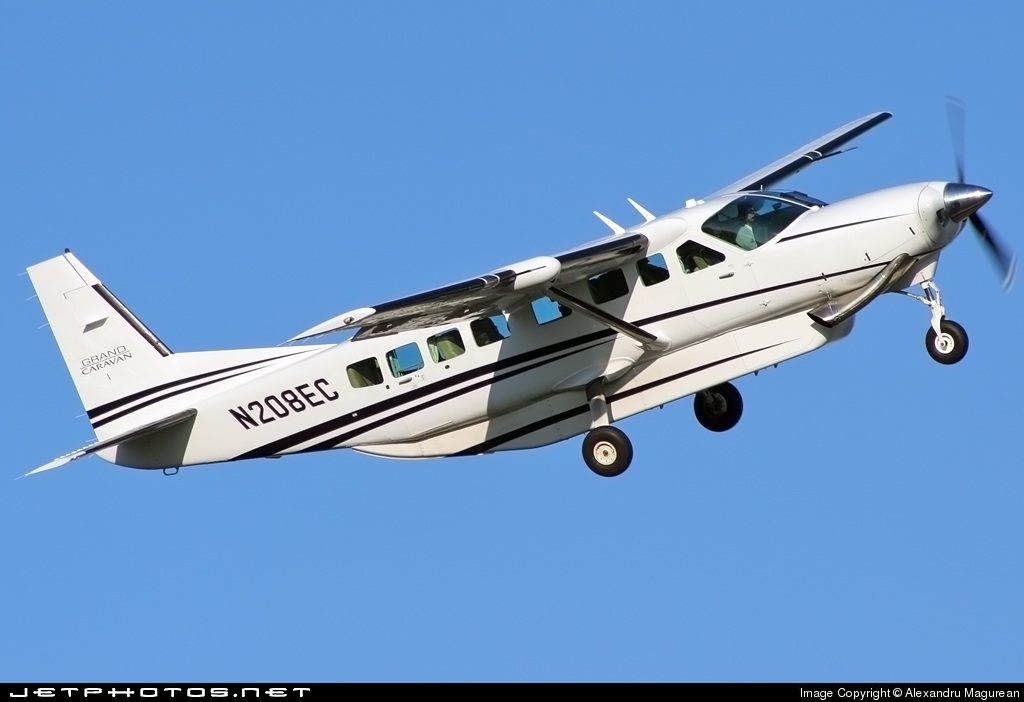
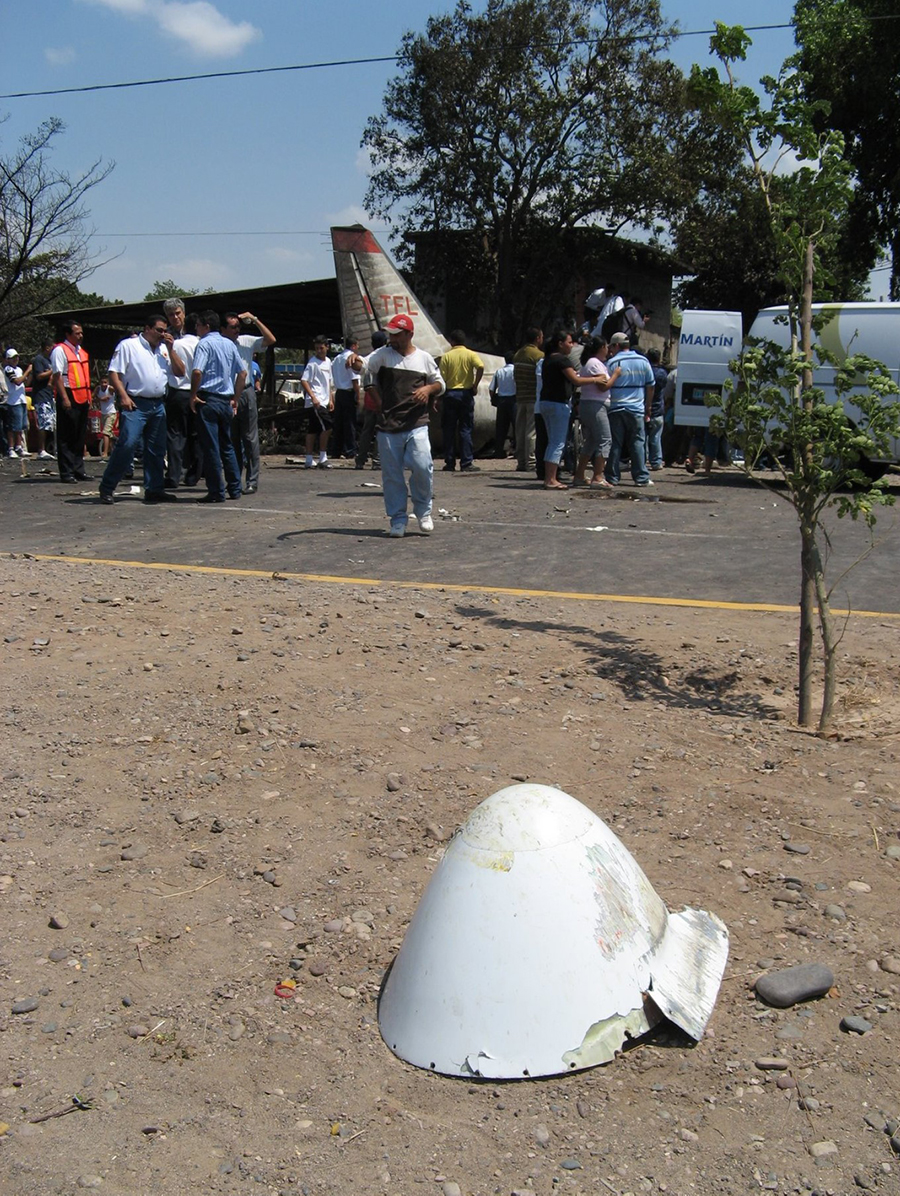
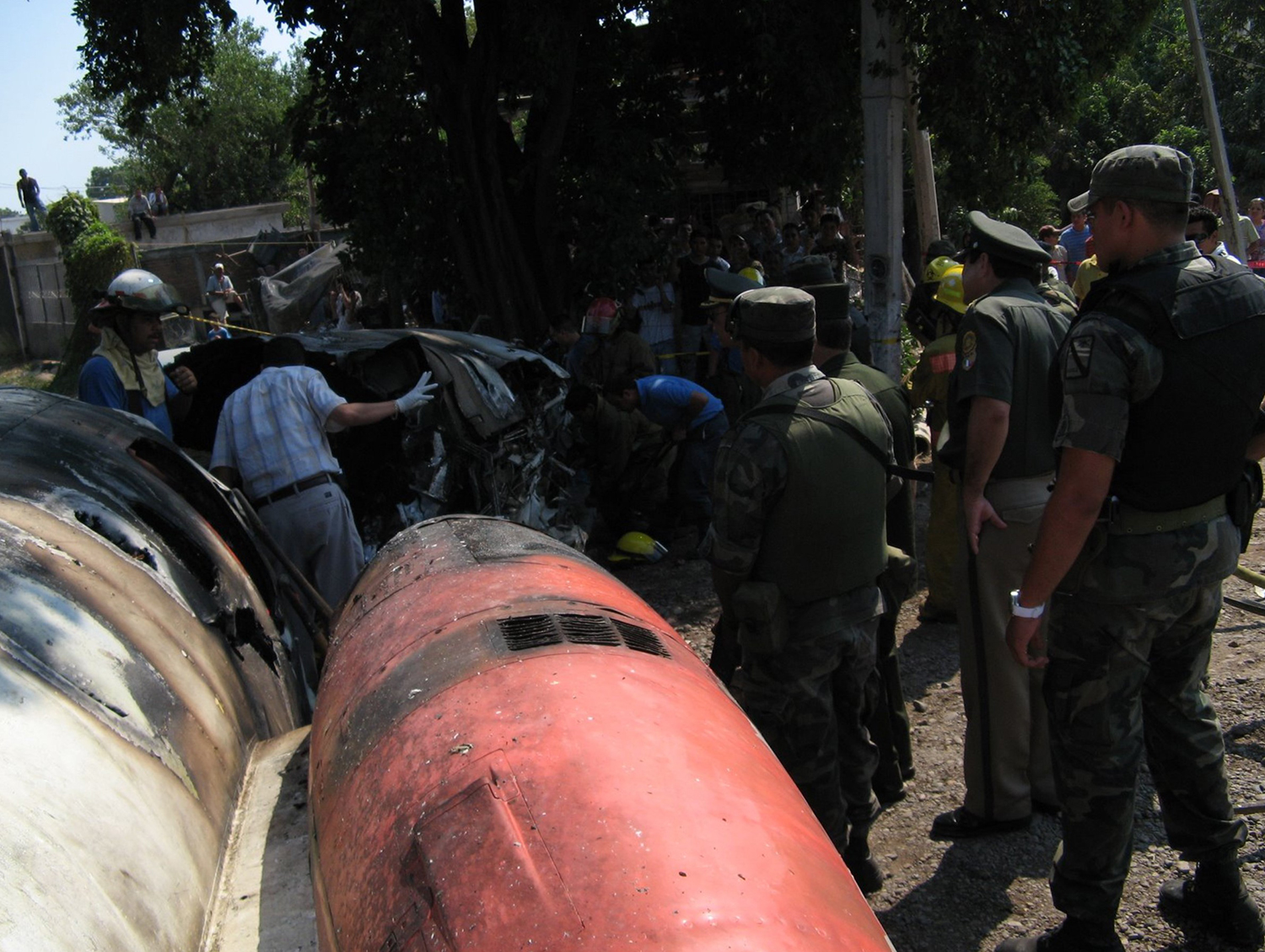
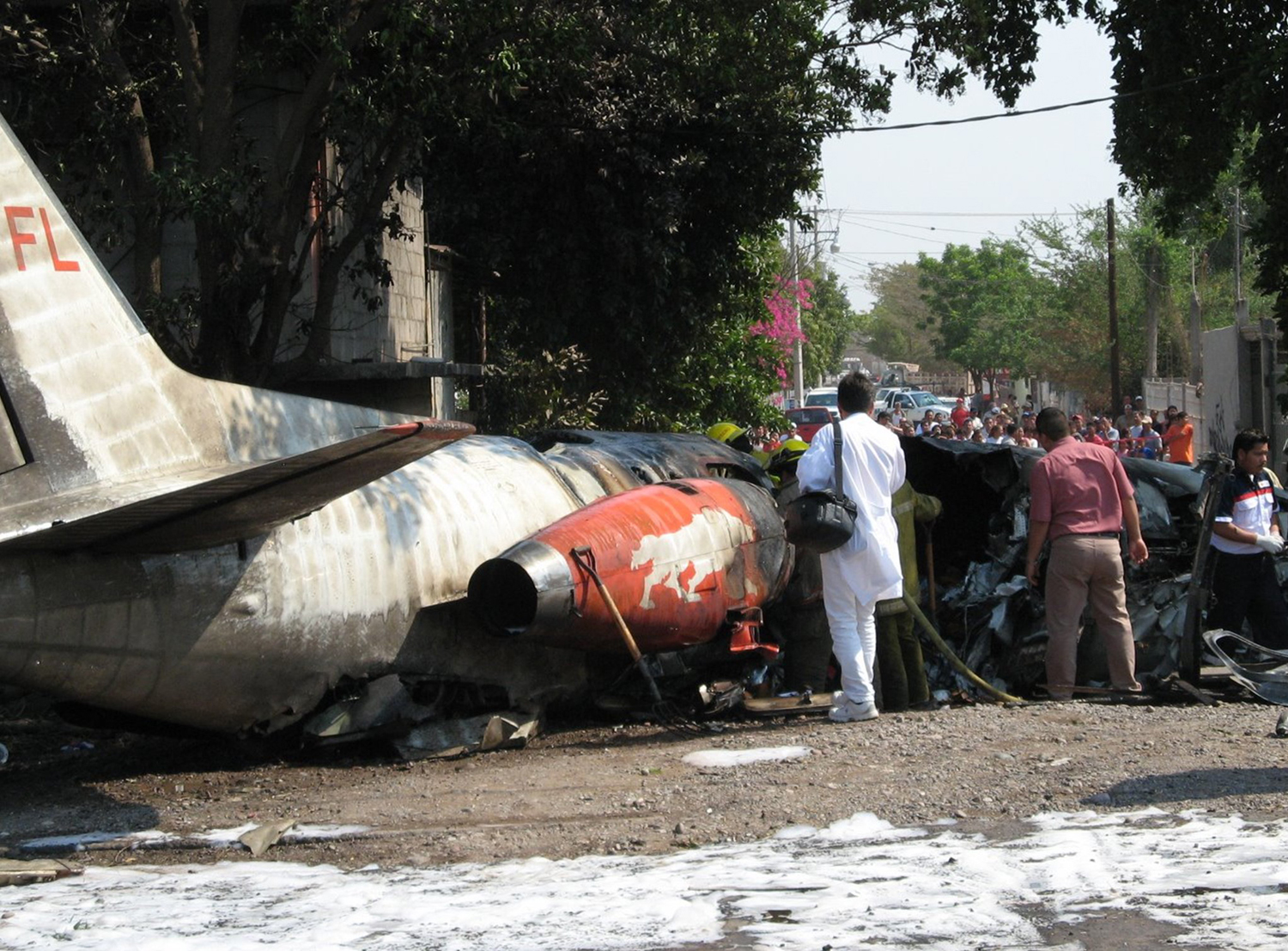
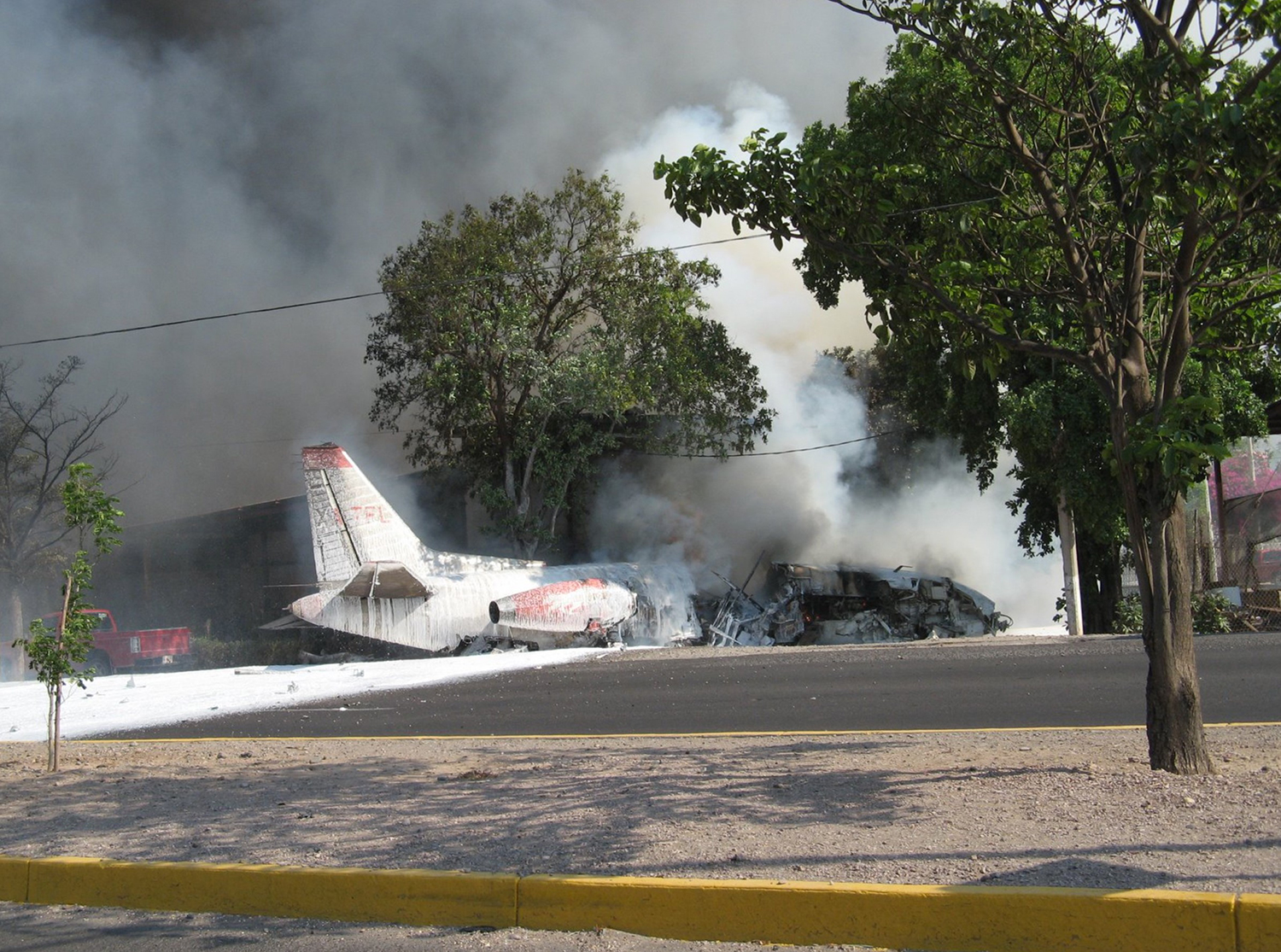
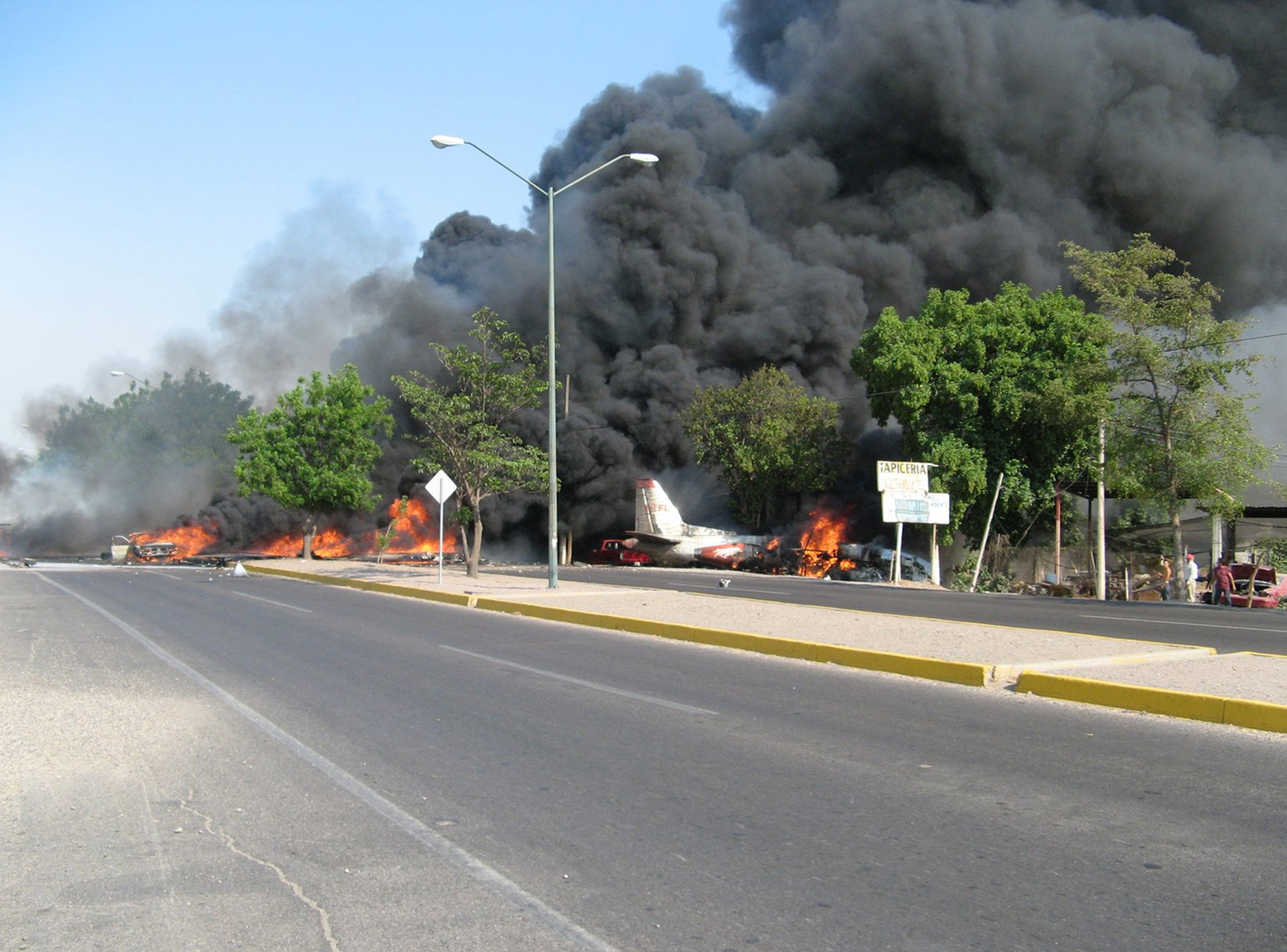
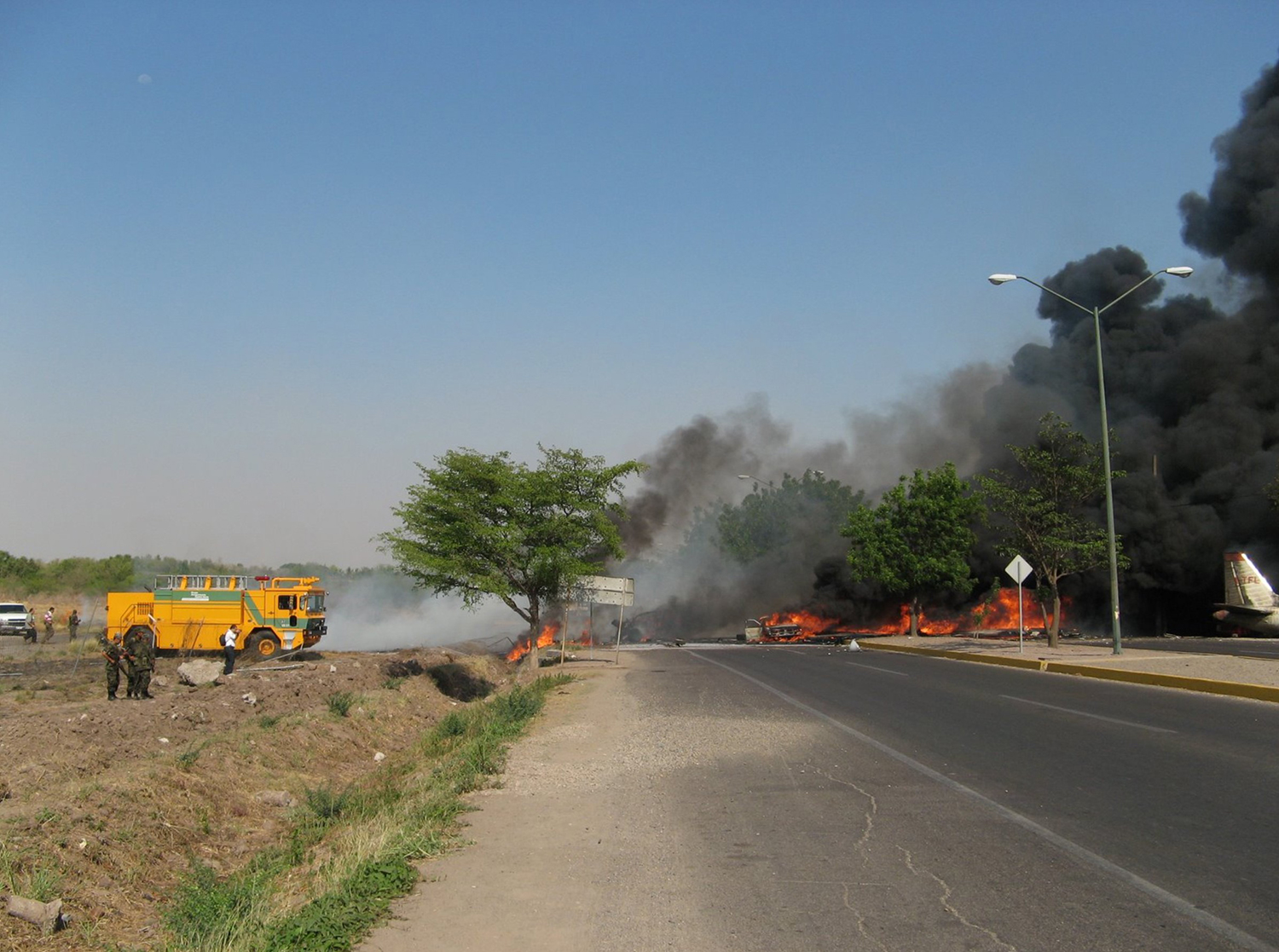
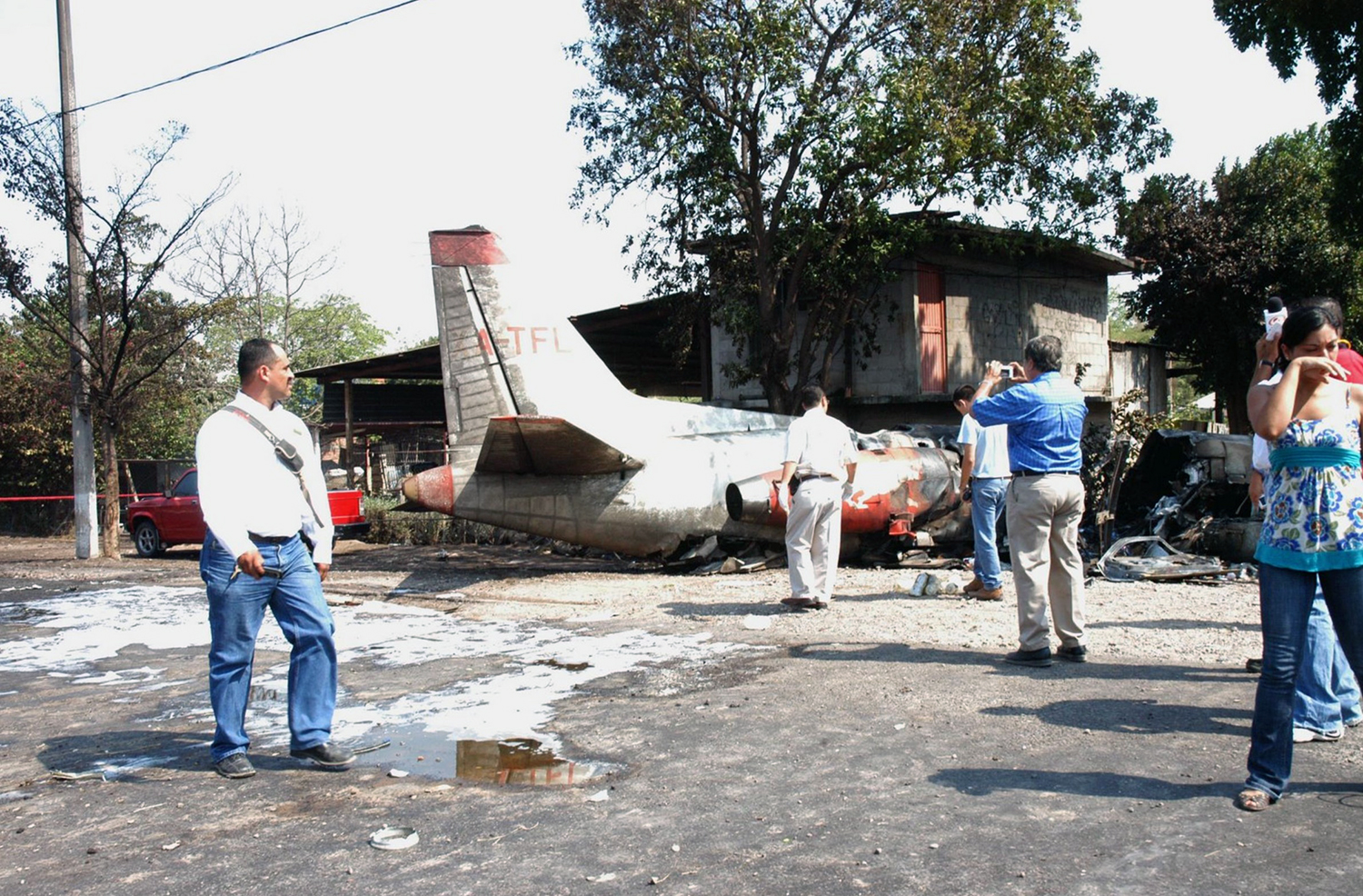
The purpose of the flight was a demonstration of an aircraft to a group of potential investors and interested parties associated with a proposed airport at Clifden, Co. Galway, some 25 nm to the northwest of EICA. The flight was organised by one of this group who requested the aircraft, a Cessna Caravan registration N208EC, through an Aircraft Services Intermediary (ASI) from the aircraft’s beneficial owner. The owner agreed to loan his aircraft and the pilot, to fly the group from EICA to EIMN, (a distance of 9 nm) and back. The aircraft departed from Weston (EIWT) aerodrome, near Dublin, at 08.20 hrs on the day of the accident. It over flew Galway (EICM) to EICA where it landed and shutdown. There were two persons on board, the Pilot and an Aircraft Maintenance Specialist (AMS). After a short discussion with ground staff, the Pilot and AMS flew a familiarisation flight to EIMN where the aircraft landed and taxied to the terminal. It did not stop or shut down but turned on the ramp and flew back to EICA where it shut down and parked while awaiting the arrival of the group. The group assembled at EICA, but as there were too many passengers to be accommodated on one aircraft, two flights were proposed with the aircraft returning to pick up the remainder. The aircraft then departed with the first part of the group. On arrival at EIMN, the Pilot contacted those remaining and informed them that he would not be returning for them. This did not cause a problem because an Aer Arran Islander aircraft, with its pilot, was available at EICA to fly the remainder of the group across to EIMN. Following lunch in a local hotel the AMS made a presentation on behalf of the ASI on the Cessna Caravan, its operation and costing. The Pilot assisted him, answering questions of an operational nature. During the presentation two members of the group, who had a meeting to attend on the mainland, travelled back on the Islander aircraft to EICA. The Islander aircraft subsequently returned to EIMN to assist in transporting the remainder of the group back to EICA. The aircraft was returning on a short flight from Inis Meáin (EIMN), one of the Aran Islands in Galway Bay, to Connemara Airport (EICA), in marginal weather conditions when the accident occurred. There had been a significant wind shift, since the time the aircraft had departed earlier from EICA that morning, of which the Pilot appeared to be unaware. As a result a landing was attempted downwind. At a late stage, a go-around was initiated, at a very low speed and high power setting. The aircraft turned to the left, did not gain altitude and maintained a horizontal trajectory. It hit a mound, left wing first and cartwheeled. The Pilot and one of the passengers were fatally injured. The remaining seven passengers were seriously injured. The aircraft was destroyed but there was no fire. The emergency fire service from the airport quickly attended. Later an ambulance, a local doctor and then the Galway Fire Services arrived. A Coastguard Search and Rescue helicopter joined in transporting the injured to hospital. The Gardaí Síochána secured the site pending the arrival of the AAIU Inspectors.
Probable cause:
The Pilot attempted to land downwind in marginal weather conditions. This resulted in a late go-around during which control was lost due to inadequate airspeed.
Contributory Factors:
1. Communications were not established between the Pilot and EICA thus denying the Pilot the opportunity of being informed of the changed wind conditions and the runway in use.
2. The aircraft was over maximum landing weight.
3. The altimeters were under-reading due to incorrect QNH settings.
4. The additional stress on the Pilot associated with the conduct of a demonstration flight.