Circumstances:
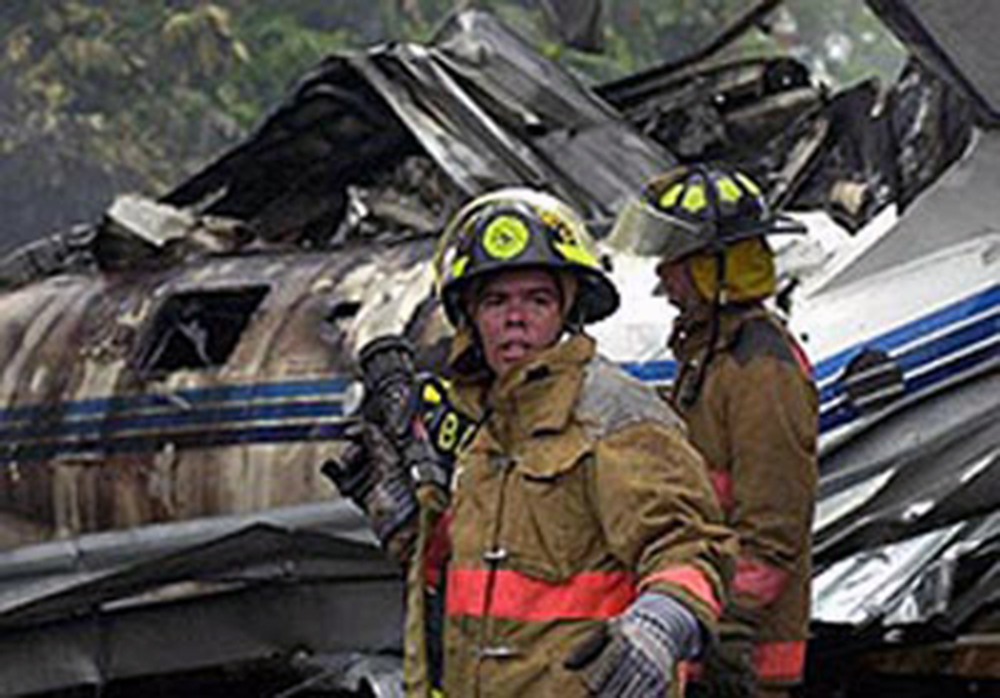
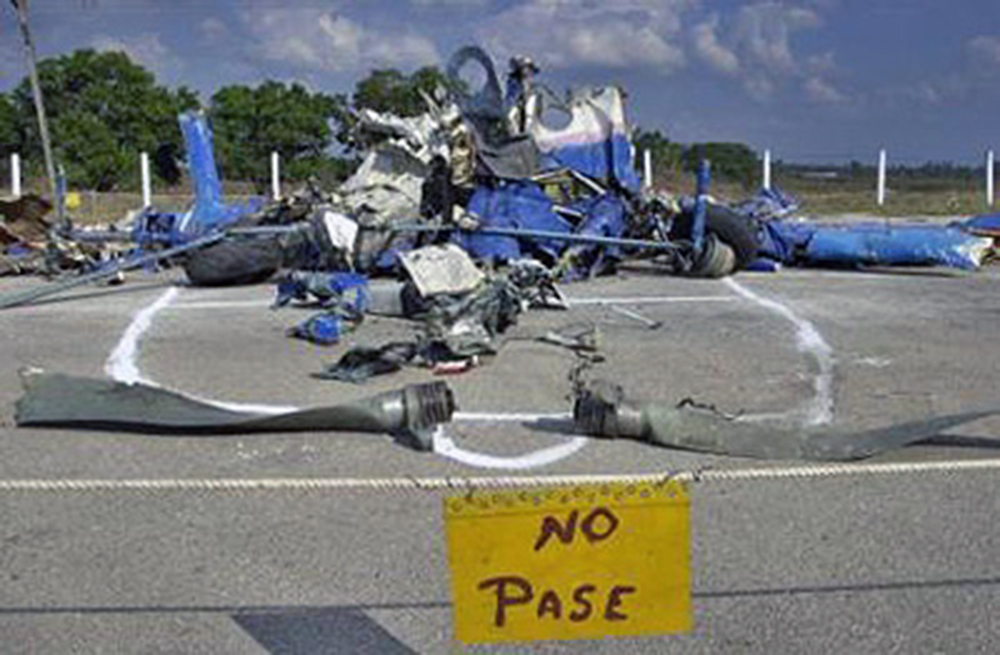
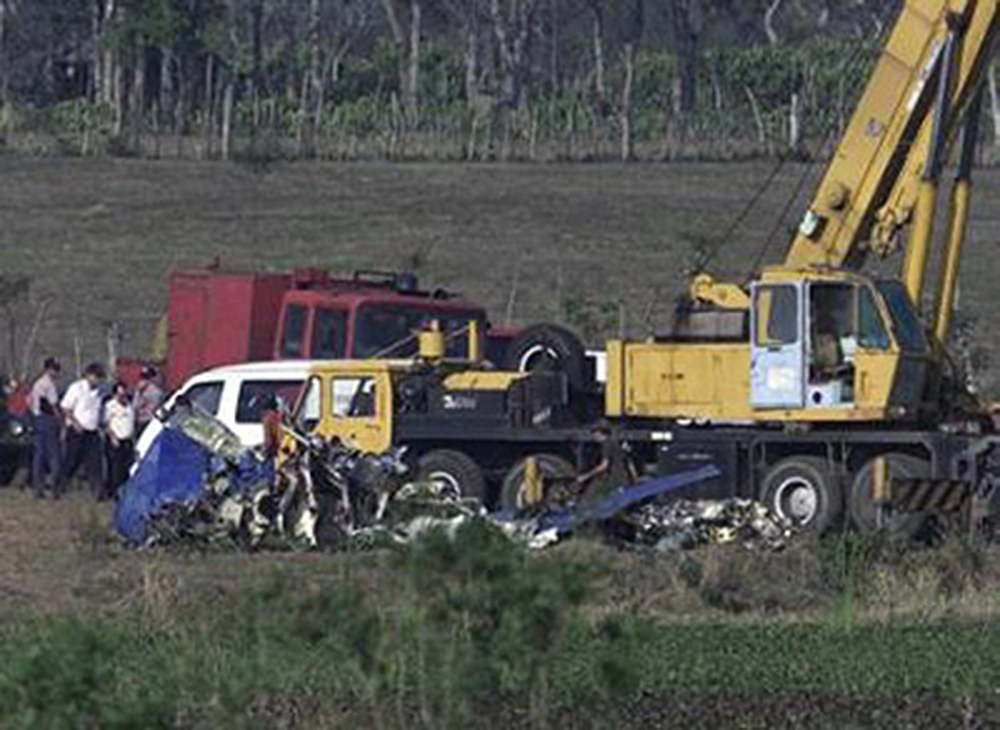
The flight departed VFR, and when near the destination airport, was advised by air traffic control to hold VFR over the "plaza" and to make left 360 degree orbits. Several witnesses reported light rain was occurring at the time of the accident; there was no lightning or thunder. One witness located where the airplane came to rest reported observing the airplane emerge from the base of the clouds in a 45-degree left wing low and 20 degrees nose low attitude. He momentarily lost sight of the airplane but then noted it rolled to a wings level attitude. He also reported hearing the engine(s) "cutting in an out." Another witness located approximately 1/4 mile north of the accident site observed the airplane flying eastbound beneath the clouds in a right wing and nose low attitude, he also reported hearing the engine(s) sounding like they were "cutting in and out." A pilot-rated witness located an estimated 1,000 feet from where the airplane came to rest estimated that the ceiling was at 300 feet and there was light drizzle. He observed the airplane in a 45-degree angle of bank to the right and in a slight nose low attitude. He stated that the airplane continued in that attitude before he lost sight of the airplane at 250 feet. The airplane impacted trees then a concrete wall while in a nose and right wing low attitude. The airplane then traveled through automobile hoists/lifts which were covered by corrugated metal, and came to rest adjacent to a building of an automobile facility. Impact and a post crash fire destroyed the airplane, along with a building and several vehicles parked at the facility. Examination of the airplane revealed the flaps were symmetrically retracted and landing gears were retracted. No evidence of preimpact failure or malfunction was noted to the flight controls. Examination of the engines revealed no evidence of preimpact failure or malfunction; impact and fire damage precluded testing of several engine accessories from both engines. Examination of the propellers revealed no evidence of preimpact failure or malfunction. Parallel slash marks were noted in several of the corrugated metal panels that covered the hoists/lifts, the slashes were noted 25 and 21 inches between them. According to the airplane manufacturer, the 25 inch distance between the propeller slashes corresponds to an airspeed of 123 knots. Additionally, the power-off stall speed at the airplanes calculated weight with the flaps retracted and 48 degree angle of bank was calculated to be 122 knots. Review of NTSB plotted radar data revealed that the pilot performed one 360-degree orbit to the left with varying angles of left bank and while flying initially at 1,300 feet, climbing to near 1,500 feet, then descending to approximately 800 feet. The airplane continued in the left turn and between 1502:10 and 1502:27, the calibrated airspeed decreased from 160 to 100 knots. At 1502:27, the bank angle was 48 degrees, and the angle of attack was 26 degrees. Between 1502:30 and 1502:35, the true heading changed indicating a bank to the right. The last plotted altitude was 200 feet, which occurred at 1502:35. A NTSB weather study indicated that at the area and altitude the airplane was operating, NWS VIP level 1 to 2 echoes (light to moderate intensity) were noted. Additionally, the terminal aerodrome forecast (TAF) for the destination airport indicated that temporarily between 1400 and 1800 (the flight departed at approximately 1436 and the accident occurred at approximately 1503), visibility 5 miles with moderate rain showers, scattered clouds at 1,500 feet, and a broken ceiling at 3,000 feet.
Probable cause:
The failure of the pilot to maintain airspeed (Vs) while maneuvering following inadvertent encounter with clouds resulting in an inadvertent stall and uncontrolled descent and subsequent in-flight collision with trees, a wall, and a building.