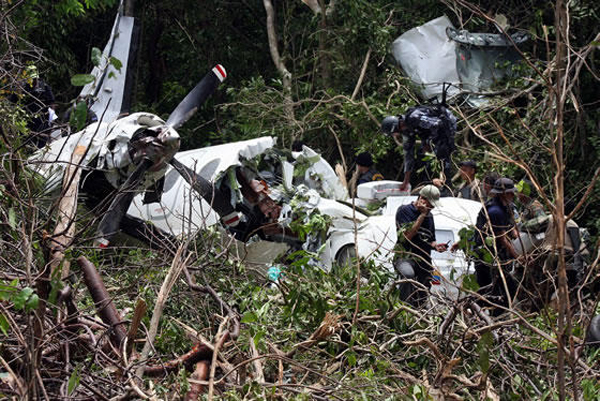
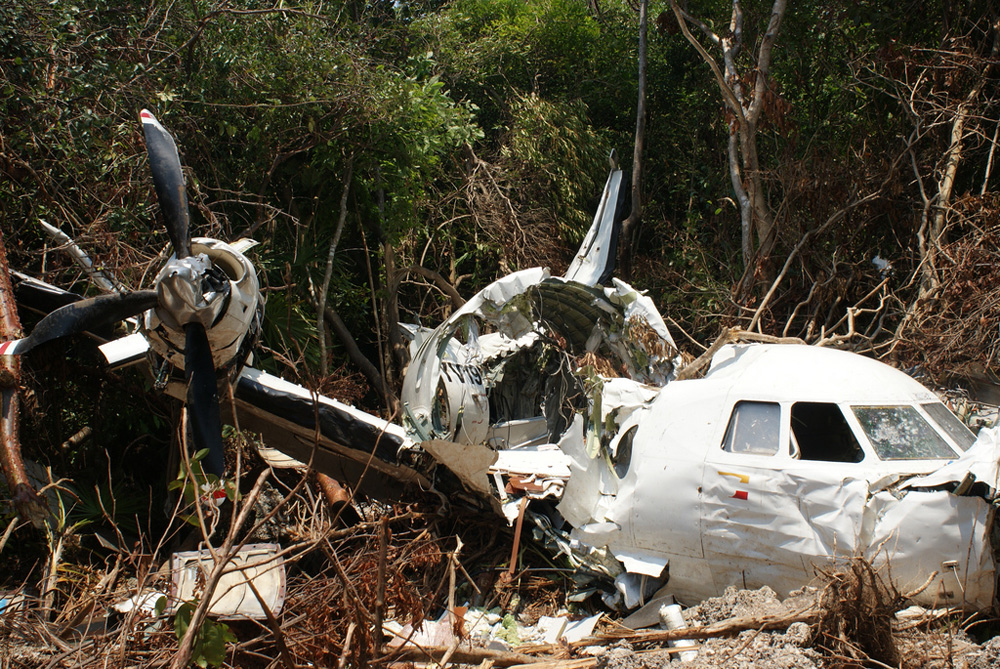
Crash of a Beechcraft 350 Super King Air in Porto Seguro: 14 killed
Date & Time:
May 22, 2009 at 2053 LT
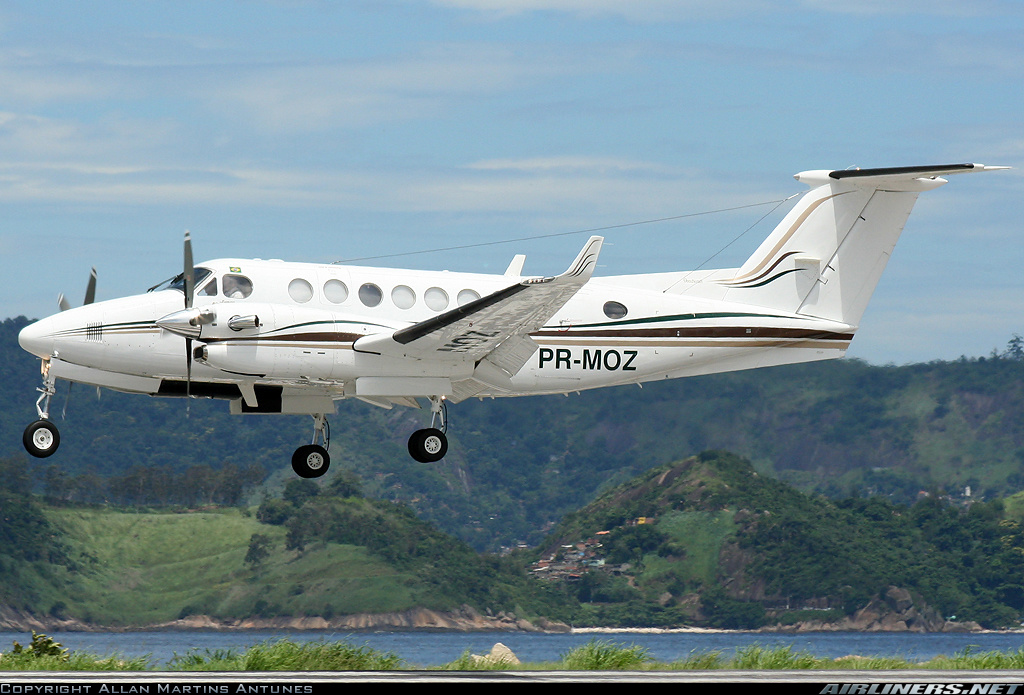
Registration:
PR-MOZ
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
São Paulo – Porto Seguro
MSN:
FL-237
YOM:
1999
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
12
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
14
Captain / Total hours on type:
5000.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
107
Circumstances:
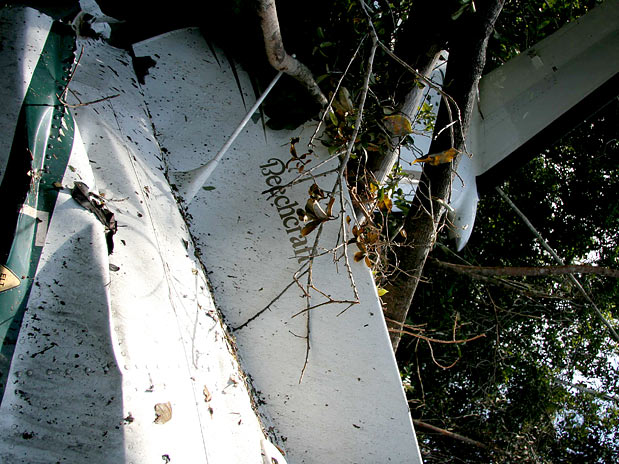
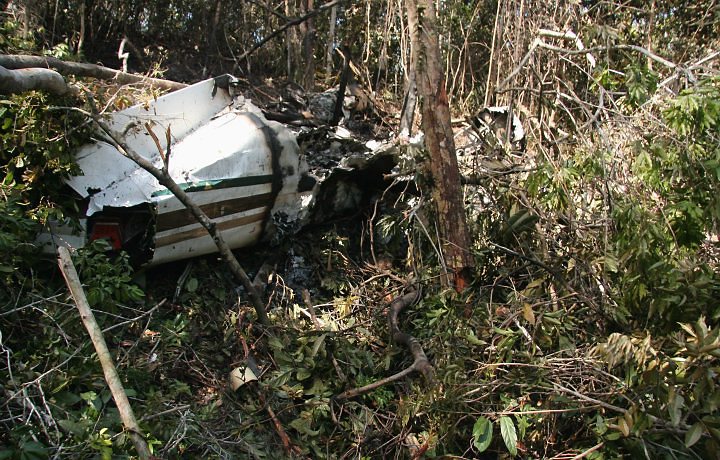
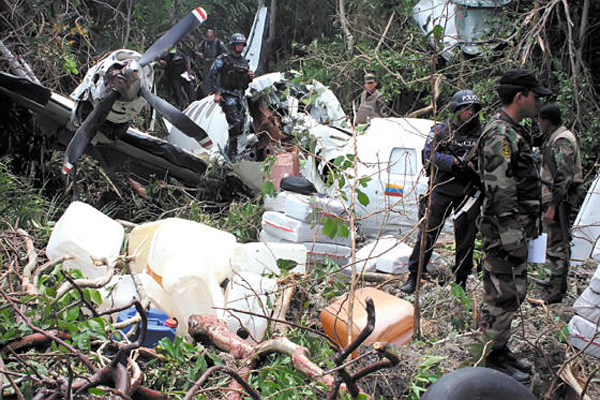
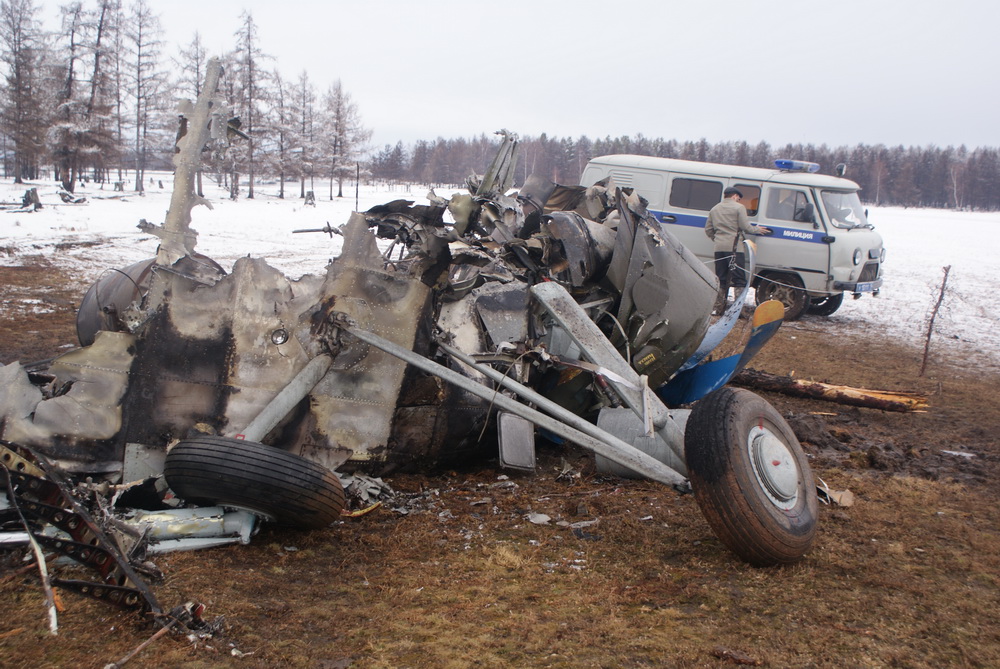
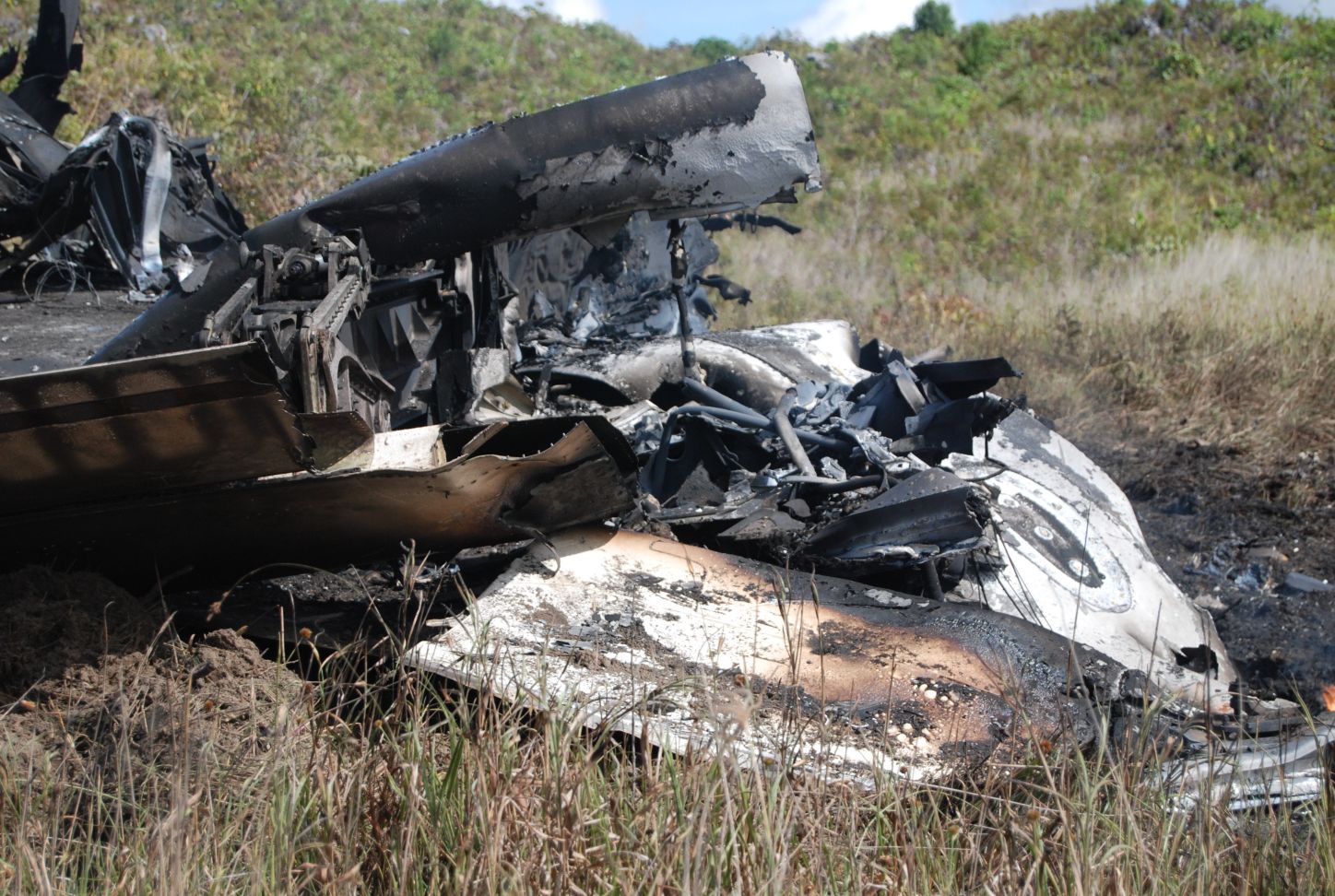
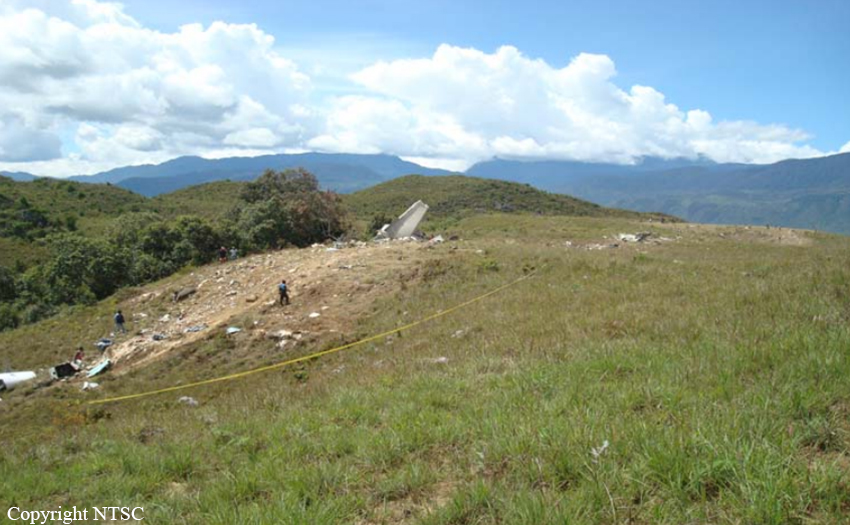
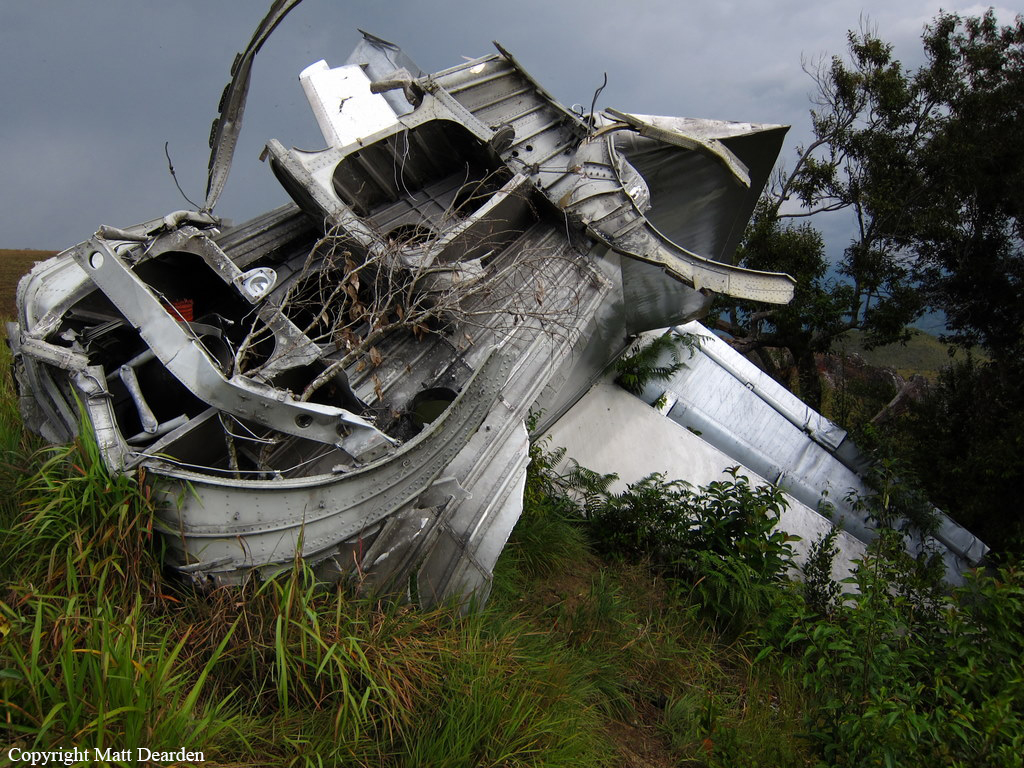
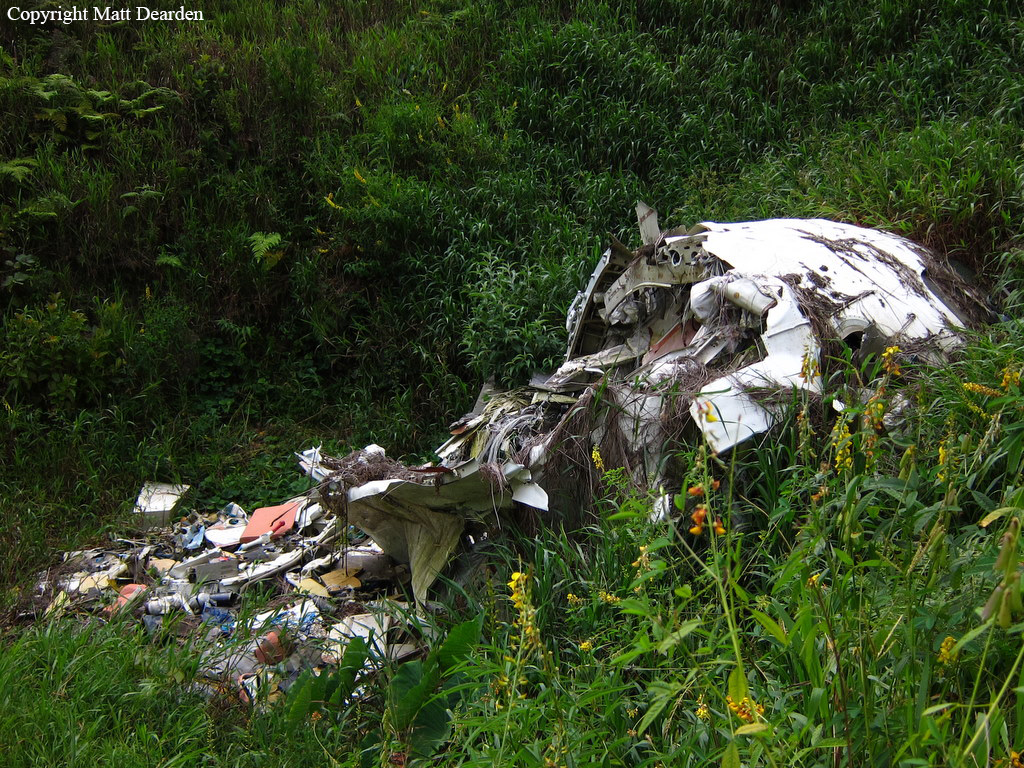
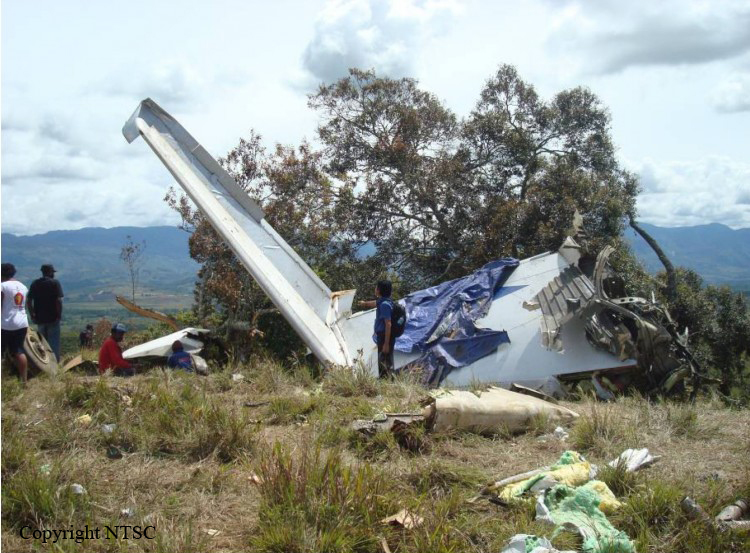
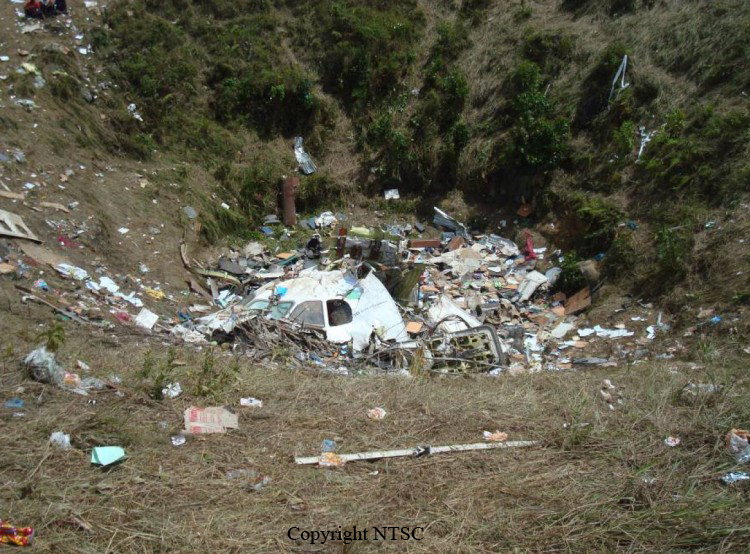
The twin engine aircraft departed São Paulo-Congonhas Airport at 1831LT on a private flight to Porto Seguro, carrying 12 passengers and two pilots, among them the Brazilian Businessman Roger Wright, his wife, children and grandchildren. On approach to Porto Seguro-Terravista Golf Club Airport, the crew encountered poor weather conditions and the visibility was low due to the night. On final approach to runway 15, the aircraft impacted trees located 900 metres from the runway threshold. The aircraft continued for about 700 metres then struck others trees and crashed 200 metres short of runway, bursting into flames. The aircraft was totally destroyed and all 14 occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
The crew's decision to continue the approach in poor weather conditions following a high motivation to land at destination.
The following contributing factors were identified:
- The crew failed to follow the published procedures,
- The crew did not take the bad weather conditions into consideration and took the decision to land,
- Limited visibility due to rain falls and night,
- Weather conditions affected the perception of the pilots who suffered a loss of situational awareness,
- Poor judgment of the situation and flight conditions on part of the crew,
- The crew continued the approach under VFR mode in IMC conditions,
- The crew carried out an improvised VFR approach via a GPS system,
- Excessive approach speed,
- Poor crew coordination,
- Lack of crew discipline.
The following contributing factors were identified:
- The crew failed to follow the published procedures,
- The crew did not take the bad weather conditions into consideration and took the decision to land,
- Limited visibility due to rain falls and night,
- Weather conditions affected the perception of the pilots who suffered a loss of situational awareness,
- Poor judgment of the situation and flight conditions on part of the crew,
- The crew continued the approach under VFR mode in IMC conditions,
- The crew carried out an improvised VFR approach via a GPS system,
- Excessive approach speed,
- Poor crew coordination,
- Lack of crew discipline.
Final Report: