Crash of a PZL-Mielec AN-2R in Verkhnyaya Toyma
Date & Time:
Dec 5, 1995 at 1235 LT
Registration:
RA-17725
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Verkhnyaya Toyma – Kotlas
MSN:
1G202-45
YOM:
1983
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
13
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
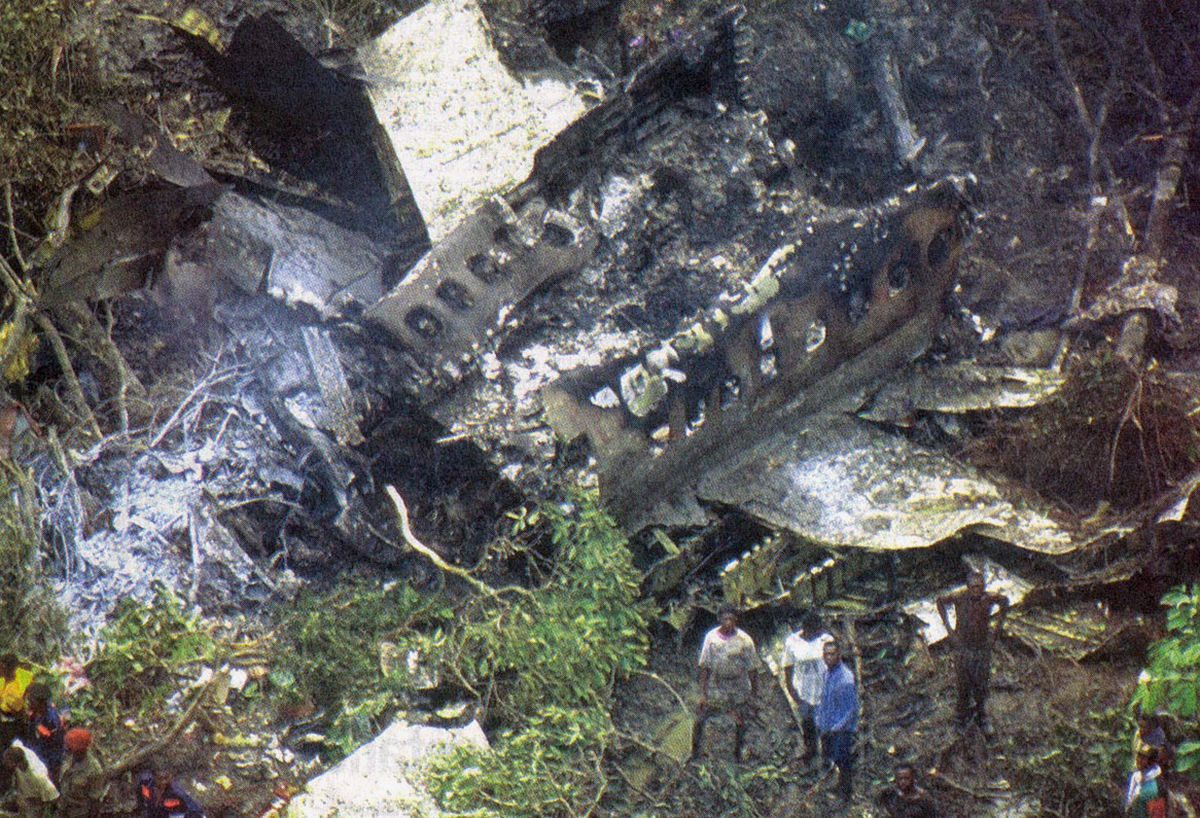
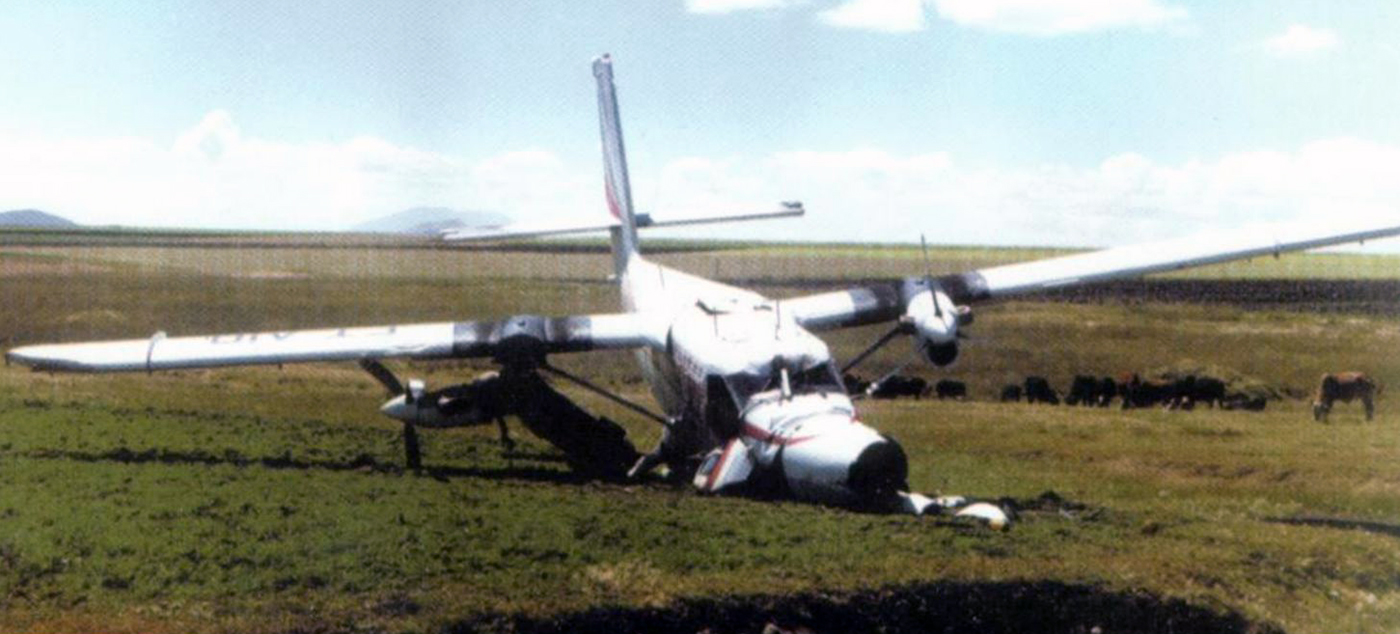
Circumstances:
During initial climb, the crew encountered difficulties to gain height. The crew elected to make an emergency landing when the aircraft crashed in an open field some three minutes after takeoff. The wreckage was found 500 metres from the runway end. Four occupants escaped uninjured while 11 others were injured. The aircraft was written off.
Probable cause:
It was determined that the aircraft was overloaded.