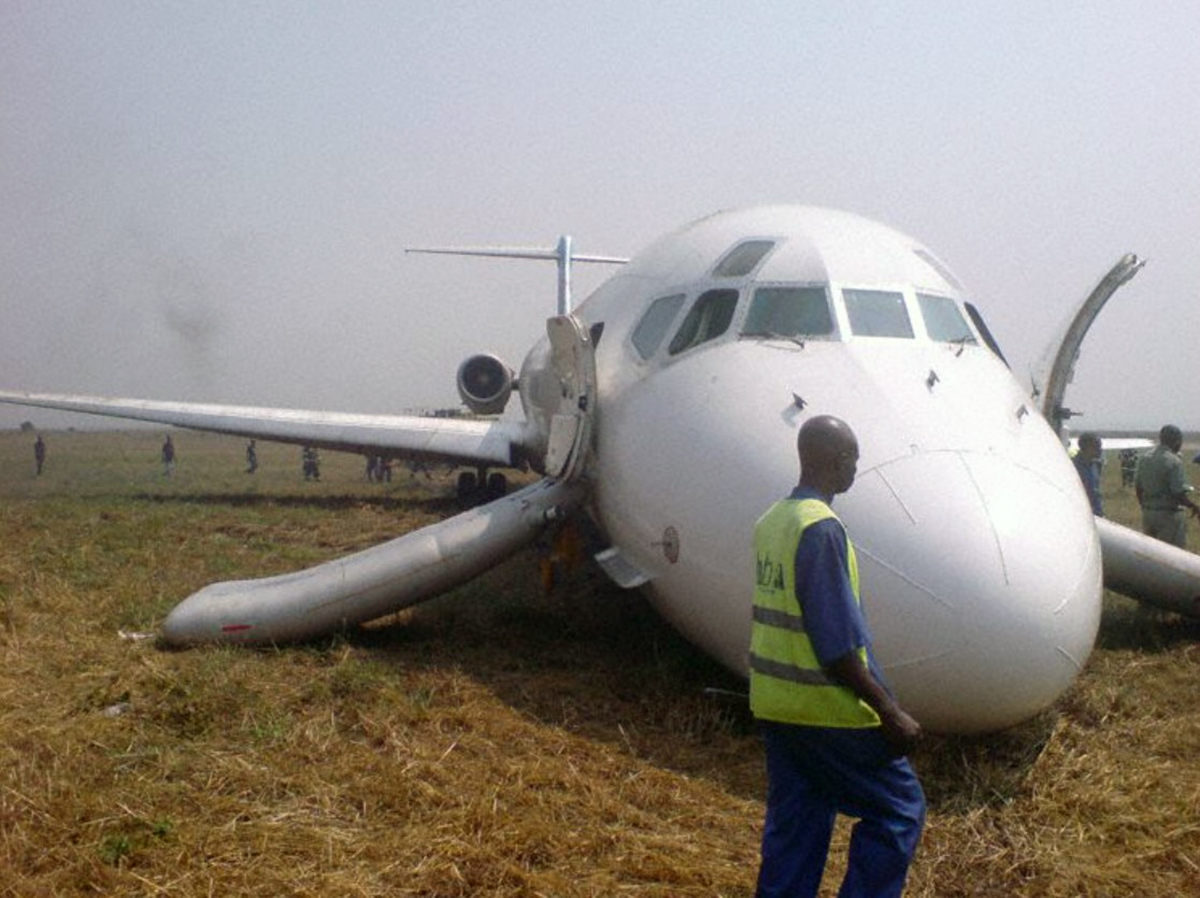
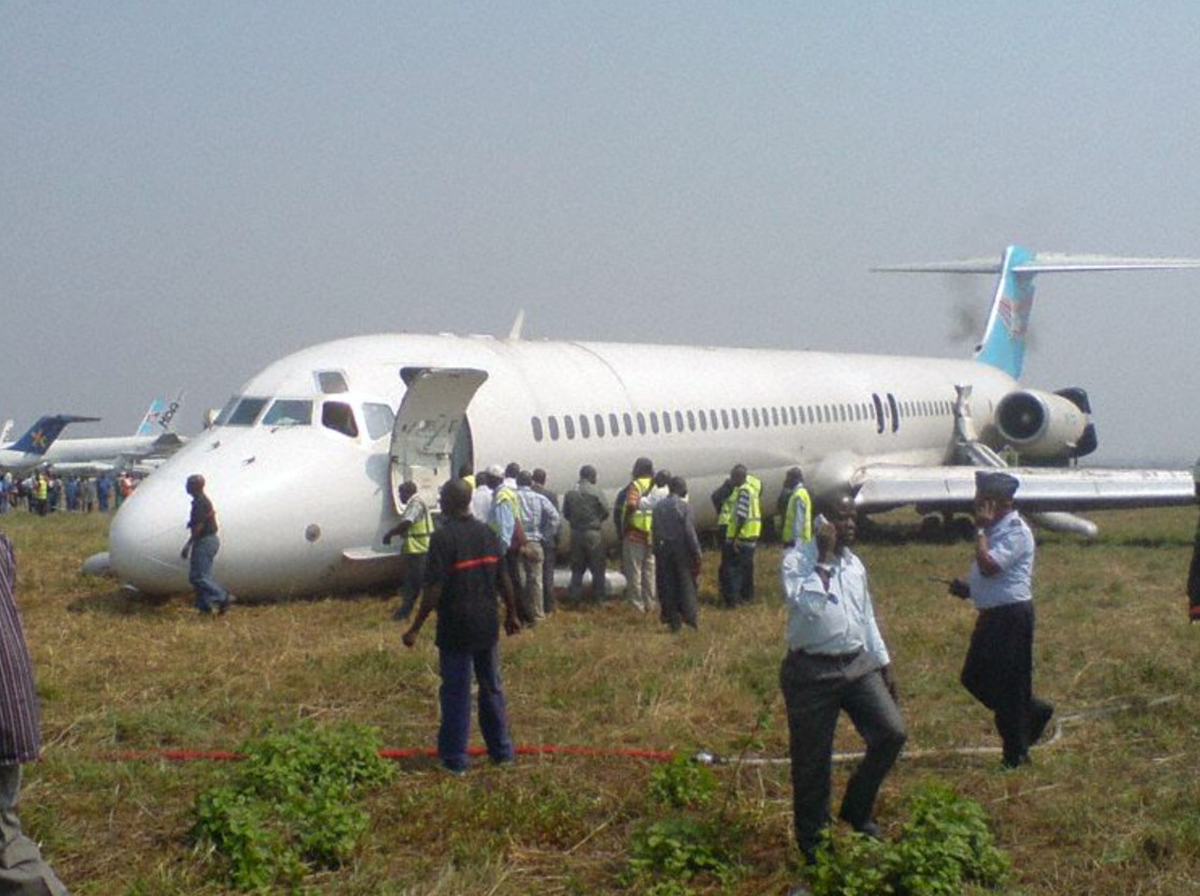
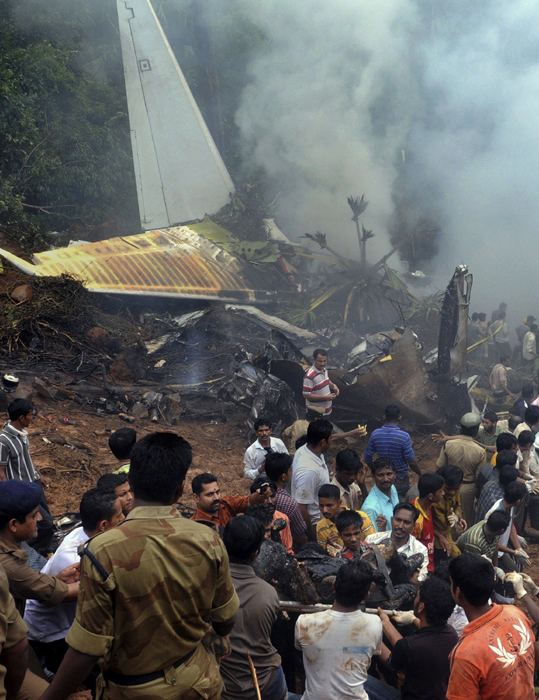
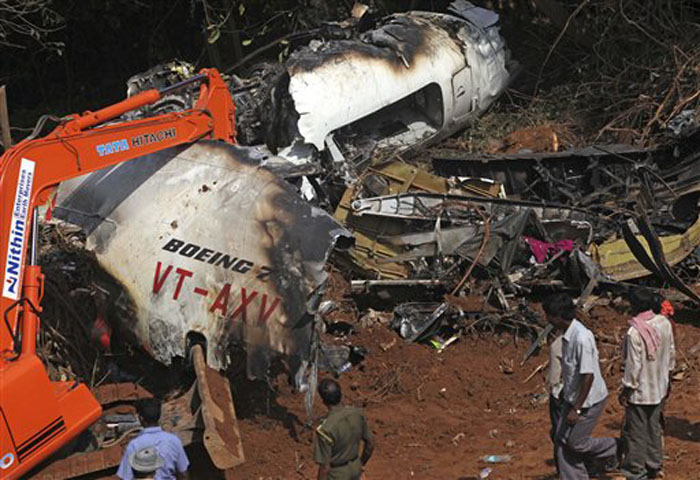
Circumstances:
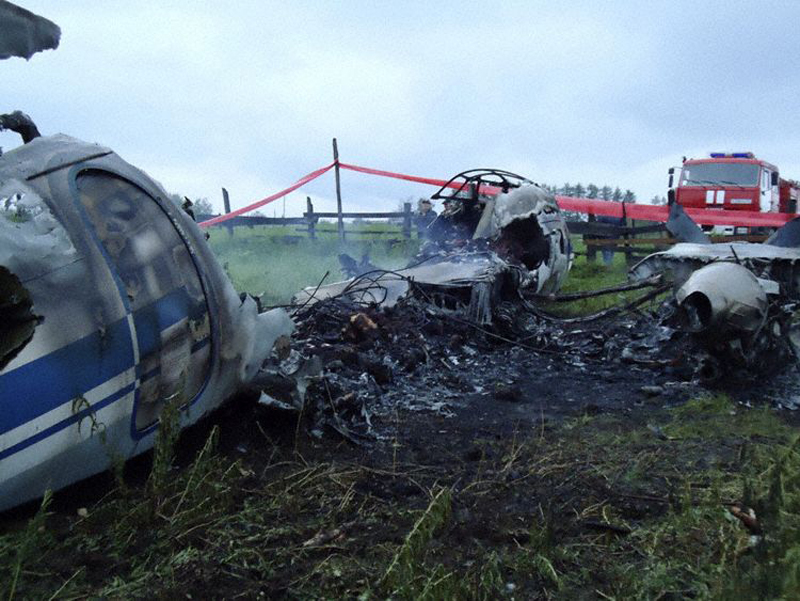
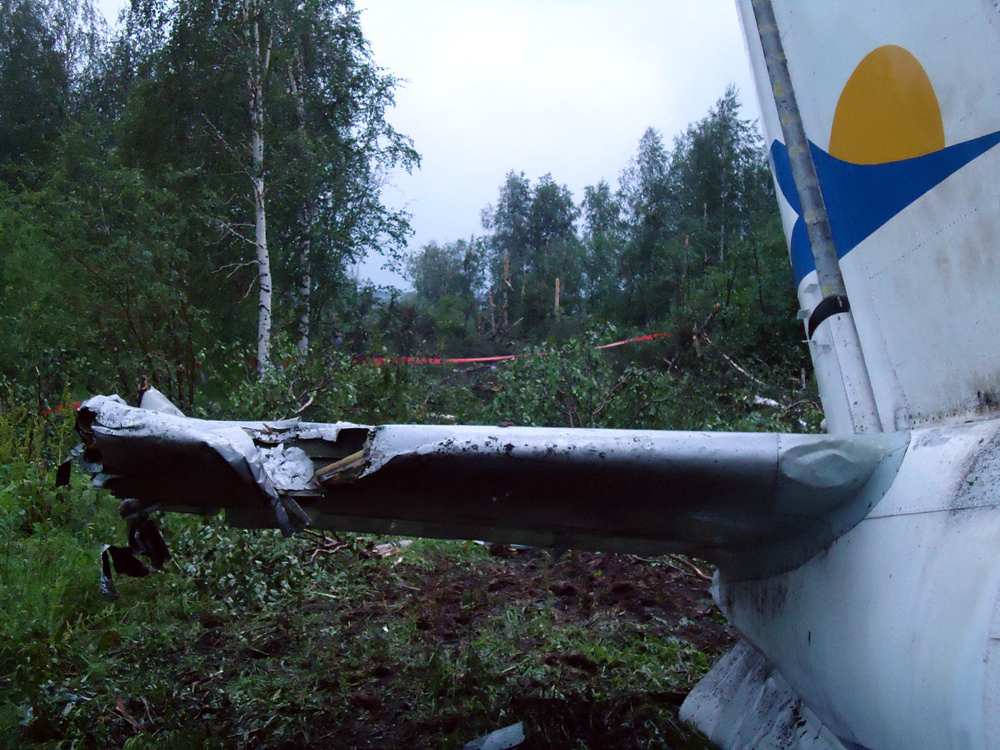
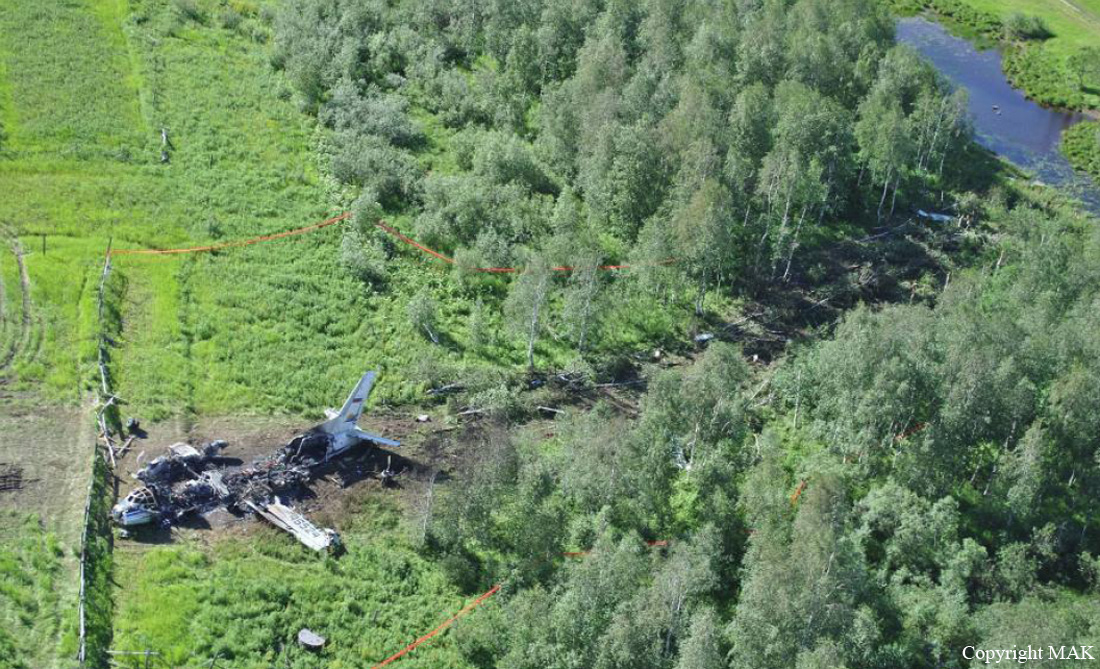
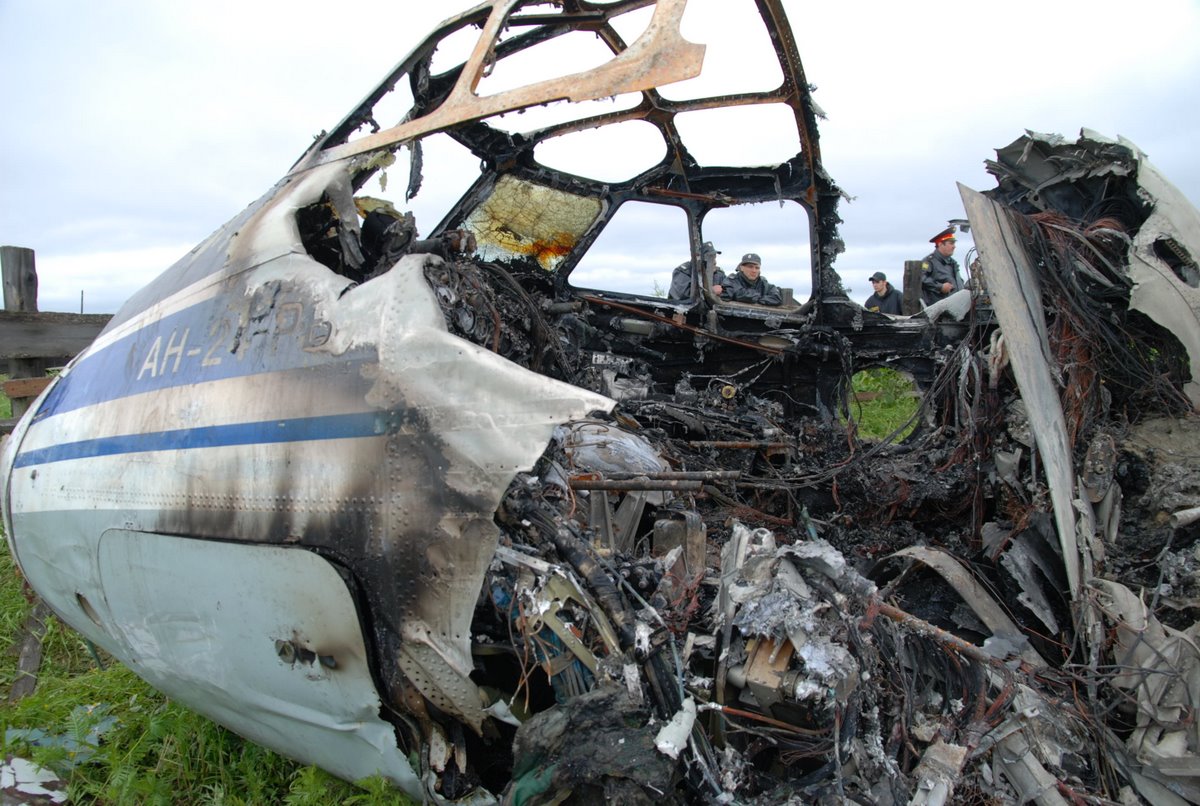
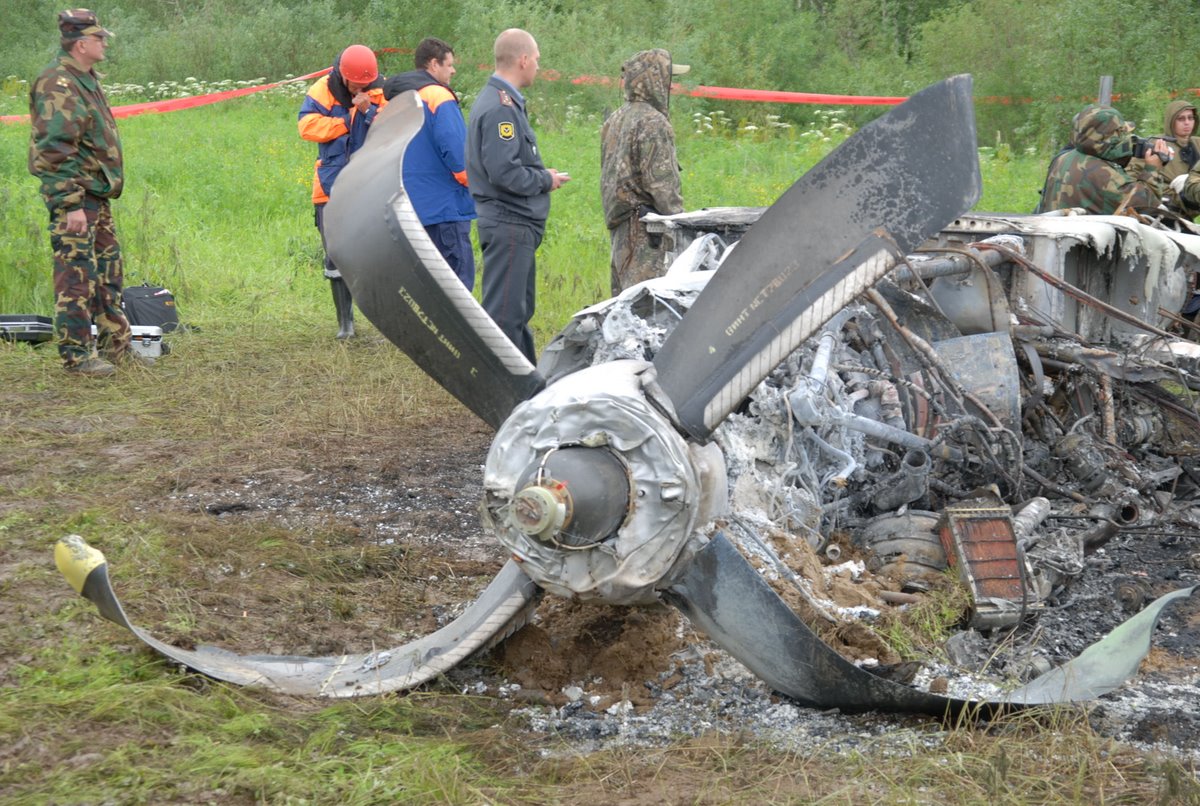
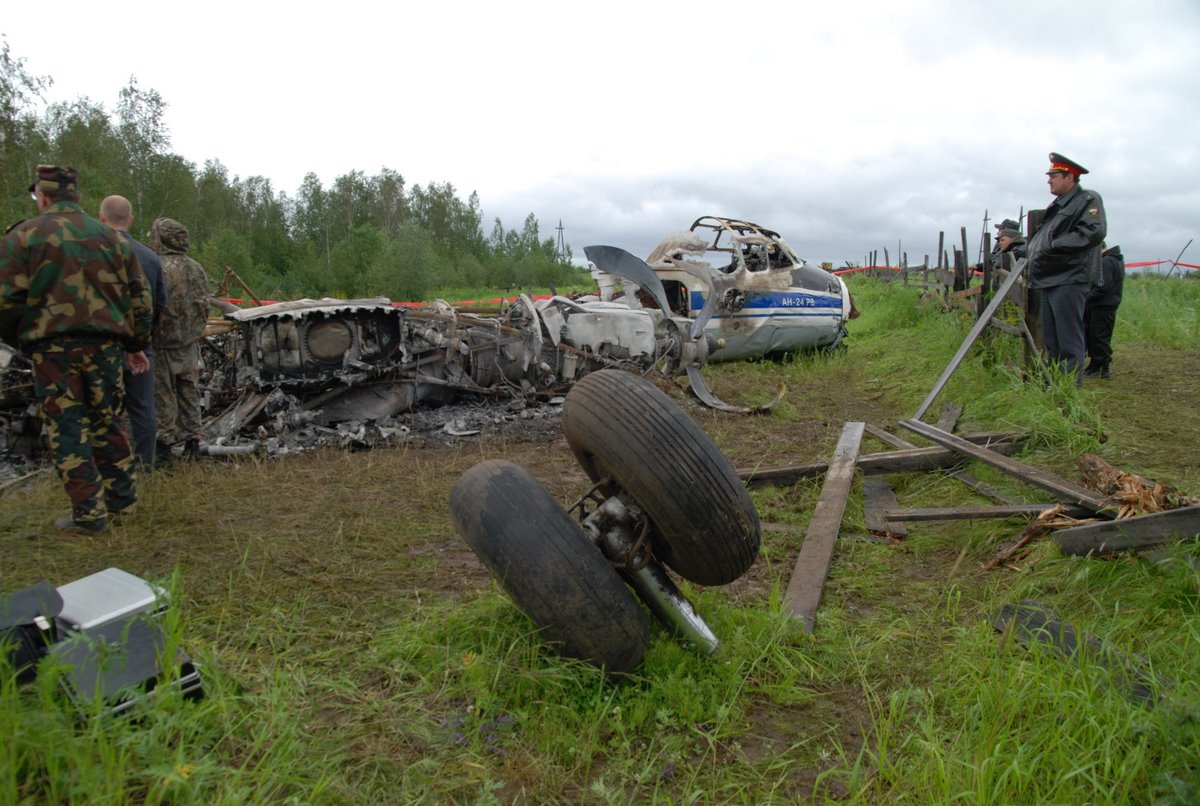
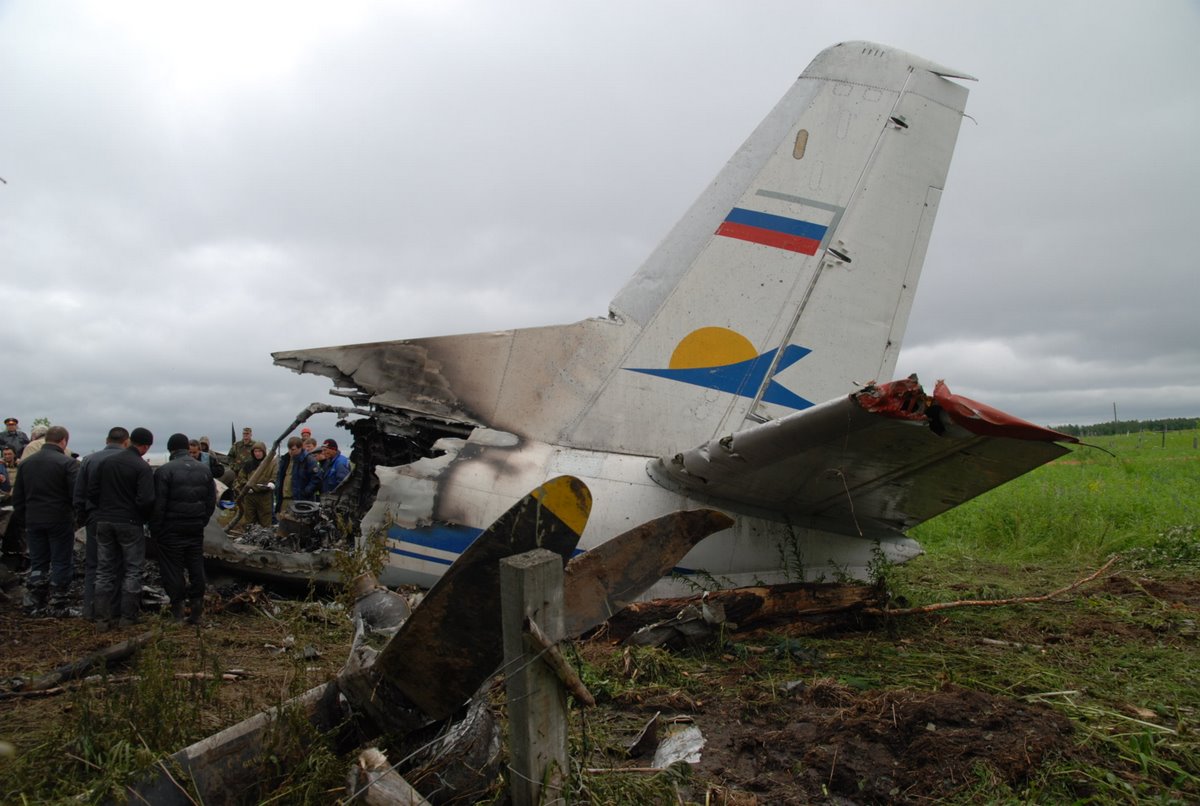
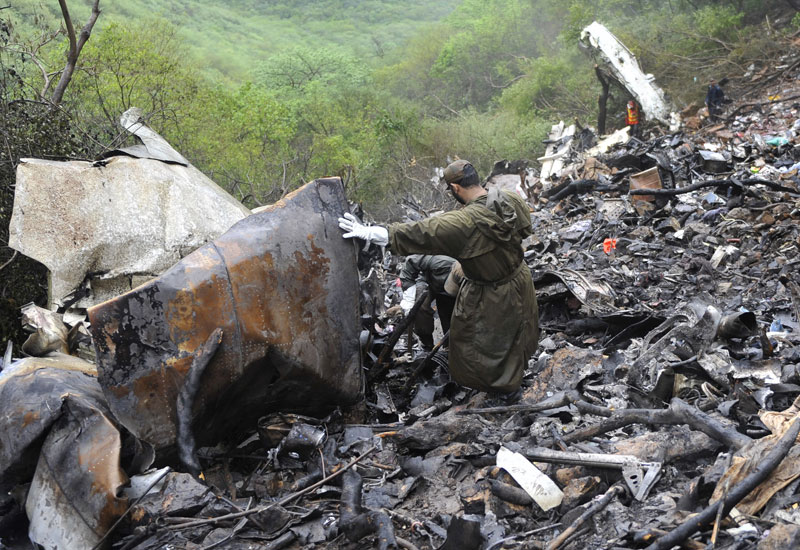
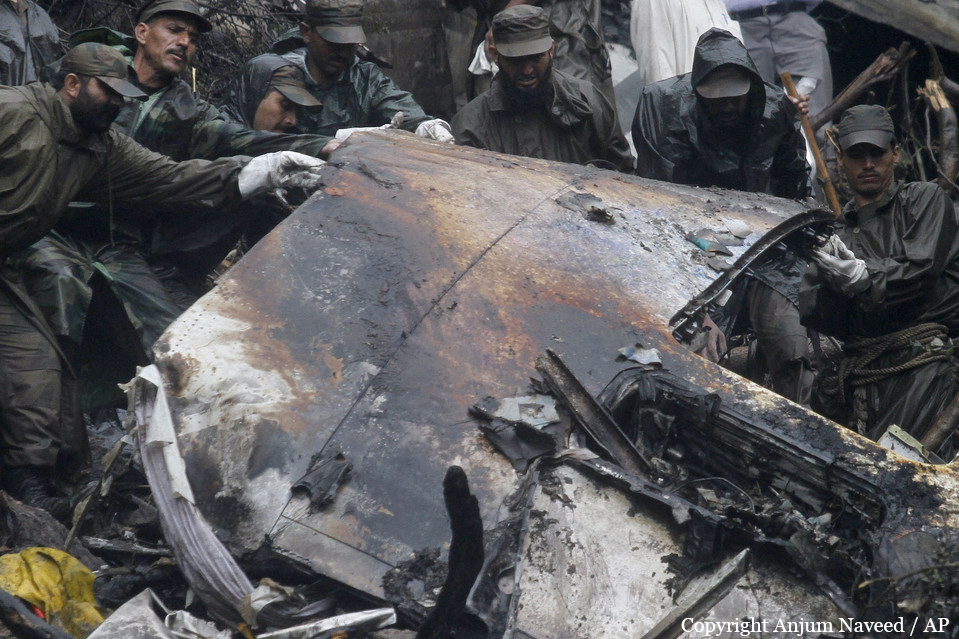
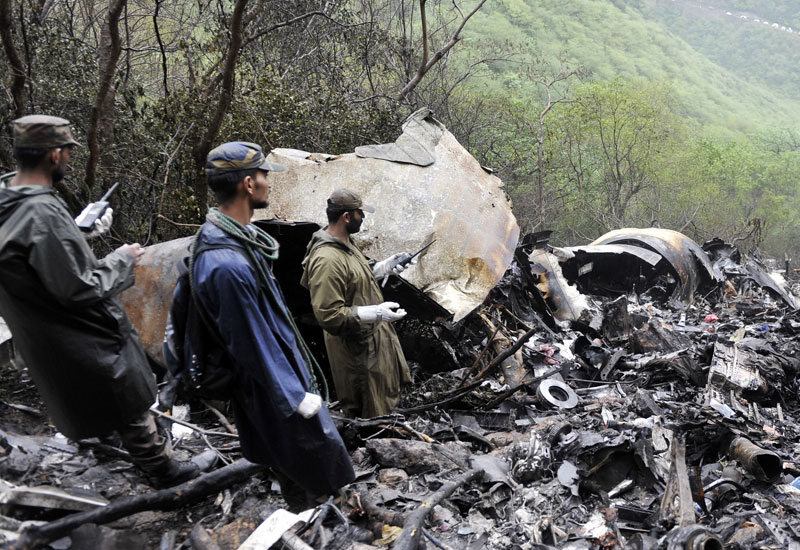
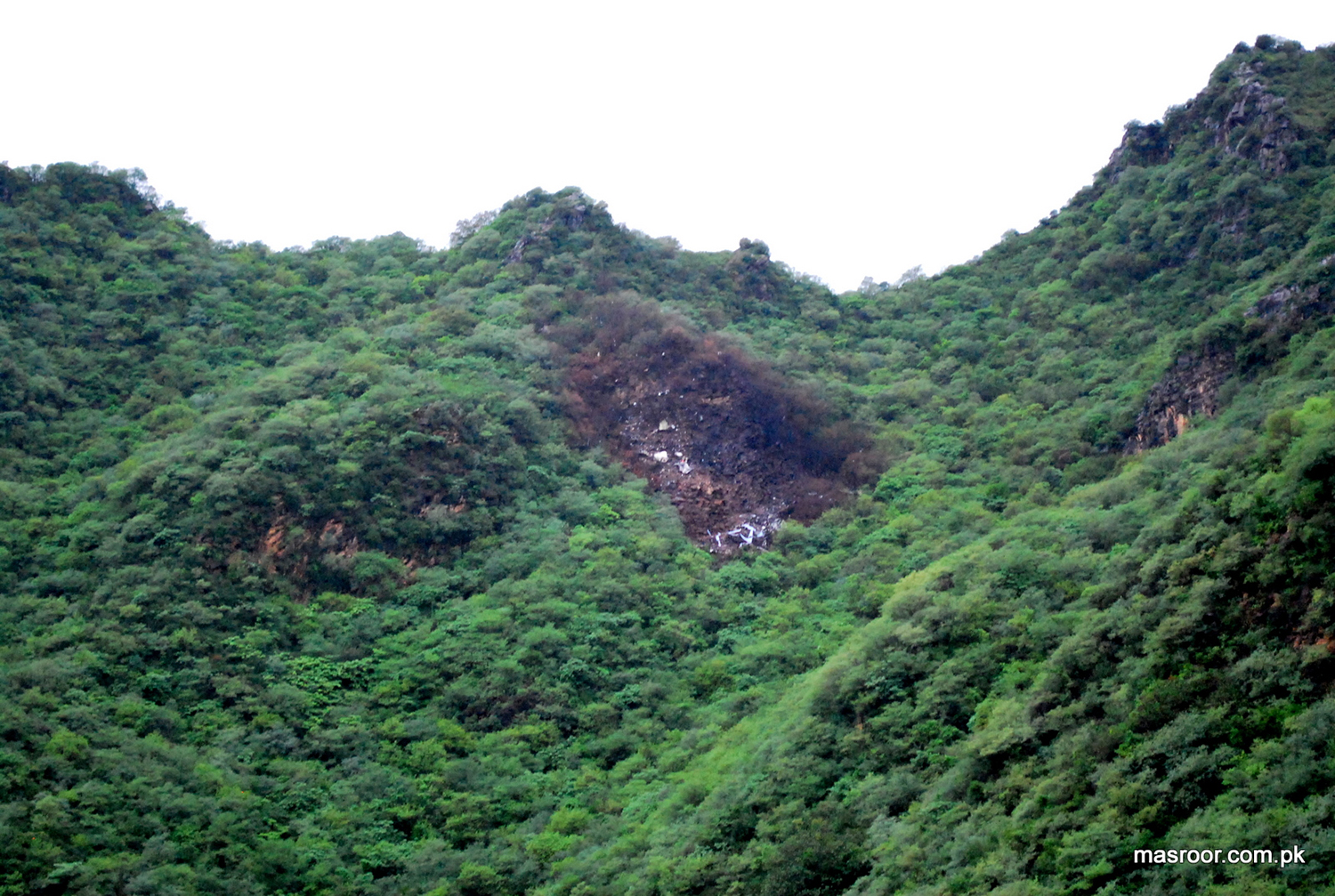
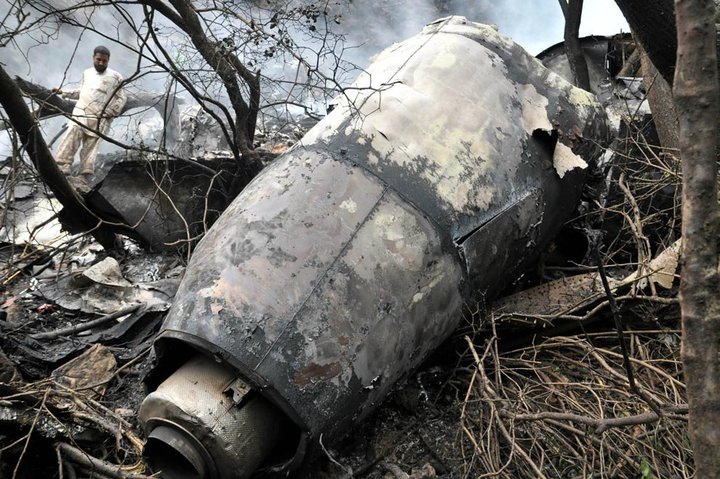
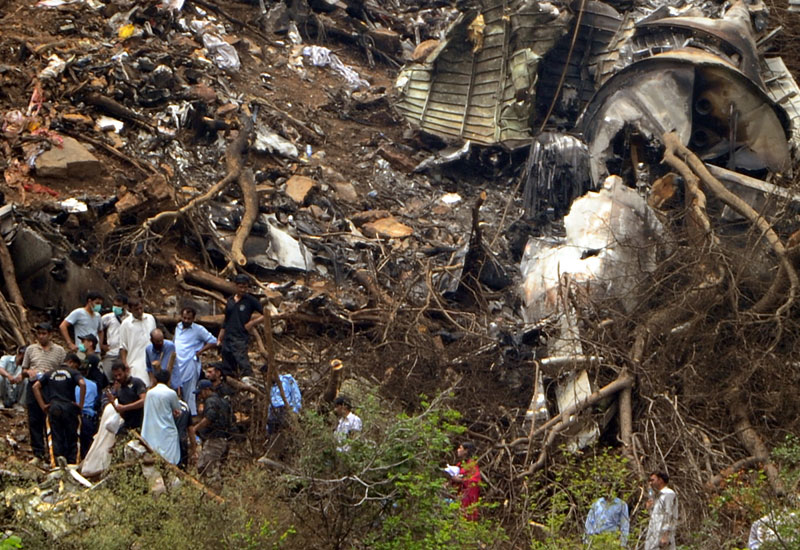
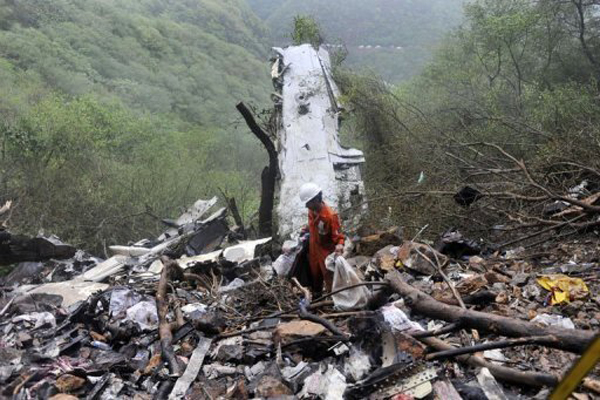
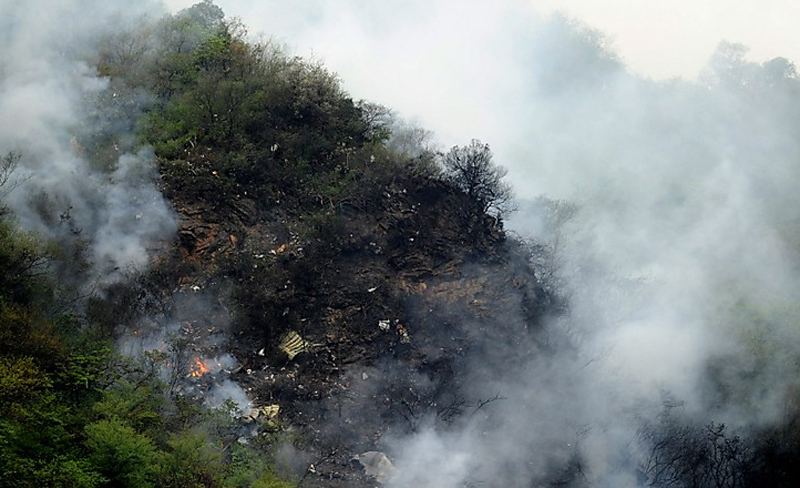
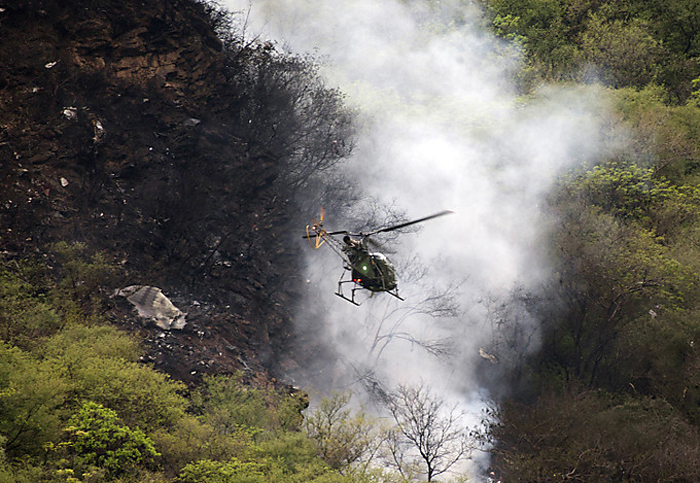
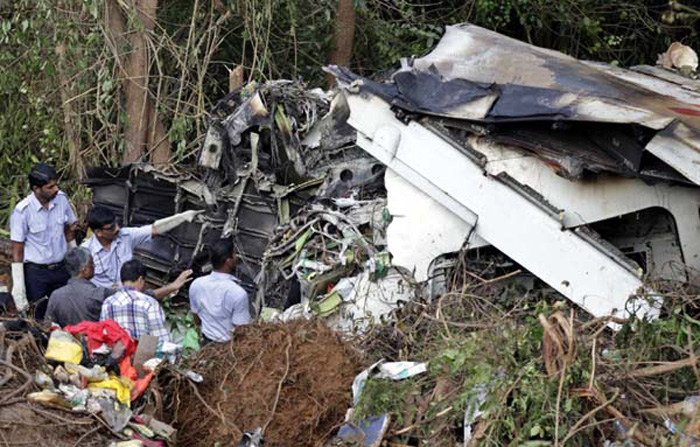
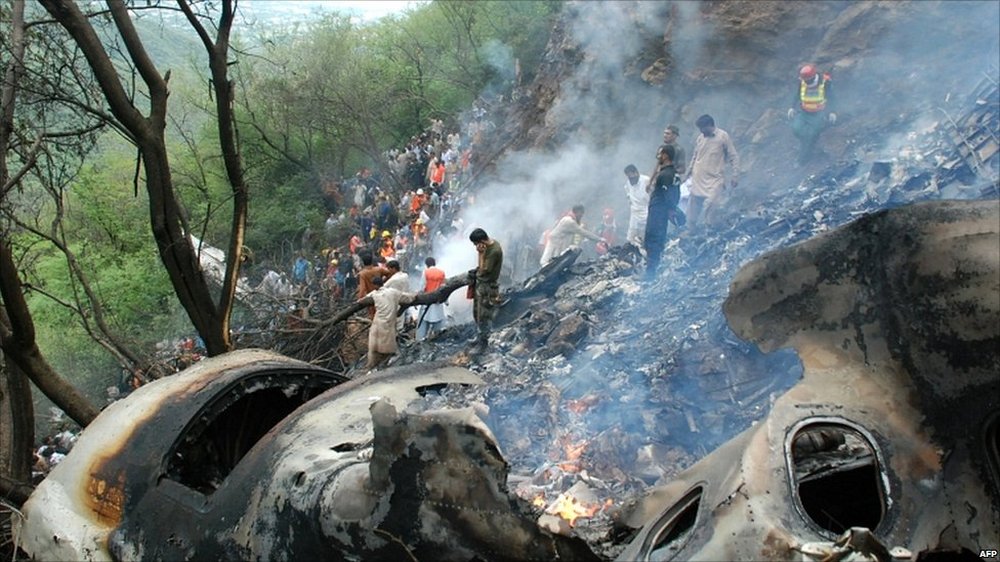
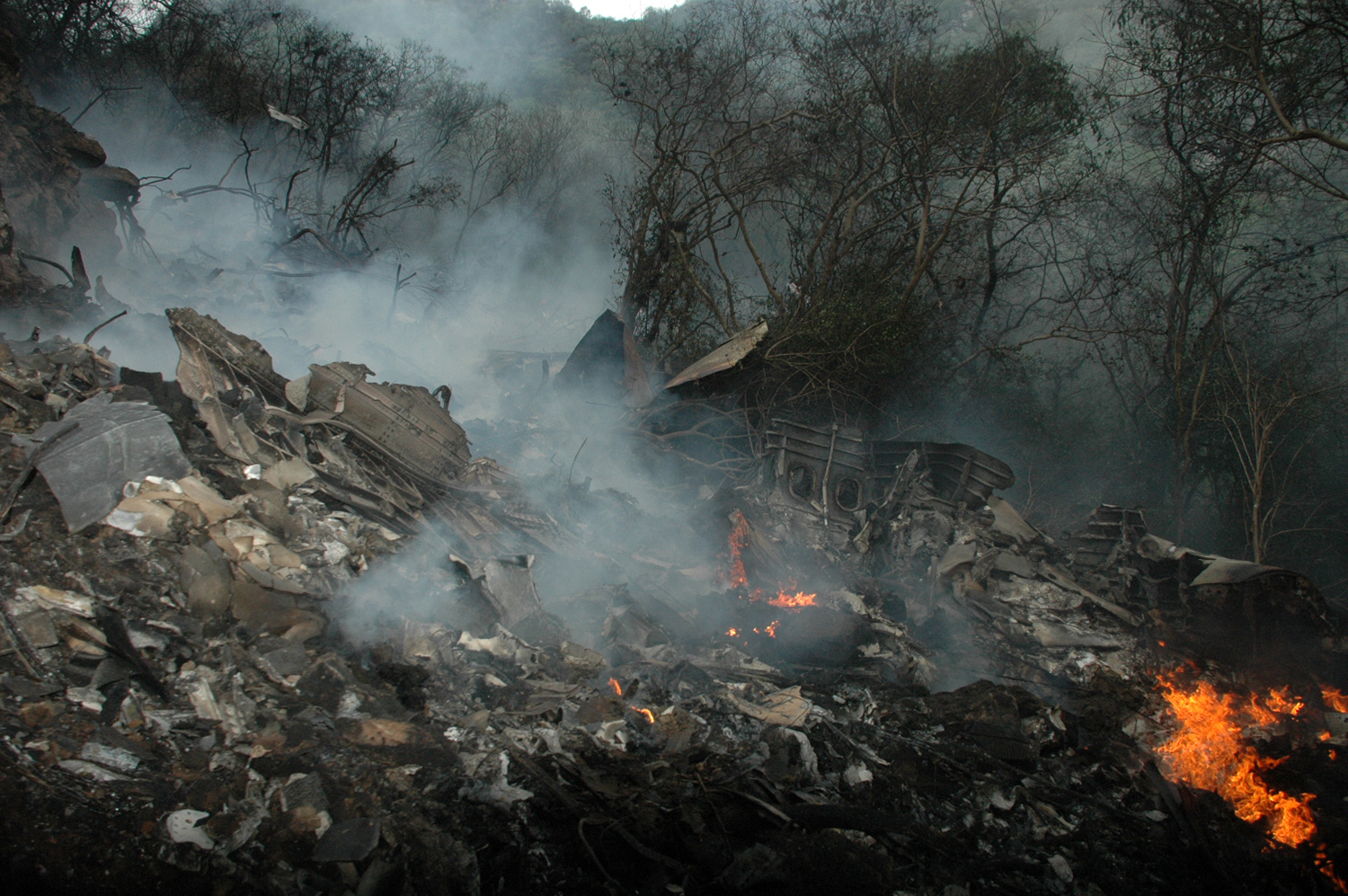
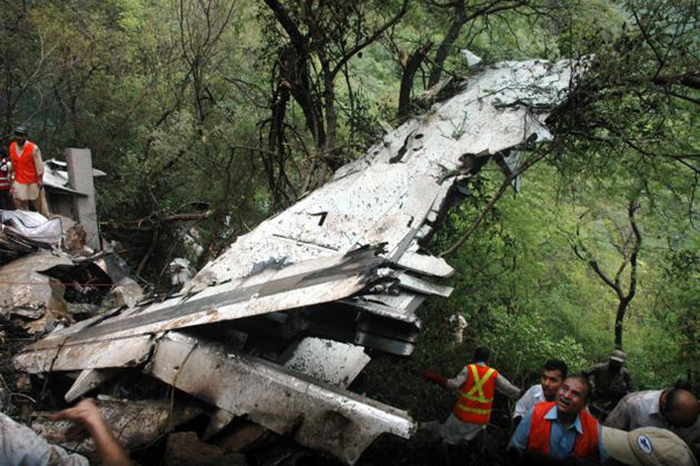
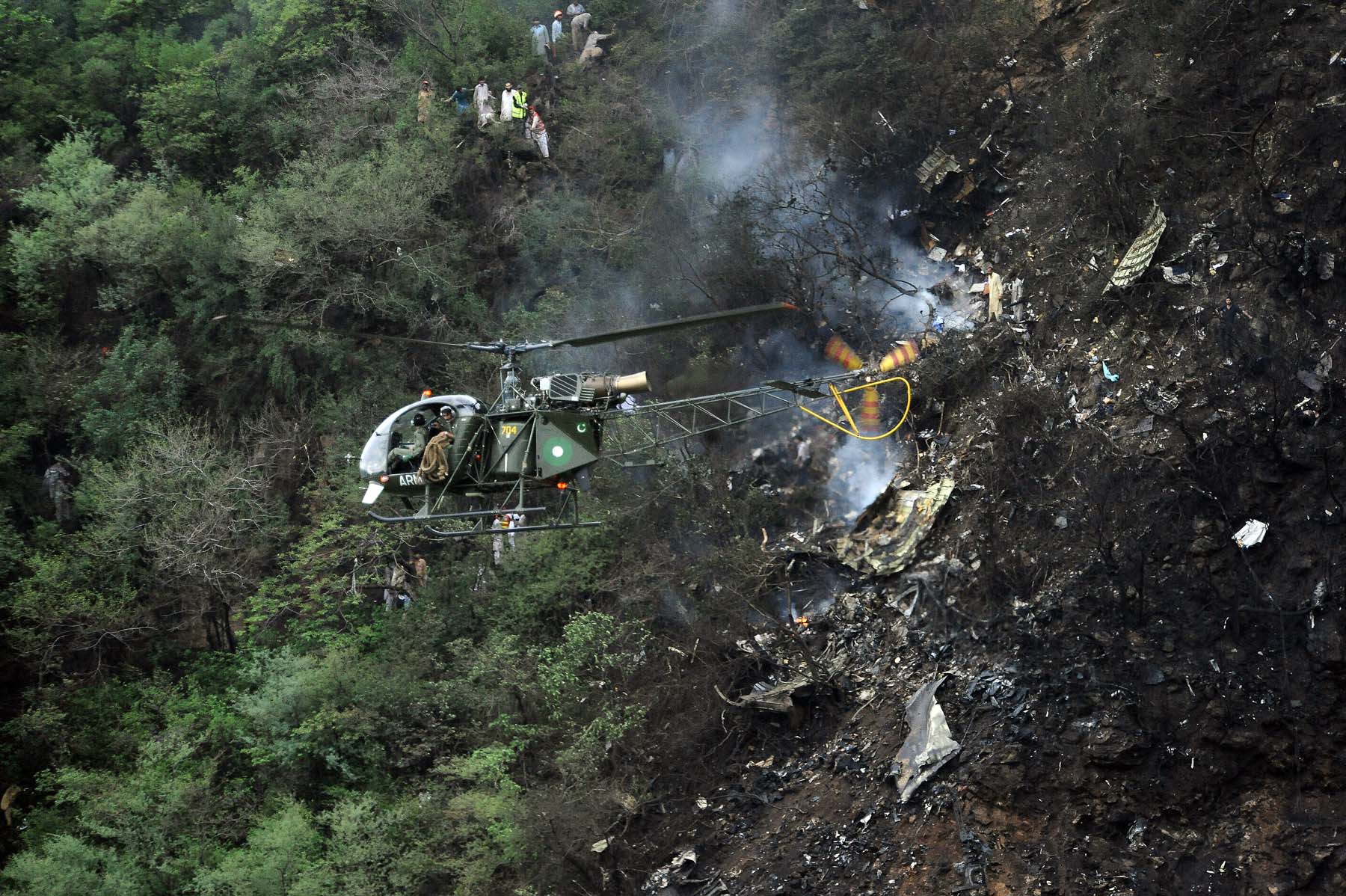
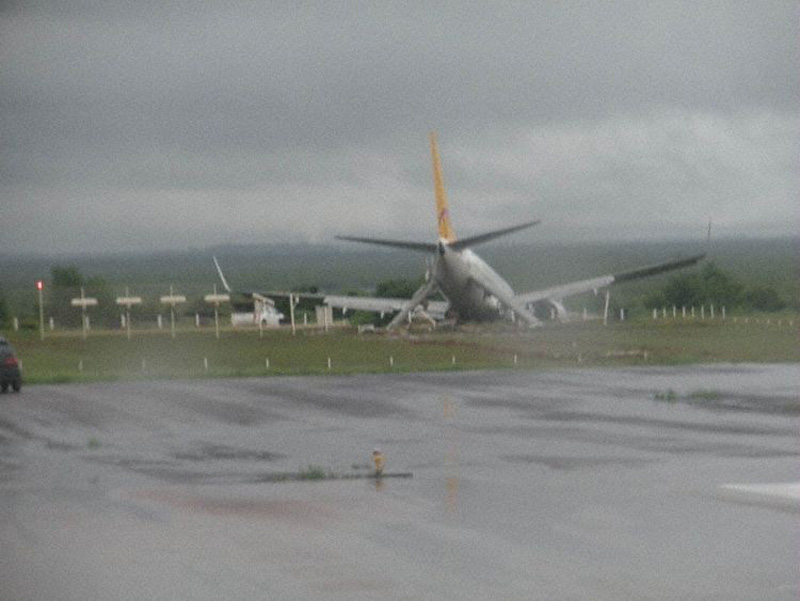
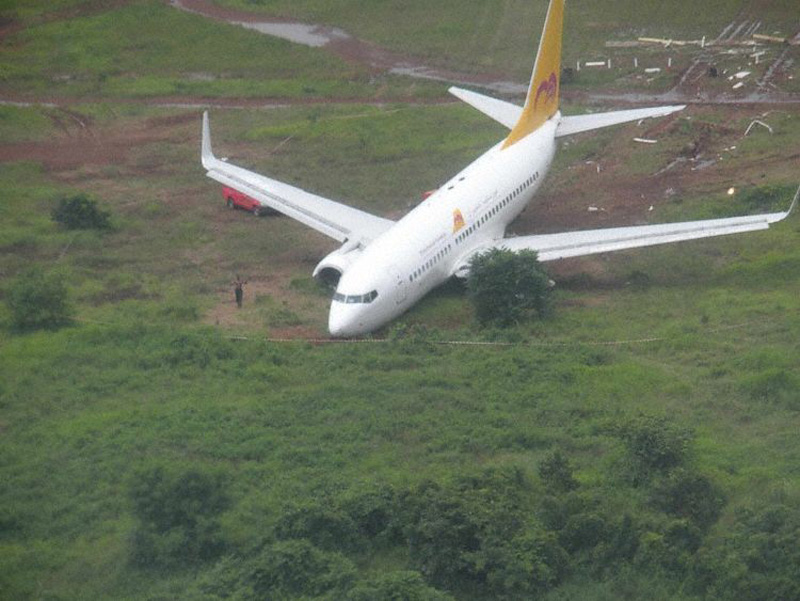
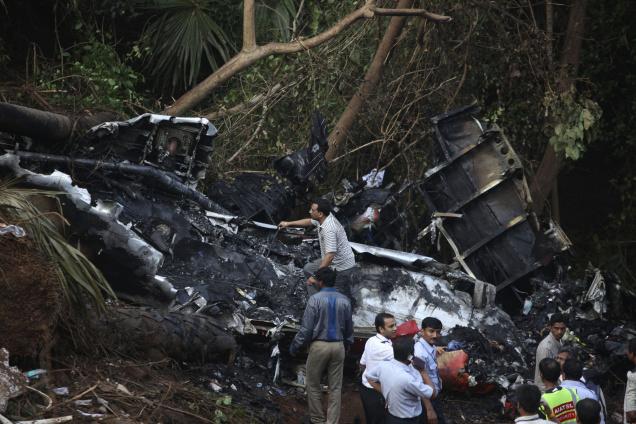
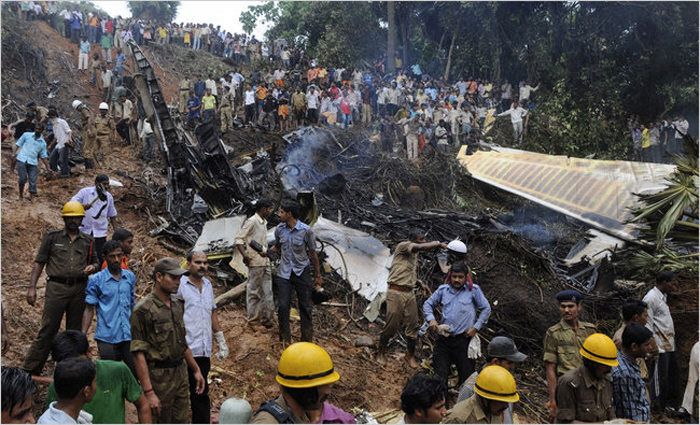
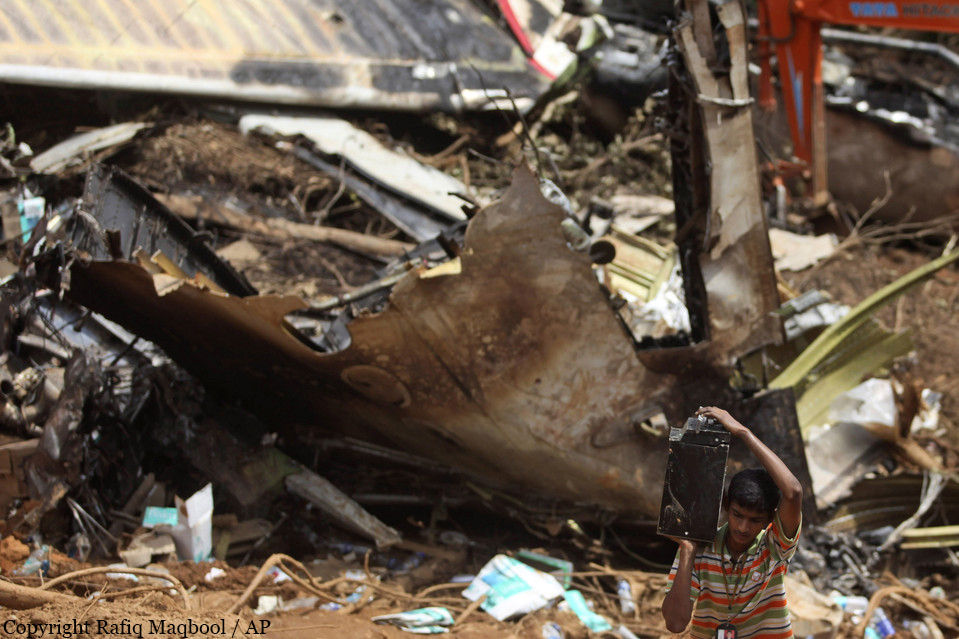
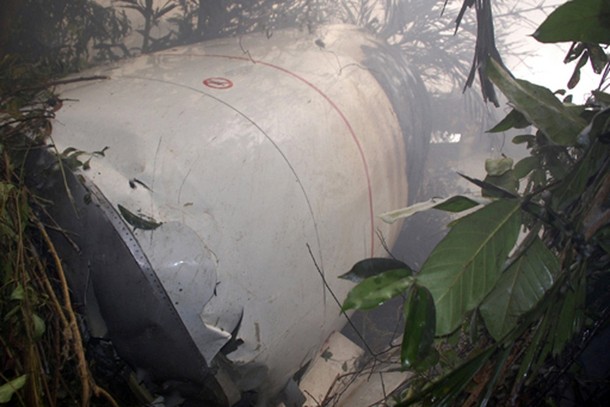
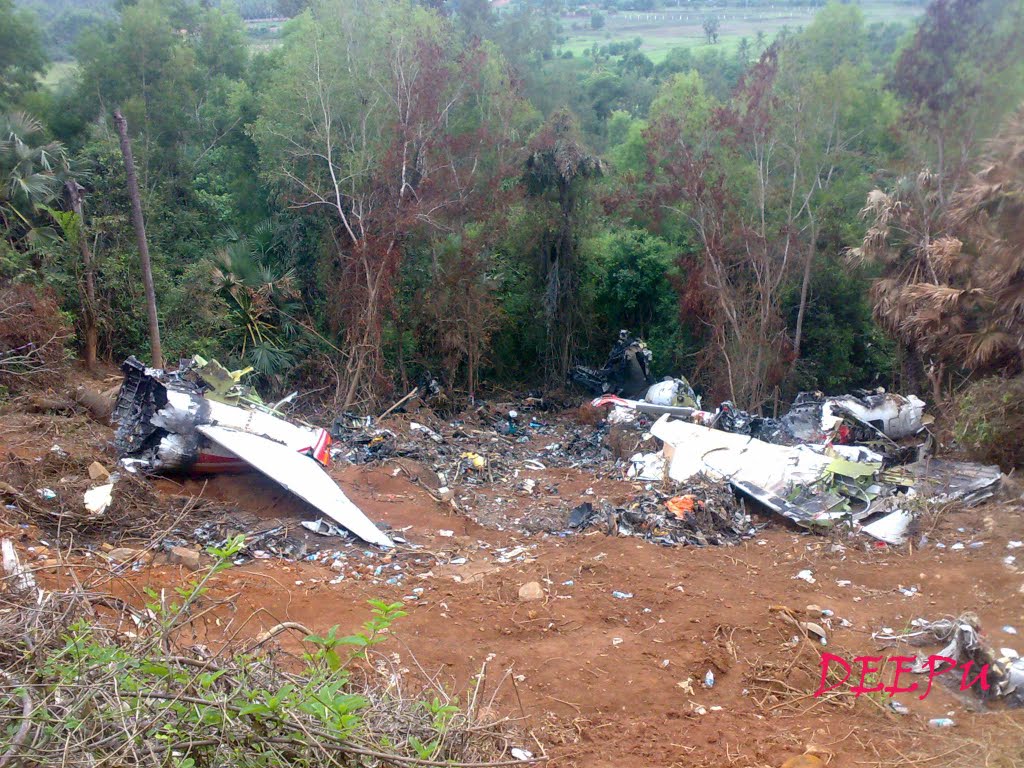
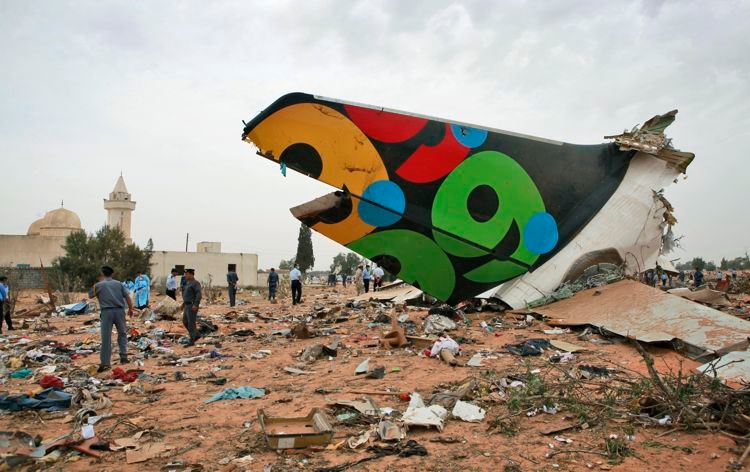
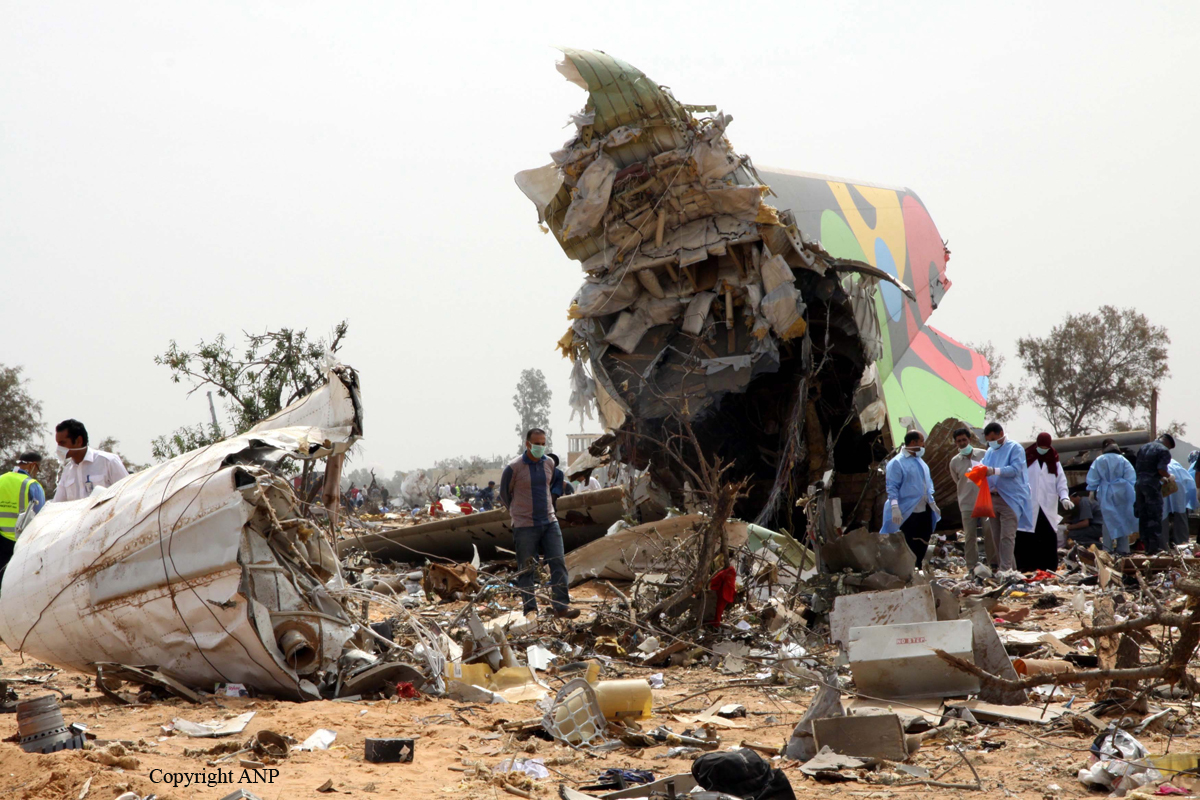
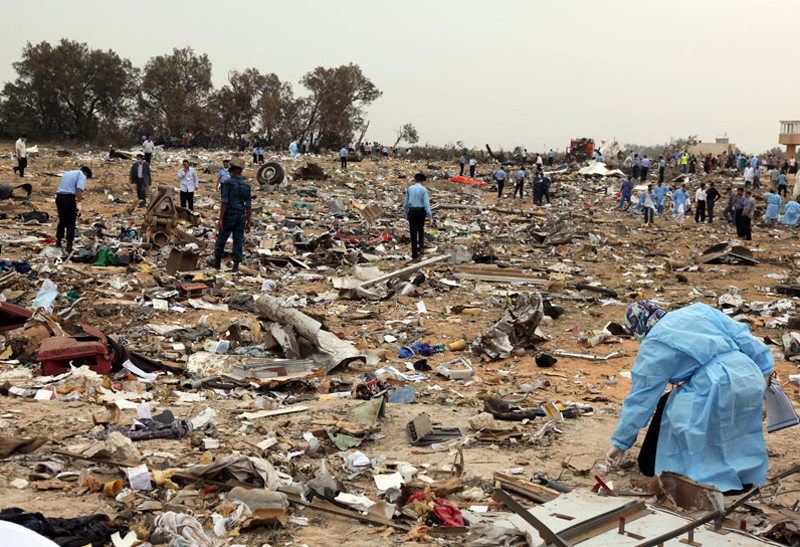
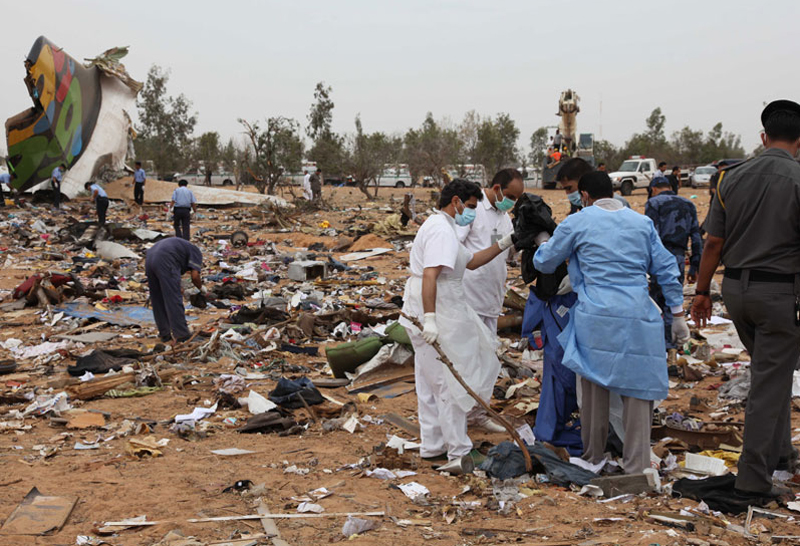
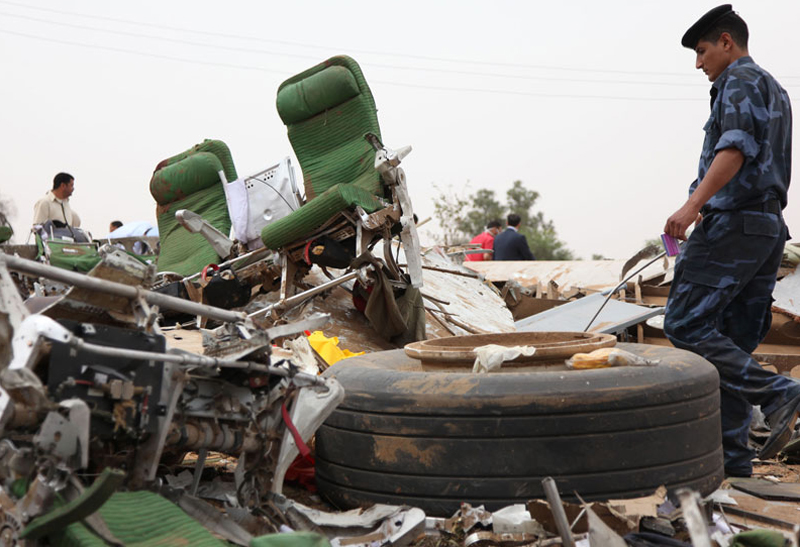
Air India Express flight IX-811/812 is a daily round trip between Mangalore and Dubai. The outbound flight IX-811 was uneventful and landed at Dubai at 23:44 hours Local Time. The airplane was serviced and refuelled. The same flight crew operated the return leg, flight IX-812. The airplane taxied out for departure at 01:06 LT (02:36 IST). The takeoff, climb and cruise were uneventful. There was no conversation between the two pilots for about 1 hour and 40 minutes because the captain was asleep. The First Officer was making all the radio calls. The aircraft reported position at IGAMA at 05:33 hours IST and the First Officer was told to expect an ILS DME Arc approach to Mangalore. At about 130 miles from Mangalore, the First Officer requested descent clearance. This was, however, denied by the ATC Controller, who was using standard procedural control, to ensure safe separation with other air traffic. At 05:46 IST, the flight reported its position when it was at 80 DME as instructed by Mangalore Area Control. The aircraft was cleared to 7000 ft and commenced descent at 77 DME from Mangalore at 05:47 IST. The visibility reported was 6 km. Mangalore airport has a table top runway. As the AIP India states "Aerodrome located on hilltop. Valleys 200ft to 250ft immediately beyond paved surface of Runway." Owing to the surrounding terrain, Air India Express had made a special qualification requirement that only the PIC shall carry out the take off and landing. The captain on the accident flight had made a total of 16 landings in the past at this airport and the First Officer had operated as a Co-pilot on 66 flights at this airport. While the aircraft had commenced descent, there was no recorded conversation regarding the mandatory preparation for descent and landing briefing as stipulated in the SOP. After the aircraft was at about 50 miles and descending out of FL295, the conversation between the two pilots indicated that an incomplete approach briefing had been carried out. At about 25 nm from DME and descending through FL184, the Mangalore Area Controller cleared the aircraft to continue descent to 2900 ft. At this stage, the First Officer requested, if they could proceed directly to Radial 338 and join the 10 DME Arc. Throughout the descent profile and DME Arc Approach for ILS 24, the aircraft was much higher than normally expected altitudes. The aircraft was handed over by the Mangalore Area Controller to ATC Tower at 05:52 IST. The Tower controller, thereafter, asked the aircraft to report having established on 10 DME Arc for ILS Runway 24. Considering that this flight was operating in WOCL (Window Of Circadian Low), by this time the First Officer had also shown signs of tiredness. This was indicated by the sounds of yawning heard on the CVR. On having reported 10 DME Arc, the ATC Tower had asked aircraft to report when established on ILS. It appears that the captain had realized that the aircraft altitude was higher than normal and had selected Landing Gear 'DOWN' at an altitude of approximately 8,500 ft with speed brakes still deployed in Flight Detent position, so as to increase the rate of descent. As indicated by the DFDR, the aircraft continued to be high and did not follow the standard procedure of intercepting the ILS Glide Path at the correct intercept altitude. This incorrect procedure led to the aircraft being at almost twice the altitude as compared to a Standard ILS Approach. During approach, the CVR indicated that the captain had selected Flaps 40 degrees and completed the Landing Check List. At 06:03 hours IST at about 2.5 DME, the Radio Altimeter had alerted an altitude of 2500 ft. This was immediately followed by the First Officer saying "It is too high" and "Runway straight down". In reply, the captain had exclaimed "Oh my god". At this moment, the captain had disconnected the Auto Pilot and simultaneously increased the rate of descent considerably to establish on the desired approach path. At this stage, the First Officer had queried "Go around?" To this query from the First Officer, the captain had called out "Wrong loc .. ... localiser .. ... glide path". The First Officer had given a second call to the captain for "Go around" followed by "Unstabilized". However, the First Officer did not appear to take any action, to initiate a Go Around. Having acquired the runway visually and to execute a landing, it appears that the captain had increased the rate of descent to almost 4000 ft per minute. Due to this, there were numerous warnings from EGPWS for 'SINK RATE' and 'PULL UP'. On their own, the pilots did not report having established on ILS Approach. Instead, the ATC Tower had queried the same. To this call, the captain had forcefully prompted the First Officer to give a call of "Affirmative". The Tower controller gave landing clearance thereafter and also indicated "Winds calm". The aircraft was high on approach and touched down on the runway, much farther than normal. The aircraft had crossed the threshold at about 200 ft altitude with indicated speed in excess of 160 kt, as compared to 50 ft with target speed of 144 kt for the landing weight. Despite the EGPWS warnings and calls from the First Officer to go around, the captain had persisted with the approach in unstabilized conditions. Short of touchdown, there was yet another (Third) call from the First Officer, "Go around captain...We don't have runway left". However, the captain had continued with the landing and the final touchdown was about 5200 ft from the threshold of runway 24, leaving approximately 2800 ft of remaining paved surface. The captain had selected Thrust Reversers soon after touchdown. Within 6 seconds of applying brakes, the captain had initiated a 'Go Around', in contravention of Boeing SOP. The aircraft overshot the runway including the strip of 60 metres. After overshooting the runway and strip, the aircraft continued into the Runway End Safety Area (RESA) of 90 metres. Soon after which the right wing impacted the localiser antenna structure located further at 85 metres from the end of RESA. Thereafter, the aircraft hit the boundary fence and fell into a gorge.
Probable cause:
The Court of Inquiry determines that the cause of this accident was Captain's failure to discontinue the unstabilized approach and his persistence in continuing with the landing, despite three calls from the First Officer to go around and a number of warnings from the EGPWS.
Contributing Factors were:
1. In spite of availability of adequate rest period prior to the flight, the Captain was in prolonged sleep during flight, which could have led to sleep inertia. As a result of relatively short period of time between his awakening and the approach, it possibly led to impaired judgment. This aspect might have got accentuated while flying in the Window of Circadian Low (WOCL).
2. In the absence of Mangalore Area Control Radar (MSSR), due to unserviceability, the aircraft was given descent at a shorter distance on DME as compared to the normal. However, the flight crew did not plan the descent profile properly, resulting in remaining high on approach.
3. Probably in view of ambiguity in various instructions empowering the 'copilot' to initiate a 'go around ', the First Officer gave repeated calls to this effect, but did not take over the controls to actually discontinue the ill-fated approach.