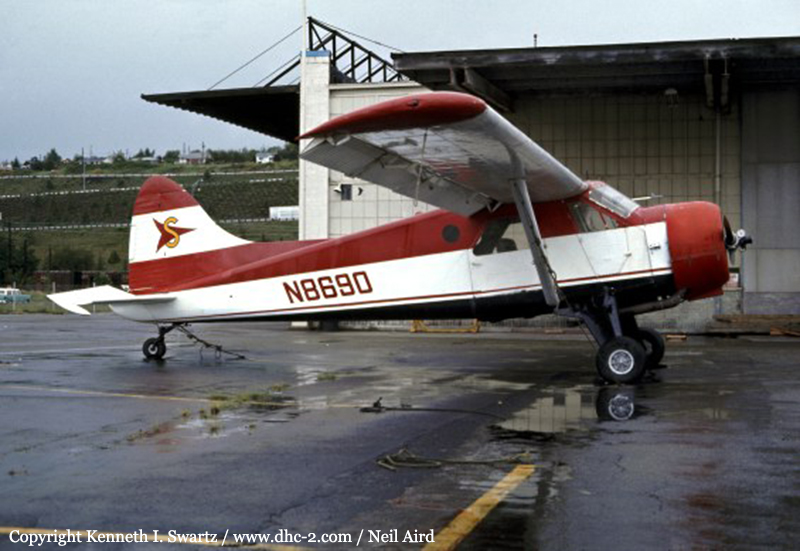
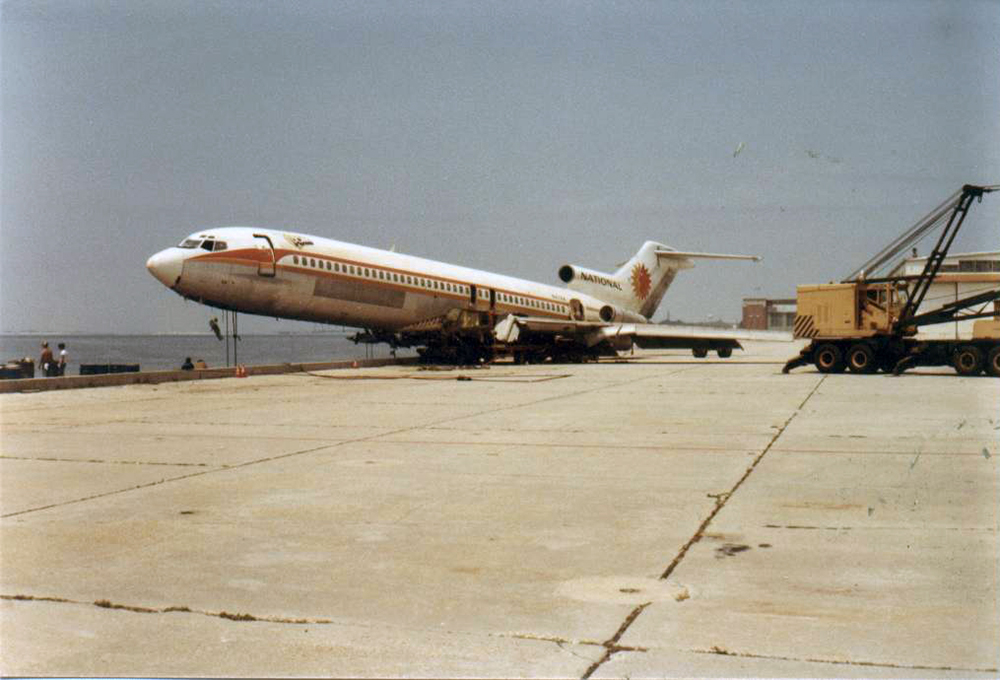
Crash of a De Havilland DHC-2 Beaver in Pelican
Date & Time:
Jul 3, 1978 at 1930 LT
Registration:
N8690
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Elfin Cove - Herbert Graves Island
MSN:
811
YOM:
1955
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
2
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
125.00
Circumstances:
While cruising under VFR mode in adverse weather conditions, the pilot entered a narrow channel at an altitude of 100 feet when he lost control of the aircraft that spiraled to the ground. The wreckage was found in the region of Pelican. All three occupants were injured and the aircraft was destroyed.
Probable cause:
Stall during normal cruise due to improper in-flight decisions. The following contributing factors were reported:
- Continued VFR flight into adverse weather conditions,
- Failed to maintain flying speed,
- Low ceiling,
- Fog,
- High obstructions,
- Flew to blind canyon,
- Float equipped,
- Entered narrow channel at 100 feet AGL.
- Continued VFR flight into adverse weather conditions,
- Failed to maintain flying speed,
- Low ceiling,
- Fog,
- High obstructions,
- Flew to blind canyon,
- Float equipped,
- Entered narrow channel at 100 feet AGL.
Final Report: