Circumstances:
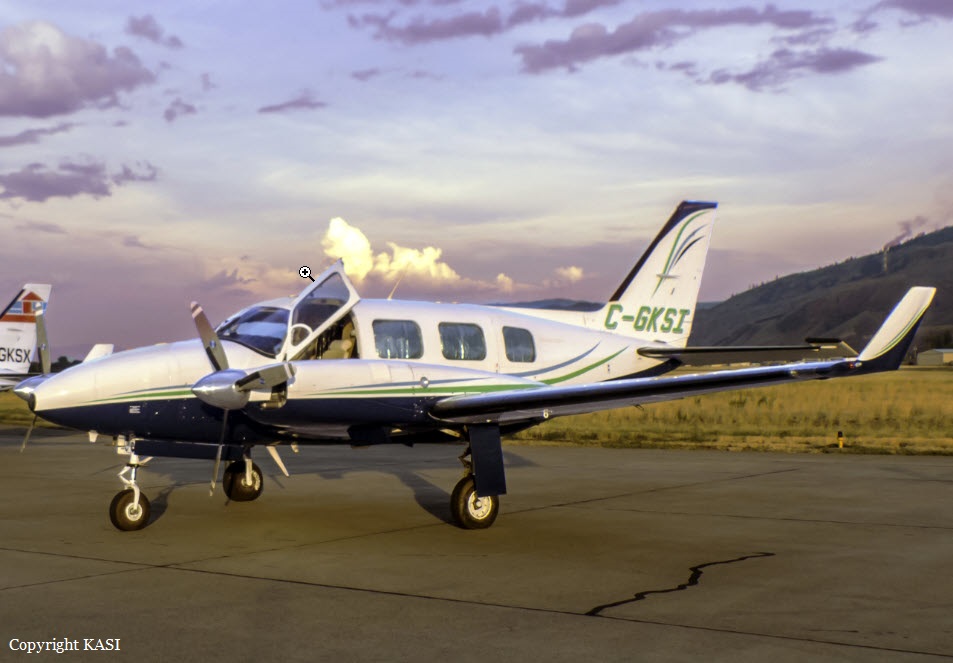
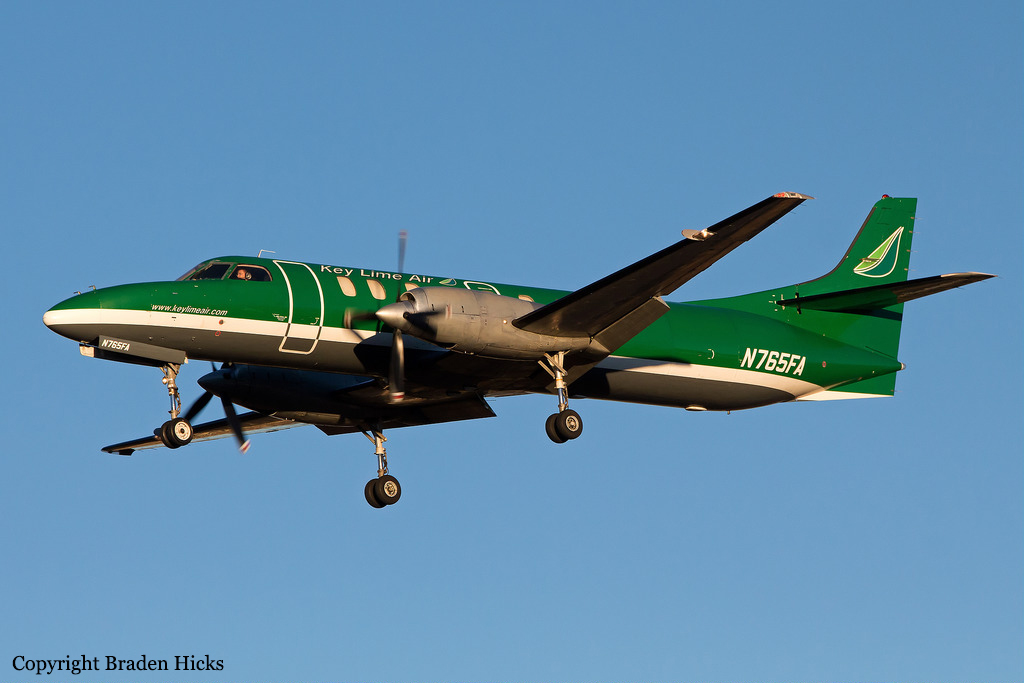
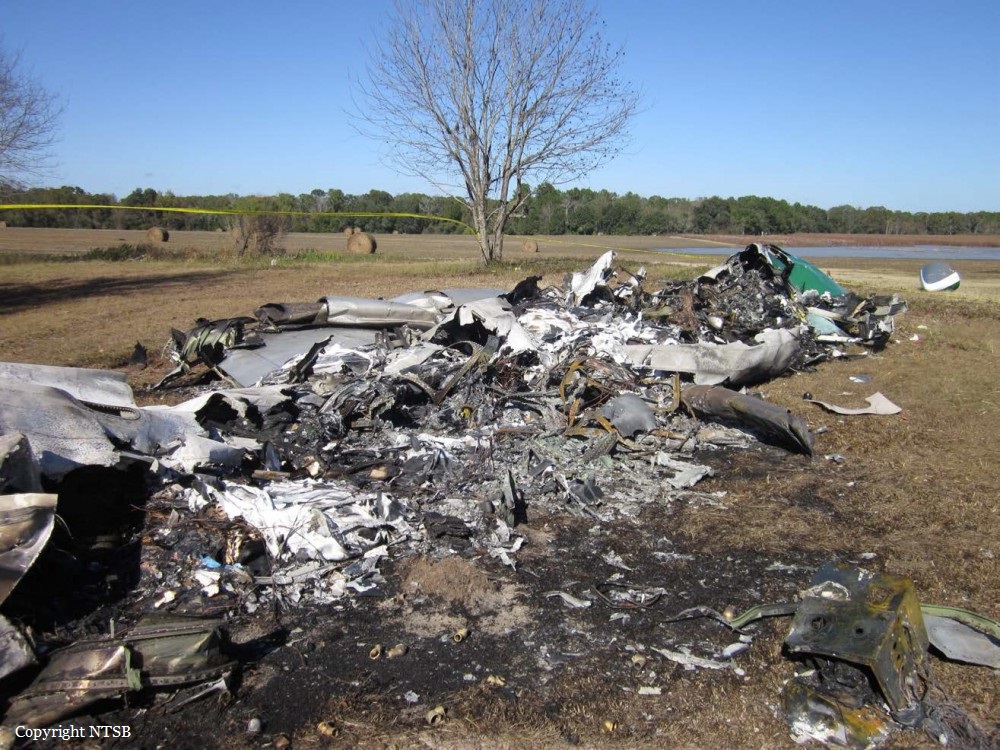
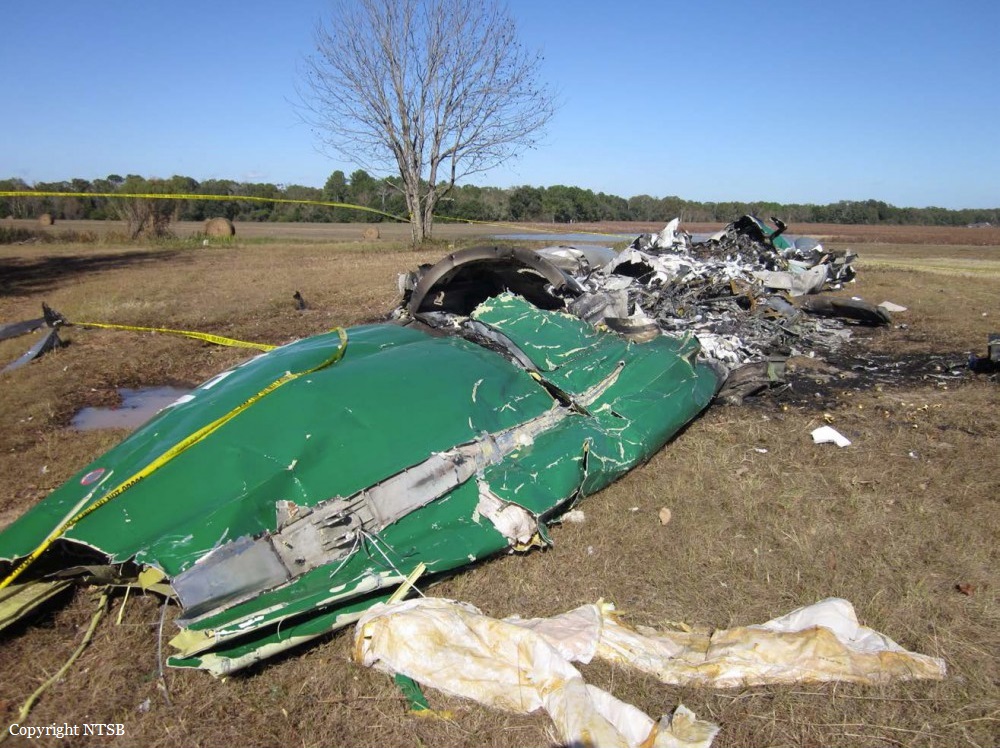
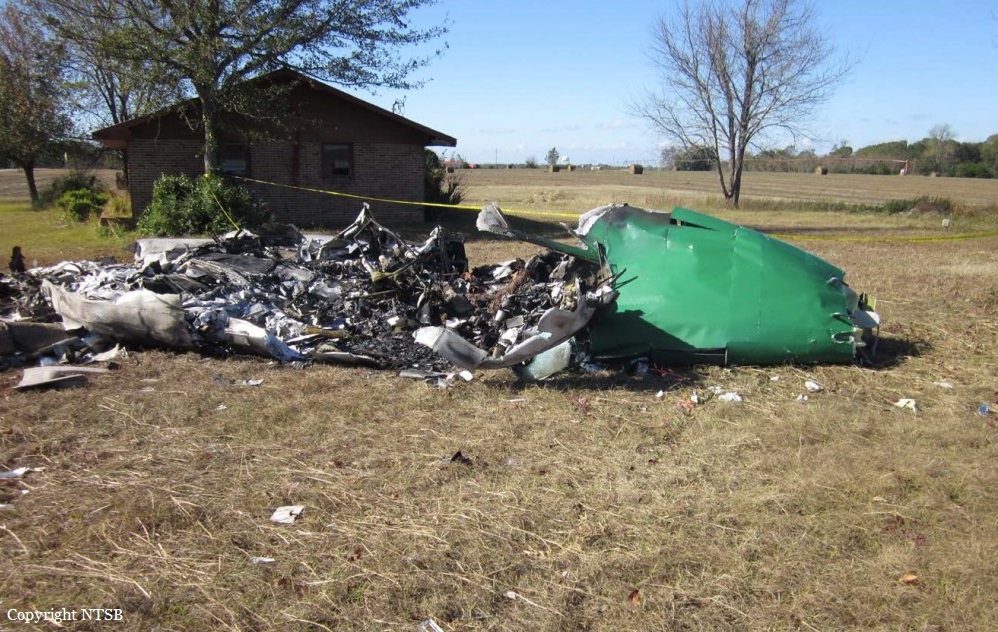
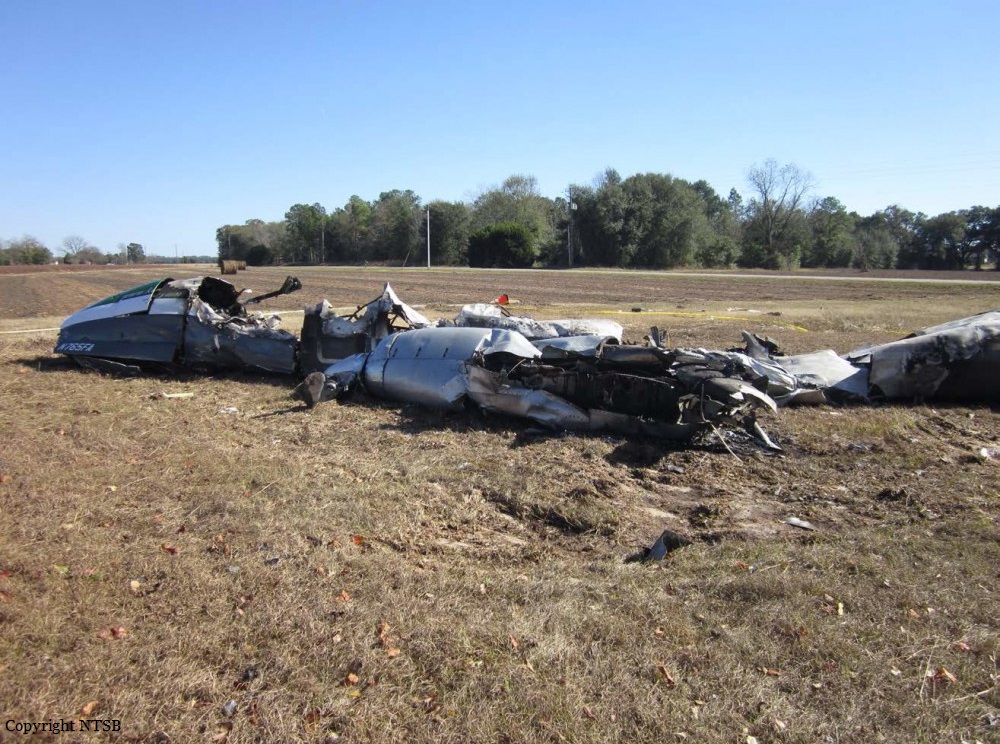
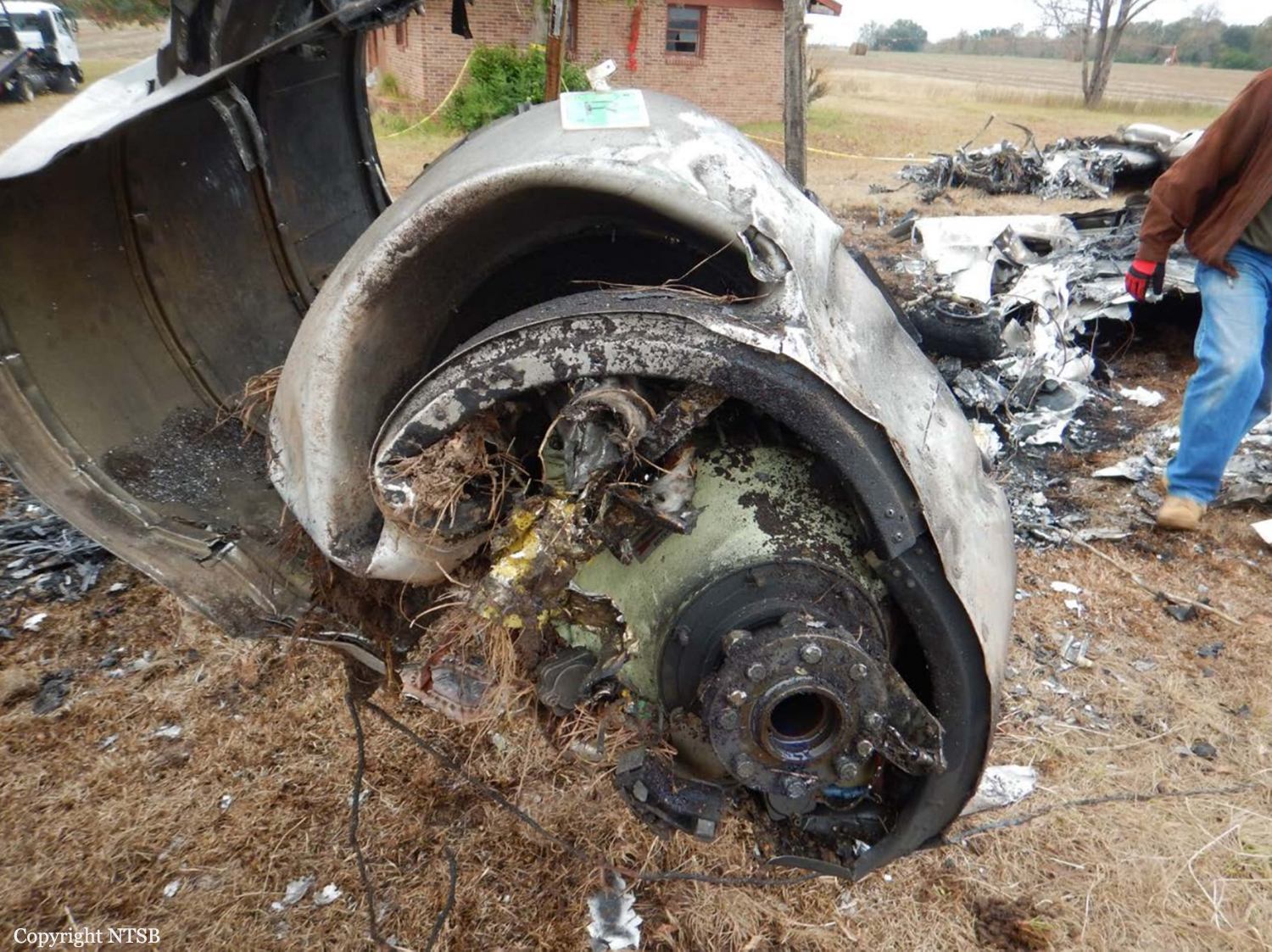
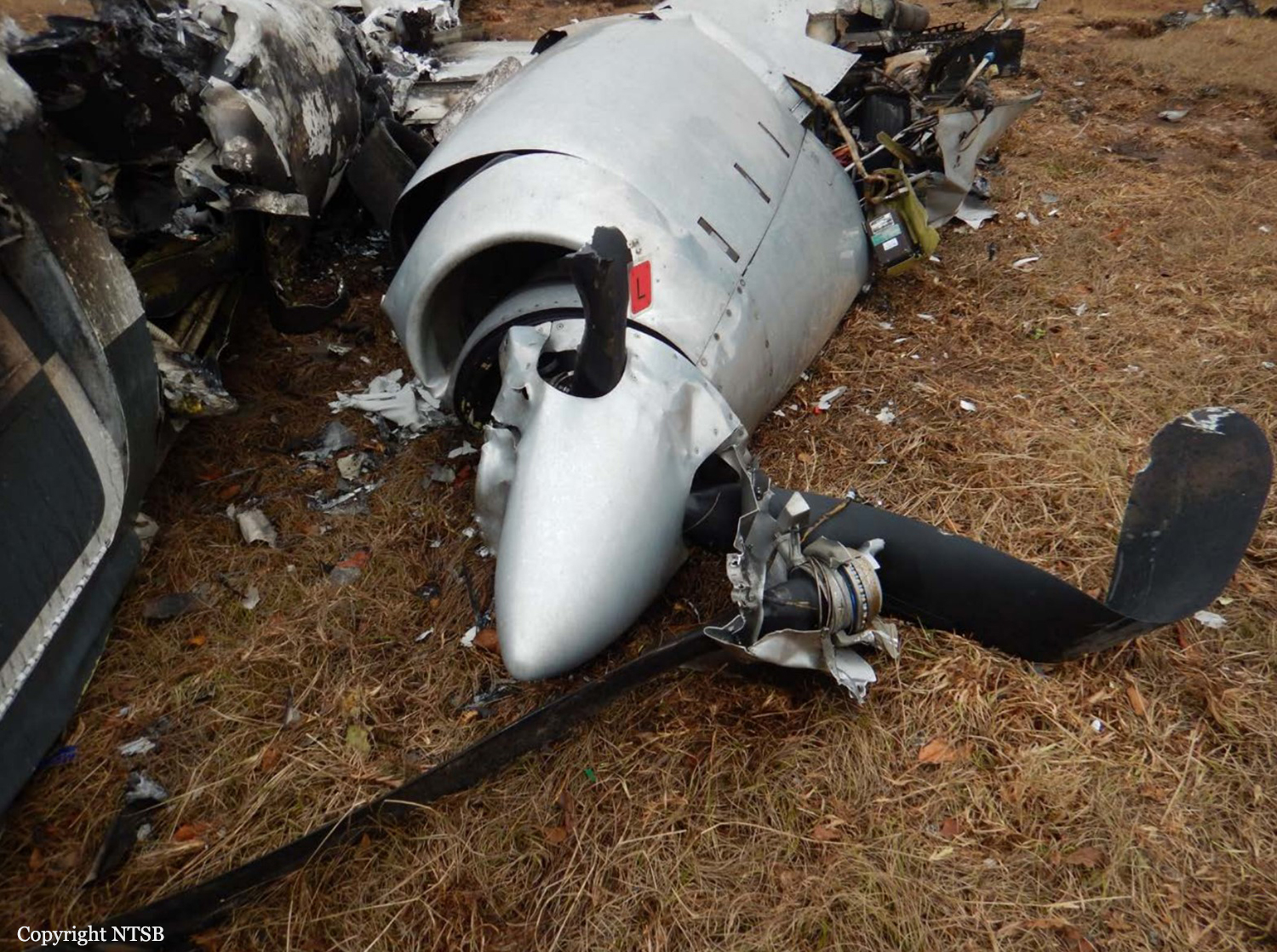
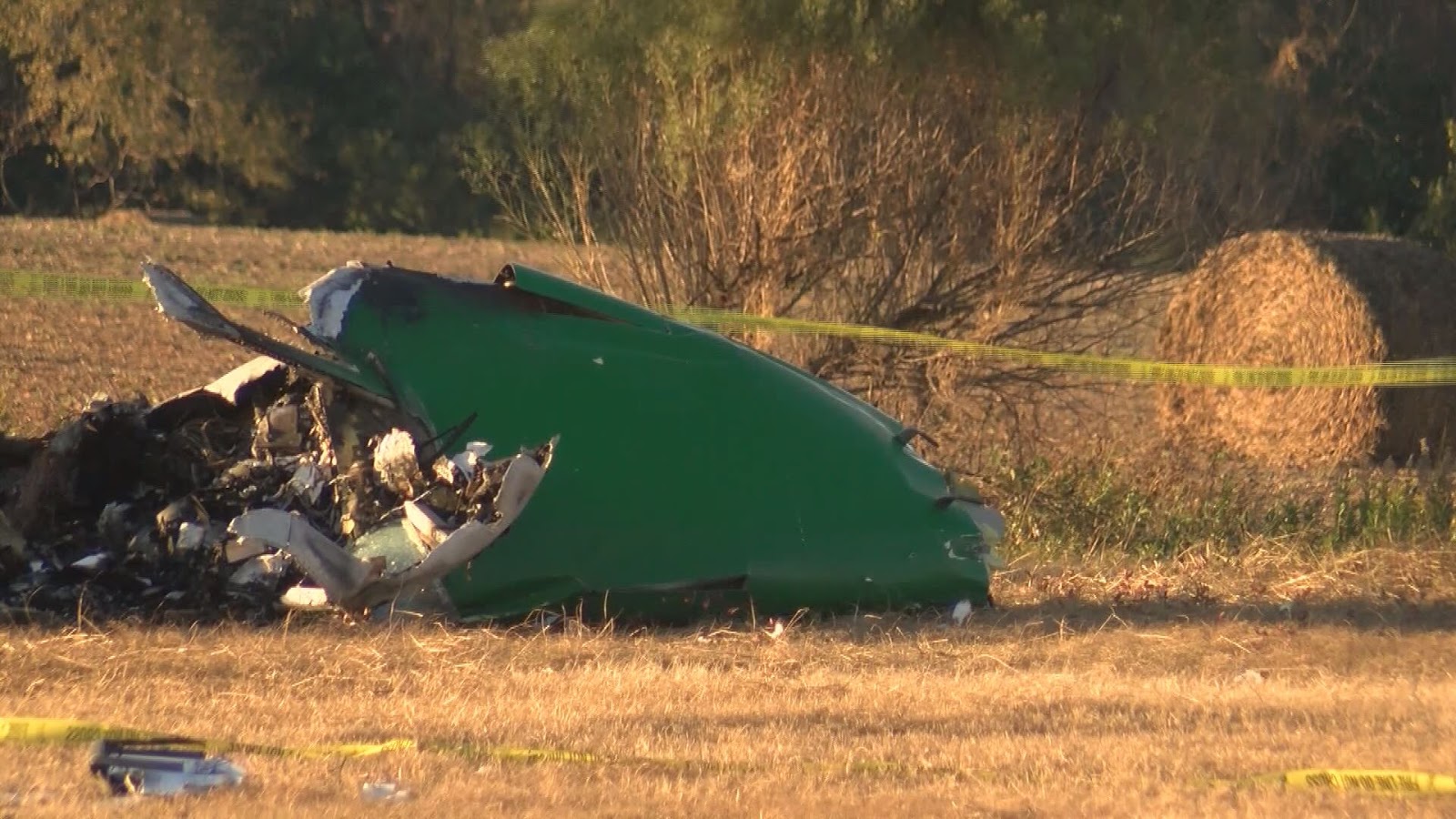
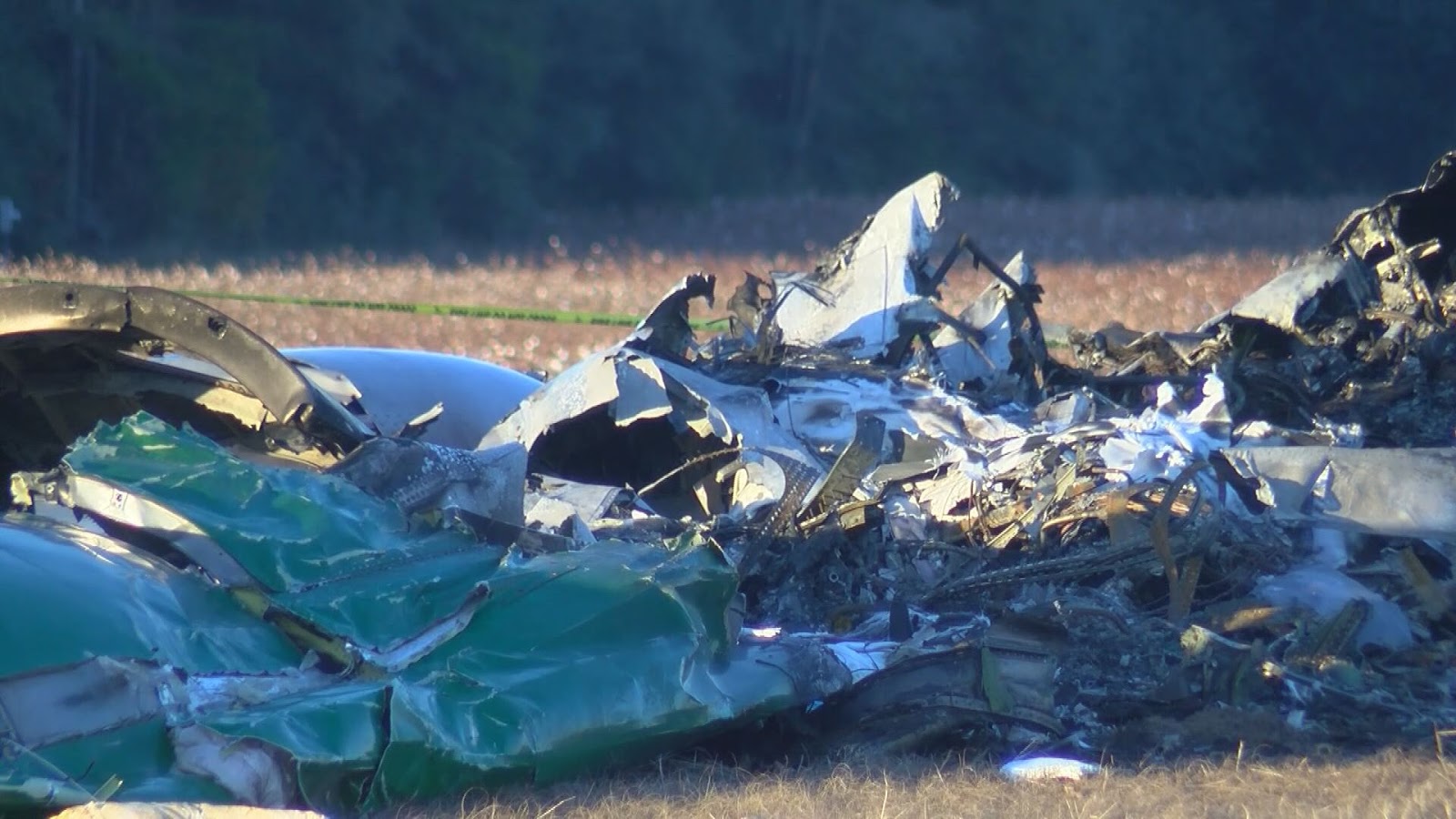
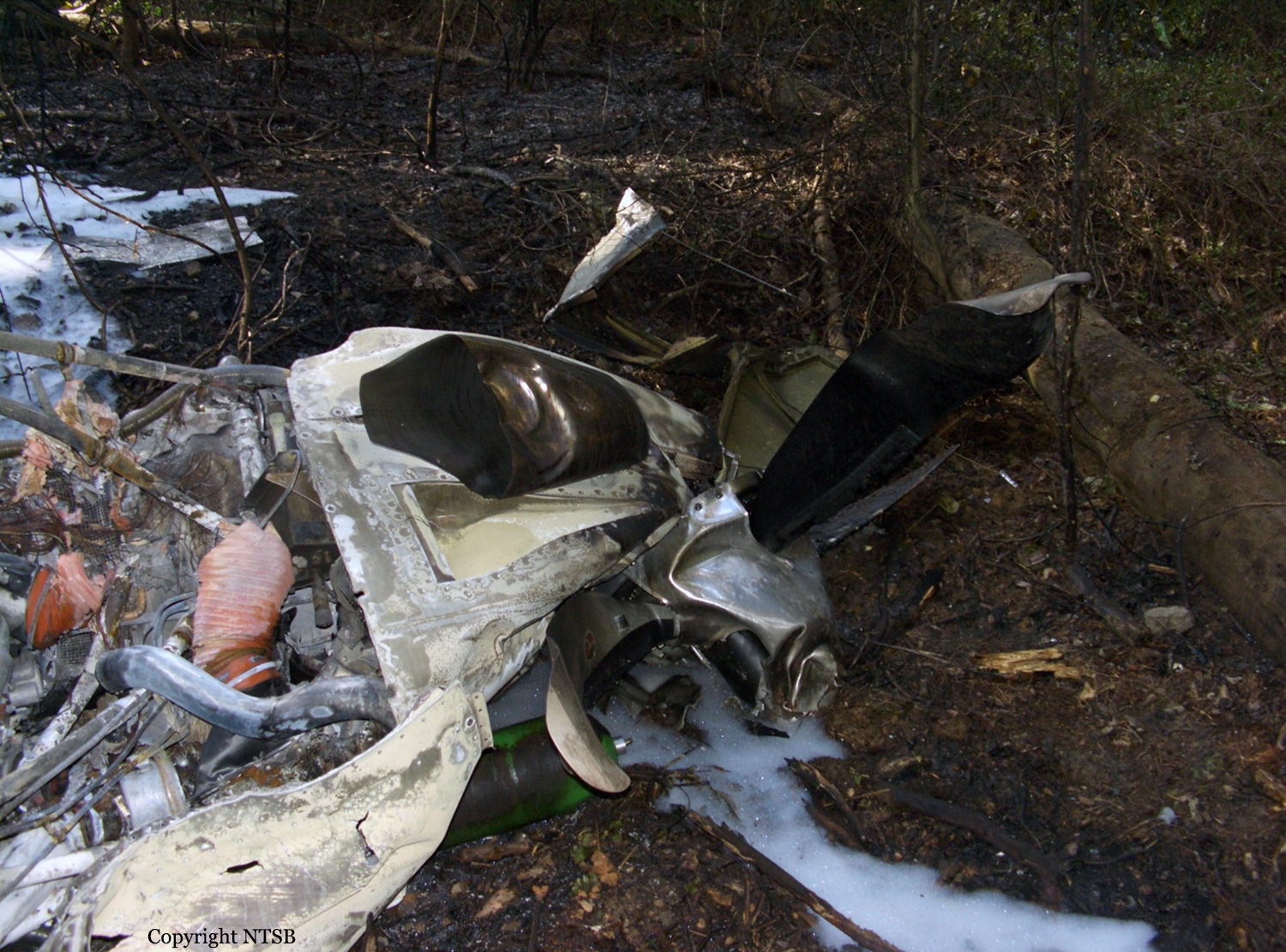
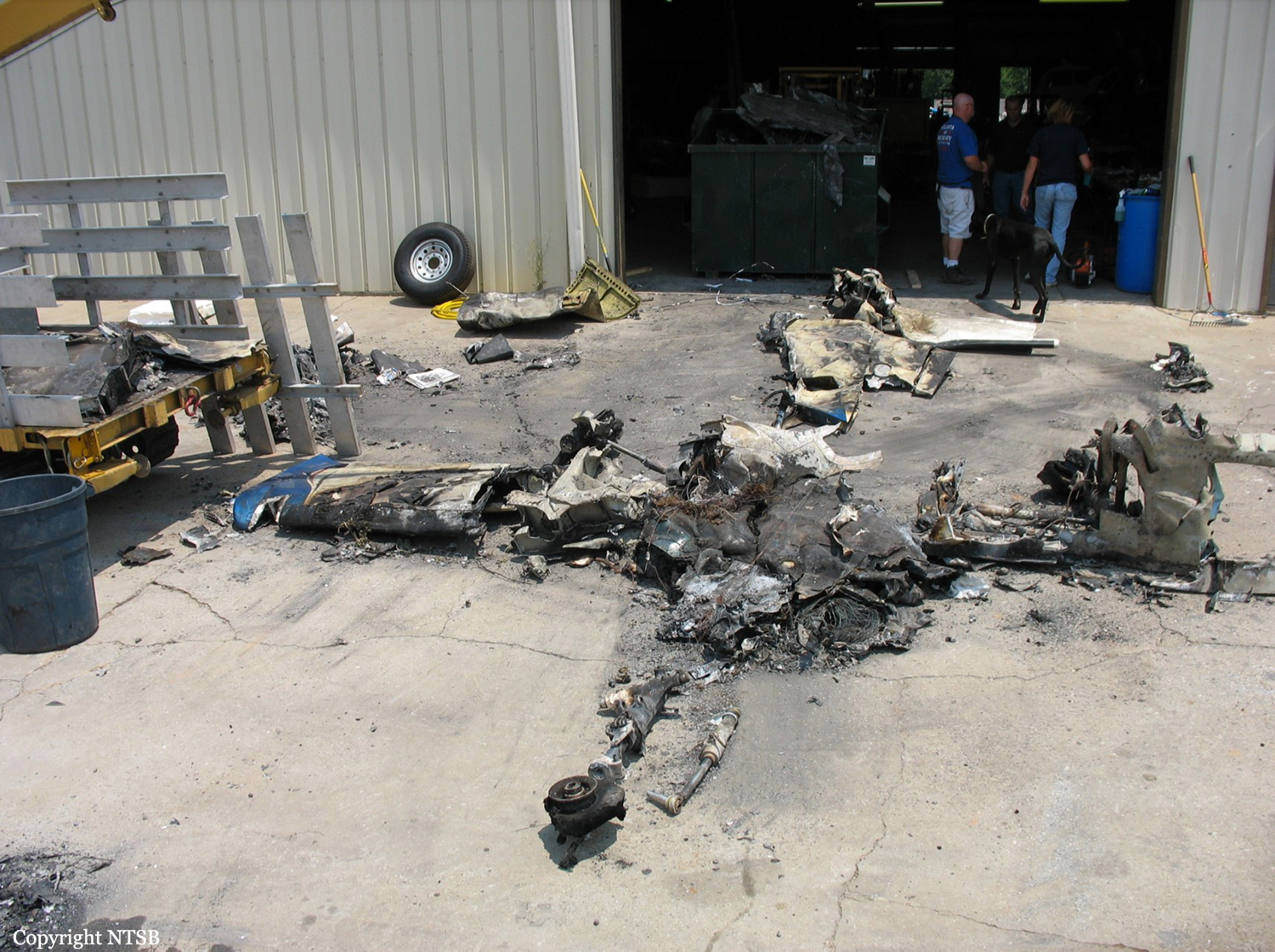
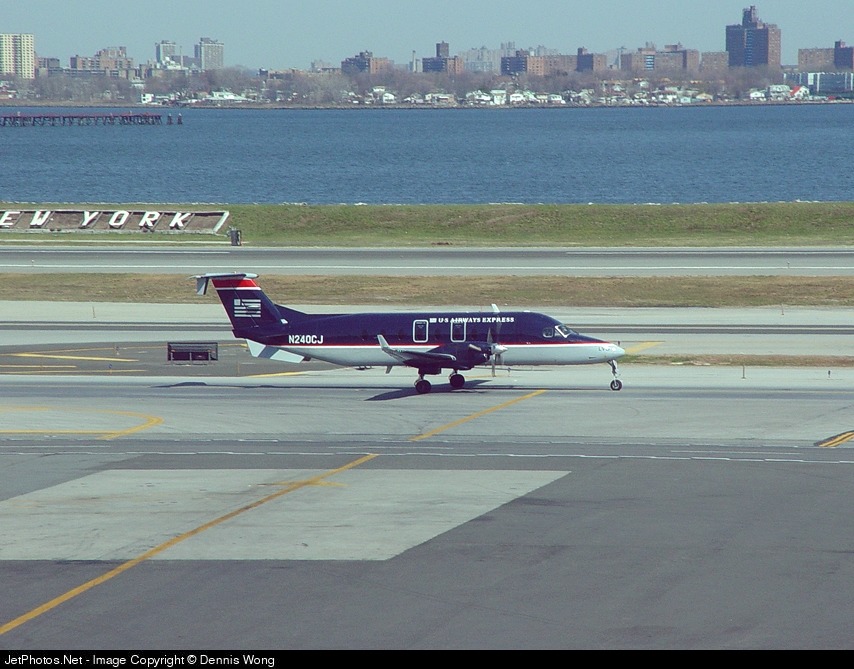
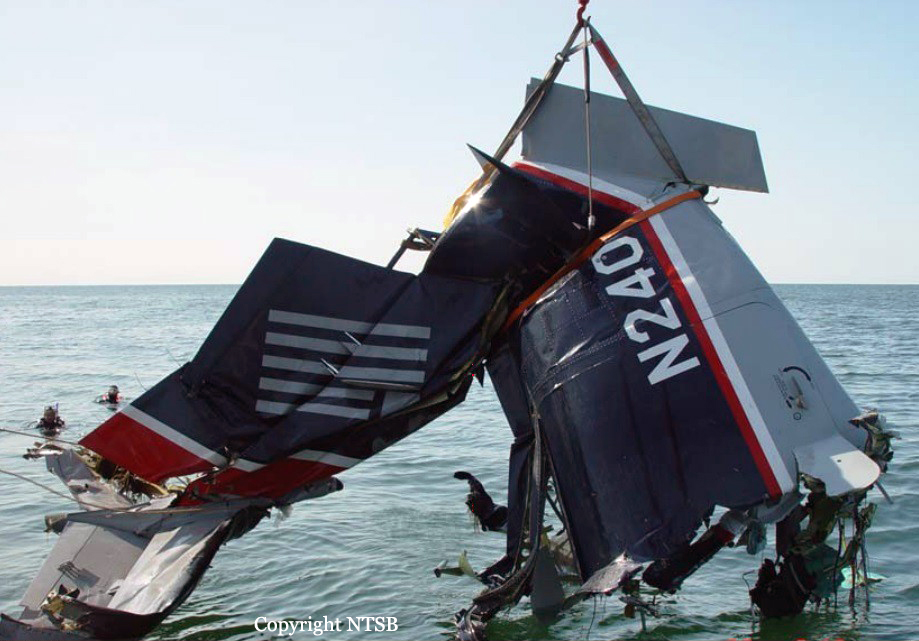
The airline transport pilot delayed his scheduled departure for the night cargo flight due to thunderstorms along the route. Before departing, the pilot explained to the flight follower assigned to the flight that if he could not get though the thunderstorms along the planned route, he would divert to the alternate airport. While en route, the pilot was advised by the air traffic controller in contact with the flight of a "ragged line of moderate, heavy, and extreme" precipitation along his planned route. The controller also stated that he did not see any breaks in the weather. The controller cleared the pilot to descend at his discretion from 7,000 ft mean sea level (msl) to 3,000 ft msl, and subsequently, the controller suggested a diversion to the northeast for about 70 nautical miles that would avoid the most severe weather. The pilot responded that he had enough fuel for such a diversion but concluded that he would "see what the radar is painting" after descending to 3,000 ft msl. About 1 minute 30 seconds later, as the airplane was descending through 7,000 ft msl, the controller stated, "I just lost you on radar, I don't show a transponder, it might have to do with the weather." About 40 seconds later, the pilot advised the controller that he intended to deviate to the right of course, and the controller told the pilot that he could turn left and right as needed. Shortly thereafter, the pilot stated that he was going to turn around and proceed to his alternate airport. The controller cleared the pilot direct to his alternate and instructed him to maintain 3,000 ft msl. The pilot acknowledged the instruction, and the controller then stated, "do you want to climb back up? I can offer you any altitude." The pilot responded that he would try to climb back to 3,000 ft msl. The controller then recommended a heading of 180° to "get you clear of the weather quicker," and the pilot responded, "alright 180." There were no further communications from the pilot. Shortly thereafter, radar data showed the airplane enter a right turn that continued through about 540°. During the turn its airspeed varied between 198 and 130 knots, while its estimated bank angles were between 40 and 50°. Examination of the wreckage indicated that airplane experienced an in-flight breakup at relatively low altitude, consistent with radar data that showed the airplane's last recorded altitudes to be around 3,500 ft msl. The symmetrical nature of the breakup, damage to the outboard wings, and damage to the upper fuselage were all signatures indicative that the left and right wings failed in positive overload almost simultaneously. All of the fracture surfaces examined had a dull, grainy appearance consistent with overstress separation. There was no evidence of pre-existing cracking noted at any of the separation points, nor was there evidence of any mechanical anomalies that would have prevented normal operation. Review of base reflectivity weather radar data showed that, while the pilot was maneuvering to divert to the alternate airport, the airplane was operating in an area of light precipitation that rapidly intensified to heavy precipitation, as shown by radar scans completed shortly after the accident. During this time, the flight was likely operating in clouds along the leading edge of the convective line, where the pilot most likely would have encountered updrafts and severe or greater turbulence. The low visibility conditions that existed during the flight, which was conducted at night and in instrument meteorological conditions, coupled with the turbulence the flight likely encountered, were conducive to the development of spatial disorientation. Additionally, the airplane's maneuvering during the final moments of the flight was consistent with a loss of control due to spatial disorientation. The pilot's continued flight into known convective weather conditions and his delayed decision to divert the flight directly contributed to the accident. Although the operator had a system safety-based program, the responsibility for the safe outcome of the flight was left solely to the pilot. Written company policy required completion of a flight risk assessment tool (FRAT) before each flight by the assigned flight follower; however, a FRAT was not completed for the accident flight. The flight followers responsible for completing the FRATs were not trained to complete them for night cargo flights, and the operator's management was not aware that the FRATs were not being completed for night cargo flights. Further, if a FRAT had been completed for the accident flight, the resultant score would have allowed the flight to commence into known hazardous weather conditions without any further review. If greater oversight had been provided by the operator, it is possible that the flight may have been cancelled or re-routed due to the severity of the convective weather conditions present along the planned route of flight.
Probable cause:
The pilot's decision to initiate and continue the flight into known adverse weather conditions, which resulted spatial disorientation, a loss of airplane control, and a subsequent in-flight breakup.