Country
Crash of a Cessna 500 Citation I in Canela: 3 killed
Date & Time:
Oct 31, 1997 at 1650 LT
Registration:
PT-LQG
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Curitiba - Canela
MSN:
500-0271
YOM:
1975
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
1
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
3
Circumstances:
The approach to Canela Airport was completed in marginal weather conditions with rain falls and a visibility estimated to be 1,500 - 2,000 metres. The landing was completed with a tail wind component of 15-20 knots and the aircraft landed too far down a wet runway which is 1,250 metres long. Unable to stop within the remaining distance, the aircraft overran, went down an embankment, crossed a road and came to rest against houses, bursting into flames. The aircraft was destroyed and all three occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
The following findings were reported:
- Wrong approach configuration,
- Marginal weather conditions with limited visibility due to rain falls,
- The crew completed the landing with a tailwind component of 15-20 knots,
- The runway surface was wet,
- The runway length was 1,250 metres only,
- The aircraft landed too far down the runway, reducing the landing distance available,
- The braking action was poor because the runway surface was wet,
- The crew failed to initiate a go-around procedure.
- Wrong approach configuration,
- Marginal weather conditions with limited visibility due to rain falls,
- The crew completed the landing with a tailwind component of 15-20 knots,
- The runway surface was wet,
- The runway length was 1,250 metres only,
- The aircraft landed too far down the runway, reducing the landing distance available,
- The braking action was poor because the runway surface was wet,
- The crew failed to initiate a go-around procedure.
Crash of a Cessna 500 Citation I in Rio de Janeiro
Date & Time:
Jul 3, 1997 at 1000 LT
Registration:
PT-ILJ
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Rio de Janeiro – São José dos Campos
MSN:
500-0057
YOM:
1973
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
3
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
During the takeoff roll at Rio de Janeiro-Santos Dumont Airport, the captain realized that all conditions were not met for a safe takeoff and decided to abort. Unable to stop within the remaining distance, the aircraft overran and came to rest in the Guanabara Bay. All five occupants escaped with minor injuries and the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.


Crash of a Cessna 500 Citation I near La Felisa: 2 killed
Date & Time:
Mar 7, 1997 at 0934 LT
Registration:
HK-3885
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Pereira - Medellín
MSN:
500-0135
YOM:
1973
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
2
Aircraft flight hours:
6274
Circumstances:
After takeoff from Pereira-Matecaña Airport, while climbing, the copilot declared an emergency and reported problems. Shortly later, the aircraft entered an uncontrolled descent and crashed near La Felisa. The aircraft was destroyed and both pilots were killed.
Probable cause:
In-flight braking and subsequent separation of both wing tips due to positive wing loading imposed by the unqualified crew exceeding the structural limit stipulated by the manufacturer.
Final Report:
Crash of a Cessna 500 Citation I on Mt Balatukan: 2 killed
Date & Time:
Feb 1, 1997
Registration:
RP-C1500
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Cagayan de Oro – Butuan City
MSN:
500-0225
YOM:
1974
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
2
Circumstances:
Few minutes after takeoff from Cagayan de Oro Airport, while climbing to a height of 8,000 feet, the aircraft struck the slope of Mt Balatukan located about 57 km northeast of Cagayan de Oro Airport. Both pilots were killed.
Probable cause:
Controlled flight into terrain for unknown reasons.
Crash of a Cessna 500 Citation I in Ensenada: 8 killed
Date & Time:
Feb 6, 1996 at 2020 LT
Registration:
XA-SLQ
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Tijuana - Ensenada
MSN:
500-0111
YOM:
1973
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
6
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
8
Circumstances:
While approaching Ensenada Airport by night and foggy conditions, the crew failed to realize his altitude was insufficient when the aircraft struck a hill located few km from the airport. The aircraft was destroyed upon impact and all eight occupants were killed. It is believed that the crew did not receive any clearance to approach Ensenada Airport and continued the descent at an insufficient altitude.
Crash of a Cessna 500 Citation I in Fazenda Matary
Date & Time:
Feb 4, 1996 at 1628 LT
Registration:
PT-KPA
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Recife – Imperatriz – Fazenda Matary
MSN:
500-0181
YOM:
1974
Crew on board:
3
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
2752.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
6
Circumstances:
En route from Imperatriz to Fazenda Matary, the captain informed the copilot he would perform training upon arrival as there are no passengers on board. On descent, he informed ATC he would perform a touch-and-go manoeuvre. With the flaps down at 15°, the aircraft landed at a speed of 125 knots, about 10 knots above the speed reference of 116 knots. After touchdown, the captain changed his mind and decided to perform a complete stop without informing the copilot. The copilot noted that the speed was dropping so he decided to increase engine power to takeoff. Shortly later, the captain reduced power and initiated a braking procedure. Unable to stop within the remaining distance, the aircraft overran and came to rest few dozen metres further, bursting into flames. All three occupants escaped uninjured while the aircraft was destroyed by a post crash fire.
Probable cause:
The following findings were reported:
- There was overconfidence, coupled with an impulsive attitude on the part of the instructor, making him convinced that he could land without problems, even changing the procedure already established and not communicating his decision to the copilot/student.
- The instructor did not properly plan the landing procedure that he decided to carry out, contrary to the briefing.
- There was an error in the instructor's judgment, due to the inadequate assessment of normal landing with 15º flap configuration and speed about 10kt above the predicted, contrary to previous briefing.
- The instructor did not inform the student of his decision to complete the landing, without rush, as well as not responding to the request to start the rush. The student accelerated the engines without the instructor's authorization.
- There was overconfidence, coupled with an impulsive attitude on the part of the instructor, making him convinced that he could land without problems, even changing the procedure already established and not communicating his decision to the copilot/student.
- The instructor did not properly plan the landing procedure that he decided to carry out, contrary to the briefing.
- There was an error in the instructor's judgment, due to the inadequate assessment of normal landing with 15º flap configuration and speed about 10kt above the predicted, contrary to previous briefing.
- The instructor did not inform the student of his decision to complete the landing, without rush, as well as not responding to the request to start the rush. The student accelerated the engines without the instructor's authorization.
Final Report:
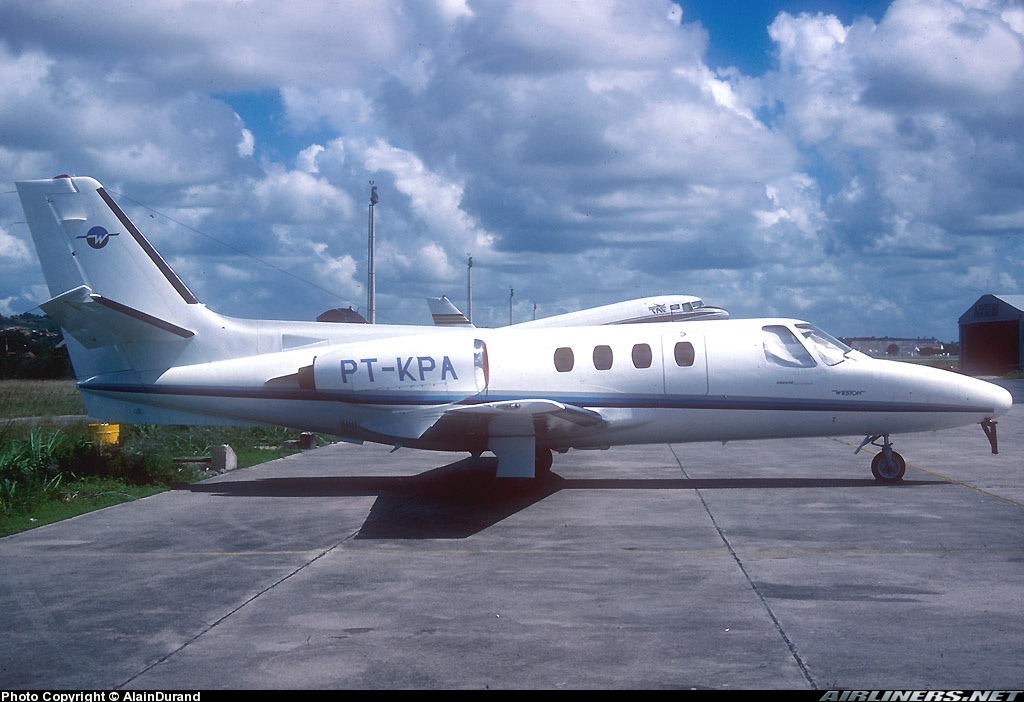

Crash of a Cessna 500 Citation I/SP in Ciudad Alemán: 2 killed
Date & Time:
Mar 25, 1994
Registration:
XA-SMH
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Veracruz - Ciudad Alemán
MSN:
500-0084
YOM:
1973
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
2
Circumstances:
The crew was completing a positioning flight from Veracruz. After touchdown, the crew encountered difficulties to stop the aircraft within the remaining distance (runway 13/31 is 1,300 metres long). It overran and eventually crashed past the runway end. The aircraft was destroyed and both pilots were killed.
Probable cause:
Apparently following a wrong approach configuration (the aircraft was too high on approach), the crew landed too far down the runway and failed to initiate a go-around procedure. After touchdown, the landing distance available was insufficient.
Crash of a Cessna 500 Citation in San Luis Obispo: 4 killed
Date & Time:
Sep 24, 1990 at 0702 LT
Registration:
N79DD
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Van Nuys - San Luis Obispo
MSN:
500-0254
YOM:
1975
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
2
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
4
Captain / Total hours on type:
95.00
Aircraft flight hours:
4197
Circumstances:
The flight was cleared for a loc runway 11 approach. About 3 minutes later, the 2nd-in-command (sic) reported '. . . We don't get the localizer can you see if we're on course.' The LAX ARTCC R-15 controller confirmed the flight was right of course and below the required altitude. The aircraft's mode C indicated an altitude of 1,400 feet; the controller advised the flight crew to maintain at least 2,300 feet until past the final approach fix (faf). The crew then replied that they were in VMC. Radar svc was terminated and a frequency change to tower was approved. Shortly thereafter, the aircraft hit a eucalyptus tree at about 90 feet agl, 2.05 miles from the approach end of the runway and about 195 feet right of the loc. Elevation of the crash site was 101 feet; minimum descent altitude (MDA) for the approach was 640 feet. The 0645 pdt weather was, in part: indefinite ceiling, 100 feet obscured, vis 1/8 mile with fog, wind from 220° at 4 kts. No preimpact part failure or malfunction of the aircraft was found. All four occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
The pilot's improper IFR (instrument) procedure, and his failure to maintain the minimum descent altitude (MDA) for the approach. The adverse weather was a related factor.
Final Report:
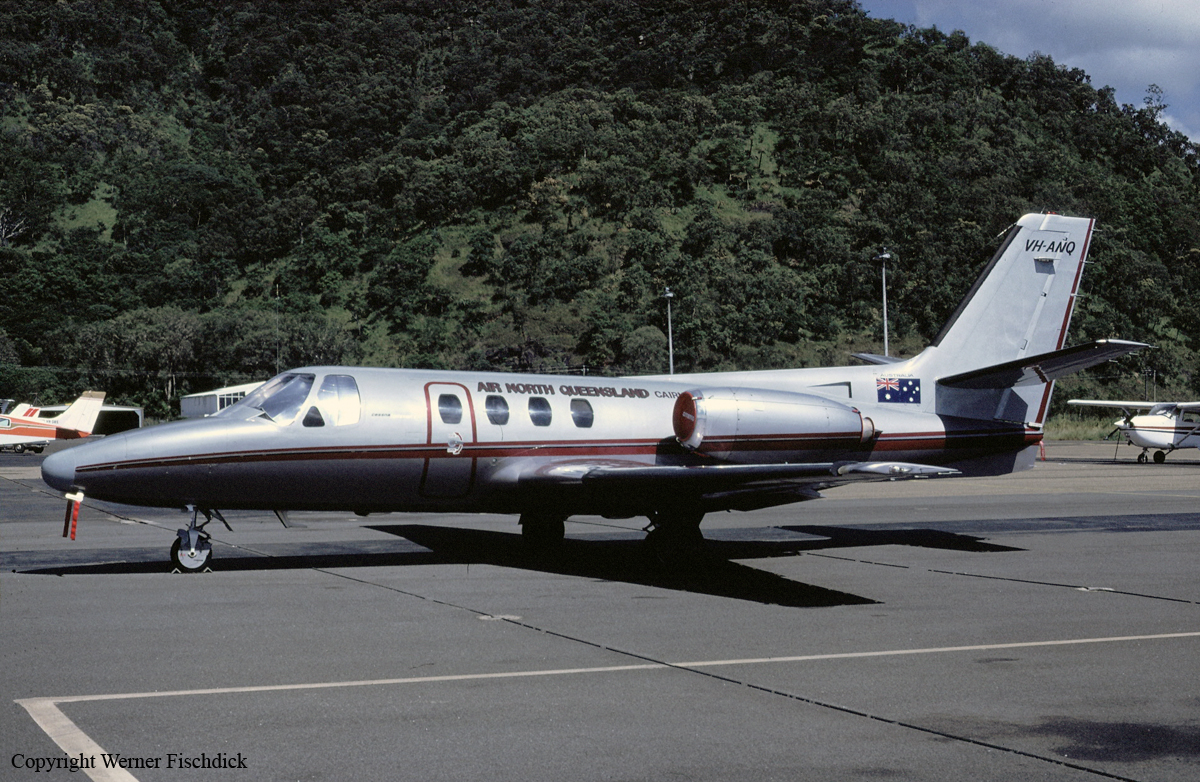
Crash of a Cessna 500 Citation near Mareeba: 11 killed
Date & Time:
May 11, 1990 at 1740 LT
Registration:
VH-ANQ
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Proserpine – Mareeba – Cairns
MSN:
500-0283
YOM:
1975
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
10
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
11
Captain / Total hours on type:
1000.00
Circumstances:
Cessna 500 VH-ANQ was operating the Proserpine to Mareeba leg of a charter flight The aircraft departed Proserpine at 16:35 hours. The charter flight had been organised to transport members of five local government authorities from the Cairns/Atherton Tablelands area to a Local Government Association Conference at Airlie Beach, Queensland. The flight plan indicated that the flight would follow Instrument Flight Rules (IFR) with a planned cruising altitude of FL330. The aircraft was planned to track via overhead Townsville then direct to Mareeba with a flight time interval of 68 minutes. The flight apparently continued normally and at 17:26 the aircraft was cleared to descend to FL170 and instructed to call Cairns Approach. On first contact with Cairns Approach, the pilot advised that the aircraft was tracking for Mareeba via the 163 radial at 41 miles (76 kilometres) DME from Biboohra. (There are no radio navigational aids at Mareeba, the nearest aids for tracking and instrument approach purposes are at Biboohra, about 16 kilometres north of Mareeba). The aircraft was advised to maintain FL170 but a short time later was cleared to descend to FL120. The pilot stated that he would not be closing down the engines at Mareeba and that his estimated departure time was 17:50. At 17:35 hours VH-ANQ was cleared to descend to 10,000 feet and one minute later the pilot advised that the aircraft was "approaching over Mareeba and visual". Cairns Approach advised VH-ANQ that there would be a short delay at 10,000 feet and following a request from the pilot gave approval for the aircraft to circle over Mareeba. At 17:40 hours, Cairns Approach instructed the aircraft to descend to 7,000 feet. This transmission, and other subsequent transmissions to the aircraft, went unanswered. The wreckage of VH-ANQ was ultimately located on the eastern slopes of Mt Emerald, 15 kilometres south of Mareeba Airport, by searching helicopters at 0240 hours on 12 May 1990. The aircraft initially impacted the mountainside with the left wingtip, while travelling on a track of about 340 degrees Magnetic. At the time it was in a wings level attitude at an angle of descent of eight degrees. It then struck the ground just below the apex of a ridge and the wreckage spread in a fan shape, at an angle of 30 degrees, along a centreline track of 350 degrees Magnetic.
Probable cause:
This accident was unusual in that the last report by the pilot indicated that the aircraft was at 10,000 feet and on a track that was 55 kilometres to the east of the accident site. There was no substantiated, and very little circumstantial evidence to suggest what caused the aircraft to descend 6,400 feet and to be displaced a considerable distance to the west of track. As a result the causal factors associated with this accident remain undetermined.
Final Report: