Crash of a Cessna 402A near Mount Hagen: 8 killed
Date & Time:
Apr 1, 1981
Registration:
P2-GKJ
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Port Moresby – Goroka – Mount Hagen
MSN:
402A-0081
YOM:
1969
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
7
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
8
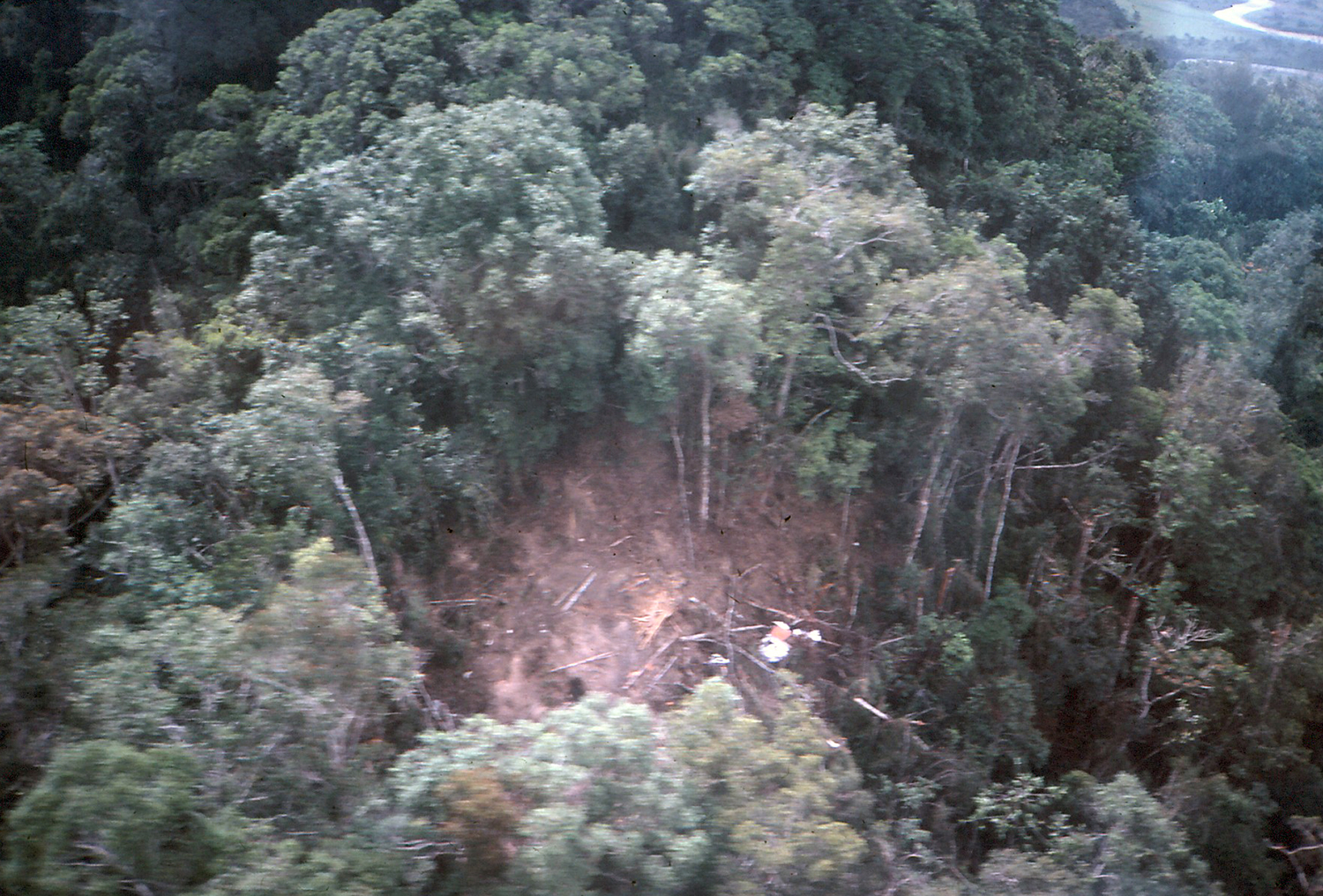
Circumstances:
While approaching Mount Hagen Airport in poor weather conditions, the twin engine airplane struck the slope of a wooded mountain. The aircraft was totally destroyed and all eight occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
Controlled flight into terrain.