Circumstances:
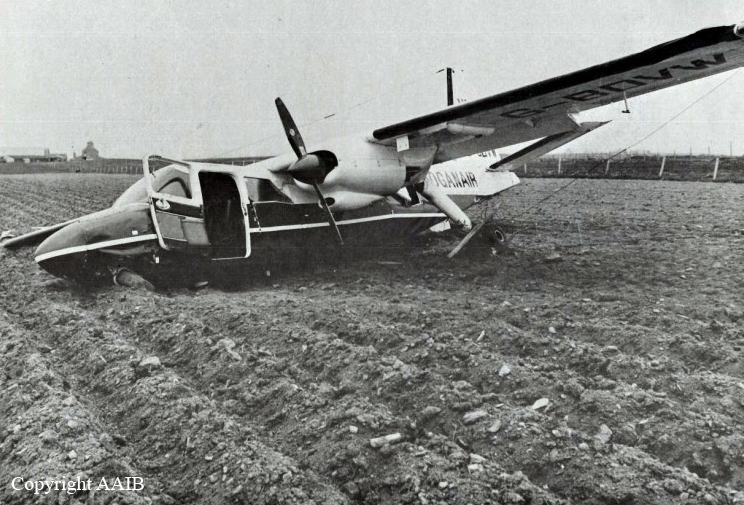
Loganair flight LC 621 was scheduled to fly from Kirkwall, on Orkney Island, to the Islands of Stronsay and Sanday, departing from Kirkwall at 07:30. The weather at Kirkwall was predominantly misty with low cloud and thus unsuitable for an on-schedule departure; accordingly, the commander decided to delay the flight pending an improvement. Because there are no formal weather reporting facilities at Stronsay or Sanday, crews must rely upon the area forecast and on any informal information passed by the respective aerodrome attendants. At about 07:25 hrs, the two airfield attendants telephoned, in turn, to say that the weather at Sanday was suitable for landing and that at Stronsay the visibility was then about 1½ miles. At 07:50 the commander decided that the weather conditions at Kirkwall were now better than the published takeoff minima and that the flight could be conducted under the Visual Flight Rules (VFR). Accordingly, the BN-2 Islander took off for Stronsay with six passengers on board. The flight was uneventful and the aircraft landed at Stronsay at 07:58. There two passengers disembarked and three joined for the 6 mile flight to Sanday, which departed at 08:03. As they passed the south-west tip of Sanday Island, the visibility was 2 miles with very low patchy stratus and with a higher layer of cloud. The pilot therefore flew the route below the upper layer of cloud, at 300 feet amsl and at a reduced airspeed of 90 knots, compared with the normal cruising speed of 130 knots. When the aircraft was about 3/4 mile out from Sanday airfield the commander recognised the chequered marker boards near the end of the grass runway 03. He next saw the windsock, which showed the wind to be about 140°/15-20 knots, and slowly descended to 250 feet amsl (190 feet above the aerodrome) to position the aircraft downwind for runway 11. Whilst doing so, he lost sight of the airfield in deteriorating visibility and, as the cloudbase ahead appeared to be getting lower, he climbed away in a northwesterly direction and levelled off above the layer of cloud, at 600 feet amsl. Whilst establishing the aircraft on the track to Kirkwall, the commander noticed some areas clear of cloud about 3 miles off the northwest coast of Sanday. As, in the opinion of the commander, these provided a safe area for descent over the sea, he used them to descend to 300 feet again and approached the northwest coast at 90 knots with the intention of map-reading his way back to Sanday aerodrome. Having carried out the descent and the relevant aircraft checks the commander saw the headland, which he knew to be Whale Point, some 2-3 miles distant. By reference to his map he was aware that he could follow the road which ran in a southwesterly direction and then turn southeast to a specific point which would lead him directly onto the final approach to runway 11. However, having failed to recognise the turning point, he navigated by reference to his map around the south, east and north of the aerodrome in order to intercept the road running southwest and thus relocate the turn-in point to the runway. The commander stated that he was aware that the meteorological conditions were very conducive to the formation of carburettor icing, so he applied the normal period of carburettor heat to each engine just before the final approach. He then turned the aircraft onto the final approach and, not yet seeing the airfield, used the school - which he could see and knew to be almost directly beneath the final approach path - to align the aircraft with the runway. As the aircraft passed abeam of the school the commander was able to identify the runway markers of runway 11. By this time the aircraft speed had reduced from the 65 knots at which the approach had been flown, but the speed actually achieved is not known. The left wing of the aircraft then dropped and the aircraft established a rate of sink. The stall warning system activated and the application of full throttle could not arrest the descent before ground contact. During this final descent, the aircraft turned through 55° to the left and struck the ground in a manner quoted by some passengers as not very different from a normal landing, although at a point some 450 feet (137 metres) short of the runway threshold. Thinking that the aircraft had merely bounced on the ground, the commander left the power applied and attempted to climb away. With full throttle still applied, the aircraft continued through two barbed wire fences, across a small quarry and a shallow ditch. It finally came to rest, after passing through another barbed wire fence, some 1,065 feet (325 metres) from the initial impact point. The commander then closed the throttles and shut down the engines.