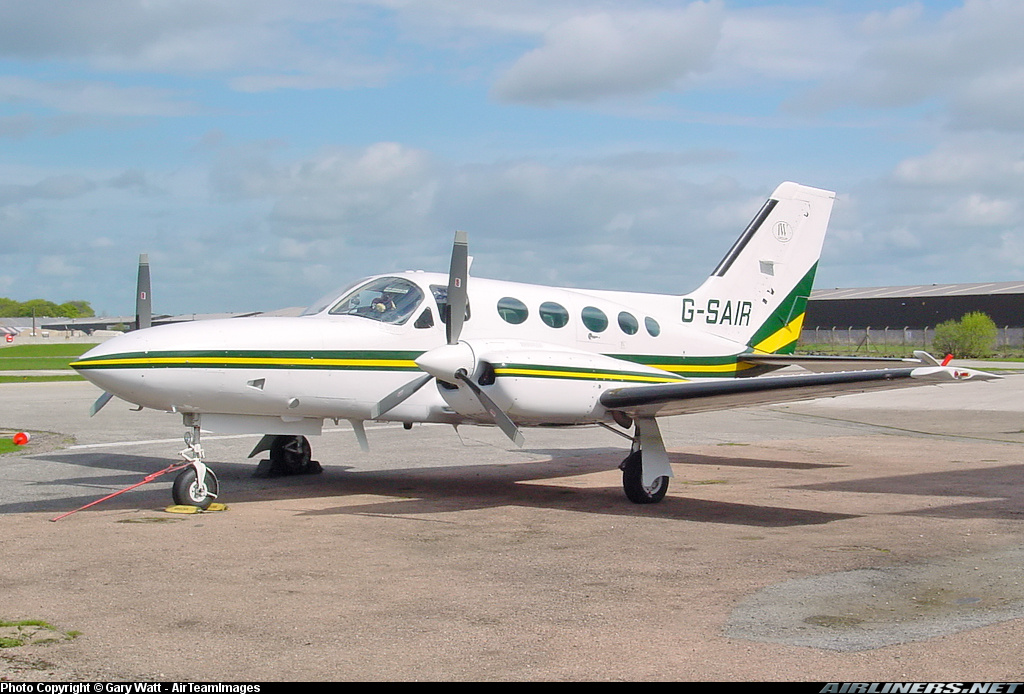
Crash of a Cessna 421C Golden Eagle III in Humberside: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Mar 29, 2003 at 1229 LT
Registration:
G-SAIR
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Humberside - Humberside
MSN:
421C-0471
YOM:
1978
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
1
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
1850.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
600
Circumstances:
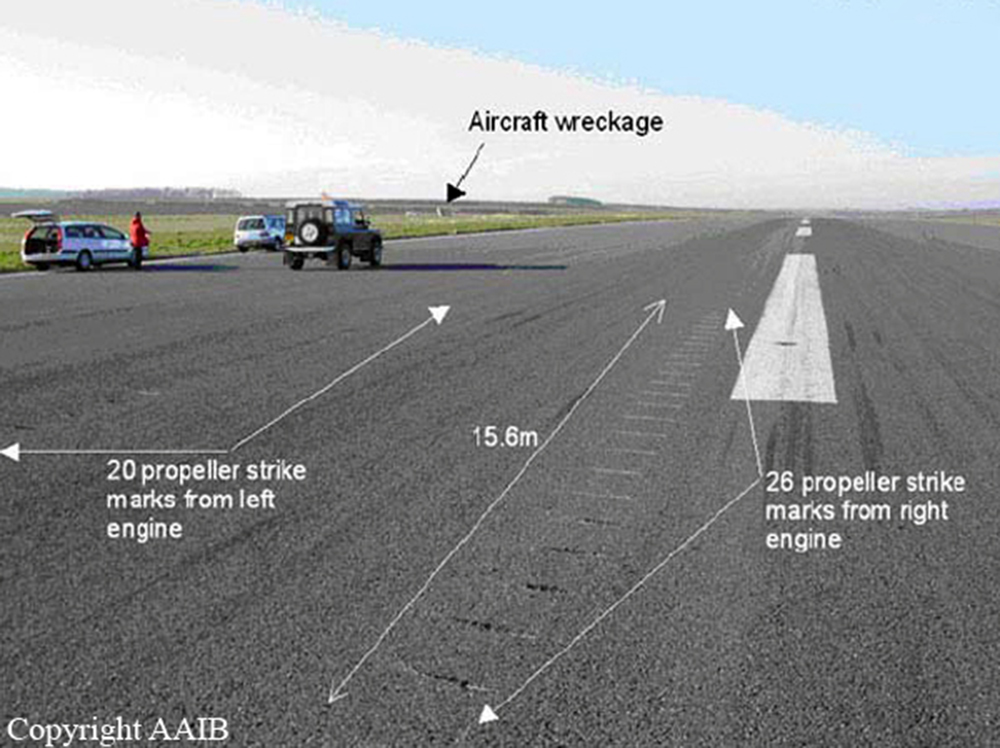
About 50 minutes into the flight, the aircraft returned to Humberside circuit and was cleared by ATC for a touch-and-go landing on Runway 21. The landing was firm but otherwise uneventful and witnesses heard the power being applied as it accelerated for takeoff. Just before rotation two large "puffs of smoke" were seen to come from the vicinity of the mainwheels as both propellers struck the runway. The aircraft then lifted off and almost immediately began to yaw and roll to the left. The left bank reached an estimated maximum of 90° but reduced just before the left wing tip struck the ground. The aircraft then cartwheeled across the grass to the south of the runway and burst into flames. The owner in the left pilot's seat and the pilot in the right pilot's seat escaped from the wreckage, but the flight examiner, who was occupying a seat in the passenger cabin, was unable to vacate the aircraft and subsequently died of injuries sustained in the post impact fire. An engineering investigation found no fault with the aircraft that might have caused the accident. The investigation concluded that the most probable cause was an inadvertent retraction of the landing gear whilst the aircraft was still on the ground.
Probable cause:
An engineering investigation found no fault with the aircraft that might have caused the accident. The investigation concluded that the most probable cause was an inadvertent retraction of the landing gear whilst the aircraft was still on the ground. The confusion over individual roles would have been resolved if the examiner had given a pre-flight briefing in line with the guidance contained in the FAA Designated Examiners' Handbook, but both pilots have stated that this briefing did not take place. In any event, the FAA Handbook and FARs are unclear on who should be the commander of the flight although FAR 61.47 states the examiner is not normally to be the Pilot in Command except by prior agreement with the applicant or other person who would normally be acting as Pilot in Command. Nevertheless, it is clear that the instructor should have been briefed that he was fulfilling the safety pilot role and was responsible for "protect(ing) the overall safety of the flight to whatever extent is necessary". If the instructor had clearly understood this responsibility, he might have monitored the owner's actions more closely during the touch-and-go and might have intervened earlier. Notwithstanding the confusion, the instructor took control when he considered that the owner was not taking appropriate action to control the aircraft, although the actual moment that he took control is in dispute. Given the owner's belief that the instructor was the commander and that the instructor was in any case by far the more experienced pilot, it is not surprising that he relinquished control even though, unknowingly, he had a more complete understanding of the aircraft's predicament. The flight time from the propeller strikes to the next ground impact was only a few seconds. Once the aircraft became airborne with a significant amount of power applied and a badly damaged left propeller, the situation was well beyond any emergency for which either pilot might have trained. The options for action were very limited and would have required a full appreciation of the circumstances, plus extremely rapid analysis and reactions if those actions were to be successful.
Final Report: