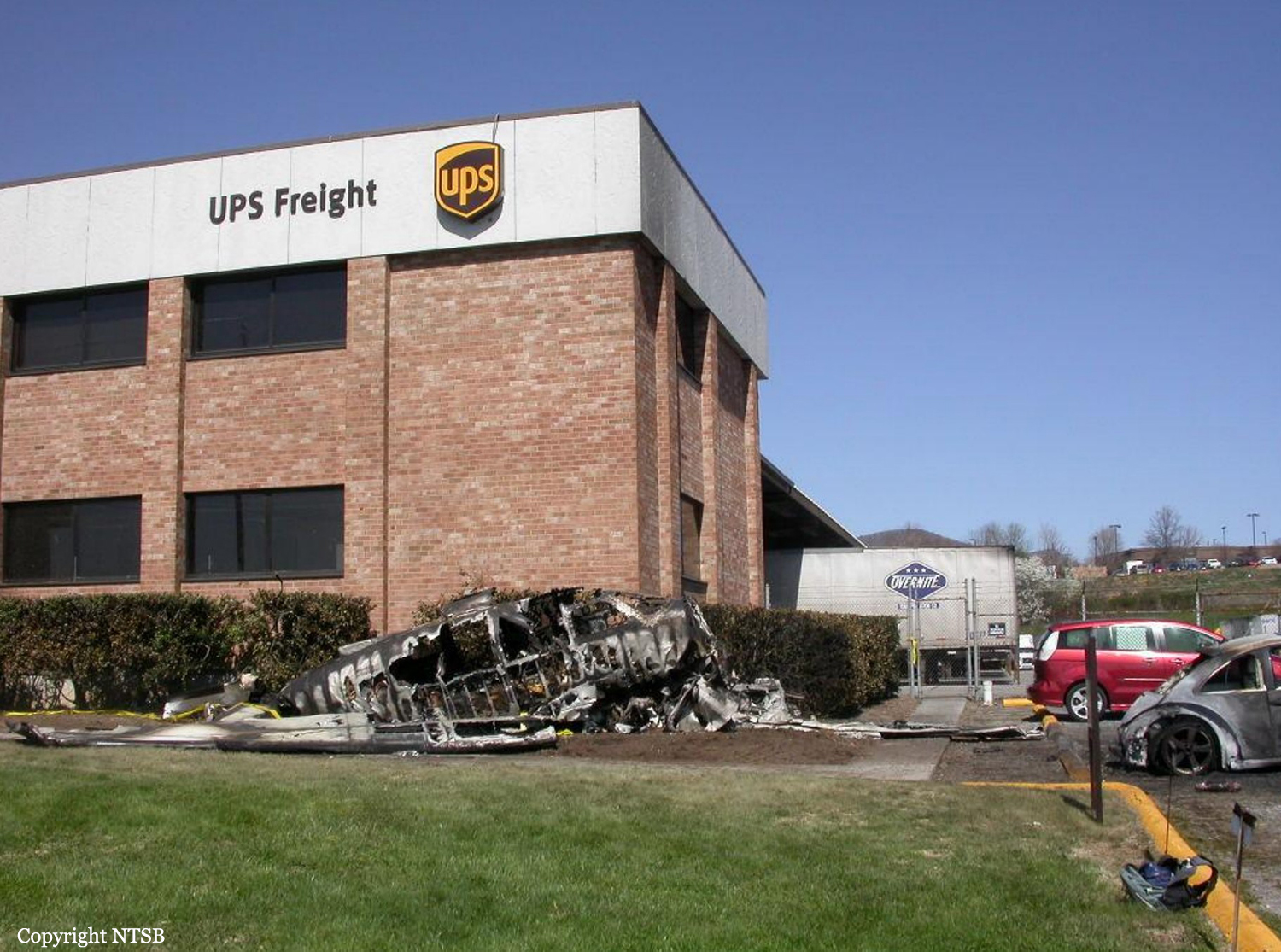
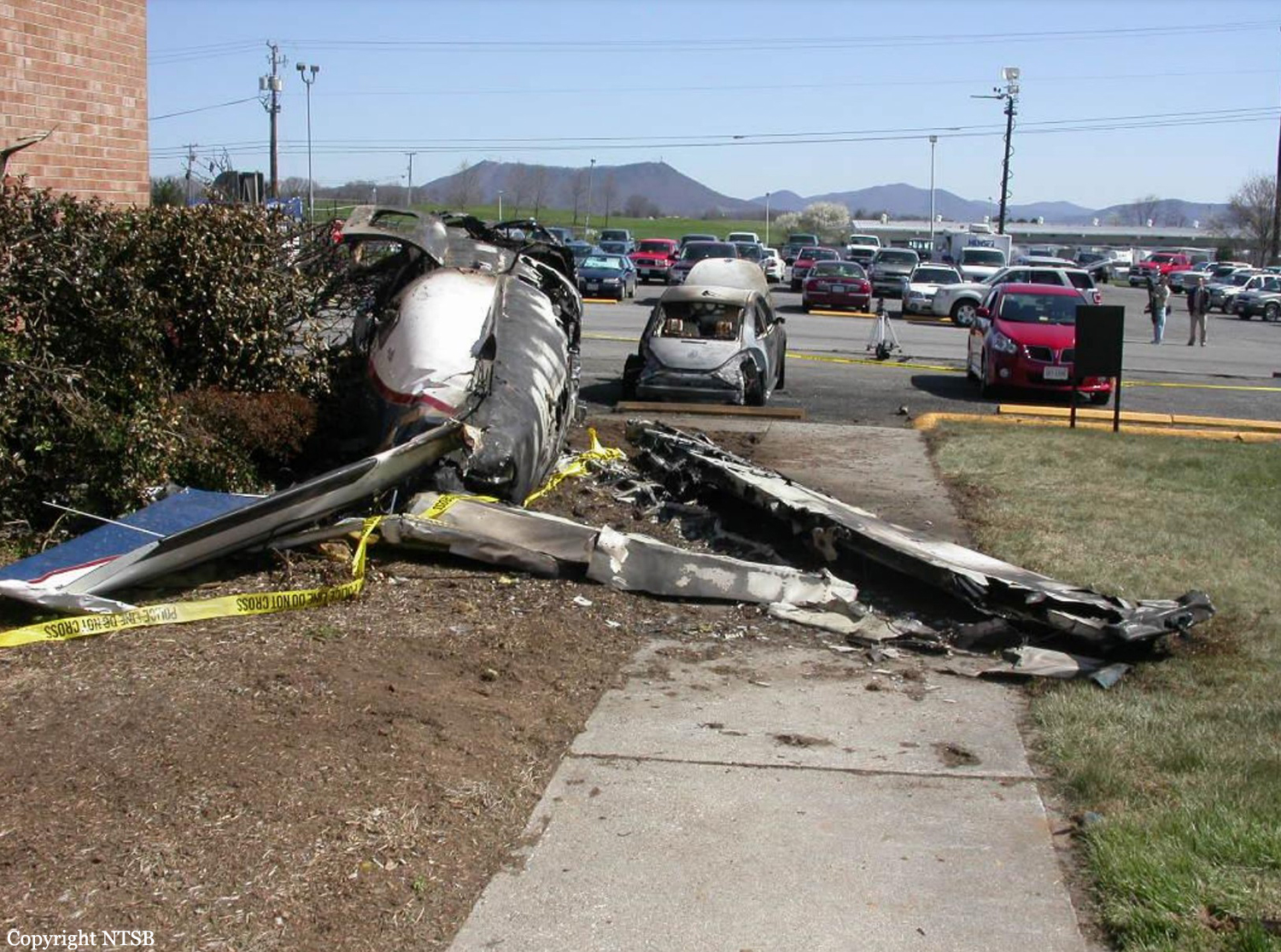
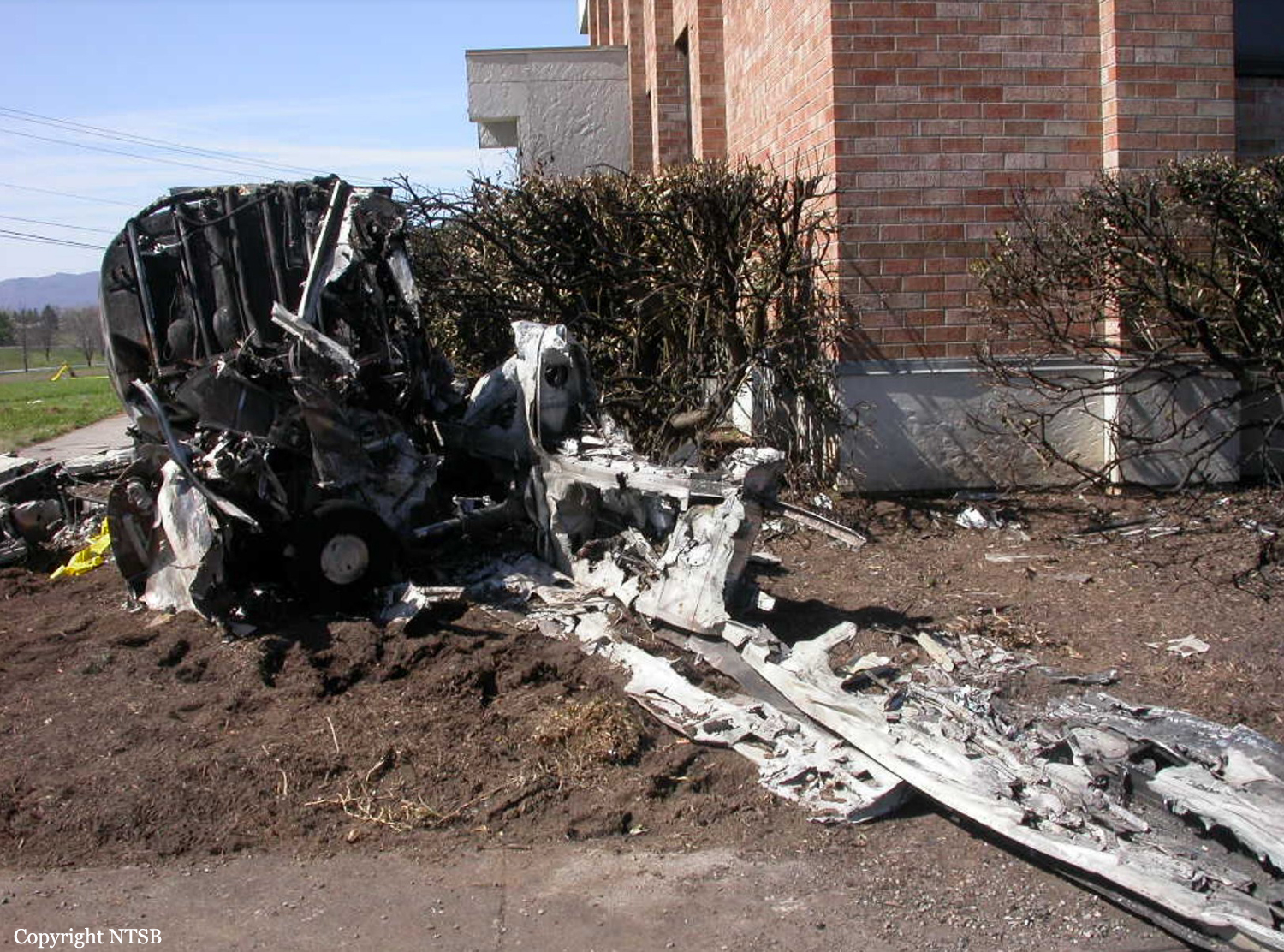
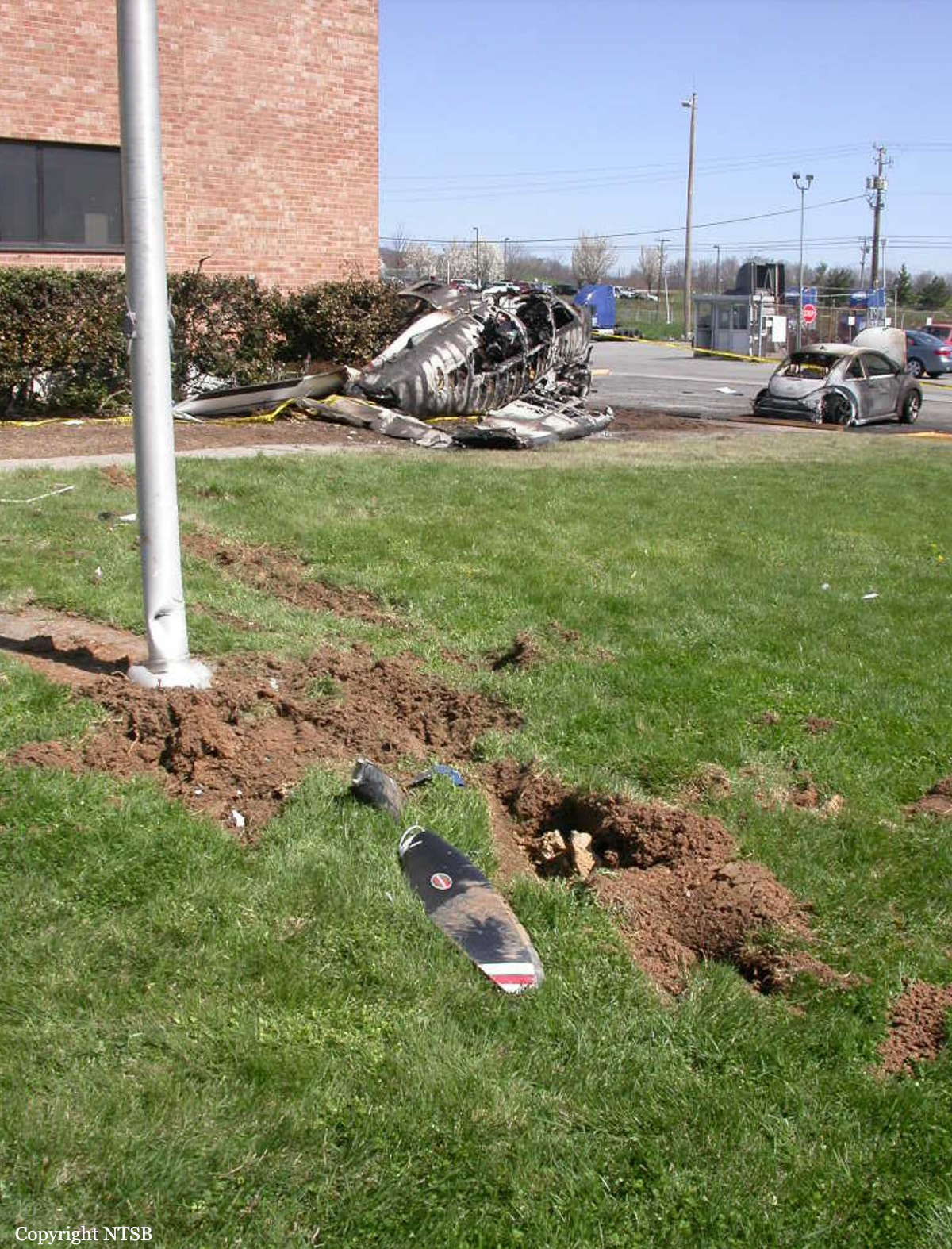
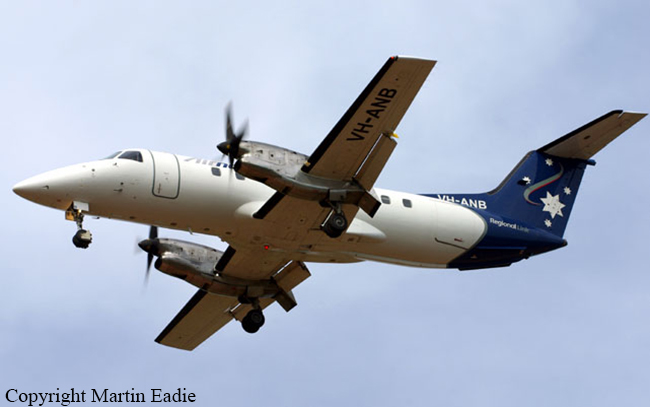
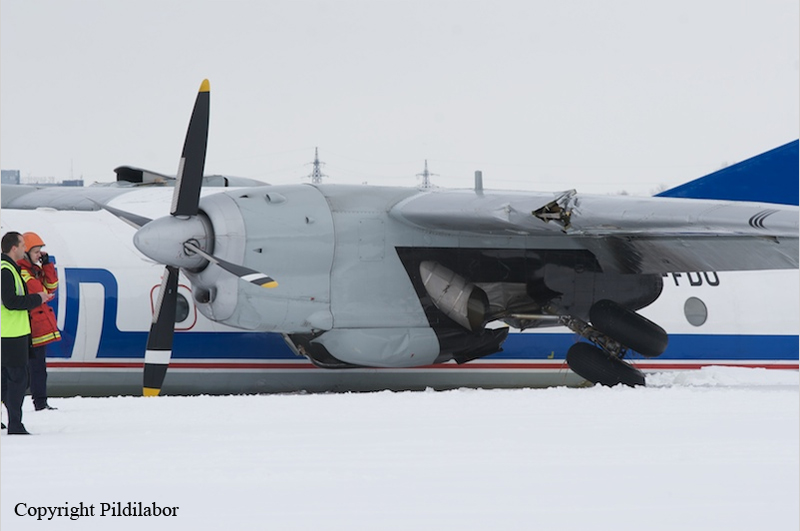
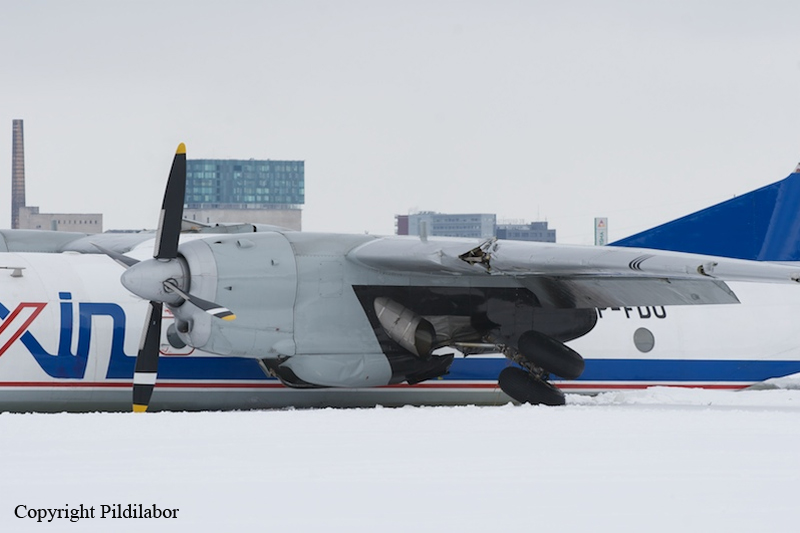
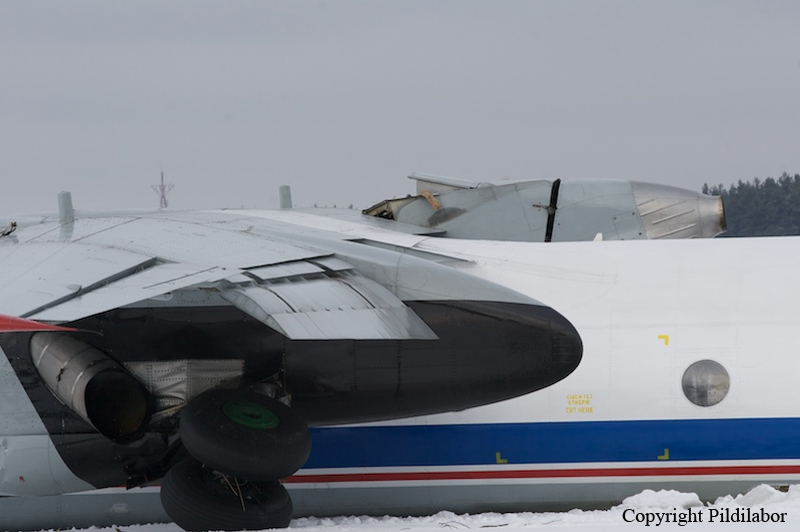
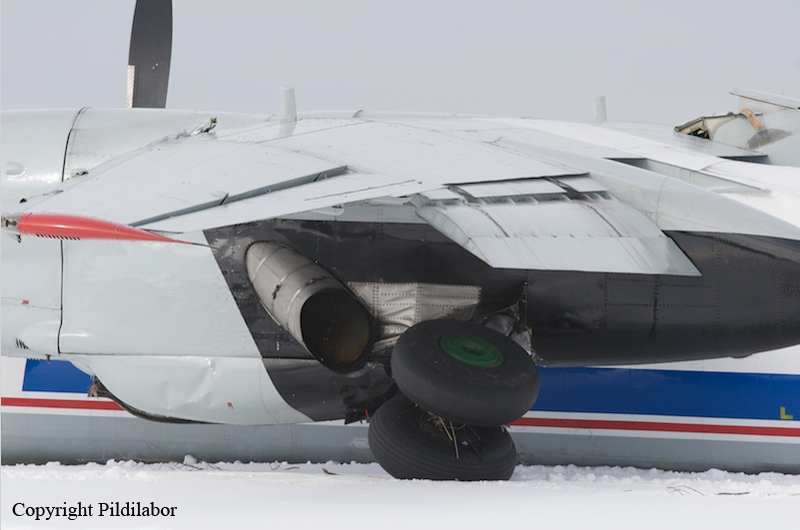
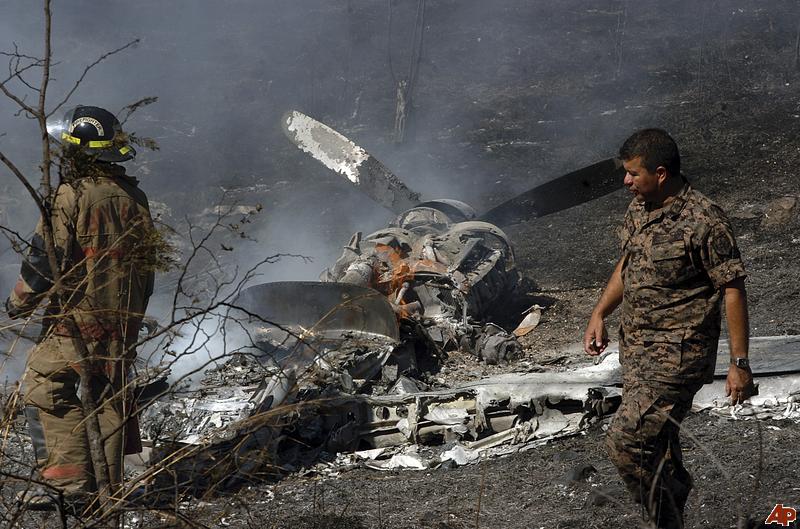
Crash of a Piper PA-46-310P Malibu in Roanoke: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Mar 30, 2010 at 1310 LT
Registration:
N6913Z
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Roanoke – Charlottesville
MSN:
46-8508073
YOM:
1985
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
1
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Aircraft flight hours:
956
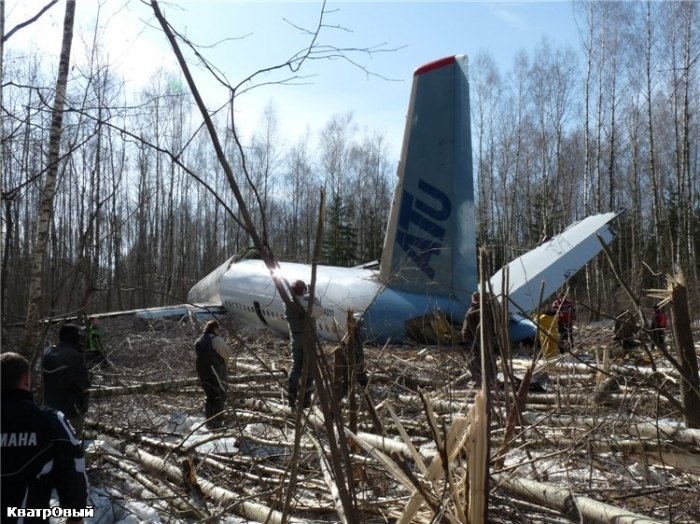
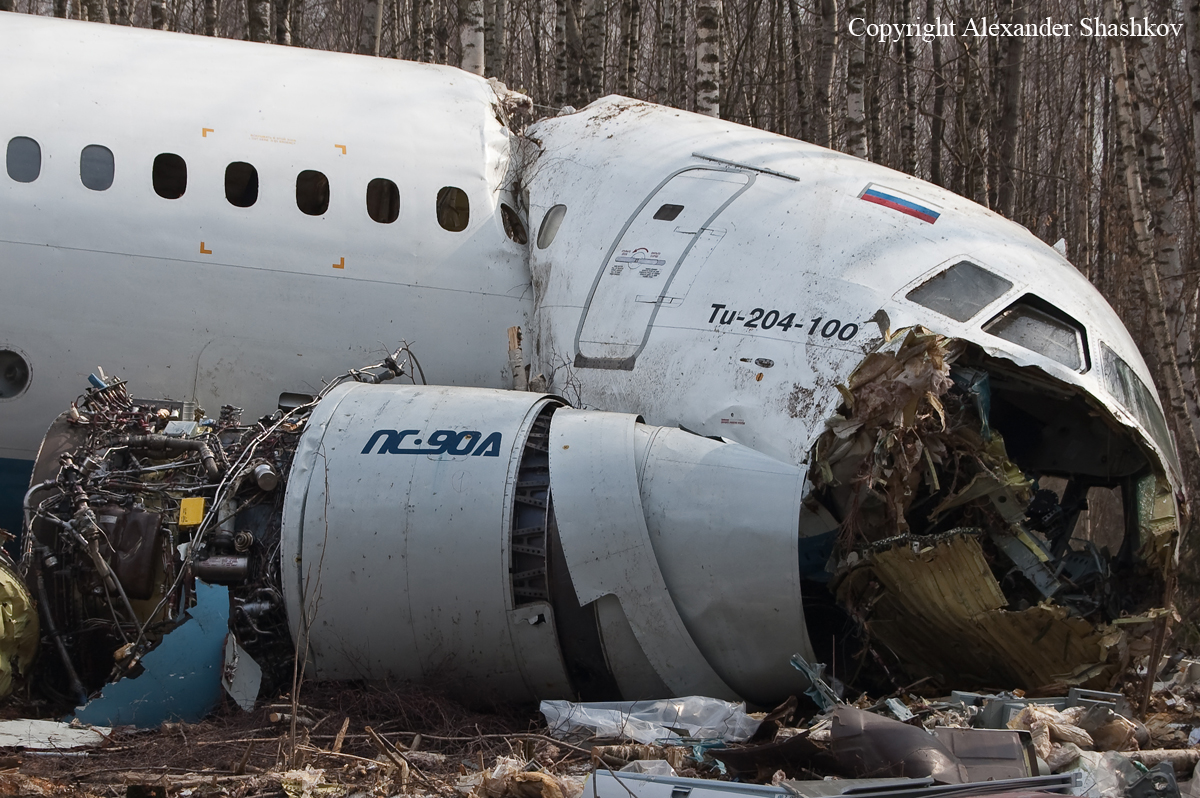
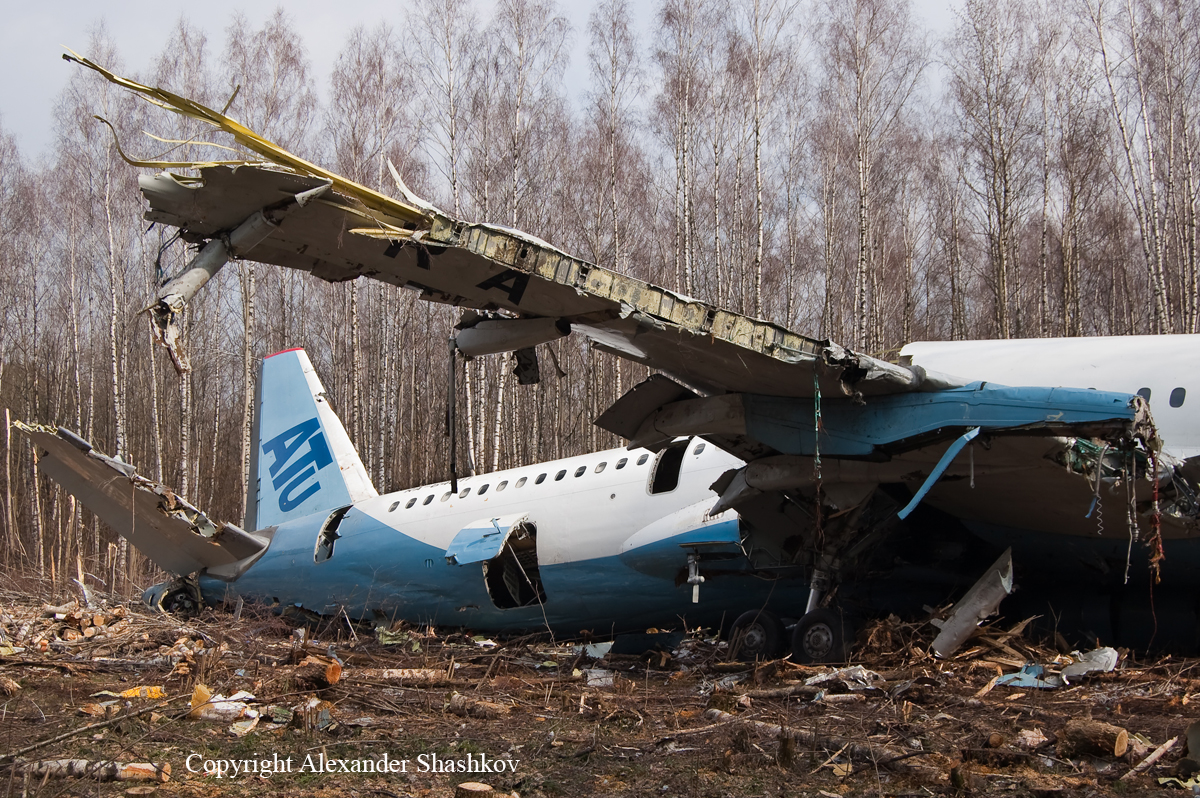
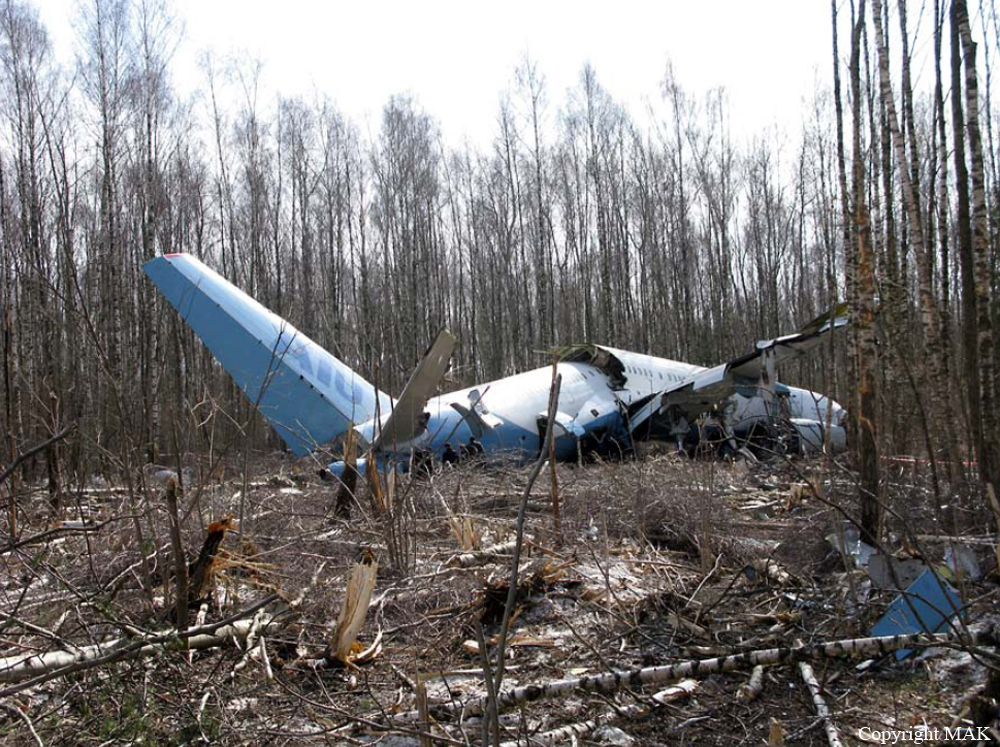
Circumstances:
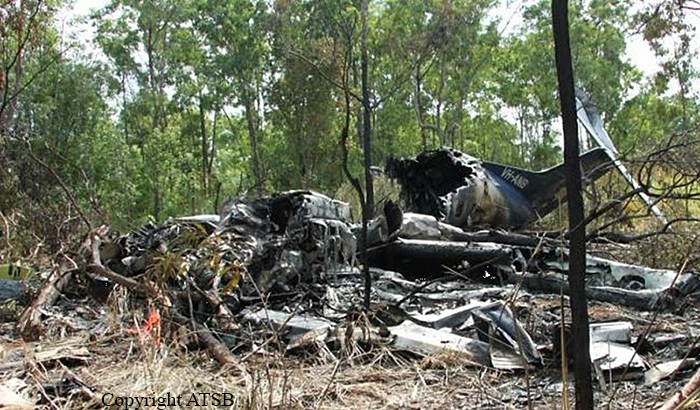
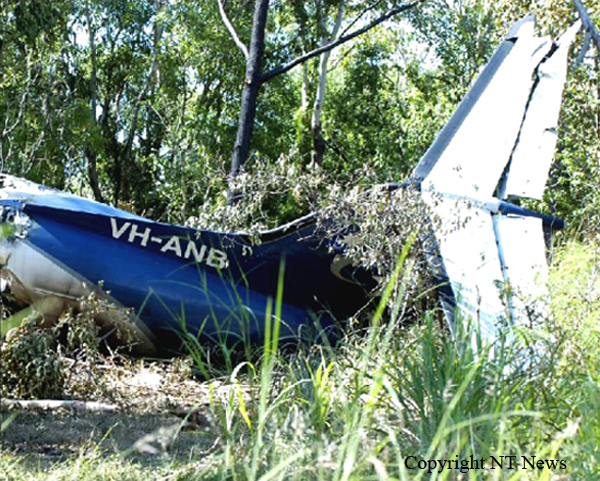
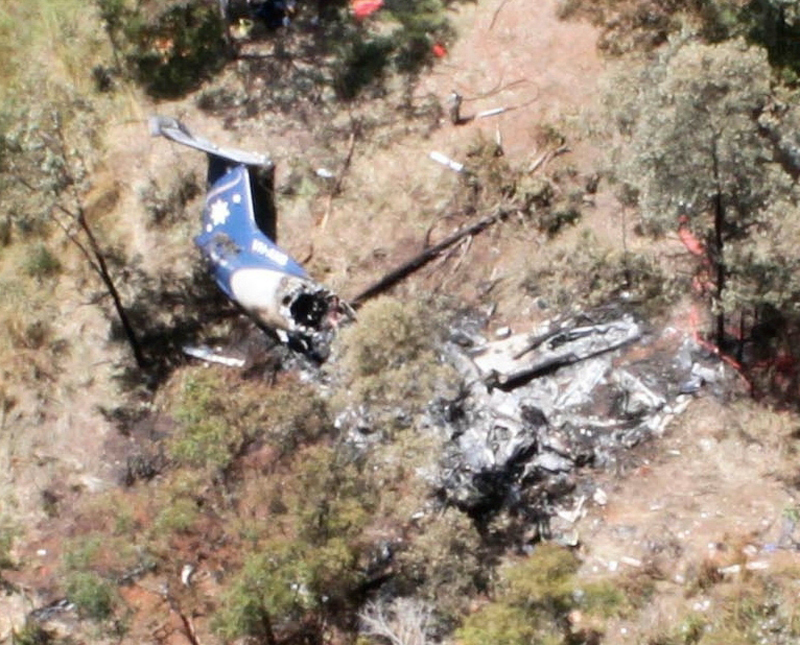
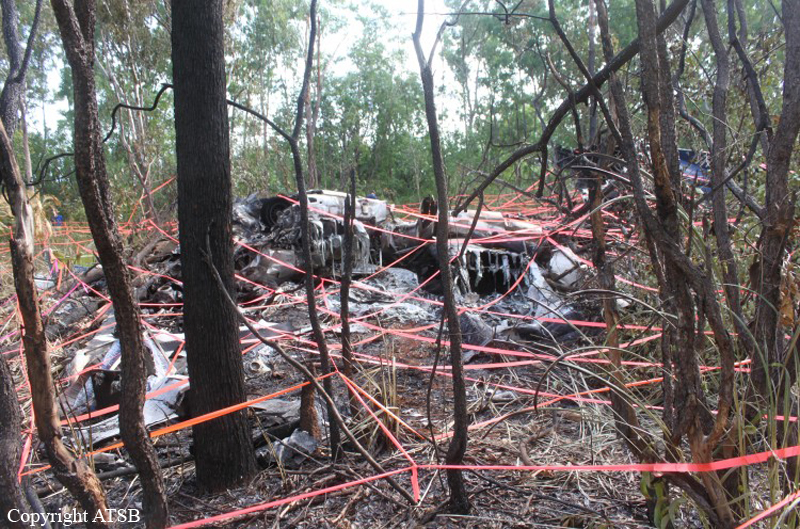
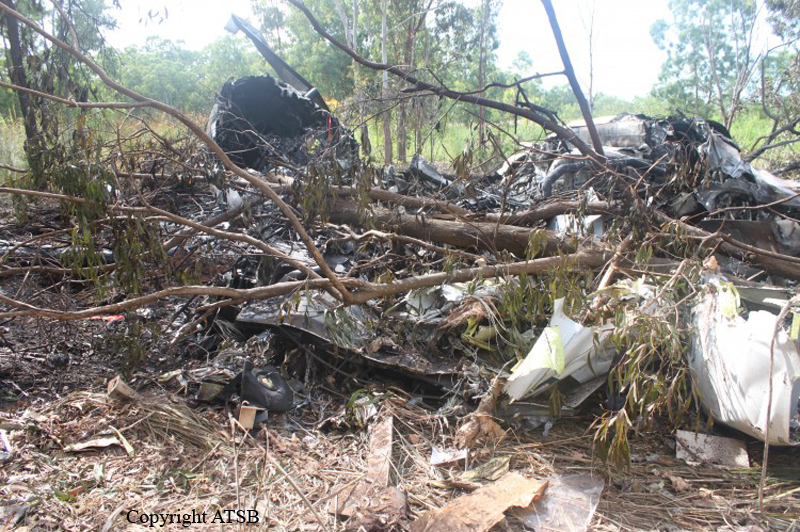
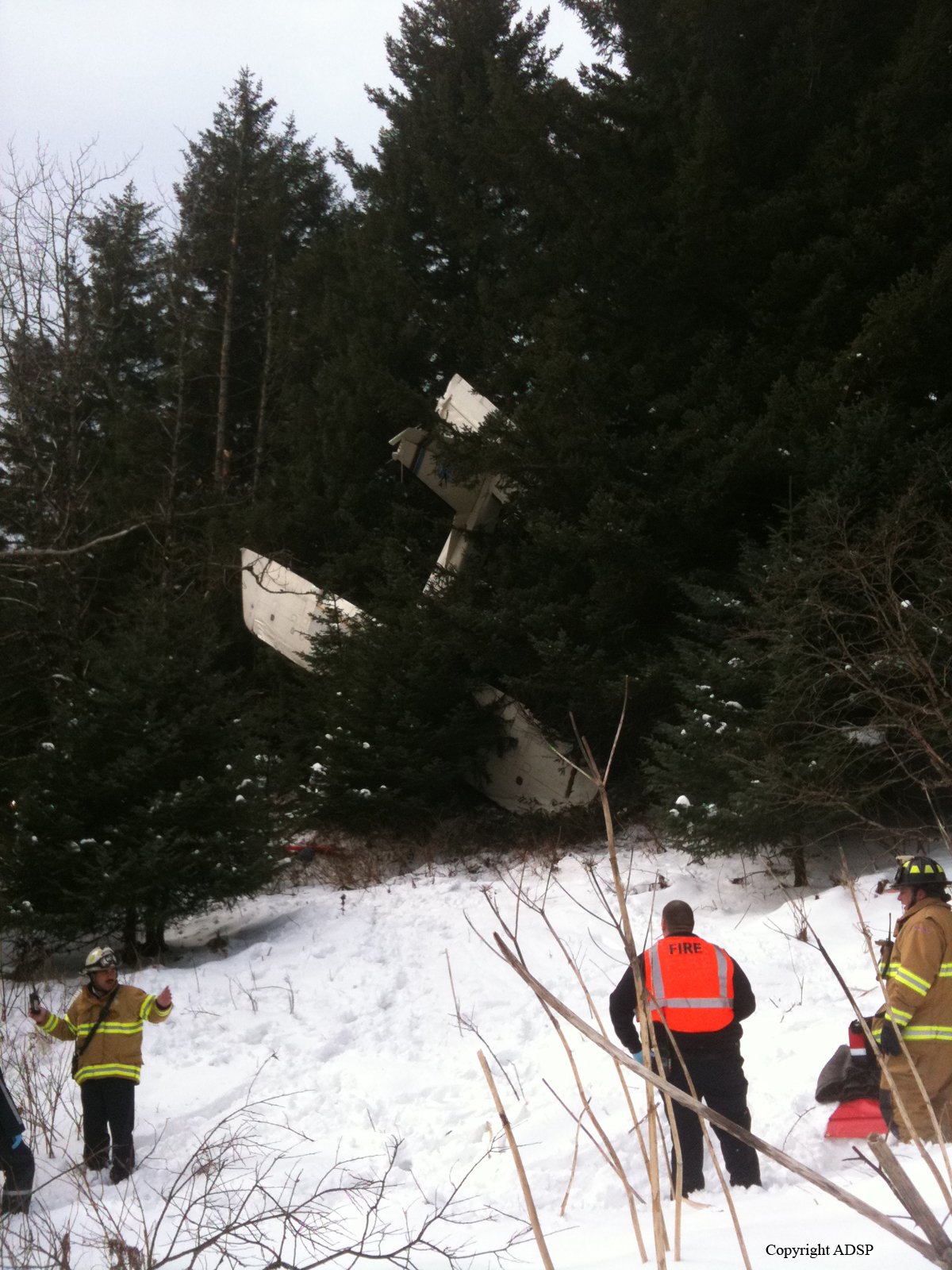
About one minute after takeoff, the pilot reported to the air traffic controller that the airplane's control wheels were locked. The controller subsequently cleared the pilot to land on any runway. No further transmissions were received from the pilot and the airplane continued straight ahead. Witnesses observed the airplane in a slow, level descent, until it impacted wires and then the ground. During a postaccident examination of the airplane, flight control continuity was confirmed to all the flight controls. Due to the impact and post-crash fire damage, a cause for the flight control anomaly, as reported by the pilot, could not be determined; however, several unsecured cannon plugs and numerous unsecured heat damaged wire bundles were found lying across the control columns forward of the firewall. Examination of the airplane logbooks revealed the most recent maintenance to the flight controls was performed about four months prior to the accident. The airplane had flown 91 hours since then.
Probable cause:
A malfunction of the flight controls for undetermined reasons.
Final Report: