Crash of a Tupolev TU-154B-2 in New Delhi
Date & Time:
Jan 9, 1993 at 0408 LT
Registration:
85533
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Hyderabad - New Delhi
MSN:
82A533
YOM:
1982
Flight number:
IC840
Crew on board:
13
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
152
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
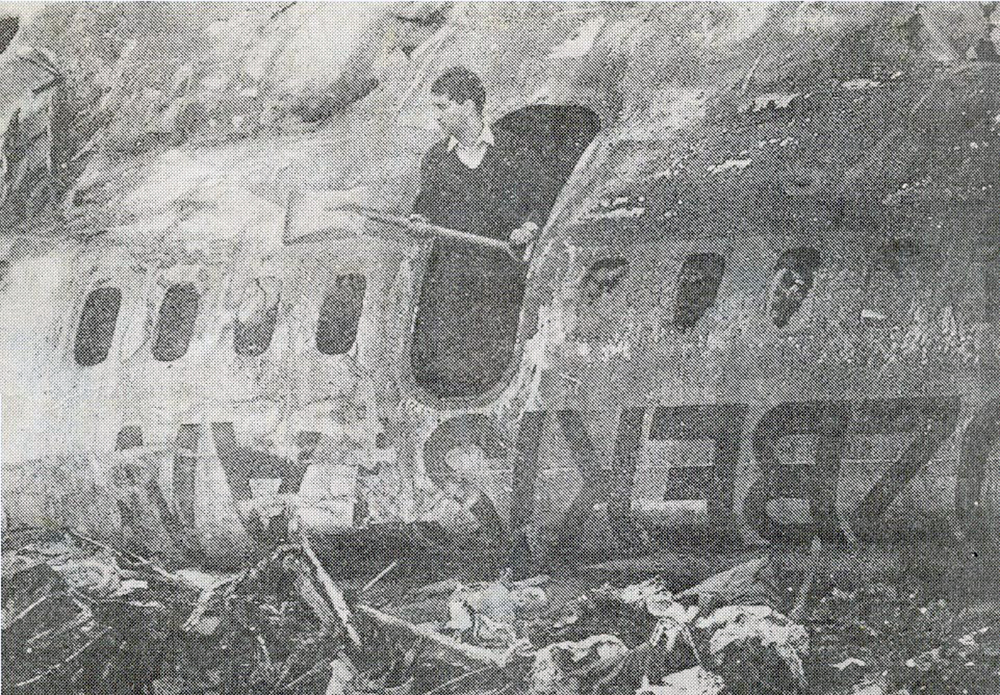
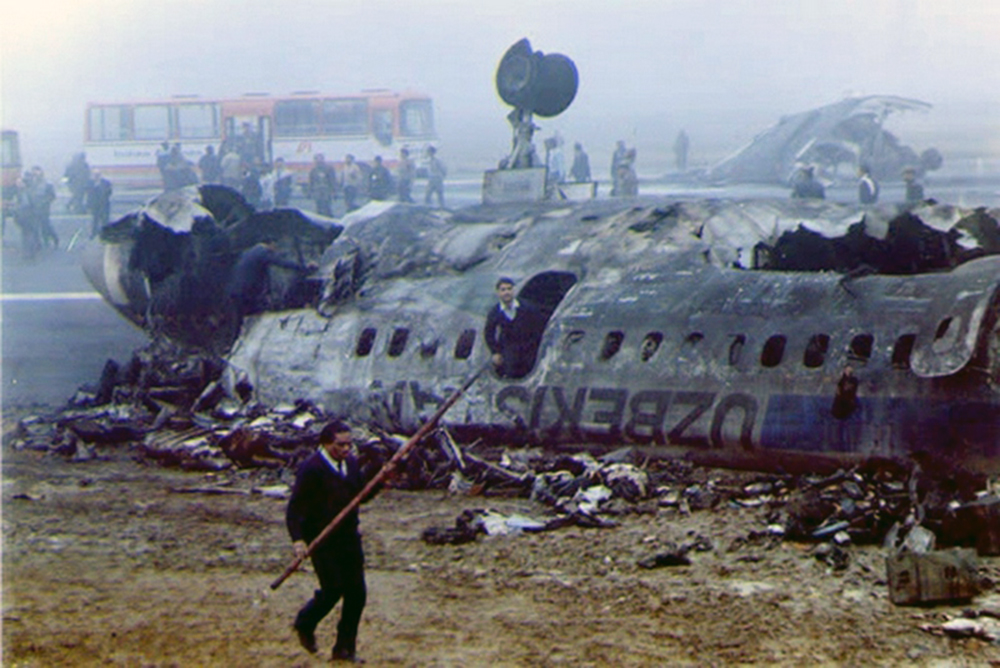
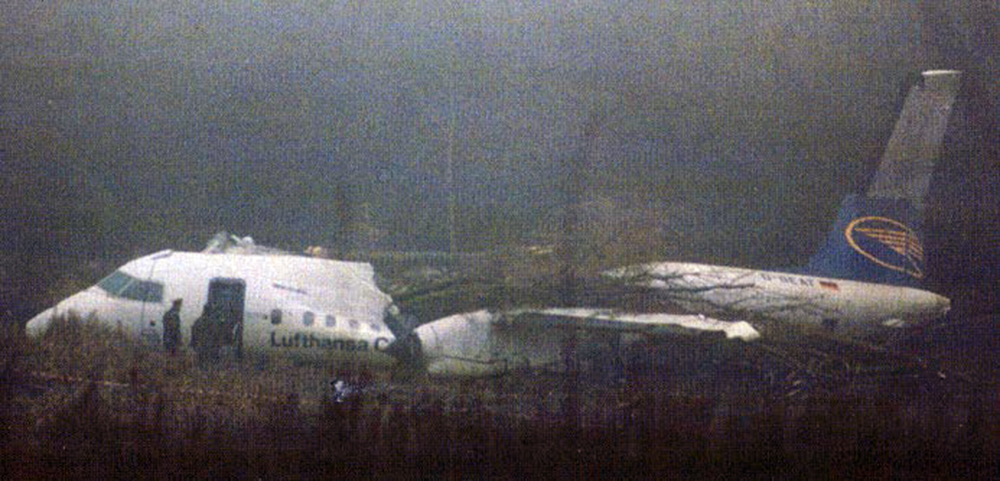
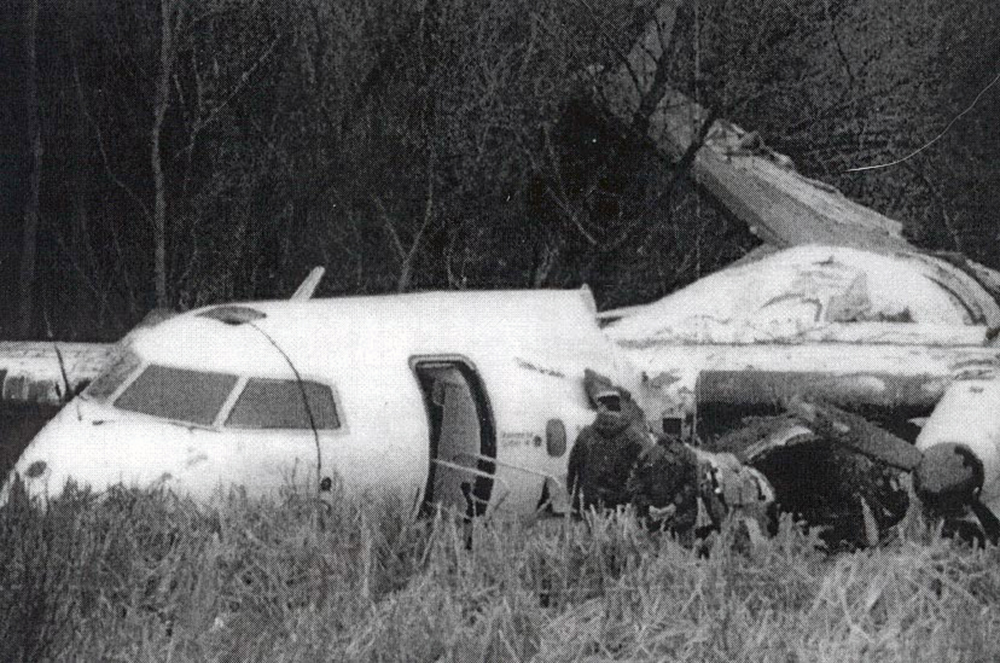
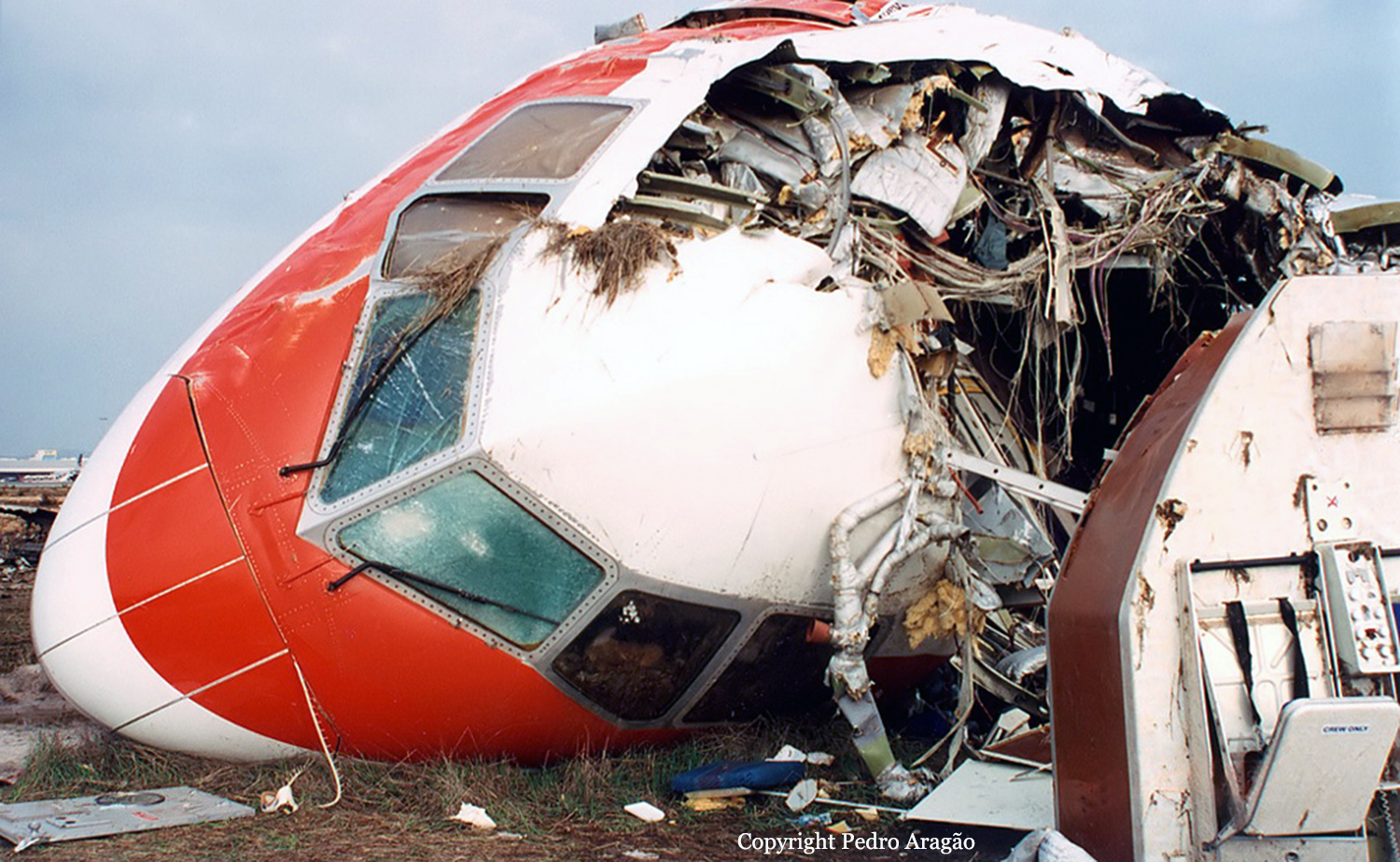
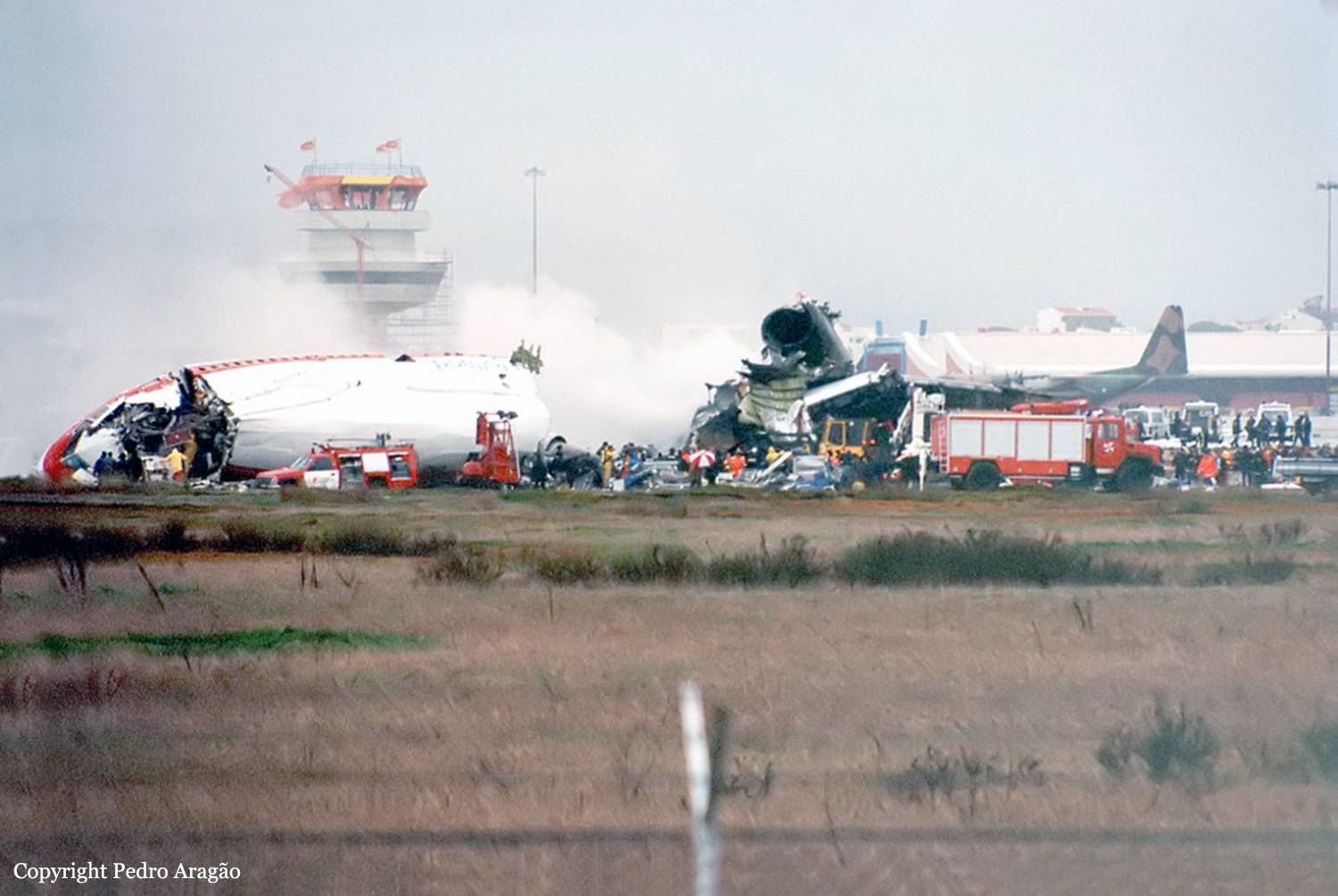
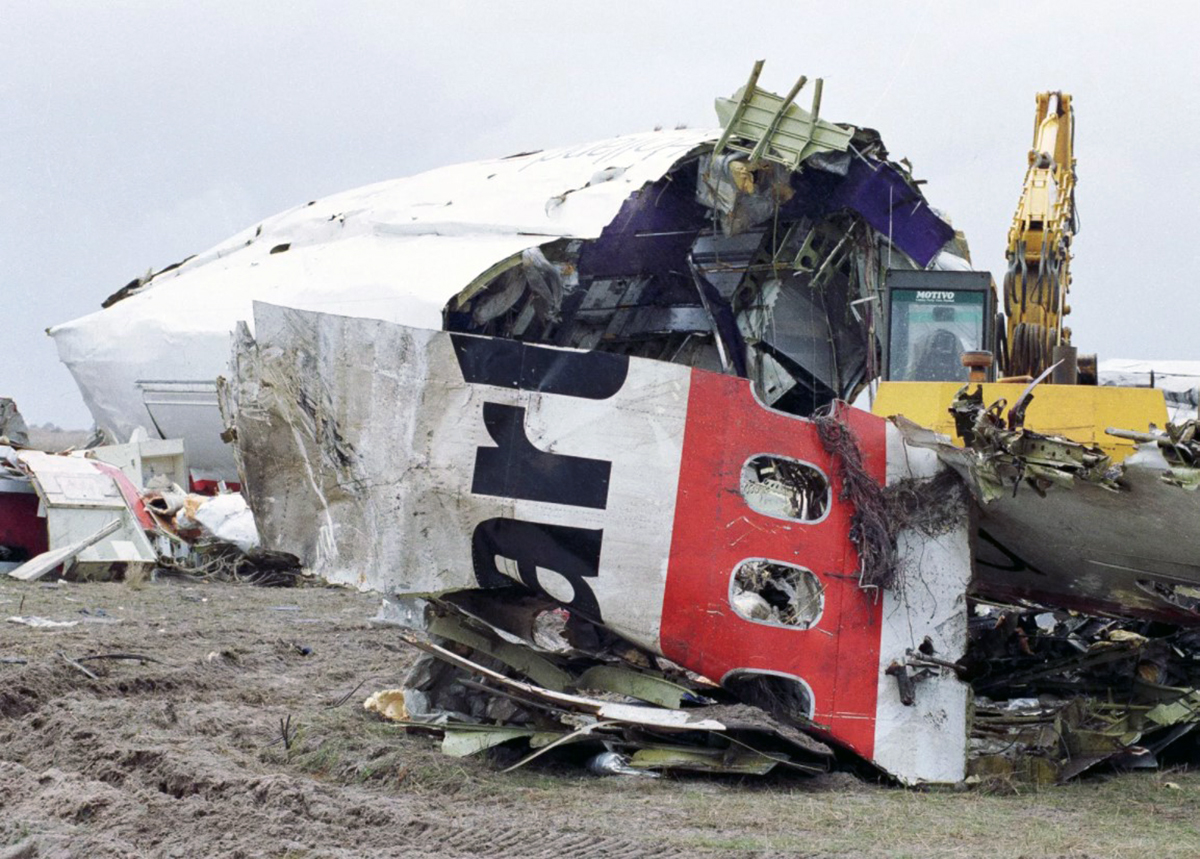
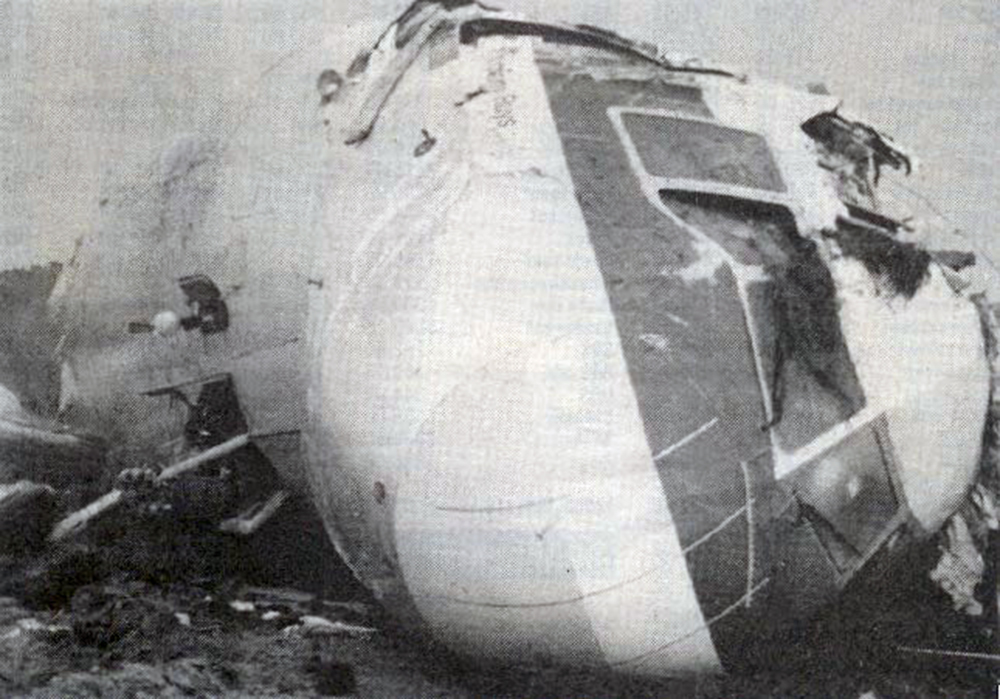
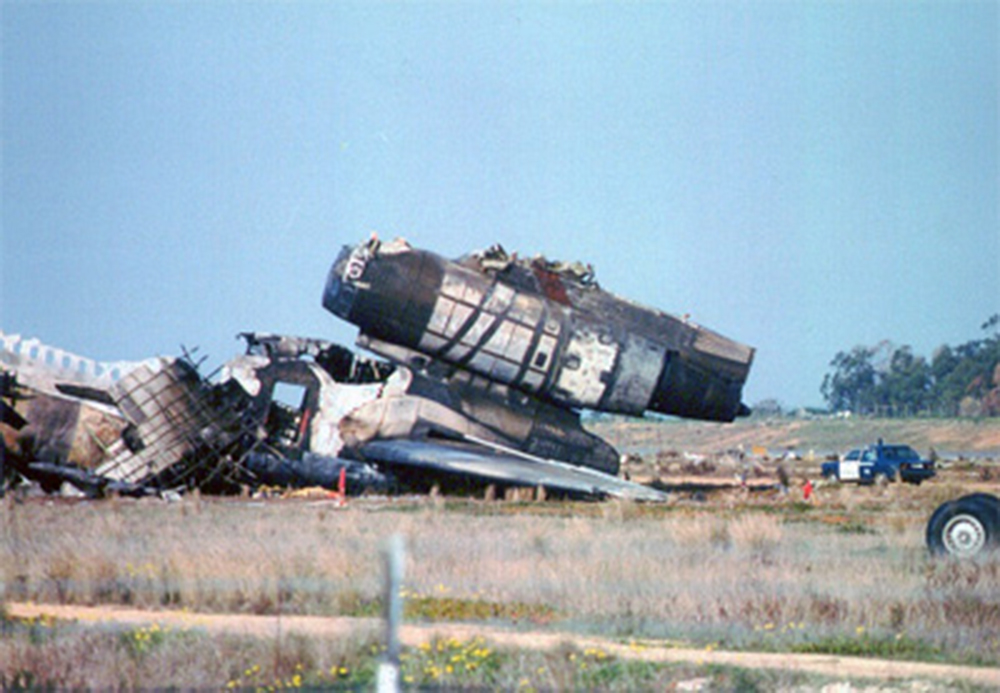
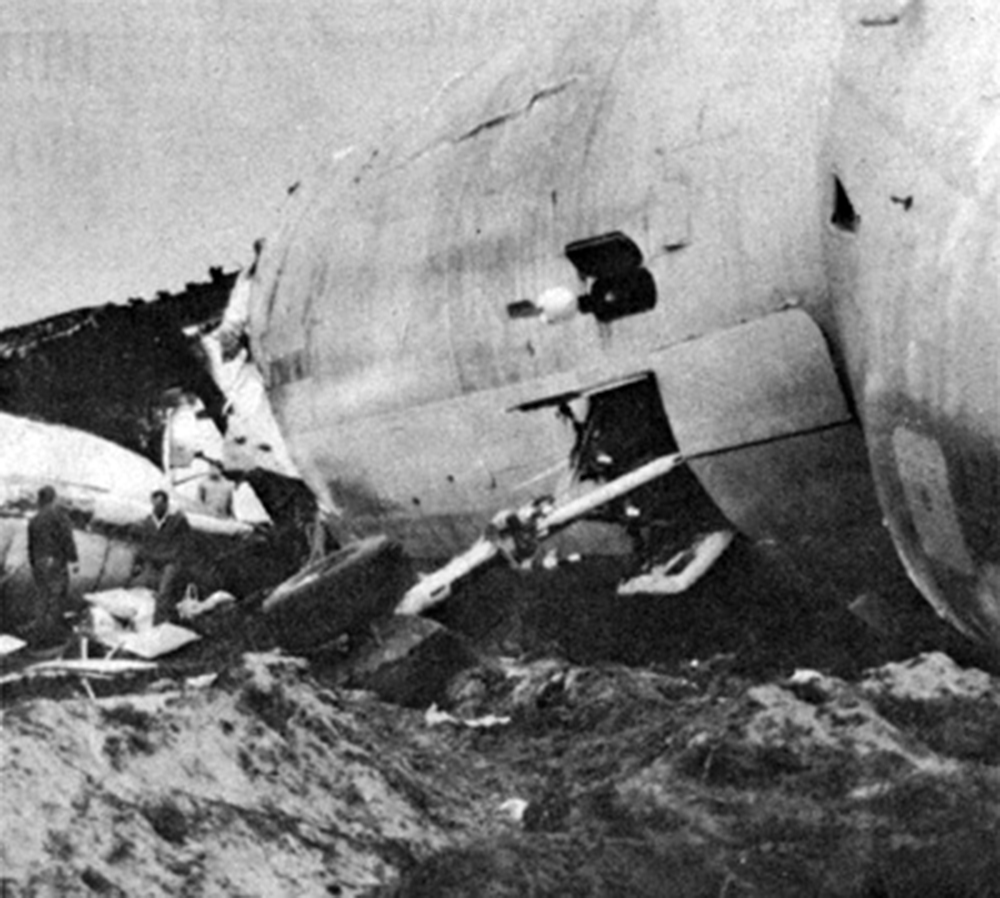
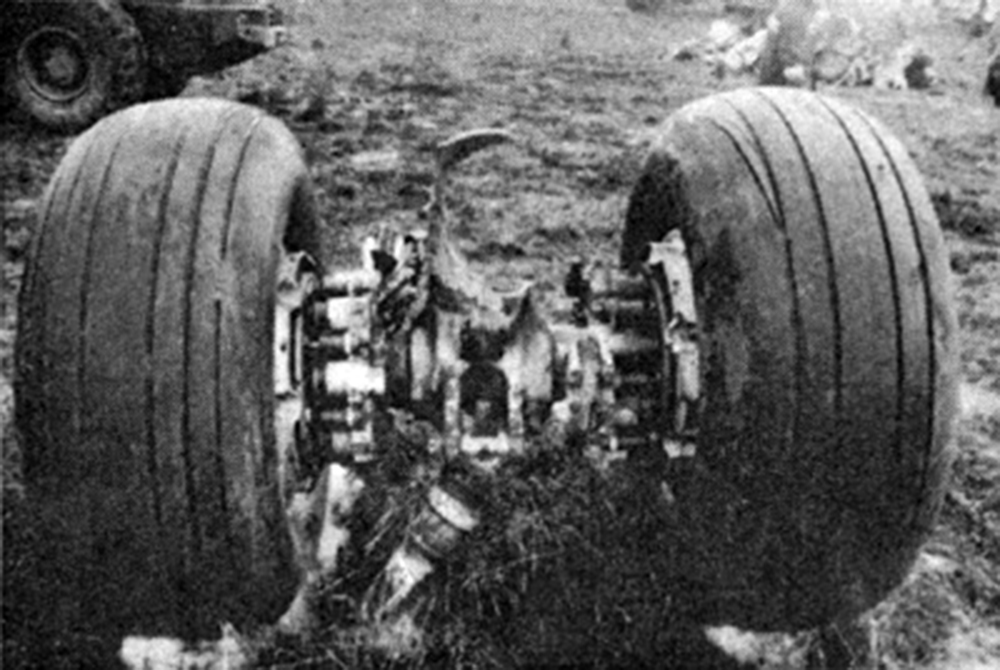
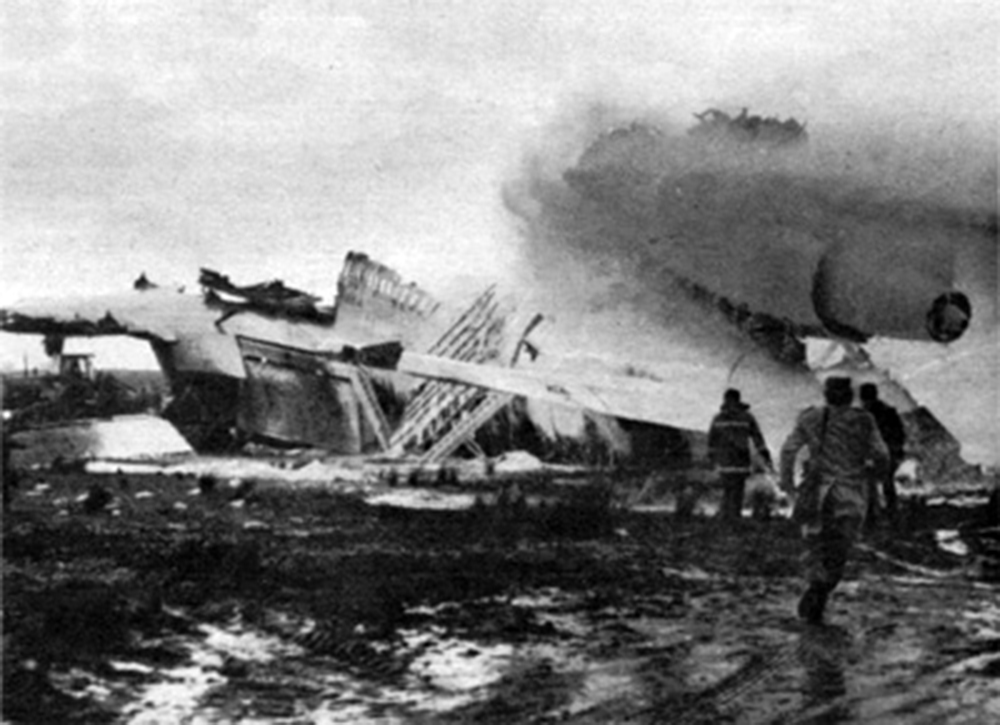
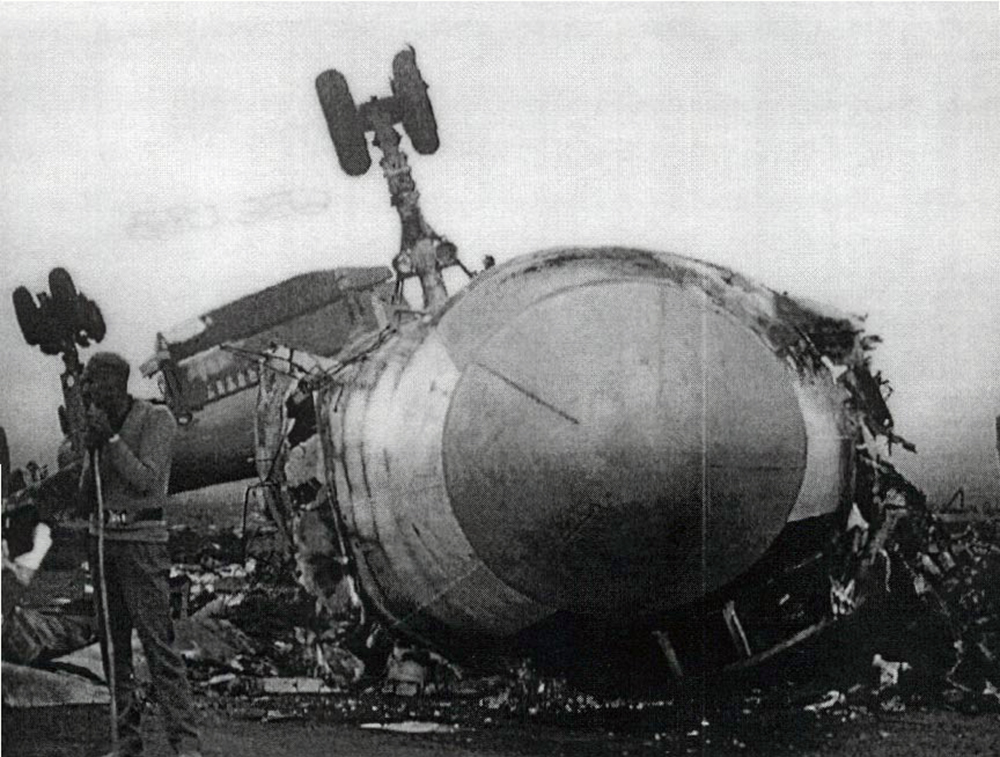
On 9th January, 1993 TU-154 aircraft No. 85533 wet leased by Indian Airlines from Uzbekistan Airways was operating flight IC-840 from Hyderabad to Delhi. The aircraft was being flown by Uzbeki operating crew and there were 165 persons on board including the crew. The aircraft touched down slightly outside the right edge of the runway, collided with some fixed installations on the ground, got airborne once again and finally touched down on kutcha ground on the right side of the runway. At this stage the right wing and the tail of the aircraft broke away and it came to rest in an inverted position. During the process, the aircraft caught fire and was destroyed. Most occupants of the aircraft escaped unhurt. Six persons suffered either limb fracture or other serious injuries while 45 persons suffered injuries of a minor nature.
Probable cause:
The probable cause of accident has been attributed to :
- The failure of the Pilot-in-Command to divert to Ahmedabad when he was informed that the RVR on runway 28 was below the minima applicable to his flight.
- The switching on of landing lights, on the instruction of the second Captain, at a height of only about ten metres, resulting in the loss of all visual references due to the blinding effect of
light reflections from fog.
- The failure of captain to carry out a missed approach when visual reference to the runway was lost.
- The failure of the Pilot-in-Command to divert to Ahmedabad when he was informed that the RVR on runway 28 was below the minima applicable to his flight.
- The switching on of landing lights, on the instruction of the second Captain, at a height of only about ten metres, resulting in the loss of all visual references due to the blinding effect of
light reflections from fog.
- The failure of captain to carry out a missed approach when visual reference to the runway was lost.
Final Report: