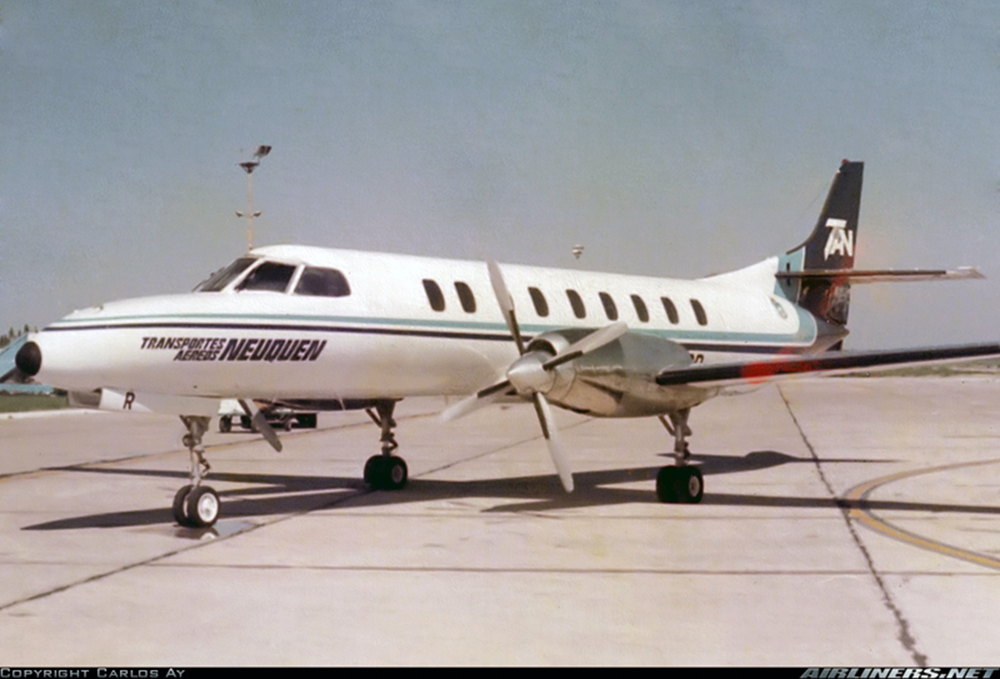
Crash of a Swearingen SA227AC Metro III in Rincón de Los Sauces
Date & Time:
Jan 25, 1996 at 2115 LT
Registration:
LV-AOR
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Chos Malal - Rincón de Los Sauces
MSN:
AC-478
YOM:
1981
Flight number:
NEQ413
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
4
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
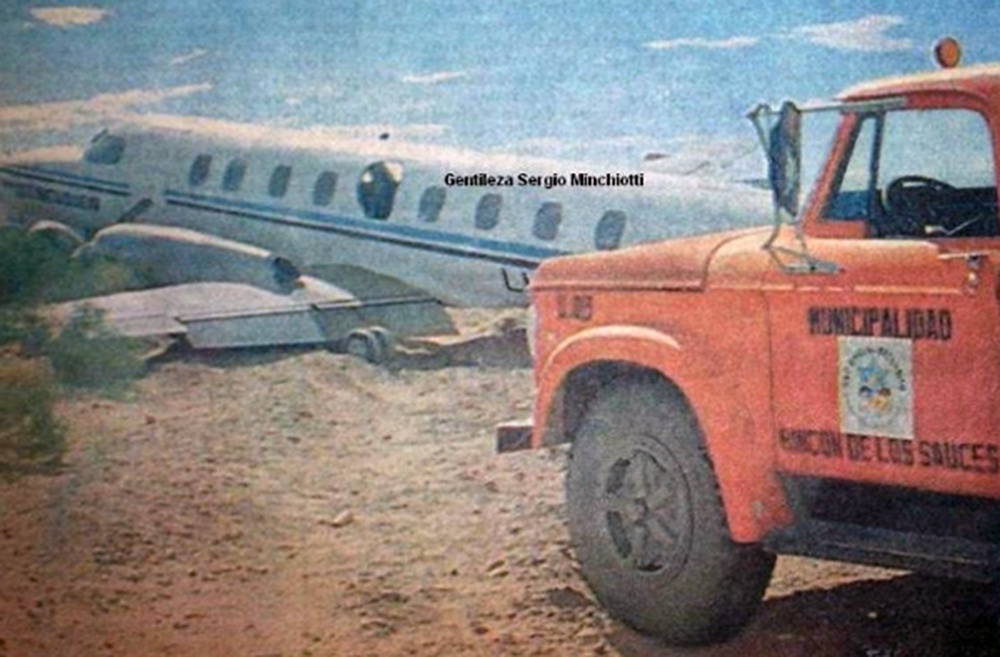
On final approach to Rincón de Los Sauces Airport, the aircraft struck the ground short of runway threshold. The left main gear collapsed and the airplane slid for few dozen metres then veered off runway and came to rest. All six occupants escaped uninjured while the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.
Probable cause:
For unknown reasons, the crew was approaching the airport at an insufficient altitude. The following contributing factors were reported:
- Failure of the operator to consider the restrictions at the destination airport,
- Possible windshear on short final.
- Failure of the operator to consider the restrictions at the destination airport,
- Possible windshear on short final.