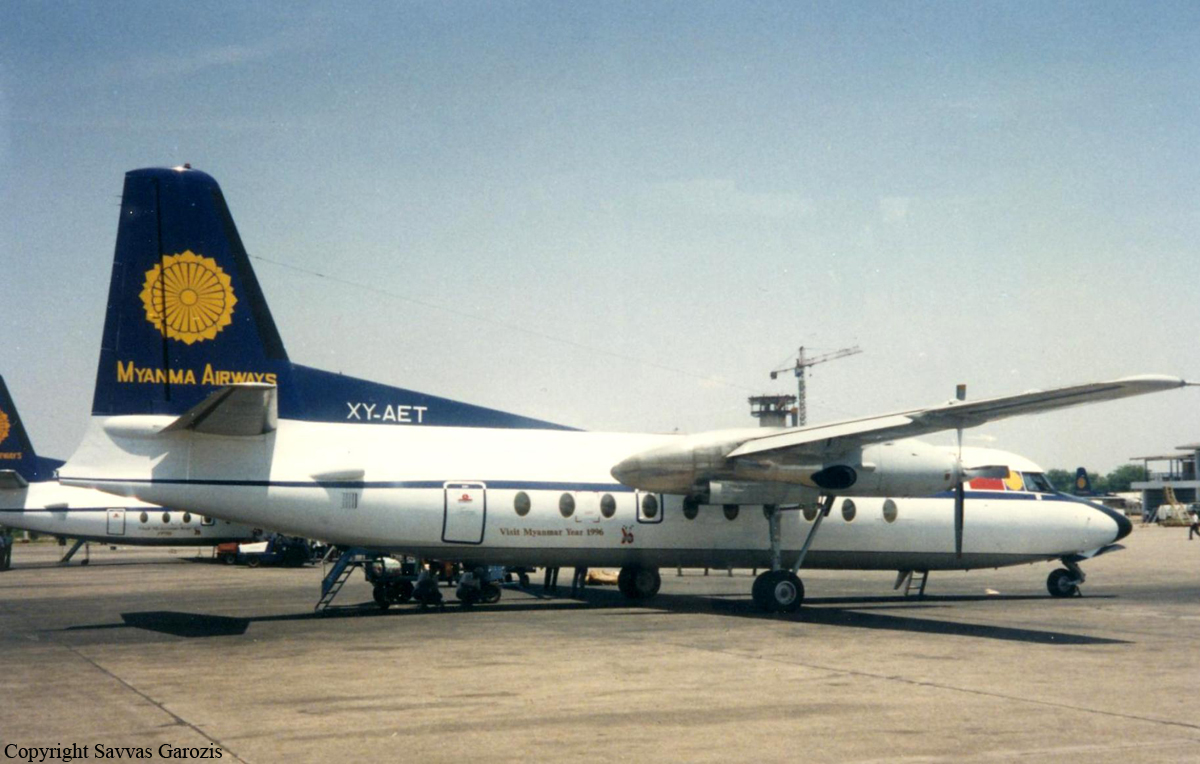
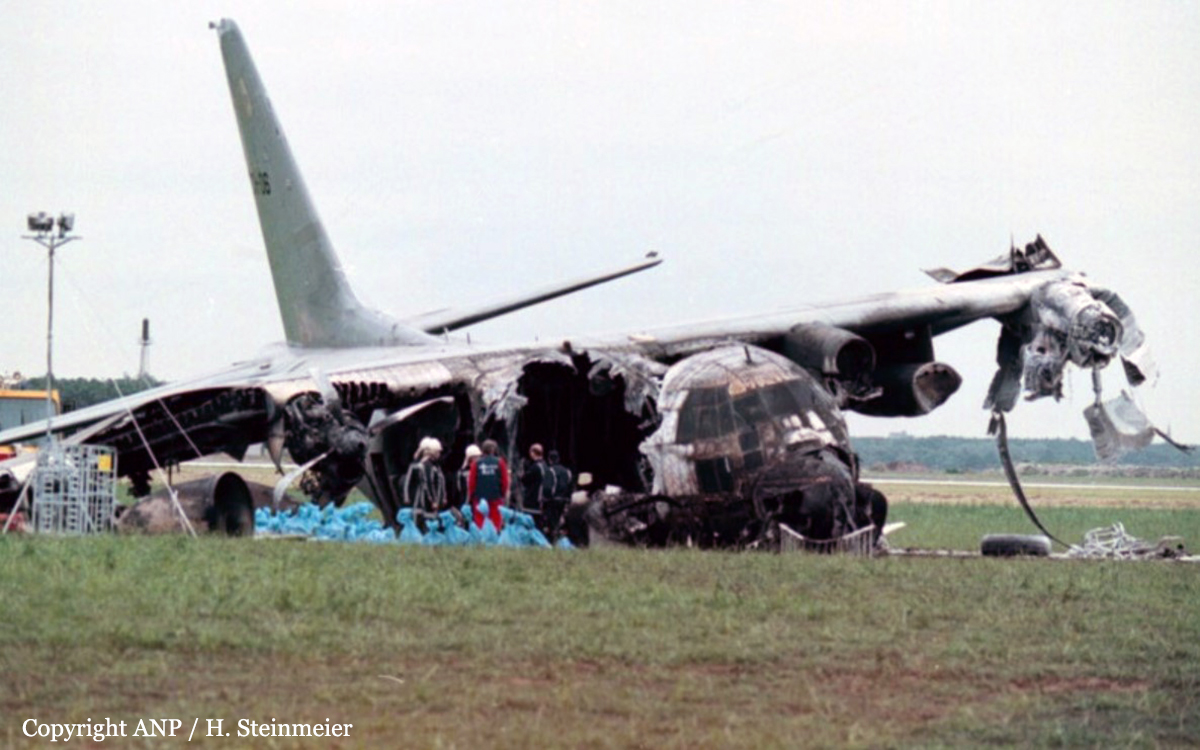
Crash of a Fokker F27 Friendship 600 in Mergui: 8 killed
Date & Time:
Jul 24, 1996
Registration:
XY-AET
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Yangon - Mergui
MSN:
10433
YOM:
1970
Flight number:
UB309
Crew on board:
4
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
45
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
8
Circumstances:
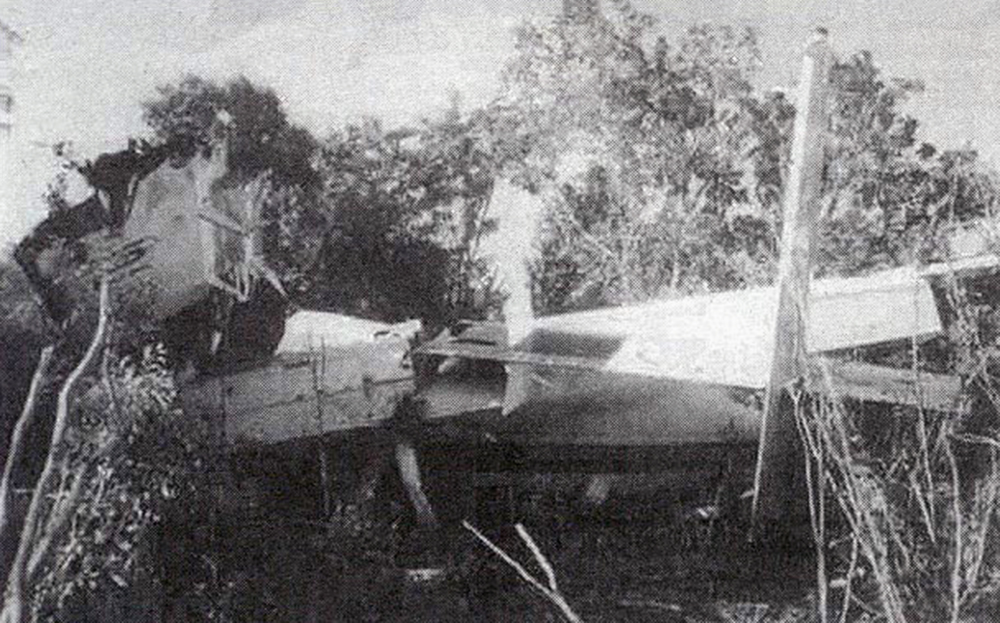
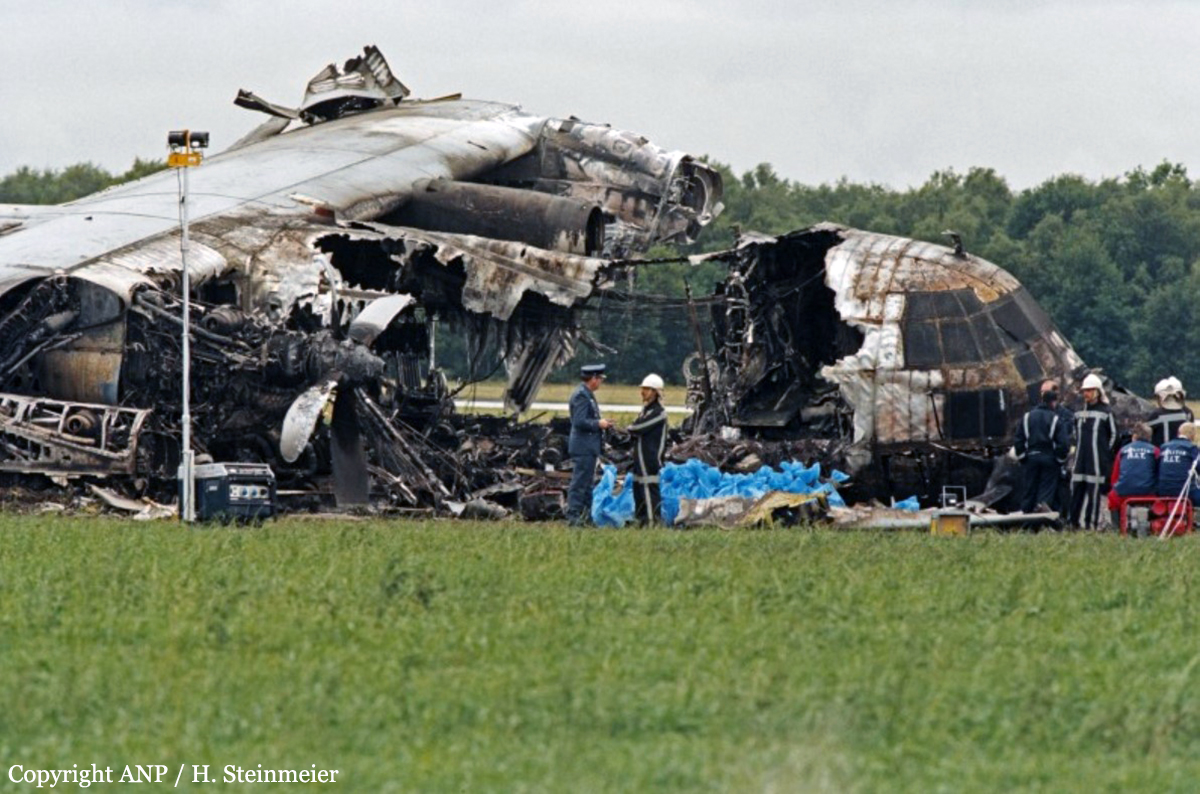
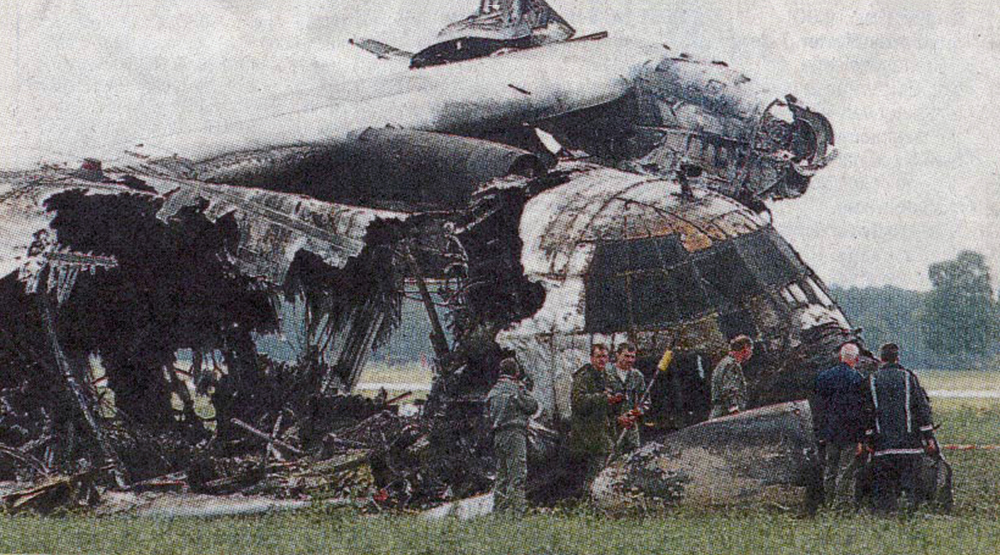
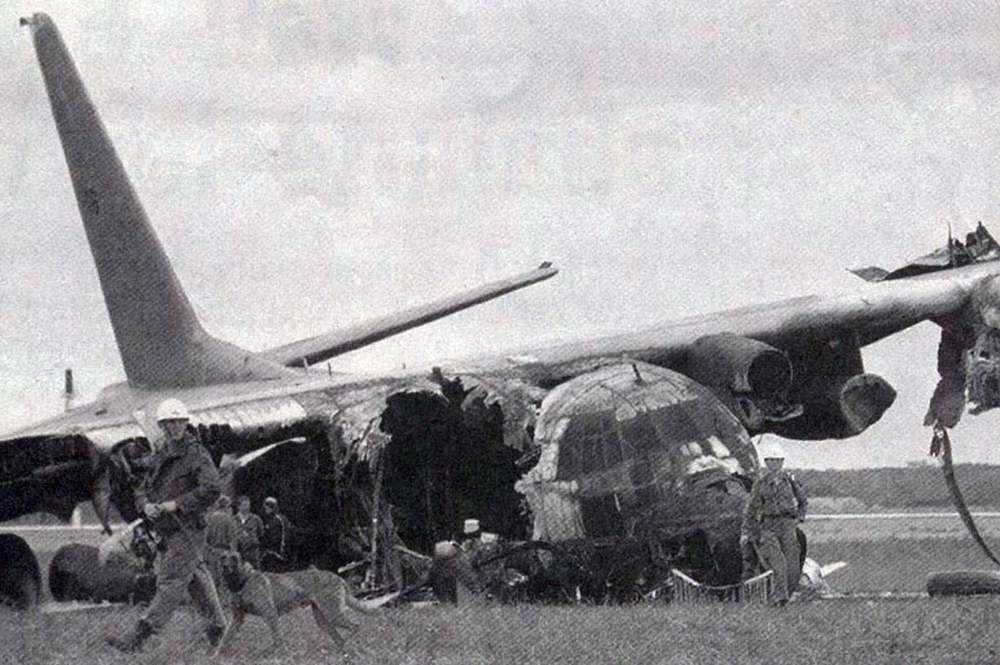
While descending to Mergui Airport, the crew encountered poor weather conditions with heavy rain falls. On short final, the aircraft lost height and struck the ground about 250 metres short of runway 18. On impact, the undercarriage were torn off and the aircraft slid for few dozen metres before coming to rest in a 1,2 metre deep excavation located short of runway threshold. Eight passengers were killed while 16 others were seriously injured.
Probable cause:
It was reported that the crew initiated the approach while maintaining a visual contact with the runway. At an altitude of 1,500 feet, visual contact with the runway was lost due to heavy rain falls and the aircraft lost height and struck the ground in a relative flat attitude. The horizontal visibility at the time of the accident was estimated to be 1,500 metres and it is possible that the aircraft encountered windshear.