Circumstances:
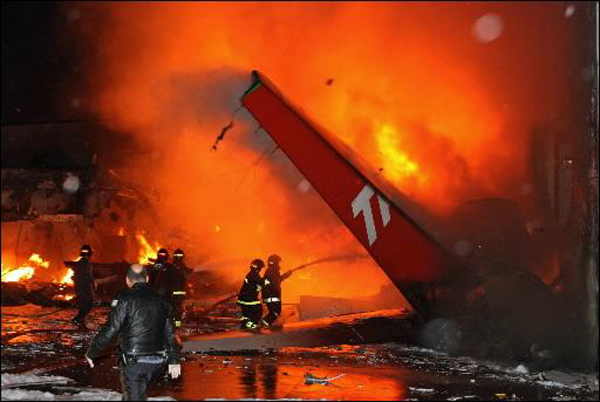
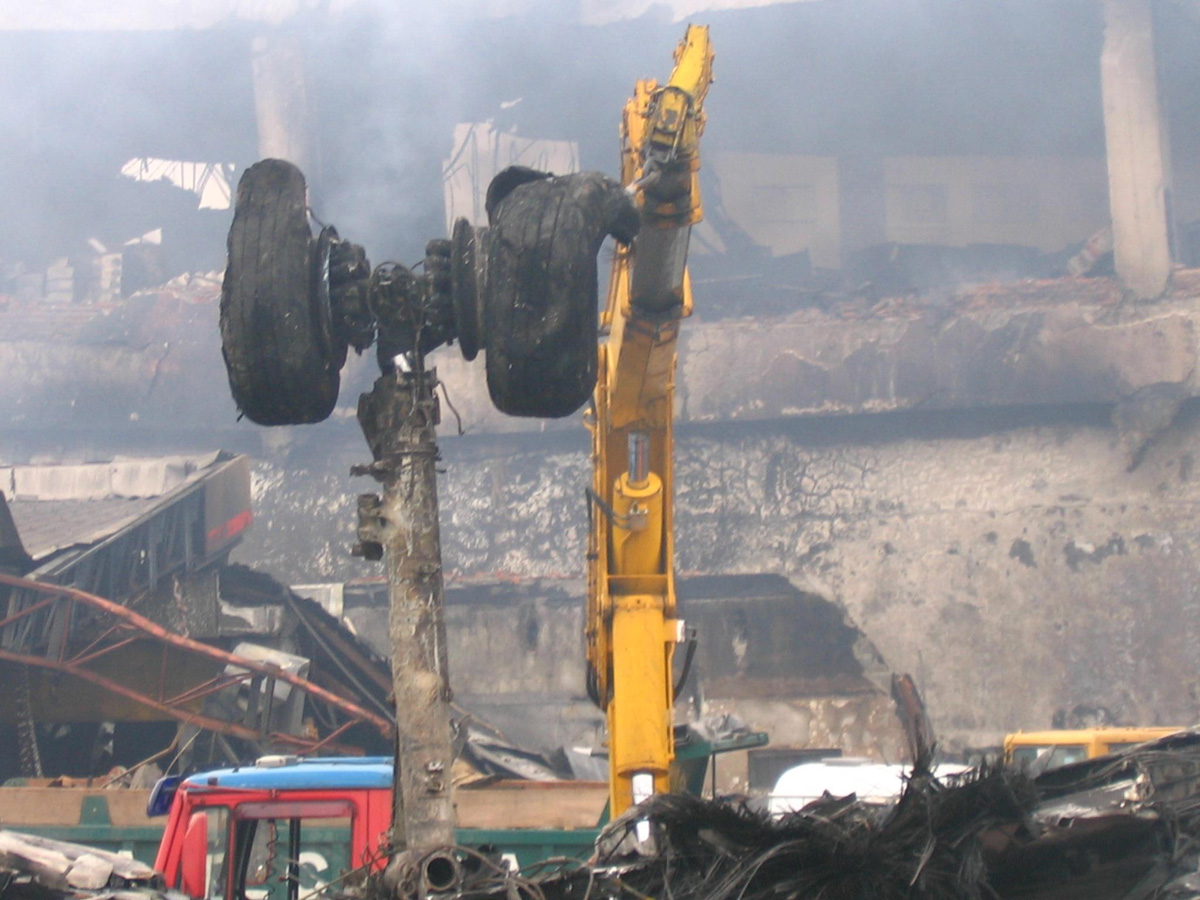
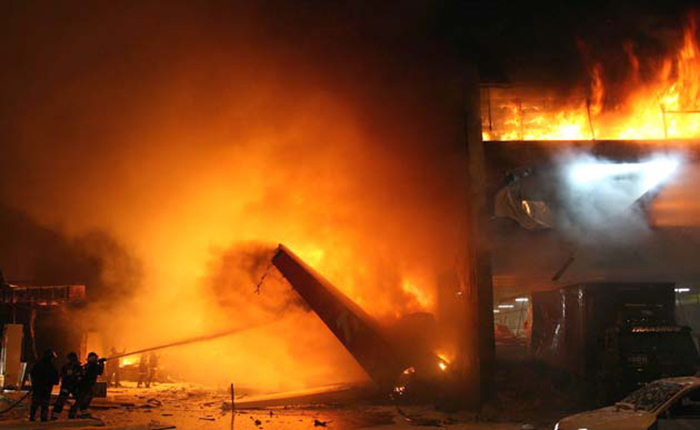
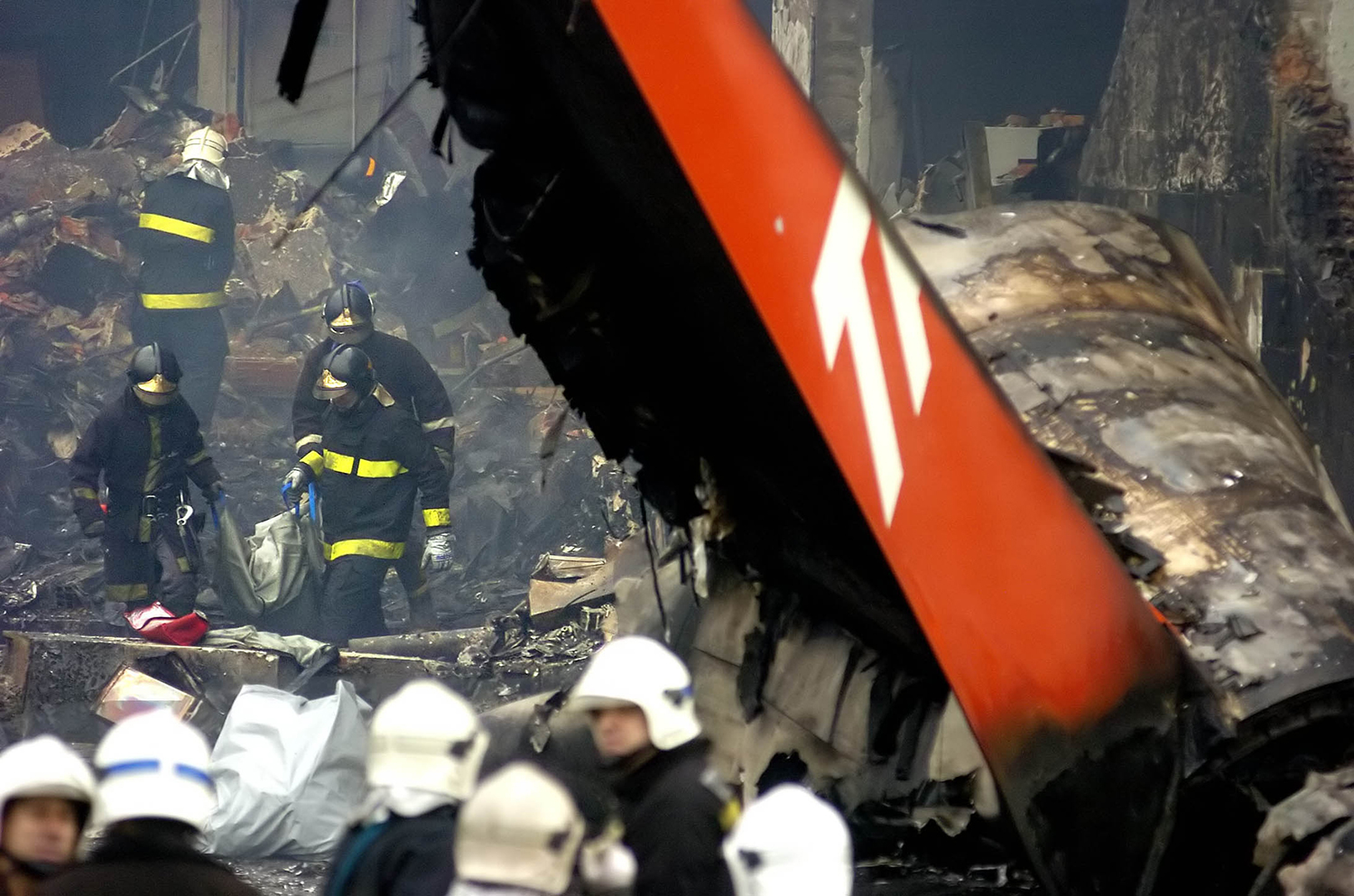
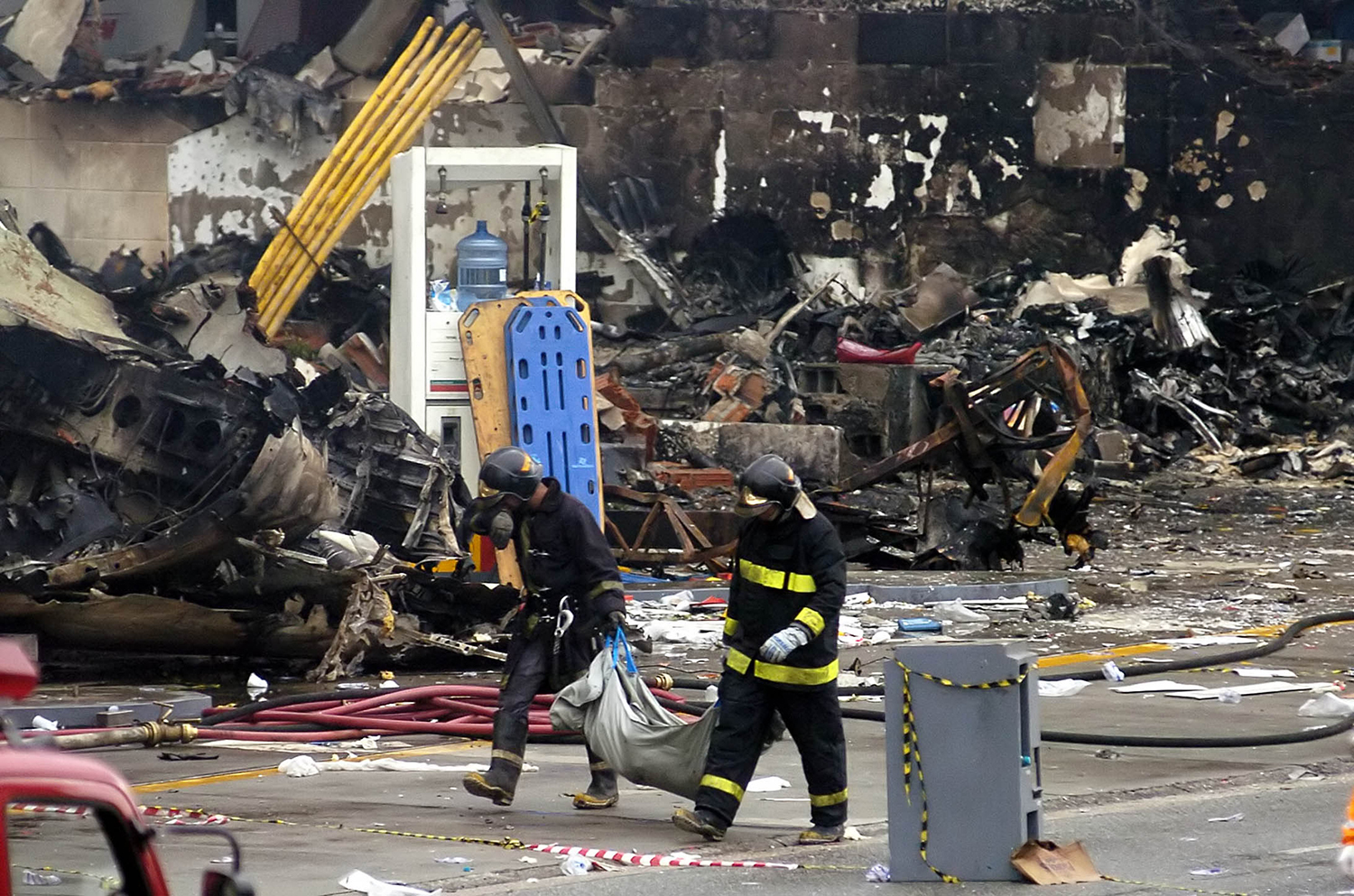
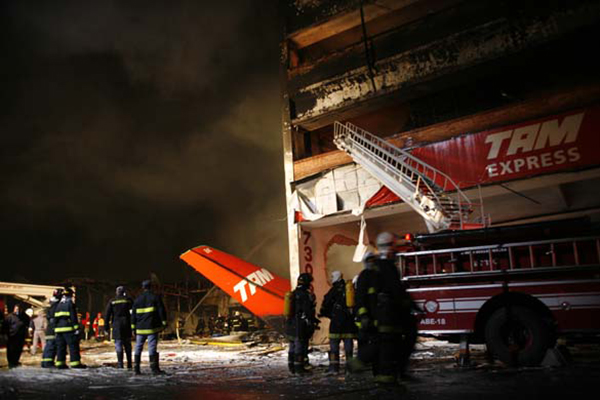
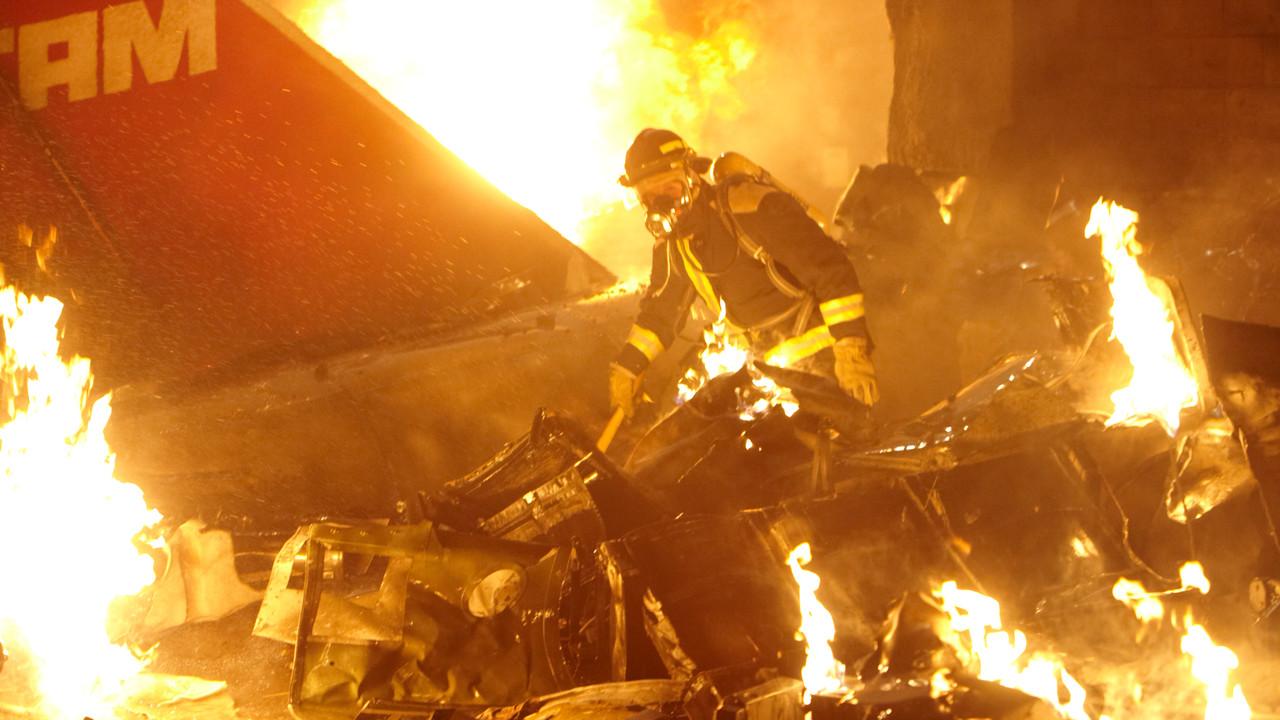
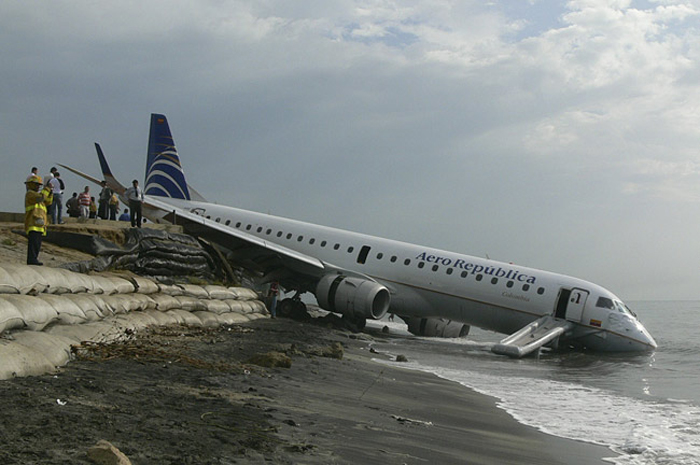
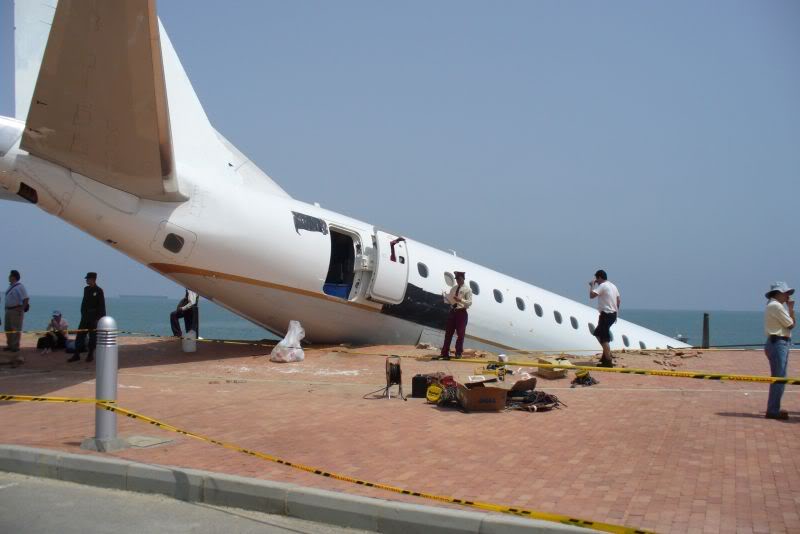
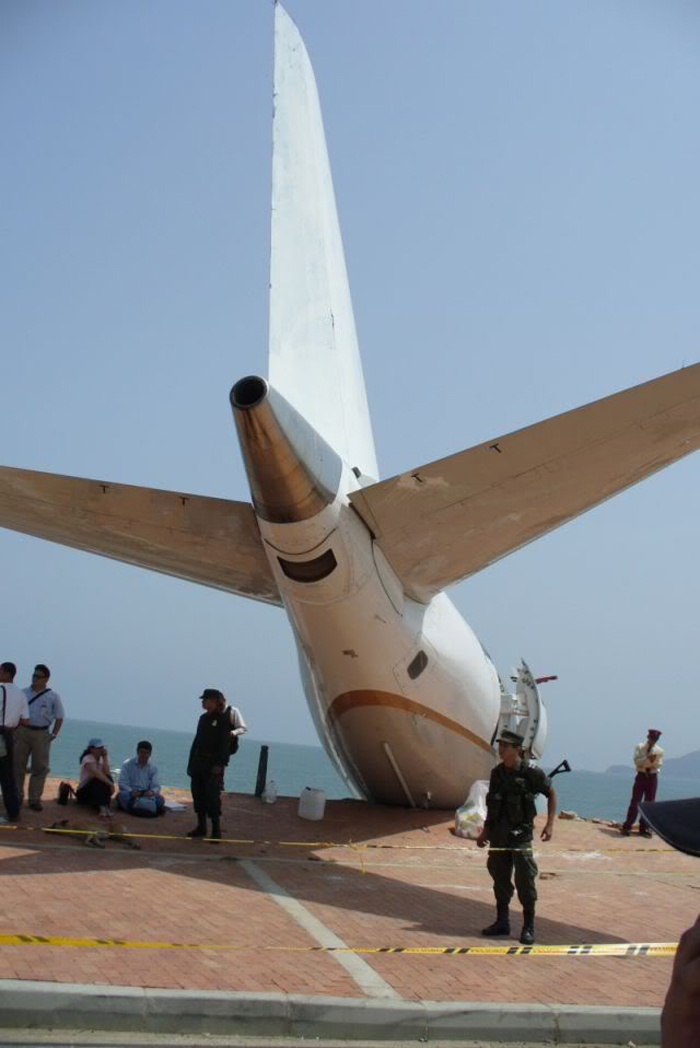
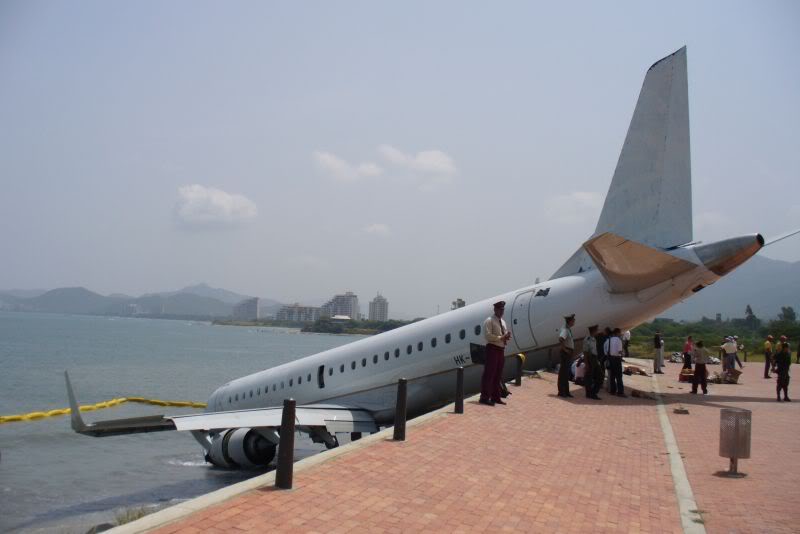
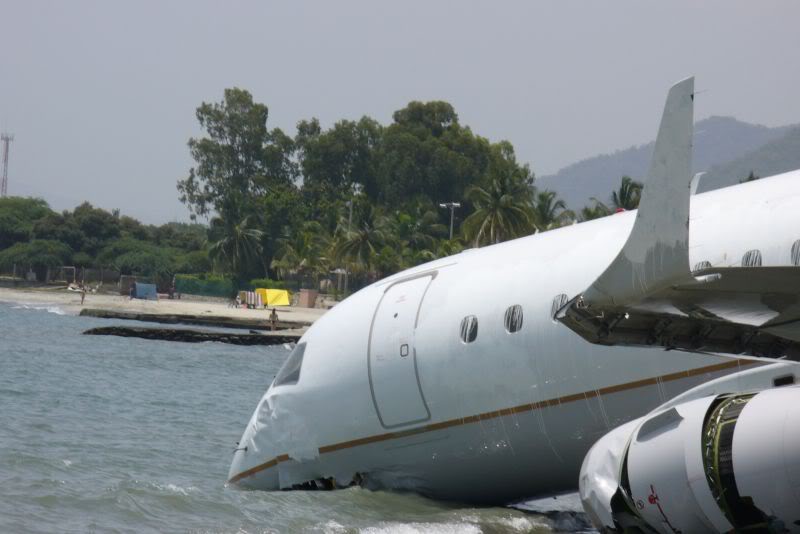
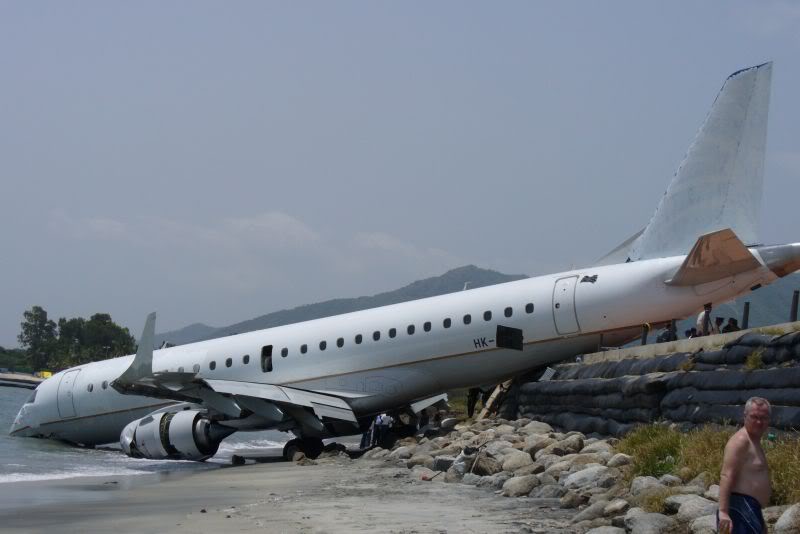
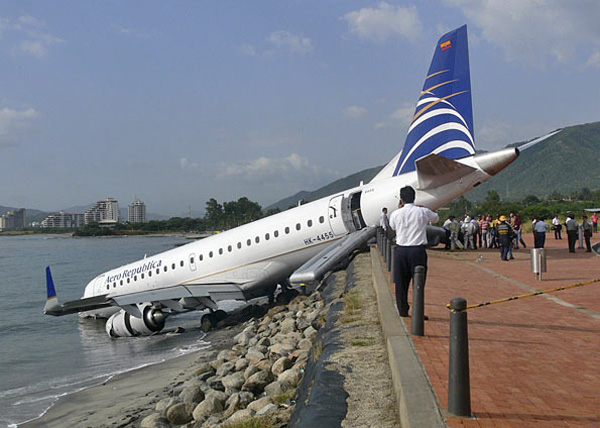
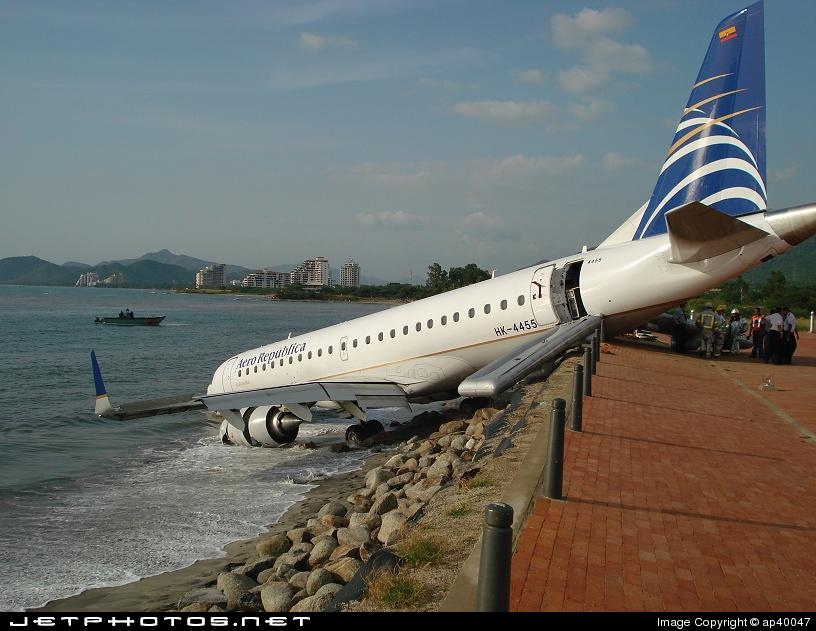
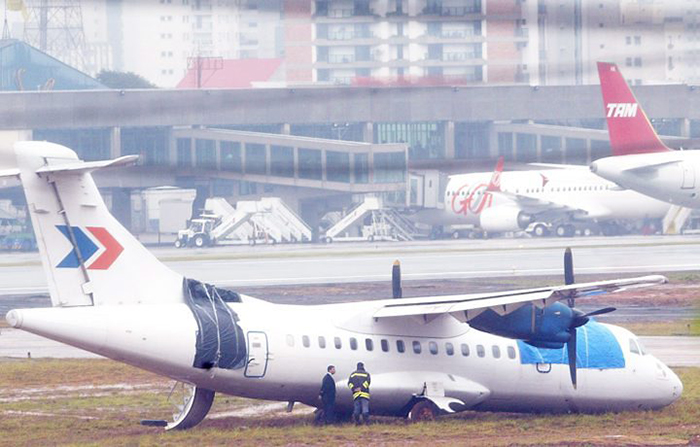
On 17 July 2007, at 17:19 local time (20:19 UTC), the Airbus aircraft, model A320, registration PR-MBK, operating as flight JJ3054, departed from Porto Alegre (SBPA) destined to Congonhas Airport (SBSP) in São Paulo city, São Paulo State. There were a total of 187 souls on board the aircraft, being six active crew members and 181 passengers, including 2 infants and 5 extra crew members (not on duty). The weather prevailing along the route and at the destination was adverse, and the crew had to make a few deviations. Up to the moment of the landing, the flight occurred within the expected routine. The aircraft was operating with the number 2 engine reverser de-activated, in accordance with the Minimum Equipment List (MEL). According to information provided to the TWR by crews that had landed earlier, the active runway at Congonhas (35L) was wet and slippery. During the landing, at 18:54 local time (21:54 UTC), the crew noticed that the ground spoilers had not deflected, and the aircraft, which was not slowing down as expected, veered to the left, overran the left edge of the runway near the departure end, crossed over the Washington Luís Avenue, and collided with a building in which the cargo express service of the very operator (TAM Express) functioned, and with a fuel service station. All the persons on board perished. The accident also caused 12 fatalities on the ground among the people that were in the TAM Express building. The aircraft was completely destroyed as a result of the impact and of the raging fire, which lasted for several hours. The accident caused severe damage to the convenience shop area of the service station and to some vehicles that were parked there. The TAM Express building sustained structural damages that determined its demolition. The aircraft was completely destroyed.
Probable cause:
Human factors
1.1 Medical aspect
a. Pain - Undetermined
At a certain moment, during the approach, the PIC reported having a mild headache. Although it was not possible to verify which type of headache it was, or even to evaluate its intensity, it is possible that this trouble may have influenced his cognitive and psychomotor capabilities during the final moments of the flight, when the unpredictability of the situation demanded a higher effectiveness of performance. This factor was considered undetermined due to the impossibility of confirming its contribution in factual terms.
1.2 Operational aspect
a. Training - A contributor
The theoretical qualification of their pilots was founded on the exclusive use of computer interactive courses (CBT), which allowed a massive training, but did not ensure the quality of the training received. In addition, the formation of the SIC was restricted to the “Right Seat Certification”, something that proved insufficient for him to deal with the critical situation experienced after the landing. Lastly, there was a perception among the crews interviewed that the training through the years and on account of the high demand resulting from the company’s growth was being abbreviated.
b. Application of the commands - Undetermined
One of the hypotheses considered in this investigation was that the pilot may have attempted to perform a procedure no longer in force at the time of the accident for the landing with a pinned reverser. This procedure consisted in the receding of both levers to the “IDLE” position during the flare at about a 10-foot altitude, and, after touching down, in activating the only reverser available, maintaining the thrust lever of the other engine in the “IDLE” position.
This procedure, though being more efficient from a braking perspective, could induce the crew to making mistakes, as there were several reports of occurrences in which there was a wrong setting of the levers, motivating the manufacturer to establish a new procedure, months before the accident. Thus, there is a high probability that the PIC inadvertently left one of the thrust levers in the “CL” position, placing the other one first in “IDLE” and later in the “REV” position. This factor was considered undetermined due to the impossibility of confirming its contribution in factual terms.
c. Cockpit coordination - A contributor
Independently of the hypothesis considered, the monitoring of the flight at the landing was not appropriate, since the crew did not have perception of what was happening in the moments that preceded the impact. This loss of situational awareness hindered the adoption of an efficient and timely corrective action.
d. Forgetfulness by the pilot - Undetermined
It is possible that the pilot has inadvertently left one of the levers at the “CL” position, while trying to perform a procedure no longer in force for the operation with a pinned reverser. This factor was considered undetermined due to the impossibility of confirming its contribution in factual terms.
e. Flight indiscipline - Undetermined
The procedure prescribed for the operation with a pinned reverser had been modified by the manufacturer and, according to the FDR recordings, the procedure in force was known to the crew and executed by them on the leg that preceded the accident. However, as this procedure imposed an increase of up to 55 meters in the calculations of runway distance required for landing, it is possible that the PIC deliberately tried to perform adoption of a procedure no longer in force would characterize flight indiscipline. This factor was considered undetermined due to the impossibility of confirming its contribution in factual terms.
f. Influence from the environment - Undetermined
The operating conditions of the Congonhas runway, may have affected the crew’s performance from a psychological perspective, considering the state of anxiety that was present in the cockpit.
In addition, the lack of luminosity resulting from the operation at night time, associated with the size and color of the thrust levers may have hindered the verification of a contingent inappropriate positioning of those controls during the landing. This factor was considered undetermined due to the impossibility of confirming, in factual terms, the psychological influence of the runway operating conditions and/or lack of luminosity on the performance of the crew.
g. Judgment of pilotage - Undetermined
In view of all the operation scenario - the 55 meters added on account of the reverser procedure, the 2.4 extra tons of fuel on account of the tankering, the crowded aircraft, the pressure to proceed to Congonhas, the PIC’s physiological condition (headache), a SIC with little experience in the A-320 and in its autothrust system, the wet and slippery runway, the occurrences of the preceding days - there is a high probability that the PIC deliberately tried to perform the procedure no longer in force for the operation with a pinned reverser, in order to increase the braking efficiency, inadvertently leaving the number 2 engine thrust lever in the “CL” position. Considering this hypothesis, the diversion to an alternate airport would be desirable, instead of trying to perform a procedure that was not prescribed. This factor was considered undetermined due to the impossibility of confirming its contribution in factual terms.
h. Management planning - A contributor
At the time of the accident, the operator had a disproportional number of captains in comparison with the number of co-pilots, a fact that obliged the scheduling sector to form crews with 2 captains. Thus, although complying with the minimum requirements of the regulation in force, such a practice may have contributed to the creation of a climate of complacency in the cockpit of the JJ3054. Besides, the long experience of the SIC as a captain was not a guarantee of his competence in the co-pilot function - for which he had done only the “Right Seat Certification” training - and, added to his little experience in that aircraft, it contributed to the loss of situational awareness in the most critical moments of the flight.
i. Flight planning - Undetermined
Thus, considering the hypothesis that the PIC deliberately tried to perform the old procedure for a landing with a pinned reverser to increase the braking efficiency, it is possible that the use of that procedure was not appropriately prepared, something that could have favored the wrong positioning of the levers (according to the hypothesis mentioned above, it is possible that the PIC inadvertently left the nº2 engine thrust lever in the “CL” position.). The lack of a briefing for the descent in the CVR recording hindered the confirmation of a possible intention of applying the old procedure, no longer in force at the time. This factor was considered undetermined due to the impossibility of confirming its contribution in factual terms.
j. Little experience of the pilot - A contributor
Despite his long experience in commercial jets, the SIC possessed only about 200 flight hours in aircraft of the A320 type. Besides, his experience in the function of co-pilot was restricted to the “Right Seat Certification” training, which proved insufficient to deal with the emergency situation.
k. Management oversight - A contributor
The operator allowed the crew to be composed of two captains, with the occupant of the right-hand seat having done only the “Right Seat Certification” training. Besides, the lack of coordination between the several sectors of the company, especially between the sectors of operation and training, determined the lack of an appropriate monitoring of the processes and of the quality of the pilots’ professional formation.
Psychological aspect
a. Anxiety - Undetermined
The CVR recording allows to perceive that the PIC was showing anxiety in relation to the runway conditions for landing, and on two different occasions he asked the SIC to request from the TWR-SP the rain and runway conditions, and on one of them specifically, whether the runway was slippery. It is possible that the state of anxiety present in the PIC may have influenced the performance of the crew to some extent. This factor was considered undetermined due to the impossibility to confirm that this anxiety has effectively influenced the performance of the crew.
b. Perception error - A contributor
Although perceiving that the ground spoilers had not deflected, the pilots were not able to associate the non-deflection with the positioning of the thrust levers. In addition, there is a high probability that the pilots were led to believe that the lack of the expected deceleration after landing was a result of the conditions of operation with a wet runway, the influence of which, from a psychological aspect perspective in the field of individual variables, was perceived along the investigation.
c. Stress - Undetermined
The stress has effect on the cognitive level (diminution of the concentration, diminution of the response speed, degradation of the memory, etc.), emotional level (alteration of the characteristics of personality, weakening of the emotional control, lowering of the self-esteem, etc.), behavioral level (alterations of the sleep pattern, diminution of interests, verbal articulation problems, etc.), and physiological level (sudoresis, tachycardia, sleep pattern alterations, gastric and dermatologic symptoms, etc.). The presence of stress triggering stimuli was perceived, such as the state of anxiety on the part of the pilots, especially regarding the runway conditions, the cephalalgia of the PIC, the issues concerning the operation in Congonhas with a wet runway, the crowded aircraft and the inoperative reverser. However, it was not possible to determine whether those stimuli effectively led any of the two pilots to a high level of stress. This factor was considered undetermined due to the impossibility to confirm its contribution in factual terms.
d. Lack of perception - A contributor
Considering the hypothesis of a failure in the thrust control system, the contingent stimulus generated from the loss of resistance to the movement of the thrust levers may not have been perceived by the pilot(s), according to the CVR recordings. On the other hand, if one considers the hypothesis that the nº 2 engine thrust lever was inadvertently left in the “CL” position, while the pilots were trying to perform a procedure no longer in force, the characteristics of the autothrust system, which keep the levers motionless during the variations of thrust, in addition to the size and color of those control levers, hard to be observed on a night flight, were not sufficiently evident to be perceived by the pilots. This situation was aggravated by the lack of a warning device relative to the conflicting positioning of the thrust levers.
e. Loss of situational awareness - A contributor
Thus, no matter which hypothesis is considered, the loss of the situational awareness emerged as a result of the very lack of perception on the part of the pilots. In this sense, the automation of the aircraft, however complex, was not capable of providing the pilots with sufficiently clear and accurate stimuli, to the point of favoring their understanding of what was happening in the moments just after the landing in Congonhas.
f. Organizational climate - Undetermined
In relation to the crews of the company, the investigation identified the perception that there was a pressure on the part of the management against diversions, on account of the inconvenience they could arise for the passengers and for the company itself. If the pilots of the JJ3054 shared that perception, it is possible that this factor could have some influence on the pilot’s decision to proceed for the landing in Congonhas, in spite of his concern with the runway operating conditions. This factor was considered undetermined due to the impossibility to confirm its contribution in factual terms.
g. Regulation - A contributor
The regulatory organization, although having already considered the availability of the reversers as a requirement for the operation in Congonhas, at least since April 2006, such a requirement was only formalized as a norm in May 2008. The opportune regulation of this requisite would have prevented the aircraft from operating in Congonhas with a wet runway condition.
h. Training - Undetermined
In relation to the training, the investigation identified in the crews a perception that the company seemed to have reduced the contact hours applied to it, although in formal terms those contact hours had remained unaltered. In relation to crew professional formation, the investigation identified a tendency on the part of the company to reduce the number of hours assigned to training, which remained unaltered in formal terms. Moreover, the FDR recordings showed that, during the period in which the aircraft operated with the pinned reverser, 5 different types of landing procedures were performed by the various crews who operated it. This factor was considered undetermined due to the impossibility to confirm, in factual terms, that the crews’ perception of a shortening in the training processes being applied was consistent with reality and/or whether such alleged shortening effectively influenced the performance of the crew, contributing to the accident.
2 Material factors
a. Design - A contributor
It was verified that, for an A320 airplane proceeding to land, it is possible to place one of the thrust levers at the “REV” position and the other at “CL”, and no alerting device will advise the pilots in an efficient way. This situation may put the aircraft in a critical condition and, depending on the time it takes the crew to identify this configuration, and on the runway parameters, a catastrophic situation may occur. In the specific case of this accident, even with the aircraft on the ground (Weight on Wheels - WOW), with the number 1 engine thrust lever at the “REV” position, with the ground spoilers armed, with the autobrake selected, and with application of maximum braking pressure on the pedals, the power control system gave priority to the information that one of the levers was at “CL”, and this lever did not have any safety devices regarding a possible inadvertent setting.