Crash of a Boeing 767-3Z9ER near Phu Toey: 223 killed
Date & Time:
May 26, 1991 at 2317 LT
Registration:
OE-LAV
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Hong Kong - Bangkok - Vienna
MSN:
24628
YOM:
1989
Flight number:
NG004
Crew on board:
10
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
213
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
223
Aircraft flight hours:
7444
Aircraft flight cycles:
1135
Circumstances:
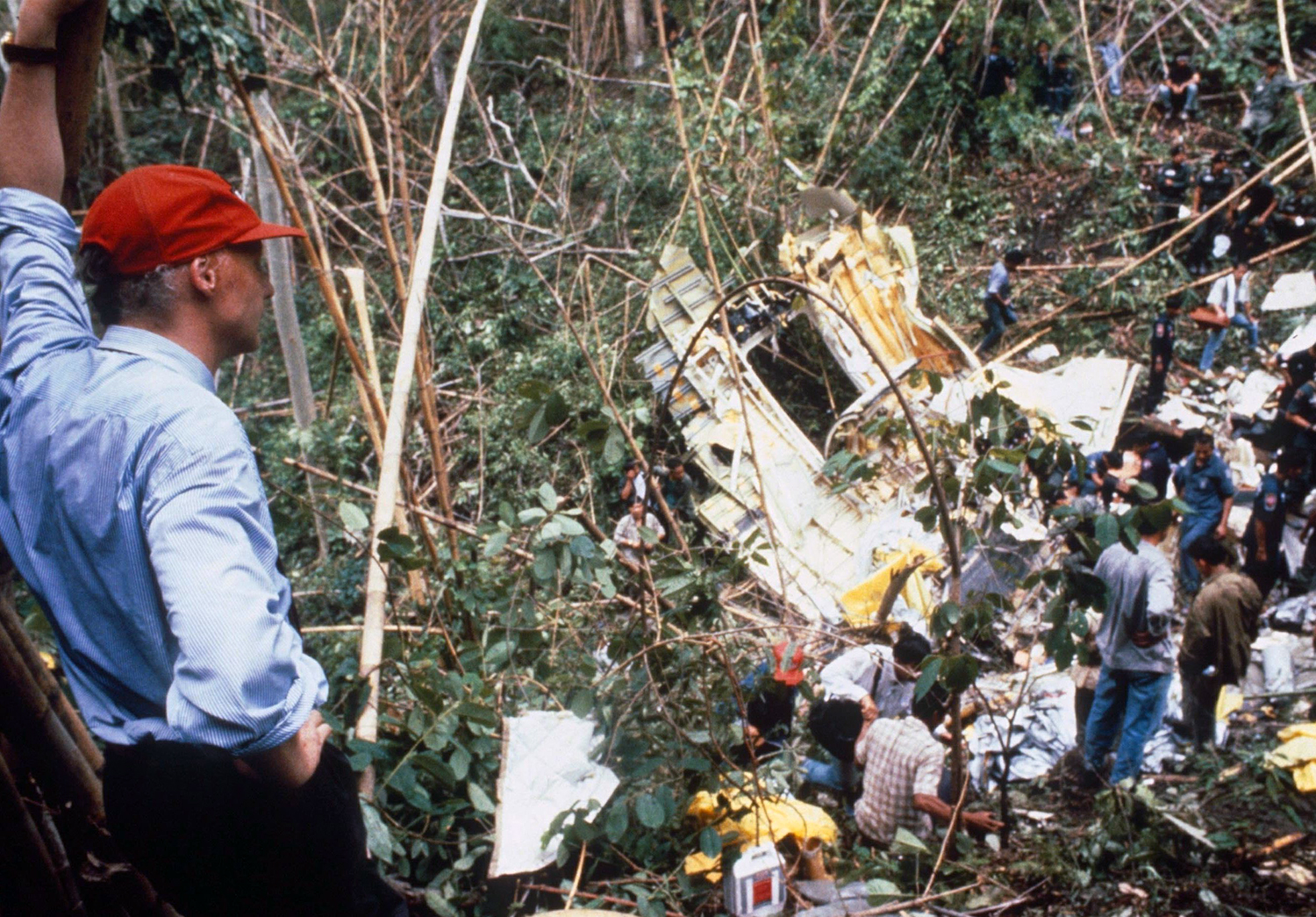
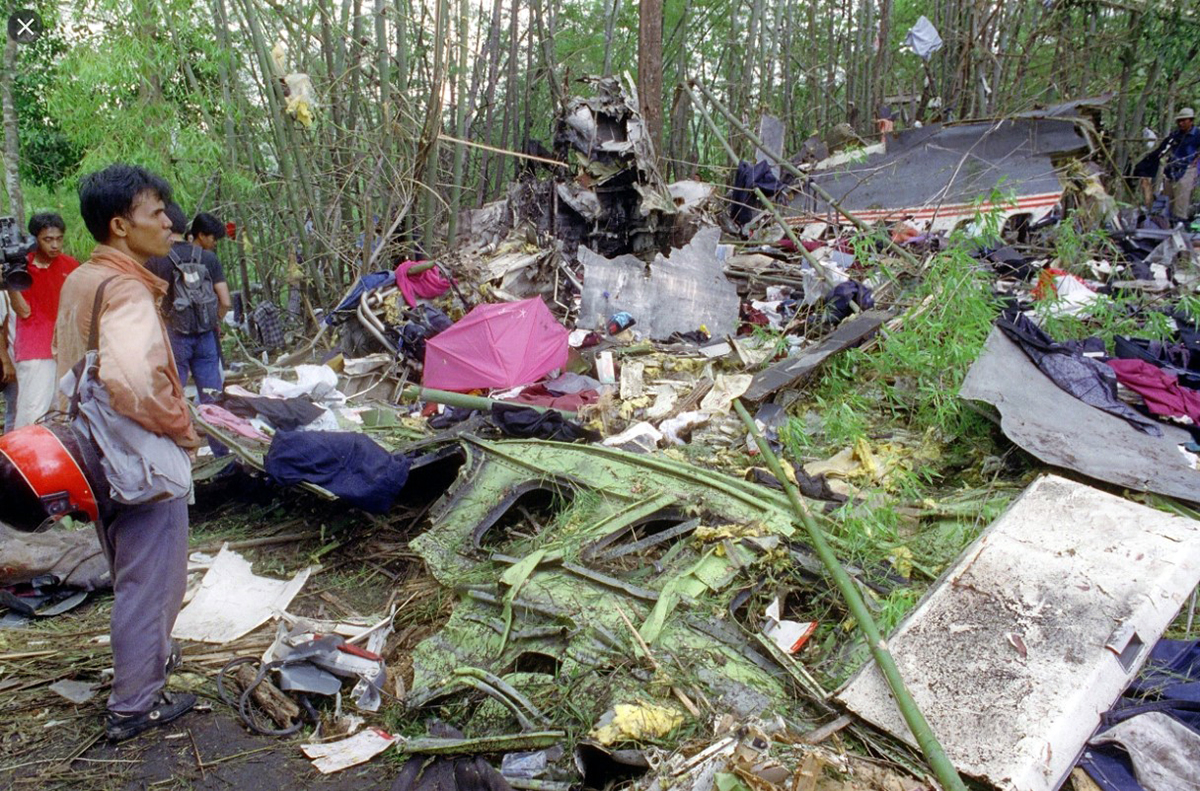
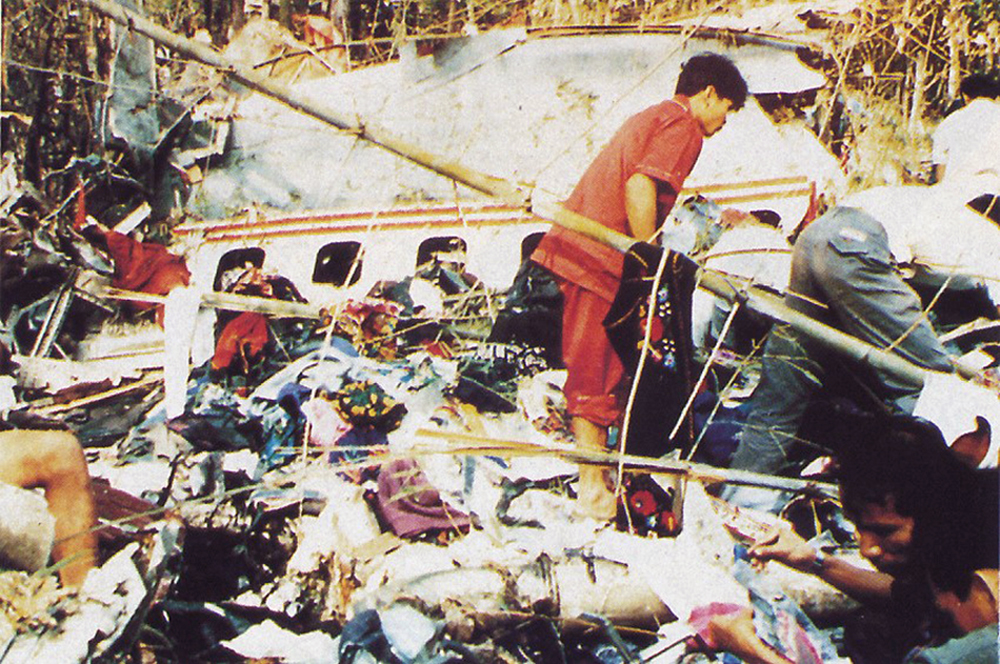
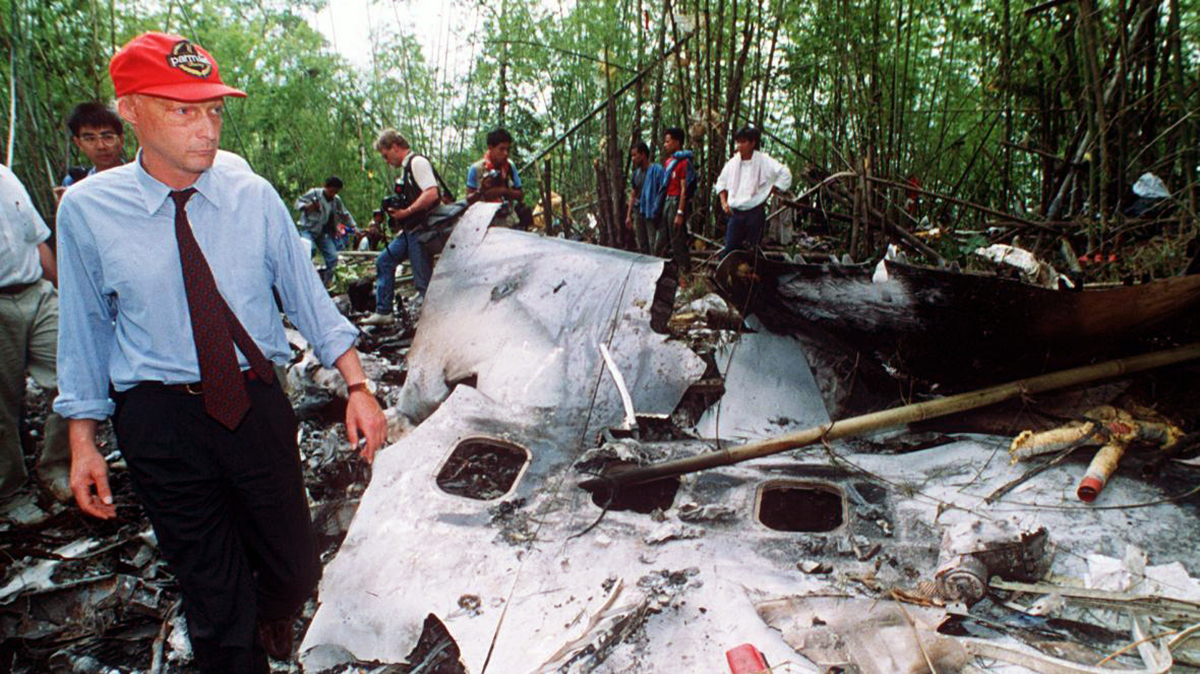
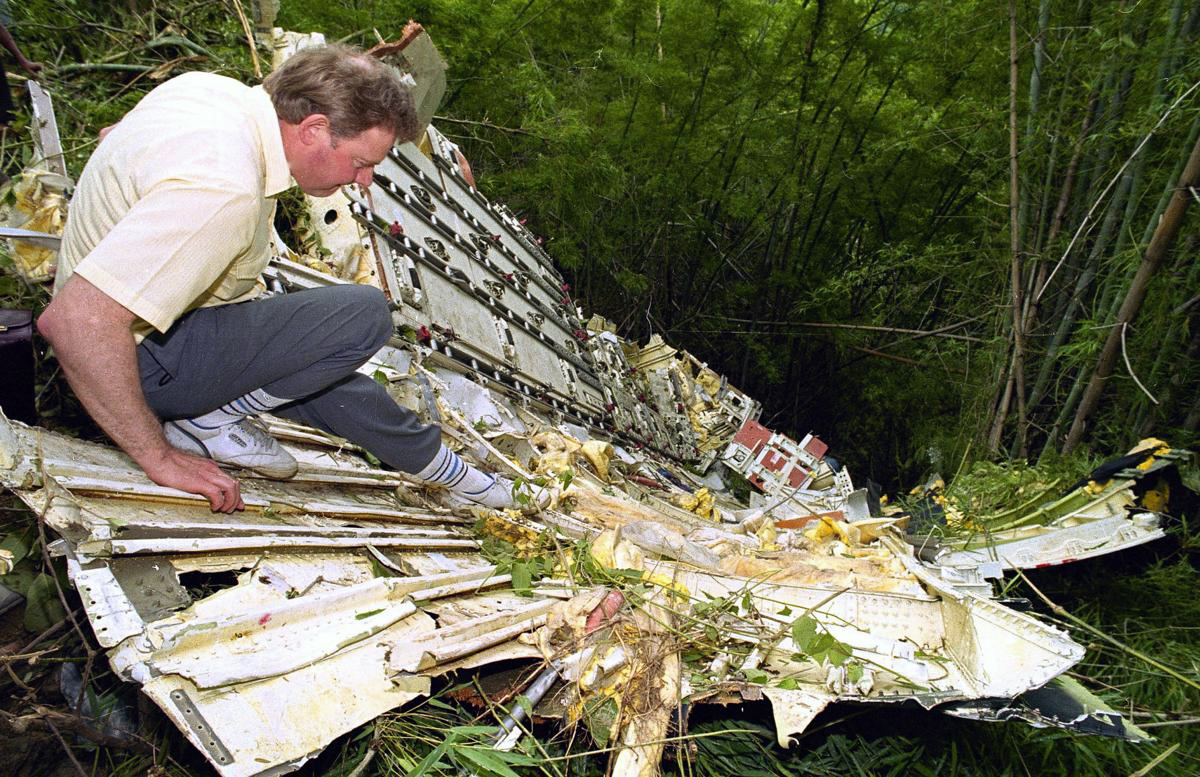
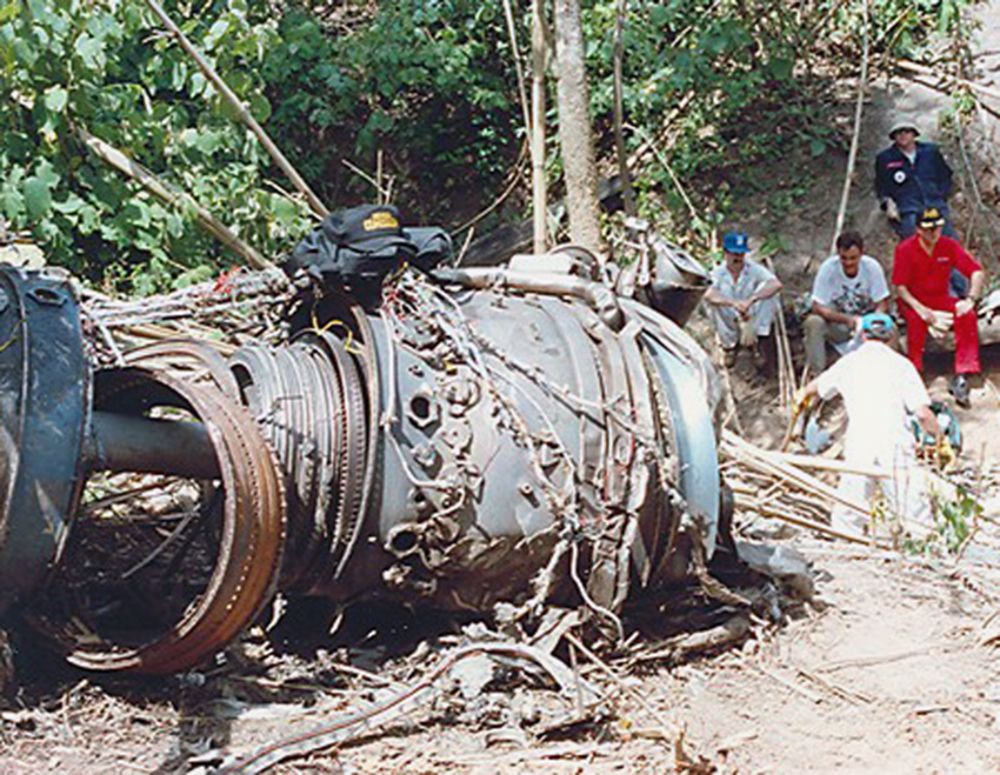
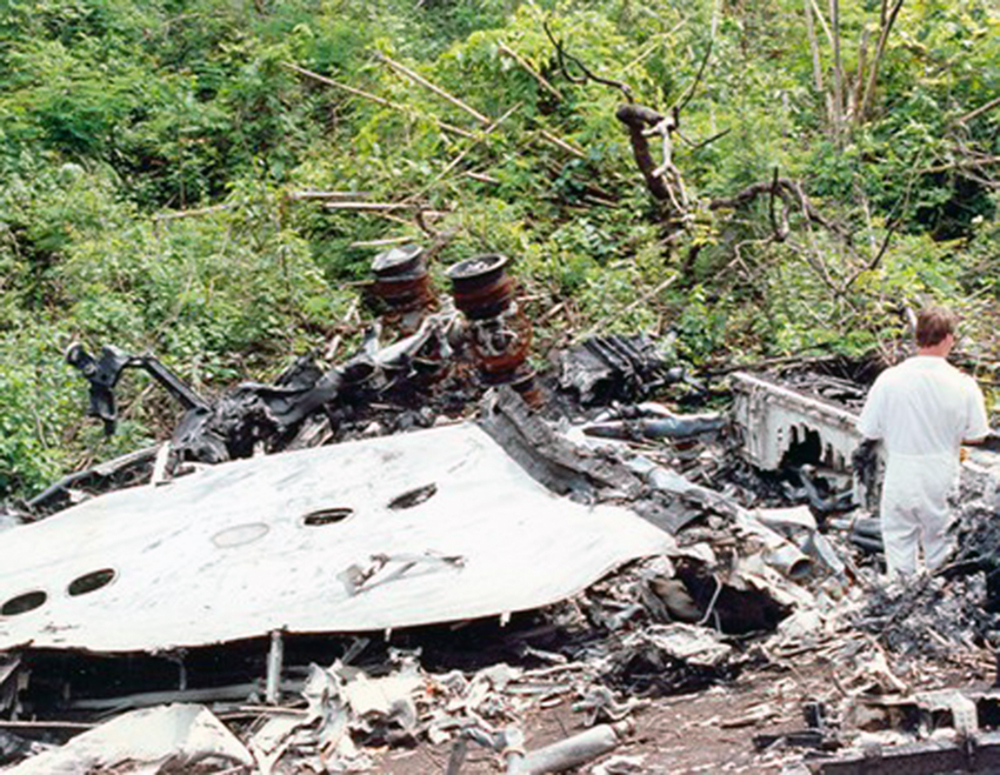
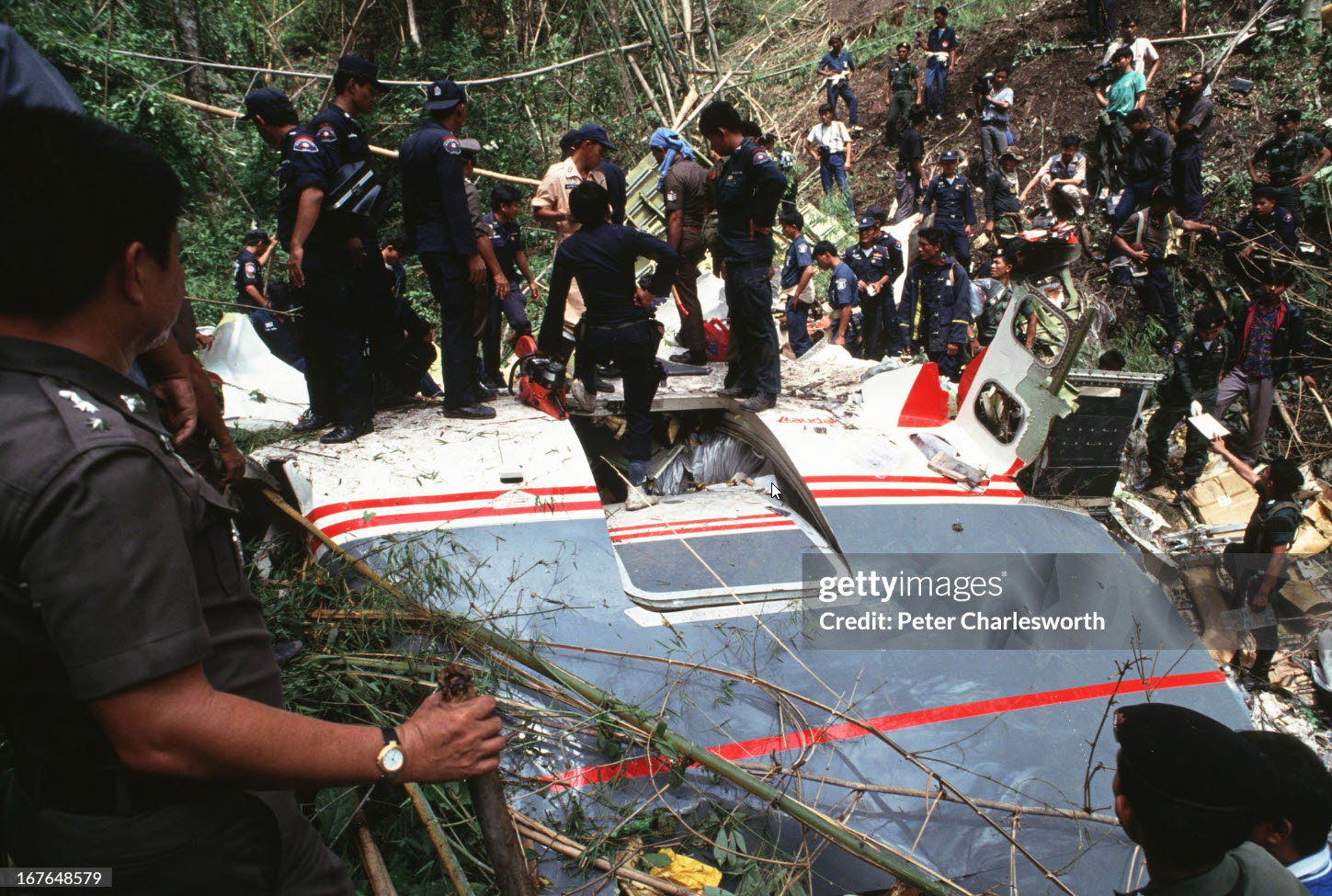
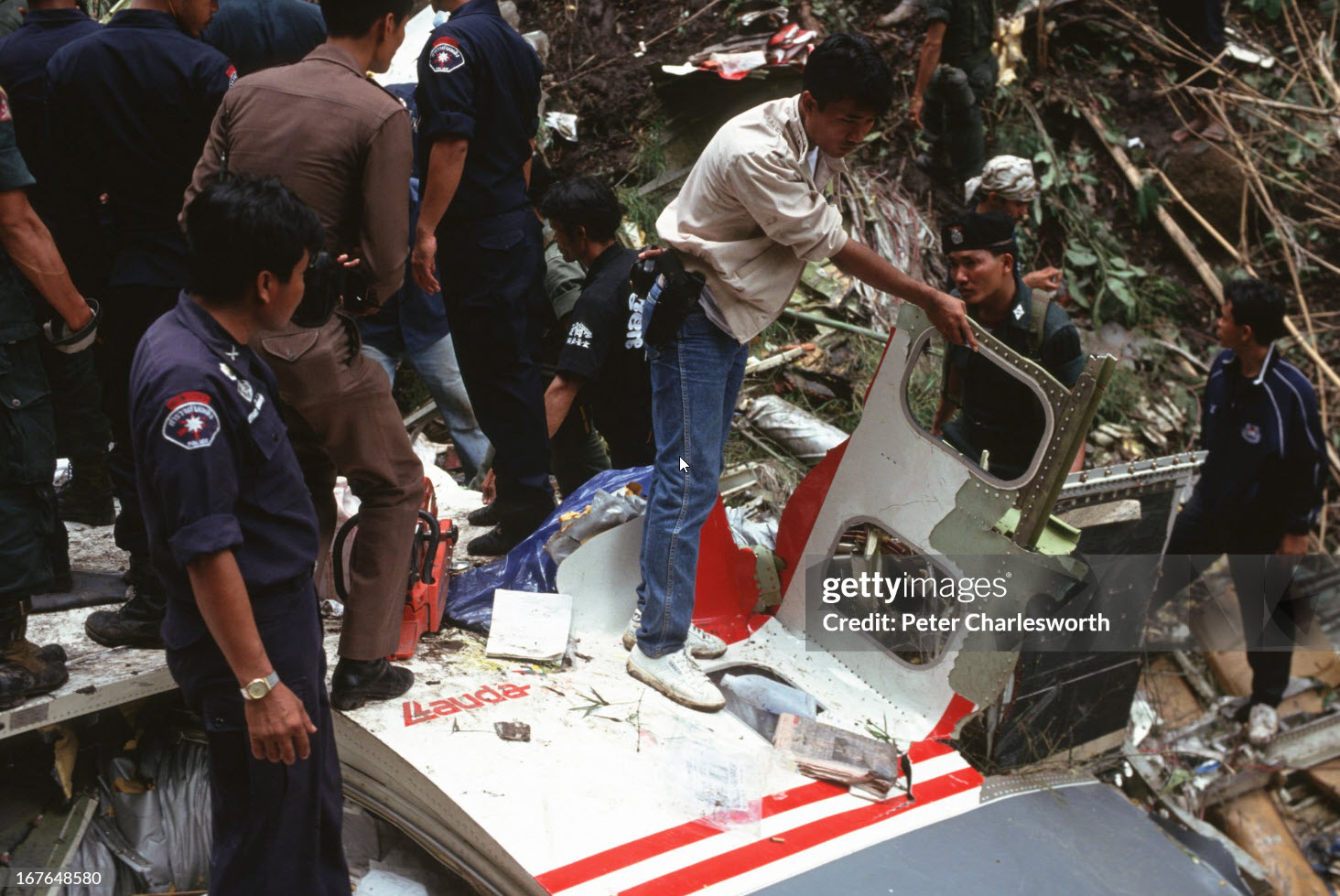
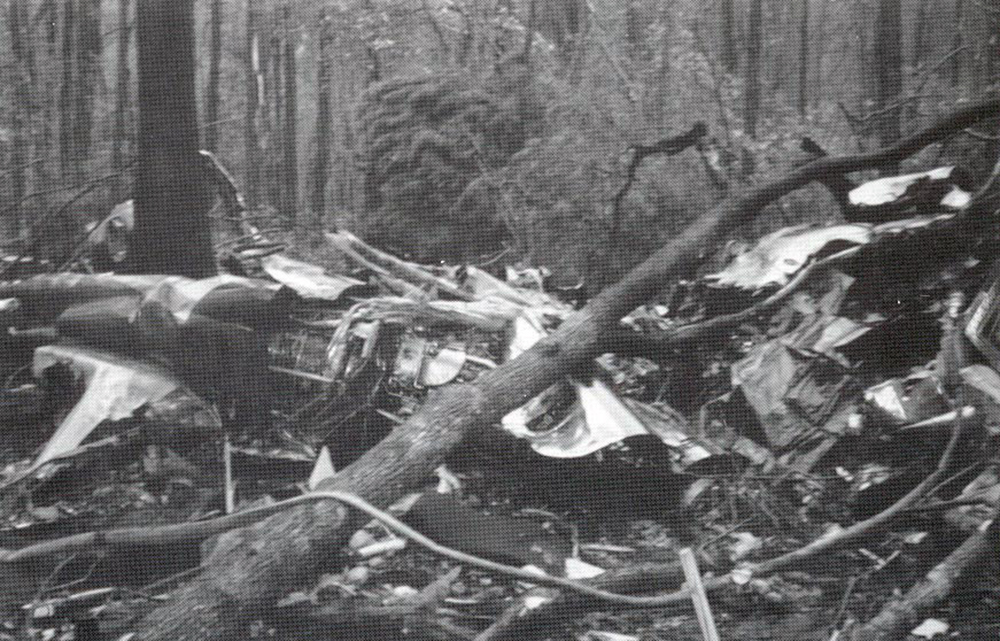
Lauda Air Flight 004 (NG004) was a scheduled passenger flight from Hong Kong to Vienna, Austria with an en route stop in Bangkok, Thailand. The flight departed Bangkok at 1602 hours on May 26, 1991 for the final flight sector to Vienna Austria. All pre-flight, ground, and flight operations appear routine until five minutes and forty five seconds after the cockpit voice recorder (CVR) recorded the sounds of engine power being advanced for takeoff. At this point a discussion ensued between the crew members regarding an event later identified as a crew alert associated with a thrust reverser isolation valve. The crew discussed this alert for some four and one half minutes. The Quick Reference Handbook (QRH) was consulted to determine appropriate crew actions in response to the alert. No actions were required, and none were identified as being taken. Ten minutes and twenty seconds into the flight the co-pilot advised the pilot-in-command of the need for rudder trim to the left. The pilot-in-command acknowledged the co-pilot's statement. Fifteen minutes and one second into the flight, the co-pilot stated "ah reverser's deployed." Sounds similar to airframe shuddering were then heard on the CVR. Twenty nine seconds later the CVR recording ended with multiple sounds thought to be structural breakup. Flight conditions were recovered from non-volatile memory in the left engine electronic engine control (EEC). At the suspected point of reverser deployment, the EEC readout indicated that the airplane was at an approximate altitude of 24,700 feet, a speed of Mach 0.78, and developing climb power. The airplane crashed in mountainous jungle terrain at 14 degrees 44 minutes North latitude and 99 degrees 27 minutes East longitude at approximately 1617 hours. Night time visual meteorological conditions prevailed. All 223 occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
The Accident Investigation Committee of the Government of Thailand determines the probable cause of this accident to be uncommanded in-flight deployment of the left engine thrust reverser, which resulted in loss of flight path control. The specific cause of the thrust reverser deployment has not been positively identified.
Final Report: