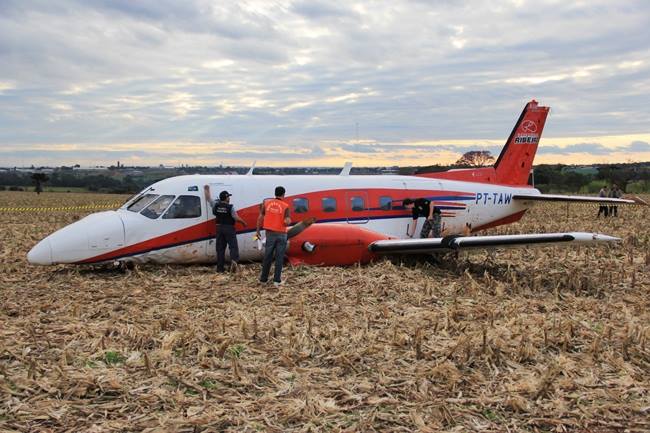
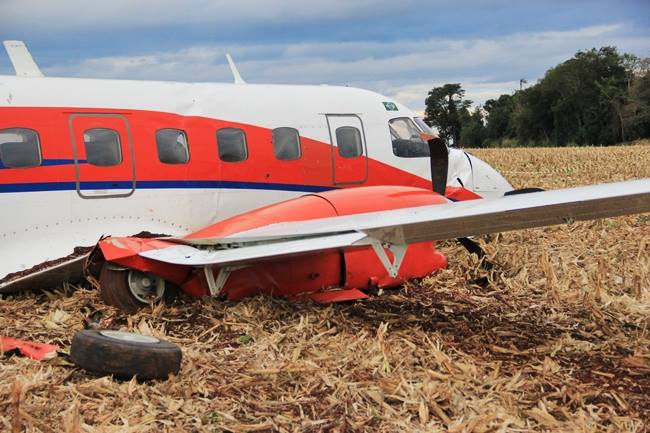
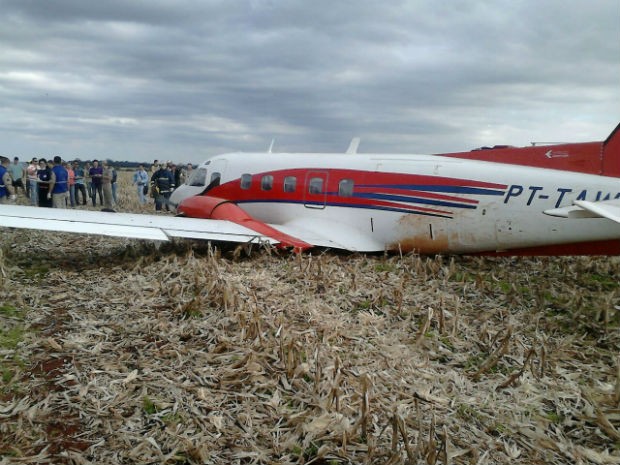
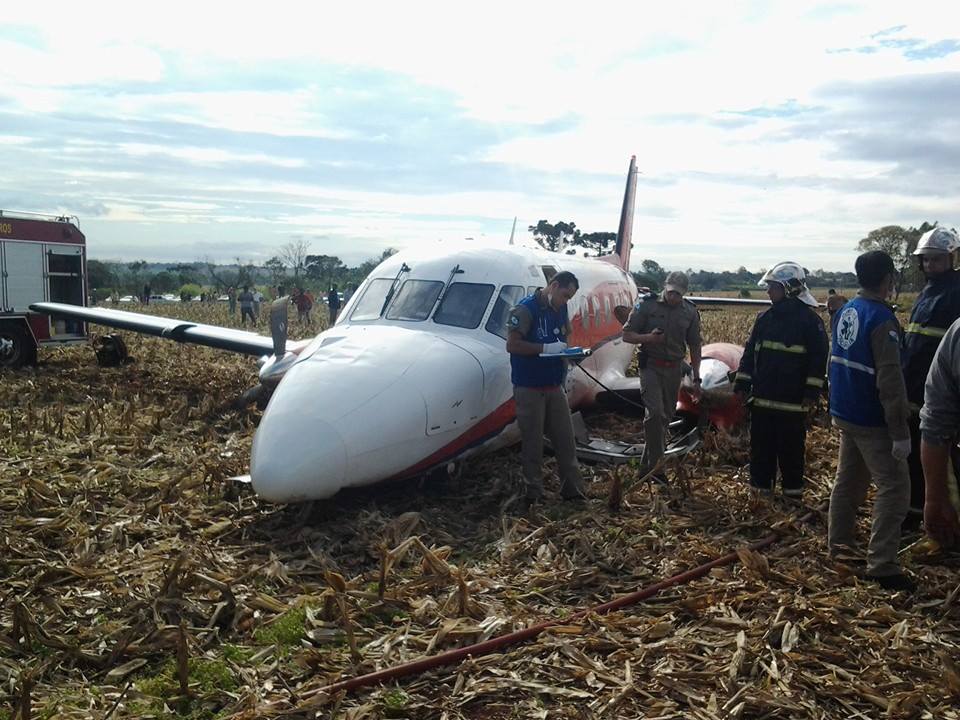
Circumstances:
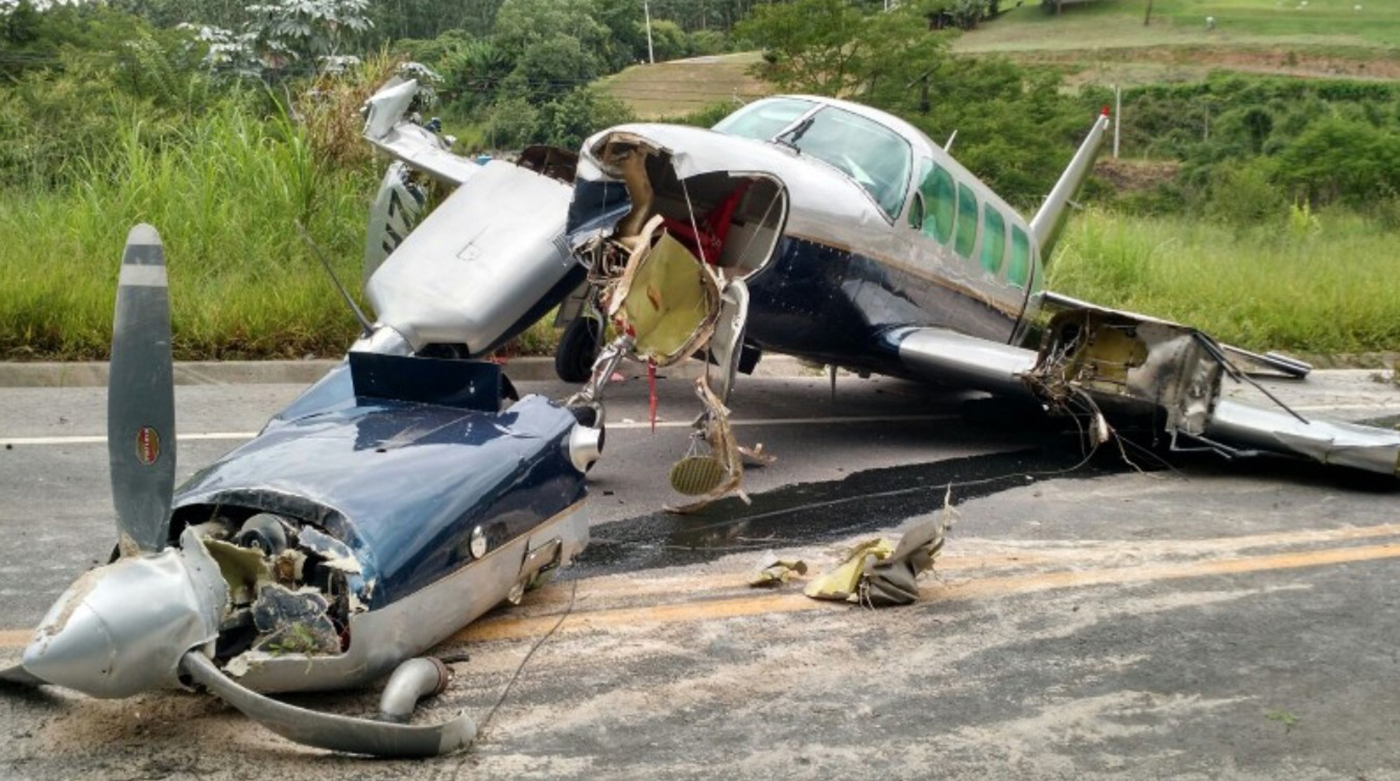
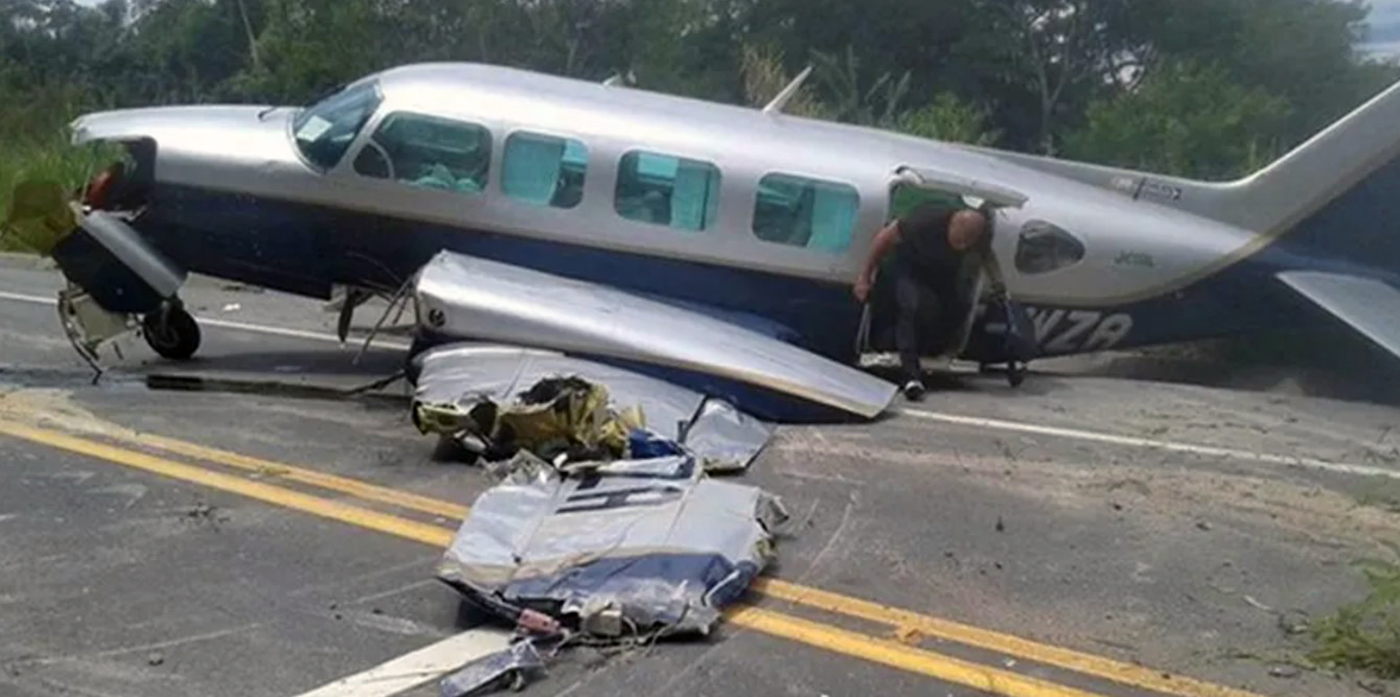
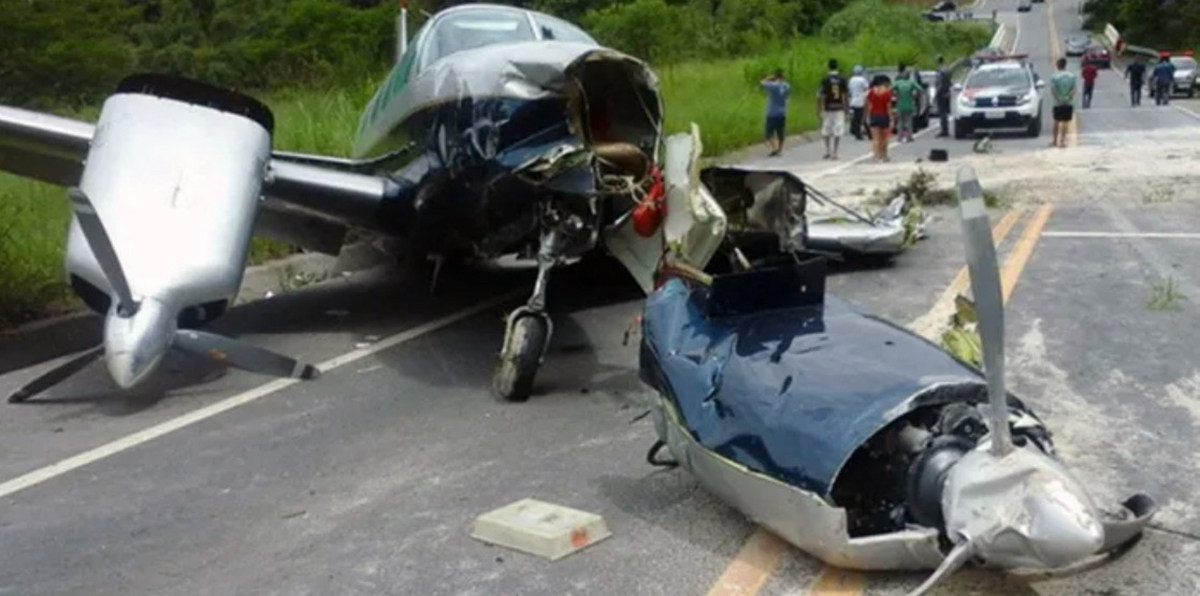
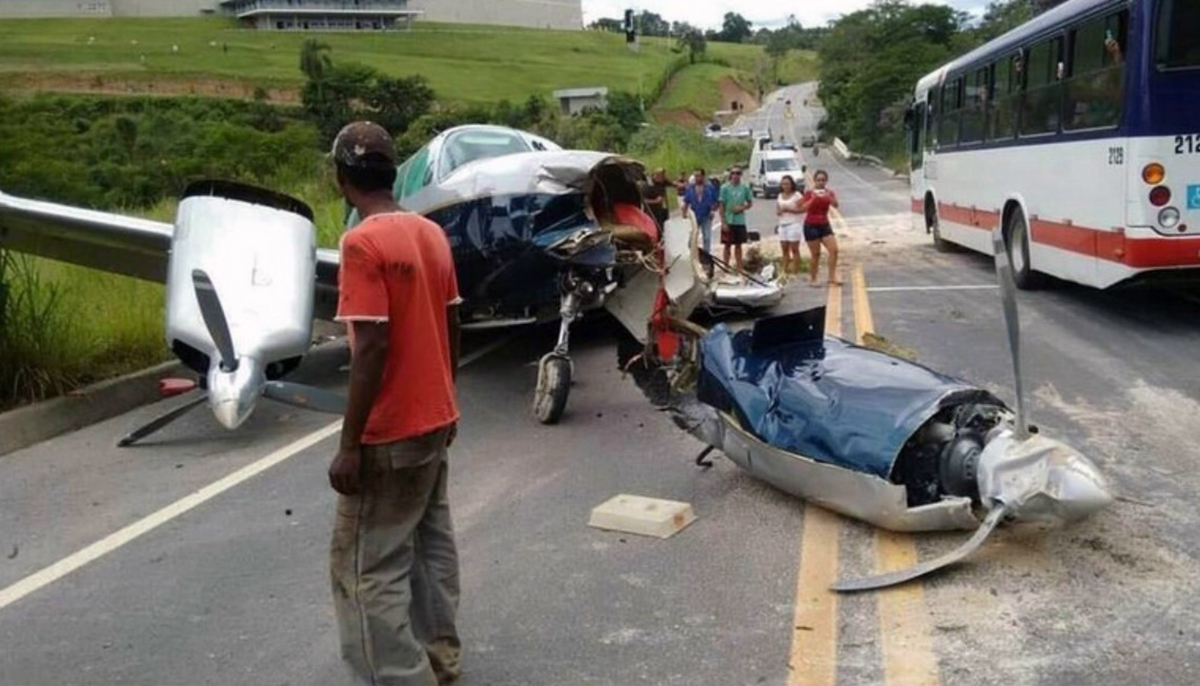
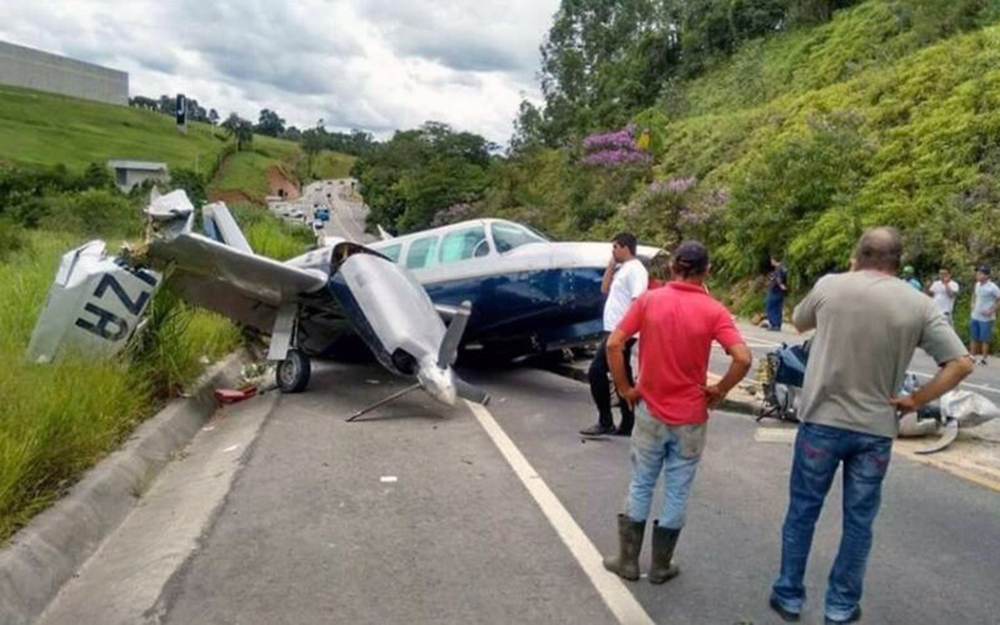
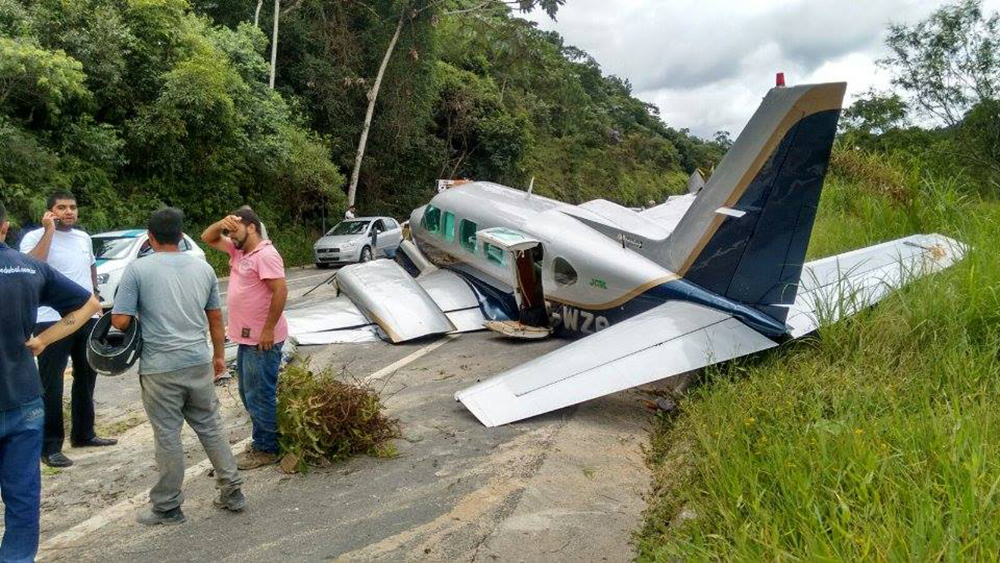
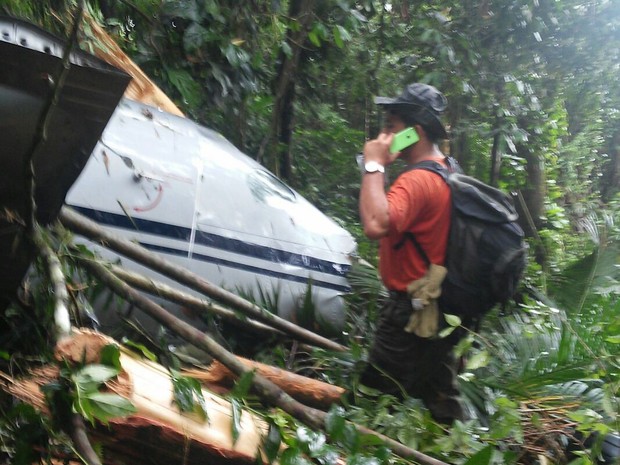
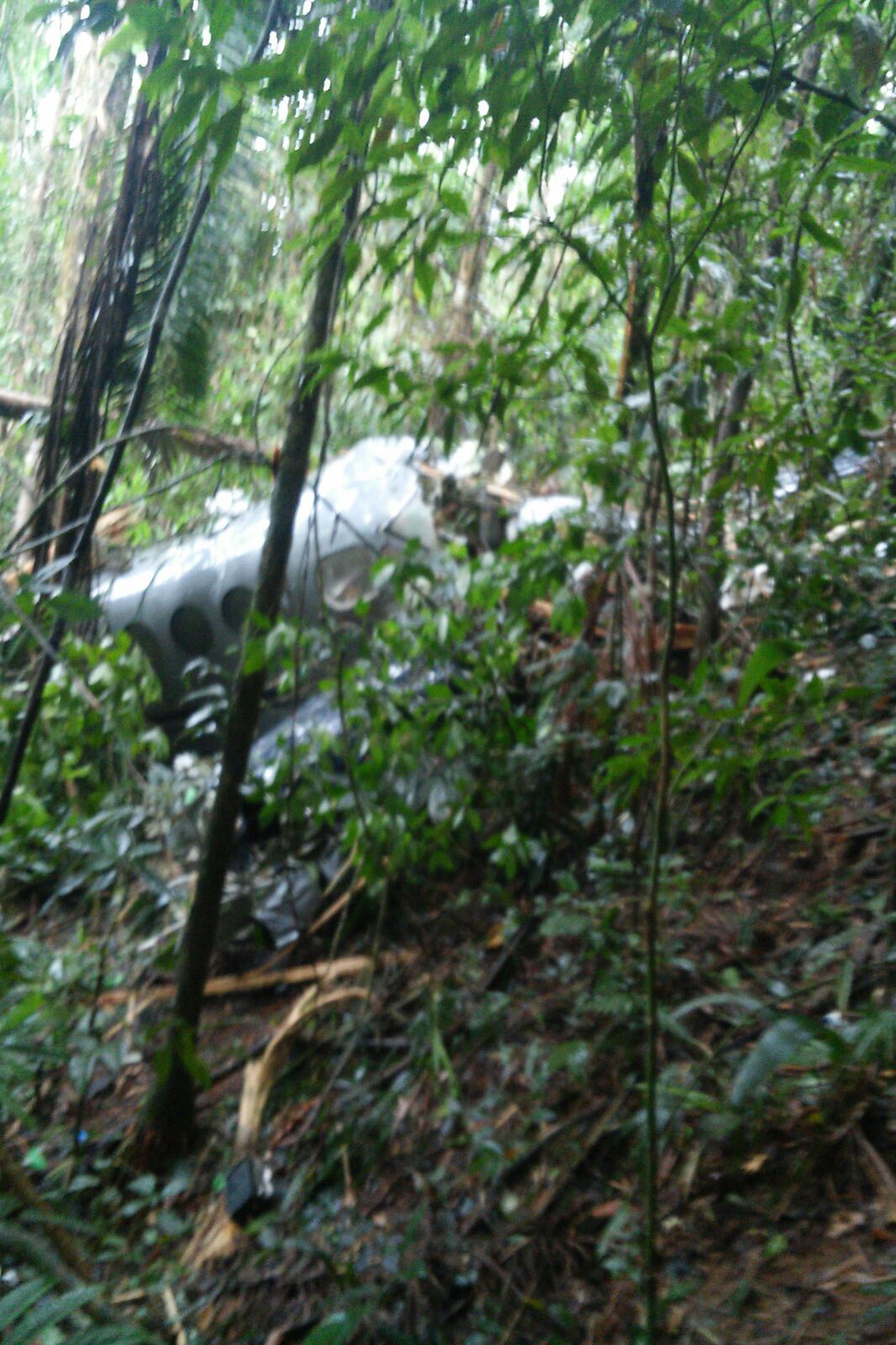
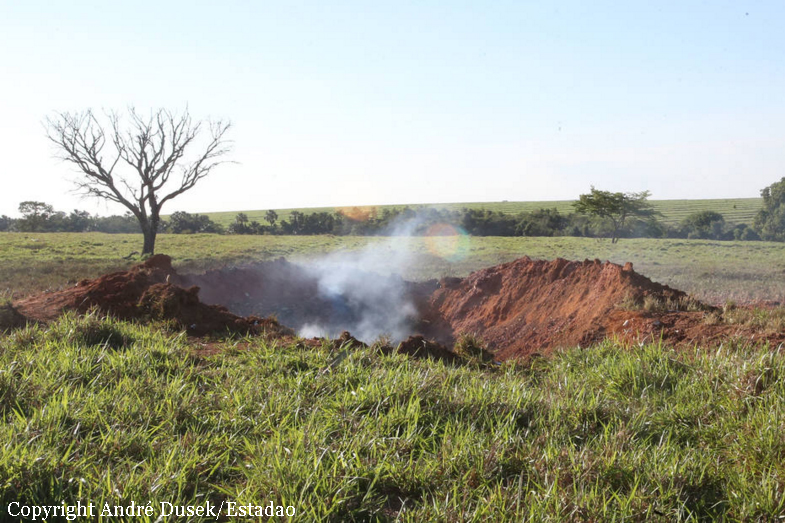
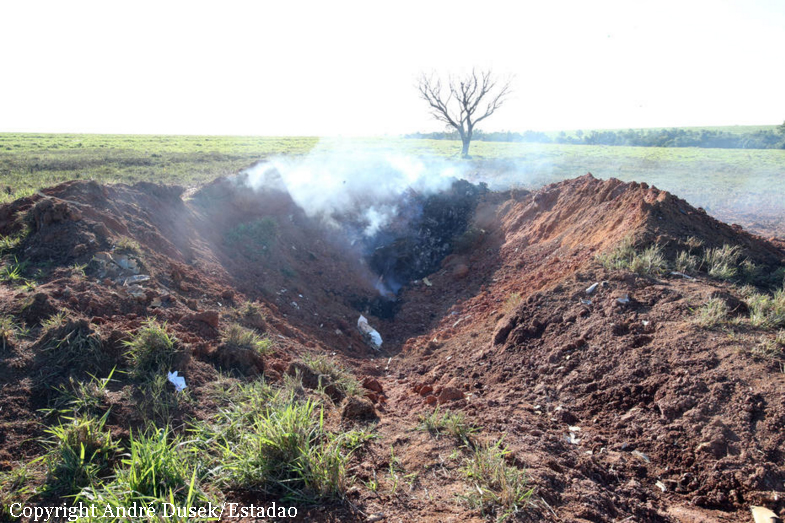
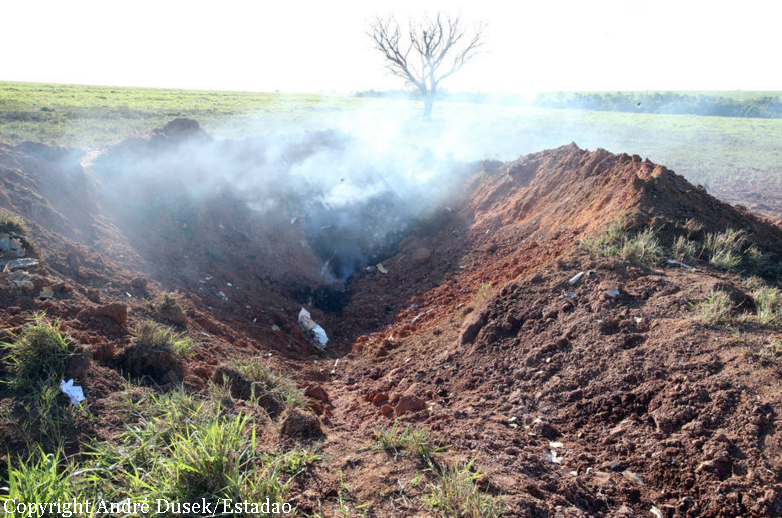
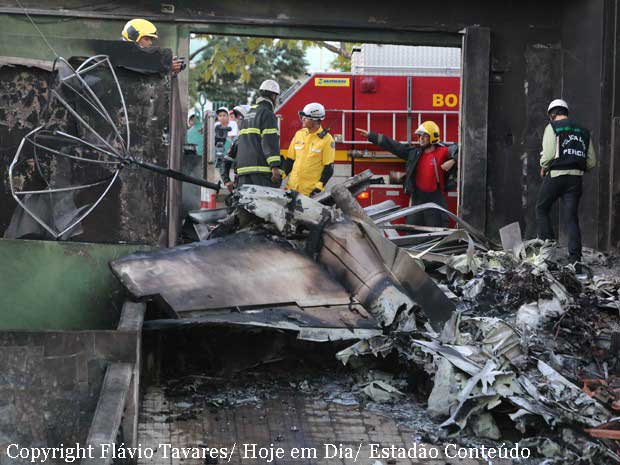
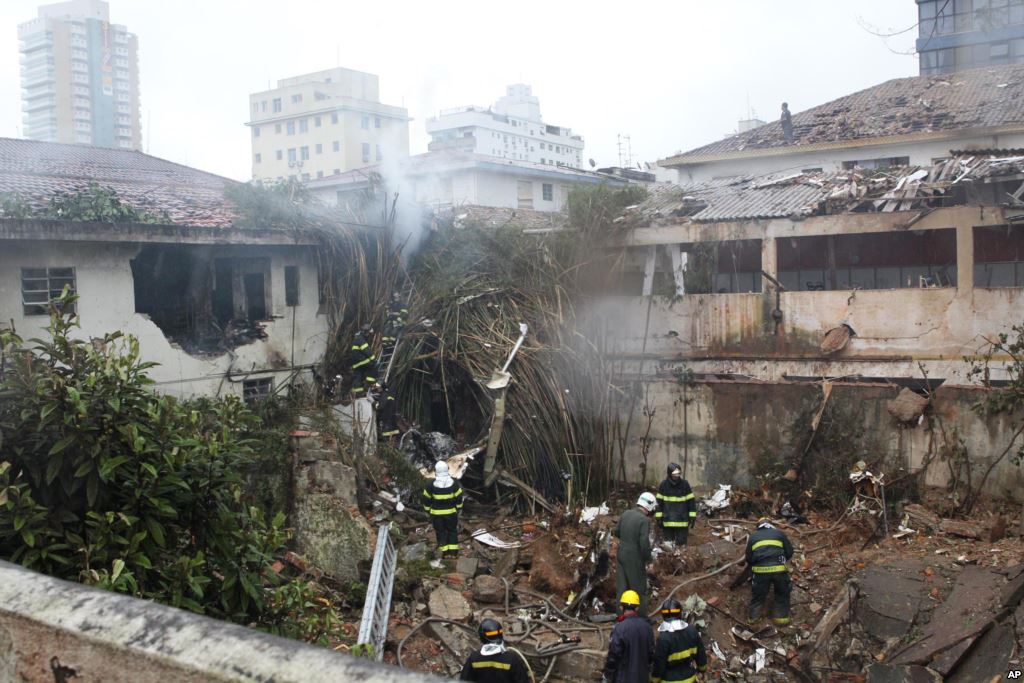
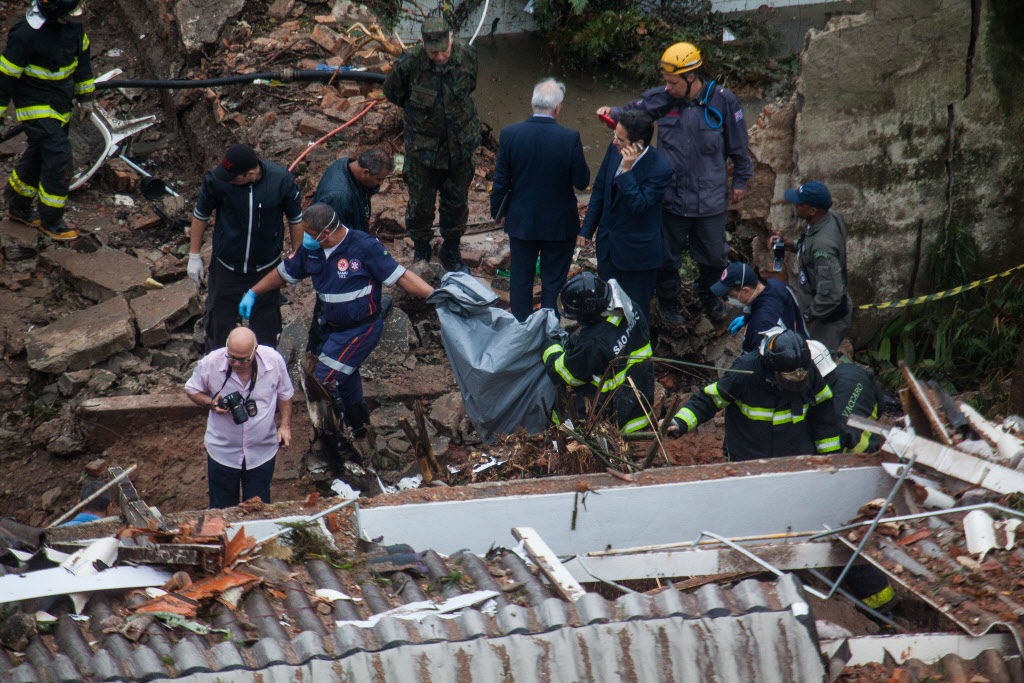
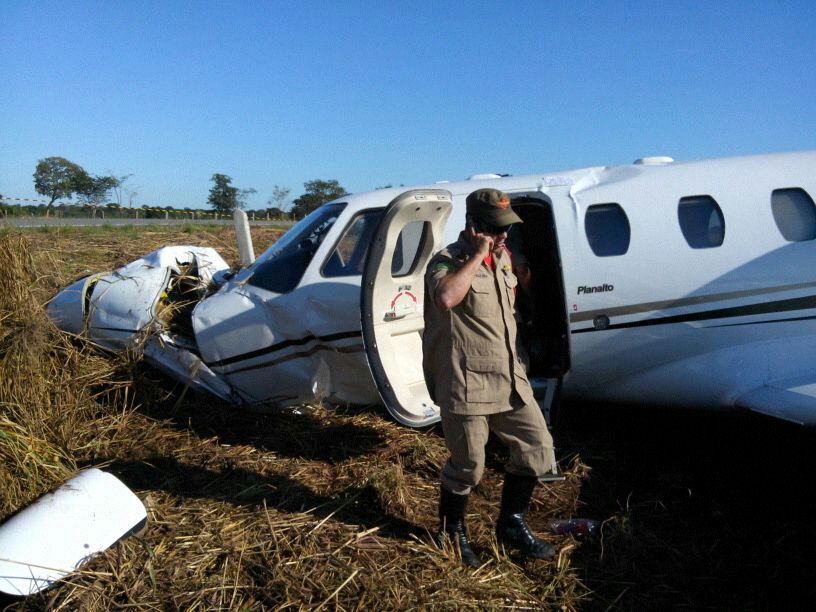
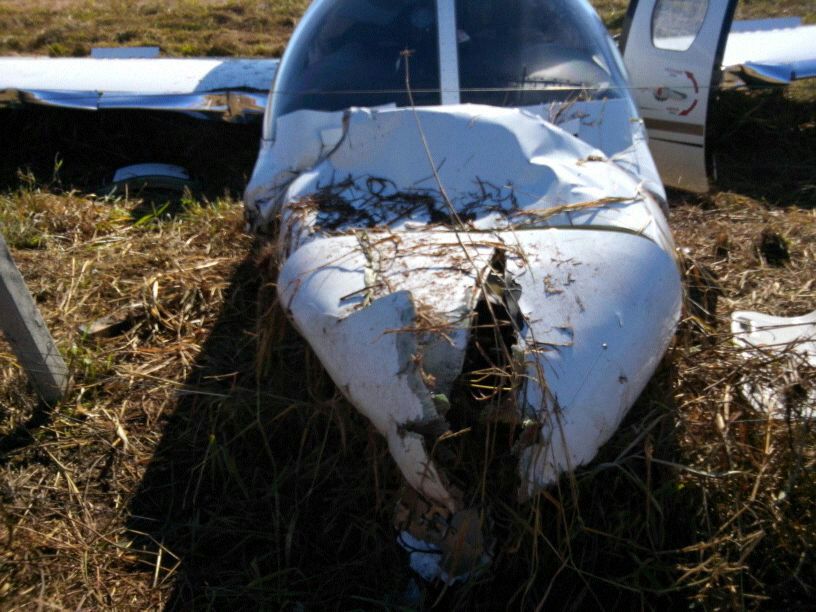
The aircraft took off from Santos Dumont Airport (SBRJ) at 12:21 UTC, on a transport flight bound for Santos Aerodrome (SBST), with two pilots and five passengers on board. During the enroute phase of the flight, the aircraft was under radar coverage of the approach control units of Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo (APP-RJ and APP-SP, respectively), and no abnormalities were observed. Upon being released by APP-SP for descent and approach toward SBST, the aircraft crew, already in radio contact with Santos Aerodrome Flight Information Service (Santos Radio), reported their intention to perform the IFR ECHO 1 RWY 35 NDB approach chart profile. After reporting final approach, the crew informed that they would make a go-around followed by a holding procedure, and call Santos Radio again. According to an observer that was on the ground awaiting the arrival of the aircraft at Santos Air Base (BAST) and to another observer at the Port of Santos, the aircraft was sighted flying over the aerodrome runway at low height, and then making a turn to the left after passing over the departure end of the runway, at which point the observers lost visual contact with the aircraft on account of the weather conditions. Moments later, the aircraft crashed into the ground. All seven occupants were killed.
Probable cause:
The following factors were identified:
- Considering the pronounced angle formed between the trajectory of the aircraft and the terrain, as well as the calculated speed (which by far exceeded the aircraft operating limit) moments before the impact, it is possible to infer that, from the moment the aircraft disappeared in the clouds, it could only have reached such speed and flown that trajectory if it had climbed considerably, to the point of being detected by the radar. Such condition presented by the aircraft may have been the result of an exaggerated application of controls.
- The making of an approach with a profile different from the one prescribed shows lack of adherence to procedures, which, in this case, may have been influenced by the self-confidence of the pilot on his piloting ability, given his prior experiences.
- Despite the lack of pressure on the part of the passengers to force compliance with the agenda, it is a known fact that this type of routine creates in the crew a self-pressure, most of the time unconscious, for accomplishing the flight schedule on account of the commitments undertaken by the candidate in campaign, and, therefore, the specific characteristics of this type of flight pose demands in terms of performance that may have influenced the pilots to operate with reduced safety margins.
- The meteorological conditions were close to the safety minimums for the approach and below the minimums for the circle-to-land procedure prescribed in the ECHO 1 approach. However, such conditions, by themselves, would not represent risk for the operation, if the profile of the ECHO 1 procedure was performed in accordance with the parameters established in the aeronautical publications and the flight parameters defined by the aircraft manufacturer. Upon verifying that the above mentioned parameters were not complied with, one observes that the meteorological conditions became a complicating factor for flying the aircraft, rendering it difficult to be stabilized on the final approach, and a go-around became necessary, as a result.
- In the scenario of the aircraft collision with the ground, there were aspects favorable to the occurrence of spatial disorientation, such as: reduction of the visibility on account of meteorological conditions, stress and workload increase due to the missed approach procedure, maneuvers with a G-load above 1.15G, and a possible loss of situational awareness. The large pitch-down angle, the high speed, and the power developed by the engines at the moment of impact are also evidence compatible with incapacitating disorientation, and point towards a contribution of this factor.
- The integration between the pilots may have been hindered by their little experience working together as one crew, and also by their different training background. In addition, the personal characteristics of the captain, as a more impositive and confident person, in contrast with the more passive posture of the copilot, may also have hampered the crew dynamics in the management of the flight.
- In the seven days preceding the day of the accident, the crew was in conformity with the Law 7183 of 5 April 1984 in relation to both duty time and rest periods. However, the analysis of copilot’s voice, speech, and language indicated compatibility with fatigue and somnolence, something that may have contributed to the degradation of the crew’s performance.
- Their lack of training of missed approach procedures in CE 560XLS+ aircraft may have demanded from the crew a higher cognitive effort in relation to the conditions required for the aircraft model, since they possibly did not have conditioned behaviors for controlling the flight and that could otherwise provide them with more agility with regard to the cockpit actions. Thus, they probably missed the skills, knowledge, and attitudes that would allow them to more adequately perform their activities in that operational context.
- Even though Santos Radio reported, in the first contact with the aircraft, that the aerodrome was operating IFR, the messages transmitted to the aircraft did not include the conditions of ceiling, visibility, and SIGMET information (ICA 100-37). This may have contributed to reducing the crew’s situational awareness, since the last information accessed by them was probably the 11:00 UTC SBST METAR, which reported VMC conditions for operation in the aerodrome. Thus, the pilots may have built a mental model of unreal SBST meteorological conditions more favorable to the operation.
- After coordination of the descent, the PR-AFA aircraft made a left turn and, for an unknown reason, deviated from the W6-airway profile, reporting six positions that were not compatible with the real flight path until the moment it started a final approach. This approach was different from the trajectory of the final approach defined for the ECHO 1 procedure, and was flown with speed parameters different from those recommended by the aircraft manufacturer. These aspects reduced the chances of the aircraft to align with the final approach in a stabilized manner. The fact that the aircraft made a low pass over the runway and then a left turn at low altitude in weather conditions below the minimum established in the circle-to-land procedure instead of performing the profile prescribed in the ECHO 1 approach chart also resulted in risks to the operation, and created conditions which were conducive to spatial disorientation.
- Since the captain had already conducted FMS visual approaches on other occasions, his acquired work-memory may have strengthened his confidence in performing the procedure again, even though in another scenario, on account of the human being tendency to rely on previous successful experiences.
- A poor perception on the part of the pilots relative to the real meteorological conditions on the approach may have compromised their level of situational awareness, thus leading the aircraft to a condition of operation below the safe minimums.
- The TAF/GAMET weather prognostics with validity up to 12:00 UTC, and available to the crew at the time the flight plan was filed at the AIS-RJ, indicated a possibility of degradation of the ceiling and visibility parameters on account of rain associated with mist, encompassing the duration of the aforementioned flight, especially in the area of SBST. The 11:00 UTC satellite image and the SIGMET valid from 10:30 UTC to 13:30 UTC, also showed an active cold front in the Southeast with stratiform cloud layers over SBST and a forecast of convective cells with northeasterly movement at an average speed of 12kt. Despite the availability of such information, the crew may not have made a more accurate analysis showing the swift deterioration of the weather conditions in the period between their takeoff from SBRJ and the approach to SBST, and thus may have failed to plan their conduct of the flight in accordance with the weather conditions forecast by the meteorological services.
- Despite having the C560 qualification required to operate the CE 560XLS+aircraft, the pilots were not checked by the employers as to their previous experience on this kind of equipment, or as to the need of transition training and/or specific formation to fly the PRAFA aircraft. The adoption of a formal process for the recruitment, selection, monitoring and evaluation of the performance of the professionals could have identified their training needs for that type of aircraft.
- Although the RBAC 61 requires pilots to undergo flight instruction and proficiency checks to switch between models of the CE 560XL family, the need of specific training was only clarified on 4 July 2014, with the publication of the ANAC Supplementary Instruction (IS 61-004, Revision A). Until that date, this need could only be determined by means of consultation of the FSB Report, made available only on the FAA website. In this context, the PR-AFA pilots would only be evaluated on the CE 560XLS+ aircraft on the occasion of their type revalidation, which would take place shortly before the expiration date of their C560 qualifications, which were valid until October 2014 (captain), and May 2015 (copilot). The fact that there was a qualification (C560) that was shared for the operation of C560 Citation V, C560 Encore, C560 Encore+, CE 560XL, CE 560XLS, or CE 560XLS + aircraft was not enough to make the DCERTA system refuse flight plans filed by pilots who lacked proper training to operate one of the aforementioned aircraft models. The RBAC 67 contained physical and mental health requirements which were not clear, inducing physicians to resort to other publications for guidance and support of their decisions and judgments relative to the civil aviation personnel. The absence of clear requirements to be adopted as the acceptable minimum for the exercise of the air activity, led the physicians responsible for judging the pilots’ health inspections’ to use their own discretion on the subject, opening gaps that could allow professionals not fully qualified to perform functions in flight below the minimum acceptable safety levels.
- Considering the possibility that the captain accumulated tasks as a result of a possible difficulty of the copilot in assisting him at the beginning of the missed approach procedure, such accumulation may have exceeded his ability to deal with the tasks, leading him to committing piloting errors and/or experiencing spatial disorientation.