Crash of a Honda HA-420 HondaJet in Foz do Iguaçu
Date & Time:
Sep 24, 2018 at 1342 LT
Registration:
PR-TLZ
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Curitiba – Foz do Iguaçu
MSN:
420-00068
YOM:
2017
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
1
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
77.00
Copilot / Total hours on type:
14
Circumstances:
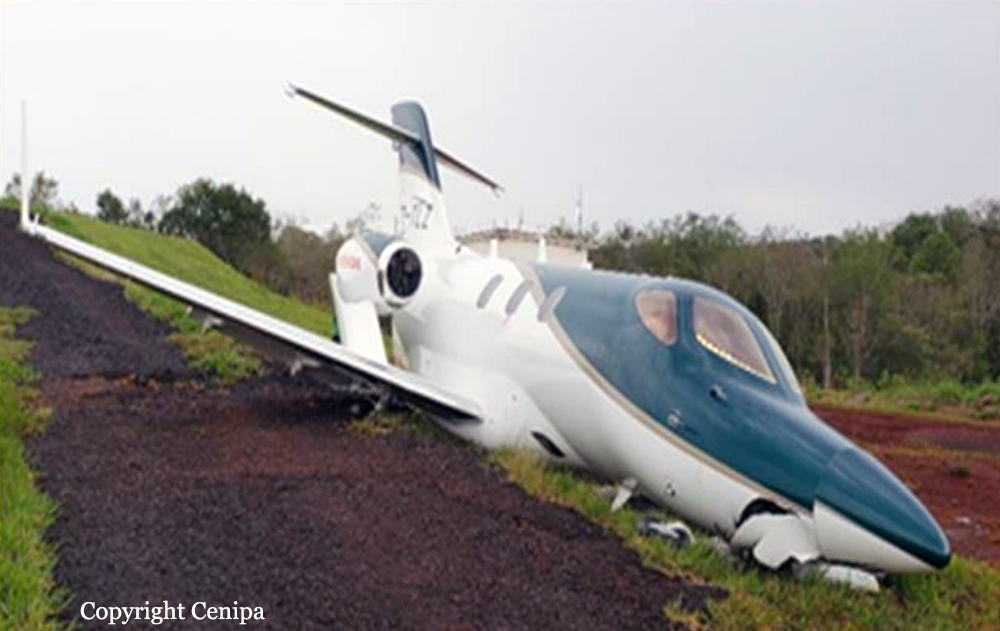
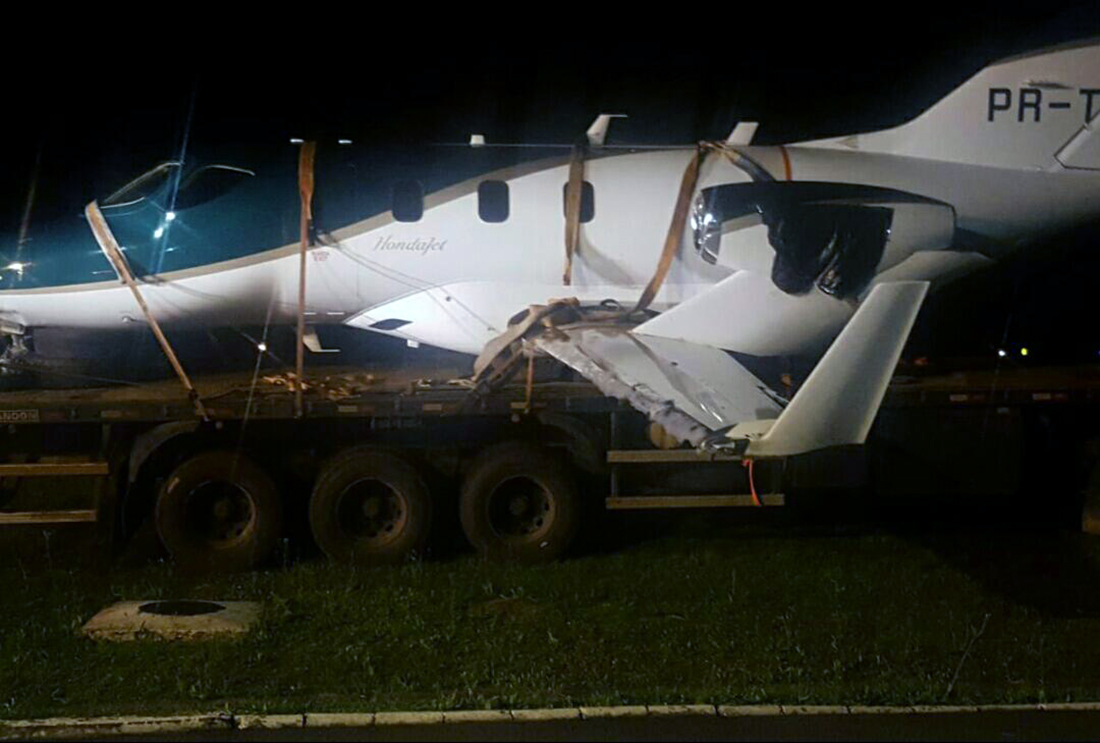
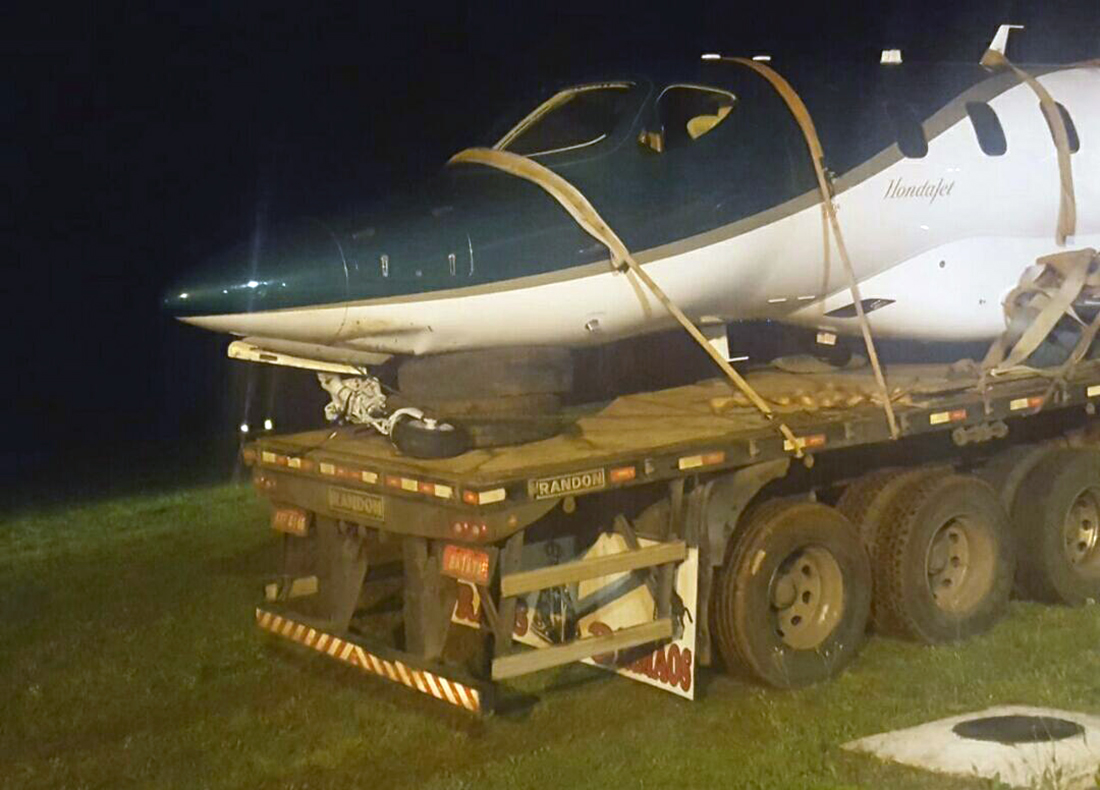
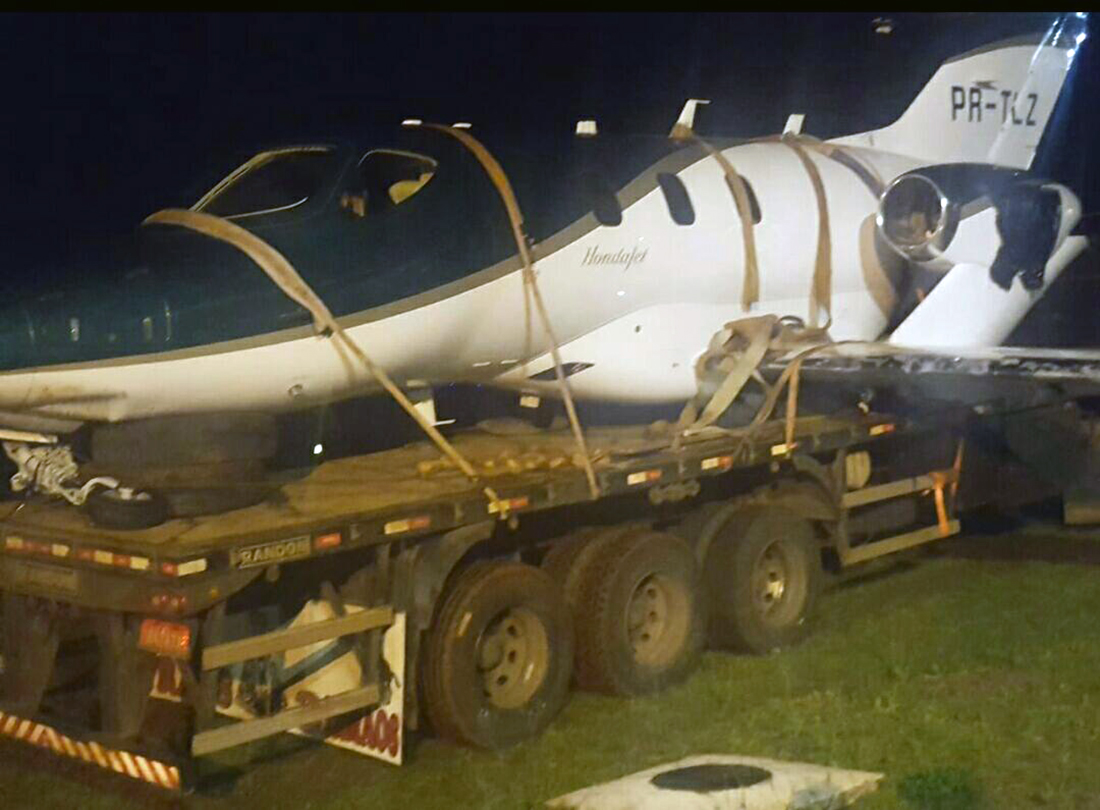
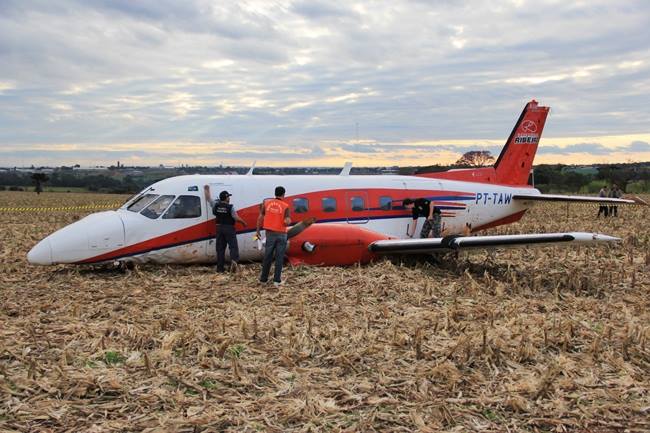
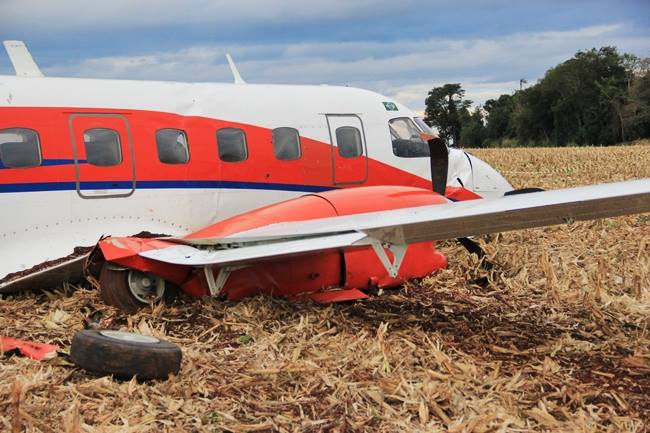
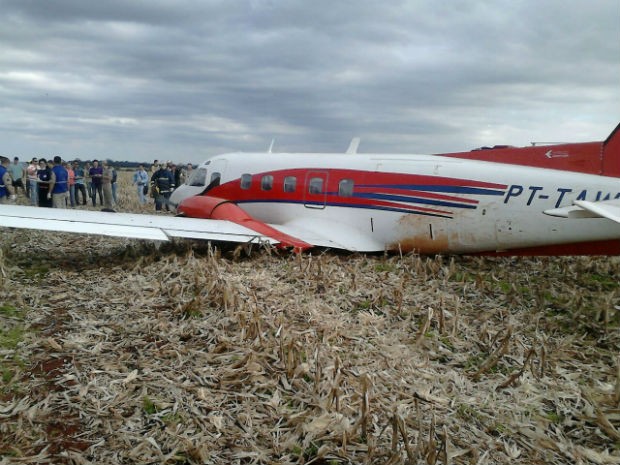
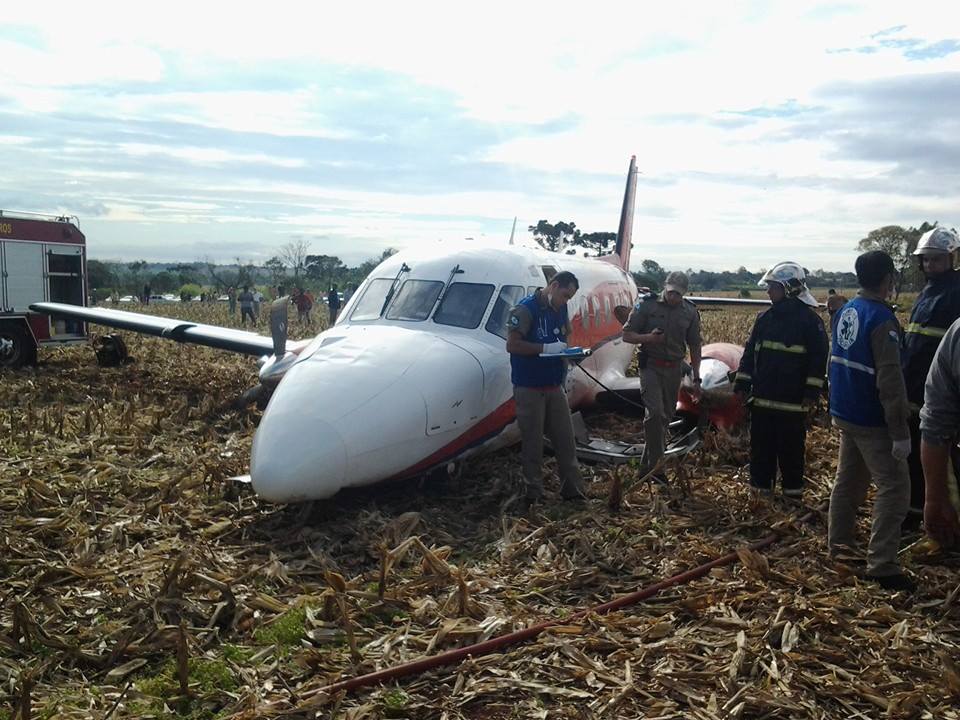
The airplane departed Curitiba-Afonso Pena Airport at 1240LT on an executive flight to Foz do Iguaçu, carrying one passenger and two pilots. Following an uneventful flight, the crew started the descent to Foz do Iguaçu-Cataratas Airport. The aircraft was stabilized and landed on wet runway 32. After touchdown, the crew encountered difficulties to stop the aircraft that overran and came to rest into a ravine. All three occupants evacued safely and the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.
Probable cause:
The following findings were identified:
- The approach was considered stabilized;
- The required landing distance of 6,431t (1,960m) was compatible for the operation, since the LDA of runway 32 at SBFI was 7,201ft (2,195m);
- There was no evidence of malfunction of the aircraft brake system that could have caused the runway excursion;
- At the time of landing, the runway was wet with a significant amount of water on the pavement;
- The estimated deceleration corresponded to what would be expected on a very wet runway (> 3mm of water) with hydroplaning of the tires at higher speeds;
- The friction and macrotexture measurements had normal parameters and did not contribute to the aircraft's poor deceleration;
- The characteristics of the precipitation over threshold 14 associated with the large variations in wind direction and intensity were consistent with the windshear phenomenon, resulting from a microburst;
- The PR-TLZ sensors did not detect the occurrence of windshear during the landing approach;
- A sudden increase in the calibrated speed that peaked at 32kt altered the aircraft's lift and, consequently, reduced the tires' grip on the ground, resulting in poor braking in the parts where the ground speed was lower;
- The speedbrakes were not extended during the run after landing, contrary to what was prevised in the AFM;
- The aircraft ran the full length of the runway, overpassed its limits and crashed into a ravine;
- There was a windshear alert issued about 30 seconds after the landing of the PRTLZ by an aircraft that was at the threshold 32;
- The aircraft had substantial damage; and
- The crewmembers and the passenger left unharmed.
Contributing factors:
- Control skills – undetermined
Despite the low contribution of the speedbrakes to the reduction of the landing distance, this device represents a deceleration resource through aerodynamic drag that should not be neglected, especially during landing on wet runways, and could have contributed to avoiding runway excursion.
- Adverse meteorological conditions – a contributor
The large variation in wind intensity peaked at 32 kt. This variation lasted 13 seconds and raised the indicated speed from 76 kt to 108 kt. Considering that the speed of 108 kt was very close to the VREF (111 KCAS), it can be stated that this phenomenon altered the aircraft's lift and, consequently, reduced the tires' grip on the ground, leading to poor braking.
- The approach was considered stabilized;
- The required landing distance of 6,431t (1,960m) was compatible for the operation, since the LDA of runway 32 at SBFI was 7,201ft (2,195m);
- There was no evidence of malfunction of the aircraft brake system that could have caused the runway excursion;
- At the time of landing, the runway was wet with a significant amount of water on the pavement;
- The estimated deceleration corresponded to what would be expected on a very wet runway (> 3mm of water) with hydroplaning of the tires at higher speeds;
- The friction and macrotexture measurements had normal parameters and did not contribute to the aircraft's poor deceleration;
- The characteristics of the precipitation over threshold 14 associated with the large variations in wind direction and intensity were consistent with the windshear phenomenon, resulting from a microburst;
- The PR-TLZ sensors did not detect the occurrence of windshear during the landing approach;
- A sudden increase in the calibrated speed that peaked at 32kt altered the aircraft's lift and, consequently, reduced the tires' grip on the ground, resulting in poor braking in the parts where the ground speed was lower;
- The speedbrakes were not extended during the run after landing, contrary to what was prevised in the AFM;
- The aircraft ran the full length of the runway, overpassed its limits and crashed into a ravine;
- There was a windshear alert issued about 30 seconds after the landing of the PRTLZ by an aircraft that was at the threshold 32;
- The aircraft had substantial damage; and
- The crewmembers and the passenger left unharmed.
Contributing factors:
- Control skills – undetermined
Despite the low contribution of the speedbrakes to the reduction of the landing distance, this device represents a deceleration resource through aerodynamic drag that should not be neglected, especially during landing on wet runways, and could have contributed to avoiding runway excursion.
- Adverse meteorological conditions – a contributor
The large variation in wind intensity peaked at 32 kt. This variation lasted 13 seconds and raised the indicated speed from 76 kt to 108 kt. Considering that the speed of 108 kt was very close to the VREF (111 KCAS), it can be stated that this phenomenon altered the aircraft's lift and, consequently, reduced the tires' grip on the ground, leading to poor braking.
Final Report: