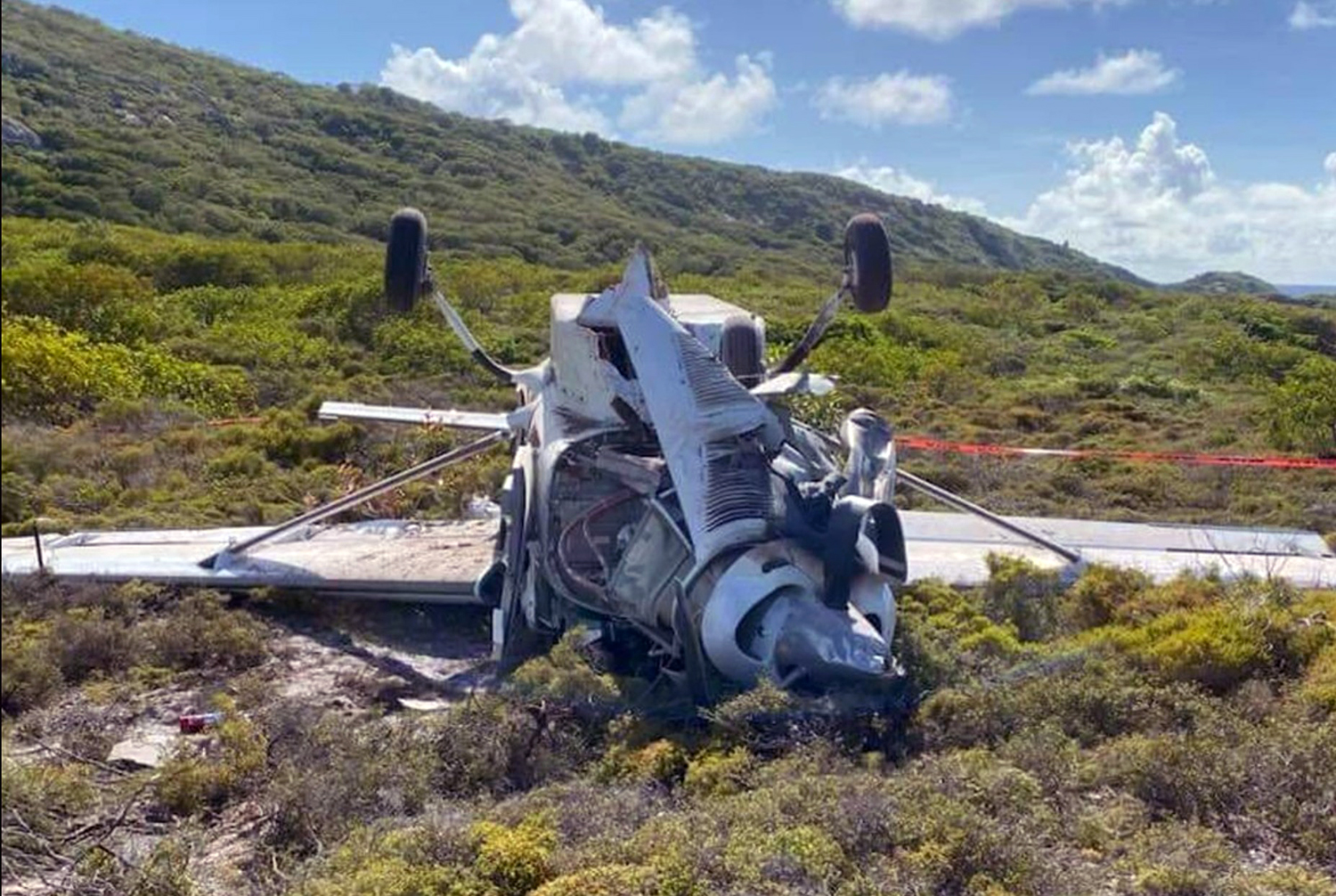
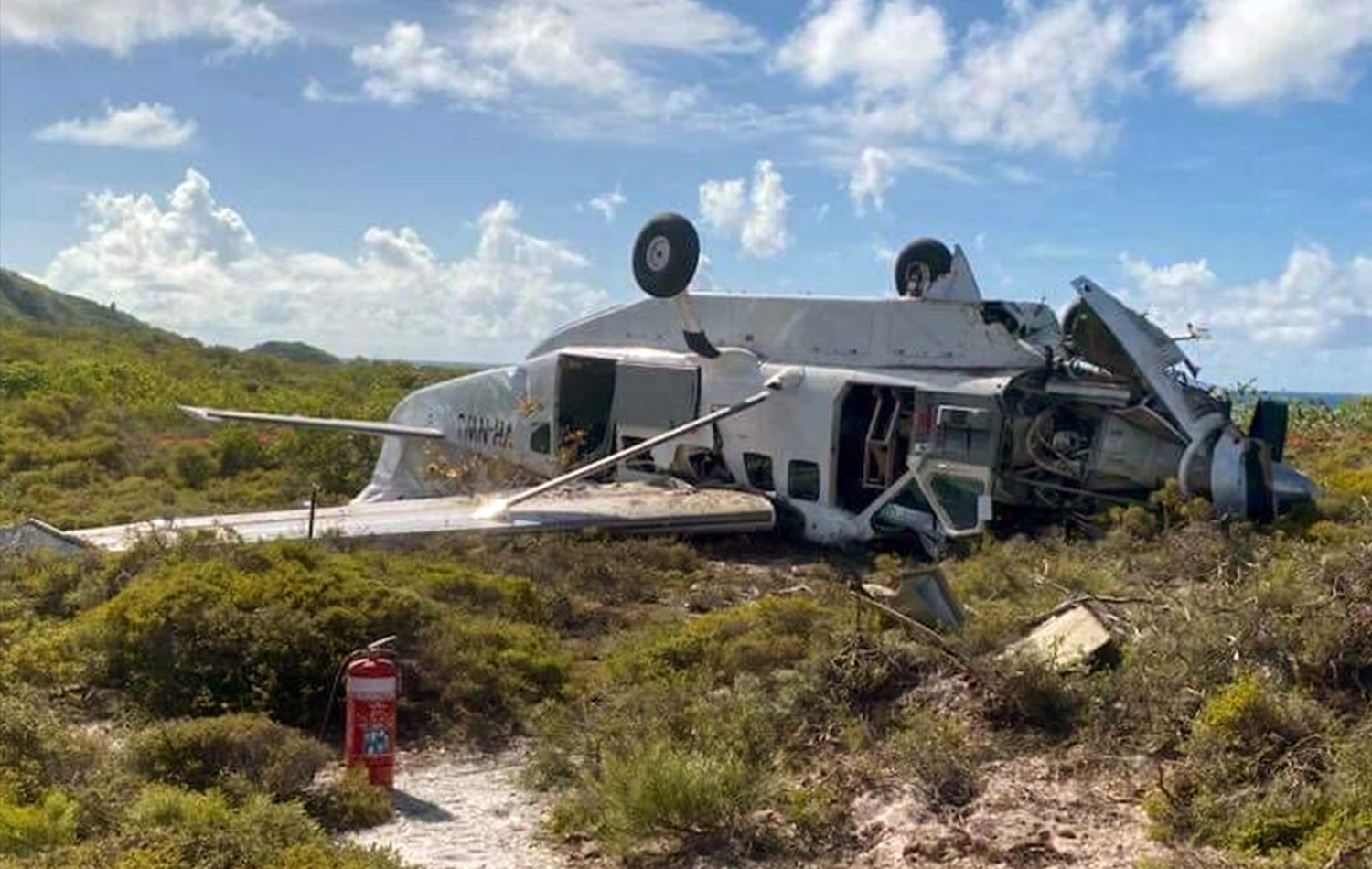
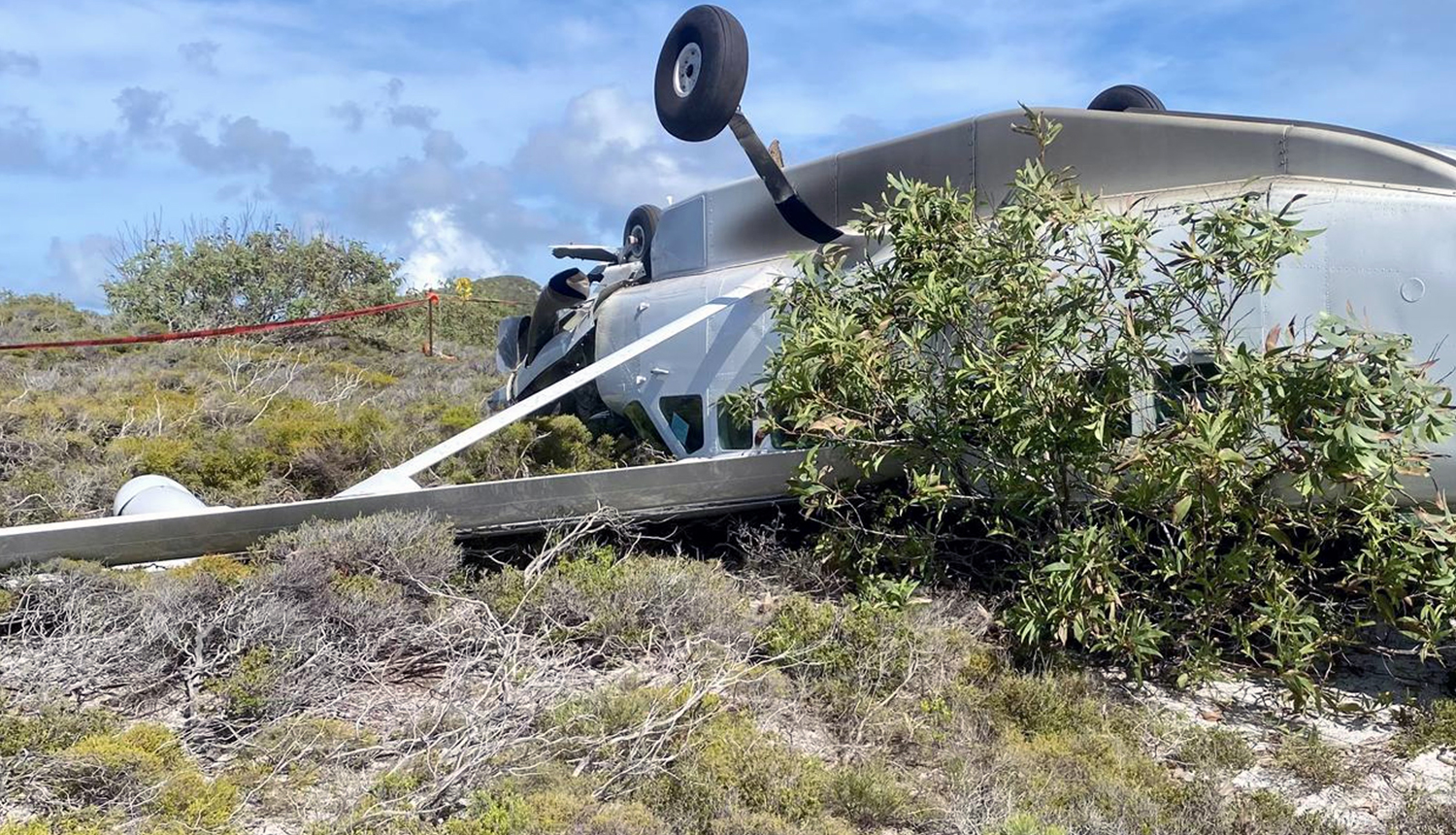
Circumstances:
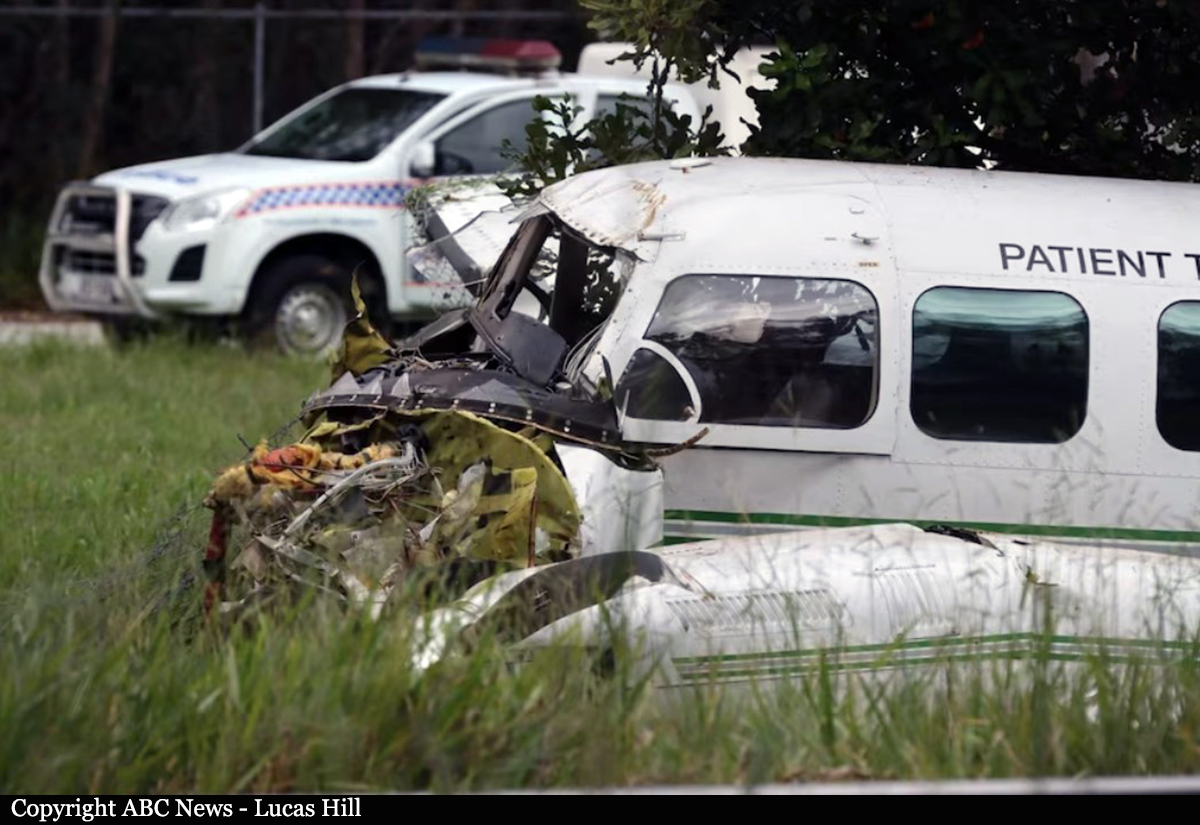
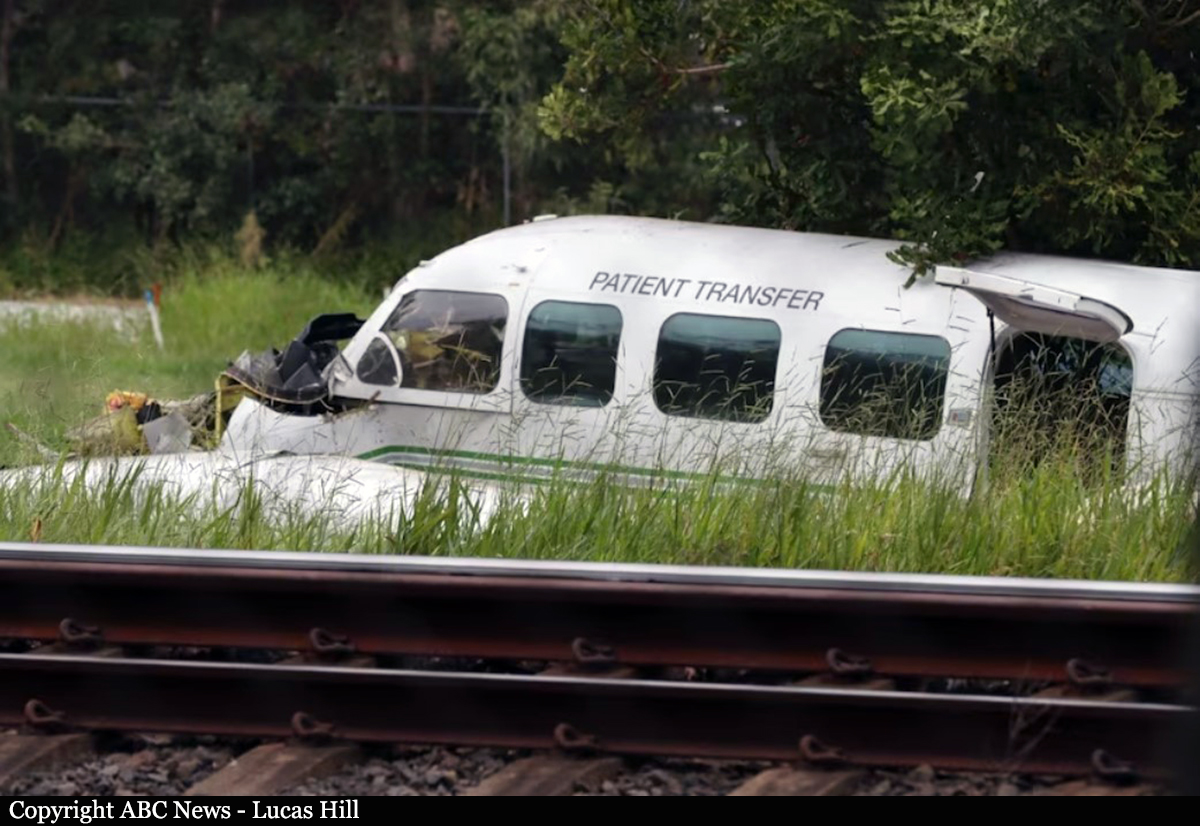
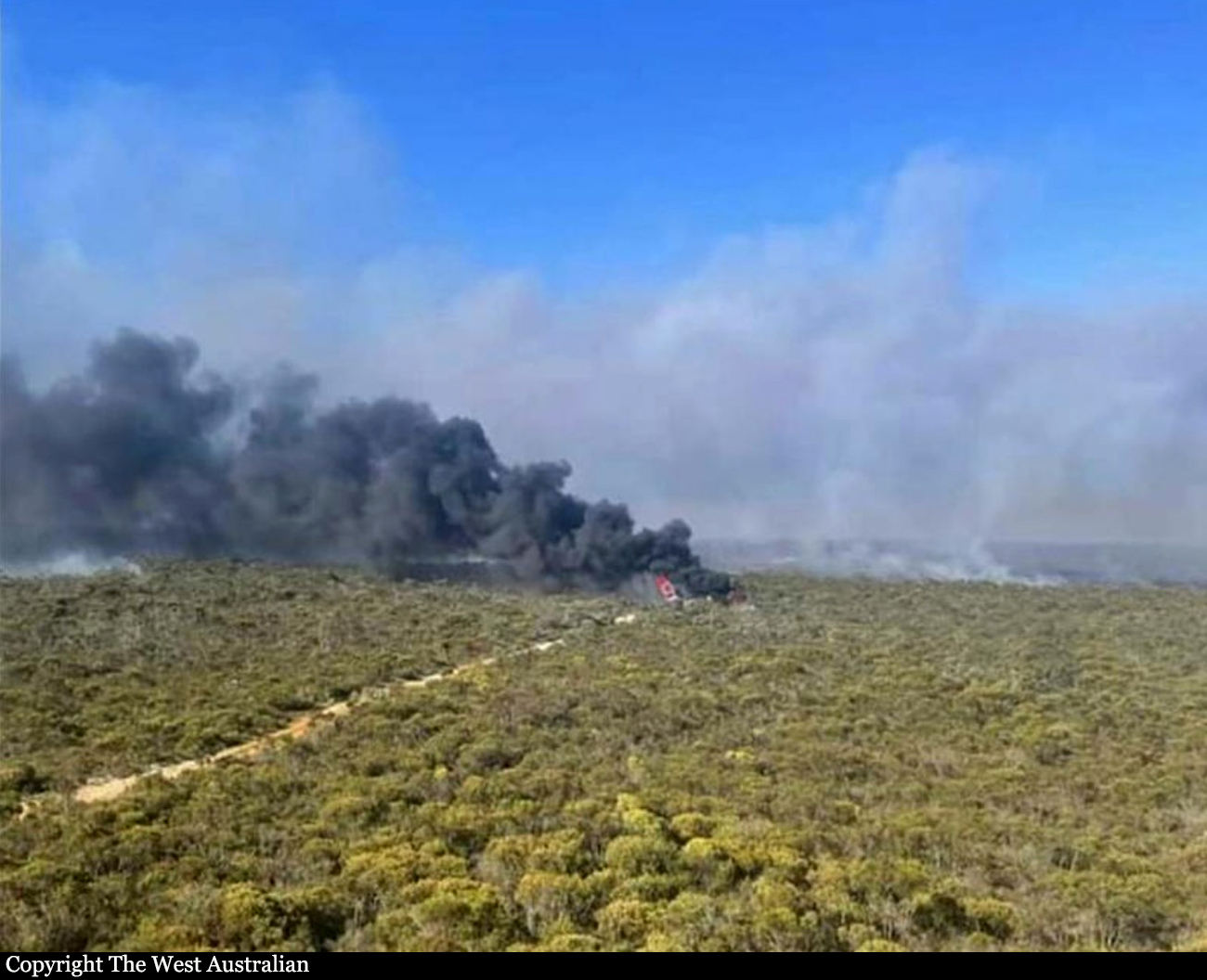
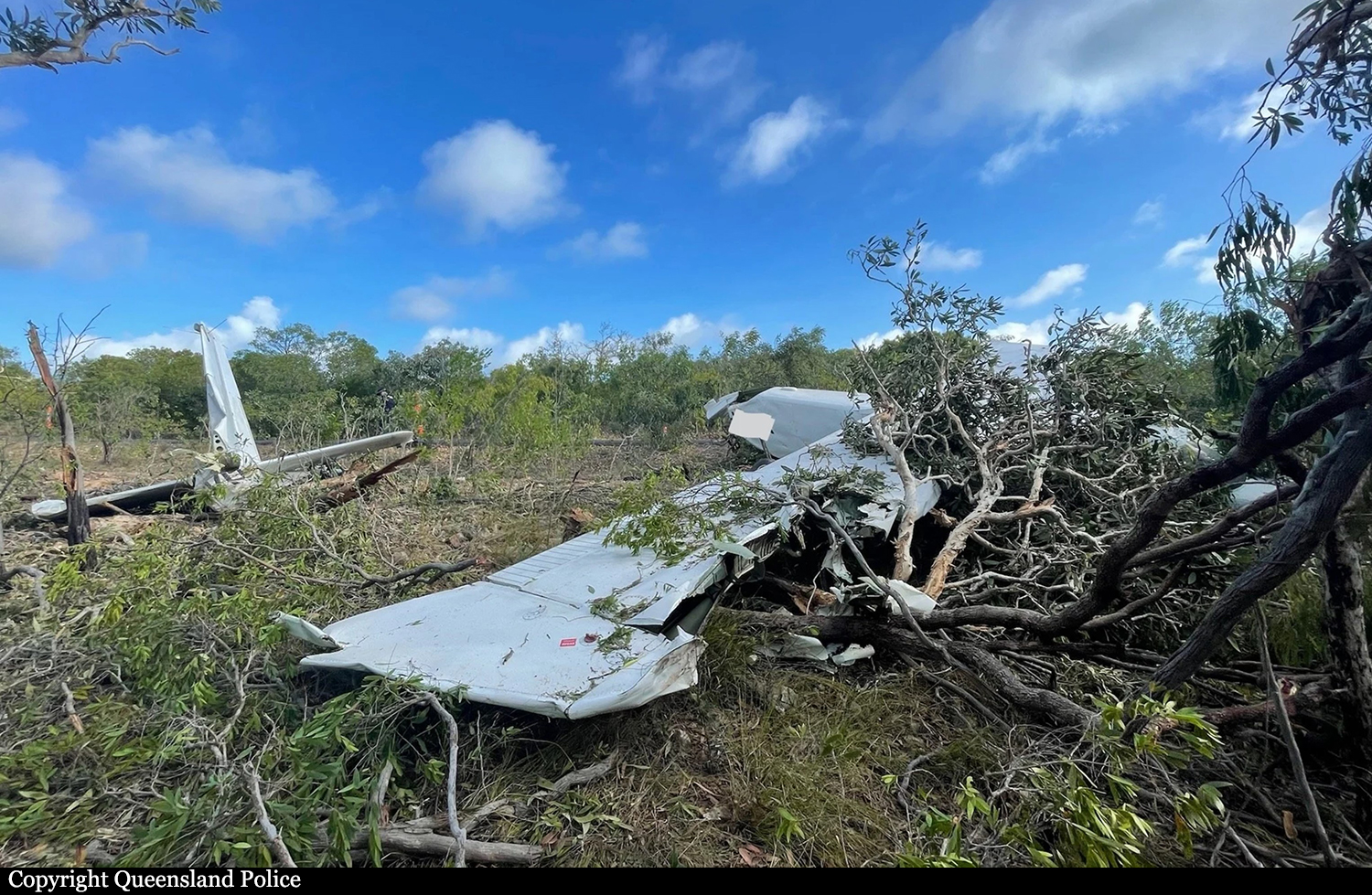
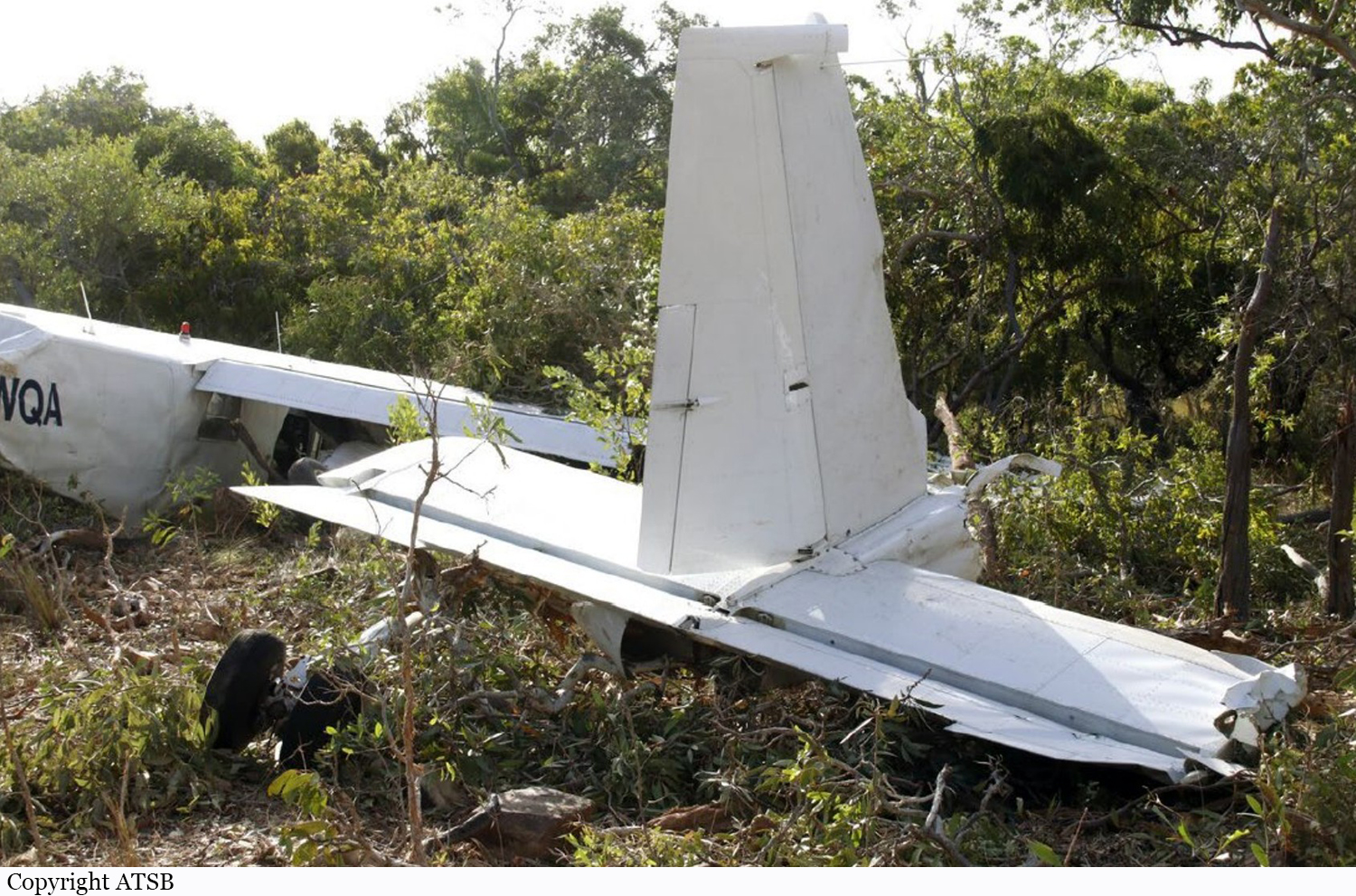
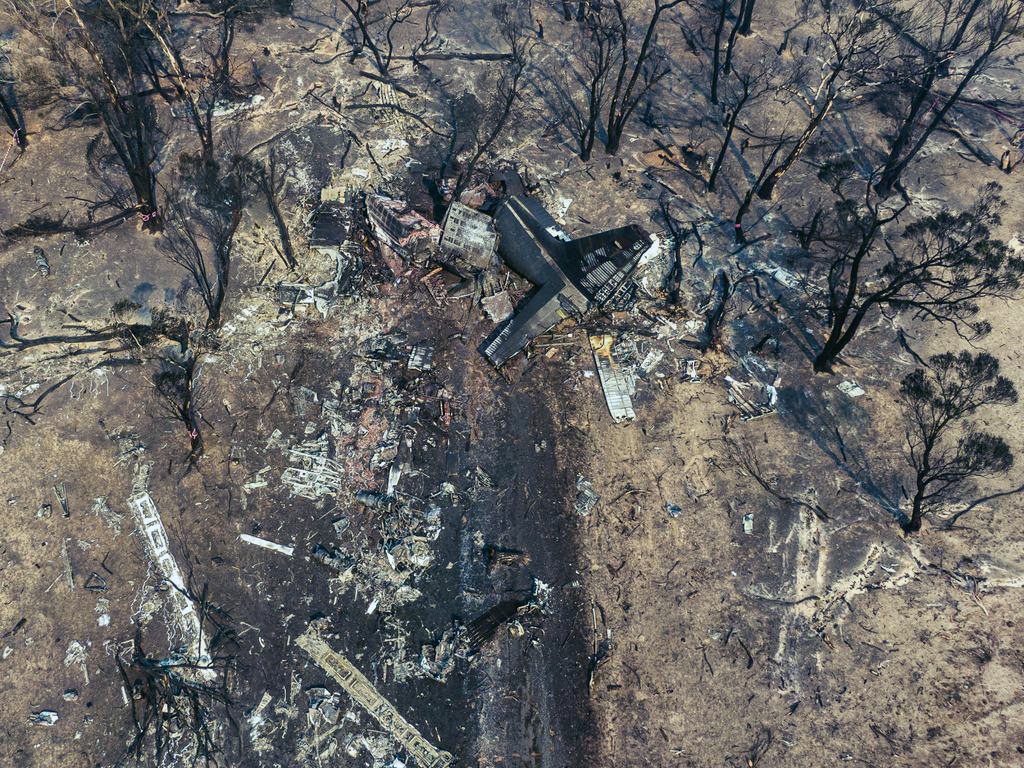
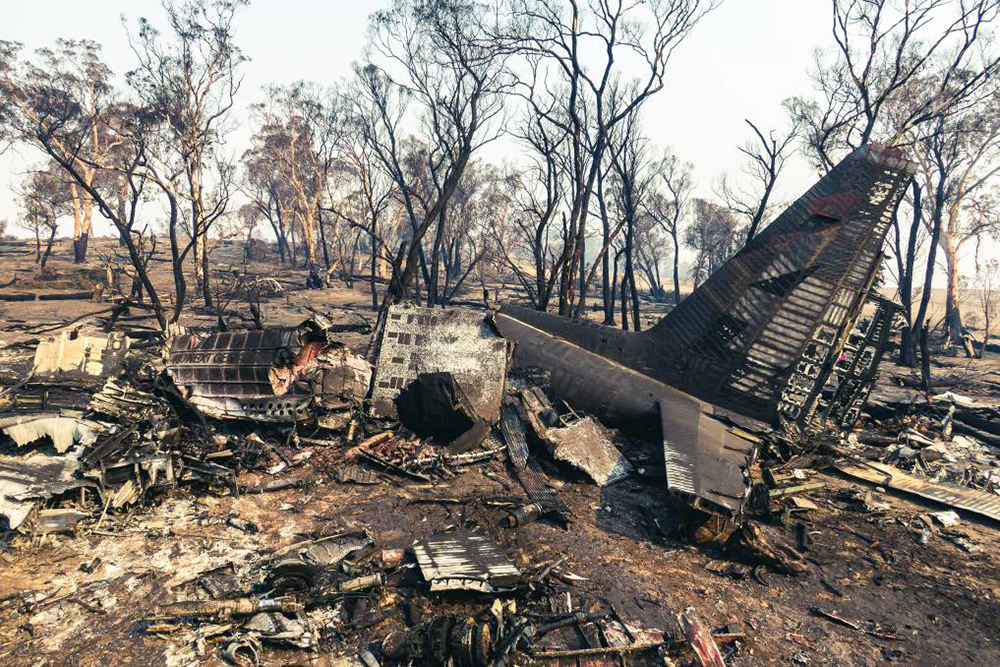
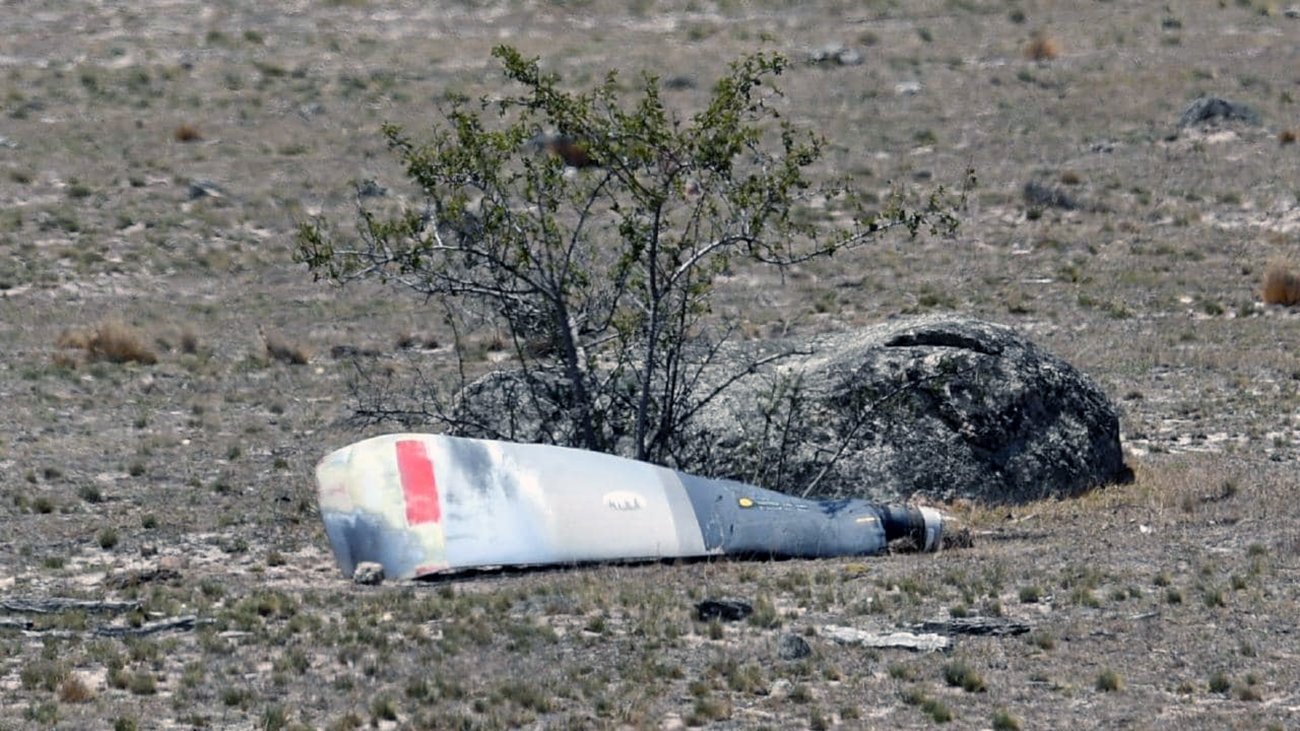
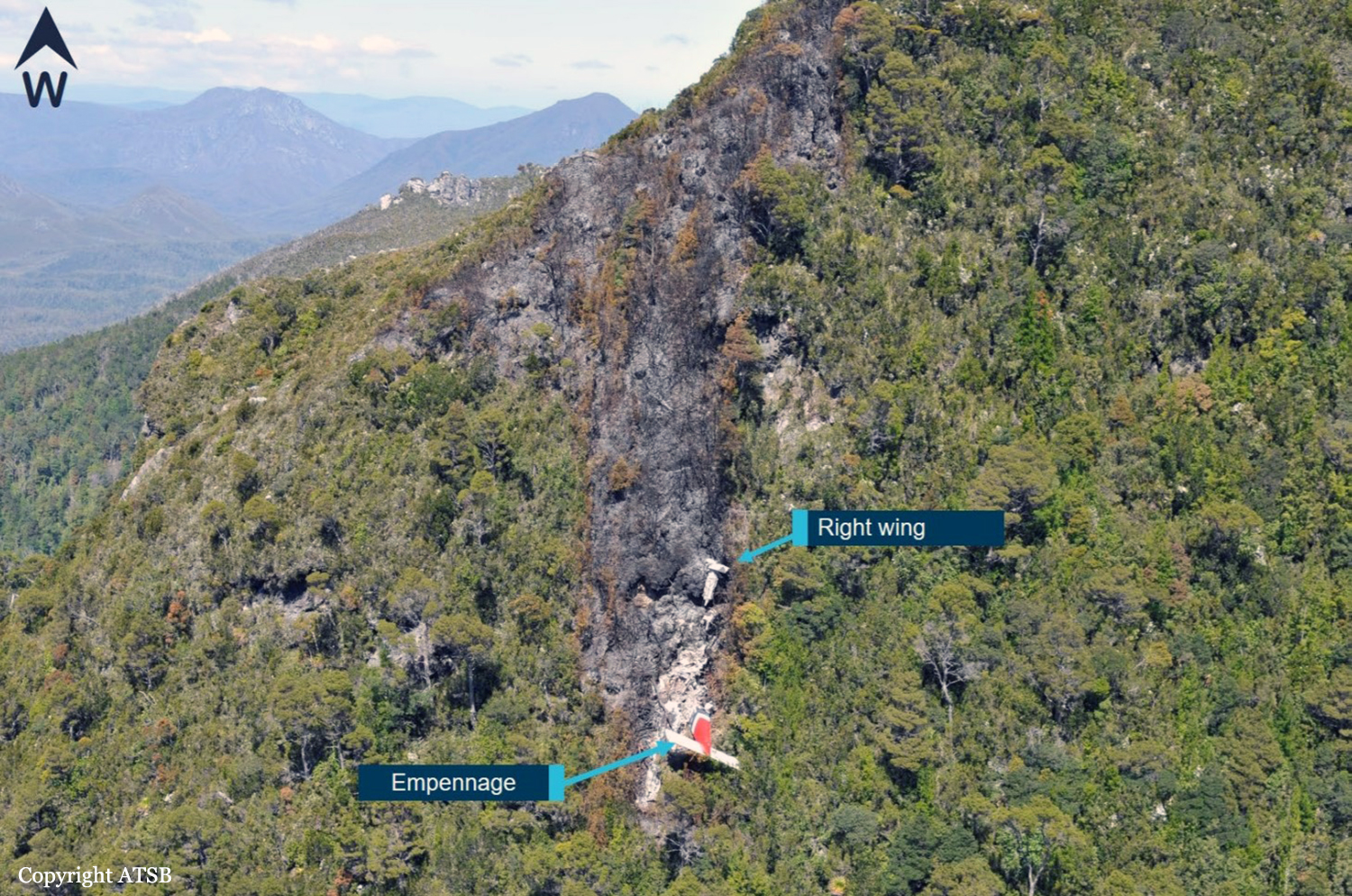
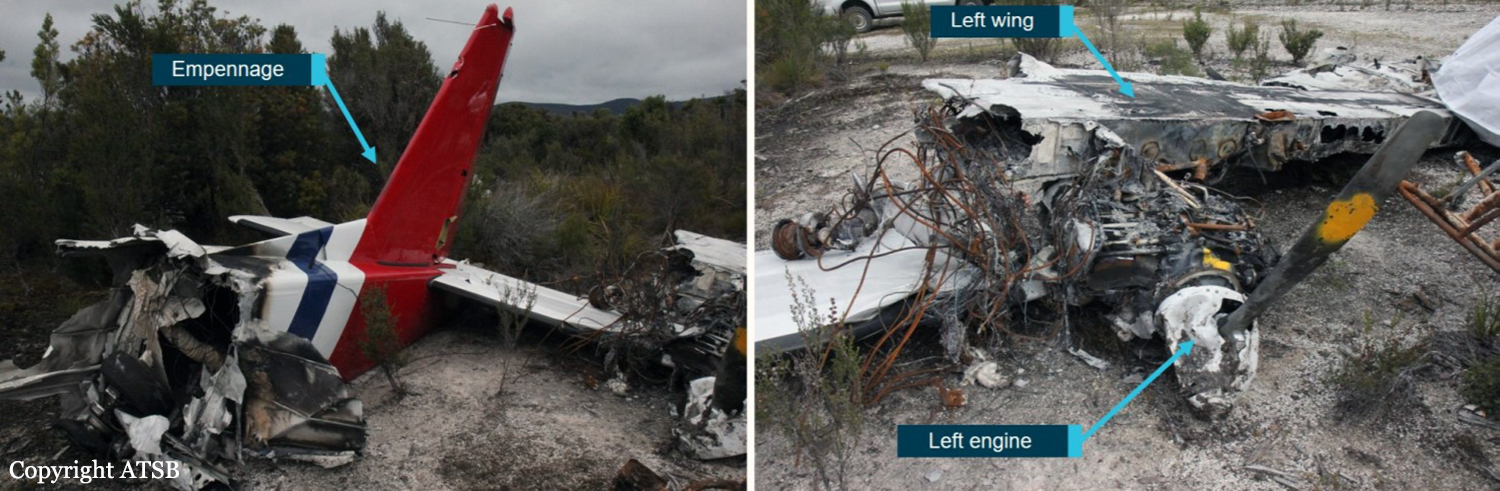
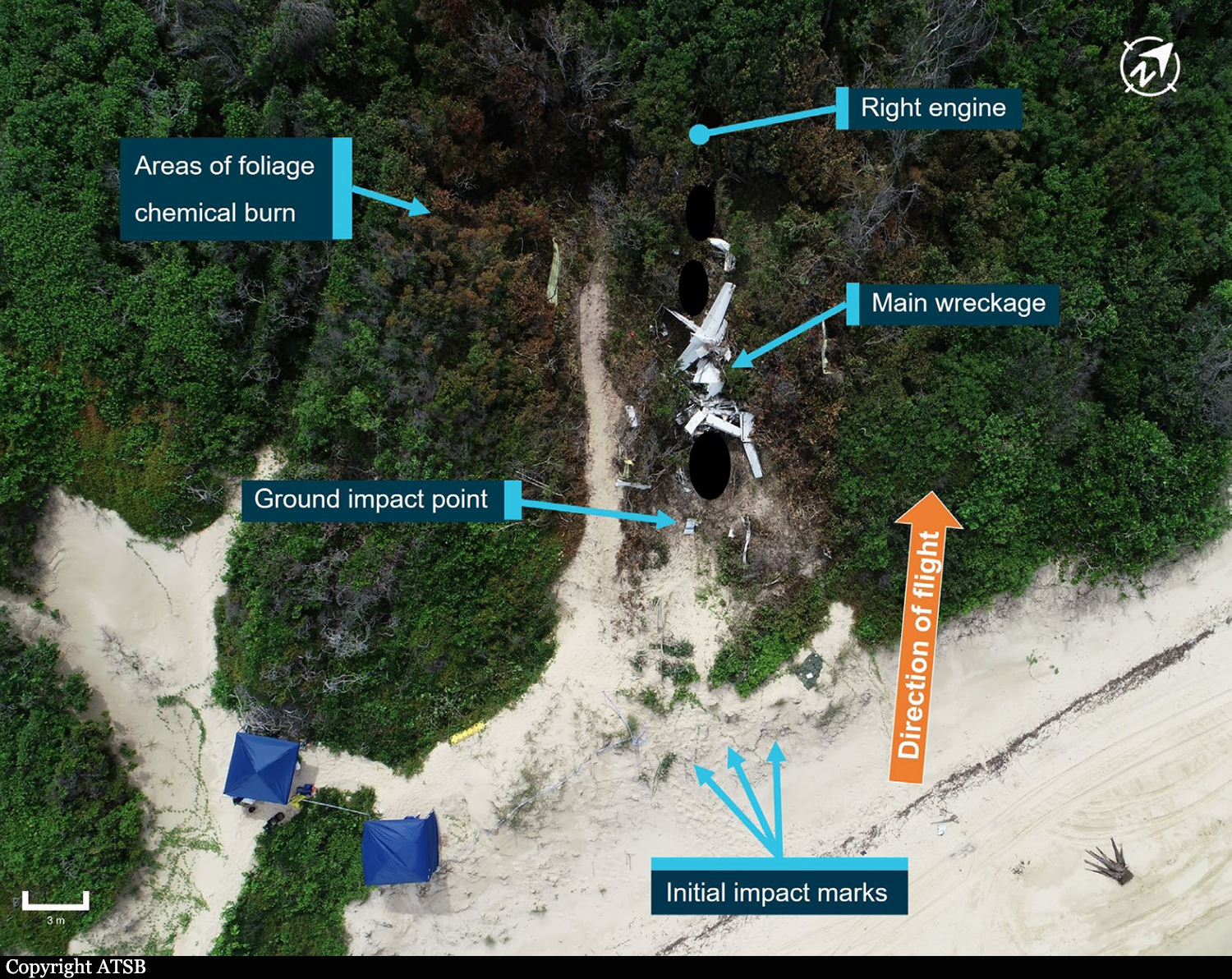
At about 1205, while B137 was overhead the Adaminaby fire-ground, and about the same time the SAD logged the birddog rejection, B134 departed Richmond as initial attack. On board were the PIC, the copilot and flight engineer. In response to the draft report, the RFS provided excerpts from the state operations controller (SOC) log. An entry was written in the log by the SOC following the accident. The SOC noted having been advised that the birddog had indicated it was ‘not safe to fly’ and that B137 was not returning to the area until the conditions had eased. However, B134 would continue with the PIC to make the ‘decision of safety of bombing operations’. The RFS advised the ATSB that the SOC had the authority to cancel B134’s tasking, but instead allowed it to proceed, with the intention of gathering additional intelligence to assist in determining whether further aerial operations would proceed. The RFS further reported that this indicated an ongoing intelligence gathering and assessment process by the SOC. At about 1235, while returning to Richmond, the PIC of B137 heard the PIC of B134 on the Canberra approach frequency, and contacted them via their designated operating frequency. At that time, B134 was about 112 km north-east of Adaminaby, en route to the fire-ground. In this conversation, the PIC of B137 informed them of the actual conditions and that they would not be returning to Adaminaby. The PIC of B137 reported that they could not recall the specific details of the call, but that the conversation included that they were ‘getting crazy winds’ and ‘you can go take a look’ ’but I am not going back’. It was also noted that the PIC of B134 had asked several questions. It was reported by the majority of the operator’s pilots that, despite receiving information from another pilot, they would have also continued with the tasking under these circumstances, to assess the conditions themselves. At about 1242, the crew of B134 contacted air traffic control to advise them of the coordinates they would be working at, provide an ‘ops normal’ call time, and confirm there was no reported instrument flight rules aircraft in the area. About 5 minutes later, the Richmond ABM also attempted to contact the crew of B134 to confirm ‘ops normal’, firstly by radio, and then by text to the PIC’s mobile phone, but did not receive a response. The automatic dependent surveillance broadcast (ADS-B) data showed that, after arriving at the Adaminaby fire-ground at about 1251, the crew of B134 completed several circuits at about 2,000 ft AGL. At about 1255, the crew advised the Cooma ARO that it was too smoky and windy to complete a retardant drop at that location. The Cooma ARO then provided the crew with the approximate coordinates of the Good Good fire, about 58 km to the east of Adaminaby. The ARO further indicated that they had no specific requirements, but they could look for targets of opportunity, with the objective of conducting structure and property protection near Peak View. At about 1259, the crew of B134 contacted air traffic control to advise that they had been re-tasked to the Good Good fire-ground, and provided updated coordinates. At about the same time, the RFS ground firefighters at the Good Good fire-ground, near Feeney’s Road in Peak View, contacted the Cooma FCC and requested additional assets for property protection. They were advised that a LAT would be passing overhead in about 10 minutes. The firefighters acknowledged the intention of a LAT retardant drop and advised the Cooma FCC they would wait in open country on Feeney’s Road, clear of any properties targeted for protection. At about 1307, B134 arrived overhead the drop area. The drop area was located to the east of a ridgeline, with the fire on the western side of the ridgeline. The aircraft’s recorded track data (SkyTrac) showed that the crew conducted 3 left circuits, at about 1,500 ft, 500 ft and 1,000 ft AGL respectively, prior to commencing the drop circuit. At about 1312, after conducting about 2 circuits, they advised the Cooma ARO of their intention to complete multiple drops on the eastern side of the Good Good fire, and that they would advise the coordinates after the first delivery. At 1315:15, a partial retardant drop was conducted on a heading of about 190°, at about 190 ft AGL (3,600 ft above mean sea level). During the drop, about 1,200 US gallons (4,500 L) of fire retardant was released over a period of about 2 seconds. A ground speed of 144 kt was recorded at the time of the drop. A witness video taken by ground fire-fighters captured the drop and showed the aircraft immediately after the drop in an initial left turn with a positive rate of climb, before it became obscured by smoke. While being intermittently obscured by smoke, the aircraft climbed to about 330 ft AGL (3,770 ft above mean sea level). At about this time, ATSB analysis of the video showed that the aircraft was rolling from about 18° left angle of bank to about a 6° right angle of bank. Following this, the aircraft descended and about 17 seconds after the completion of the partial retardant drop, it was seen at a very low height above the ground, in a slight left bank. Video analysis and accident site examination showed there was no further (emergency) drop of retardant. Throughout this period, the recorded groundspeed increased slightly to a maximum of 151 kt. Shortly after, there was a significant left roll just prior to ground impact. At about 1315:37, the aircraft collided with terrain and a post-impact fuel-fed fire ensued. The 3 crew were fatally injured and the aircraft was destroyed. A review of the Airservices Australia audio recording of the applicable air traffic control frequency found no distress calls were received by controllers prior to the impact.
Probable cause:
The following contributing factors were identified:
- Hazardous weather conditions were forecast and present at the drop site near Peak View, which included strong gusting winds and mountain wave activity, producing turbulence. These
conditions were likely exacerbated by the fire and local terrain.
- The Rural Fire Service continued the B134 tasking to Adaminaby when they learned that no other aircraft would continue to operate due to the environmental conditions. In addition, they relied on the pilot in command to assess the appropriateness of the tasking to Adaminaby without providing them all the available information to make an informed decision on flight safety.
- The pilot in command of B134 accepted the Adaminaby fire-ground tasking, which was in an area of forecast mountain wave activity and severe turbulence. After assessing the conditions as unsuitable, the crew accepted an alternate tasking to continue to the Good Good (Peak View) fire-ground, which was subject to the same weather conditions. The acceptance of these taskings were consistent with company practices.
- Following the partial retardant drop and left turn, the aircraft was very likely subjected to hazardous environmental conditions including low-level windshear and an increased tailwind component, which degraded the aircraft’s climb performance.
- While at a low height and airspeed, it was likely the aircraft aerodynamically stalled, leading to a collision with terrain.
- Coulson Aviation's safety risk management processes did not adequately manage the risks associated with large air tanker operations. There were no operational risk assessments conducted or a risk register maintained. Further, as safety incident reports submitted were mainly related to maintenance issues, operational risks were less likely to be considered or monitored. Overall, this limited their ability to identify and implement mitigations to manage the risks associated with their aerial firefighting operations. (Safety issue)
- Coulson Aviation did not provide a pre-flight risk assessment for their firefighting large air tanker crews. This would provide predefined criteria to ensure consistent and objective decision-making with accepting or rejecting tasks, including factors relating to crew, environment, aircraft and external pressures. (Safety issue)
- The New South Wales Rural Fire Service had limited large air tanker policies and procedures for aerial supervision requirements and no procedures for deployment without aerial supervision.(Safety issue)
- The New South Wales Rural Fire Service did not have a policy or procedures in place to manage task rejections, nor to communicate this information internally or to other pilots working in the same area of operation. (Safety issue)
Other factors that increased risk:
- The B134 crew were very likely not aware that the 'birddog' pilot had declined the tasking to Adaminaby fire-ground, and the smaller fire-control aircraft had ceased operations in the area, due to the hazardous environmental conditions
- In the limited time available, the remainder of the fire-retardant load was not jettisoned prior to the aircraft stalling.
- Coulson Aviation did not include a windshear recovery procedure or scenario in their C-130 Airplane Flight Manual and annual simulator training respectively, to ensure that crews consistently and correctly responded to a windshear encounter with minimal delay. (Safety issue)
- Coulson Aviation fleet of C-130 aircraft were not fitted with a windshear detection system, which increased the risk of a windshear encounter and/or delayed response to a windshear encounter during low level operations. (Safety issue)
- The New South Wales Rural Fire Service procedures allowed operators to determine when pilots were initial attack capable. However, they intended for the pilot in command to be certified by the United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service certification process. (Safety issue)
Other findings:
- The aircraft's cockpit voice recorder did not record the accident flight, which resulted in a valuable source of safety information not being available. This limited the extent to which potential factors contributing to the accident could be identified.