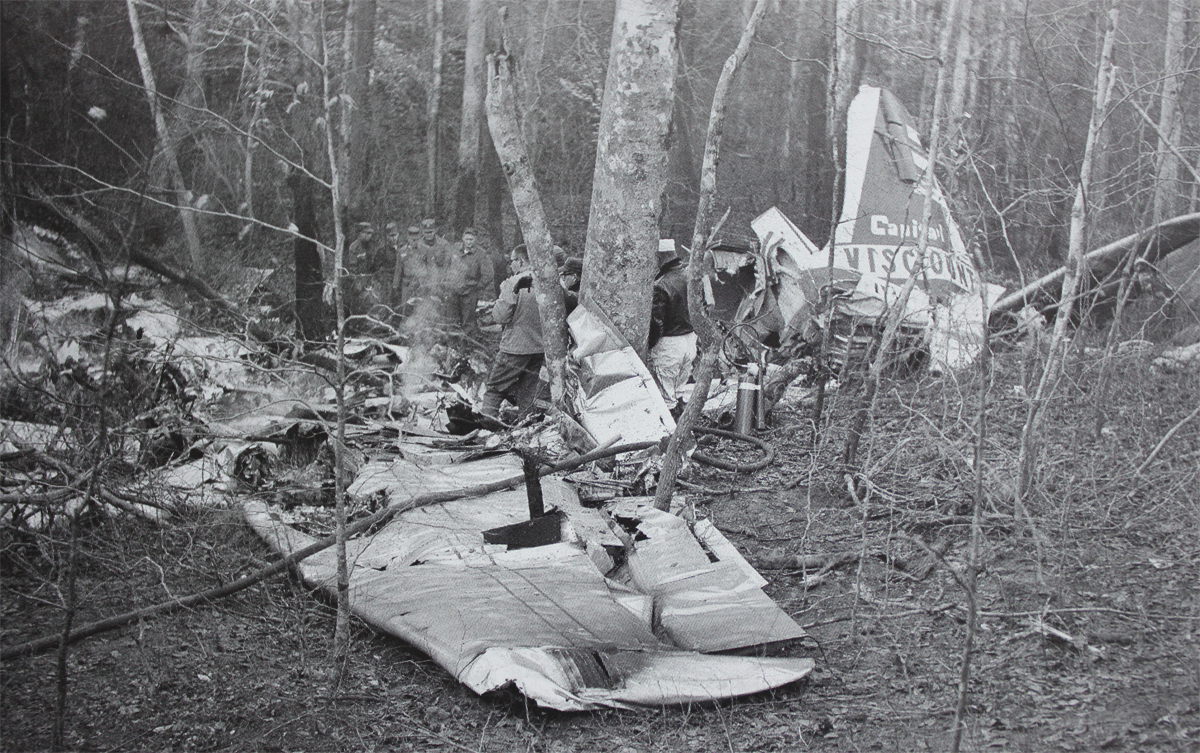
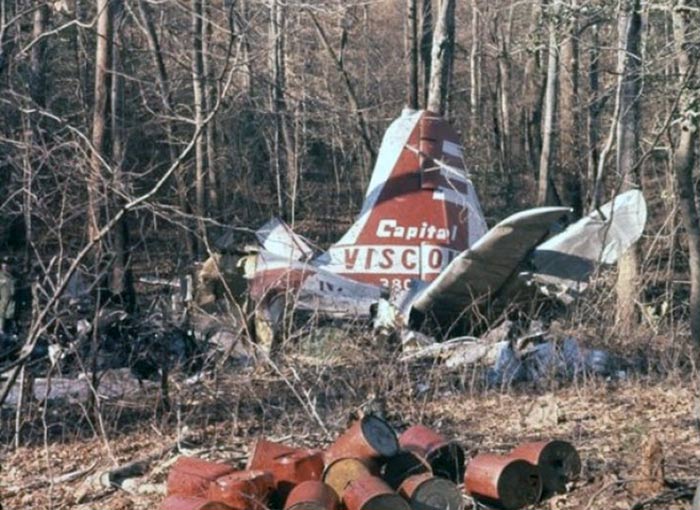
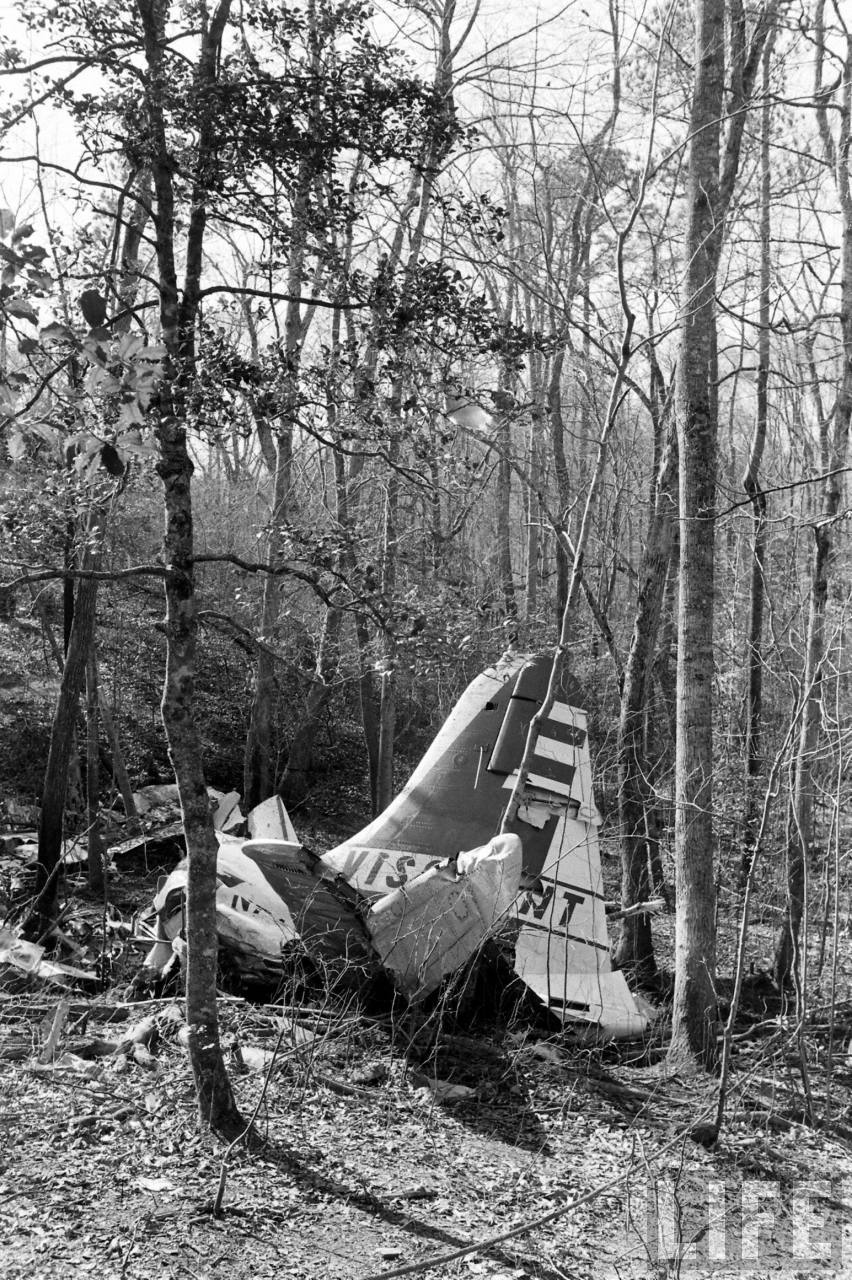
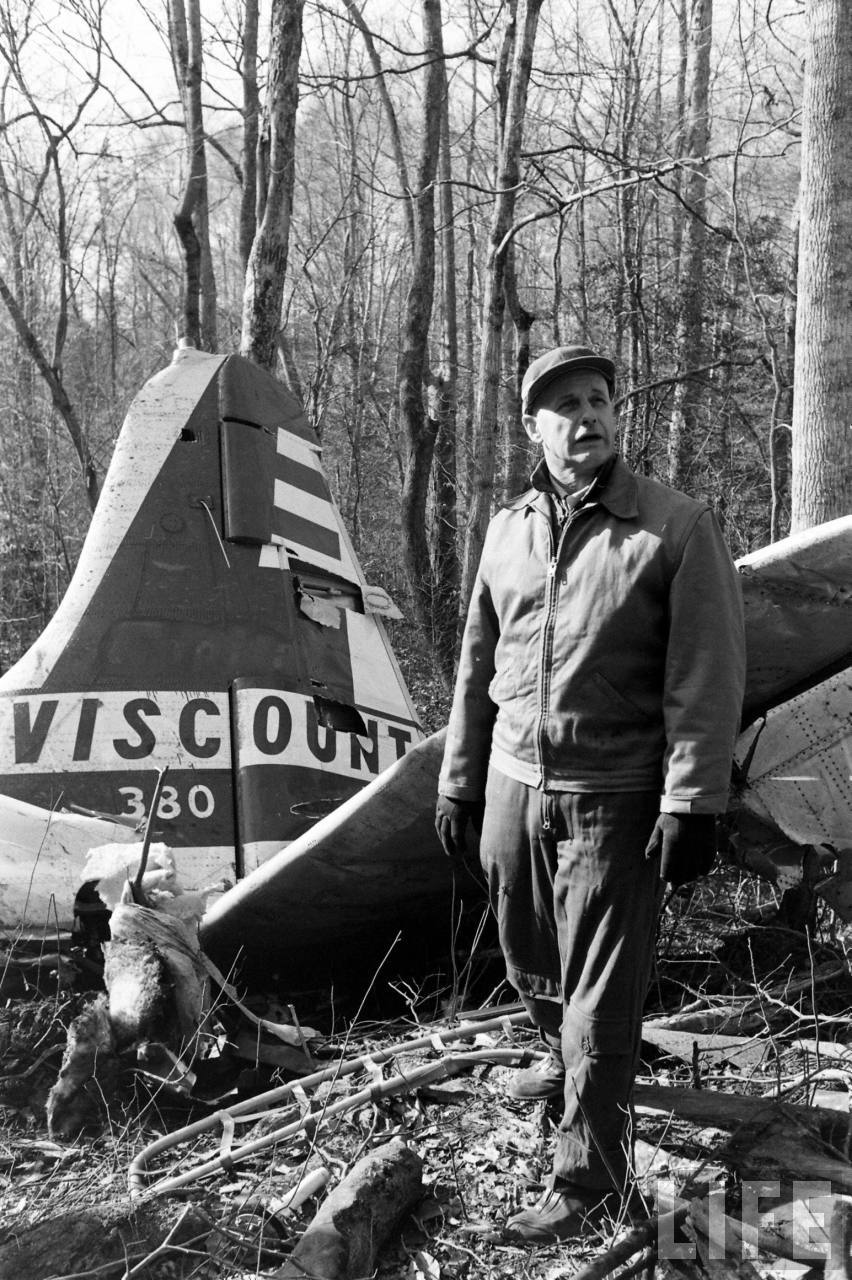
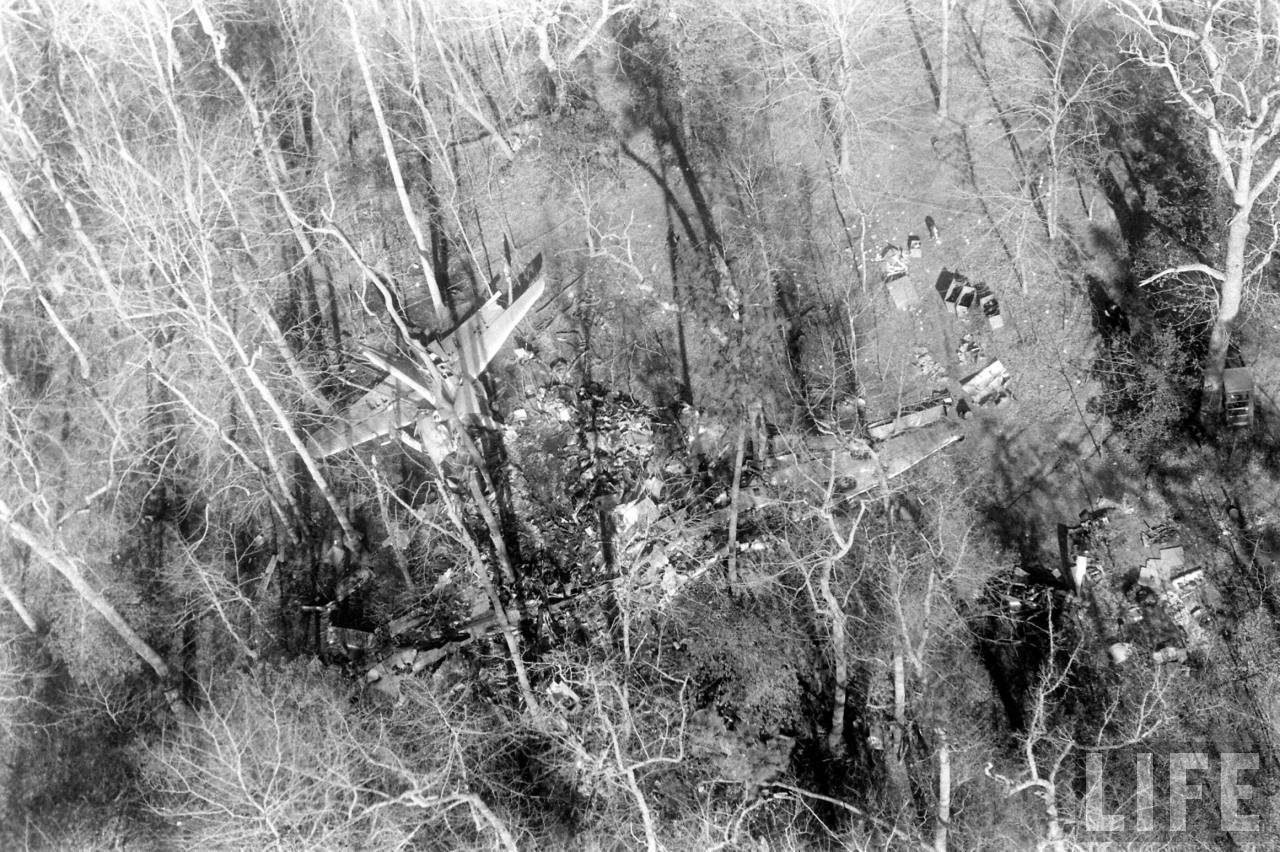
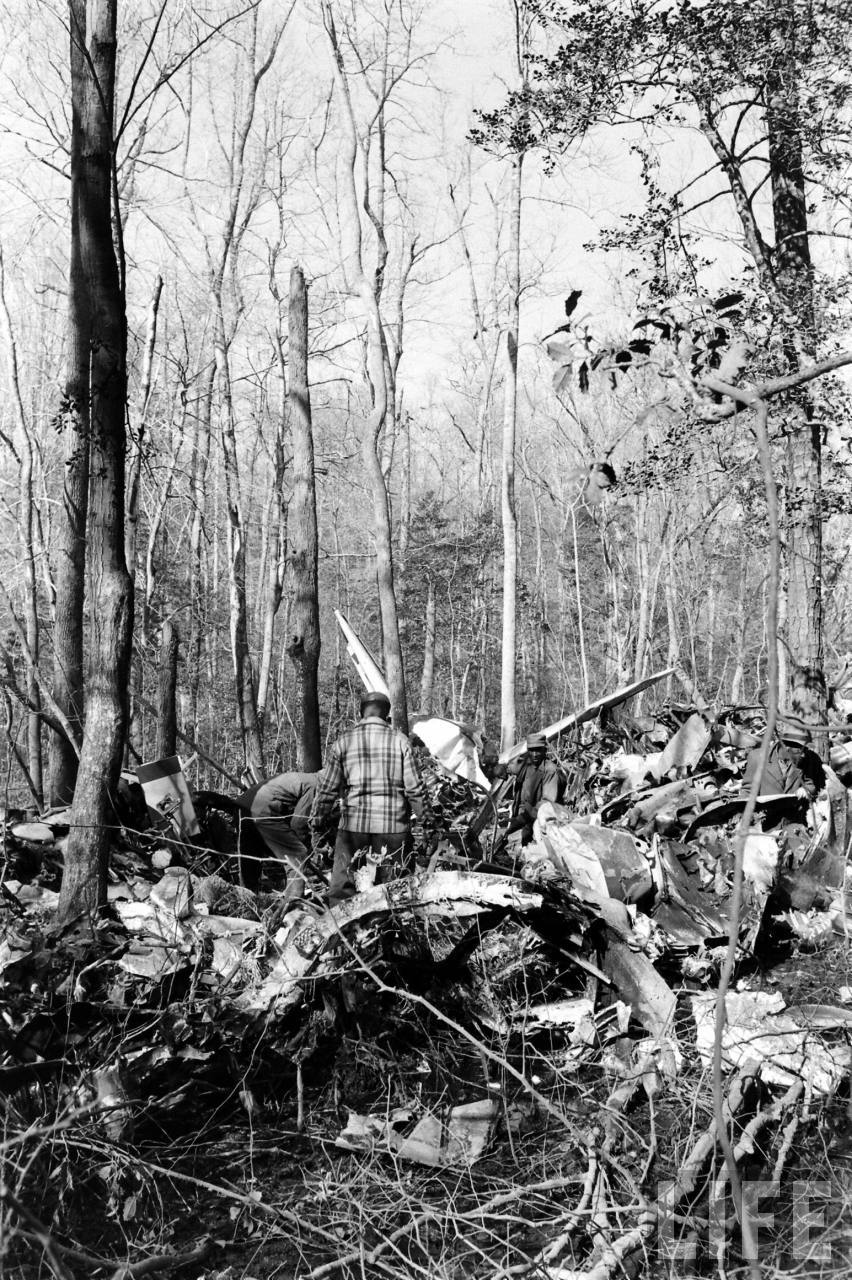
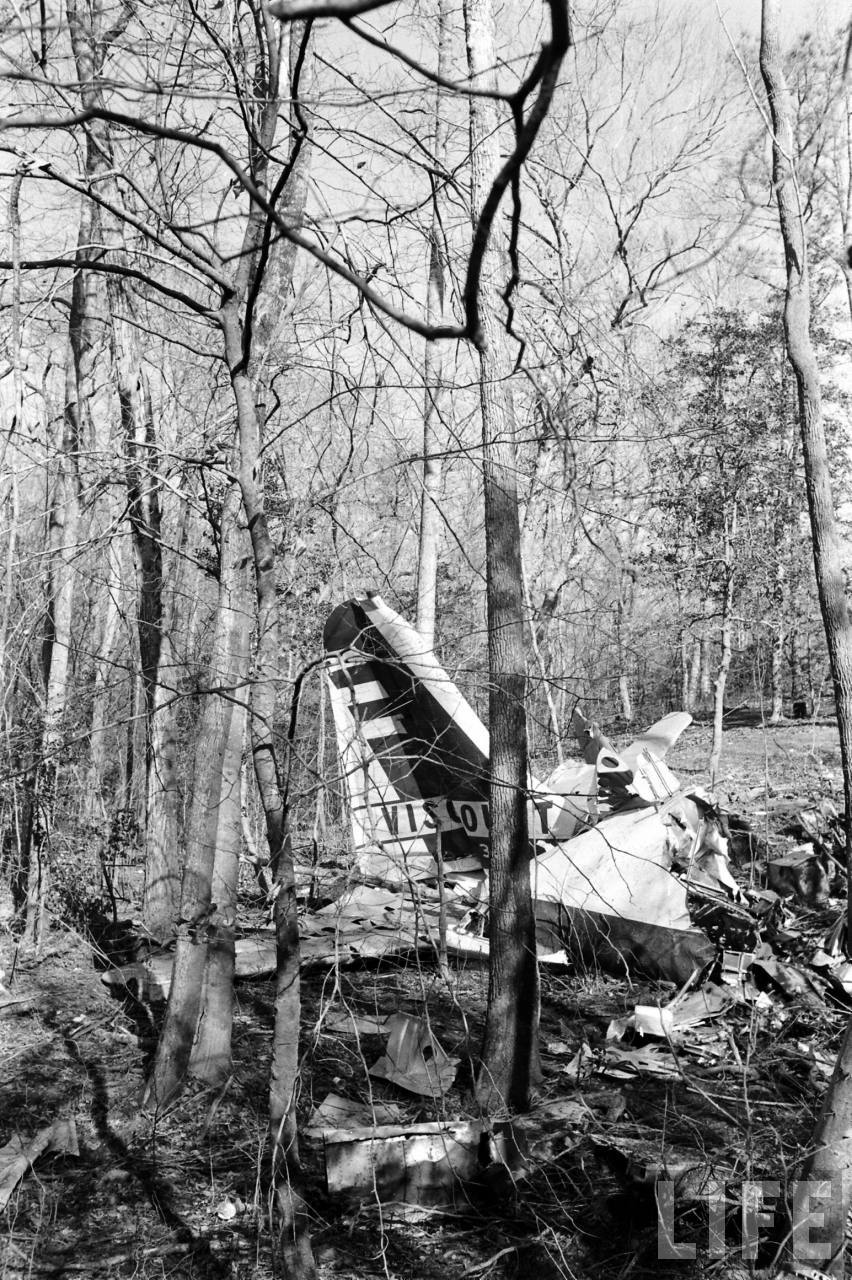
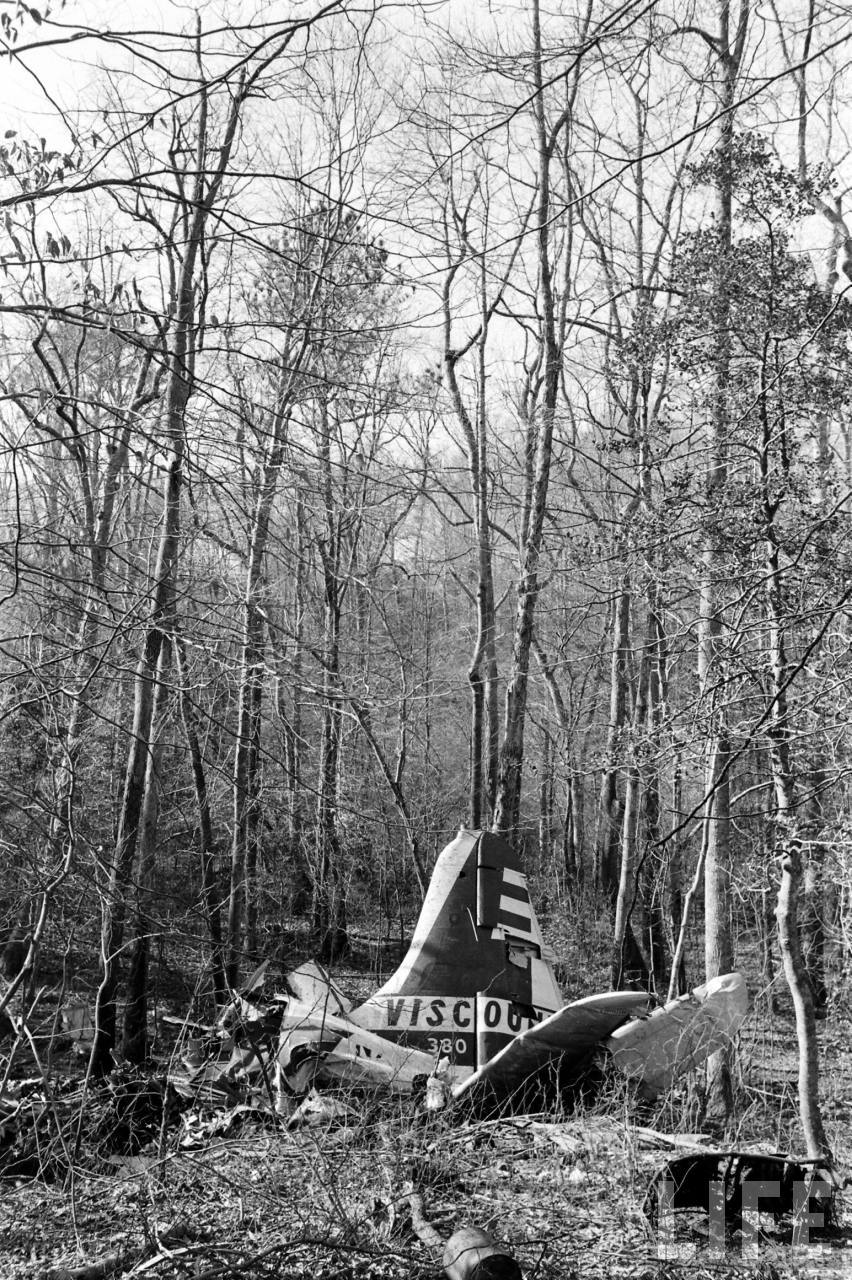
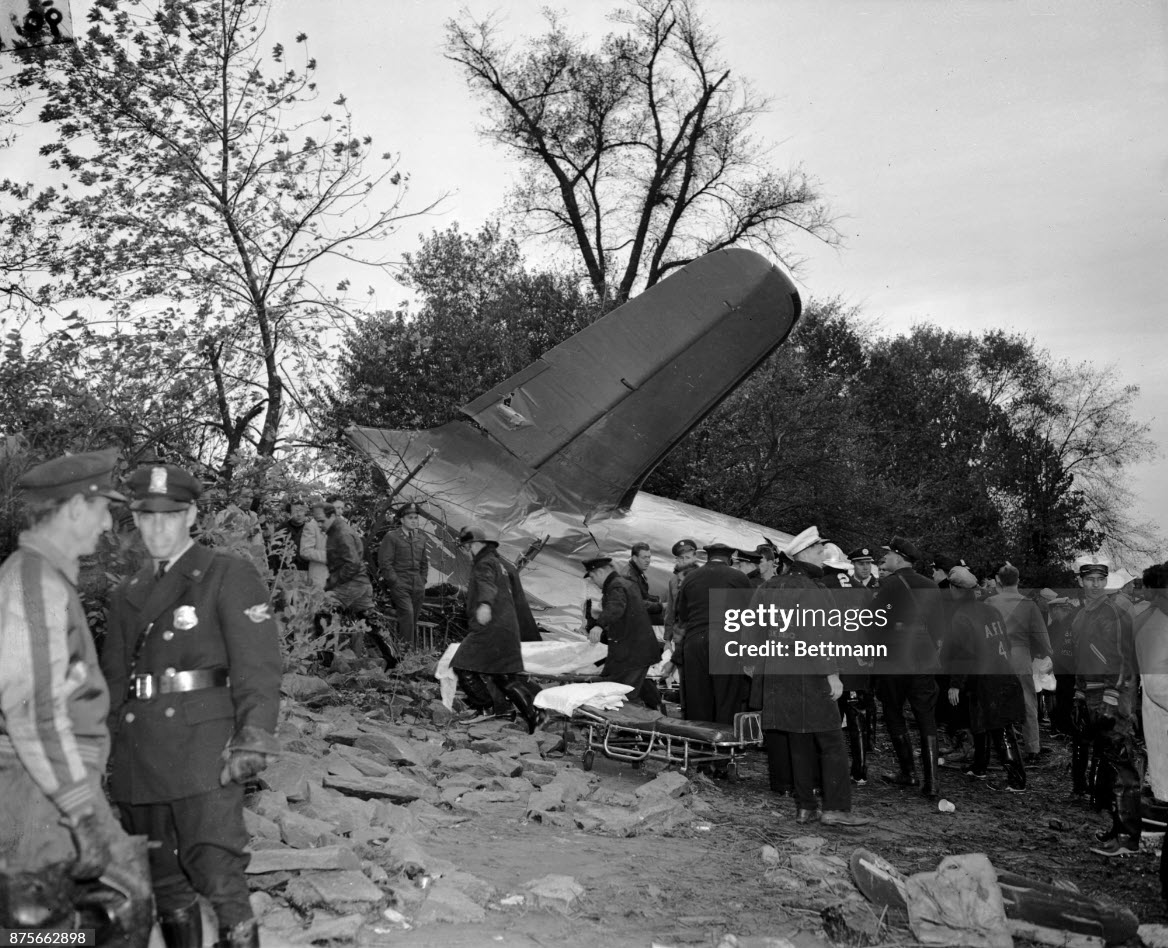
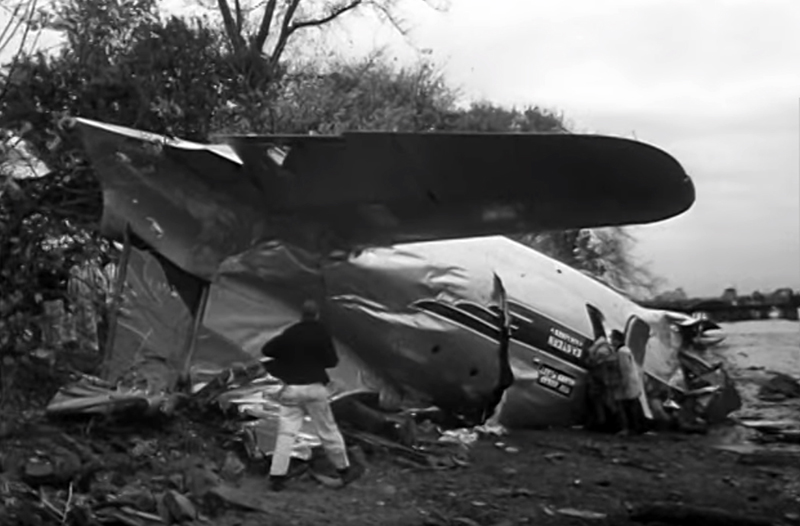
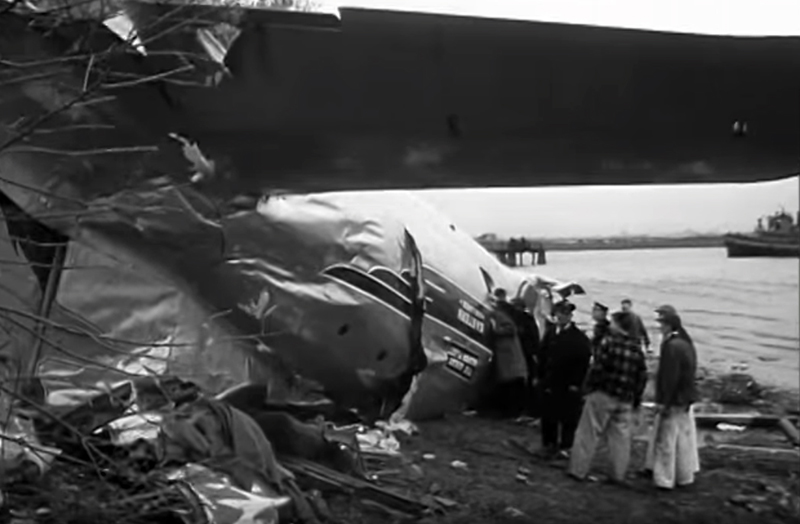
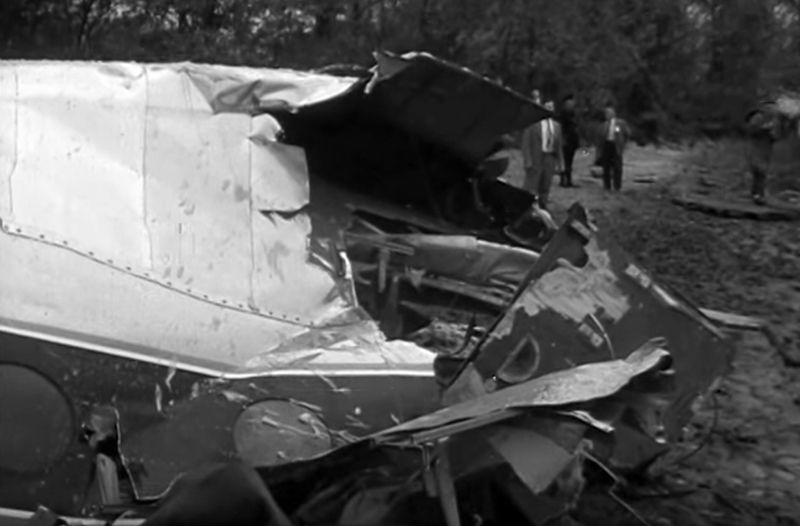
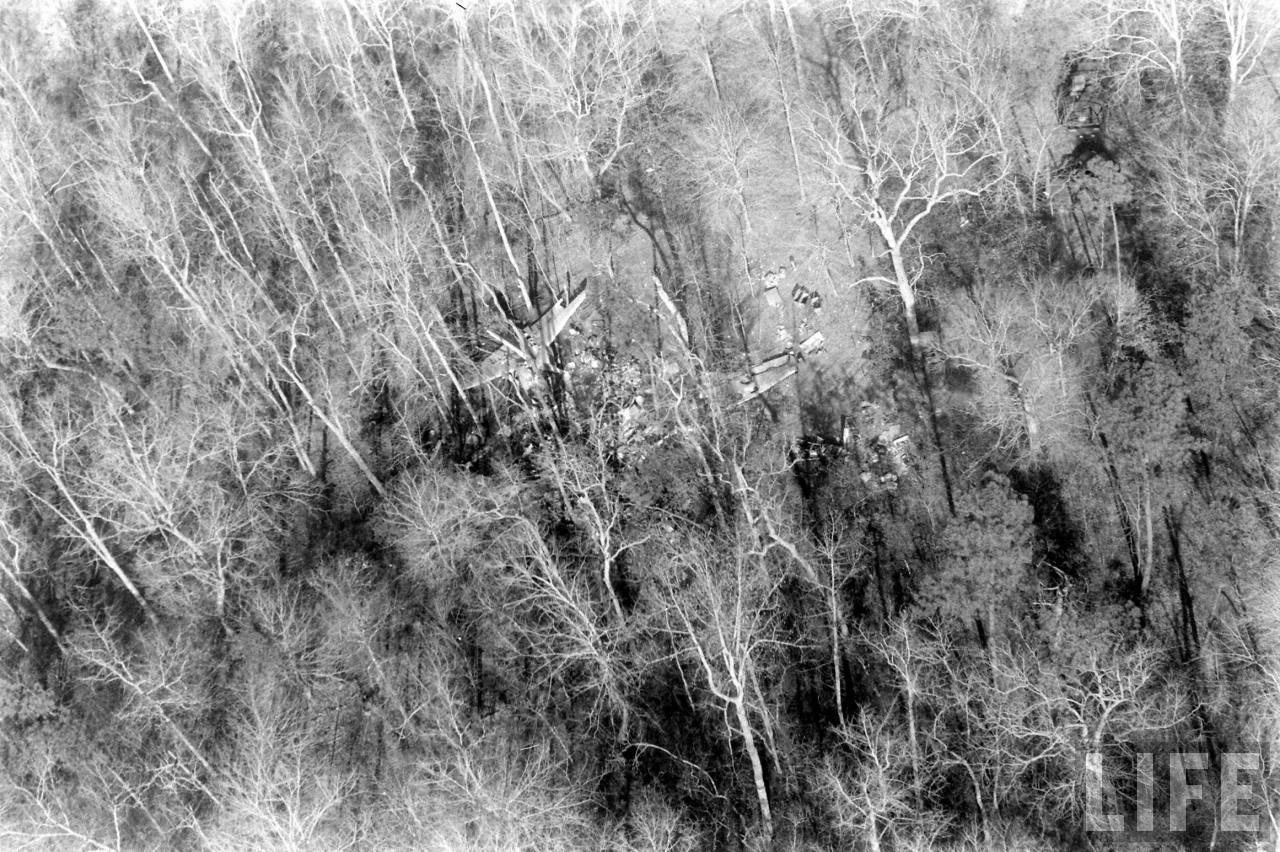
Circumstances:
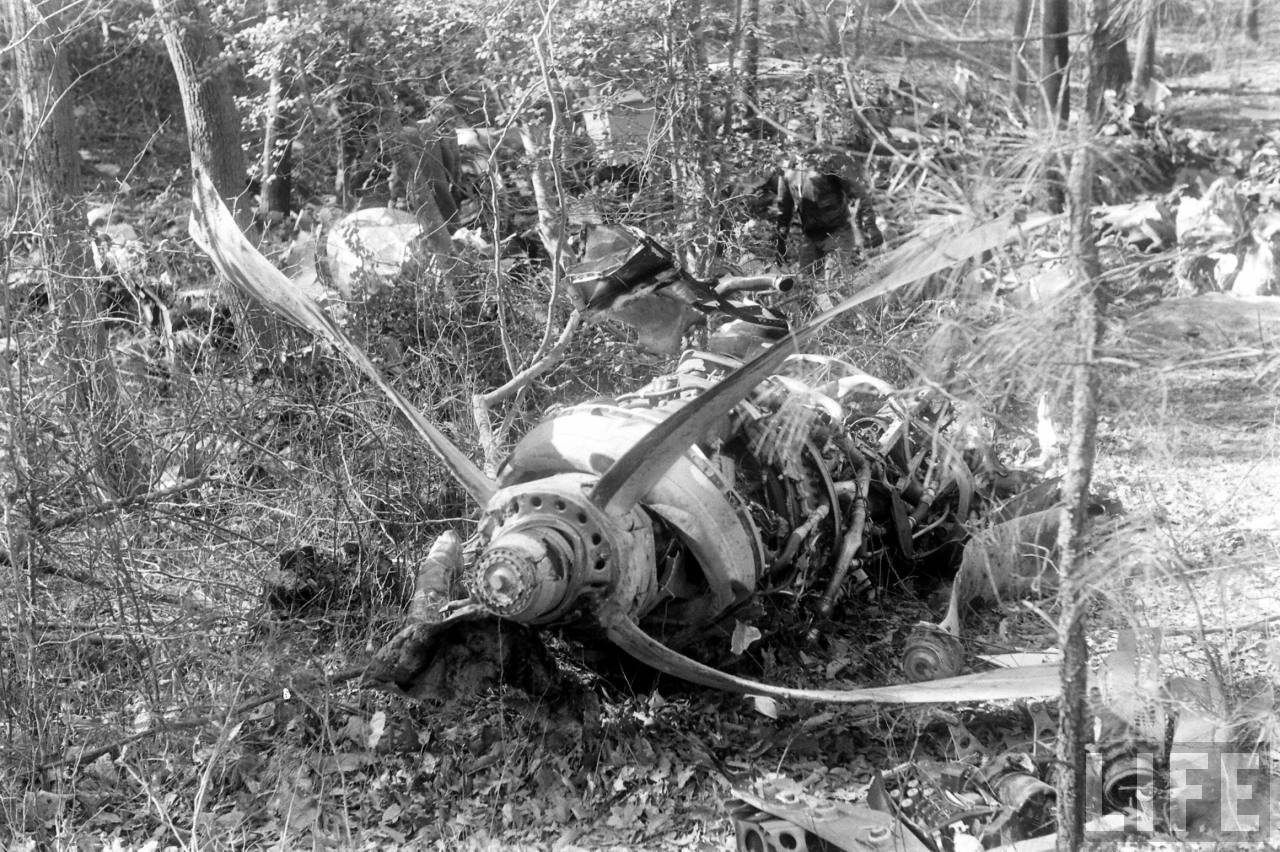
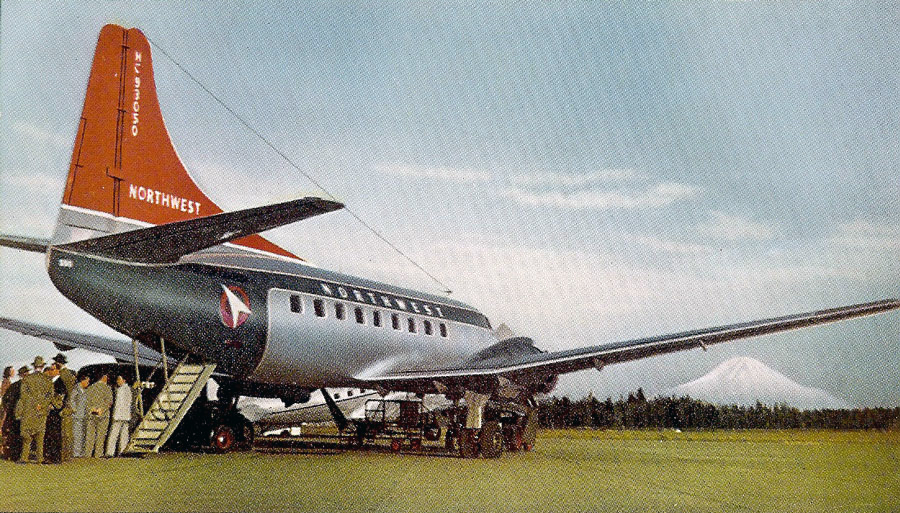
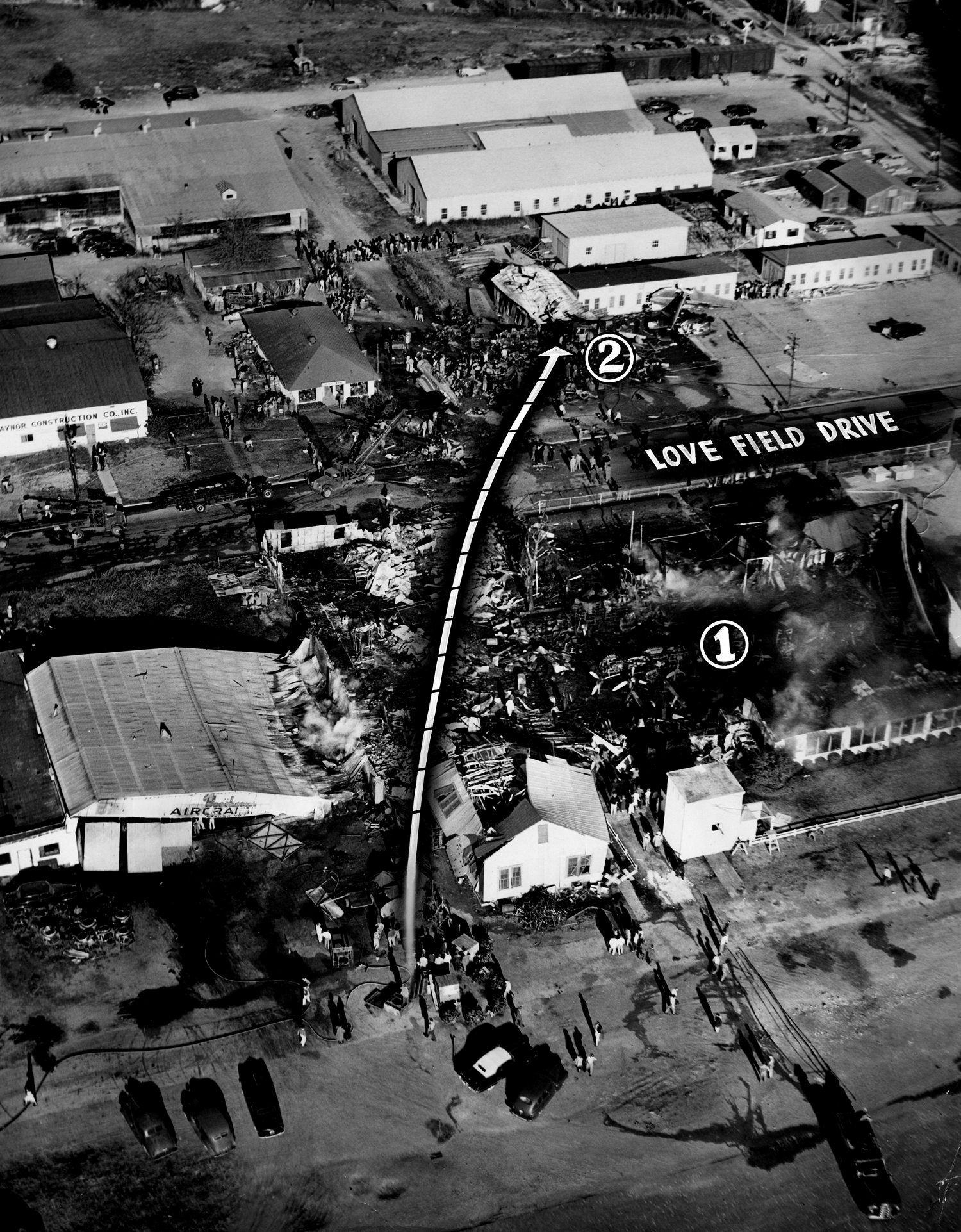
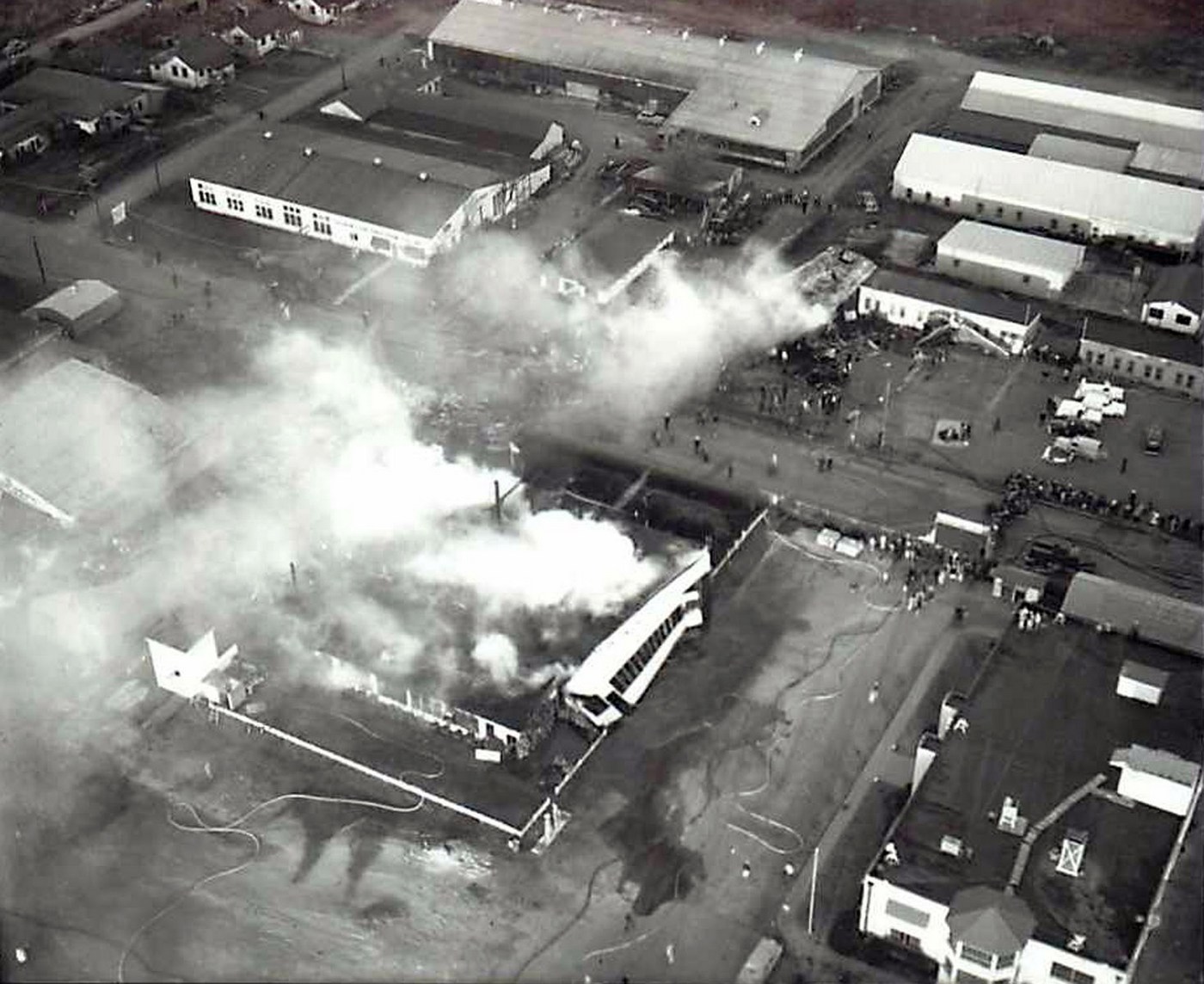
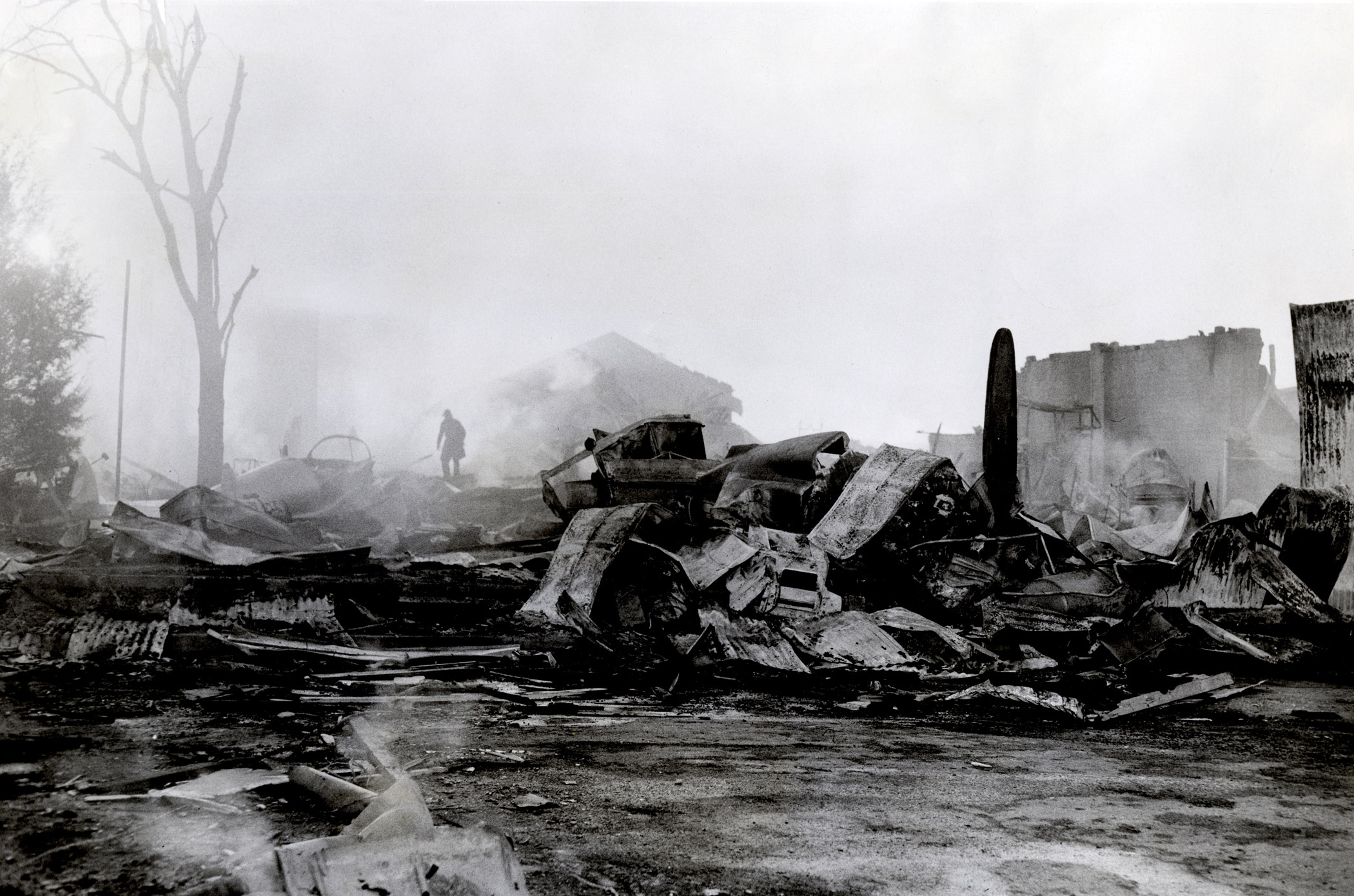
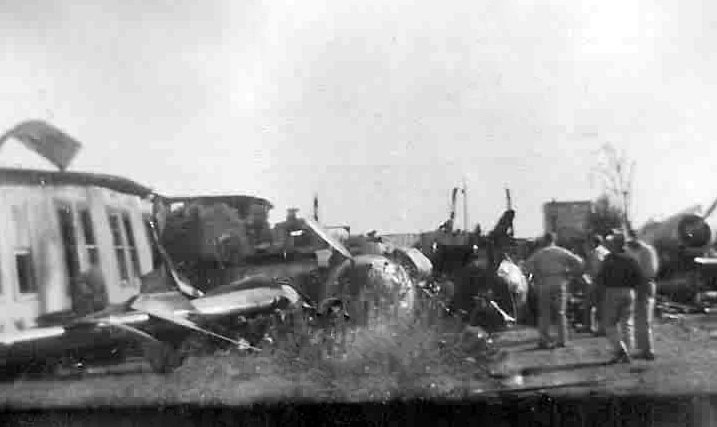
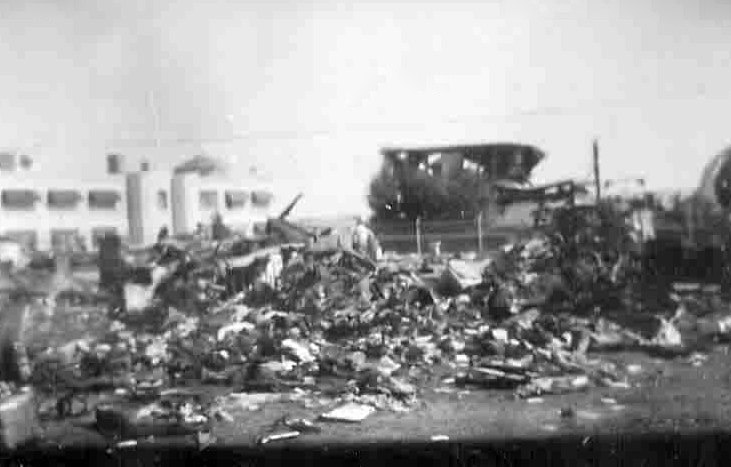
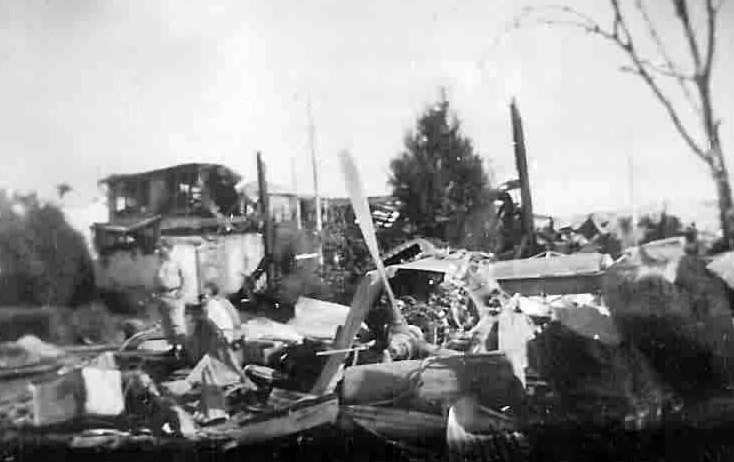
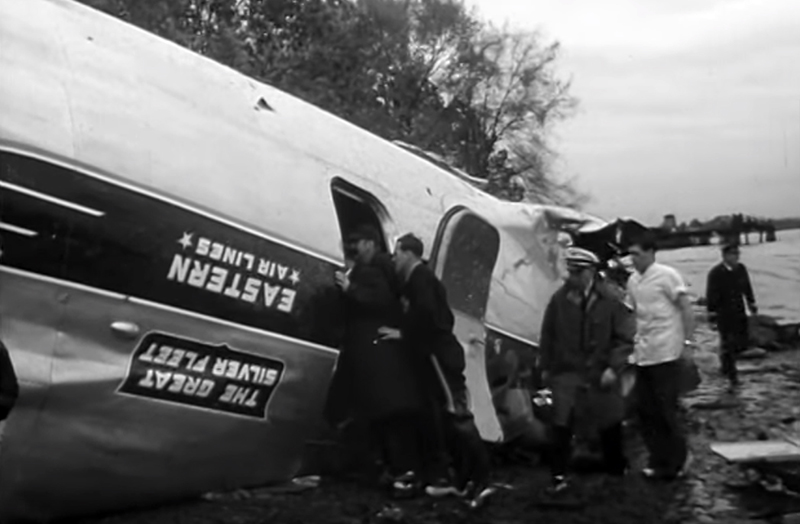
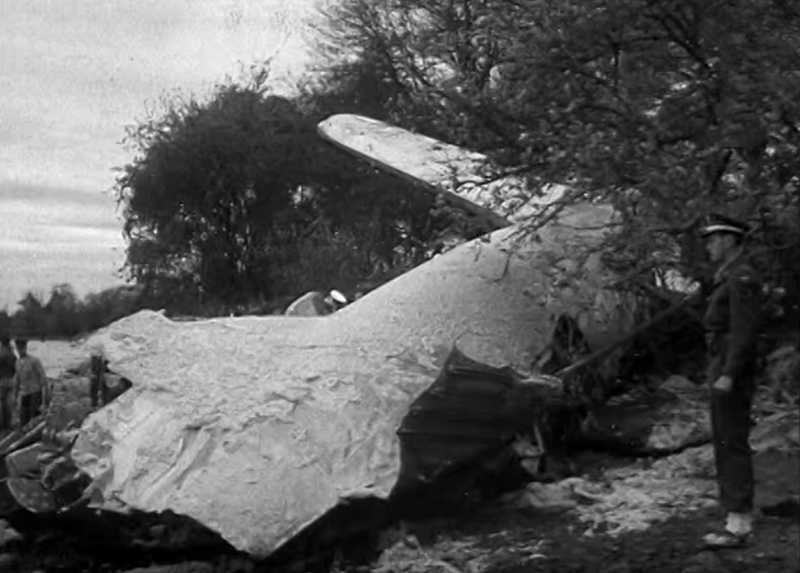
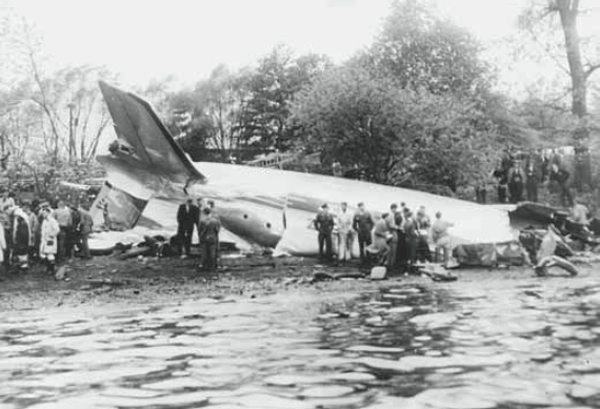
On November 1, 1949, Eastern's Flight 537 was flying from Boston via intermediate points to Washington. Over Beltsville, 15 miles northeast of the Washington National airport, it contacted the Washington Control Tower on 119 1 megacycles voice communications and was cleared by the tower to enter a left traffic pattern for landing on Runway 3 One minute before, at 11 37, the P-38 flown by Erick Rios Bridoux, a Bolivian national, had taken off from Runway 3 at Washington National Airport. Rios was test flying the P-38 for acceptance by the Bolivian Government Previously, he had notified the tower through Paul M. Aubin, that he intended to make the flight and that his communications with the tower would be accomplished over VHF radio, Channel B on 126 18 megacycles. Rios also stated that he requested Aubin to notify the tower to give him a light if radio contact could not be established. This message was not transmitted to the tower and Aubin denied hearing Rios make this last request. Throughout the entire ground operation of the P-38, including clearance for take-off, no difficulty was experienced by either the tower or Rios in communication. Departure of the P-38 was noted by the tower to be at 11 37, and from that time until after the accident, visibility in the vicinity of the airport remained at 15 miles, ceiling was 6,500 feet with scattered clouds at 3,500, and surface wind was from the northeast 20 to 25 miles per hour. Testimony of control tower personnel and that of the pilot of the P-38 were in conflict. Rios stated that he had taken off not from Runway 3, but from Runway 36, turning left at an altitude of about 300 feet. His climb was made, he said, to the north of the Pentagon, and because of the erratic operation of the right engine, he decided to land as soon as possible. Continuing to climb to about 2,500 feet or more, he made a second left turn so as to fly south, parallel to Runway 36, and when abeam of the control tower, he transmitted, "Washington Tower, this is Bolivian P-38 I got engine trouble--request landing instructions." His testimony continues to the effect that because no answer was received, he turned left again to circle the field where he could see light signals from the tower. He stated that he received none, but that when he was between Bolling Field and the National Airport and at about 3,500 feet altitude, the tower asked, "Bolivian P-38, you were asking landing instructions?" Rios stated that he answered, "Yes, I have engine trouble. I am in a hurry," and that the tower at that time responded, "Bolivian P-38 cleared to land number two on Runway 3" Rios stated that the tower did not inform him that the aircraft ahead of him was an Eastern DC-4 Rios said that he continued to turn left, and at a reduced speed of 150 miles per hour, started a descent of 500 to 600 feet per minute, completing a second 360-degree turn around the airport until reaching an altitude of approximately 2,400 feet. Rios said that a downwind leg was flown at about 1,500 feet, and when about five miles south of the field, he turned left 90 degrees, flying east on a short base leg at an altitude of about 1,200 feet. During his downwind leg, he observed a C-60 or C-45 on approach to Runway 3 or 36, and while on his base leg, he saw it complete its landing and turn off the runway to the left. Rios made a left turn from the base leg to an approach course of 20 degrees for landing on Runway 3. As soon as the turn had been completed, Rios transmitted, "Washington Tower, this is Bolivian P-38 on approach." The tower responded, said Rios, "Bolivian P-38 cleared to land on Runway 3." Rios stated that his approach was made a little higher than normal, for safety reasons, and that one minute after leaving the base leg, he extended the flaps, the landing gear having been put down previously when he was west of the field Rios heard the tower say, "Clear to the left, clear to the left," but he stated that he did not know for whom it was intended because the tower did not use any call sign. Almost immediately afterwards, he felt the shock of the collision with the DC-4. According to control tower personnel, the P-38 took off from Runway 3, turned left, and proceeded in a climb 10 miles west of the field. Then a second left turn was made, and the aircraft, still climbing, continued in a southerly direction. The P-38 was next observed from the control tower circling left, south of Alexandria at an estimated altitude between 3,000 and 4,000 feet. The tower operators stated that while the P-38 was circling south of Alexandria, they received, "Washington Tower, this is Bolivian 927 requesting landing instruction." After the controller had asked if Bolivian 927 had requested landing instructions, and the pilot had replied affirmatively, the controller instructed the P-38 to enter a left traffic pattern for Runway 3 and to report when west of the tower on downwind leg. When the instruction was not acknowledged by Rios, it was repeated. Prior to these instructions, the tower had cleared the Eastern flight to land number one on Runway 3. Shortly after the Eastern DC-4 was observed 1 1/2 miles west to southwest from the end of Runway 3, making a continuous left turn from the downwind leg to final approach, tower personnel observed the P-38 on a long high final approach. The controller thereupon requested Rios to make a 360-degree turn to his left, saying that he was number two to land following an Eastern DC-4 turning on its final approach below. Since there was neither acknowledgment nor compliance with this second instruction, another transmission was made to the P-38, which was identified as Bolivian 927, and Rios was then told. "Turn left, turn left," and was again told that the DC-4 was turning on final approach below. Again there was no response or compliance by the P-38, whereupon the tower then instructed the Eastern DC-4 to turn left. The DC-4 promptly acted in response to this instruction, but before 5 degrees of turn were made, the two aircraft collided at an approximate altitude of 300 feet about 1/2 mile southwest of Runway 3. While the Bolivian pilot survived, all 55 occupant on board the DC-4 were killed, among them George Bates and Michael Kennedy, two US politicians.