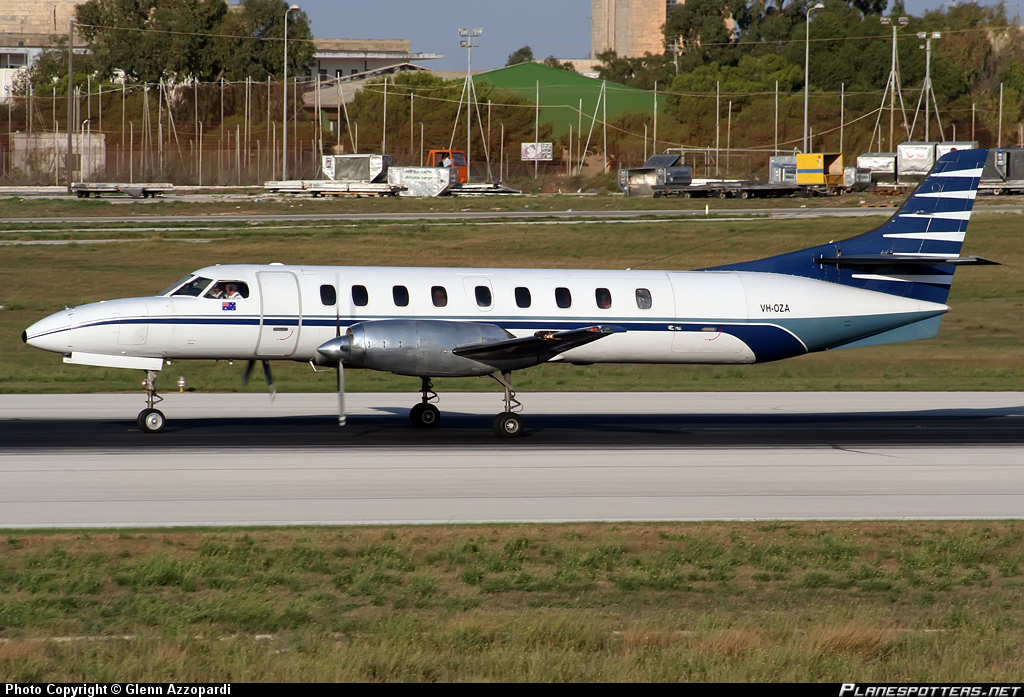
Crash of a Swearingen SA227AC Metro III off Sydney: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Apr 9, 2008 at 2327 LT
Registration:
VH-OZA
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Sydney – Brisbane
MSN:
AC-600
YOM:
1984
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
175.00
Aircraft flight hours:
32339
Aircraft flight cycles:
46710
Circumstances:
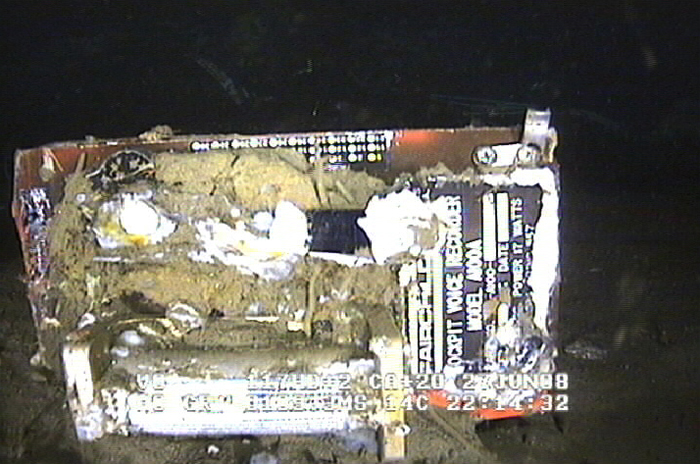
On 9 April 2008, at 2325 Eastern Standard Time, a Fairchild Industries Inc. SA227-AC (Metro III) aircraft, registered VH-OZA, departed Sydney Airport, New South Wales on a freight charter flight to Brisbane, Queensland with one pilot on board. The aircraft was subsequently observed on radar to be turning right, contrary to air traffic control instructions to turn left to an easterly heading. The pilot reported that he had a ‘slight technical fault’ and no other transmissions were heard from the pilot. Recorded radar data showed the aircraft turning right and then left, followed by a descent and climb, a second right turn and a second descent before radar returns were lost when the aircraft was at an altitude of 3,740 ft above mean sea level and descending at over 10,000 ft/min. Air traffic control initiated search actions and search vessels later recovered a small amount of aircraft wreckage floating in the ocean, south of the last recorded radar position. The pilot was presumed to be fatally injured and the aircraft was destroyed. Both of the aircraft’s on-board flight recorders were subsequently recovered from the ocean floor. They contained data from a number of previous flights, but not for the accident flight. There was no evidence of a midair breakup of the aircraft.
Probable cause:
Contributing Safety Factors:
- It was very likely that the aircraft’s alternating current electrical power system was not energised at any time during the flight.
- It was very likely that the aircraft became airborne without a functioning primary attitude reference or autopilot that, combined with the added workload of managing the ‘slight technical fault’, led to pilot spatial disorientation and subsequent loss of control.
Other Safety Factors:
- The pilot’s Metro III endorsement training was not conducted in accordance with the operator’s approved training and checking manual, with the result that the pilot’s competence and ultimately, safety of the operation could not be assured. [Significant safety issue].
- The chief pilot was performing the duties and responsibilities of several key positions in the operator’s organisational structure, increasing the risk of omissions in the operator’s training and checking requirements.
- The conduct of the flight single-pilot increased the risk of errors of omission, such as not turning on or noticing the failure of aircraft items and systems, or complying with directions.
- It was very likely that the aircraft’s alternating current electrical power system was not energised at any time during the flight.
- It was very likely that the aircraft became airborne without a functioning primary attitude reference or autopilot that, combined with the added workload of managing the ‘slight technical fault’, led to pilot spatial disorientation and subsequent loss of control.
Other Safety Factors:
- The pilot’s Metro III endorsement training was not conducted in accordance with the operator’s approved training and checking manual, with the result that the pilot’s competence and ultimately, safety of the operation could not be assured. [Significant safety issue].
- The chief pilot was performing the duties and responsibilities of several key positions in the operator’s organisational structure, increasing the risk of omissions in the operator’s training and checking requirements.
- The conduct of the flight single-pilot increased the risk of errors of omission, such as not turning on or noticing the failure of aircraft items and systems, or complying with directions.
Final Report: