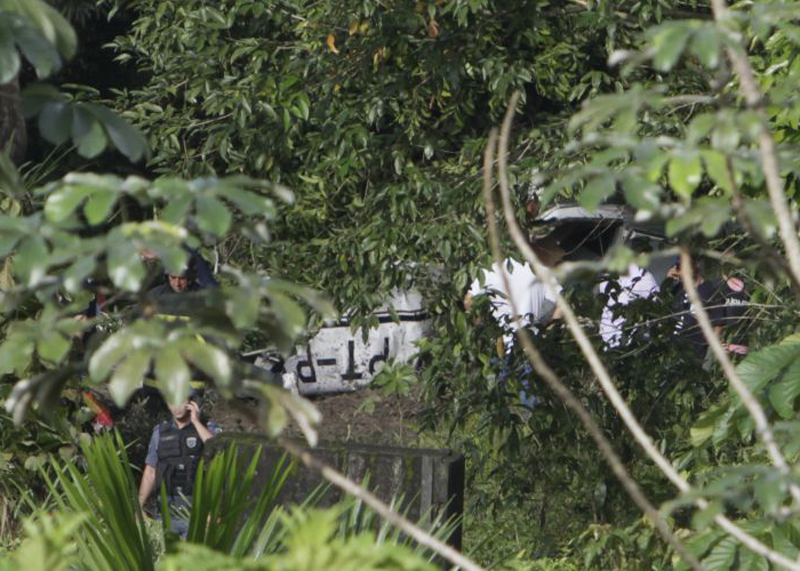Country
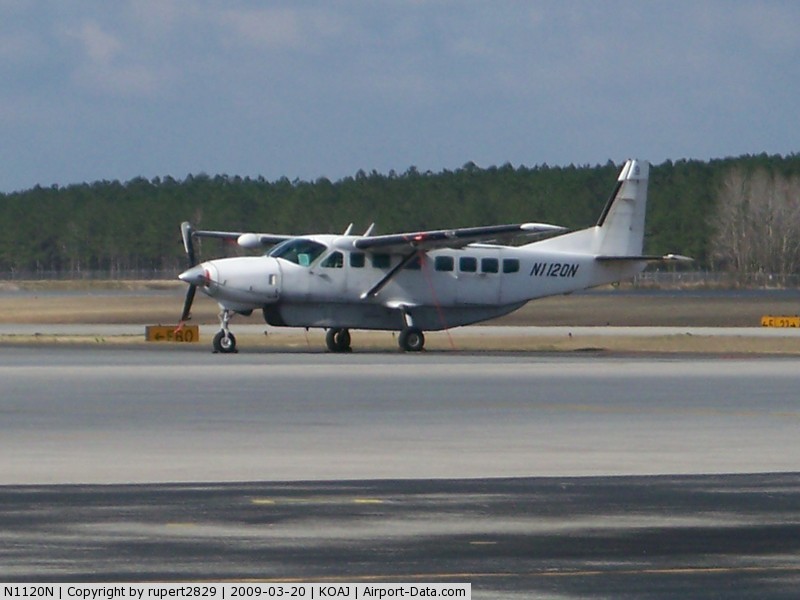
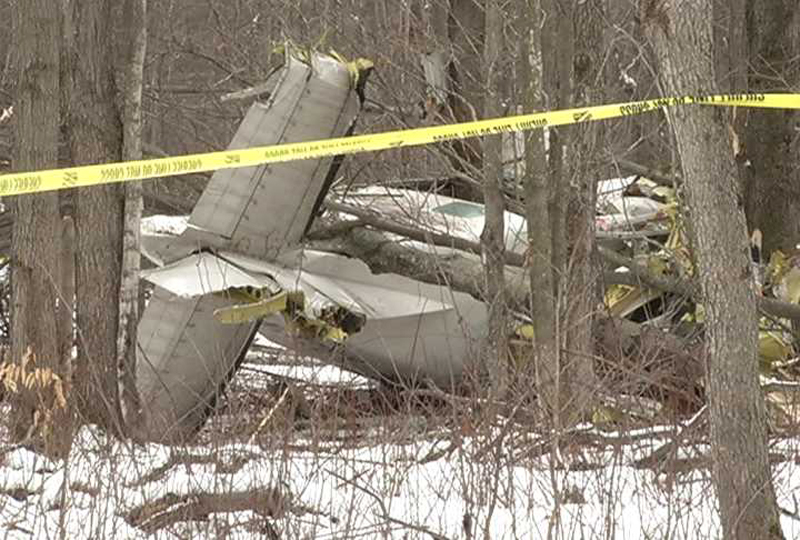
Crash of a Cessna 208B Super Cargomaster in Pellston: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Jan 15, 2013 at 1958 LT
Registration:
N1120N
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Pellston - Lansing
MSN:
208B-0386
YOM:
1994
Flight number:
MRA605
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
34.00
Aircraft flight hours:
10132
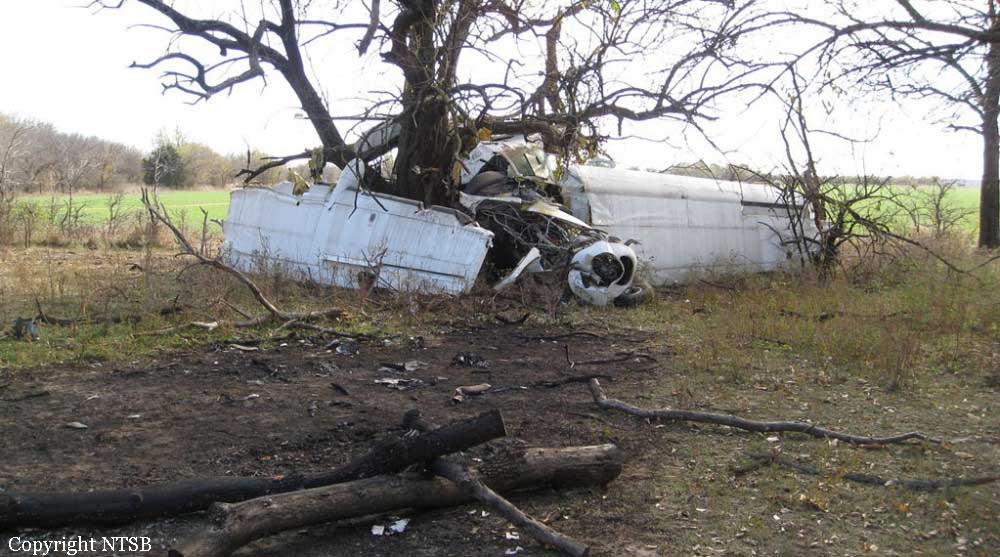
Circumstances:
The pilot landed at the airport to refuel the airplane and pick up cargo. The pilot spoke with three employees of the fixed base operator who stated that he seemed alert and awake but wanted to make a "quick turn." After the airplane was fueled and the cargo was loaded, the pilot departed; the airplane crashed 1 minute later. Night visual meteorological conditions prevailed at the time. An aircraft performance GPS and simulation study indicated that the airplane entered a right bank almost immediately after takeoff and then made a 42 degree right turn and that it was accelerating throughout the flight, from about 75 knots groundspeed shortly after liftoff to about 145 knots groundspeed at impact. The airplane was climbing about 500 to 700 feet per minute to a peak altitude of about 260 feet above the ground before descending. The simulation showed a gas generator speed of about 93 percent throughout the flight. The study indicated that the load factor vectors, which were the forces felt by the pilot, could have produced a somatogravic illusion of a climb, even while the airplane was descending. The postaccident examination of the airframe and engine revealed no evidence of mechanical malfunctions or failures that would have precluded normal operation. Based on the findings from the aircraft performance GPS and simulation study, the degraded visual reference conditions present about the time of the accident, and the forces felt by the pilot, it is likely that he experienced spatial disorientation, which led to his inadvertent controlled descent into terrain.
Probable cause:
The pilot's inadvertent controlled descent into terrain due to spatial disorientation. Contributing to the accident was lack of visual reference due to night conditions.
Final Report:


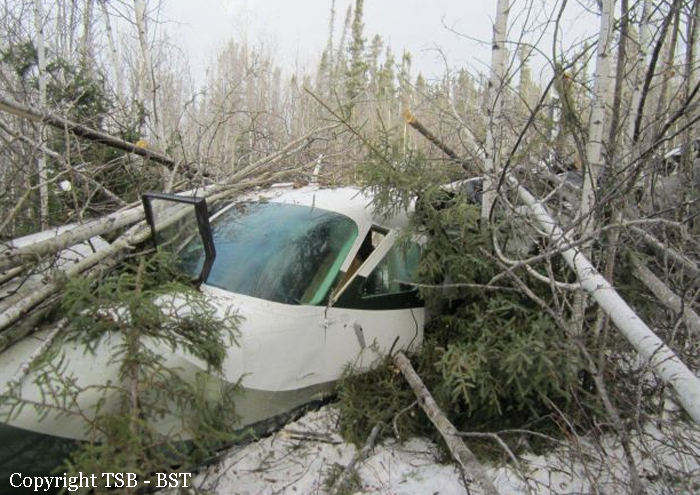
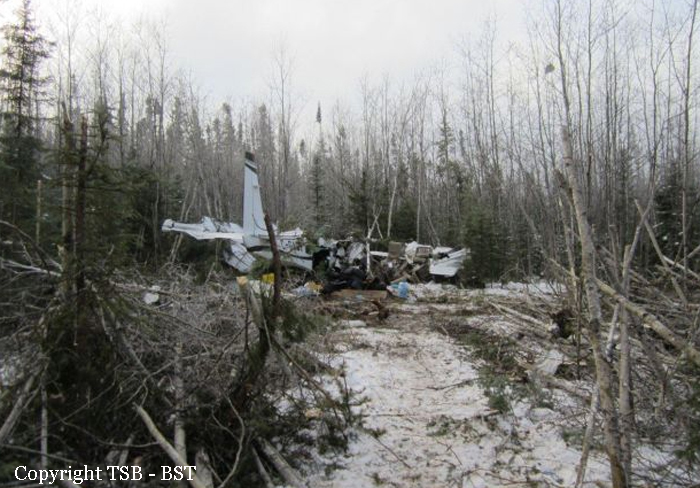
Crash of a Cessna 208B Grand Caravan in Snow Lake: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Nov 18, 2012 at 0956 LT
Registration:
C-GAGP
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Snow Lake - Winnipeg
MSN:
208B-1213
YOM:
2006
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
7
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
1020.00
Aircraft flight hours:
1487
Circumstances:
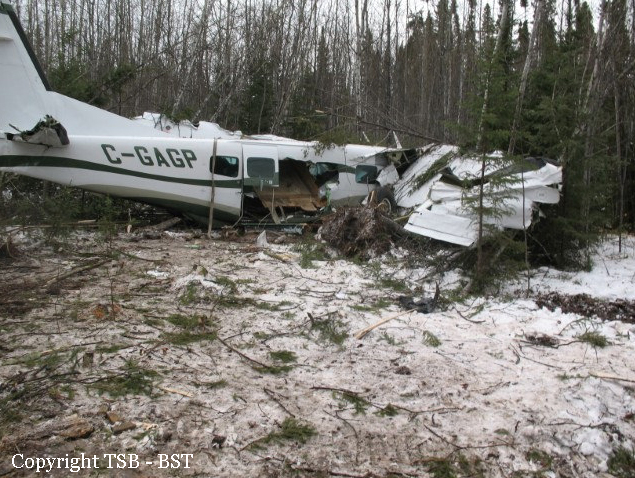
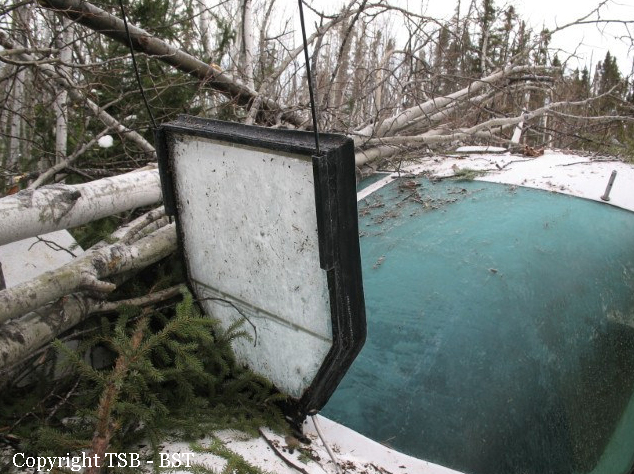
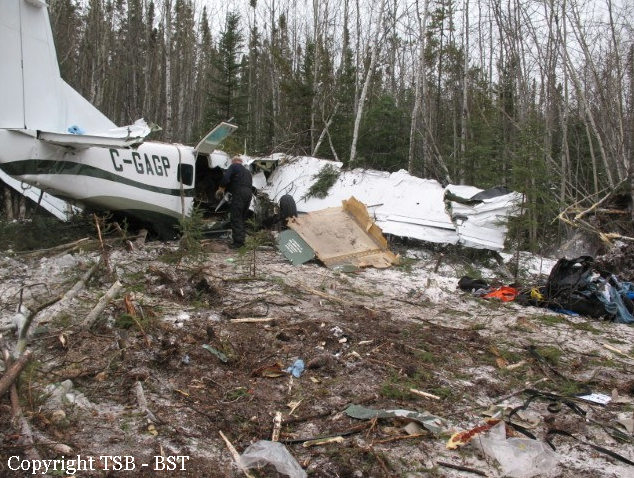
The Gogal Air Services Limited Cessna 208B (registration C-GAGP, serial number 208B1213) departed Runway 21 at Snow Lake en route to Winnipeg, Manitoba, with the pilot and 7 passengers on board. At approximately 0956 Central Standard Time, shortly after take-off, the aircraft descended and struck the terrain in a wooded area approximately 0.9 nautical miles beyond the departure end of the runway. The pilot was fatally injured, and the 7 passengers sustained serious injuries. The aircraft was destroyed by impact forces, and a small fire ensued near the engine. The aircraft’s emergency locater transmitter activated. First responders attended the scene, and the injured passengers were taken to area hospitals. The aircraft’s fuel cells ruptured, and some of the onboard fuel spilled at the site.
Probable cause:
Findings as to causes and contributing factors:
1. The aircraft departed Snow Lake overweight and with an accumulation of ice on the leading edges of its wings and tail from the previous flight. As a result, the aircraft had reduced take-off and climb performance and increased stall speed, and the protection afforded by its stall warning system was impaired.
2. A breakdown in the company’s operational control resulted in the flight not operating in accordance with the Canadian Aviation Regulations and the company operations manual.
3. As a result, shortly after departure, the aircraft stalled at an altitude from which recovery was not possible.
Findings as to risk:
1. If companies operate in instrument meteorological conditions for which they are not authorized, there is an increased risk that accidents may occur.
2. If Transport Canada does not provide the same degree of oversight for repetitive charter operations as it does for a scheduled operator, the risks in the operator’s activities may not be fully evaluated.
3. If passenger briefings are not provided and passengers are not properly seated and restrained, there is an increased risk of injuries to those passengers and the other occupants in the event of an accident.
4. If flights are conducted without ensuring an ice-free airframe, there is a risk of decreased aircraft performance and of loss of control and collision with terrain.
Other findings:
1. On impact, the aircraft’s seats and cabin deformed as designed, and this deformation partially attenuated the impact forces.
1. The aircraft departed Snow Lake overweight and with an accumulation of ice on the leading edges of its wings and tail from the previous flight. As a result, the aircraft had reduced take-off and climb performance and increased stall speed, and the protection afforded by its stall warning system was impaired.
2. A breakdown in the company’s operational control resulted in the flight not operating in accordance with the Canadian Aviation Regulations and the company operations manual.
3. As a result, shortly after departure, the aircraft stalled at an altitude from which recovery was not possible.
Findings as to risk:
1. If companies operate in instrument meteorological conditions for which they are not authorized, there is an increased risk that accidents may occur.
2. If Transport Canada does not provide the same degree of oversight for repetitive charter operations as it does for a scheduled operator, the risks in the operator’s activities may not be fully evaluated.
3. If passenger briefings are not provided and passengers are not properly seated and restrained, there is an increased risk of injuries to those passengers and the other occupants in the event of an accident.
4. If flights are conducted without ensuring an ice-free airframe, there is a risk of decreased aircraft performance and of loss of control and collision with terrain.
Other findings:
1. On impact, the aircraft’s seats and cabin deformed as designed, and this deformation partially attenuated the impact forces.
Final Report:






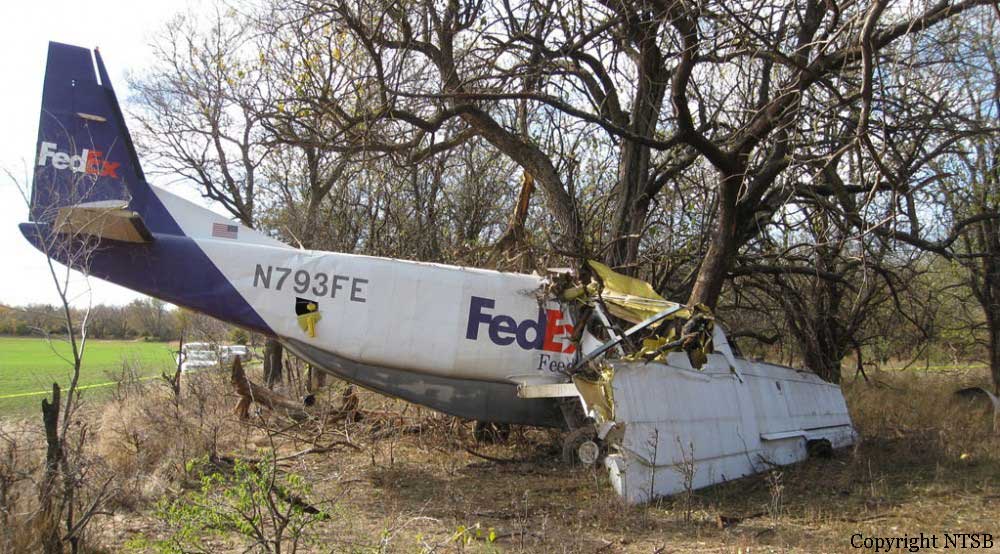
Crash of a Cessna 208B Super Cargomaster in Wichita: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Nov 6, 2012 at 0745 LT
Registration:
N793FE
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Wichita - Garden City
MSN:
208B-0291
YOM:
1991
Flight number:
FDX8588
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Aircraft flight hours:
10852
Circumstances:
The aircraft was substantially damaged when it collided with a hedgerow during a forced landing following a loss of engine power near Wichita, Kansas. The loss of engine power occurred about 4-1/2 minutes after departing Wichita Mid-Continent Airport (ICT), Wichita, Kansas. The commercial pilot, who was the sole occupant, was fatally injured. The airplane was registered to the Federal Express Corporation and operated by Baron Aviation Services Incorporated, under the provisions of 14 Code of Federal Regulations Part 135 while on an instrument flight plan. Day visual meteorological conditions prevailed for the cargo flight that had the intended destination of Garden City Regional Airport (GCK), Garden City, Kansas. According to air traffic control transmissions, at 0734:35 (hhmm:ss), the pilot requested an instrument flight rules clearance from ICT to GCK. Radar track data indicated that the airplane departed runway 19R approximately 0737:45. At 0738:18, the tower controller told the pilot to change to the departure control frequency. The departure controller then cleared the flight to proceed direct to GCK and to climb to 8,000 ft mean sea level (msl). The airplane continued to climb on a westerly heading until 0742:02, at which time the airplane began a left 180-degree turn back toward the departure airport. According to radar data, the airplane had reached 4,700 ft msl when it began the left turn. At 0742:13, the pilot transmitted that his airplane had experienced a loss of engine power and that he was attempting to return to the departure airport. At 0742:31, the pilot asked if there were any nearby airports because he was unable to reach ICT. The departure controller provided vectors toward an airstrip that was approximately 2.5 miles southeast of the airplane's position. At 0743:46, the pilot advised that he could not see the airstrip because the airplane's windshield was contaminated with oil. At 0744:57, the pilot's final transmission was that he was landing in a grass field. The airplane was located about 2.2 miles south of ICT at 1,600 feet msl, about 300 feet above ground level (agl) at the time of the last transmission. The radar data continued northeast another 1/2 mile before radar contact was lost at 0745:15. A witness to the accident reported that he was outside his residence when he observed the accident airplane overfly his position. He recalled that the airplane's propeller was not rotating and that he did not hear the sound of the engine operating. He stated that the airplane landed in a nearby agricultural field on a northeast heading. He reported that during the landing rollout the airplane impacted a hedgerow located at the northern edge of the field. The witness indicated that the pilot was unresponsive when he arrived at the accident site and that there was a small grass fire located 8 to 10 feet in front of the main wreckage.
Probable cause:
The total loss of engine power as a result of a fractured compressor turbine blade due to high-cycle fatigue.
Final Report:





Crash of a Cessna 208B Grand Caravan in Yola
Date & Time:
Oct 25, 2012 at 1830 LT
Registration:
5N-BMJ
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Jalingo – Yola
MSN:
208B-2098
YOM:
2009
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
3
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Aircraft flight hours:
999
Circumstances:
On the 25th of October, 2012 at 17: 48 h, a Cessna Caravan 208B, 5N-BMJ, departed Jalingo for Yola on a Visual Flight Rules (VFR) flight plan with four Persons-On-Board (one crew and three passengers). At 18:00 h, the Airport Manager stationed at Jalingo by Taraba State Government, called Yola Control Tower (CT) by phone to advise that the aircraft had departed Jalingo for Yola. At 18:25 h the pilot reported field in sight. CT then advised him to “continue approach and report final, wind calm” and the pilot acknowledged “will continue approach, to report final”. At 18:27 h CT had the aircraft in sight and advised the pilot to report “final, wind calm”, the pilot acknowledged. At 18:30 h, CT lost visual contact with 5N-BMJ and tried to raise her on radio but there was no response. At 18:37 h, information was received from witnesses, regarding a possible plane crash at Yola-Numan road close to Nigerian National Petroleum Corporation (NNPC) depot. This information was subsequently passed to the fire watch room. Rescue team and other security personnel were mobilized to the location of the crash. However, before the arrival of the rescue team from the airport, the locals had rescued the occupants from the wreckage. The occupants were subsequently taken to Federal Medical Centre (FMC), Yola for medical treatment. The accident occurred at dusk. The aircraft was destroyed.
Probable cause:
The Bureau could not conclusively determine the cause of this accident; however, the investigation identified the following factors:
- The pilot was not certified, qualified and not competent to fly the aircraft.
- The decision of the pilot to operate a VFR flight after sunset.
- Inadequate oversight by the Regulatory Authority.
- The pilot was not certified, qualified and not competent to fly the aircraft.
- The decision of the pilot to operate a VFR flight after sunset.
- Inadequate oversight by the Regulatory Authority.
Final Report:
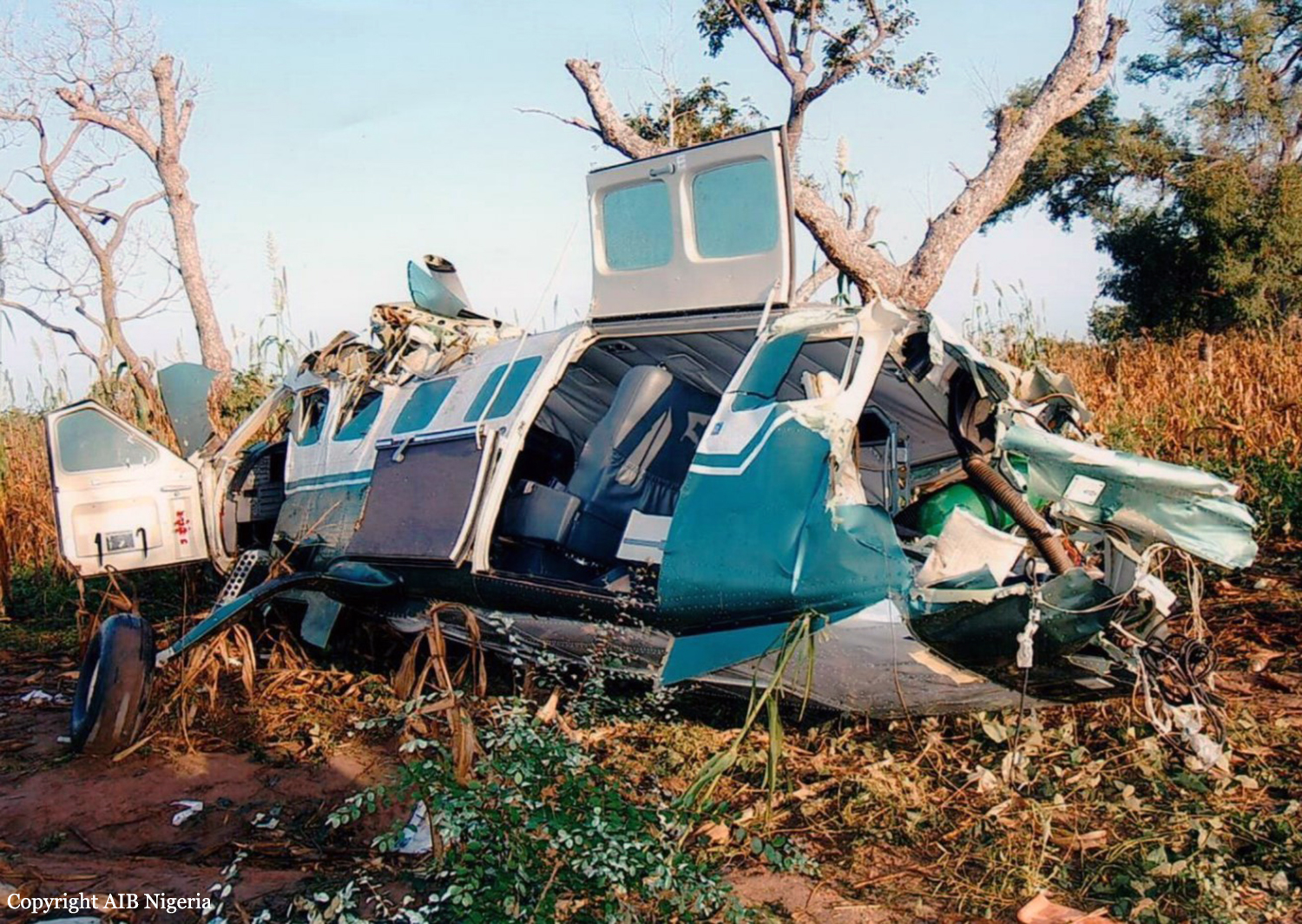
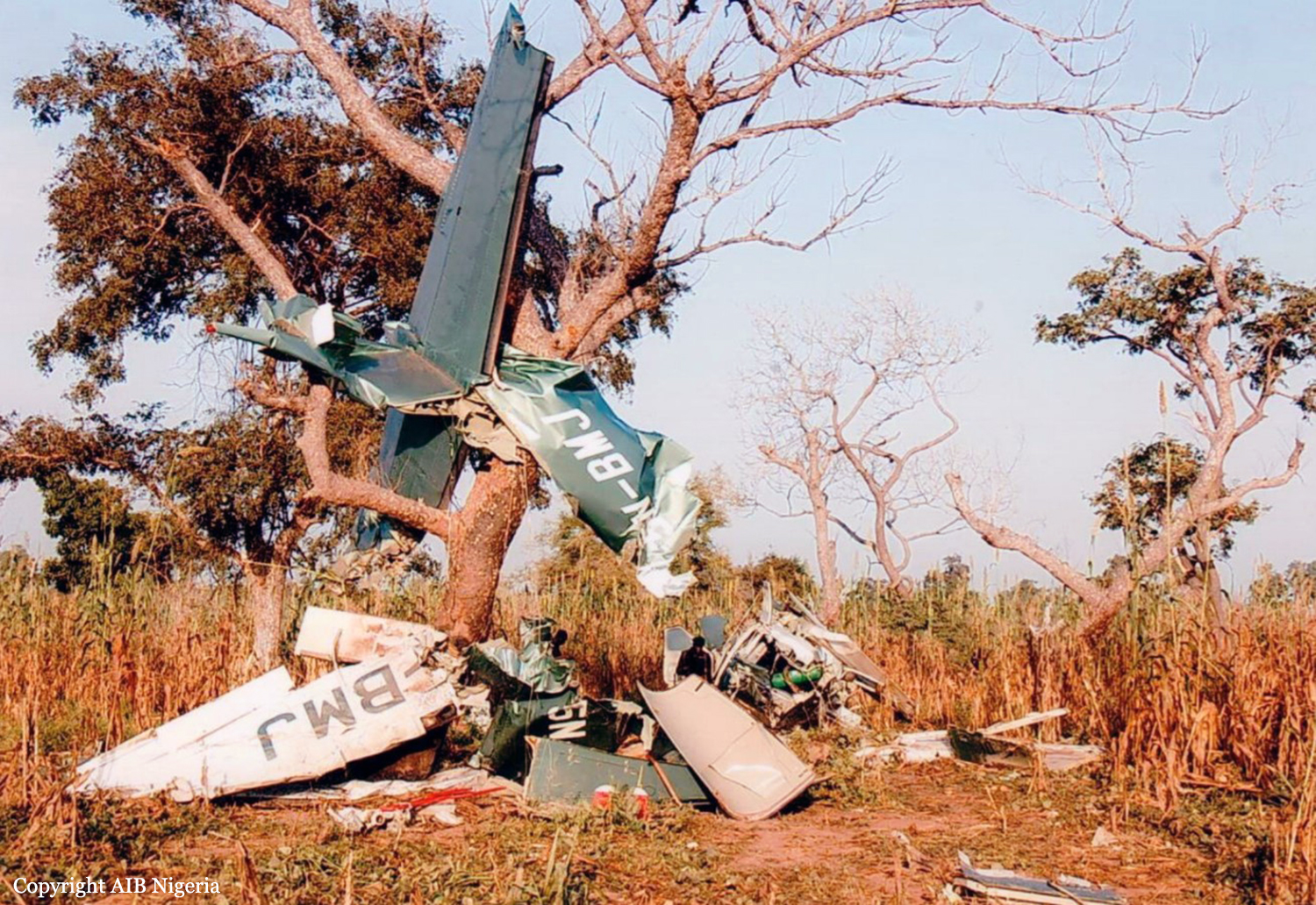
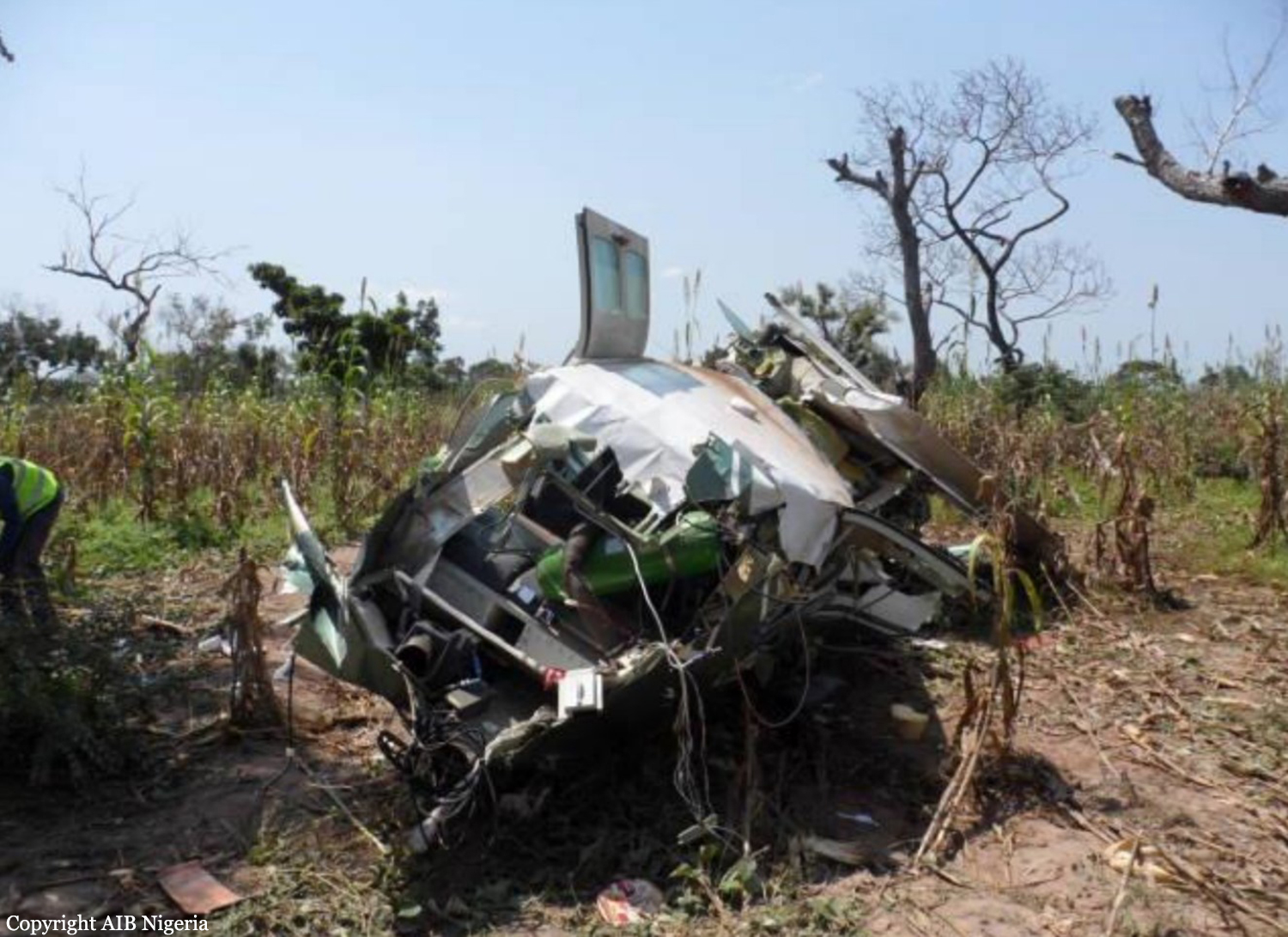




Crash of a Cessna 208B Grand Caravan in La Leona: 4 killed
Date & Time:
Jun 23, 2012 at 1100 LT
Registration:
EJC-1131
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Tolemaida - Saravena
MSN:
208B-1199
YOM:
2007
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
2
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
4
Circumstances:
The crew was performing a flight from the Tolemaida Air Base to the airport of Saravena-Los Colonizadores. Few minutes after takeoff, while flying some 35 km from its departure point, the single engine aircraft crashed in unknown circumstances in a field located in La Leona. All four occupants were killed.

Crash of a Cessna 208B Grand Caravan in Lézignan-Corbières
Date & Time:
May 25, 2012 at 1710 LT
Registration:
D-FAAF
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Lézignan-Corbières - Lézignan-Corbières
MSN:
208B-1125
YOM:
2005
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
850.00
Circumstances:
The single engine aircraft departed Lézignan-Corbières Airport at 1650LT with a pilot and several skydivers on board. At 10,500 feet, all skydivers jumped out and the pilot reduced his altitude to return to his base. On final approach to runway 08, at a height of 700 feet and at a speed of 90 knots, the pilot slightly increased the engine power to maintain the glide and then reduced again the power. At this time, the engine stopped and the propeller auto-feathered. Unable to reach the runway, the pilot attempted an emergency landing in a vineyard located some 800 meters short of runway 08, to the right of its extended centerline. While the pilot was uninjured, the aircraft was damaged beyond repair.
Probable cause:
Investigation were unable to determine the cause of the turbine failure on final approach. Sufficient fuel (about 500 pounds) was still present in the tanks and all analysis of the engine, fuel supply control system and the fuel pump did not reveal any anomalies.
Final Report:

Crash of a Cessna 208B Grand Caravan in Yambio
Date & Time:
May 2, 2012 at 1055 LT
Registration:
5Y-NGO
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Juba - Yambio
MSN:
208B-0322
YOM:
1992
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
9
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
It was reported that the aircraft had taken-off from Juba for Yambio, Sothern Sudan with two crew members and nine passengers onboard. The flight was uneventful up to and until after touchdown, twenty metres after the threshold of runway 03, when it was noted that the aircraft steadily veered to the left. Efforts by the captain to prompt the pilot flying and intercession by taking control of the aircraft and initiating the necessary corrective measures by applying full right rudder yielded no positive results. The aircraft left wheel entered the trench at high speed, causing the aircraft to flip over and crash 200metrs from threshold of runway 03 and came rest in an inverted position. All persons exited safely on their own, except two passengers who were assisted by the captain to disembark. The captain used the portable fire extinguisher to put off the fire that flickered in the engine compartment. The flying pilot sustained injuries on his right foot, while the other passengers were reported to have hard minor injuries. The prevailing weather at the time of occurrence was reported as CAVOK (clear sky, and visibility better than 10Km) with calm North Easterly winds (030/05).
Final Report:



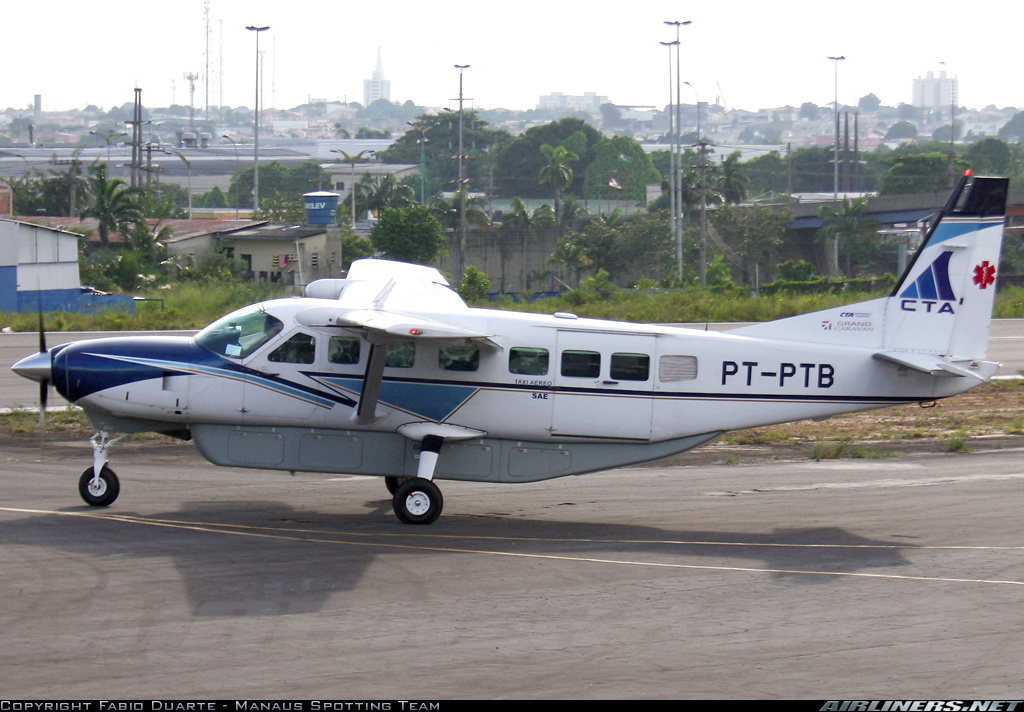
Crash of a Cessna 208B Grand Caravan in Manaus: 1 killed
Date & Time:
Feb 28, 2012 at 0715 LT
Registration:
PT-PTB
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Manaus - Manaus
MSN:
208B-0766
YOM:
1999
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
1
Captain / Total hours on type:
158.00
Circumstances:
The pilot was performing a positioning flight from Manaus-Aeroclube de Flores Airport to the international Airport of Manaus-Eduardo Gomes. Shortly after takeoff from runway 11 which is 860 metres long, the single engine aircraft failed to gain sufficient altitude. It collided with an electric pole, stalled and crashed in a wooded area. The pilot, sole occupant, was killed.
Probable cause:
It was determined that the loss of control results from the fact that the flight controls were locked. Investigations show that the pilot failed to prepare the flight properly, that he did not follow the pre takeoff checklist and that he rushed the departure. It was reported that the operator was using since two years a control lock that had not been approved by the Civil Aviation Authority, and that no procedure had been put in place place concerning this lock system.
Final Report: