Crash of a Cessna 501 Citation I/SP in Franklin: 5 killed
Date & Time:
Mar 15, 2012 at 1350 LT
Registration:
N7700T
Survivors:
No
Schedule:
Venice - Franklin
MSN:
501-0248
YOM:
1982
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
4
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
5
Captain / Total hours on type:
185.00
Aircraft flight hours:
4825
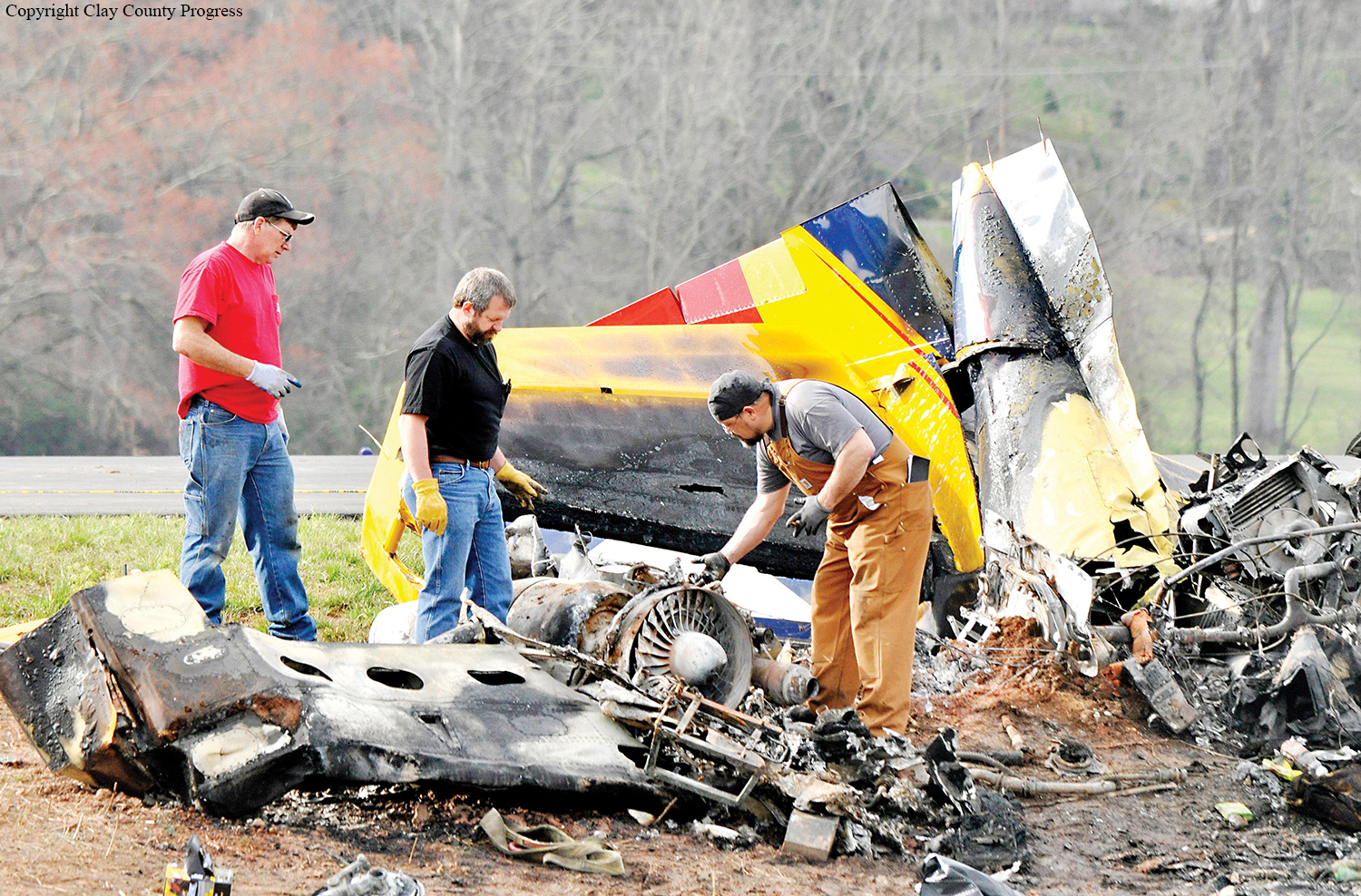
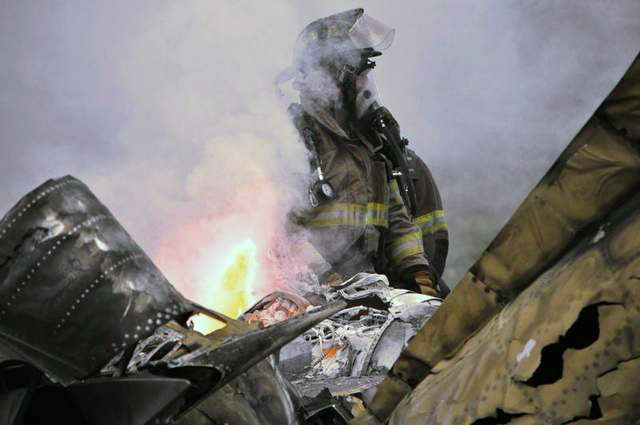
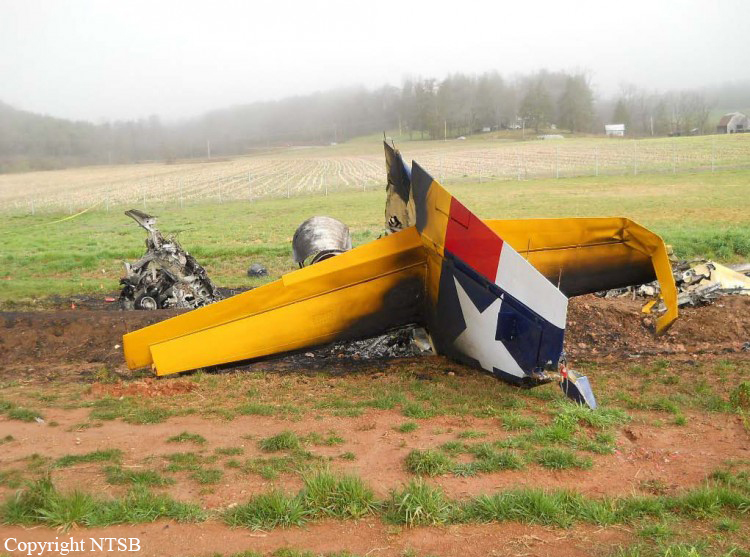
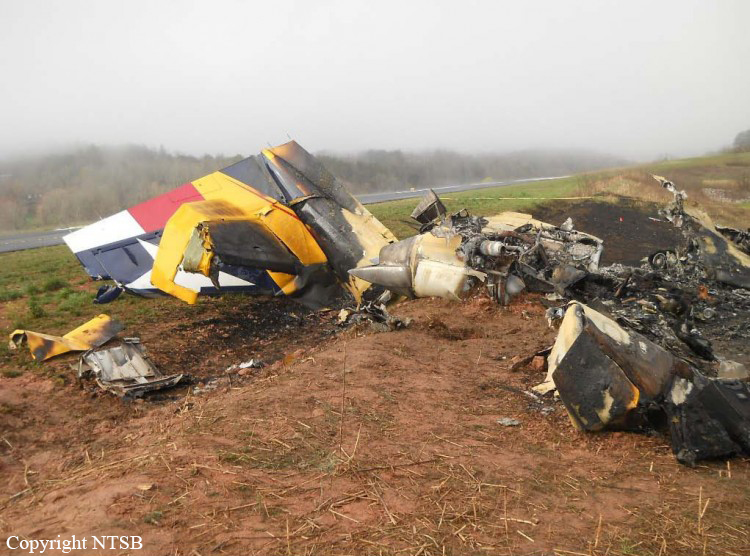
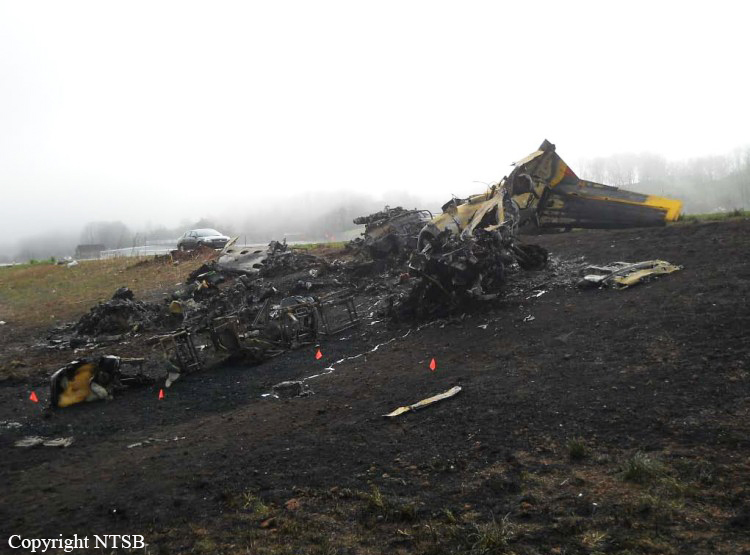
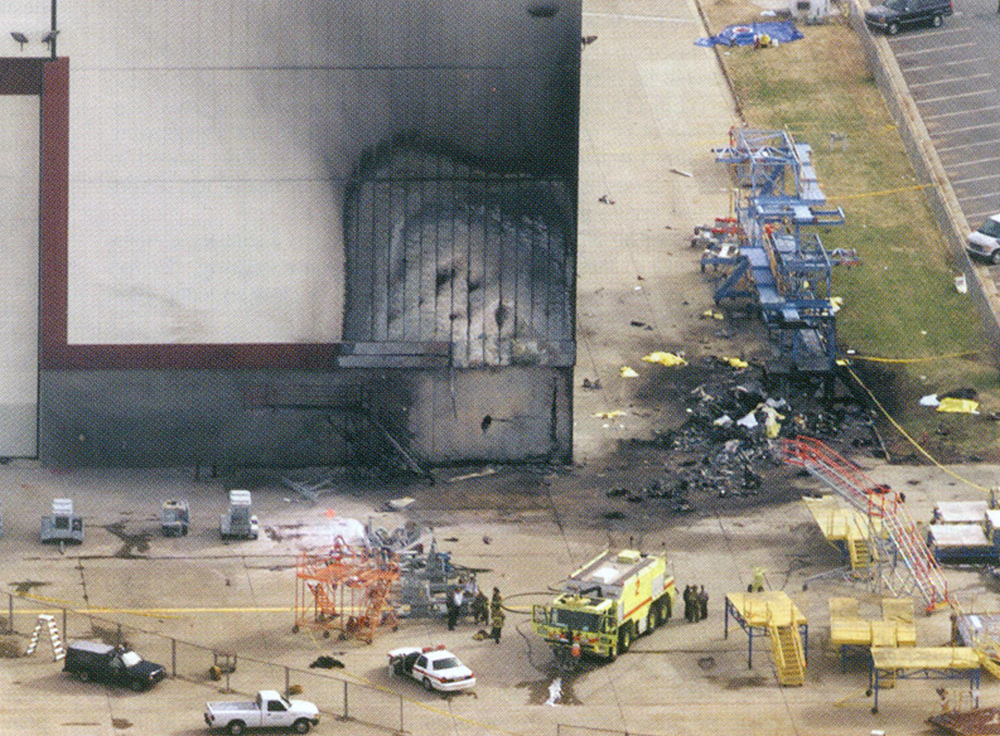
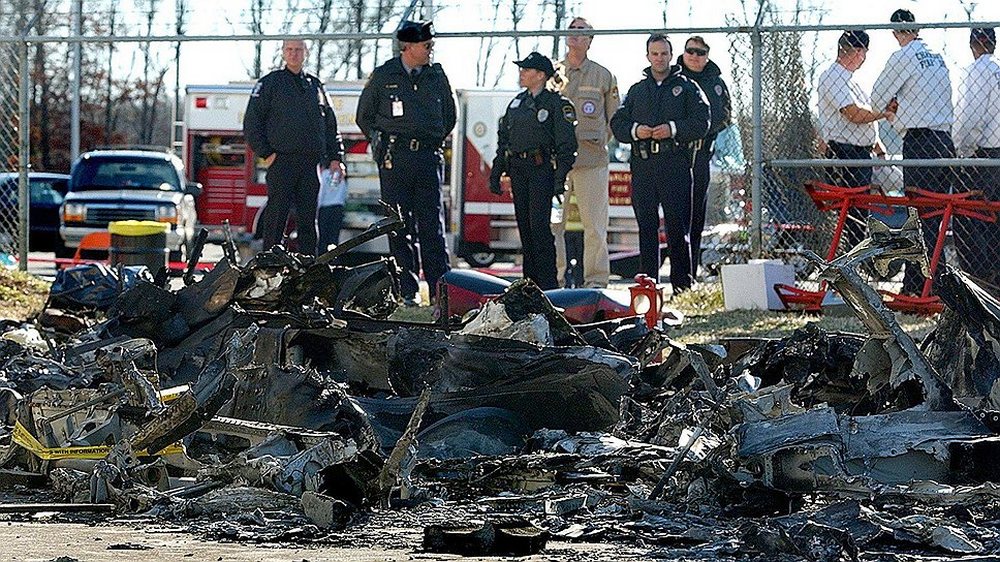
Circumstances:
The pilot was not familiar with the mountain airport. The airplane was high during the first visual approach to the runway. The pilot performed a go-around and the airplane was again high for the second approach. During the second approach, the approach angle steepened, and the airplane pitched nose-down toward the runway. The nosegear touched down about halfway down the runway followed by main gear touchdown. The airplane then bounced and the sound of engine noise increased as the airplane banked right and the right wing contacted the ground. The airplane subsequently flipped over and off the right side of the runway, and a postcrash fire ensued. Examination of the airframe and engines did not reveal any preimpact mechanical malfunctions. The examination also revealed that the right engine thrust reverser was deployed during the impact sequence, and the left engine thrust reverser was stowed. Although manufacturer data revealed single-engine reversing has been demonstrated during normal landings and is easily controllable, the airplane had already porpoised and bounced during the landing. The pilot’s subsequent activation of only the right engine’s thrust reverser would have created an asymmetrical thrust and most likely exacerbated an already uncontrolled touchdown. Had the touchdown been controlled, the airplane could have stopped on the remaining runway or the pilot could have performed a go-around uneventfully.
Probable cause:
The pilot's failure to achieve a stabilized approach, resulting in a nose-first, bounced landing. Contributing to the accident was the pilot's activation of only one thrust reverser, resulting in asymmetrical thrust.
Final Report: