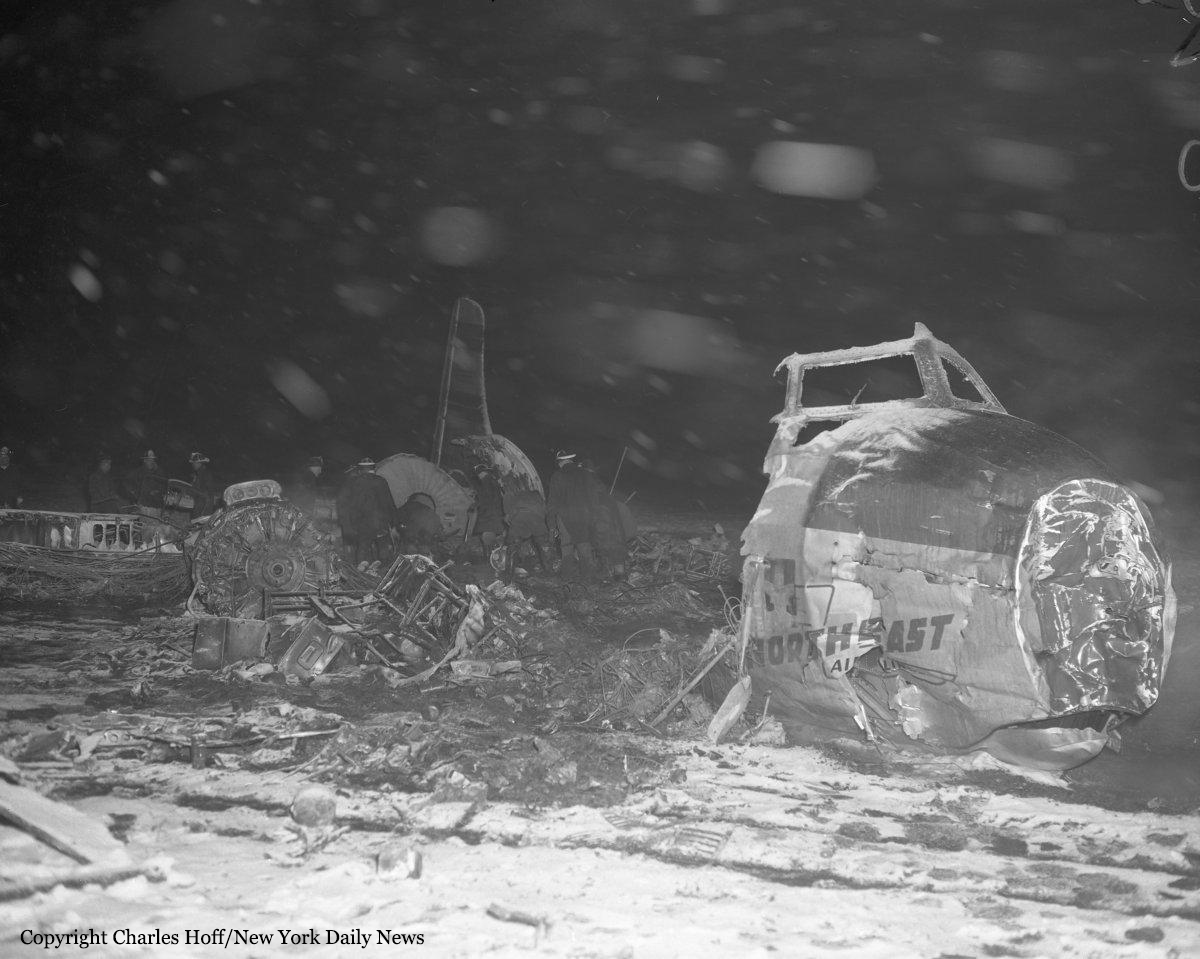
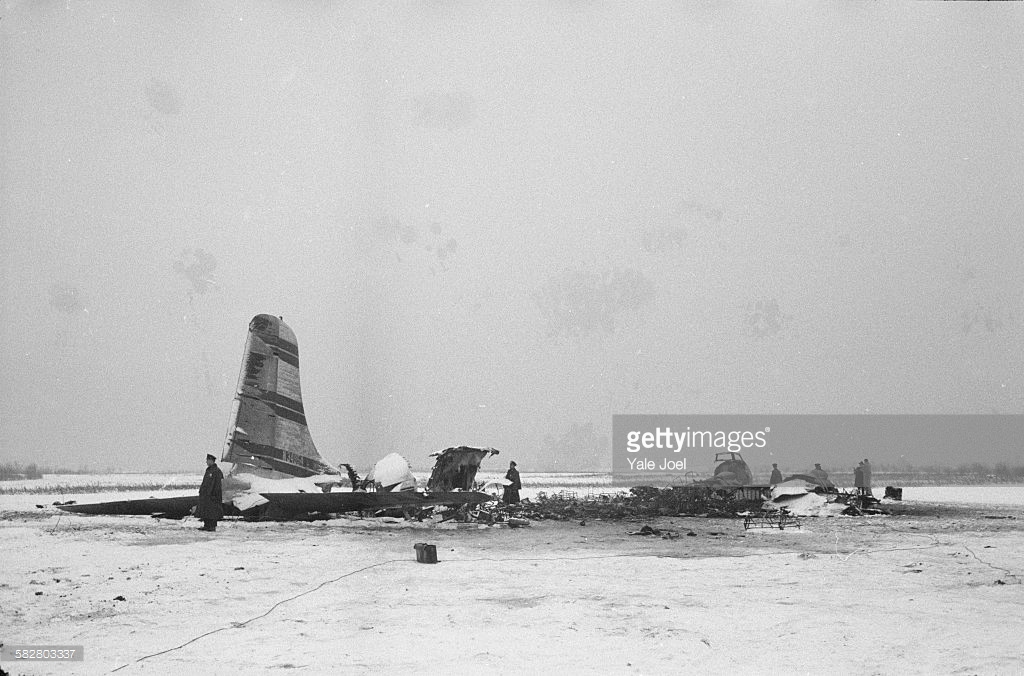
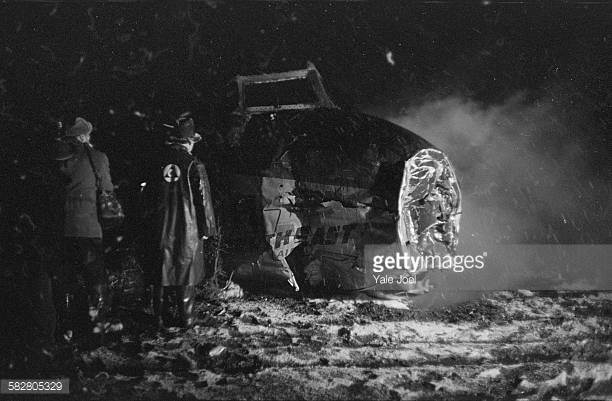
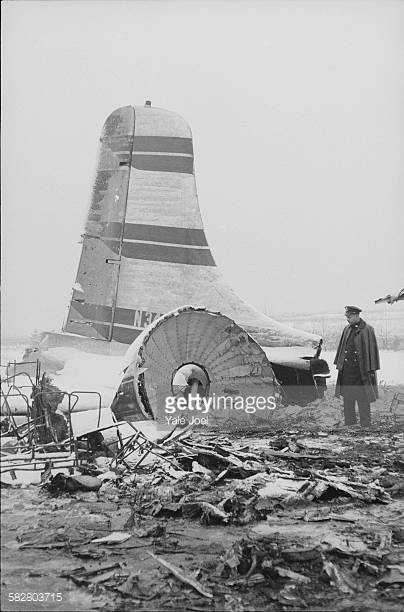
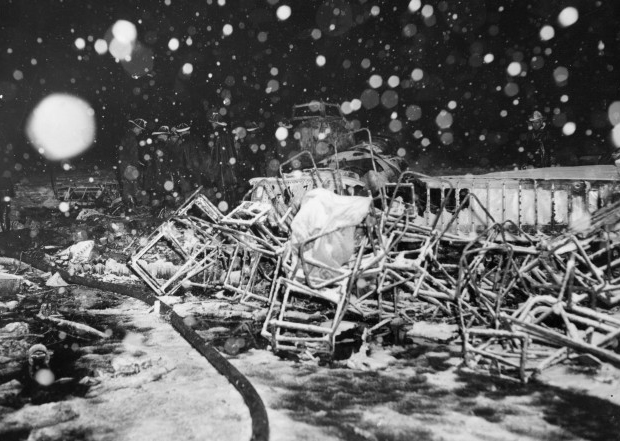
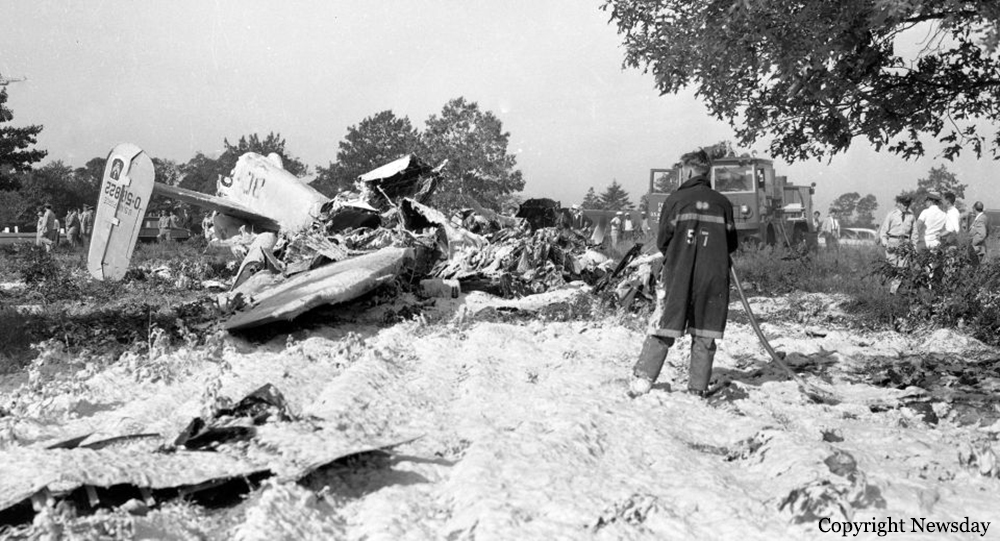
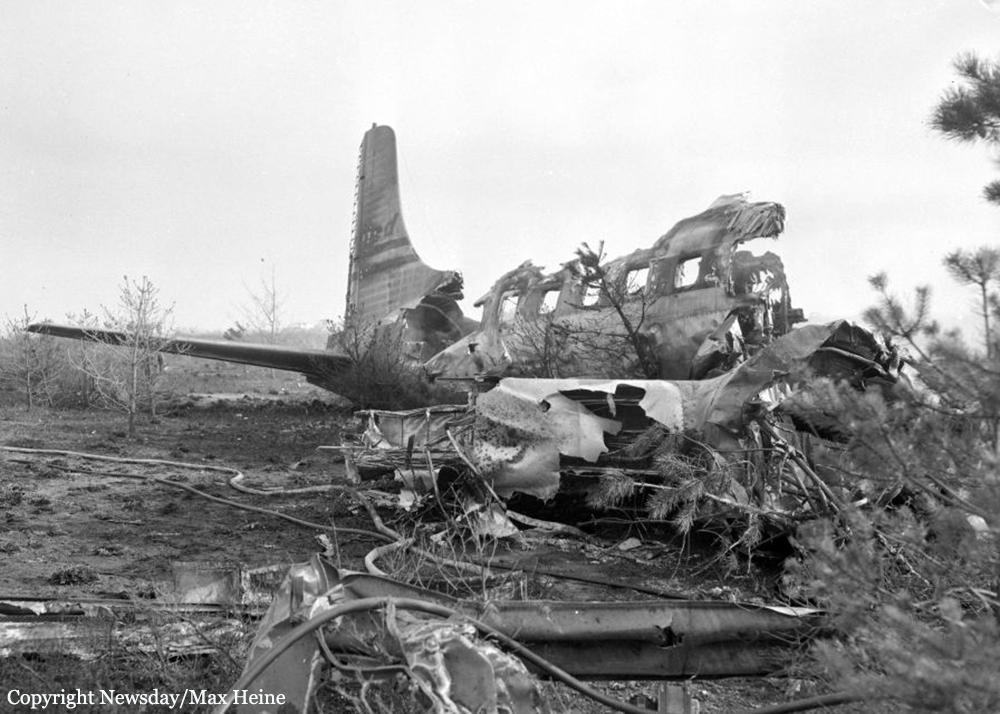
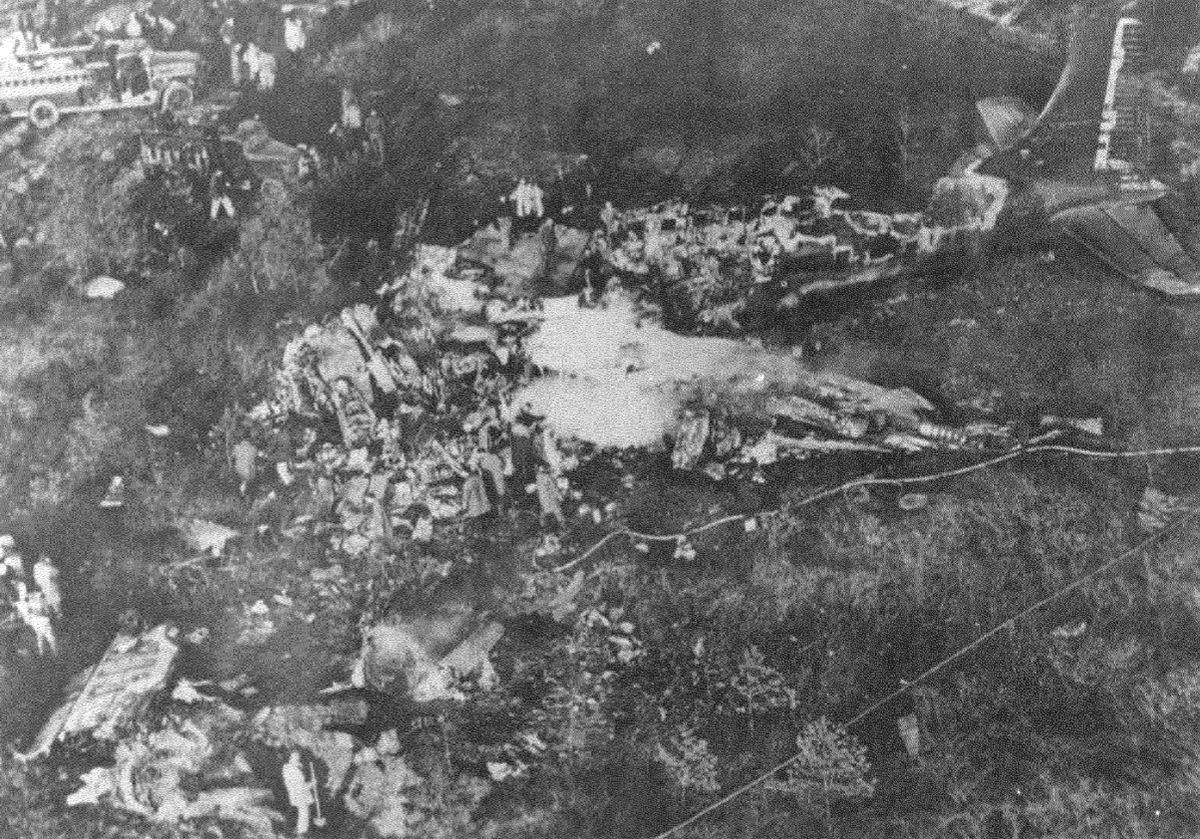
Crash of a Grumman HU-16E in Floyd Bennett Field: 4 killed
Date & Time:
Aug 22, 1957
Registration:
1259
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Floyd Bennett Field - Floyd Bennett Field
MSN:
G-106
YOM:
1952
Crew on board:
6
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
4
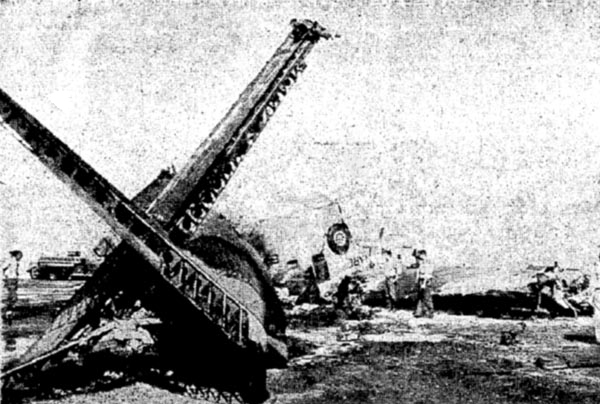
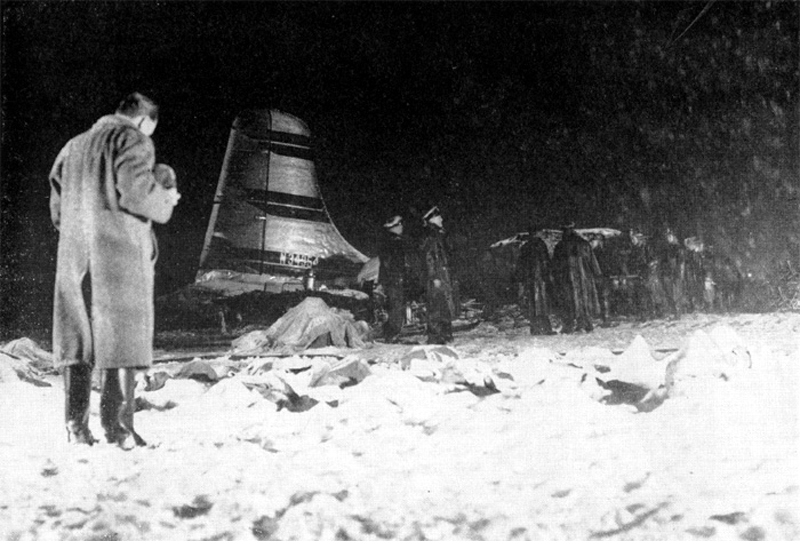
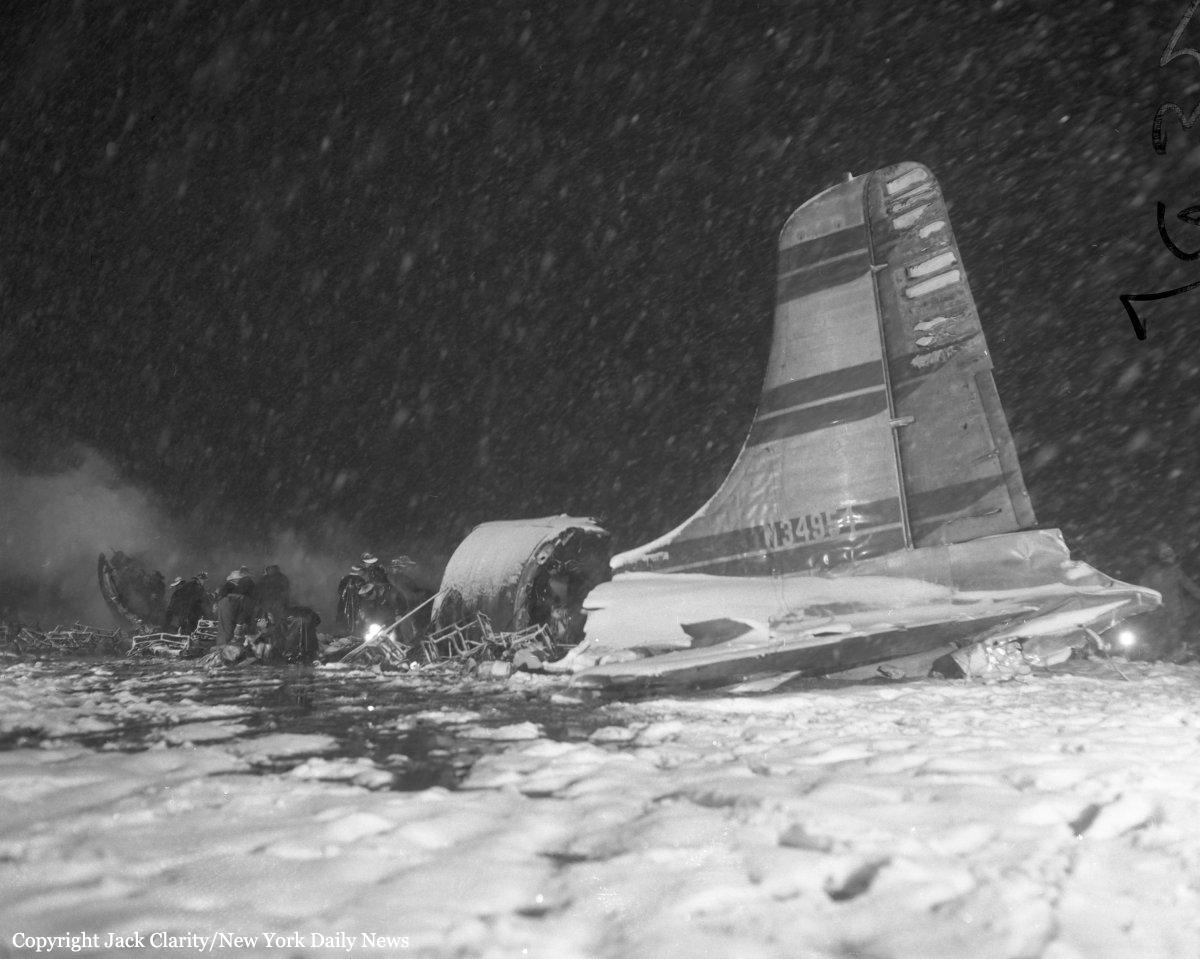
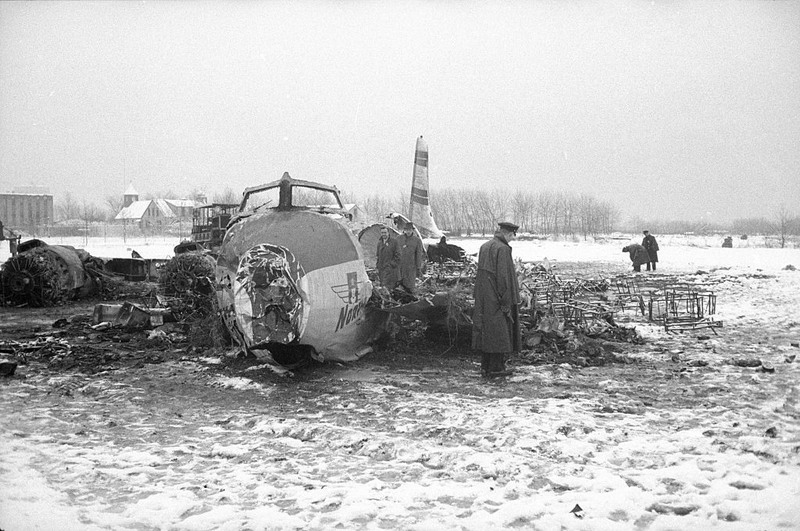
Circumstances:
The crew was performing a test flight after the aircraft had undergone an intermediate inspection in which the control columns were removed and inspected for fatigue cracks in the bottom casting. The plane was cleared for take-off and instructed to turn right immediately after take-off to avoid other traffic. Take-off was normal but immediately after leaving the runway the plane banked slightly to the left, hesitated, and then banked and then banked very rapidly to the left until it was in a 90° bank. The left wing tip struck the ground and the plane broke in two and crashed. Four crew members were killed while two others were injured.
Those killed were:
Lcdr Claude S. Labaw,
Lt Rolland A. Faucher,
AD3 Matthew R. Ross,
AT3 Gerald R. Fox.
Those killed were:
Lcdr Claude S. Labaw,
Lt Rolland A. Faucher,
AD3 Matthew R. Ross,
AT3 Gerald R. Fox.
Probable cause:
The Accident Board was not able to determine the cause of this accident but certain items all pointed strongly toward reversed aileron control cable rigging as the most probably cause.