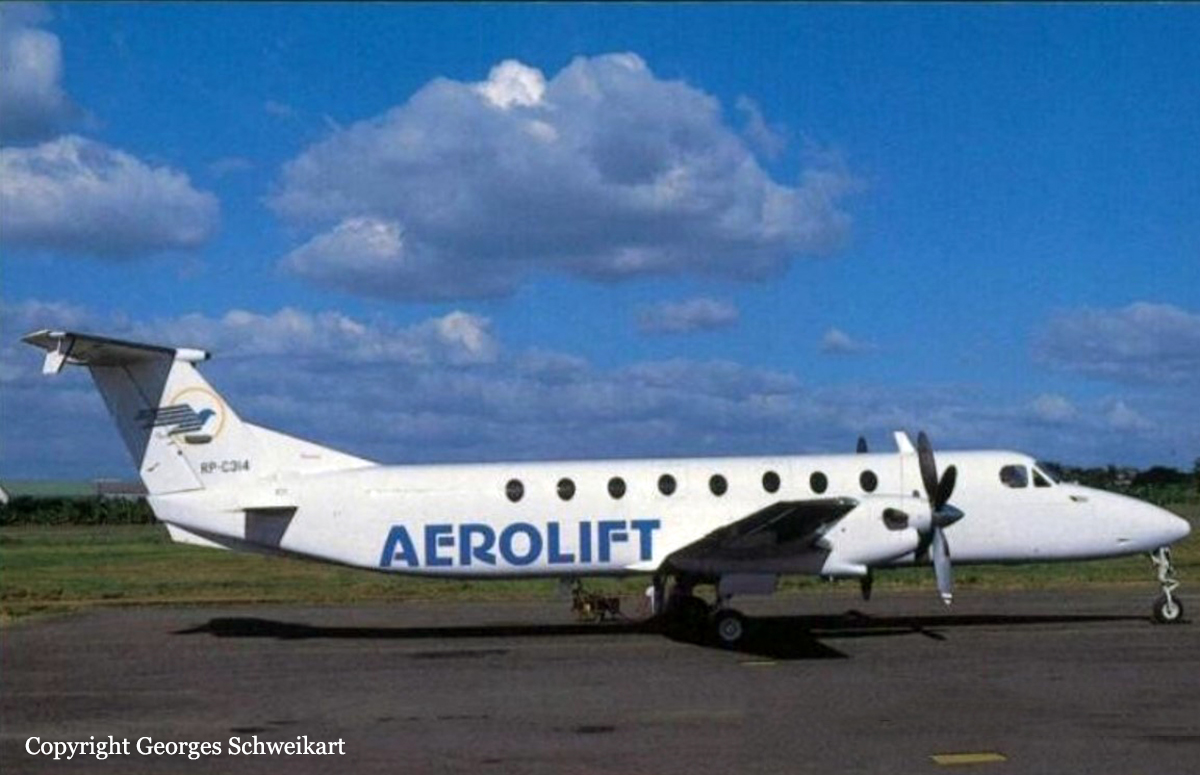
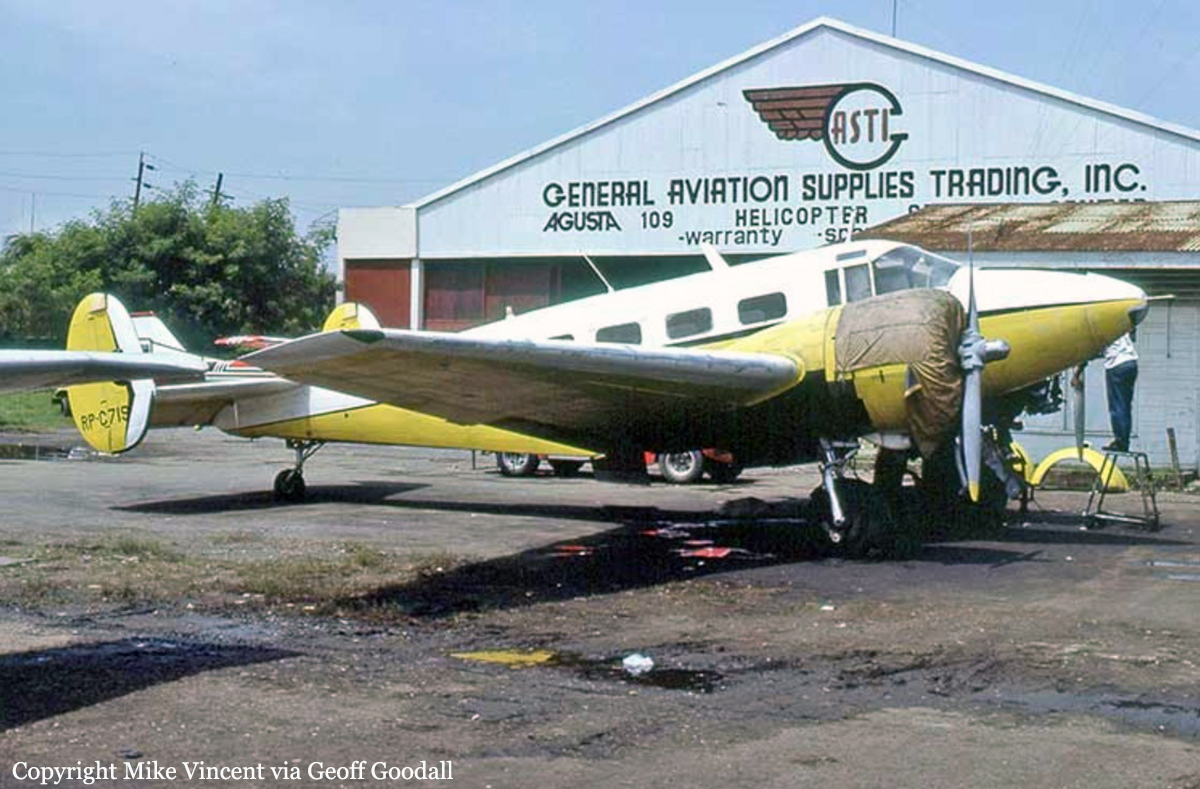
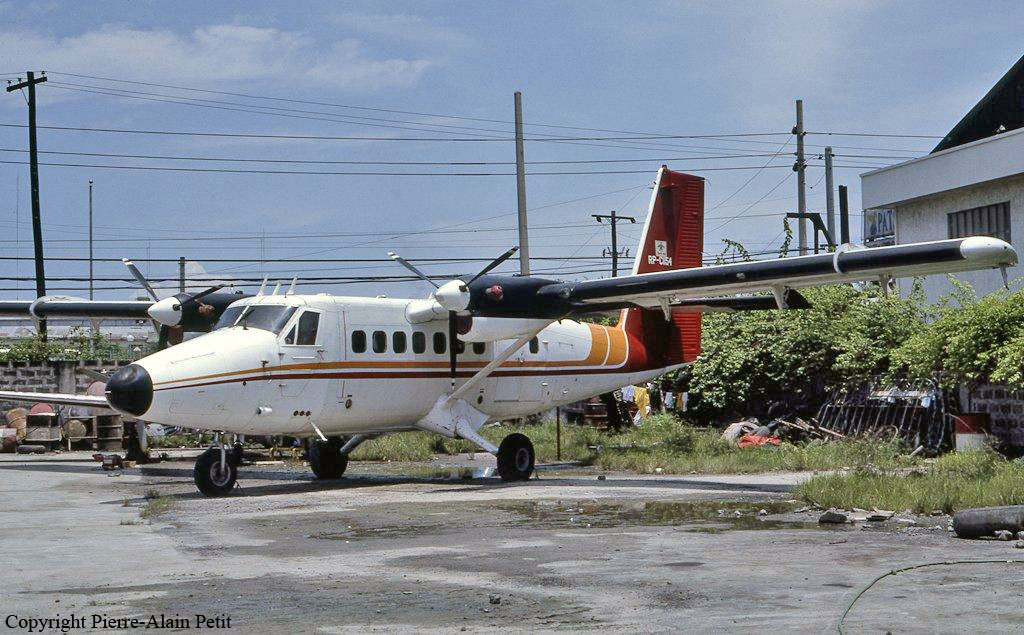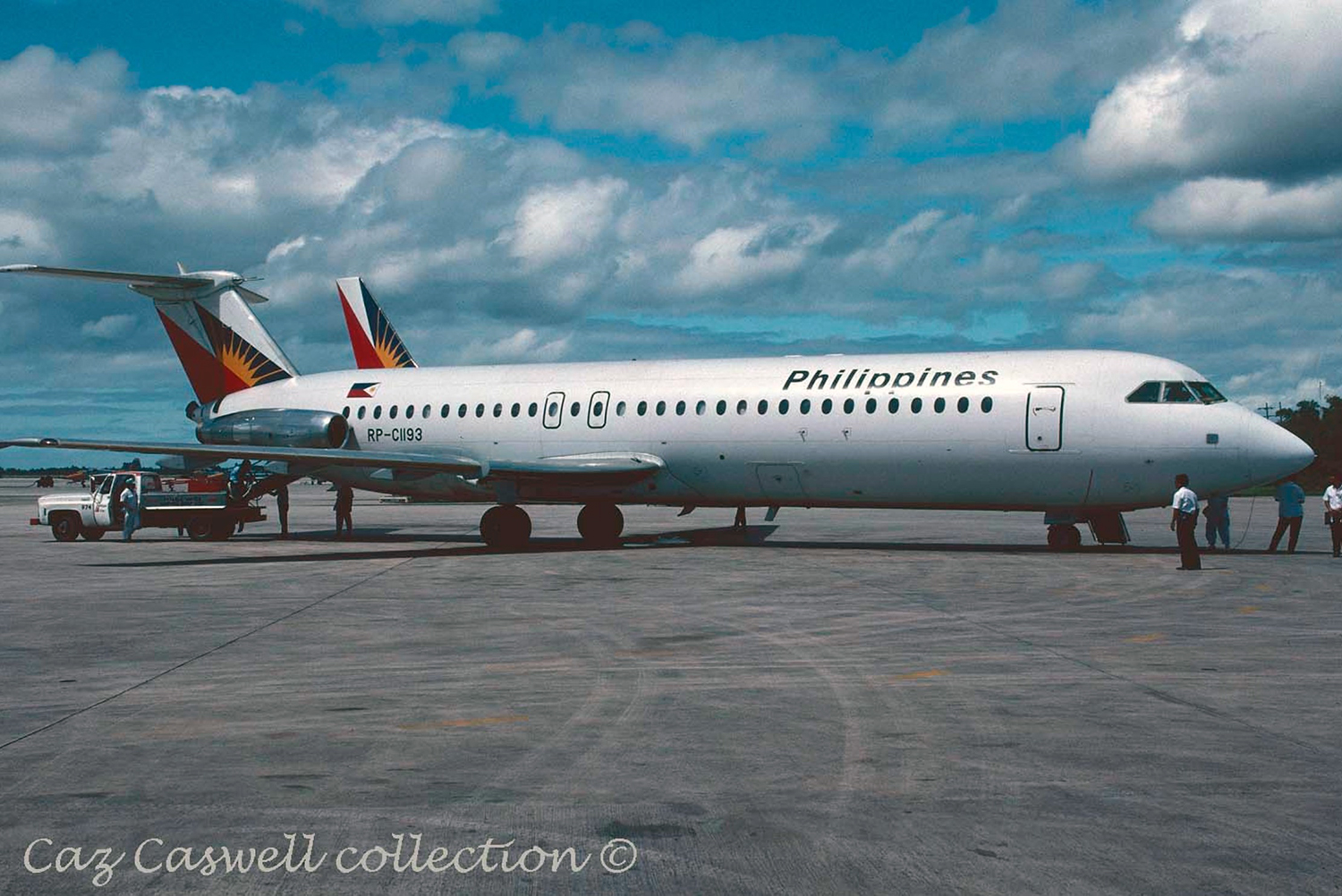Crash of a De Havilland DHC-6 Twin Otter 200 in Manila
Date & Time:
Apr 2, 1996 at 1919 LT
Registration:
RP-C1154
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
El Nido Palawan - Manila
MSN:
177
YOM:
1968
Crew on board:
2
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Circumstances:
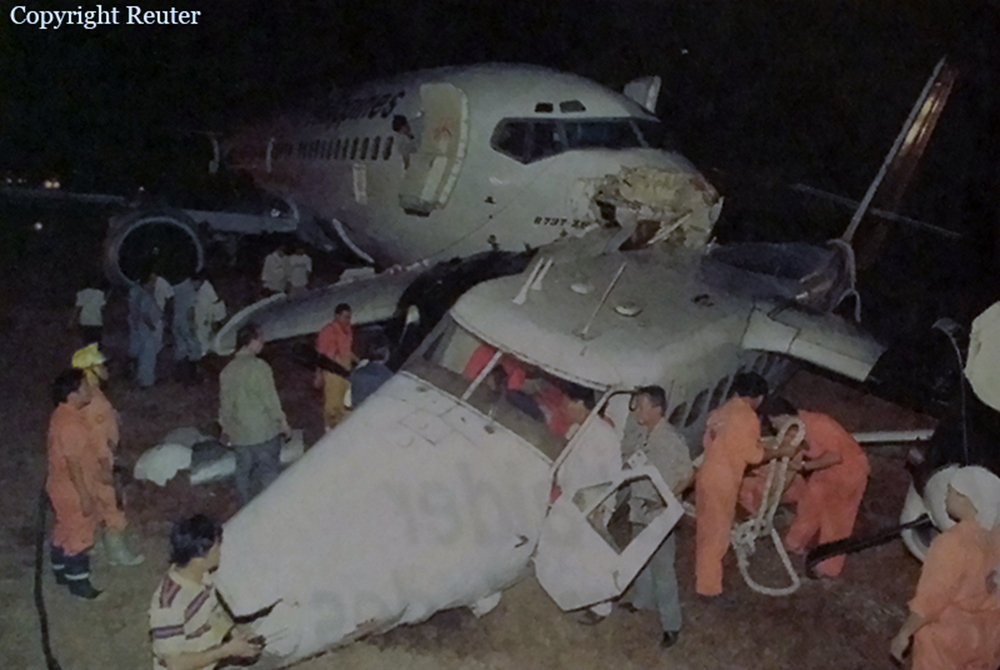
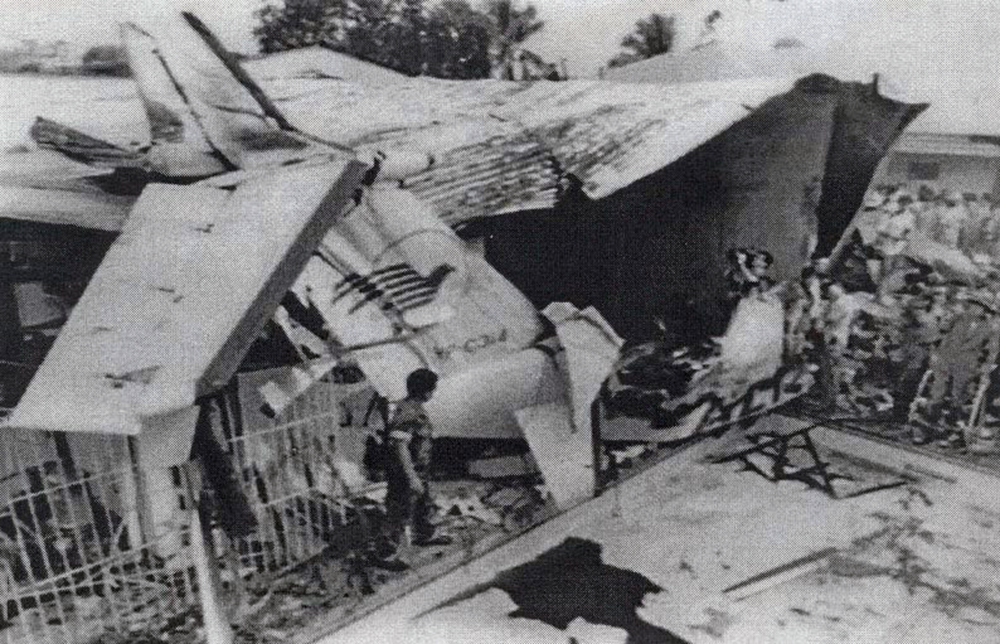
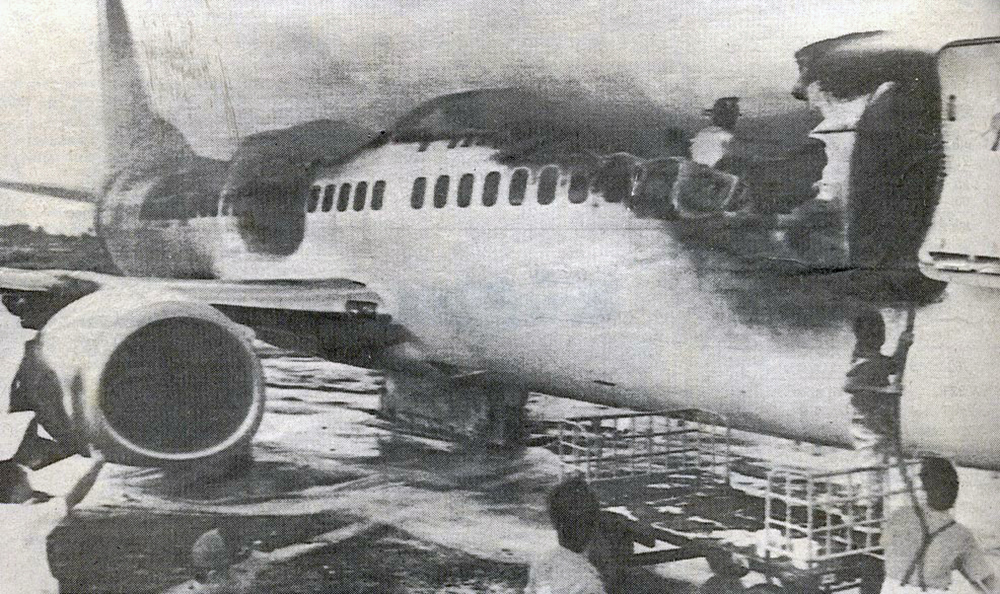
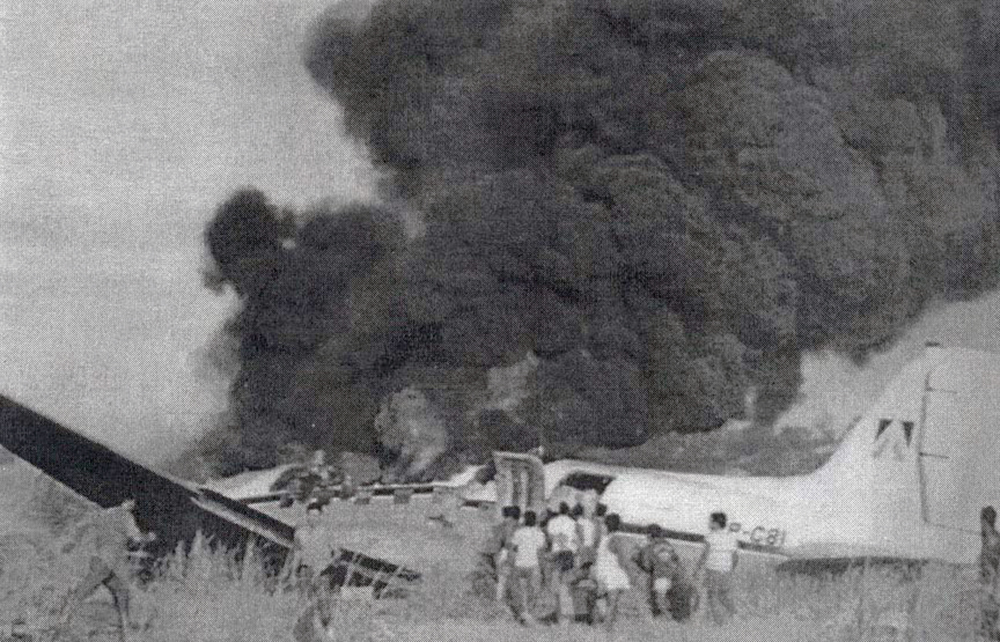
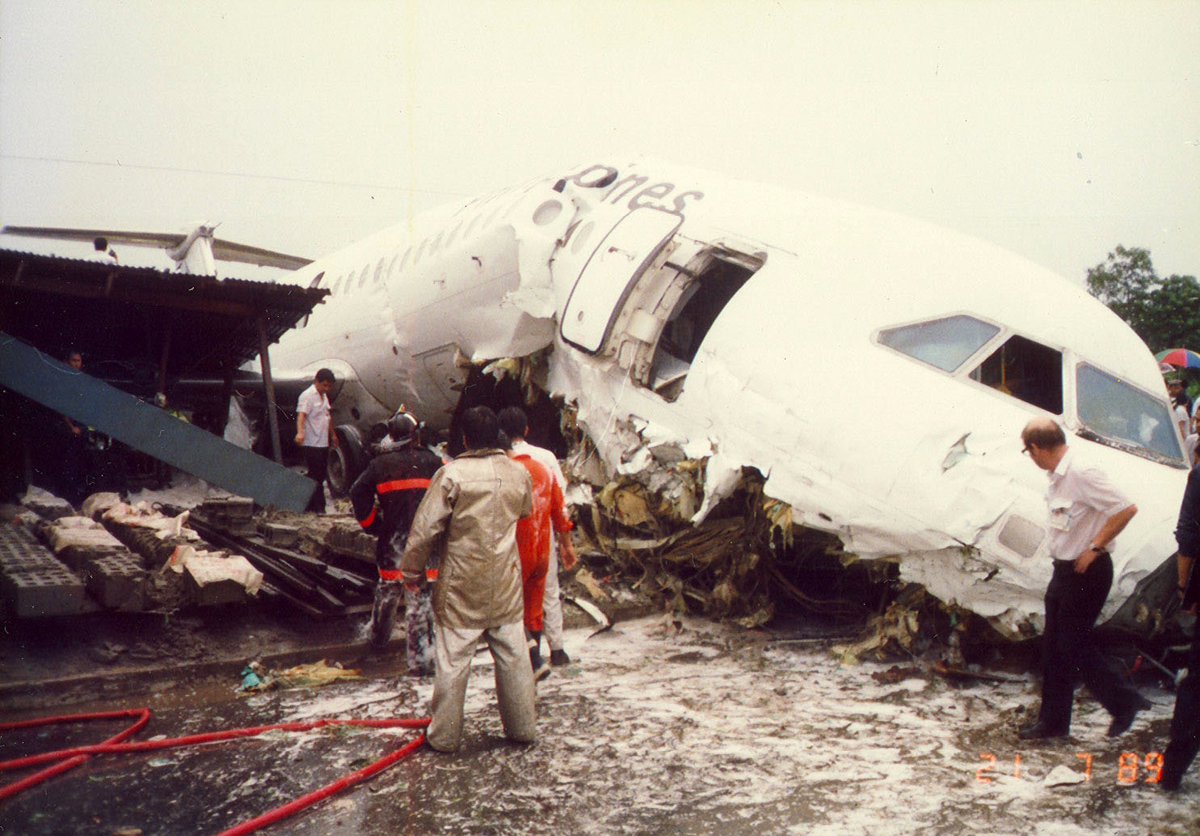
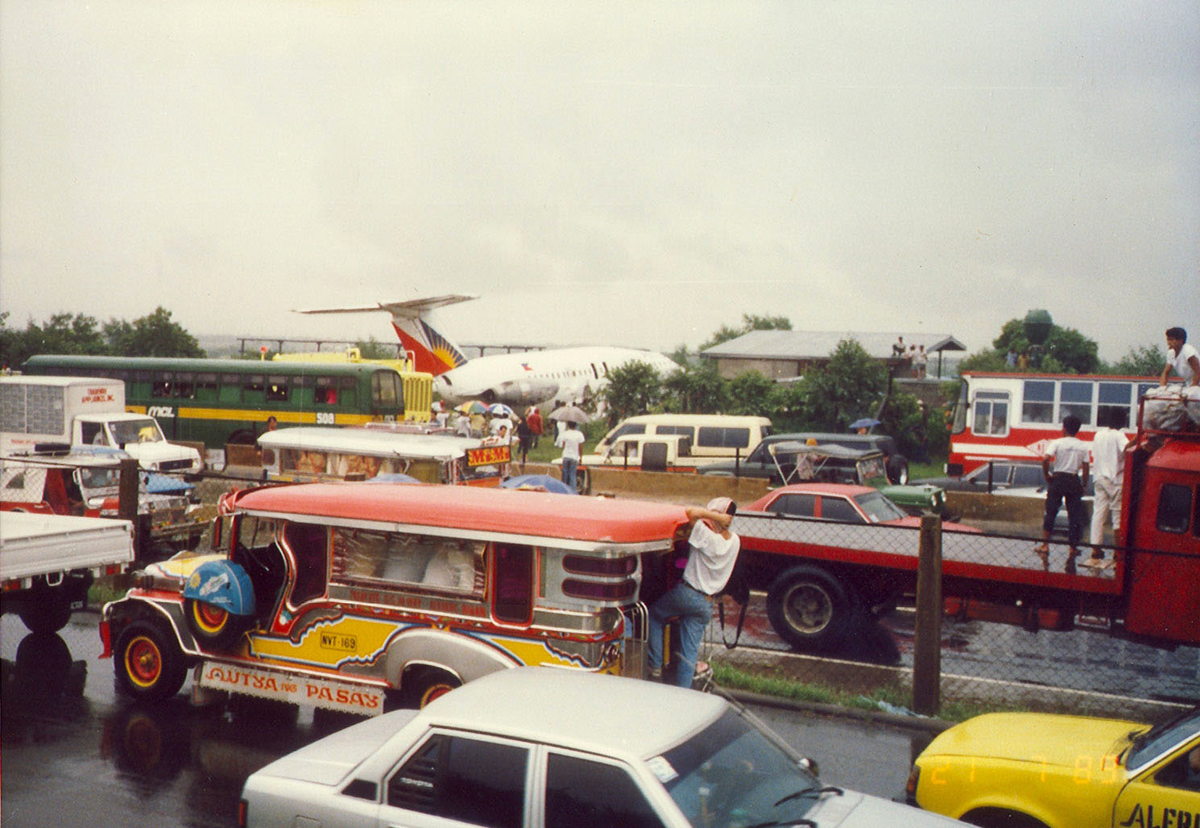
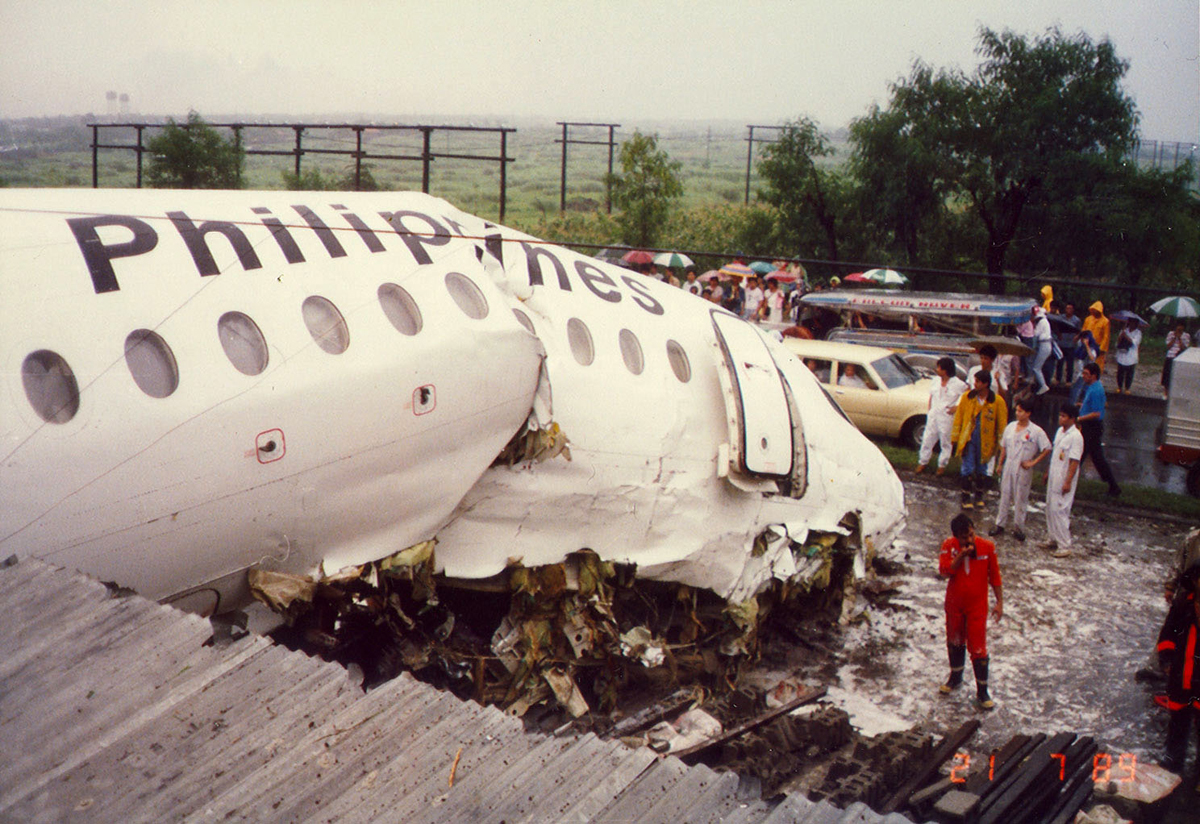
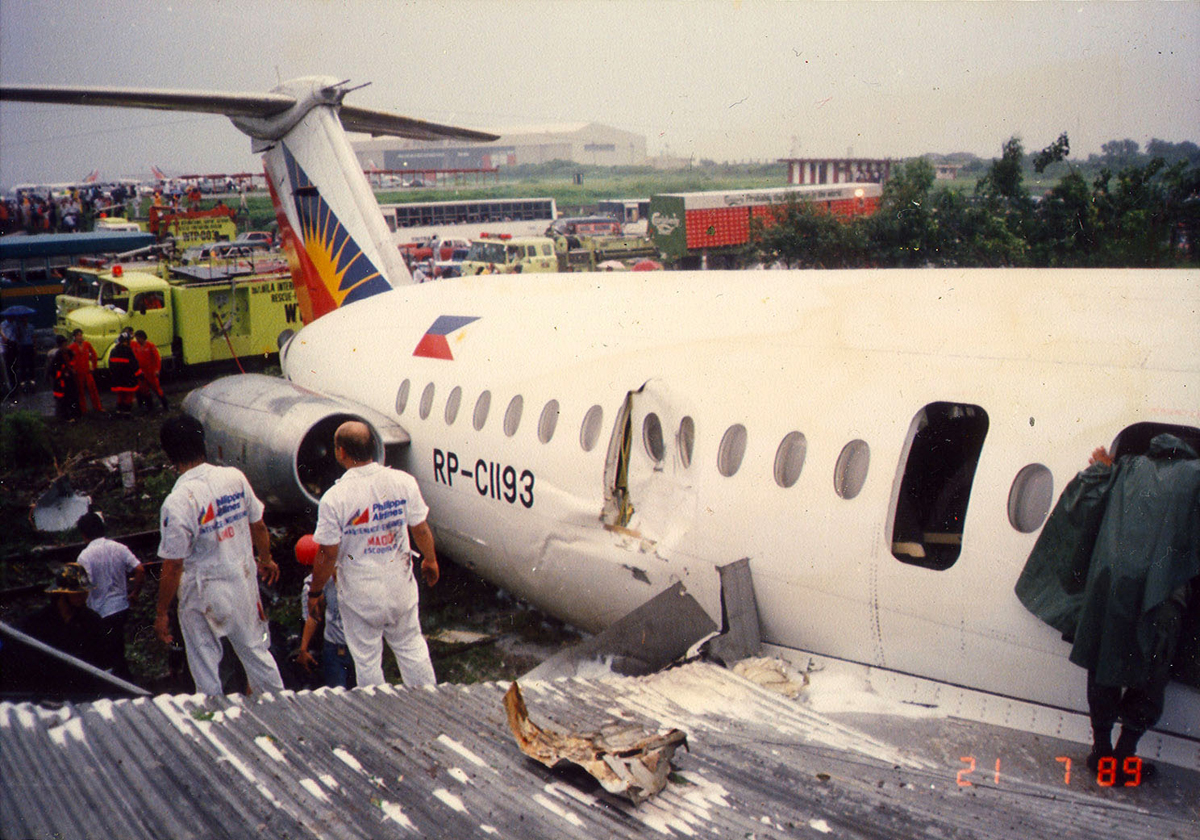
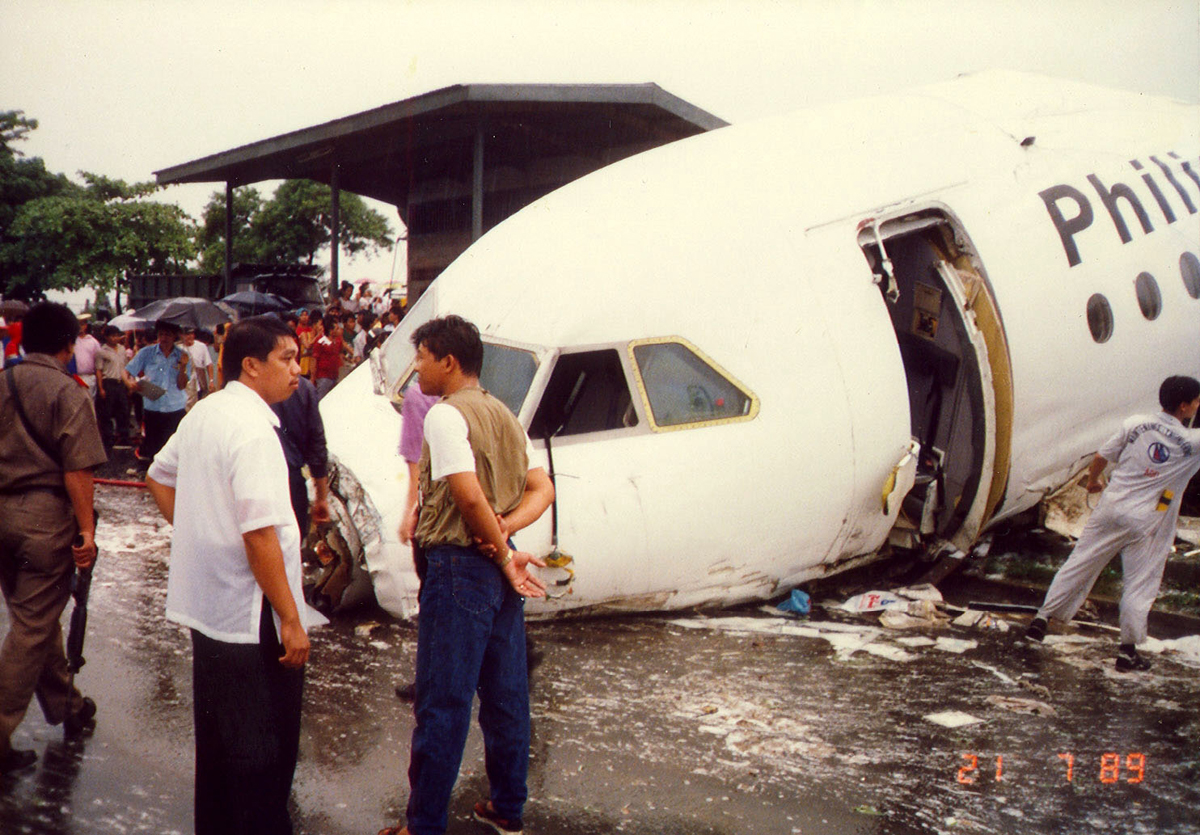
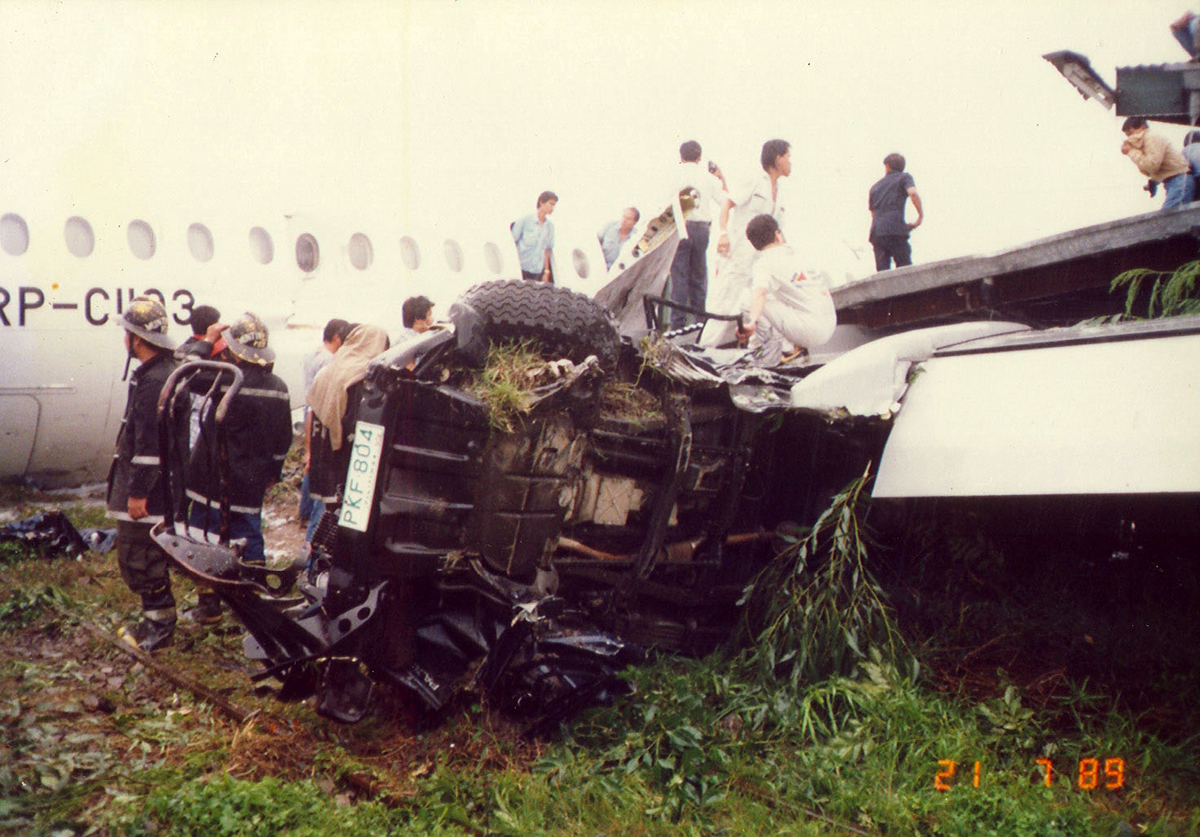
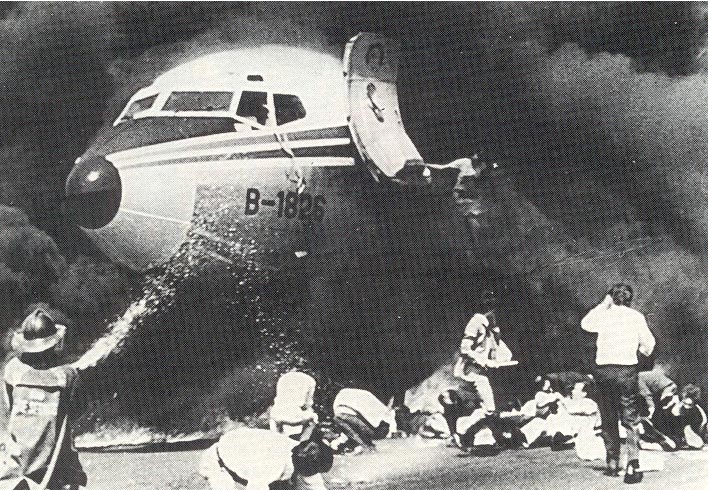
Following a flight from El Nido Palawan, the crew of the Twin Otter landed at Manila-Ninoy Aquino Airport and was instructed to taxi via F1 to reach his parking place. At the same time, a Boeing 737-3Y0 operated by Philippine Airlines (flight PR1370 from Manila to Bacolod) was taking off from runway 13 so the crew of the Twin Otter was instructed to hold on taxiway F1. For unknown reasons, the crew misinterpreted this instruction and started to cross the runway when the Boeing 737 collided with the DHC-6 that was dragged for 130 metres. The Boeing was slightly damaged on its nose while the Twin Otter was destroyed. Both pilots were injured.
Probable cause:
Failure of the crew to follow ATC instruction, starting to cross the runway in use while a Boeing 737 was taking off at the same time.