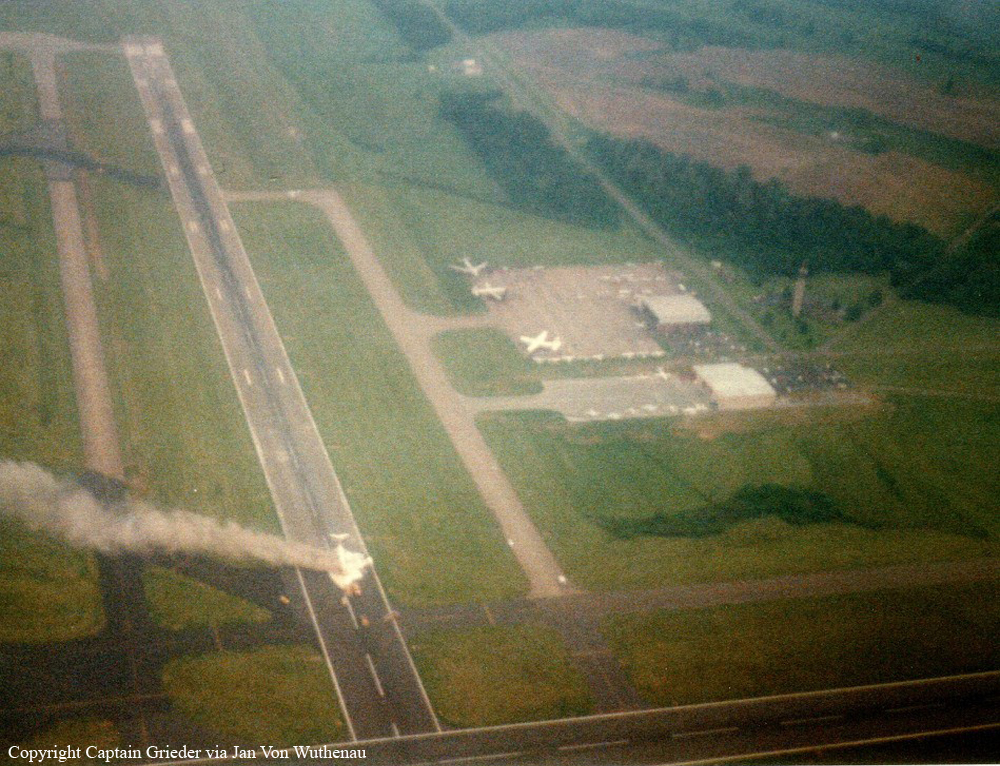
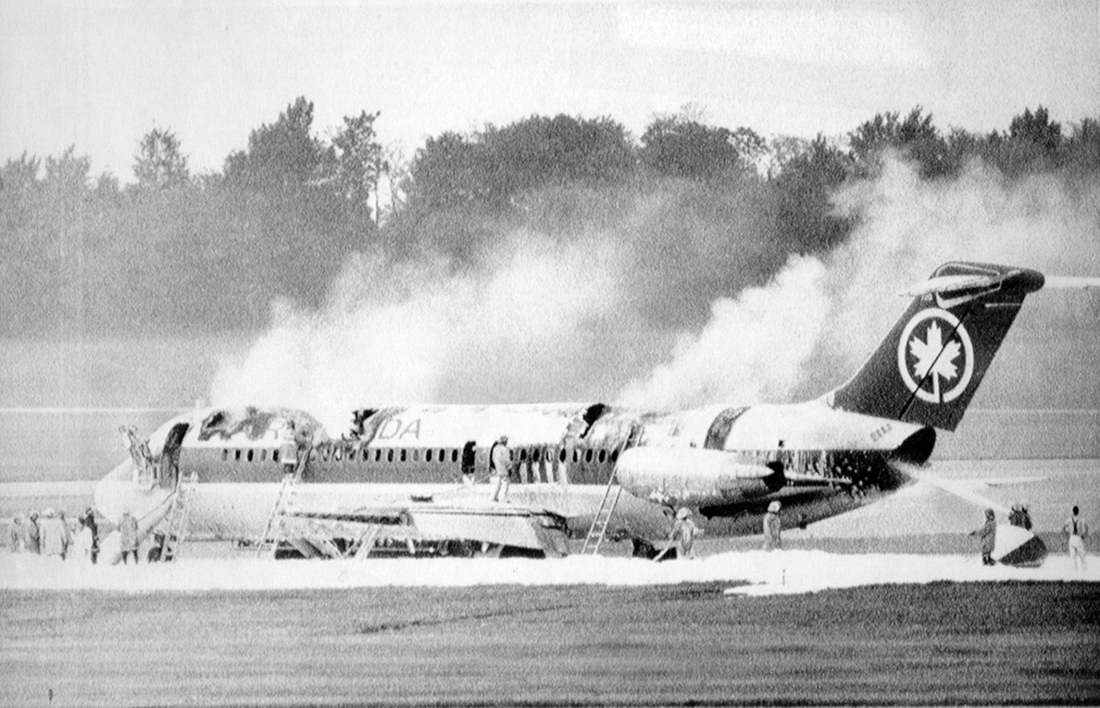
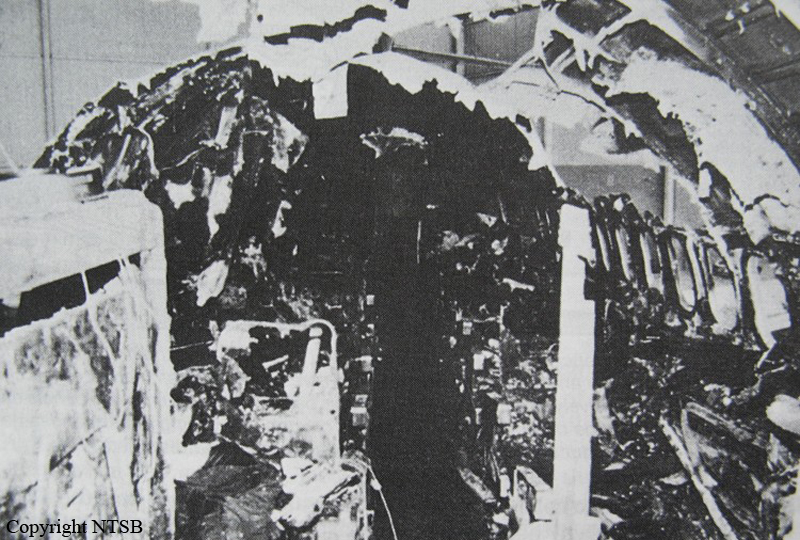
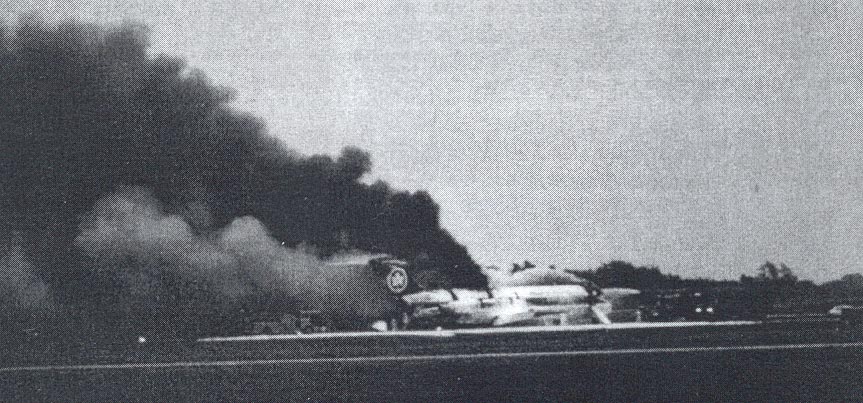
Crash of a Beechcraft H18 in Louisville
Date & Time:
Feb 11, 1986 at 2052 LT
Registration:
N148PA
Survivors:
Yes
Schedule:
Louisville - Columbus
MSN:
BA-645
YOM:
1963
Crew on board:
1
Crew fatalities:
Pax on board:
0
Pax fatalities:
Other fatalities:
Total fatalities:
0
Captain / Total hours on type:
203.00
Aircraft flight hours:
6405
Circumstances:
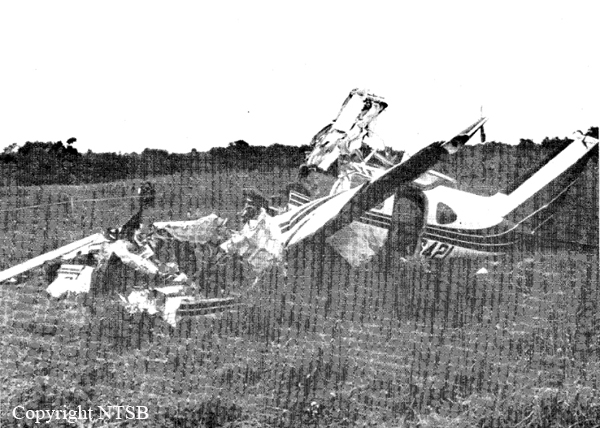
The aircraft collided with the ground after stalling during takeoff. Witnesses reported that the aircraft pitched up in two increments, climbed sharply to about 200 feet agl, stalled dropped the right wing and descended, impacting the ground in a flat attitude.
Probable cause:
Occurrence #1: loss of control - in flight
Phase of operation: takeoff - initial climb
Findings
1. (c) proper climb rate - not maintained - pilot in command
2. (c) stall - not corrected - pilot in command
----------
Occurrence #2: in flight collision with terrain/water
Phase of operation: descent - uncontrolled
Phase of operation: takeoff - initial climb
Findings
1. (c) proper climb rate - not maintained - pilot in command
2. (c) stall - not corrected - pilot in command
----------
Occurrence #2: in flight collision with terrain/water
Phase of operation: descent - uncontrolled
Final Report: